Prevalence and Antibiogram of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Aeromonas hydrophila in the Flesh of Nile Tilapia, with Special Reference to Their Virulence Genes Detected Using Multiplex PCR Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Environmental Parameter at Manzala Farm
2.2. Clinical Signs and Postmortem Examination of Diseased Tilapia
2.3. Prevalence of Comfirmed Isolates of V. parahaemolyticus and A. hydrophila in the Examined Nile tilapia Based on Biochemical Tests
2.4. Molecular Identification:
2.4.1. Molecular identification of V. parahaemolyticus
2.4.2. Molecular identification of A. hydrophila
2.5. Antibiotic Susceptibility of V. parahaemolyticus and A. hydrophila Positive Strains Confirmed by Multiplex PCR Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Farm Information
4.2. Fish Sampling
4.3. Bacteriological Examination
4.3.1. Preparation of Fish Samples
4.3.2. Culture Characters
4.3.3. Biochemical Examination
4.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and MAR Index Value
4.5. Molecular Identification of V. parahaemolyticus and A. hydrophila Virulence Genes
4.5.1. Molecular Identification of A. hydrophila Virulence Genes
4.5.2. Molecular Identification of V. parahaemolyticus Virulence Genes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soliman, N.F.; Yacout, D.M.M. Aquaculture in Egypt: Status, constraints and potentials. Aquac. Int. 2016, 24, 1201–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Ghany, H.M.; El-Sayed, A.F.M.; Ezzat, A.A.; Essa, M.A.; Helal, A.M. Dietary lipid sources affect cold tolerance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Therm. Biol. 2019, 79, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyat, M.S.; Ayyat, A.M.N.; Naiel, M.A.E.; Al-Sagheer, A.A. Reversal effects of some safe dietary supplements on lead contaminated diet induced impaired growth and associated parameters in Nile tilapia. Aquaculture 2020, 515, 734580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei, E.; Albert, J. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Encycl. Food Health 2015, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Ayers, T.; Mahon, B.E.; Swerdlow, D.L. Epidemiology of seafood-associated infections in the United States. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, M.; Li, Y. Intervention Strategies for Reducing Vibrio Parahaemolyticus in Seafood: A Review. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, R10–R19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pech, Z.G.H.; Chavez, M.R.C.; Reynoso, F.L. Pathogenic Bacteria in Oreochromis Niloticus Var. Stirling Tilapia Culture. Fish. Aquac. J. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Macedo, M.L.; Barancelli, G.V.; Contreras-Castillo, C.J. Microbial deterioration of vacuum-packaged chilled beef cuts and techniques for microbiota detection and characterization: A review. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissa, I.A.M.; El-Lamei, M.; Sherif, M.; Youssef, F.; Zaki, M.S.; Bakry, M. Detection of hemolysin gene and antibiogramme of Aeromonas veronii biovar sobria isolated from mass mortalities in cultured Nile Tilapia in El-Sharkia governorate, Egypt. Life Sci. J. 2015, 12, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.T.; Techatanakitarnan, C.; Jindakittikul, P.; Thaiprayoon, A.; Taengphu, S.; Charoensapsri, W.; Khunrae, P.; Rattanarojpong, T.; Senapin, S. Aeromonas jandaei and Aeromonas veronii caused disease and mortality in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). J. Fish. Dis. 2017, 40, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, F.P. Aquaculture disease and health management. J. Anim. Sci. 1991, 69, 4201–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeney, Z.; Jeney, G. Recent achievements in studies on diseases of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquaculture 1995, 129, 397–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, A.E. Innate host defense mechanisms of fish against viruses and bacteria. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsen, O.B.; Nerland, A.H.; Jørgensen, T.; Schrøder, M.B.; Svåsand, T.; Bergh, Ø. Viral and bacterial diseases of Atlantic cod Gadus morhua, their prophylaxis and treatment: A review. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2006, 71, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricknell, I.R.; Bron, J.E.; Bowden, T.J. Diseases of gadoid fish in cultivation: A review. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 63, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerset, I.; Krossøy, B.; Biering, E.; Frost, P. Vaccines for fish in aquaculture. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2005, 4, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M. Shrimp diseases and current diagnostic methods. Aquaculture 1998, 164, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimohata, T.; Takahashi, A. Diarrhea induced by infection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Med. Investig. 2010, 57, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, T.; Iida, T. The pathogenicity of vibrio parahaemolyticus and the role of the thermostable direct haemolysin and related haemolysins. Rev. Med. Microbiol. 1993, 4, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez West, C.K.; Klein, S.L.; Lovell, C.R. High frequency of virulence factor genes tdh, trh, and tlh in Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains isolated from a pristine estuary. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2247–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, K.; Oshima, K.; Kurokawa, K.; Yokoyama, K.; Uda, T.; Tagomori, K.; Iijima, Y.; Najima, M.; Nakano, M.; Yamashita, A.; et al. Genome sequence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: A pathogenic mechanism distinct from that of V cholerae. Lancet 2003, 361, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zheng, A.; Bromfield, E.S.P.; Zhu, J.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Deng, Q.; Li, P. 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis of halophilic and halotolerant bacteria isolated from a hypersaline pond in Sichuan, China. Ann. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazhani, G.P.; Bhowmik, S.K.; Ghosh, S.; Guin, S.; Dutta, S.; Rajendran, K.; Saha, D.R.; Nandy, R.K.; Bhattacharya, M.K.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; et al. Trends in the Epidemiology of Pandemic and Non-pandemic Strains of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Isolated from Diarrheal Patients in Kolkata, India. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pinto, A.; Ciccarese, G.; Tantillo, G.; Catalano, D.; Forte, V.T. A collagenase-targeted multiplex PCR assay for identification of Vibrio alginolyticus, Vibrio cholerae, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Gil, B.; Roque, A. Isolation, Enumeration, and Preservation of the Vibrionaceae. Biol. Vibrios 2006, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Deen, A.E.N.; Dorgham, S.M.; Hassan, A.H.M.; Hakim, A.S. Studies on Aeromonas hydrophila in Cultured Oreochromis niloticus at Kafr El Sheikh Governorate, Egypt with Reference to Histopathological Alterations in Some Vital Organs. World J. Fish. Mar. Sci. 2014, 6, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Carnahan, A.; Joseph, S.W. Aeromonadalesord. Nov. In Bergey’s Manual® of Systematic Bacteriology: Volume Two the Proteobacteria Part B The Gammaproteobacteria; Brenner, D.J., Krieg, N.R., Staley, J.T., Garrity, G.M., Boone, D.R., De Vos, P., Goodfellow, M., Rainey, F.A., Schleifer, K.H., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 556–587. [Google Scholar]
- Demarta, A.; Küpfer, M.; Riegel, P.; Harf-Monteil, C.; Tonolla, M.; Peduzzi, R.; Monera, A.; José Saavedra, M.; Martínez-Murcia, A. Aeromonas tecta sp. nov., isolated from clinical and environmental sources. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 31, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trakhna, F.; Harf-Monteil, C.; Abdelnour, A.; Maaroufi, A.; Gadonna-Widehem, P. Rapid Aeromonas hydrophila identification by TaqMan PCR assay: Comparison with a phenotypic method. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboyadak, I.M.; Ali, N.G.; Goda, A.M.; Saad, W.; Salam, A.M. Non-Selectivity of R-S Media for Aeromonas hydrophila and TCBS Media for Vibrio Species Isolated from Diseased Oreochromis niloticus. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2017, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P. Breakpoints for disc diffusion susceptibility testing of bacteria associated with fish diseases: A review of current practice. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunke, G.; Namshikar, V.; Gaonkar, R.; Gaonkar, T. A case of Aeromonas hydrophila meningitis in septic shock. Trop. J. Med. Res. 2015, 18, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, M.R.; Figueras, M.J.; Castro-Escarpulli, G.; Soler, L.; Guarro, J. Distribution of virulence genes in clinical and environmental isolates of Aeromonas spp. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2003, 84, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozaki, S.; Asao, T.; Kamata, Y.; Sakaguchi, G. Characterization of Aeromonas sobria hemolysin by use of monoclonal antibodies against Aeromonas hydrophila hemolysins. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 1782–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, L.; Yáñez, M.A.; Chacon, M.R.; Aguilera-Arreola, M.G.; Catalán, V.; Figueras, M.J.; Martínez-Murcia, A.J. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Aeromonas based on two housekeeping genes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, R.; Surendran, P.K.; Chakraborty, K. Antibiotic resistance and plasmid profiling of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from shrimp farms along the southwest coast of India. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.A.; El Bayomi, R.M.; Hussein, M.A.; Khedr, M.H.E.; Abo Remela, E.M.; El-Ashram, A.M.M. Molecular characterization, antibiotic resistance pattern and biofilm formation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and V. cholerae isolated from crustaceans and humans. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 274, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumperman, P.H. Multiple antibiotic resistance indexing of Escherichia coli to identify high-risk sources of fecal contamination of foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Deyab, M.A.I.; Desouki, S.S.; Eladl, M. Phytoplankton compositions as a response of water quality in el salam canal hadous drain and Damietta branch of river Nile Egypt. Pakistan J. Bot. 2010, 42, 2621–2633. [Google Scholar]
- Zaky, M.M.M.; Mansour, F.A.; Persson, K.M. Factors influencing multi-drug resistant and plasmid DNA harbouring Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from Lake Manzala, Egypt. J. Bacteriol. Res. 2010, 2, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.H.; El Leithy, B.M.; Thompson, J.R.; Flower, R.J.; Ramdani, M.; Ayache, F.; Hassan, S.M. Application of remote sensing to site characterisation and environmental change analysis of North African coastal lagoons. Hydrobiologia 2009, 622, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, Y.A.; Abdelmoneim, T.S.; ElKiki, M.H.; Hassan, M.A.; Berndtsson, R. Assessment of heavy metals pollution and microbial contamination in water, sediments and fish of Lake Manzala, Egypt. Life Sci. J. 2013, 10, 86–99. [Google Scholar]
- Moraes, F.R.; Martins, M.L. Favourable conditions and principal teleostean diseases in intensive fish farming. In Especial Topics in Tropical Intensive Freshwater Fish Farming; Cyrino, J.E.P., Urbinati, E.C., Fracalossi, D.M., Castagnolli, N., Eds.; Tec Art Publ.: Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2004; pp. 343–383. [Google Scholar]
- Dahdouh, B.; Basha, O.; Khalil, S.; Tanekhy, M. Molecular Characterization, Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Salt Tolerance of Aeromonas hydrophila from Fresh, Brackish and Marine fishes. Alexandria J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 48, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, M.J.A.; Rashid, M.M. Pathogenicity of the bacterial isolate Aeromonas hydrophila to catfishes, carps and perch. J. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 2012, 10, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Abdel-Rahman, M.; Mansour, E.S.; Monir, W. Isolation, phenotypic characterization and antibiotic susceptibility of prevalent bacterial pathogens implicating the mortality of cultured Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Egypt. J. Aquac. 2020, 10, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorlis, A.; Ghazali, F.M.; Cheah, Y.K.; Tuan Zainazor, T.C.; Ponniah, J.; Tunung, R.; Tang, J.Y.H.; Nishibuchi, M.; Nakaguchi, Y.; Son, R. Prevalence and quantification of Vibrio species and Vibrio parahaemolyticus in freshwater fish at hypermarket level. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18, 689–695. [Google Scholar]
