A Review of the Construction of Nano-Hybrids for Electrochemical Biosensing of Glucose
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Role/Function of Nanomaterials in Electrochemical Biosensors
- (1)
- Immobilization support for enzyme
- (2)
- Nanomaterials as mediator
- (3)
- Nanomaterials as signal amplifier
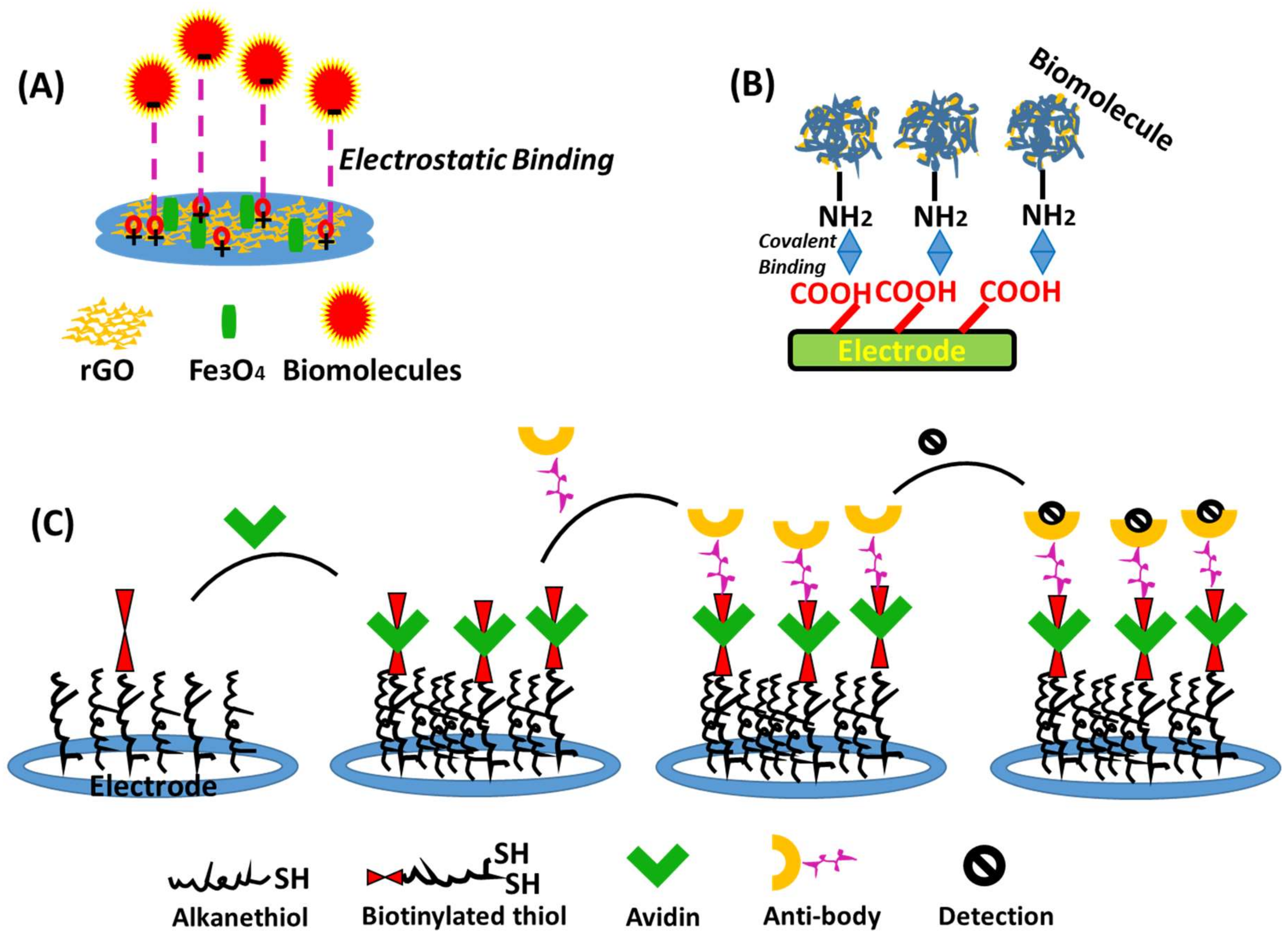
2.1. Immobilization Support for Enzyme
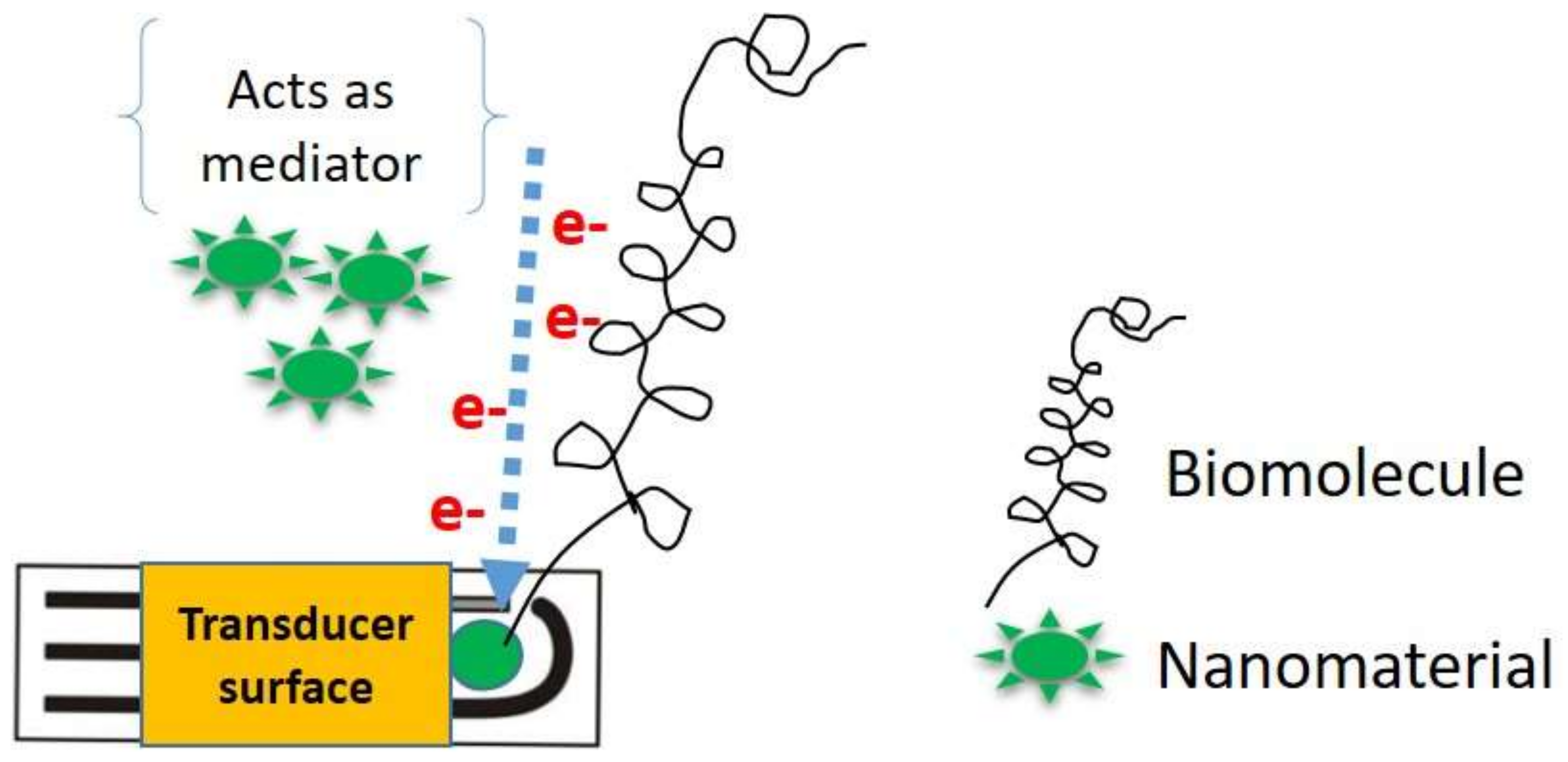
2.2. Nanomaterials as Mediators
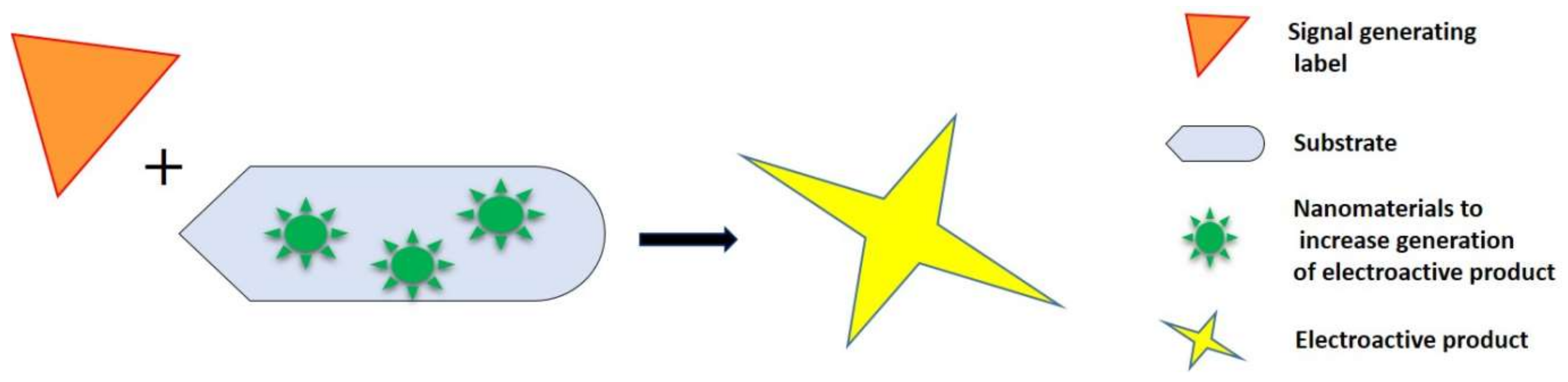
2.3. Nanomaterials as Signal Amplifiers
3. Electrochemical Biosensors for Glucose Detection
3.1. Glucose Monitoring
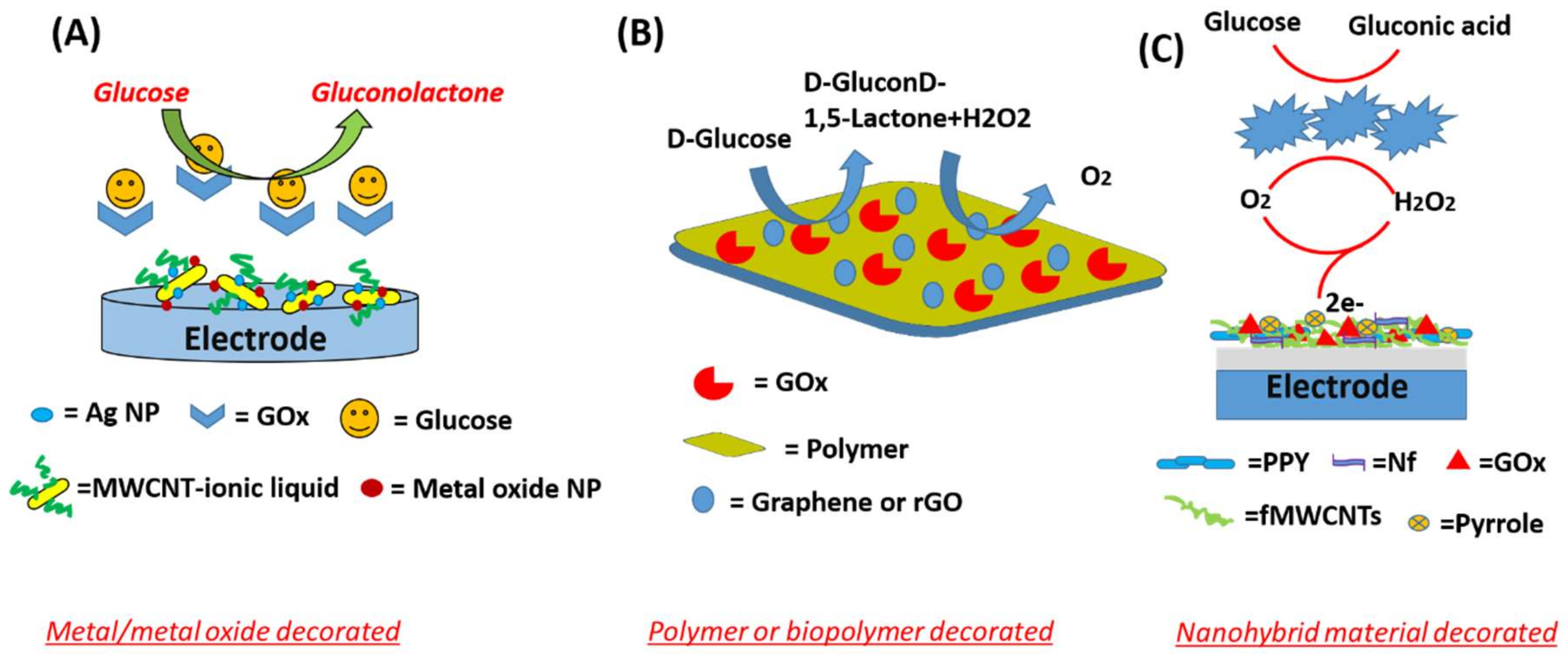
3.2. Carbon-Based Nano-Hybrids and Nano-Composites
3.3. Metal/Metal Oxide-Based Nano-Hybrids and Nano-Composites
3.4. Other Nano-Composites
4. Conclusions and Prospective Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iost, R.M.; da Silva, W.C.; Madurro, J.M.; Madurro, A.; Ferreira, L.; Crespilho, F. Recent advances in nano-based electrochemical biosensors: Application in diagnosis and monitoring of diseases. Front. Biosci. 2011, 3, 663–689. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, L.C., Jr.; Lyons, C. Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1962, 102, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagadevan, S.; Periasamy, M. Recent trends in nanobiosensors and their applications—A review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2014, 36, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Kalcher, K. Renaissances and current trends with electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Int. J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 3, 00083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, P. Biosensors in clinical chemistry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 334, 41–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöning, M.J.; Poghossian, A. Recent advances in biologically sensitive field-effect transistors (BioFETs). Analyst 2002, 127, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on nanomaterials and nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2014, 87, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gole, A.; Dash, C.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Sainkar, S.; Mandale, A.; Rao, M.; Sastry, M. Pepsin-gold colloid conjugates: Preparation, characterization, and enzymatic activity. Langmuir 2001, 17, 1674–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gole, A.; Vyas, S.; Phadtare, S.; Lachke, A.; Sastry, M. Studies on the formation of bioconjugates of endoglucanase with colloidal gold. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2002, 25, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, A.; Catanante, G.; Marty, J. Current trends in nanomaterial-based amperometric biosensors. Sensors 2014, 14, 23439–23461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Patolsky, F.; Katz, E.; Hainfeld, J.F.; Willner, I. “Plugging into enzymes”: Nanowiring of redox enzymes by a gold nanoparticle. Science 2003, 299, 1877–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ju, H. Reagentless glucose biosensor based on direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase immobilized on colloidal gold modified carbon paste electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 19, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalkhani, M.; Shahrokhian, S.; Ghorbani-Bidkorbeh, F. Voltammetric studies of sumatriptan on the surface of pyrolytic graphite electrode modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with silver nanoparticles. Talanta 2009, 80, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claussen, J.C.; Artiles, M.S.; McLamore, E.S.; Mohanty, S.; Shi, J.; Rickus, J.L.; Fisher, T.S.; Porterfield, D.M. Electrochemical glutamate biosensing with nanocube and nanosphere augmented single-walled carbon nanotube networks: A comparative study. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 11224–11231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claussen, J.C.; Hengenius, J.B.; Wickner, M.M.; Fisher, T.S.; Umulis, D.M.; Porterfield, D.M. Effects of carbon nanotube-tethered nanosphere density on amperometric biosensing: Simulation and experiment. