Grapevine Xylem Sap Is a Potent Elicitor of Antibiotic Production in Streptomyces spp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
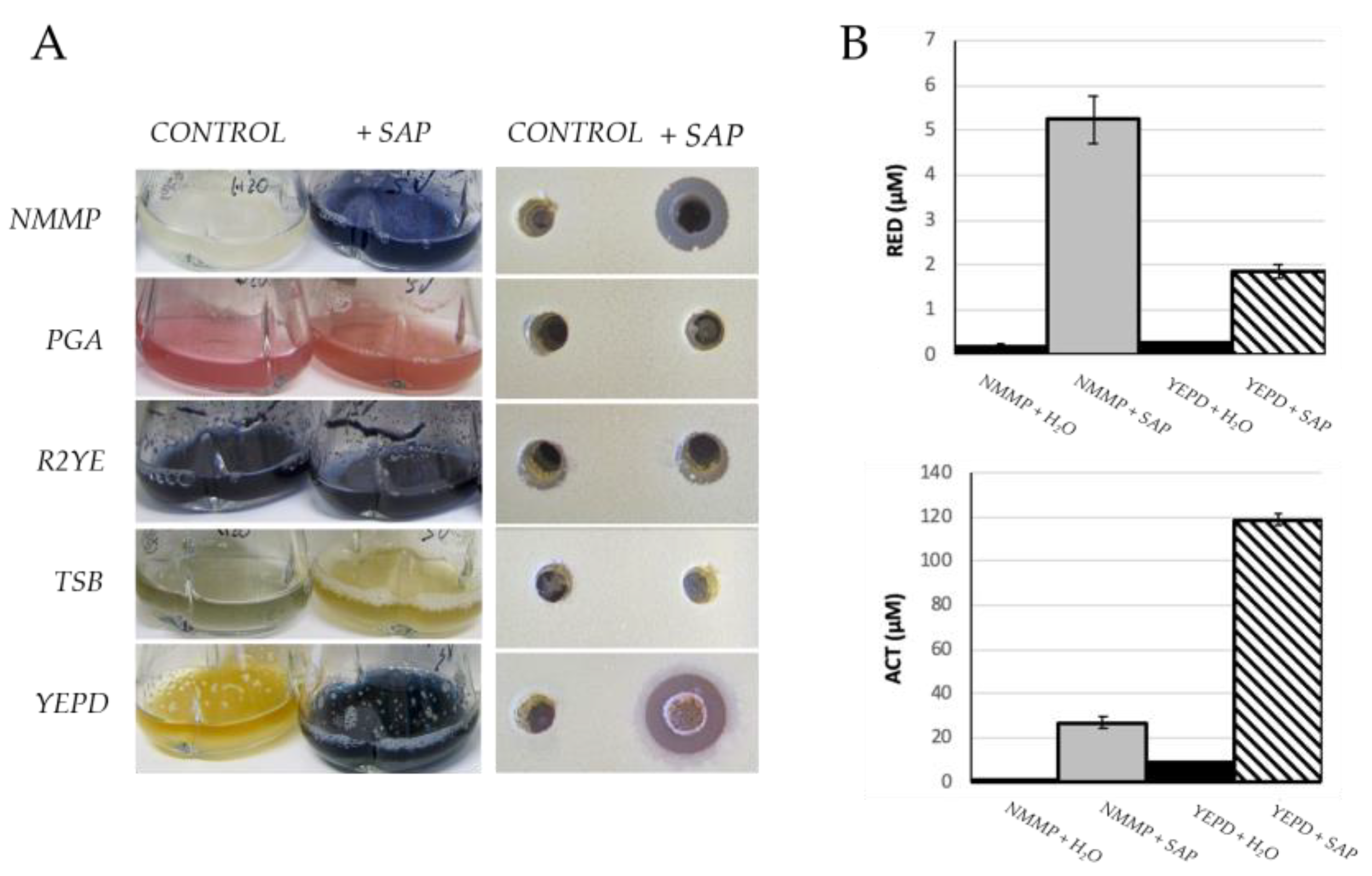
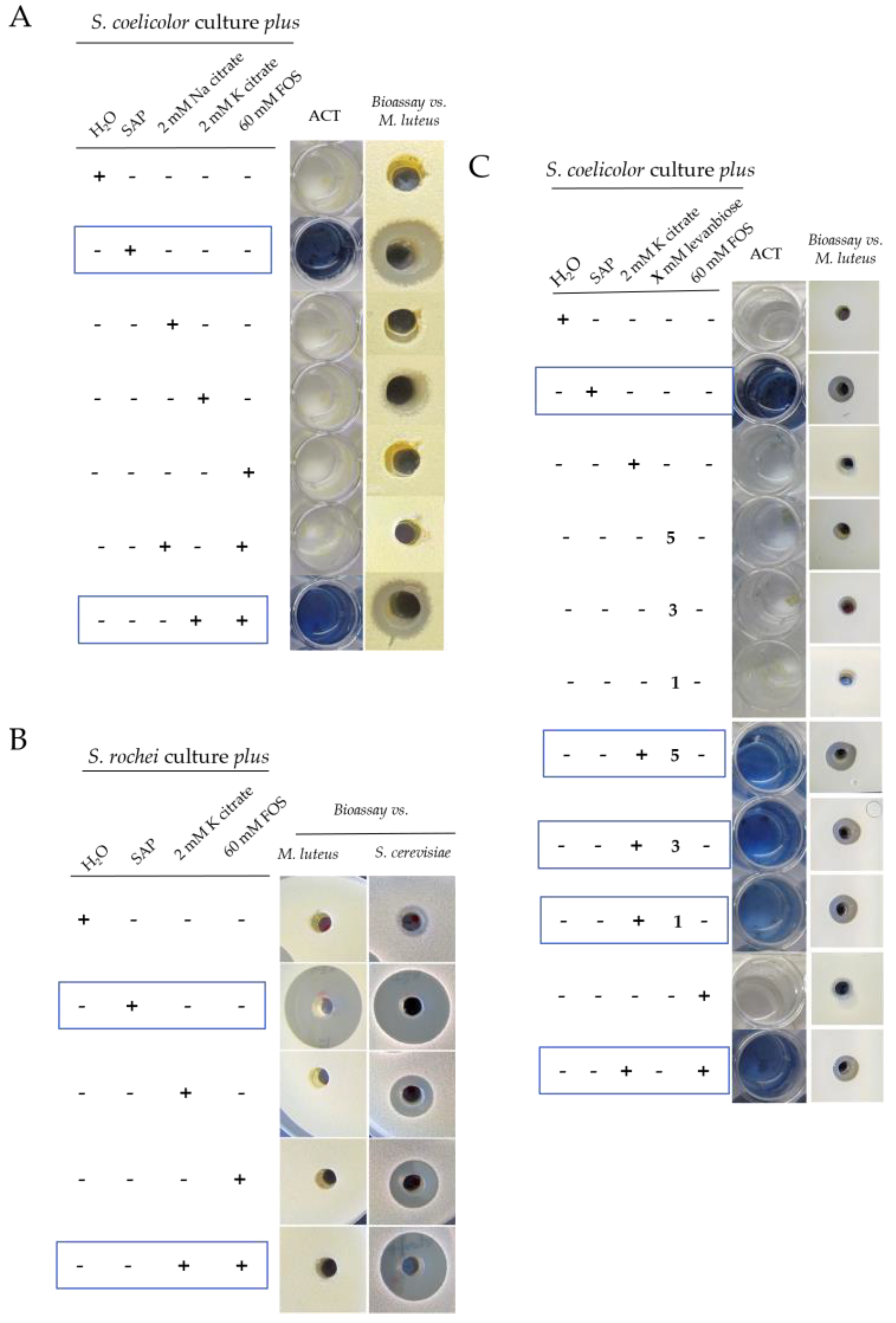
2.1. Grapevine Xylem Sap Induces Antibiotic Production in S. coelicolor
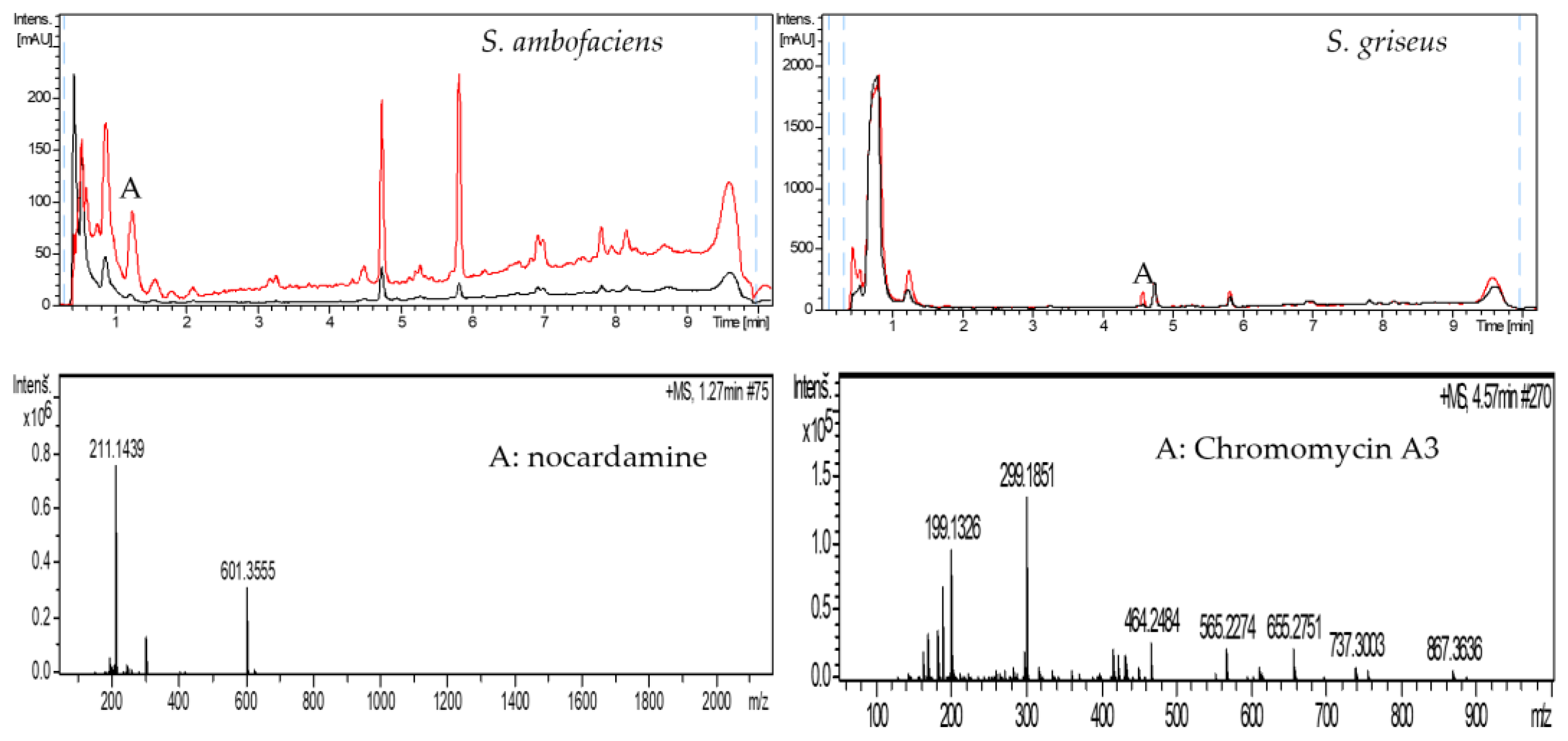
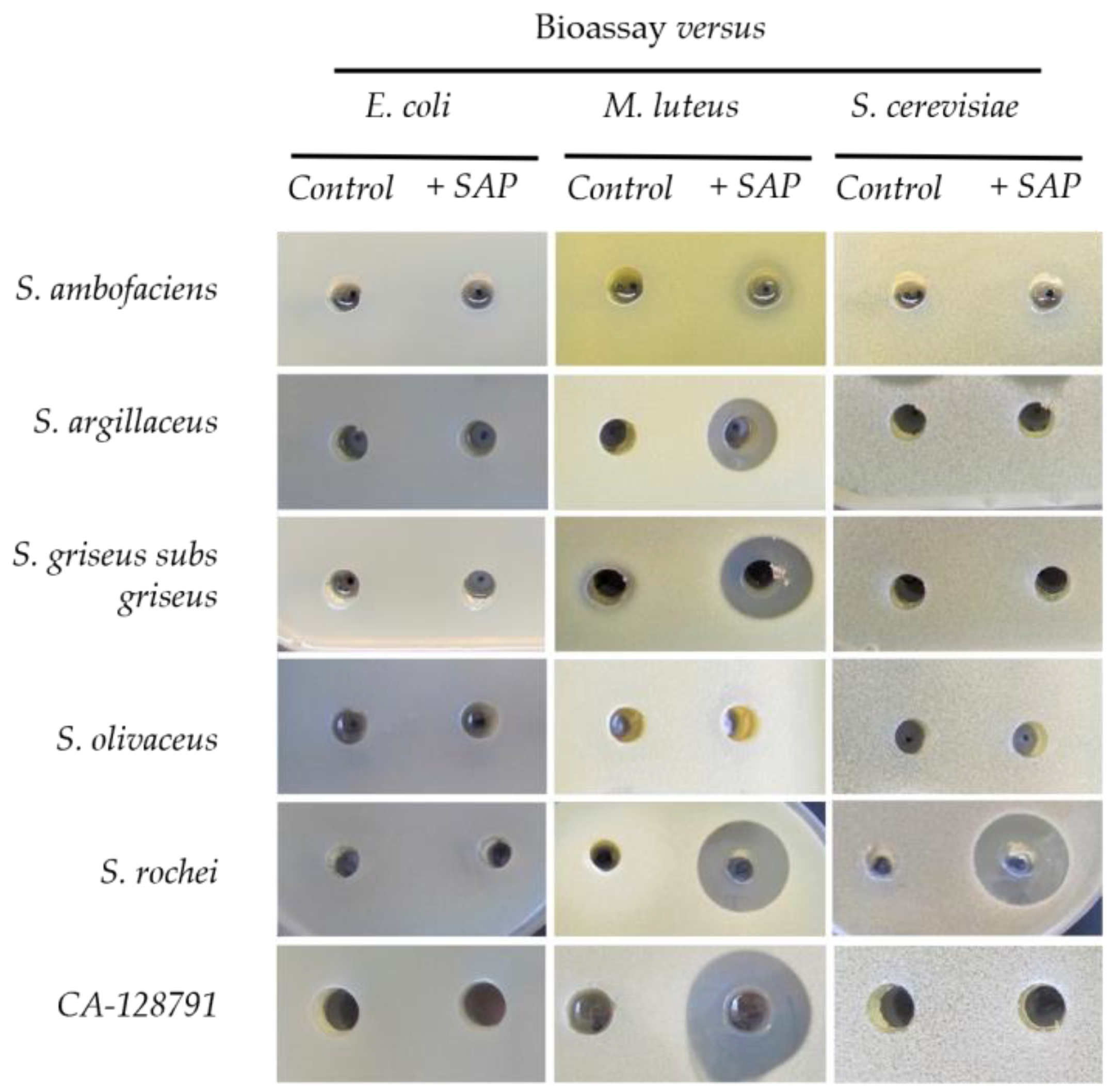
2.2. Grapevine Xylem Sap Elicits Antibiotic Production in Other Streptomyces Species
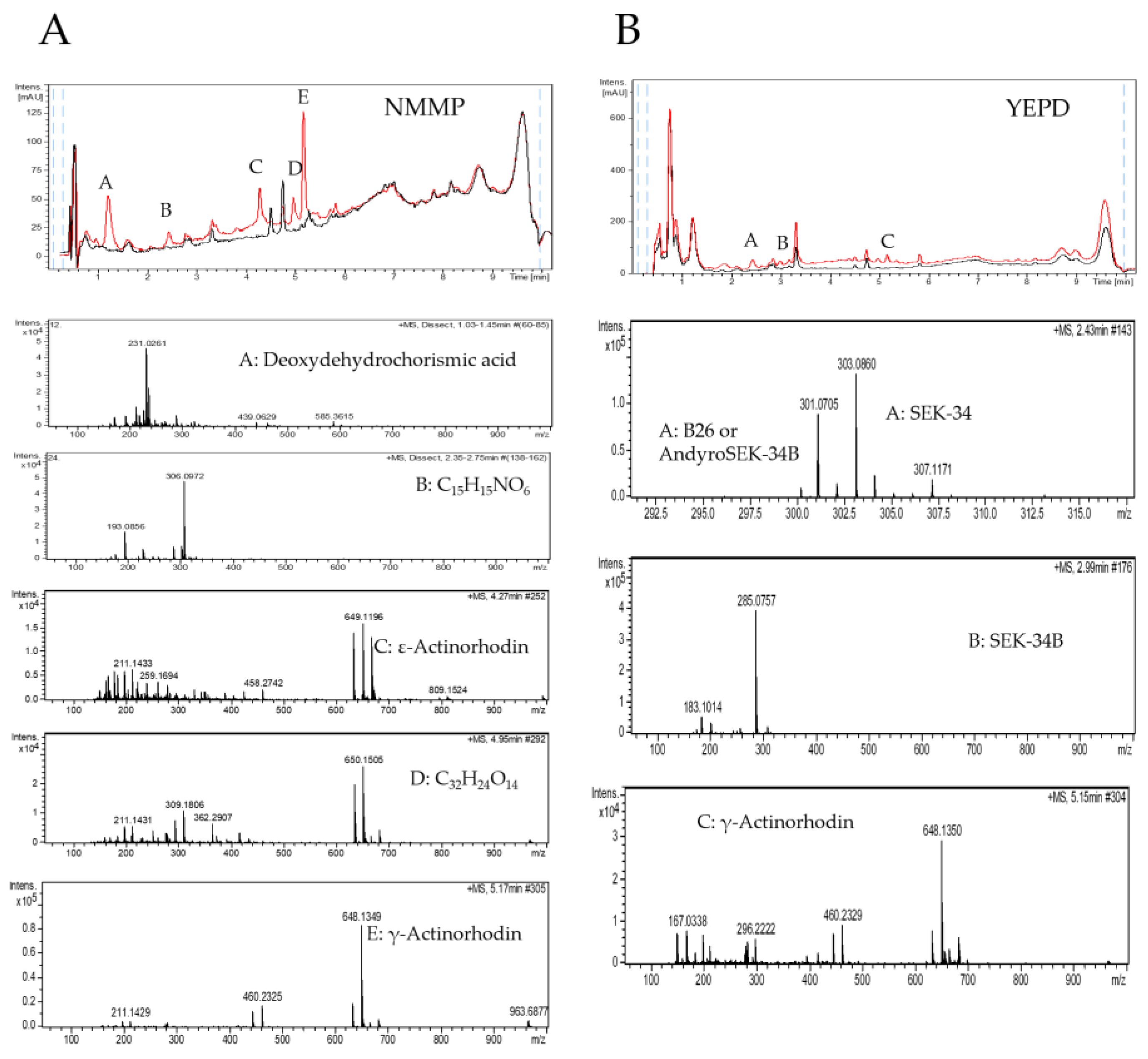
2.3. Purification of the Elicitor Molecule from Xylem Sap
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. Xylem Sap Collection
4.3. Liquid Cultures and Bioactivity
4.4. LC-HRMS-Analyses
4.5. Xylem Sap Fractionation and Elicitor Purification and Identification
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spasic, J.; Mandic, M.; Djokic, L.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J. Streptomyces spp. in the biocatalysis toolbox. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 3513–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopwood, D.A. Highlights of Streptomyces genetics. Heredity 2019, 123, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemung, H.M.; Tan, L.T.; Khan, T.M.; Chan, K.G.; Pusparajah, P.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.H. Streptomyces as a Prominent Resource of Future Anti-MRSA Drugs. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Nakashima, T. Actinomycetes, an Inexhaustible Source of Naturally Occurring Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rutledge, P.J.; Challis, G.L. Discovery of microbial natural products by activation of silent biosynthetic gene clusters. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazal, A.; Thankachan, D.; Harris, E.; Seipke, R.F. A chromatogram-simplified Streptomyces albus host for heterologous production of natural products. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komatsu, M.; Komatsu, K.; Koiwai, H.; Yamada, Y.; Kozone, I.; Izumikawa, M.; Hashimoto, J.; Takagi, M.; Omura, S.; Shin-ya, K.; et al. Engineered Streptomyces avermitilis host for heterologous expression of biosynthetic gene cluster for secondary metabolites. ACS Synth. Biol. 2013, 2, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, Y.; Rebets, Y.; Estevez, M.R.; Zapp, J.; Myronovskyi, M.; Luzhetskyy, A. Engineering of Streptomyces lividans for heterologous expression of secondary metabolite gene clusters. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Escribano, J.P.; Bibb, M.J. Engineering Streptomyces coelicolor for heterologous expression of secondary metabolite gene clusters. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Keulen, G.; Dyson, P.J. Production of specialized metabolites by Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 89, 217–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril, A.; Alvarez, S.; Braña, A.F.; Rico, S.; Díaz, M.; Santamaría, R.I.; Salas, J.A.; Méndez, C. Uncovering production of specialized metabolites by Streptomyces argillaceus: Activation of cryptic biosynthesis gene clusters using nutritional and genetic approaches. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamaría, R.I.; Sevillano, L.; Martín, J.; Genilloud, O.; González, I.; Díaz, M. The XRE-DUF397 Protein Pair, Scr1 and Scr2, Acts as a Strong Positive Regulator of Antibiotic Production in Streptomyces. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z. Positive regulation of the MarR-type regulator slnO and improvement of salinomycin production by Streptomyces albus by multiple transcriptional regulation. Can. J. Microbiol. 