- Algammal, A.M.; Mohamed, M.F.; Tawfiek, B.A.; Hozzein, W.N.; Kazzaz, W.M.E.; Mabrok, M. Molecular typing, antibiogram and PCR-RFLP based detection of Aeromonas hydrophila complex isolated from Oreochromis niloticus. Pathogens 2020, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wamala, S.P.; Mugimba, K.K.; Mutoloki, S.; Evensen, O.; Mdegela, R.; Byarugaba, D.K.; Sørum, H. Occurrence and antibiotic susceptibility of fish bacteria isolated from Oreochromis niloticus (Nile tilapia) and Clarias gariepinus (African catfish) in Uganda. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehinmidu, J.O. Antibiotics susceptibility patterns of urine bacterial isolates in Zaria, Nigeria. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2003, 2, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pokhrel, H.; Baishya, S.; Phukan, B.; Pillai, D.; Ashraf Rather, M. Occurrence and Distribution of Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Bacteria of Public Health Significance in Backwaters and Aquaculture Farm. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesley, M.B.; Velnetti, L.; Cheah, Y.K.; Son, R.; Kasing, A.; Samuel, L.; Micky, V.; Nishibuchi, M. Antibiotic resistance and plasmid profiling of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from cockles (Anadara granosa) at Tanjung Karang, Kuala Selangor. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Manjusha, S.; Sarita, G.B. Plasmid associated antibiotic resistance in Vibrios isolated from coastal waters of Kerala. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Noorlis, A.; Ghazali, F.M.; Cheah, Y.K.; Tuan Zainazor, T.C.; Wong, W.C.; Tunung, R.; Pui, C.F.; Nishibuchi, M.; Nakaguchi, Y.; Son, R. Antibiotic resistance and biosafety of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio parahaemolyticus from freshwater ish at retail level. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Odeyemi, O.A.; Stratev, D. Occurrence of antimicrobial resistant or pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood. A mini review. Rev. Med. Vet. (Toulouse) 2016, 167, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.; Chen, L. Virulence, resistance, and genetic diversity of Vibrio parahaemolyticus recovered from commonly consumed aquatic products in Shanghai, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauzi, N.A.; Mohamad, N.; Azzam-Sayuti, M.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Saad, M.Z.; Nasruddin, N.S.; Azmai, M.N.A. Antibiotic susceptibility and pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus×Oreochromis mossambicus) in Malaysia. Vet. World 2020, 13, 2166–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, L.; Chenia, H.Y. Characterization of integrons and tetracycline resistance determinants in Aeromonas spp. isolated from South African aquaculture systems. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 114, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreedharan, K.; Philip, R.; Singh, I.S.B. Virulence potential and antibiotic susceptibility pattern of motile aeromonads associated with freshwater ornamental fish culture systems: A possible threat to public health. Brazilian J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.A.; Mohamed, M.E.M.; Rezk, M.M.; Gharieb, R.M.A.; Abdel-Maksoud, S.A. Aeromonas hydrophila in fish and humans; prevalence, virulotyping and antimicrobial resistance. Slov. Vet. Res. 2018, 55, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiru, A.W.; Uaboi-Egbeni, P.O.; Oguntowo, J.E.; Idika, C.N. Isolation and antibiotic profile of aeromonas species from tilapia fish (Tilapia nilotica) and catfish (Clarias betrachus). Pakistan J. Nutr. 2011, 10, 982–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.H.; Mutalib, N.S.A.; Law, J.W.F.; Wong, S.H.; Letchumanan, V. Discovery on antibiotic resistance patterns of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Selangor reveals carbapenemase producing Vibrio parahaemolyticus in marine and freshwater fish. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunung, R.; Margaret, S.P.; Jeyaletchumi, P.; Chai, L.C.; Zainazor, T.C.T.; Ghazali, F.M.; Nakaguchi, Y.; Nishibuchi, M.; Son, R. Prevalence and quantification of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in raw salad vegetables at retail level. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, M.; Chan, C.S.W.; Apun, K. Molecular confirmation and characterization of Vibrio parahaemolyticus from retailed fish. Int. Food Res. J. 2015, 22, 1705–1710. [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Pillot, A.; Guénolé, A.; Lesne, J.; Delesmont, R.; Fournier, J.M.; Quilici, M.L. Occurrence of the tdh and trh genes in Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates from waters and raw shellfish collected in two French coastal areas and from seafood imported into France. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 91, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.F.; Peng, C.F.; Lin, Y.H.; Lin, S.R.; Chen, Y.H. Molecular diversity of class 1 integrons in human isolates of Aeromonas spp. from southern Taiwan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 343–349. [Google Scholar]
- Fuenzalida, L.; Armijo, L.; Zabala, B.; Hernández, C.; Rioseco, M.L.; Riquelme, C.; Espejo, R.T. Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains isolated during investigation of the summer 2006 seafood related diarrhea outbreaks in two regions of Chile. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 117, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, J.; Li, H.; Tan, S.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H. Prevalence, antibiotic susceptibility and diversity of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates in seafood from South China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Sallam, K.I. Occurrence and molecular identification of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in retail shellfish in Mansoura, Egypt. Food Control. 2013, 33, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Liu, B.; Cao, J.; Zhou, B.; Levin, R. Incidence and enumeration of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shellfish from two retail sources and the genetic diversity of isolates as determined by RAPD-PCR analysis. Food Biotechnol. 2006, 20, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, G.; Büyüktanir, Ö.; Yurdusev, N. Detection of the tdh and trh genes in Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates in fish and mussels from Middle Black Sea Coast of Turkey. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhapol, C.; Tinrat, S. Virulence Genes Analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Anti-vibrio Activity of the Citrus Extracts. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 1390–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.L.; Lüdeke, C.H.M.; Bowers, J.C.; Garrett, N.; Fischer, M.; Parsons, M.B.; Bopp, C.A.; DePaola, A. Biochemical, serological, and virulence characterization of clinical and oyster Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2343–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xie, X.; Shi, X.; Lin, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Mou, J.; Chen, Q.; Lu, Y. Southern Coastal. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 2012–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, S.; Küçüksari, R. Phenotypic and Genotypic Virulence Factors and Antimicrobial Resistance of Motile Aeromonas spp. from Fish and Ground Beef. J. Food Saf. 2015, 35, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingombe, C.I.B.; Huys, G.; Tonolla, M.; Albert, M.J.; Swings, J.; Peduzzi, R.; Jemmi, T. PCR detection, characterization, and distribution of virulence genes in Aeromonas spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 5293–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Clark, C.G.; Liu, C.; Pucknell, C.; Munro, C.K.; Kruk, T.M.A.C.; Caldeira, R.; Woodward, D.L.; Rodgers, F.G. Detection and characterization of the hemolysin genes in Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas sobria by multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, S.P.; Buckley, J.T. Activation of the hole-forming toxin aerolysin by extracellular processing. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 163, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buller, N.B. Preparation of media for culture and identification. In Bacteria from Fish and Other Aquatic Animals: A Practical Identification Manual; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2009; pp. 244–277. ISBN 9780851997384. [Google Scholar]
