Electrochemical Biosensors as Potential Diagnostic Devices for Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
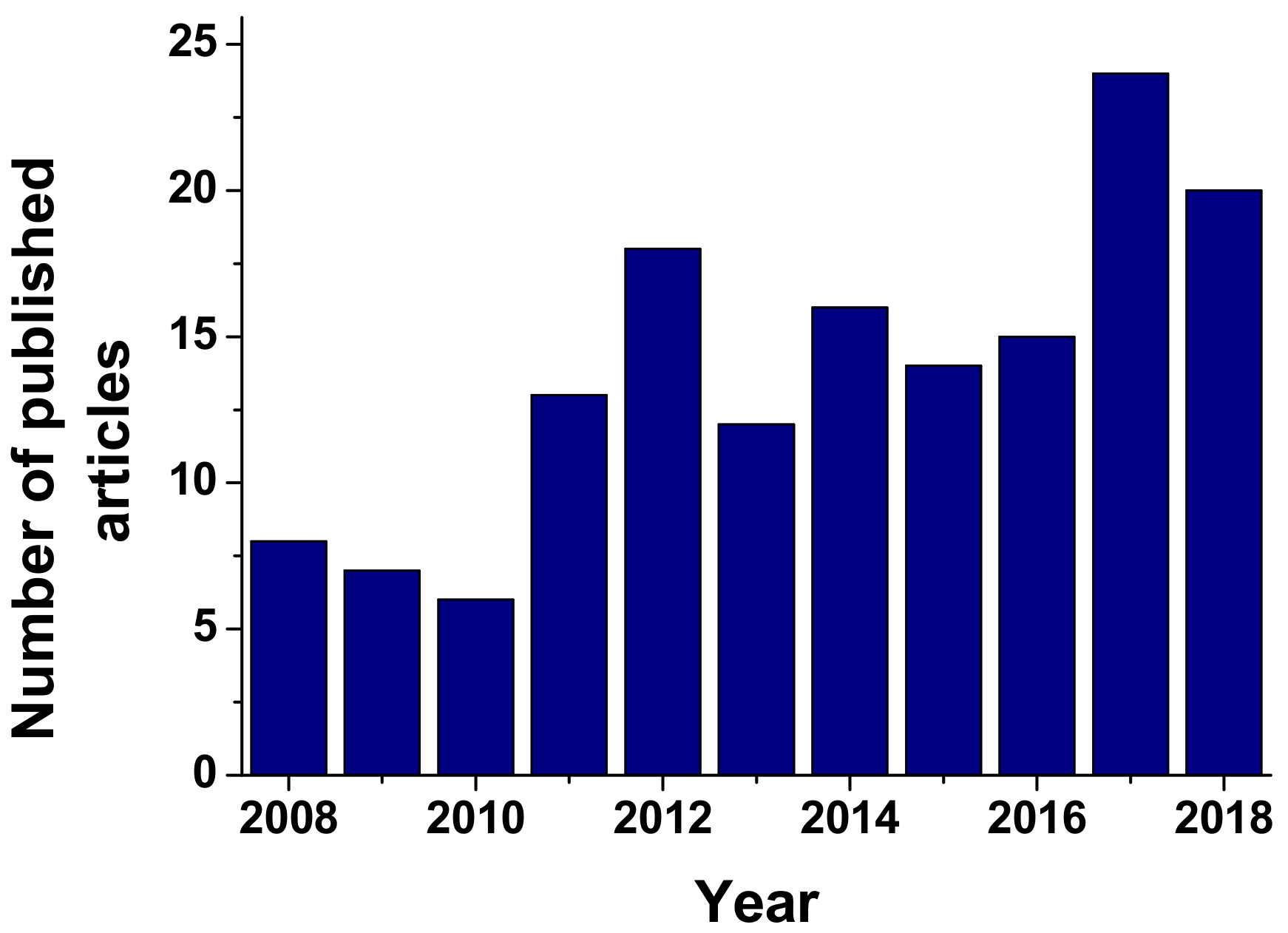
1. Introduction
2. Platform Design for AD Biosensors
2.1. Bioelement Immobilization Methods
2.2. Signal Generation
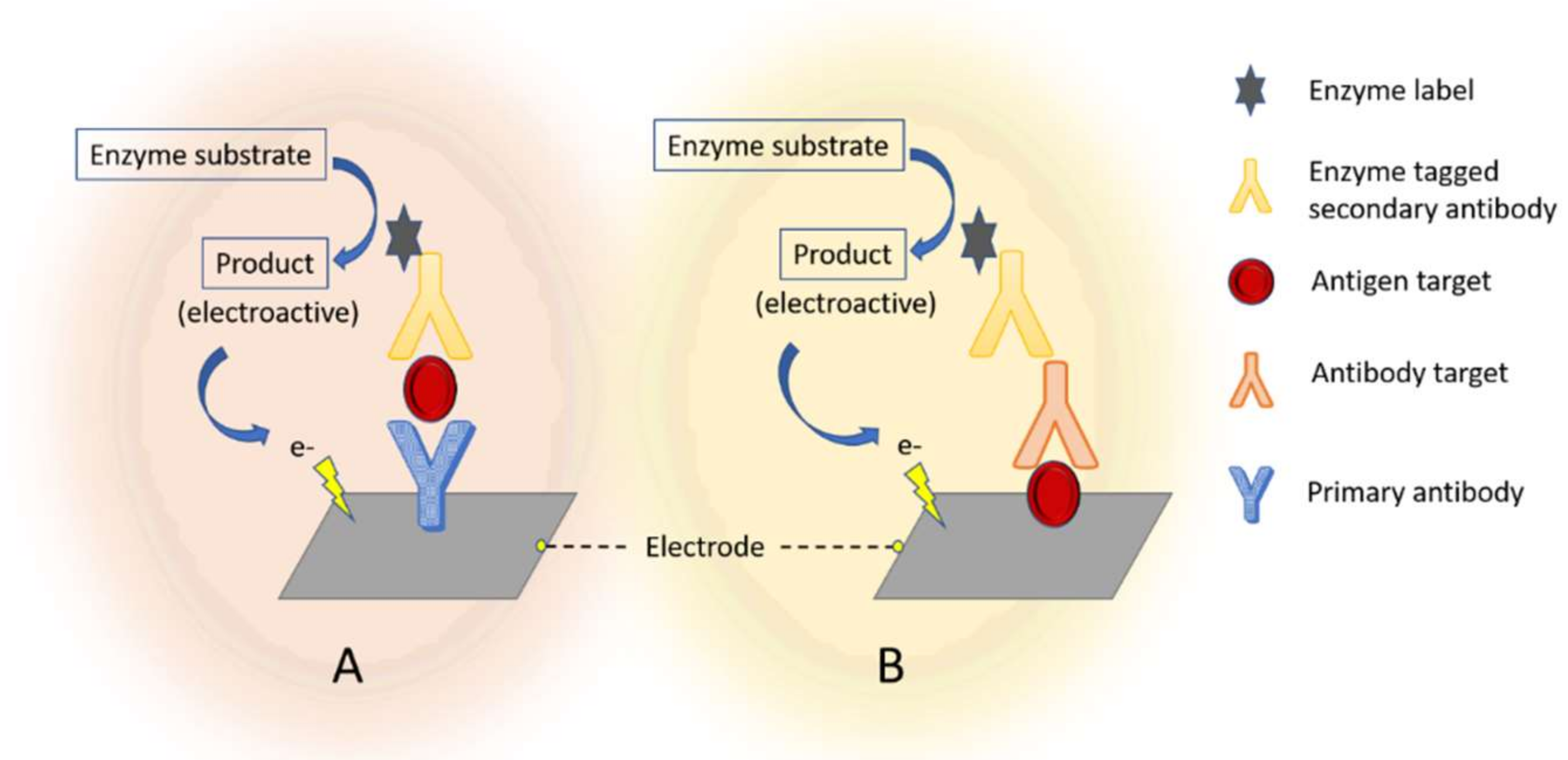
2.2.1. Labels in Electrochemical Immunosensors
2.2.2. Label-Free Electrochemical Immunosensors
3. Biosensors for ADs Based on Antibodies and Antigens
4. Biosensors for ADs Based on Peptides
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scanlin, A. Autoimmune Diseases: The Growing Impact. BioSupply Trends Quarterly. 2014. Available online: http://www.bstquarterly.com (accessed on 12 September 2018).
- European Parliament. Directorate-General for Internal Policies: Autoimmune Disease—Modern Diseases. Available online: http://www.europarl.europa.eu/cmsdata/133620/ENVI%202017-09%20WS%20Autoimmune%20diseases%20%20PE%20614.174%20.
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Autoimmune Diseases. Available online: https://www.niaid.nih.gov/diseases-conditions/autoimmune-diseases (accessed on 7 December 2018).