2022, 68, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asamizu, S.; Ozaki, T.; Teramoto, K.; Satoh, K.; Onaka, H. Killing of mycolic acid-containing bacteria aborted induction of antibiotic production by Streptomyces in combined-culture. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netzker, T.; Fischer, J.; Weber, J.; Mattern, D.J.; König, C.C.; Valiante, V.; Schroeckh, V.; Brakhage, A.A. Microbial communication leading to the activation of silent fungal secondary metabolite gene clusters. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onaka, H.; Mori, Y.; Igarashi, Y.; Furumai, T. Mycolic acid-containing bacteria induce natural-product biosynthesis in Streptomyces species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez, J.; Muñoz-Dorado, J.; Braña, A.F.; Shimkets, L.J.; Sevillano, L.; Santamaría, R.I. Myxococcus xanthus induces actinorhodin overproduction and aerial mycelium formation by Streptomyces coelicolor. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroeckh, V.; Scherlach, K.; Nützmann, H.W.; Shelest, E.; Schmidt-Heck, W.; Schuemann, J.; Martin, K.; Hertweck, C.; Brakhage, A.A. Intimate bacterial-fungal interaction triggers biosynthesis of archetypal polyketides in Aspergillus nidulans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14558–14563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wakefield, J.; Hassan, H.M.; Jaspars, M.; Ebel, R.; Rateb, M.E. Dual Induction of New Microbial Secondary Metabolites by Fungal Bacterial Co-cultivation. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, H.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Zhan, X.; Mao, X.; Li, Y. The Application of Regulatory Cascades in Streptomyces: Yield Enhancement and Metabolite Mining. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Sandiford, S.K.; Van Wezel, G.P. Triggers and cues that activate antibiotic production by actinomycetes. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Wang, X.; Nie, J.; Niu, G. Regulation of Antibiotic Production by Signaling Molecules in Streptomyces. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manteca, Á.; Yagüe, P. Streptomyces differentiation in liquid cultures as a trigger of secondary metabolism. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyurin, A.P.; Alferova, V.A.; Korshun, V.A. Chemical Elicitors of Antibiotic Biosynthesis in Actinomycetes. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zong, G.; Fu, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Cao, G.; Zhang, R. Use of elicitors to enhance or activate the antibiotic production in Streptomyces. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Wang, D.; Wei, L.; Zhang, Y. Fungal elicitor-induced transcriptional changes of genes related to branched-chain amino acid metabolism in Streptomyces natalensis HW-2. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 4471–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Yuan, J.; Gu, S.; Shi, Q. Influence of fungal elicitors on biosynthesis of natamycin by Streptomyces natalensis HW-2. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 5527–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Jamwal, V.; Singh, V.P.; Wazir, P.; Awasthi, P.; Singh, D.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Gandhi, S.G.; Chaubey, A. Revelation and cloning of valinomycin synthetase genes in Streptomyces lavendulae ACR-DA1 and their expression analysis under different fermentation and elicitation conditions. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 253, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Ma, Z.; Bechthold, A.; Yu, X. Effects of addition of elicitors on rimocidin biosynthesis in Streptomyces rimosus M527. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 4445–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Nazari, B.; Moon, K.; Bushin, L.B.; Seyedsayamdost, M.R. Discovery of a Cryptic Antifungal Compound from Streptomyces albus J1074 Using High-Throughput Elicitor Screens. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9203–9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glad, P.; Regnard, J.L.; Querou, Y.; Brun, O.; Morot-Gaudry, J. Flux and Chemical Composition of Xylem Exudates from Chardonnay Grapevines: Temporal Evolution and Effect of Recut. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1992, 43, 275–682. [Google Scholar]
- Le, L.; Umar, A.; Iburaim, A.; Moore, N. Constituents and Antioxidant Activity of Bleeding Sap from Various Xinjiang Grapes. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, S726–S730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prima-Putra, D.; Botton, B. Organic and inorganic compounds of xylem exudates from five woody plants at the stage of bud breaking. J. Plant Physiol. 1998, 153, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wormall, A. The Constituents of the Sap of the Vine (Vitis vinifera L.). Biochem. J. 1924, 18, 1187–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, T.; Haider, M.S.; Zhang, K.; Jia, H.; Fang, J. Biological and functional properties of xylem sap extracted from grapevine (cv. Rosario Bianco). Sci. Hortic. 2020, 272, 109563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzoch, K.; de Mattos, M.; Neijssel, O. Production of actinorhodin by Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) grown in chemostat culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1997, 54, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsbu, E.; McIntyre, M.; Nielsen, J. The influence of carbon sources and morphology on nystatin production by Streptomyces noursei. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 95, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Rodríguez, A.; Maldonado-Carmona, N.; Ruiz-Villafán, B.; Koirala, N.; Rocha, D.; Sánchez, S. Interplay between carbon, nitrogen and phosphate utilization in the control of secondary metabolite production in Streptomyces. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 761–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, S.; Chávez, A.; Forero, A.; García-Huante, Y.; Romero, A.; Sánchez, M.; Rocha, D.; Sánchez, B.; Avalos, M.; Guzmán-Trampe, S.; et al. Carbon source regulation of antibiotic production. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coco, E.A.; Narva, K.E.; Feitelson, J.S. New classes of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) mutants blocked in undecylprodigiosin (Red) biosynthesis. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1991, 227, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieser, T.; Hopwood, D.A.; Bibb, J.M.; Chater, K.F.; Buttner, M.J. Practical Streptomyces Genetics; John Innes Foundation: Norwich, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, M.D.; Winston, F.; Hieter, P. Methods in Yeast Genetics: A Laboratory Course Manual; Cold Sping Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Yepes, A.; Rico, S.; Rodríguez-García, A.; Santamaría, R.I.; Díaz, M. Novel two-component systems implied in antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martín, J.; Crespo, G.; González-Menéndez, V.; Pérez-Moreno, G.; Sánchez-Carrasco, P.