- Yousr, A.H.; Napis, S.; Rusul, G.R.A.; Son, R. Detection of aerolysin and hemolysin genes in Aeromonas spp. isolated from environmental and shellfish sources by polymerase chain reaction. ASEAN Food J. 2007, 14, 115. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.; Ma, Z.H.; Rahman, M.H.; Wu, Z.G. PCR cloning and identification of the β-haemolysin gene of Aeromonas hydrophila from freshwater fishes in China. Aquaculture 2004, 229, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alperi, A.; Martínez-Murcia, A.J.; Ko, W.C.; Monera, A.; Saavedra, M.J.; Figueras, M.J. Aeromonas taiwanensis sp. nov. and Aeromonas sanarellii sp. nov., clinical species from Taiwan. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 2048–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Rathore, G.; Kapoor, D.; Mishra, B.N.; Lakra, W.S. Detection of aerolysin gene in Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from fish and pond water. Indian J. Microbiol. 2008, 48, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, J.M. The Main Aeromonas Pathogenic Factors. ISRN Microbiol. 2012, 2012, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.Y.F.; Heuzenroeder, M.W.; Flower, R.L.P. Inactivation of two haemolytic toxin genes in Aeromonas hydrophila attenuates virulence in a suckling mouse model. Microbiology 1998, 144, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wang, N.; Pan, Z.H.; Lu, C.P.; Liu, Y.J. Identity and virulence properties of Aeromonas isolates from diseased fish, healthy controls and water environment in China. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 55, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, P.; Bag, P.K.; Hajra, T.K.; De, R.; Sarkar, P.; Ramamurthy, T. Pathogenic potential of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from surface waters in Kolkata, India. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Escarpulli, G.; Figueras, M.J.; Aguilera-Arreola, G.; Soler, L.; Fernández-Rendón, E.; Aparicio, G.O.; Guarro, J.; Chacón, M.R. Characterisation of Aeromonas spp. isolated from frozen fish intended for human consumption in Mexico. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 84, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.W.; Fan, T.F.; Li, H.; Lu, J.F.; Jiang, H.; Hu, W.; Jiang, Q.H. Characterization of Aeromonas hydrophila from hemorrhagic diseased freshwater fishes in Anhui Province, China. Int. Food Res. J. 2013, 20, 1449–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Tahoun, A.B.M.B.; Ahmed, H.A.; Abou Elez, R.M.M.; El-Gedawy, A.A.; Elsohaby, I.; Abd El-Ghafar, A.E. Molecular characterisation, genotyping and survival of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from milk, dairy products and humans in Egypt. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 63, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.; Zahran, E.; Saad, R.; Zaki, V. Prevalence, molecular characterization, virulotyping, and antibiotic resistance of motile aeromonads isolated from Nile tilapia farms at northern Egypt. Mansoura Vet. Med. J. 2020, 21, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Xu, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J. Prevalence, molecular characterization, and antibiotic susceptibility of vibrio Parahaemolyticus from ready-to-eat foods in China. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzula, A.; Wambura, P.N.; Mdegela, R.H.; Shirima, G.M. Phenotypic and molecular detection of Aeromonads infection in farmed Nile tilapia in Southern highland and Northern Tanzania. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pinto, A.; Ciccarese, G.; De Corato, R.; Novello, L.; Terio, V. Detection of pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in southern Italian shellfish. Food Control 2008, 19, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colakoglu, F.A.; Sarmasik, A.; Koseoglu, B. Occurrence of Vibrio spp. and Aeromonas spp. in shellfish harvested off Dardanelles cost of Turkey. Food Control 2006, 17, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, J.J.; Michael Janda, J.; Brenner, F.W.; Cameron, D.N.; Birkhead, K.M. Vibrio. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Major Reference Works: London, UK, 2015; pp. 1–79. ISBN 9781118960608. [Google Scholar]