- Zhang, X.; Zambrano, A.; Lin, Z.-T.; Xing, Y.; Rippy, J.; Wu, T. Immunosensors for Biomarker Detection in Autoimmune Diseases. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2017, 65, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, A.; Jeremias, P.; Matthias, T. The World Incidence and Prevalence of Autoimmune Diseases is Increasing. Int. J. Celiac Dis. 2015, 4, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosu, O.; Selvolini, G.; Cristea, C.; Marrazza, G. Electrochemical Immunosensors for Disease Detection and Diagnosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. Electrochemical Sensors, Biosensors and their Biomedical Applications; Academic Press, Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 237–260. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, M.F.; Aatif, M. The footprints of cancer development: Cancer biomarkers. Cancer Treat Rev. 2009, 35, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.Z.; Florea, A.; Cristea, C.; Bessueille, F.; Vocanson, F.; Goutaland, F.; Zhang, A.; Sandulescu, R.; Lagarde, F.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. 1,3,5-Trinitrotoluene detection by a molecularly imprinted polymer sensor based on electropolymerization of a microporous-metal-organic framework. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2015, 207, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, A.; Cristea, C.; Vocanson, F.; Sandulescu, R.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Electrochemical sensor for the detection of estradiol based on electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polythioaniline film with signal amplification using gold nanoparticles. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 59, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, A.; Guo, Z.Z.; Cristea, C.; Bessueille, F.; Vocanson, F.; Goutaland, F.; Dzyadevych, S.; Sandulescu, R.; Lagarde, F.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Anticancer drug detection using a highly sensitive molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on an electropolymerized microporous metal organic framework. Talanta 2015, 138, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, A.; Kalra, P.; Bansal, V.; Bruno, J.G.; Sharma, T.K. Aptamer-based point-of-care diagnostic platforms. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2017, 246, 535–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, S.C.B.; Lakshmipriya, T.; Chen, Y.; Phang, W.M.; Hashim, U. Aptamer-based “point-of-care testing”. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patris, S.; Vandeput, M.; Kauffmann, J.M. Antibodies as target for affinity biosensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puiu, M.; Bala, C. Peptide-based biosensors: From self-assembled interfaces to molecular probes in electrochemical analysis. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 120, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkenhohl, T.; Lisdat, F. Screen-printed electrodes as impedimetric immunosensors for the detection of anti-transglutaminase antibodies in human sera. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, P.; Yi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Su, S.; Zhao, L.; Hu, C. Development of a novel method to measure macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis by combined electrochemical immunosensor. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristea, C.; Florea, A.; Tertiș, M.; Săndulescu, R. Immunosensors in Biosensors-Micro and Nanoscale Applications; House Intech.: London, UK, 2016; pp. 165–202. [Google Scholar]
- Holzinger, M.; le Goff, A.; Holzinger, S.C.M.; le Goff, A.; Cosnier, S. Nanomaterials for biosensing applications: A review. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, F.S.; Angnes, L. Electrochemical immunosensors—A powerful tool for analytical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleat, Z.; Ravalli, A.; Mazloum-Ardakani, M.; Marrazza, G. CA125 Immunosensor based on poly-anthranilic acid modified screen-printed electrodes. Electroanalysis 2012, 25, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraket, A.; Lee, M.; Zine, N.; Sigaud, M.; Bausells, J.; Errachid, A. A fully integrated electrochemical biosensor platform fabrication process for cytokines detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernat, A.; Tertis, M.; Papara, C.N.; Bodoki, E.; Sandulescu, R. Nanostructured platform based on graphene-polypyrrole composite for immunosensor fabrication. Procedia Technol. 2017, 27, 108–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghaly, O.A.; Abdel Hameed, R.S.; Abu-Nawwas, A.A.H. Analytical application using modern electrochemical techniques. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 3287–3318. [Google Scholar]
- Trojanowicz, M. Flow chemistry vs flow analysis. Talanta 2016, 146, 621–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunakaran, C.; Pandiaraj, M.; Santharaman, P. Immunosensors. Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, I.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, J. Current technologies of electrochemical immunosensors: Perspective on signal amplification. Sensors 2018, 18, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, P.; Li, F.; Chu, Q.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y. An ultrasensitive sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor based on the signal amplification strategy of mesoporous core–shell Pd@Pt nanoparticles/amino group functionalized graphene nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Jan, M.R. Ultrasensitive electrical biosensing of proteins and DNA: Carbon-nanotube derived amplification of the recognition and transduction events. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 3010–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Munge, B.; Patel, V.; Jensen, G.; Bhirde, A.; Gong, J.D.; Kim, S.N.; Gillespie, J.; Gutkind, J.S.; Papadimitrakopoulos, F.; et al. Carbon nanotube amplification strategies for highly sensitive immunodetection of cancer biomarkers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.A.; Yoshikawa, H.; Tamiya, E.; Yasin, H.M.; Ahmed, M.U. A highly sensitive gold nanoparticle bioprobe based electrochemical immunosensor using screen printed graphene biochip. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 58460–58466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dequaire, M.; Degrand, C.; Limoges, B. An electrochemical metalloimmunoassay based on a colloidal gold label. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 5521–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Lin, Y. A renewable electrochemical magnetic immunosensor based on gold nanoparticle labels. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, J.; Aziz, M.A.; Yang, H. A Nanocatalyst-Based Assay for Proteins: DNA-Free Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Detection Using Catalytic Reduction of p-Nitrophenol by Gold-Nanoparticle Labels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16022–16023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, X.; Fu, X.; Chen, K.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. An electrochemical stripping metalloimmunoassay based on silver-enhanced gold nanoparticle label. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, H.; Lai, G.; Yan, F. Electrochemical immunosensors. In Immunosensing for the Detection of Protein Biomarkers; Ju, H., Lai, G., Yan, F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 77–110. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, G.S.; Wu, J.; Leng, C.; Ju, X.U.; Yan, F. Disposable immunosensor array for ultrasensitive detection of tumor markers using glucose oxidase-functionalized silica nanosphere tags. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3782–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.F.; Deng, L.; Gan, H.; Shen, R.J.; Yang, M.H.; Zhang, Y. Sensitive immunosensor for tumor necrosis factor α based on dual signal amplification of ferrocene modified self-assembled peptide nanowire and glucose oxidase functionalized gold nanorod. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, S.; Xue, Y.; Liang, J.; Cui, L.; Li, Q.; Zhou, S.; Hunag, Y.; Li, G.; Zao, Y. A Fe3O4@Au-basedpseudo-homogenous electrochemical immunosensor for AFP measurements using AFP-antibody-GNPs-HRP as detection probe. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 534, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beitollahi, H.; Nekooei, S.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M. Amperometric immunosensor for prolactin hormone measurement using antibodies loaded on a nano-Au monolayer ionic-liquid carbon paste electrode. Talanta 2018, 188, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Yan, F.; Chen, Z.; Ju, H.X. Reagentless amperometric immunosensor based on direct electrochemistry of horseradish peroxidase for the determination of carcinoma antigen 125. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 5429–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Lu, X.B.; Li, J.; Yao, J.; Li, J.H. Direct electrochemistry of glucose-oxidase and electrochemical biosensing of glucose on quantum dots/carbon nanotubes electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 3203–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkus, B.; Emregul, E.; Yucesan, C.; Cebesoy Emregul, K. Myelin basic protein immunosensor for multiple sclerosis detection based upon label-free electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 46, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar, K.; Fairchild, A.; Alonas, E.; Bishop, D.; La Belle, J.; Sweeney, J.; Alford, T.L.; Joshi, L. A cytokine immunosensor for Multiple Sclerosis detection based upon label-free electrochemical impedance spectroscopy using electroplated printed circuit board electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydın, E.B.; Aydın, M.; Sezgintürk, M.K. A highly sensitive immunosensor based on ITO thin films covered by a new semi-conductive conjugated polymer for the determination of TNFα in human saliva and serum samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 97, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahato, K.; Kumar, S.; Srivastava, A.; Maurya, P.K.; Singh, R.; Chandra, P. Chapter 14—Electrochemical Immunosensors: Fundamentals and Applications in Clinical Diagnostics. In Handbook of Immunoassay Technologies; Vashist, S.K., Luong, J.H.T., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 359–414. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Liao, J.; Li, Q.; Yang, M.; Zhao, M.; Lu, Q. Epigenetics as biomarkers in autoimmune diseases. Clin. Immunol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronson, J.K. Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 59, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipriani, P.; Ruscitti, P.; Carubbi, F.; Liakouli, V.; Giacomelli, R. Methotrexate: An old new drug in autoimmune disease. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 10, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szentpétery, Á.; Horváth, Á.; Gulyás, K.; Petho, Z.; Bhattoa, H.; Szanto, S.; Szucs, G.; Fitzgerald, O.; Schett, G. Effects of targeted therapies on the bone in arthritides. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mowat, A.M. Coeliac Disease—A Meeting Point for Genetics, Immunology, and Protein Chemistry. Lancet 2003, 361, 1290–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tack, G.J.; Verbeek, W.H.M.; Schreurs, M.W.J.; Mulder, C.J.J. The spectrum of celiac disease: Epidemiology, clinical aspects and treatment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briani, C.; Samaroo, D.; Alaedini, A. Celiac disease: From gluten to autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2008, 7, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales-Rivera, L.C.; Acero-Sánchez, J.L.; Lozano-Sánchez, P.; Katakis, I. O’Sullivan, C.K. Electrochemical immunosensor detection of antigliadin antibodies from real human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4471–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlbom, I.; Olsson, M.; Forooz, N.K.; Sjöholm, A.G.; Truedsson, L.; Hansson, T. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) Anti-Tissue Transglutaminase Antibodies used as Markers for IgA-Deficient Celiac Disease Patients. Clin. Diagn. Lab Immunol. 2005, 12, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannetto, M.; Bianchi, V.; Gentili, S.; Fortunati, S.; De Munari, I.; Careri, M. An integrated IoT-Wi-Fi board for remote data acquisition and sharing from innovative immunosensors. Case of study: Diagnosis of celiac disease. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 273, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.M.P.S.; González-García, M.B.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Costa-García, A. Multiplexed electrochemical immunosensor for detection of celiac disease serological markers. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2013, 187, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real-Fernandez, F.; Passalacqua, I.; Peroni, E.; Chelli, M.; Lolli, F.; Papini, A.M.; Rovero, P. Glycopeptide-based antibody detection in multiple sclerosis by surface plasmon resonance. Sensors 2012, 12, 5596–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanson, J.B.; Paolini, I.; Collongues, N.; Alcaro, M.C.; Blanc, F.; Barbetti, F.; Fleury, M.; Peroni, E.; Rovero, P.; Rudolf, G.; et al. Evaluation of new immunological targets in neuromyelitis optica. J. Pept. Sci. 2013, 19, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Real-Fernandez, F.; Rossi, G.; Lolli, F.; Papini, A.M.; Rovero, P. Label-free method for anti-glucopeptide antibody detection for multiple sclerosis. MethodX 2015, 2, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellagha-Chenchah, W.; Sella, C.; Real-Fernandez, F.; Peroni, E.; Lolli, F.; Amatore, C.; Thouin, L.; Papini, A.M. Interactions between Human Antibodies and Synthetic Conformational Peptide Epitopes: Innovative Approach for Electrochemical Detection of Biomarkers of Multiple Sclerosis at Platinum Electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 176, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkó, J.; Besenyei, T.; Laki, J.; Glant, T.T.; Mikecz, K.; Szekanecz, Z. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis—A comprehensive review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 45, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.J.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T. Biomarkers as a treatment guide in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 186, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raptopoulou, A.; Sidiropoulos, P.; Katsouraki, M.; Boumpas, D.T. Anti-Citrulline Antibodies in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Evolving Concepts. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab Sci. 2007, 44, 339–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, N.; Lu, Q.; Liu, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. A double signal electrochemical human immunoglobulin G immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles-polydopamine functionalized reduced graphene oxide as a sensor platform and AgNPs/carbon nanocomposite as signal probe and catalytic substrate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, M.M.P.S.; González-García, M.B.; Santos-Silva, A.; Costa-García, A. Voltammetric immunosensor for the diagnosis of celiac disease based on the quantification of anti-gliadin antibodies. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2012, 163, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetto, M.; Mattarozzi, M.; Umiltà, E.; Manfredi, A.; Quaglia, S.; Careri, M. An amperometric immunosensor for diagnosis of celiac disease based on covalent immobilization of open conformation tissue transglutaminase for determination of anti-tTG antibodies in human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pividori, M.I.; Lermo, A.; Bonanni, A.; Alegret, S.; del Valle, M. Electrochemical immunosensor for the diagnosis of celiac disease. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 388, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Kaushal, A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, D. Ultrasensitive transglutaminase based nanosensor for early detection of celiac disease in human. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Yerga, D.; González-García, M.B.; Costa-García, A. Electrochemical immunosensor for anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies based on the in situ detection of quantum dots. Talanta 2014, 130, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thunkhamrak, C.; Reanpang, P.; Ounnunkad, K.; Jakmunee, J. Sequential injection system with amperometric immunosensor for sensitive determination of human immunoglobulin G. Talanta 2017, 171, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Li, T.; Qu, F.; Ding, L.; Shen, Z.; Yang, M. Electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of interleukin-17 based on Cd2+incorporated polystyrene spheres. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2013, 185, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Pan, D.; Xue, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y. A photoelectrochemical immunoassay for tumor necrosis factor-α using a GO-PTCNH2nanohybrid as a probe. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 824, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopus. Available online: www.scopus.com (accesed on 4 December 2018).
