Synergistic Integration of Laboratory and Numerical Approaches in Studies of the Biomechanics of Diseased Red Blood Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sickle Cell Disease
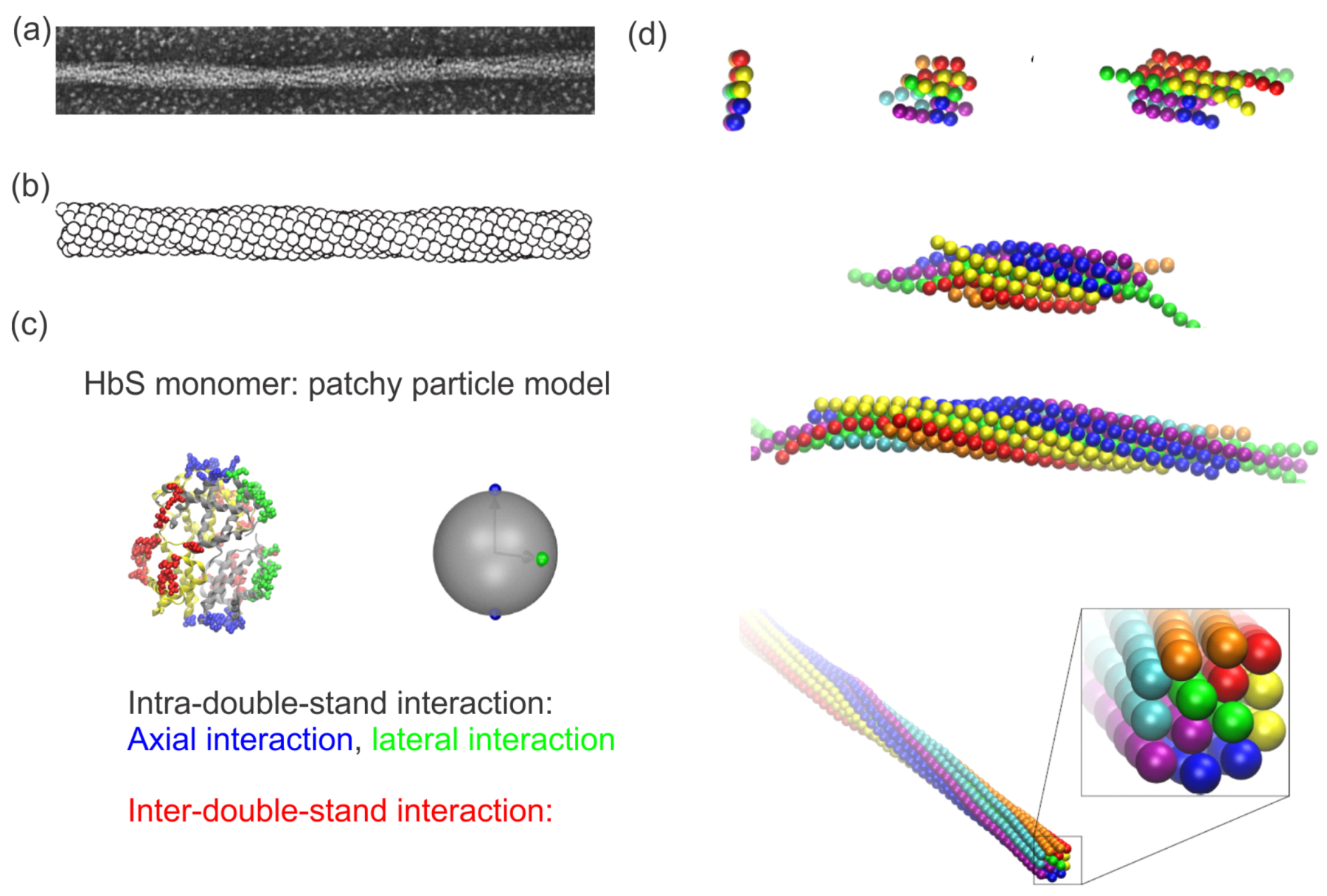
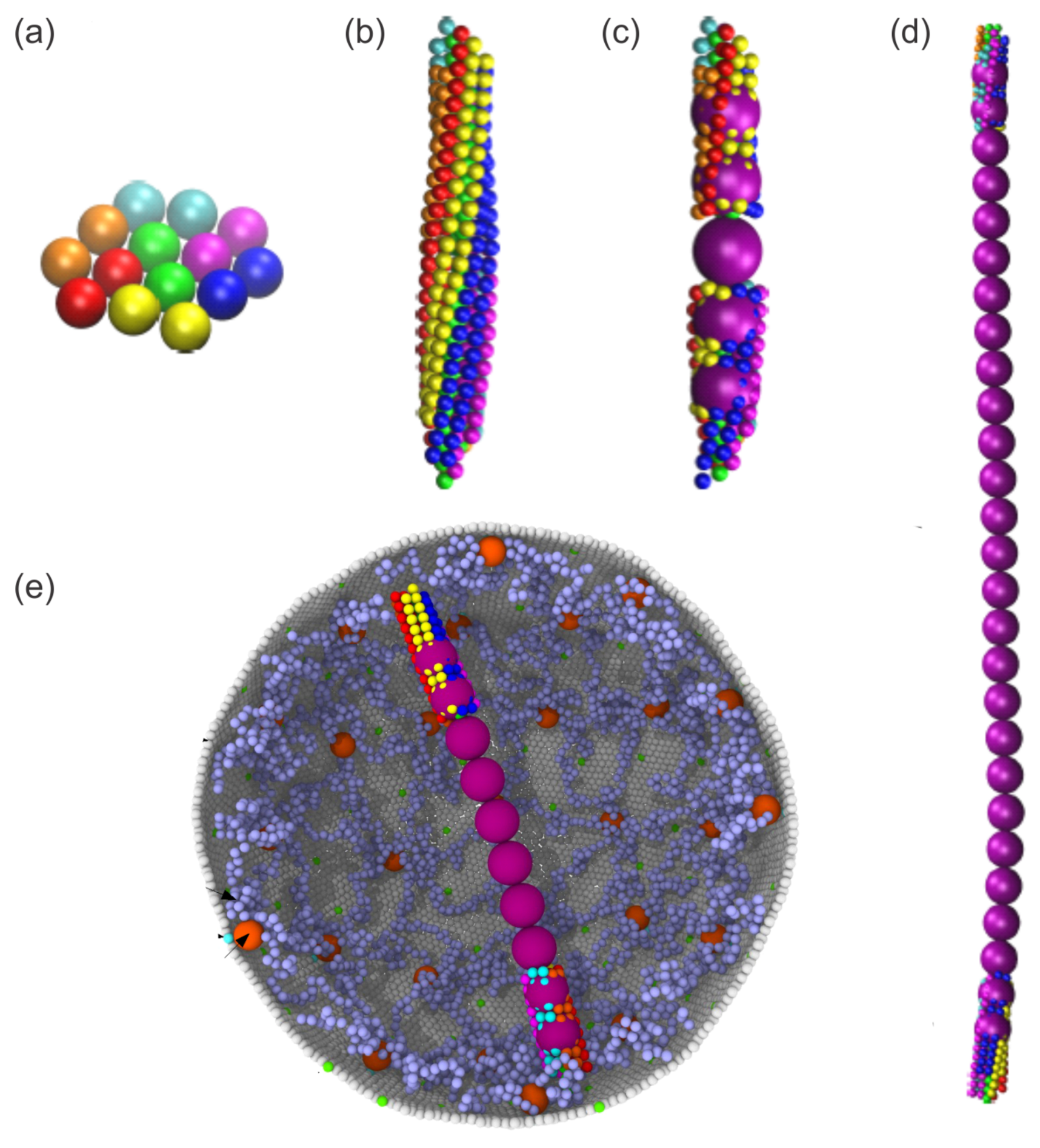