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 20896–20904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claussen, J.C.; Kim, S.S.; Haque, A.; Artiles, M.S.; Porterfield, D.M.; Fisher, T.S. Electrochemical glucose biosensor of platinum nanospheres connected by carbon nanotubes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Ju, H. Signal amplification using functional nanomaterials for biosensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2122–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Bond, A.M.; Zhai, J.; Zhang, J. Utilization of nanoparticle labels for signal amplification in ultrasensitive electrochemical affinity biosensors: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 797, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, C.M. Nanocomposites: From fabrications to electrochemical bioapplications. Electroanal. Int. J. Devoted Fundam. Pract. Asp. Electroanal. 2008, 20, 648–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xiong, E.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J. Nanomaterials as signal amplification elements in DNA-based electrochemical sensing. Nano Today 2014, 9, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, P.; Li, F.; Chu, Q.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y. An ultrasensitive sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor based on the signal amplification strategy of mesoporous core–shell Pd@Pt nanoparticles/amino group functionalized graphene nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruen, D.; Delaney, C.; Florea, L.; Diamond, D. Glucose sensing for diabetes monitoring: Recent developments. Sensors 2017, 17, E1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Song, C.; Hong, Y.S.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, H.R.; Kang, T.; Shin, K.; Choi, S.H.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.H. Wearable/disposable sweat-based glucose monitoring device with multistage transdermal drug delivery module. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1601314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Gal, A.; Mayzel, Y.; Horman, K.; Bahartan, K. Non-invasive glucose monitoring: A review of challenges and recent advances. Curr. Trends Biomed. Eng. Biosci. 2017, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama, E.C.; Costa-Garcia, A.; Fernandez-Abedul, M.T. Pin-based electrochemical glucose sensor with multiplexing possibilities. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 88, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, S.; Nawaz, M.A.H.; Badea, M.; Marty, J.L.; Hayat, A. Nano-engineered biomimetic optical sensors for glucose monitoring in diabetes. Sensors 2016, 16, E1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Nawaz, M.H.; Latif, U.; Yaqub, M.; Hayat, A.; Rahim, A. An overview on enzyme-mimicking nanomaterials for use in electrochemical and optical assays. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.X.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Pan, Y.C.; Si, P.C. Non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on controllable nanoporous gold/copper oxide nanohybrids. Talanta 2014, 125, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Lu, Z.; Li, J.; Hao, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhu, C.; Shen, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, L. MoS2–Au@Pt nanohybrids as a sensing platform for electrochemical nonenzymatic glucose detection. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 6750–6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.L.; Zheng, J.B.; Sheng, Q.L. A highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on nickel and multi-walled carbon nanotubes nanohybrid films fabricated by one-step co-electrodeposition in ionic liquids. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 65, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.M.; Li, H.B.; Qu, F.L.; Zhang, X.B.; Shen, G.L.; Yu, R.Q. In situ synthesis of palladium nanoparticle-graphene nanohybrids and their application in nonenzymatic glucose biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3500–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solnica, B.; Naskalski, J.W.; Sieradzki, J. Analytical performance of glucometers used for routine glucose self-monitoring of diabetic patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 331, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.G.; Garcia-Gancedo, L.; Flewitt, A.J.; Xie, H.Q.; Moussy, F.; Milne, W.I. A critical review of glucose biosensors based on carbon nanomaterials: Carbon nanotubes and graphene. Sensors 2012, 12, 5996–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Ahammad, A.J.S.; Jin, J.H.; Ahn, S.J.; Lee, J.J. A comprehensive review of glucose biosensors based on nanostructured metal-oxides. Sensors 2010, 10, 4855–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, E. Electrochemical biosensors on platforms of graphene. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9526–9539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; You, T. Carbon nanofiber based electrochemical biosensors: A review. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Lu, X.; Li, J.; Yao, X.; Li, J. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and electrochemical biosensing of glucose on quantum dots/carbon nanotubes electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 3203–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, J.N.; Vij, V.; Kemp, K.C.; Kim, K.S. Engineered carbon-nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors for biomolecules. Acs Nano 2016, 10, 46–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, K.; Burghard, M. Biosensors based on carbon nanotubes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.J.; Zhou, X.Z.; Zhang, J.; Boey, F.; Zhang, H. Direct electrochemical reduction of single-layer graphene oxide and subsequent functionalization with glucose oxidase. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 14071–14075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Aksay, I.A.; Liu, J.; Lin, Y. Glucose oxidase–graphene–chitosan modified electrode for direct electrochemistry and glucose sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahsepar, M.; Foroughi, F.; Kim, H. A new enzyme-free biosensor based on nitrogen-doped graphene with high sensing performance for electrochemical detection of glucose at biological pH value. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, X. Nitrogen and sulfur dual-doped graphene for glucose biosensor application. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 738, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Liu, L.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Guan, X.; Chen, S.; Hou, H. Three-dimensional N-doped carbon nanotube@carbon foam hybrid: An effective carrier of enzymes for glucose biosensors. Rsc Adv. 2017, 7, 26574–26582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Li, L.; You, T. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase on novel free-standing nitrogen-doped carbon nanospheres@carbon nanofibers composite film. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.-L.; Xu, J.-J.; Wang, J.-L.; Chen, H.-Y. Electrochemically deposited nanocomposite of chitosan and carbon nanotubes for biosensor application. Chem. Commun. 2005, 2169–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.H.; Choi, B.G.; Park, H.; Hong, W.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, T.J. Development of a glucose biosensor using advanced electrode modified by nanohybrid composing chemically modified graphene and ionic liquid. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, T.J.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, K.G.; Choi, B.G. Polyoxometalate-grafted graphene nanohybrid for electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 468, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokoglan, T.C.; Kesik, M.; Soylemez, S.; Yuksel, R.; Unalan, H.E.; Toppare, L. Paper based glucose biosensor using graphene modified with a conducting polymer and gold nanoparticles. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, G59–G64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, N.; Wang, S.; Xie, H.; Xu, S.; Niu, S.; Luo, X. Nickel nanoparticles modified conducting polymer composite of reduced graphene oxide doped poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for enhanced nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Q.; Liu, D.; Zheng, J. Nico alloy nanoparticles anchored on polypyrrole/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 6658–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Gu, S.