- Kou, B.B.; Zhang, L.; Xie, H.; Wang, D.; Yuan, Y.L.; Chai, Y.Q.; Yuan, R. DNA enzyme-decorated DNA nanoladders as enhancer for peptide cleavage-based electrochemical biosensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22869–22874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
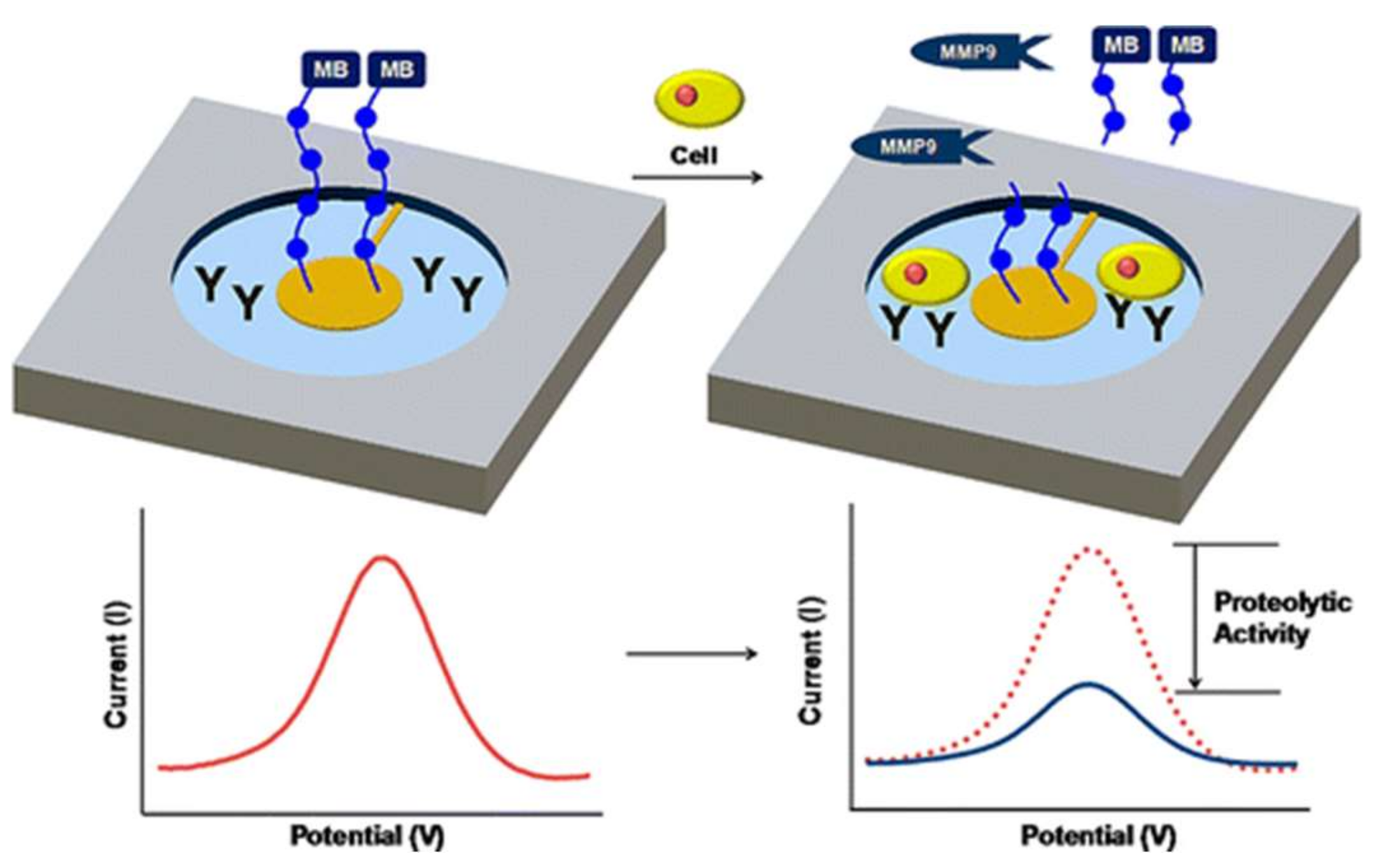
- Shin, D.S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Kwa, T.; Matharu, Z.; Revzin, A. Micropatterned surfaces functionalized with electroactive peptides for detecting protease release from cells. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X. Labeled and non-label electrochemical peptide inhibitor-based biosensing platform for determination of hemopexin domain of matrix. Talanta 2019, 194, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, J.M.; Lima, L.R.; Moraes, M.L. Immunosensor for diagnosis of Alzheimer disease using amyloid-β 1–40 peptide and silk fibroin thin films. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
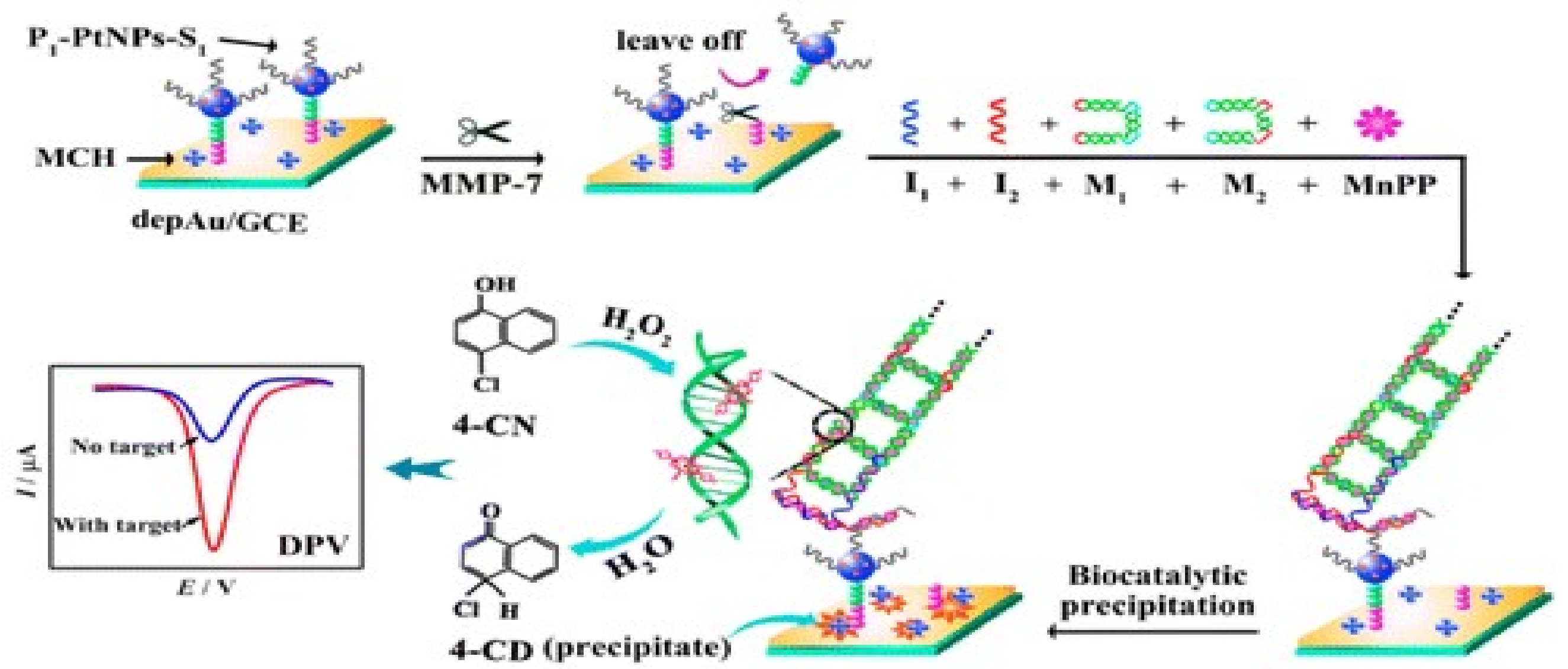
- Zheng, Y.; Ma, Z. Dual-reaction triggered sensitivity ampli fi cation for ultrasensitive peptide- cleavage based electrochemical detection of matrix metalloproteinase-7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 108, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Huang, H.; Huang, L.; Lin, Z.; Guo, L.; Qiu, B. Electrochemical biosensor for epidermal growth factor receptor detection with peptide ligand. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 109, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Jin, X.; Zhao, G. Amplified QCM biosensor for type IV collagenase based on collagenase- cleavage of gold nanoparticles functionalized peptide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 106, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodovalho, V.R.; Araujo, G.R.; Vaz, E.R.; Ueira-vieira, C.; Goulart, L.R.; Madurro, J.M. Peptide-based electrochemical biosensor for juvenile idiopathic arthritis detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biela, A.; Watkinson, M.; Meier, U.C.; Baker, D.; Giovannoni, G.; Becer, C.R.; Krause, S. Disposable MMP-9 sensor based on the degradation of peptide cross-linked hydrogel films using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Target | Electrode Architecture | Type of Assay | Label | Detection Method | LOD | LR | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celiac Disease | ||||||||