- Ceylan, E.; Berktas, M.; Ağaoğlu, Z. The occurrence and antibiotic resistance of motile Aeromonas in livestock. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2009, 41, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergey, D.H.; Buchanan, R.E.; Gibbons, N.E. Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Adeyemi, A.; Enyinnia, V.; Nwanze, R.; Smith, S.; Omonigbehin, E. Antimicrobial susceptibilty of potentially pathogenic halophilic Vibrio species isolated from seafoods in Lagos, Nigeria. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 3788–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratev, D.; Daskalov, H.; Vashin, I. Characterisation and determination of antimicrobial resistance of β-haemolytic Aeromonas spp. isolated from common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Rev. Med. Vet. (Toulouse) 2015, 166, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 27th ed.; CLSI supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017; ISBN 1-56238-1-56238-805-3. [Google Scholar]
- Elexson, N.; Afsah-Hejri, L.; Rukayadi, Y.; Soopna, P.; Lee, H.Y.; Tuan Zainazor, T.C.; Nor Ainy, M.; Nakaguchi, Y.; Mitsuaki, N.; Son, R. Effect of detergents as antibacterial agents on biofilm of antibiotics-resistant Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates. Food Control 2014, 35, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osundiya, O.; Oladele, R.; Oduyebo, O. Multiple Antibiotic Resistance (MAR) indices of Pseudomonas and Klebsiella species isolates in Lagos University Teaching Hospital. Afr. J. Clin. Exp. Microbiol. 2013, 14, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat Mahmud, Z.; Kassu, A.; Mohammad, A.; Yamato, M.; Bhuiyan, N.A.; Nair, G.B.; Ota, F. Isolation and molecular characterization of toxigenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus from the Kii Channel, Japan. Microbiol. Res. 2006, 161, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratev, D.; Gurova, E.; Vashin, I.; Daskalov, H. Multiplex PCR detection of haemolysin genes in β-haemolytic Aeromonas hydrophila strains isolated from fish and fish products. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 22, 308–314. [Google Scholar]

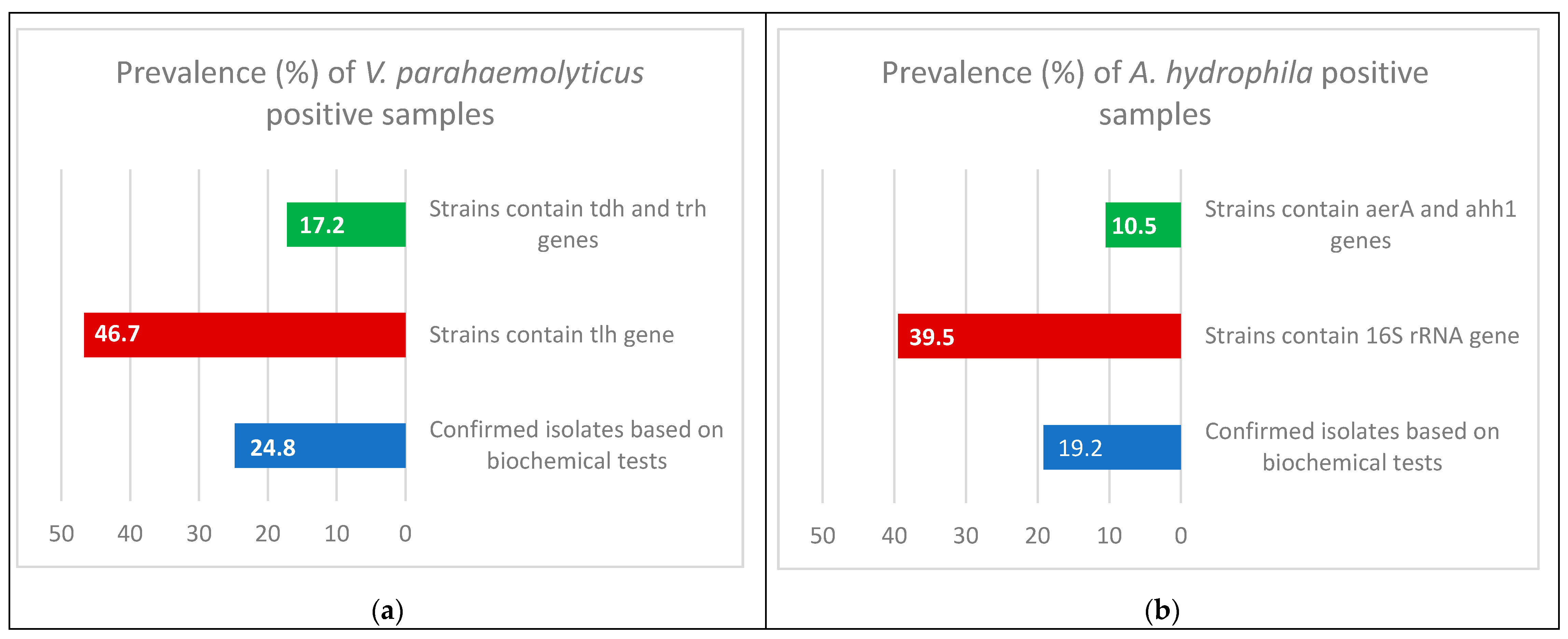
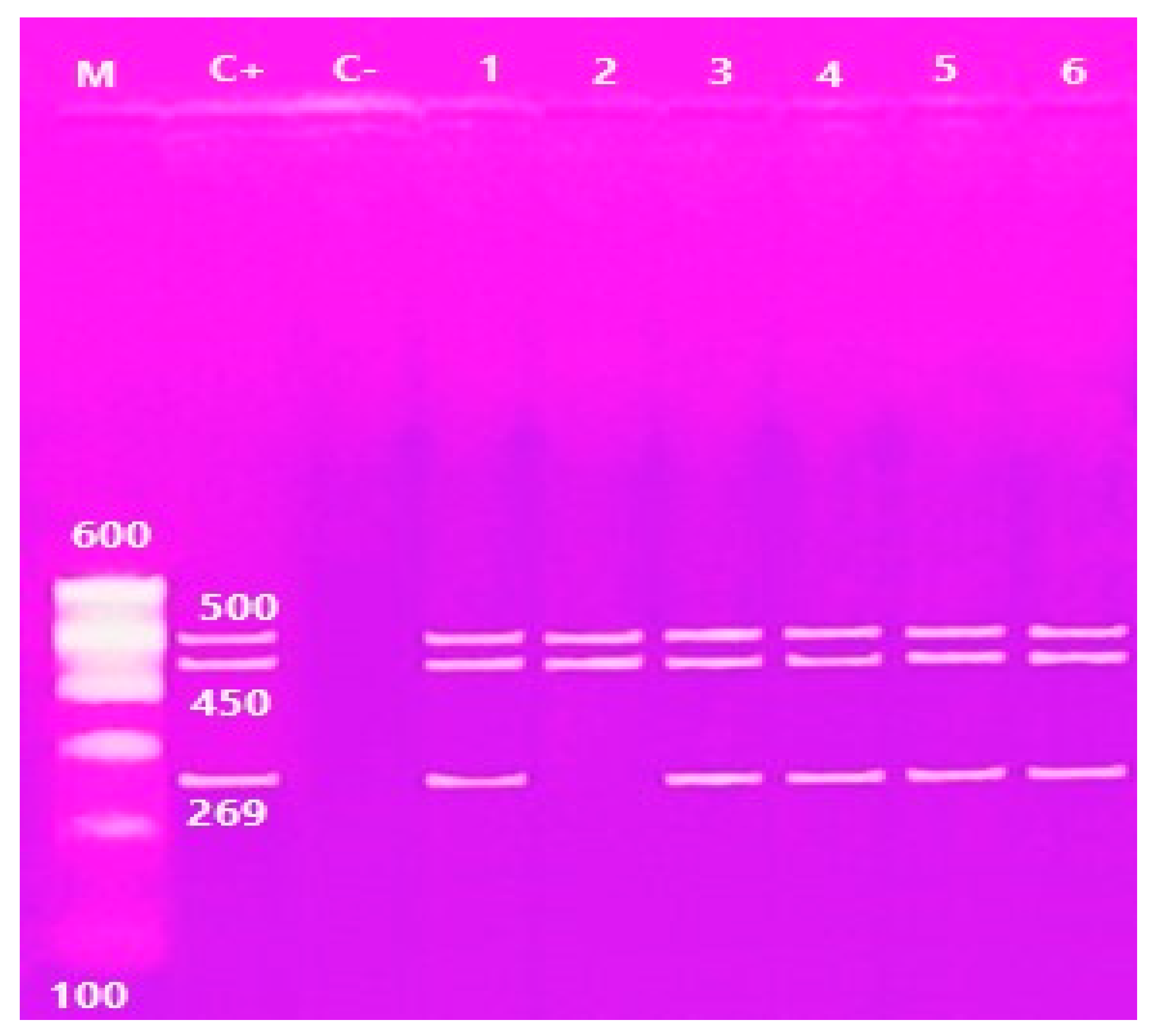

| Isolates | Confirmed Isolates | Strains Containing tlh Gene | Strains Containing tdh and trh Genes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| V. parahaemolyticus | 62 | 24.8 | 29 | 46.7 | 5 | 17.2 |
| A. hydrophila | Strains contain 16S rRNA gene | Strains contain aerA and ahh1 genes | ||||
| 48 | 19.2 | 19 | 39.5 | 2 | 10.5 | |
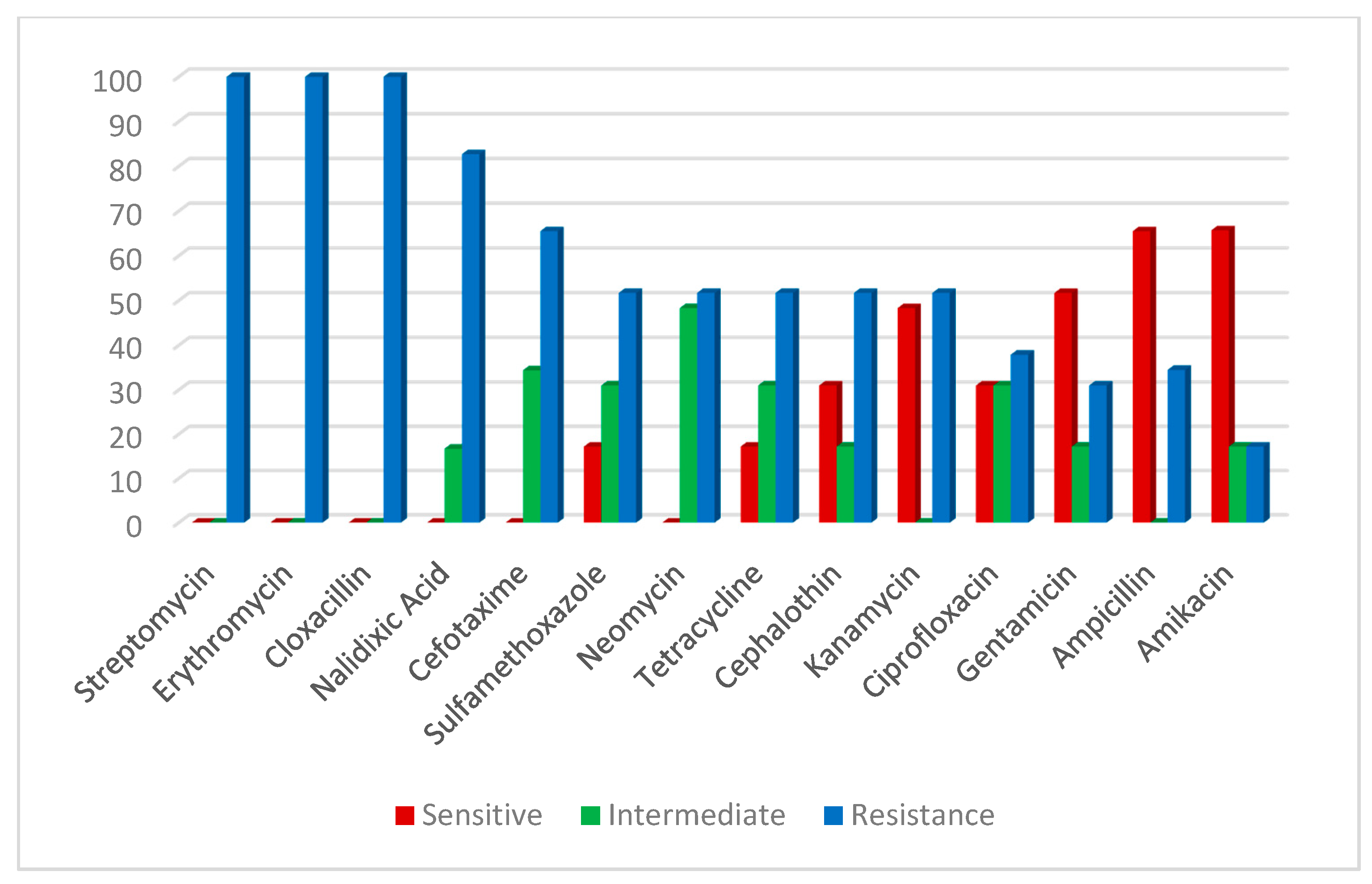
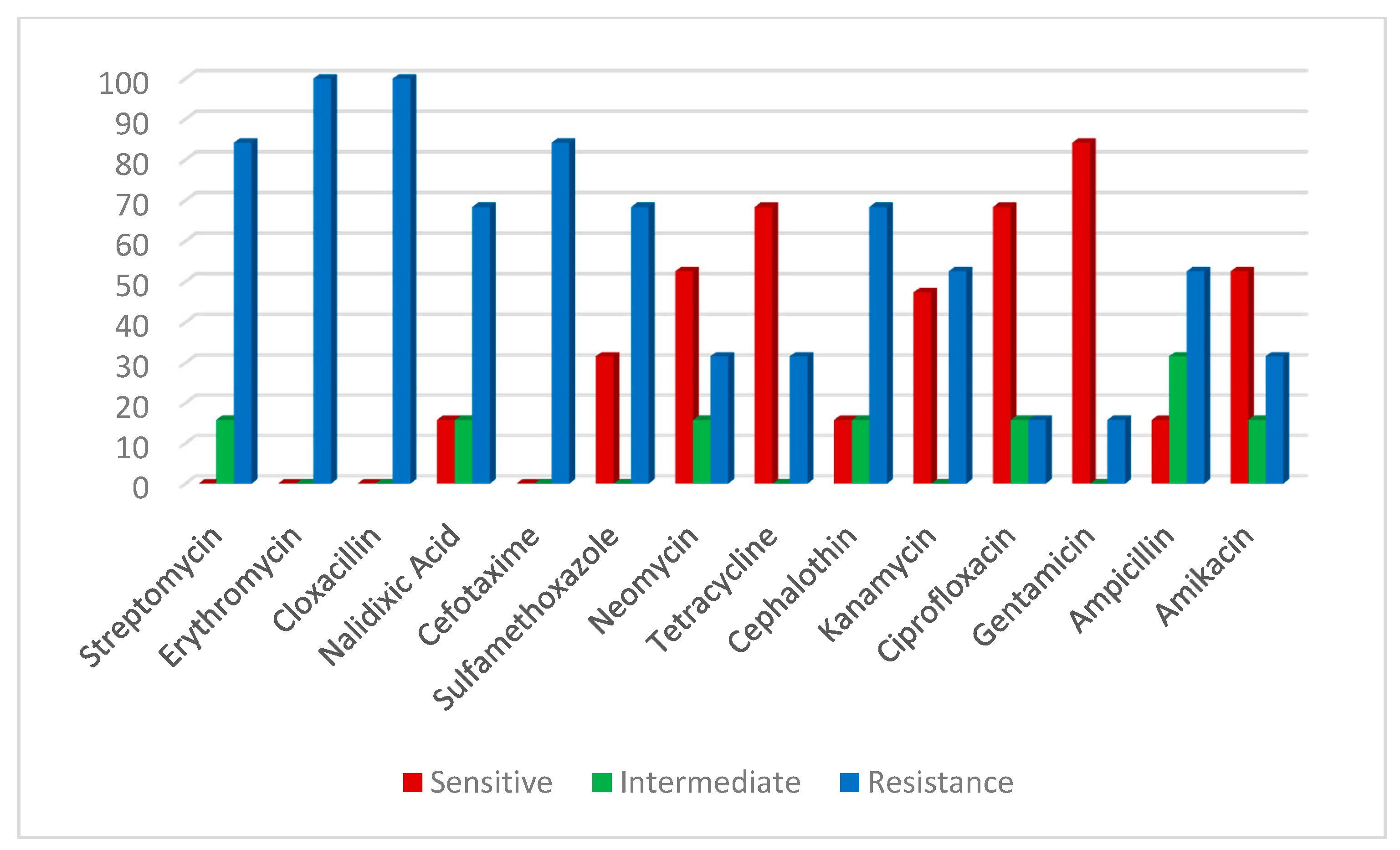
| Antimicrobial Agent | V. parahaemolyticus | A. hydrophila | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitive | Intermediate | Resistant | Sensitive | Intermediate | Resistant | |||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Streptomycin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 15.8 | 16 | 84.2 |
| Erythromycin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 100 |
| Cloxacillin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 100 |
| Nalidixic Acid | 0 | 0 | 5 | 16.7 | 24 | 82.7 | 3 | 15.8 | 3 | 15.8 | 13 | 68.4 |
| Cefotaxime | 0 | 0 | 10 | 34.4 | 19 | 65.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 84.2 |
| Sulfamethoxazole | 5 | 17.2 | 9 | 31.0 | 15 | 51.7 | 6 | 31.6 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 68.4 |
| Neomycin | 0 | 0 | 14 | 48.3 | 15 | 51.7 | 10 | 52.6 | 3 | 15.8 | 6 | 31.6 |
| Tetracycline | 5 | 17.2 | 9 | 31.0 | 15 | 51.7 | 13 | 68.4 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 31.6 |
| Cephalothin | 9 | 31.0 | 5 | 17.2 | 15 | 51.7 | 3 | 15.8 | 3 | 15.8 | 13 | 68.4 |
| Kanamycin | 14 | 48.3 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 51.7 | 9 | 47.4 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 52.6 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 9 | 31.0 | 9 | 31.0 | 11 | 37.9 | 13 | 68.4 | 3 | 15.8 | 3 | 15.8 |