-X.; Jin, L.; Zhou, Y.-E.; Yang, Z.; Wang, W.; Hu, X. Graphene/polyaniline/gold nanoparticles nanocomposite for the direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase and glucose biosensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Hu, L.; Lee, L.Y.S.; Wong, K.-Y. Copper nanoparticles/polyaniline/graphene composite as a highly sensitive electrochemical glucose sensor. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 781, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Gu, Y.; Li, C.; Zheng, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, M. A non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on the CuS nanoflakes–reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, F.; Wang, D.; Nawaz, M.H.; An, Q.; Han, D.; Niu, L. Co3O4 nanostructures on flexible carbon cloth for crystal plane effect of nonenzymatic electrocatalysis for glucose. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 123, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, P.N.; Imran, H.; Dharuman, V. Direct glucose sensing and biocompatible properties of a zinc oxide—Multiwalled carbon nanotube–poly(vinyl chloride) ternary composite. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 2691–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.K.; Ahmad, R.; Shrestha, S.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Globular shaped polypyrrole doped well-dispersed functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes/nafion composite for enzymatic glucose biosensor application. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiyi, L.; Juanjuan, Z.; Zhouping, W.; Zaijun, L.; Junkang, L.; Zhiguo, G.; Guangli, W. Novel graphene-gold nanohybrid with excellent electrocatalytic performance for the electrochemical detection of glucose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 208, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Kong, F.-Y.; Li, C.; Shi, J.-J.; Lv, W.-X.; Wang, W. One-pot preparation of reduced graphene oxide-carbon nanotube decorated with au nanoparticles based on protein for non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing of glucose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 234, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.S.; Le, Q.H.; Yoshikawa, H.; Saito, M.; Tamiya, E. Development of non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on graphene oxide nanoribbon—Gold nanoparticle hybrid. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 146, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Gao, G.; Zhu, G.; Gao, J.; Ge, Z.; Yang, H. A nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on Ni(OH)2-CNT-PVDF composite and its application in measuring serum glucose. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, B106–B110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-W.; Liu, C.-J.; Dai, C.-S. Ni3S2/carbon nanotube nanocomposite as electrode material for hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline electrolyte and enzyme-free glucose detection. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 154–155, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.G.; Garcia-Gancedo, L.; Chen, C.; Zhu, X.R.; Xie, H.Q.; Flewitt, A.J.; Milne, W.I. Enzyme-free glucose biosensor based on low density CNT forest grown directly on a Si/SiO2 substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 178, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, H.; Choi, S.-K.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, E.; Park, J.; Kim, H. Synthesis of carbon nanotube–nickel nanocomposites using atomic layer deposition for high-performance non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, R.-J.; Wang, A.-N.; Liao, Q.-L.; Chuang, K.-Y. Non-enzymatic glucose sensor composed of carbon-coated nano-zinc oxide. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Zou, R.; Wu, H.; Shi, H.; Yu, S.; Liu, Y. Multifunctional glucose biosensors from Fe3O4 nanoparticles modified chitosan/graphene nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhouati, A.; Marty, J.