| IgA anti-tTG IgB anti-tTG | AuNPs/SAM-GCE | Indirect | AP | DPV | 3.2 AU mL−1 1.4 AU mL−1 | 0–30 AU mL−1 | Real patients serum | [55] |
| CNTs/AuNPs-SPE | Indirect | AP | CV | 9.1 U mL−1 9.0 U mL−1 | - | Real patients serum | [66] | |
| Au/SAM-GCE | Indirect | HRP | CV | 1.7 AU mL−1 2.7 AU mL−1 | 0–30 AU mL−1 | Serum | [67] | |
| IgA anti-tTG | Graphite epoxy | Indirect | HRP | Chronoamperometry | - | - | Real patients serum | [68] |
| GQD/AuNPs/MWCNTS/PAMAM | Direct | - | DPV with redox probe | 20 fg mL−1 | - | Spiked serum | [69] | |
| Anti-tTG | poly (sodium-4-styrensulfonic acid)- gold SPE | Indirect | POD | EIS | - | - | Real patients serum | [16] |
| Multichannel SPE array | Indirect | CdSe QDs | DPV | 7 U mL−1 | 0–40 U mL−1 | Spiked serum | [70] | |
| AGA | Gold electrodes with carboxylic-ended bipodal alkanethiol | Indirect | HRP | Chronoamperometry | 46 ng mL−1 | 0–1 μg mL−1 | Real patients serum | [53] |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | ||||||||
| MIF | AuNPs-NTiP-Thi-gold electrode | Direct | - | DPV with redox probe | 0.7 ng mL−1 | 0.03–230 ng mL−1 | Real patients serum | [67] |
| Multiple Sclerosis | ||||||||
| Anti-MBP | Gelatin-NTiP-Pt electrodes | Direct | - | EIS | 0.15 ng mL−1 | 0.48–2500 ng mL−1 | Spiked serum Spiked CSF | [42] |
| Non-Specific Biomarkers | ||||||||
| HIgG | GO-SPE | Direct | - | CV with redox probe | 1.70 ng mL−1 | 2–100 ng mL−1 | Urine | [71] |
| AuNPs-PDA-GO | Sandwich | AgNPs/carbon nanocomposite/benzoquinone | DPV | 0.001 ng mL−1 | 0.1–100 ng mL−1 | Spiked serum | [17] | |
| IL-17 | Graphene-GC | Sandwich | cadmium-polystyrene beads | SWV | 50 fg mL−1 | 0.1 pg −1 ng mL−1 | Spiked serum | [72] |
| IL-12 | Electroplating gold onto a disposable printed circuit board electrode | Direct | - | EIS | <100 fM | 0–25 pg mL−1 | Spiked serum | [43] |
| TNFα | Poly(3-thiophene acetic acid)-ITO | Direct | - | EIS | 3.7 fg mL−1 | 0.01–2 pg mL−1 | Serum | [44] |
| GO-PTCNH2 | Direct | - | Photoeletrochemical | 3.33 pg mL−1 | 10–100 ng mL−1 | Serum | [73] | |