| Gentamicin | 15 | 51.7 | 5 | 17.2 | 9 | 31.0 | 16 | 84.2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 15.8 |
| Ampicillin | 19 | 65.5 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 34.5 | 3 | 15.8 | 6 | 31.6 | 10 | 52.6 |
| Amikacin | 19 | 65.7 | 5 | 17.2 | 5 | 17.2 | 10 | 52.6 | 3 | 15.8 | 6 | 31.6 |
| No. of Tested V. parahaemolyticus Strains | Antimicrobial Resistance Profile | MAR Index |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | S, E, CL, NA, CF, SXT, N, T, CN, K, CP, G, AM, AK | 1 |
| 4 | S, E, CL, NA, CF, SXT, N, T, CN, K, CP, G, AM | 0.928 |
| 1 | S, E, CL, NA, CF, SXT, N, T, CN, K, CP, AM | 0.857 |
| 1 | S, E, CL, NA, CF, SXT, N, T, CN, K, CP | 0.785 |
| 4 | S, E, CL, NA, CF, SXT, N, T, CN, K | 0.714 |
| 4 | S, E, CL, NA, CF | 0.357 |
| 5 | S, E, CL, NA | 0.285 |
| 4 | S, E, CL | 0.21 |
| 1 | S, E | 0.142 |
| Average | 0.587 | |
| No. of Tested A. hydrophila Strains | Antimicrobial Resistance Profile | MAR Index |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | E, CL, S, CF, NA, SXT, CN, K, AM, n, T, AK, CP, G | 1 |
| 3 | E, CL, S, CF, NA, SXT, CN, K, AM, N, T, AK | 0.857 |
| 4 | E, CL, S, CF, NA, SXT, CN, K, AM | 0.642 |
| 3 | E, CL, S, CF, NA, SXT, CN | 0.5 |
| 3 | E, CL, S, CF | 0.285 |
| 3 | E, CL | 0.214 |
| Average | 0.586 | |
| Antibiotic | Symbol | Concentration |
|---|---|---|
| Streptomycin | S | 10 μg |
| Erythromycin | E | 15 μg |
| Cloxacillin | CL | 5 μg |
| Nalidixic acid | NA | 30 μg |
| Cefotaxime | CF | 30 μg |
| Sulfamethoxazole | SXT | 25 μg |
| Neomycin | N | 30 μg |
| Tetracycline | T | 30 μg |
| Cephalothin | CN | 30 μg |
| Kanamycin | K | 30 μg |
| Ciprofloxacin | CP | 5 μg |
| Gentamycin | G | 10 μg |
| Ampicillin | AM | 10 μg |
| Amikacin | AK | 25 μg |
| Target Gene | Oligonucleotide Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Product Size (bp) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| V. parahaemolyticus | |||
| tlh | F-5′AAAGCGGATTATGCAGAAGCACTG-′3 R-5′ GCTACTTTCTAGCATTTTCTCTGC-′3 | 450 | [104] |
| tdh | F-5′ GTAAAGGTCTCTGACTTTTGGAC ′3 R-5′ TGGAATAGAACCTTCATCTTCACC ′3 | 269 | |
| trh | F-5′ TTGGCTTCGATATTTTCAGTATCT ′3 R-5′ CATAACAAACATATGCCCATTTCCG ′3 | 500 | |
| A. hydrophila | |||
| 16S rRNA | F-5′ GGGAGTGCCTTCGGGAATCAGA-′3 R-5′ TCACCGCAACATTCTGATTTG-′3 | 356 | [105] |
| aerA | F-5′CAAGAACAAGTTCAAGTGGCCA-′3 R-5′ ACGAAGGTGTGGTTCCAGT-′3 | 309 | |
| ahh1 | F-5′ GCCGAGCGCCCAGAAGGTGAGTT-′3 R-5′ GAGCGGCTGGATGCGGTTGT -′3 | 130 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaher, H.A.; Nofal, M.I.; Hendam, B.M.; Elshaer, M.M.; Alothaim, A.S.; Eraqi, M.M. Prevalence and Antibiogram of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Aeromonas hydrophila in the Flesh of Nile Tilapia, with Special Reference to Their Virulence Genes Detected Using Multiplex PCR Technique. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060654
Zaher HA, Nofal MI, Hendam BM, Elshaer MM, Alothaim AS, Eraqi MM. Prevalence and Antibiogram of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Aeromonas hydrophila in the Flesh of Nile Tilapia, with Special Reference to Their Virulence Genes Detected Using Multiplex PCR Technique. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(6):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060654
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaher, Hanan A., Mohamad I. Nofal, Basma M. Hendam, Moustafa M. Elshaer, Abdulaziz S. Alothaim, and Mostafa M. Eraqi. 2021. "Prevalence and Antibiogram of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Aeromonas hydrophila in the Flesh of Nile Tilapia, with Special Reference to Their Virulence Genes Detected Using Multiplex PCR Technique" Antibiotics 10, no. 6: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060654
APA StyleZaher, H. A., Nofal, M. I., Hendam, B. M., Elshaer, M. M., Alothaim, A. S., & Eraqi, M. M. (2021). Prevalence and Antibiogram of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Aeromonas hydrophila in the Flesh of Nile Tilapia, with Special Reference to Their Virulence Genes Detected Using Multiplex PCR Technique. Antibiotics, 10(6), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10060654