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Ruiz-Pérez, L.M.; González-Pacanowska, D.; Vicente, F.; Genilloud, O.; et al. MDN-0104, an antiplasmodial betaine lipid from Heterospora chenopodii. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2118–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Victoria, I.; Martín, J.; Reyes, F. Combined LC/UV/MS and NMR Strategies for the Dereplication of Marine Natural Products. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santamaría, R.I.; Martínez-Carrasco, A.; Martín, J.; Tormo, J.R.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; González, I.; Genilloud, O.; Reyes, F.; Díaz, M. Grapevine Xylem Sap Is a Potent Elicitor of Antibiotic Production in Streptomyces spp. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11050672
Santamaría RI, Martínez-Carrasco A, Martín J, Tormo JR, Pérez-Victoria I, González I, Genilloud O, Reyes F, Díaz M. Grapevine Xylem Sap Is a Potent Elicitor of Antibiotic Production in Streptomyces spp. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(5):672. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11050672
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantamaría, Ramón I., Ana Martínez-Carrasco, Jesús Martín, José R. Tormo, Ignacio Pérez-Victoria, Ignacio González, Olga Genilloud, Fernando Reyes, and Margarita Díaz. 2022. "Grapevine Xylem Sap Is a Potent Elicitor of Antibiotic Production in Streptomyces spp." Antibiotics 11, no. 5: 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11050672
APA StyleSantamaría, R. I., Martínez-Carrasco, A., Martín, J., Tormo, J. R., Pérez-Victoria, I., González, I., Genilloud, O., Reyes, F., & Díaz, M. (2022). Grapevine Xylem Sap Is a Potent Elicitor of Antibiotic Production in Streptomyces spp. Antibiotics, 11(5), 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11050672








