Interaction of Temporin-L Analogues with the E. coli FtsZ Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Design of the Mutated Temporin-L Peptides and Molecular Docking Analysis
2.2. Binding of the Temporin-L Analogues to FtsZ
2.3. Effect of TL Analogues on the GTPase Activity of FtsZ
2.4. Effect of TL Analogues on the Polymerization of FtsZ
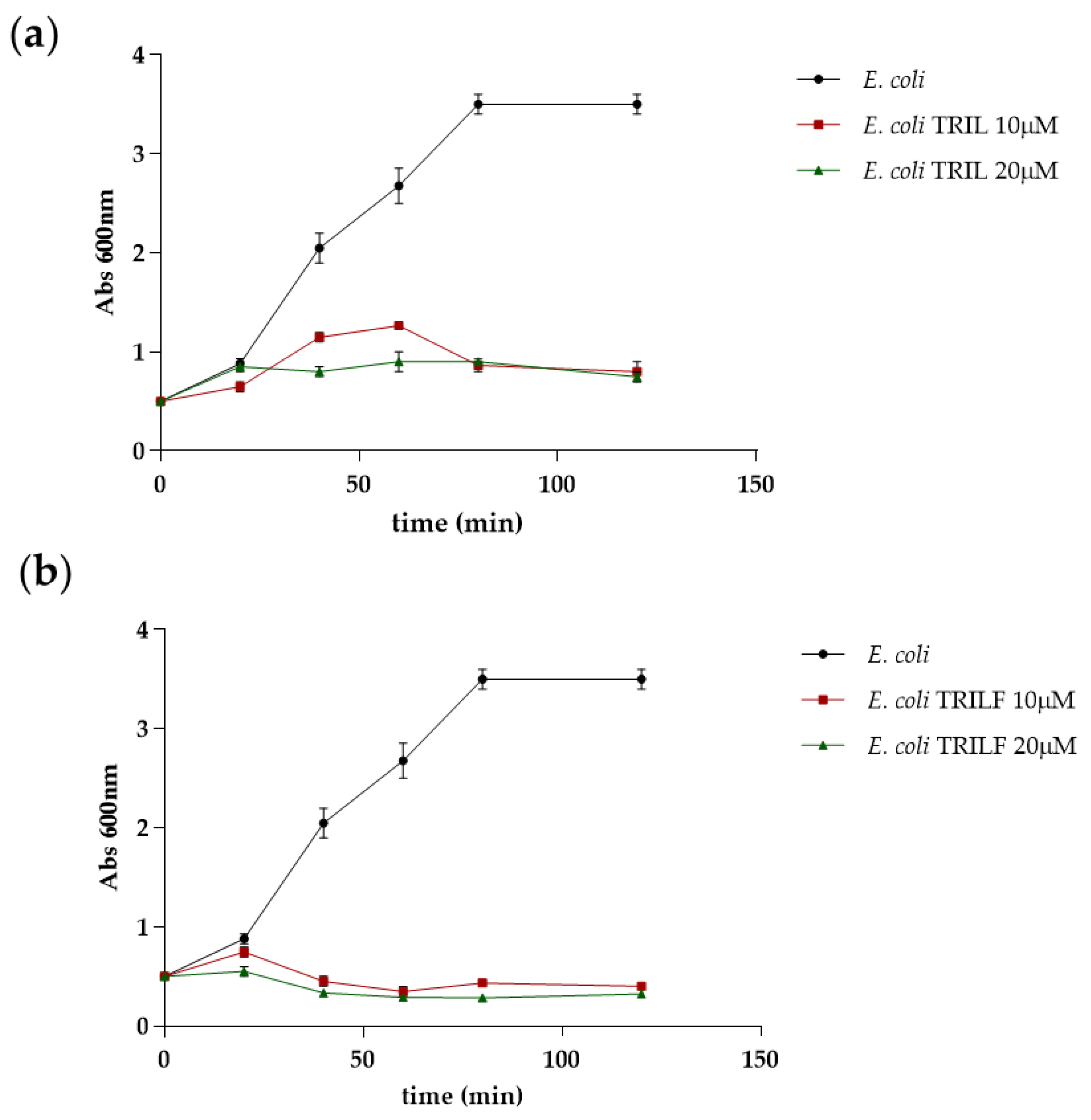
2.5. Antimicrobial Activity of TRIL and TRILF
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Design of the Temporin-L Analogues and Molecular Docking Analyses
4.2. Recombinant Production of FtsZ
4.3. Binding Experiment
4.4. GTPase Activity Assay
4.5. Polymerization Assay
4.6. Determination of Antibacterial Activity of TRIL and TRILF
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 817–823. [Google Scholar]
- Boparai, J.K.; Sharma, P.K. Mini review on antimicrobial peptides, sources, mechanism and recent applications. Protein Pept. Lett. 2020, 27, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Lu, T.K. Development and challenges of antimicrobial peptides for therapeutic applications. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewies, A.; Du Plessis, L.H.; Wentzel, J.F. Antimicrobial peptides: The Achilles’ heel of antibiotic resistance. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Roy, A. Antimicrobial peptides as potential therapeutic agents: A review. IJPRT 2021, 27, 555–577. [Google Scholar]
- Brancaccio, D.; Pizzo, E.; Cafaro, V.; Notomista, E.; De Lise, F.; Bosso, A.; Carotenuto, A. Antimicrobial peptide Temporin-L complexed with anionic cyclodextrins results in a potent and safe agent against sessile bacteria. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 584, 119437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Somma, A.; Avitabile, C.; Cirillo, A.; Moretta, A.; Merlino, A.; Paduano, L.; Duilio, A.; Romanelli, A. The antimicrobial peptide Temporin L impairs E. Coli cell division by interacting with FtsZ and the divisome complex. BBA Gen. Subj. 2020, 1864, 129606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrows, J.M.; Goley, E.D. FtsZ dynamics in bacterial division: What, how, and why? Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2021, 68, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, N.; Radler, P.; Hernández-Rocamora, V.M.; Alfonso, C.; Lòpez-Pelegrin, M.; Rivas, G.; Loose, M. Diffusion and capture permits dynamic coupling between treadmilling FtsZ filaments and cell division proteins. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmaco, M.; Mignogna, G.; Canofeni, S.; Miele, R.; Mangoni, M.L.; Barra, D. Temporins, antimicrobial peptides from the European red frog Rana temporaria. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 242, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, S.M.; Cardillo, A.B.; Martínez Ceron, M.C.; Camperi, S.A.; Giudicessi, S.L. Temporins: An Approach of Potential Pharmaceutic Candidates. SIS 2020, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, G.; Ferguson, P.M.; Hind, C.K.; Clifford, M.; Gustilo, V.B.; Ali, H.; Bansal, S.; Bui, T.; Drake, A.F.; Atkinson, R.A.; et al. Temporin L and aurein 2.5 have identical conformations but subtly distinct membrane and antibacterial activities. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, A.C.; Mangoni, M.L.; Rufo, A.; Luzi, C.; Barra, D.; Zhao, H.; Kinnunen, P.K.J.; Bozzi, A.; Di Giulio, A.; Simmaco, M. Temporin L: Antimicrobial, haemolytic and cytotoxic activities, and effects on membrane permeabilization in lipid vesicles. Biochem. J. 2002, 368, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, M.L.; Papo, N.; Barra, D.; Simmaco, M.; Bozzi, A.; Di Giulio, A.; Rinaldi, A.C. Effects of the antimicrobial peptide temporin L on cell morphology, membrane permeability and viability of Escherichia coli. Biochem. J. 2004, 380, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellavita, R.; Falanga, A.; Buommino, E.; Merlino, F.; Casciaro, B.; Cappiello, F.; Mangoni, M.L.; Novellino, E.; Catania, M.R.; Polillo, R.; et al. Novel temporin L antimicrobial peptides: Promoting self-assembling by lipidic tags to tackle superbugs. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1751–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorrilla, S.; Monterroso, B.; Robles-Ramos, M.Á.; Margolin, W.; Rivas, G. FtsZ Interactions and Biomolecular Condensates as Potential Targets for New Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Teng, D.; Mao, R.; Hao, Y.; Yang, N.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Recent progress of bacterial FtsZ inhibitors with a focus on peptides. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 1091–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, M.L.; Carotenuto, A.; Auriemma, L.; Saviello, M.R.; Campiglia, P.; Gomez-Monterrey, I.; Malfi, S.; Marcellini, L.; Barra, D.; Novellino, E.; et al. Structure-activity relationship, conformational and biological studies of temporin L analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server: New development for protein structure and function predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W174–W181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Inbar, Y.; Nussinov, R.; Wolfson, H.J. PatchDock and SymmDock: Servers for rigid and symmetric docking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W363–W367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashiach, E.; Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Andrusier, N.; Nussinov, R.; Wolfson, H.J. FireDock: A web server for fast interaction refinement in molecular docking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W229–W232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A. PDBsum new things. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 37, D355–D359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A. PDBsum: Summaries and analyses of PDB structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.C.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Kastritis, P.L.; Bonvin, A.M.; Vangone, A. PRODIGY: A web server for predicting the binding affinity of protein–protein complexes. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3676–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghu, F.H.; Barai, R.S.; Gurung, P.; Idicula, T.S. CAMPR3: A database on sequences, structures and signatures of antimicrobial peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, D1094–D1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.Y.; Du, R.L.; Cai, S.Y.; Liu, Z.H.; Fang, Z.Y.; Liu, T.; Wong, K.Y. Study of benzofuroquinolinium derivatives as a new class of potent antibacterial agent and the mode of inhibition targeting FtsZ. Front. Microb. 2018, 9, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazos, M.; Casanova, M.; Palacios, P.; Margolin, W.; Natale, P.; Vicente, M. FtsZ placement in nucleoid-free bacteria. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pla, J.; Palacios, P.; Sánchez, M.; Garrido, T.; Vicente, M. Stability of components of the Escherichia coli Septator. In Bacterial Growth and Lysis; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1993; pp. 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Pla, J.; Sanchez, M.; Patacios, P.; Vicente, M.; Aldea, M. Preferential cytoplasmic location of FtsZ, a protein essential for Escherichia coli septation. Mol. Microbiol. 1991, 5, 1681–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Peptide/Protein | C-Score | TM-Score | RMSD (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FtsZ | −0.55 | 0.64 ± 0.13 | 7.9 ± 4.4 |
| TL | 0.09 | 0.73 ± 0.11 | 0.5 ± 0.5 |
| FVKWFKKFLTRIL | 0.07 | 0.72 ± 0.11 | 0.5 ± 0.5 |
| FVKWFKKFLTRILF | −0.06 | 0.71 ± 0.12 | 0.6 ± 0.6 |
| Protein-Peptide Complex | Global Energy (Kcal/mol) | Attractive Van der Waals Forces (KJ/mol) | Repulsive Van der Waals Forces (KJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FtsZ−TL | −40.54 | −18.63 | 5.71 |
| FtsZ−TRIL (FVKWFKKFLTRIL) | −26.84 | −30.69 | 18.88 |
| FtsZ−TRILF (FVKWFKKFLTRILF) | −30.99 | −46.97 | 24.35 |
| Peptide | SVM | DA | RF | ANN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native Temporin L FVQWFSKFLGRIL | 0.876 | 0.899 | 0.9685 | AMP |
| FVKWFKKFLTRIL | 0.997 | 0.981 | 0.941 | AMP |
| (TRIL) | ||||
| FVKWFKKFLTRILF | 0.994 | 0.973 | 0.906 | AMP |
| (TRILF) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Somma, A.; Canè, C.; Moretta, A.; Duilio, A. Interaction of Temporin-L Analogues with the E. coli FtsZ Protein. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060704
Di Somma A, Canè C, Moretta A, Duilio A. Interaction of Temporin-L Analogues with the E. coli FtsZ Protein. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(6):704. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060704
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Somma, Angela, Carolina Canè, Antonio Moretta, and Angela Duilio. 2021. "Interaction of Temporin-L Analogues with the E. coli FtsZ Protein" Antibiotics 10, no. 6: 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060704
APA StyleDi Somma, A., Canè, C., Moretta, A., & Duilio, A. (2021). Interaction of Temporin-L Analogues with the E. coli FtsZ Protein. Antibiotics, 10(6), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060704