-L.; Vasilescu, A. Metal Nanomaterial-Assisted Aptasensors for Emerging Pollutants Detection. In Nanotechnology and Biosensors; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 193–231. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wei, X.; Yuan, Y. Synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles composed by prussian blue and glucose oxidase for preparing highly sensitive and selective glucose biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 139, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, D.; Luo, J.; Njoki, P.N.; Lin, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhong, C.-J. Synergistic activity of gold-platinum alloy nanoparticle catalysts. Catal. Today 2007, 122, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saei, A.A.; Dolatabadi, J.E.N.; Najafi-Marandi, P.; Abhari, A.; de la Guardia, M. Electrochemical biosensors for glucose based on metal nanoparticles. Trac Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 42, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.R.; Voigt, J.A.; Liu, J.; Mckenzie, B.; Mcdermott, M.J. Biomimetic arrays of oriented helical ZnO nanorods and columns. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12954–12955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.A.; Jirsak, T.; Dvorak, J.; Sambasivan, S.; Fischer, D. Reaction of NO2 with Zn and ZnO: Photoemission, XANES, and density functional studies on the formation of NO3. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Xian, Y.; Shi, G.; Jin, L. ZnO nanorods/Au hybrid nanocomposites for glucose biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Fang, X.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. Nanorod arrays composed of zinc oxide modified with gold nanoparticles and glucose oxidase for enzymatic sensing of glucose. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Liu, B.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Q. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase immobilized on Au nanoparticles-functionalized 3D hierarchically ZnO nanostructures and its application to bioelectrochemical glucose sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Marie, M.; Kuchuk, A.; Manasreh, M.; Benamara, M. Sensitivity enhancement in an in-vitro glucose sensor using gold nanoelectrode ensembles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 5452–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Meng, X.; Tang, F. Preparation of Ag–Au nanoparticle and its application to glucose biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 110, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samphao, A.; Butmee, P.; Jitcharoen, J.; Švorc, Ľ.; Raber, G.; Kalcher, K. Flow-injection amperometric determination of glucose using a biosensor based on immobilization of glucose oxidase onto Au seeds decorated on core Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Talanta 2015, 142, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.-L.; Xu, J.-J.; Du, Y.; Chen, H.-Y. A glucose biosensor based on chitosan–glucose oxidase–gold nanoparticles biocomposite formed by one-step electrodeposition. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 334, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.-Y.; Hou, S.-H.; Yin, F.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z.-X.; Huang, J.-D.; Chen, Q. Amperometric glucose biosensor based on layer-by-layer assembly of multilayer films composed of chitosan, gold nanoparticles and glucose oxidase modified Pt electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Luo, X.-L.; Xu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. A simple method to fabricate a chitosan-gold nanoparticles film and its application in glucose biosensor. Bioelectrochemistry 2007, 70, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.-H.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, J.-J. In situ immobilization of glucose oxidase in chitosan–gold nanoparticle hybrid film on prussian blue modified electrode for high-sensitivity glucose detection. Electrochem. Commun. 2006, 8, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Khan, R.; Solanki, P.R.; Pandey, P.; Alam, J.; Ahmad, S.; Malhotra, B. Iron oxide nanoparticles–chitosan composite based glucose biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benvenuto, P.; Kafi, A.; Chen, A. High performance glucose biosensor based on the immobilization of glucose oxidase onto modified titania nanotube arrays. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2009, 627, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, M.; Chaubey, A.; Malhotra, B. Application of conducting polymers to biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 17, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, F.; Xian, Y.; Wang, H.; Jin, L. Glucose biosensor based on Au nanoparticles–conductive polyaniline nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1996–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazeiko, V.; Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Balevicius, Z.; Ramanavicius, A. Gold nanoparticle and conducting polymer-polyaniline-based nanocomposites for glucose biosensor design. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 189, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, D.; Liu, B.; Shi, Y.; Pan, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, R.; Yu, G. Highly sensitive glucose sensor based on Pt nanoparticle/polyaniline hydrogel heterostructures. Acs Nano 2013, 7, 3540–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, N.; Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Ramanavicius, A.; Semashko, T.; Mikhailova, R.; Ramanaviciene, A. The use of different glucose oxidases for the development of an amperometric reagentless glucose biosensor based on gold nanoparticles covered by polypyrrole. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 169, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, X. Glucose biosensor based on immobilization of glucose oxidase in poly(o-aminophenol) film on polypyrrole-Pt nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2898–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapountzi, E.; Braiek, M.; Vocanson, F.; Chateaux, J.-F.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Lagarde, F. Gold nanoparticles assembly on electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol)/poly (ethyleneimine)/glucose oxidase nanofibers for ultrasensitive electrochemical glucose biosensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azak, H.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Yildiz, H.B.; Ozkan, S.A. Electrochemical glucose biosensing via new generation DTP type conducting polymers/gold nanoparticles/glucose oxidase modified electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 770, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespilho, F.N.; Ghica, M.E.; Florescu, M.; Nart, F.C.; Oliveira Jr, O.N.; Brett, C.M. A strategy for enzyme immobilization on layer-by-layer dendrimer–gold nanoparticle electrocatalytic membrane incorporating redox mediator. Electrochem. Commun. 2006, 8, 1665–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadag, M.; Geyik, C.; Demirkol, D.O.; Ertas, F.N.; Timur, S. Modified gold surfaces by 6-(ferrocenyl) hexanethiol/dendrimer/gold nanoparticles as a platform for the mediated biosensing applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, J.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, B. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase entrapped in nano gold particles-ionic liquid-N,N-dimethylformamide composite film on glassy carbon electrode and glucose sensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 587, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Qin, X.; Zhao, Z.; Miao, Z.; Huang, N.; Chen, Q. A novel glucose biosensor based on the immobilization of glucose oxidase onto gold nanoparticles-modified Pb nanowires. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Sun, H.; Xu, F.; Yuwen, L.; Fan, C.; Wang, L. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and a biosensor for glucose based on a glass carbon electrode modified with MoS2 nanosheets decorated with gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, X.; Tay, B.; Chen, J.; Han, Z.; Khor, K.A. A novel amperometric biosensor based on ZnO:Co nanoclusters for biosensing glucose. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, X.; Zhu, X.; Dong, Y.; Chen, T.; Ye, M.; Sun, W. An amperometric glucose biosensor based on the immobilization of glucose oxidase on the platinum electrode modified with NiO doped ZnO nanorods. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2012, 676, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, N.; Tan, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. Facile synthesis of NiCo2O4@polyaniline core–shell nanocomposite for sensitive determination of glucose. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uygun, A.; Yavuz, A.G.; Sen, S.; Omastová, M. Polythiophene/SiO2 nanocomposites prepared in the presence of surfactants and their application to glucose biosensing. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 2022–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadian, S.; Arya, B.D.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, S.N.; Chauhan, R.P.; Srivastava, A.; Chandra, P.; Singh, S.P. Synthesis and application of PHT-TiO2 nanohybrid for amperometric glucose detection in human saliva sample. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 2793–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, L.; Xu, L.; Tan, L.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Q.; Yao, S. An reagentless glucose biosensor based on direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase immobilized on poly(methylene blue) doped silica nanocomposites. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 165, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Jeong, H.; Bae, S.R.; Jeon, S. Modified platinum electrode with phytic acid and single-walled carbon nanotube: Application to the selective determination of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic and uric acids. Microchem. J. 2008, 88, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ni, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Fu, R.; Huang, X.; Shen, J. Innovative biocompatible nanospheres as biomimetic platform for electrochemical glucose biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 44, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, G.; Mao, C.; Huang, X.; Shen, J. Biocompatibility of CS–PPy nanocomposites and their application to glucose biosensor. Bioelectrochemistry 2012, 88, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sr# | Nanomaterials/Composites | Details | LOD (μM) | Linear Range (μM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PVC–ZnO–MWCNT | Simple mixing/drop casting/GCE | - | 20–17.8 × 103 | [56] |
| 2 | Bioengineered Nf-GOx-fMWCNTs-PPy/Pt electrode | In situ electrochemical polymerization/Pt electrode | 5.0 | 5.0–4.1 × 103 | [57] |
| 3 | Graphene-gold | Thermal annealing-freeze drying/GCE/Graphene aerogel | 4.0 | 0.01–16 × 103 | [58] |
| 4 | rGO-SWCNT-Au | One pot reduction/GCE/in situ growth of Au NPs | 0.0022 | 0.00001–80 × 103 | [59] |
| 5 | AuNP/GONR/CS | Graphene oxide nanoribbons as a supporting matrix/carbon sheet/drop casting | - | 0.5–10 × 103 | [60] |
| 6 | Ni(OH)2-CNT-PVDF | Simple dispersing/GCE | 23 | 0.25 × 103–39.26 × 103 | [61] |
| 7 | Ni3S2/carbon nanotube | Glucose-assisted hydrothermal method/Ni foam electrode | 3.3 | 30 × 103–500 × 103 | [62] |
| 8 | CNT/Si-SiO2 | Magnetron sputtering/simple dispersion/silica substrate electrode/CNT/Ni working electrode | 2.0 | 5–7 × 103 | [63] |
| 9 | ALD/CVD-assisted CNT–Ni | Carbon tetrabromide precursor and Au-assisted ALD/CVD procedure/glassy carbon electrode | 2.0 | 5–2 × 103 | [64] |
| 10 | Ni–MWNT | Electrodeposition/glassy carbon electrode/drop casting | 0.89 | 3.2–17.5 × 103 | [30] |
| 11 | Carbon-coated ZnO (ZnO@C) | Surface coating via hydrothermal process and CVD method/GCE | 1000 | 1 × 103–13.8 × 103 | [65] |
| 12 | Fe3O4/CG | One-step ball milling/EDC-assisted modification/Pt sputter-coated ITO glass | 16.0 | 16–26 × 103 | [66] |
| Sr# | Nanomaterials/Composites | Details (Substrate, Precursor, Electrode, and Synthesis Method) | LOD (µM) | Linear Range (µM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ZnO nanorods/Au nanocrystals | Facile hydrothermal route/enzyme entrapping/GCE | 0.01 | 0.1–33 | [73] |
| 2 | ZnO nanorods/AuNPs | hydrothermal and photo reduction method/fluorine-doped tin oxide | 3 | 3–3 × 103 | [74] |
| 3 | AuNPs-3D ZnO | In situ reduction for Au NPs/drop casting/GCE | 20 | 103–20 × 103 | [75] |
| 4 | ZnO nanorods/Au | Hydrothermal growth of nanorods/Au-ITO electrodes | 65 | 10–6.5 × 103 | [76] |