2.1. Sickle Hemoglobin Fibers
2.1.1. Impaired RBC Deformability
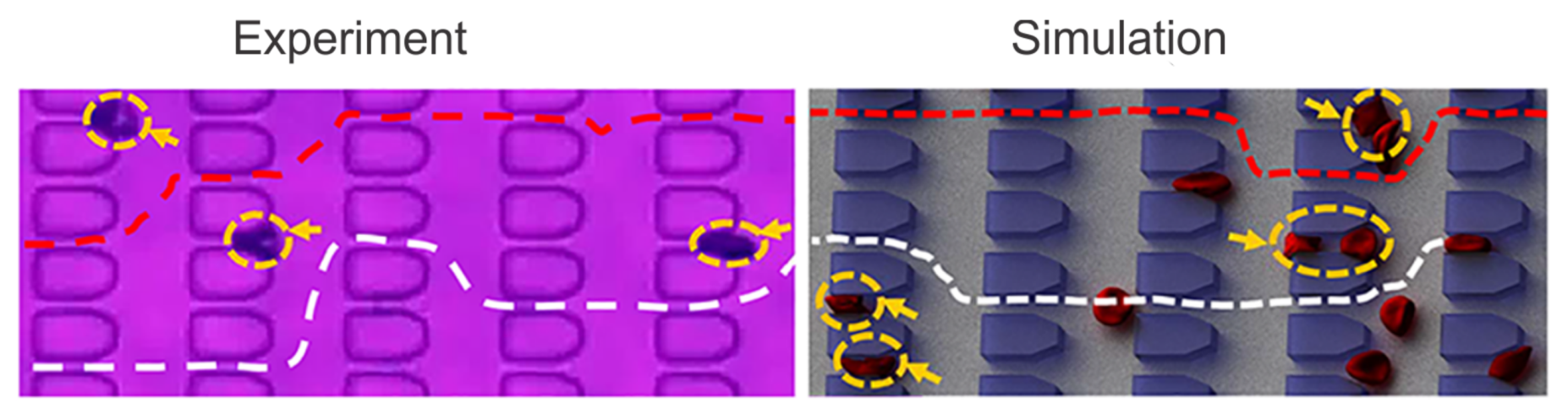
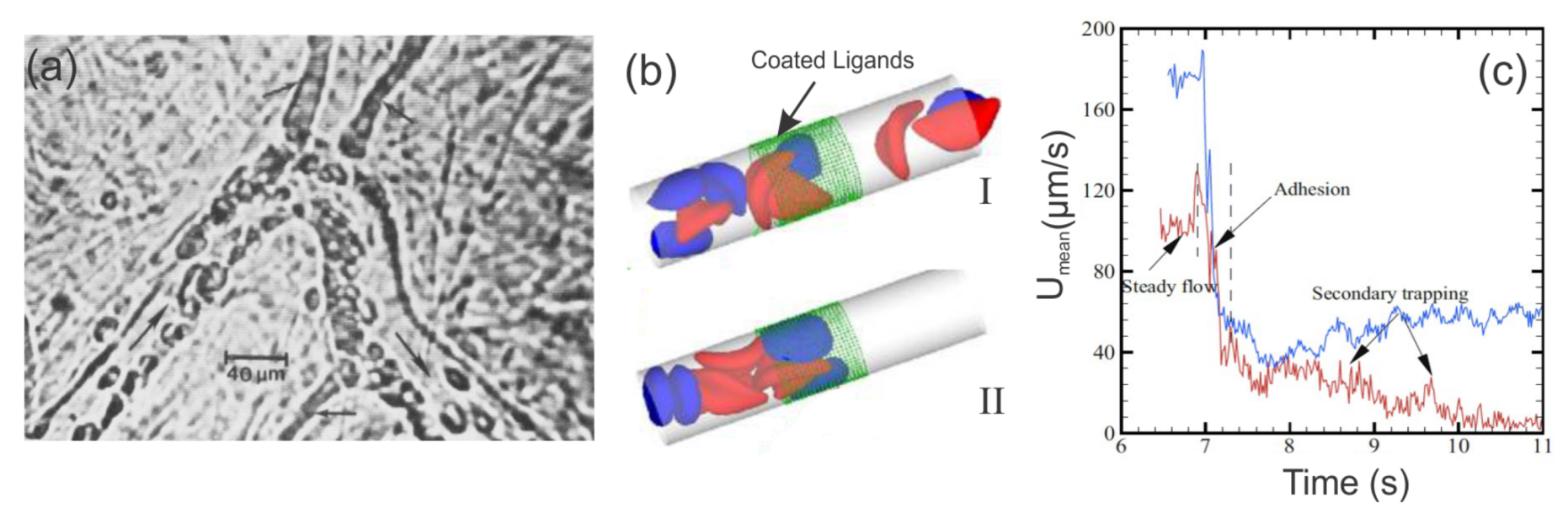