| Analyte | Electrode Architecture | Method | Peptide Sequences | Label | LD (ng mL−1) | LOQ (ng mL−1) | Linear Range (ng mL−1) | Real Samples | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMP-14 | Gold electrode | DPV | VMDGYPMP-(CH2)6-Cys | CIS-Fc | 3 10−4 | 10−3 | 10−3–10−2 | - | [78] |
| MMP-14 | EIS | Cys- (CH2)6—VMDGYPMP-NH-CO-Fe | - | 0.03 | 0.1 | 0.1–7 | - | ||
| Aβ1 Ab | SPE | CV | DAEFRHDSGYEVHHQKLVFFAEDVGSNKGAI IGLMVGGVV (Aβ1-40) | - | 0–10 | - | [79] | ||
| MMP-7 | Au-rGO/MB-SA +PdNP | SWV | NH2-KKKRPLALWRSCCC-SH | - | 3 10−6 | 10−5 | 10−5–10 | Spiked serum samples | [80] |
| EGFR | Gold electrode | DPV | YHWYGYT- PQNVI | 9-mercapto-1-nonanol | 3.7 10−5 | 10−4 | 10–10−4 | Diluted human serum | [81] |
| Type IV collagenase | QCM gold electrode | QCM | AuNP modified P | - | 0.96 | 10 | 10–60 | Spiked serum samples | [82] |
| Type IV collagenase | QCM | P | - | 21 | 40 | 40–120 | - | ||
| JIA—IgG | SPE | DPV | ACSSWLPRGCGGGS | - | 1:300 diluted serum | 1:10–1:300 diluted serum | Real patients serum | [83] | |
| MMP-9 | Gold SPE | EIS | Leu–Gly–Arg–Met–Gly–Leu–Pro–Gly–Lys | Dextran | 50 | 50–400 | - | [84] | |
| MMP-9 | Gold electrode | SWV | Gly-Pro-Leu-Gly-Met-Trp-Ser-Arg-Cys | MB | 6 10−2 nM | 6 10−2–50 nM | Spiked serum samples | [77] | |
| MMP-7 | AuNP-GCE- P-PtNPs-S1 | DPV | NH2-KKKRPLALWRSCCC-SH | - | 0.05 10−3 | 2 10−3 | 2 10−3–20 | - | [76] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Florea, A.; Melinte, G.; Simon, I.; Cristea, C. Electrochemical Biosensors as Potential Diagnostic Devices for Autoimmune Diseases. Biosensors 2019, 9, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010038
Florea A, Melinte G, Simon I, Cristea C. Electrochemical Biosensors as Potential Diagnostic Devices for Autoimmune Diseases. Biosensors. 2019; 9(1):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010038
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlorea, Anca, Gheorghe Melinte, Ioan Simon, and Cecilia Cristea. 2019. "Electrochemical Biosensors as Potential Diagnostic Devices for Autoimmune Diseases" Biosensors 9, no. 1: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010038
APA StyleFlorea, A., Melinte, G., Simon, I., & Cristea, C. (2019). Electrochemical Biosensors as Potential Diagnostic Devices for Autoimmune Diseases. Biosensors, 9(1), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010038