| 5 | Au seeds-Fe3O4 NPs | Enzyme chemisorption/SPCE/carbon substrate | 100 | 200–9 × 103 | [78] |
| 6 | Chitosan-GOx-AuNPs | Electrochemical deposition/Au disk electrode | 2.7 | 5–2.4 × 103 | [79] |
| 7 | Chitosan-AuNPs-GOx | LBL assembly/enzyme adsorption/Pt electrode/ | 7 | 500–16 × 103 | [80] |
| 8 | Chitosan-AuNPs film | Direct and facile electrochemical deposition method/GCE | 13 | 0.5–1.3 × 103 | [81] |
| 9 | Chitosan-AuNPs | In situ incorporating glucose oxidase/electrodeposition of chitosan/GCE | 0.69 | 1–1.6 × 103 | [82] |
| 10 | Chitosan-Fe3O4 NPs | Co-precipitation method/ITO/physically adsorbed enzyme | - | 550–22 × 103 | [83] |
| 11 | Chitosan-TiO2-Au | Argon plasma coating/Ti substrate/electrodeposition | 5 | 15–4 × 103 | [84] |
| 12 | PANI-AuNPs | Simple mixing/drop casting/GCE | 0.5 | 1–800 | [86] |
| 13 | PANI-AuNPs | Enzyme entrapment/simple mixing/drop casting/carbon rod electrode | - | 100–150 × 103 | [87] |
| 14 | PANI-PtNPs | Hydrogel heterostructure/GCE | 0.7 | 10–8 × 103 | [88] |
| 15 | AuNPs-polypyrrole | Adsorbed electron transfer mediator/solution casting/graphite rod electrode | 24 | 100–50 × 103 | [89] |
| 16 | Pt-polypyrrole | Electrosynthesis, GCE/film deposition | 0.45 | 1.5–13 × 103 | [90] |
| 17 | AuNPs-PVA/PEI NFs | Bioactive surface nanostructuration method/electrospun nanofibers of PVA-PEI/Au electrode | 0.9 | 10–200 | [91] |
| 18 | AuNPs-DTP | Dithionepyrrole-based conducting polymers/Au electrode | 0.0986 | 50–1000 | [92] |
| 19 | AuNPs-PAMAM | Electrocatalytic membranes/layer-by-layer/ITO electrodes/enzyme immobilization via cross-linkers | 17 | Up to 30 | [93] |
| 20 | AuNPs-PAMAM | Self-assembled monolayer/dendrimers/Au electrodes | 600 | 103 –5 × 103 | [94] |
| 21 | AuNPs-ionic liquid | Enzyme entrapment in nanogold particles/composite film forming/GCE/ | 3.49 | 2–20 | [95] |
| 22 | AuNPs-Pb nanowires | Pb decoration nanowires/matrix of bovine serum albumin/Pt electrode | 2 | 5–2200 | [96] |
| 23 | AuNPs-MoS2 | MoS2 nanosheets assisted enzyme immobilization/without electron mediator/GCE | 2.8 | 10–300 | [97] |
| 24 | ZnO:Co nanoclusters | Nanocluster-beam deposition/cross-linking/PET plate electrode | 20 | - | [98] |
| 25 | NiO-doped ZnO nanorods | NiO-doped ZnO nanorods/enzyme immobilization/Pt electrode | 2.5 | 500–8 × 103 | [99] |
| 26 | NiCo2O4@polyaniline core shell | Hydrothermal treatment/conducting polymer coating/GCE | 0.3833 | Up to 4.7 × 103 | [100] |
| Sr# | Nanocomposites | Details | LOD (μM) | Linear Range (μM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PT/SiO2 | Chemical oxidative polymerization/enzyme-immobilized polymers/enzyme immobilization via crosslinking/GCE | - | 6–1585 | [101] |
| 2 | ITO/TiO2/PHT/GOx | Solution deposition/ITO electrode | 0.62 | 1–310 | [102] |
| 3 | PMB@SiO2(nano) | Electropolymerization/glassy carbon electrode | 3 | 0.01–1.11 | [103] |
| 4 | PA-SWNTs/Pt | PA-SWNTs films/charged linker/Pt electrode | 8 | 20–10,000 | [104] |
| 5 | SiO2-PA | Reverse microemulsion and electrostatic binding/glassy carbon electrode | 0.012 | - | [105] |
| 6 | CS–PPy | Silicon–oxygen interaction/drop casting/glassy carbon electrode | 0.15 | 5–147 | [106] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batool, R.; Rhouati, A.; Nawaz, M.H.; Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. A Review of the Construction of Nano-Hybrids for Electrochemical Biosensing of Glucose. Biosensors 2019, 9, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010046
Batool R, Rhouati A, Nawaz MH, Hayat A, Marty JL. A Review of the Construction of Nano-Hybrids for Electrochemical Biosensing of Glucose. Biosensors. 2019; 9(1):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010046
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatool, Razia, Amina Rhouati, Mian Hasnain Nawaz, Akhtar Hayat, and Jean Louis Marty. 2019. "A Review of the Construction of Nano-Hybrids for Electrochemical Biosensing of Glucose" Biosensors 9, no. 1: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010046
APA StyleBatool, R., Rhouati, A., Nawaz, M. H., Hayat, A., & Marty, J. L. (2019). A Review of the Construction of Nano-Hybrids for Electrochemical Biosensing of Glucose. Biosensors, 9(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010046