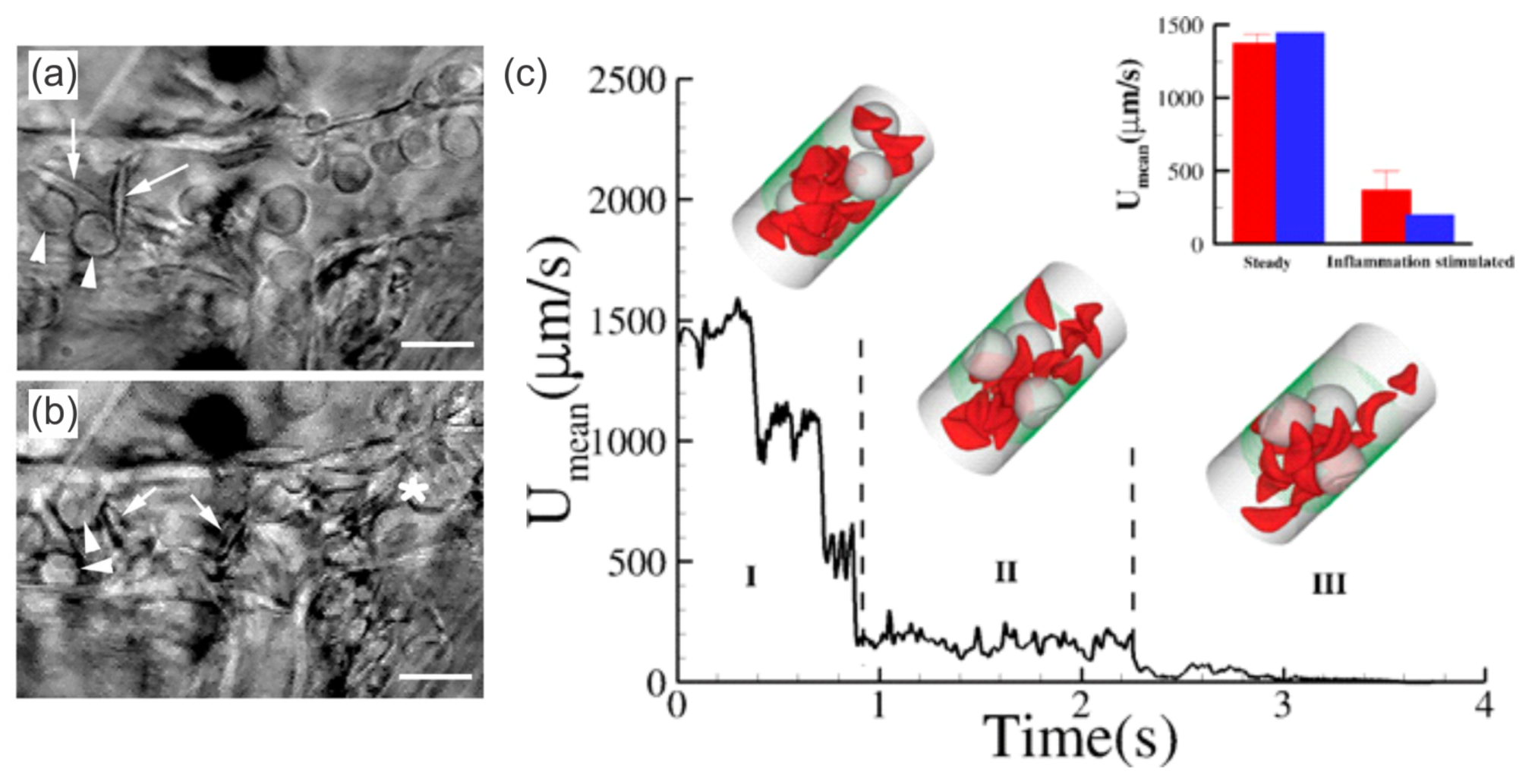
2.1.2. Enhanced SS-RBC Adhesion and Vaso-Occlusion
3. Hereditary Spherocytosis
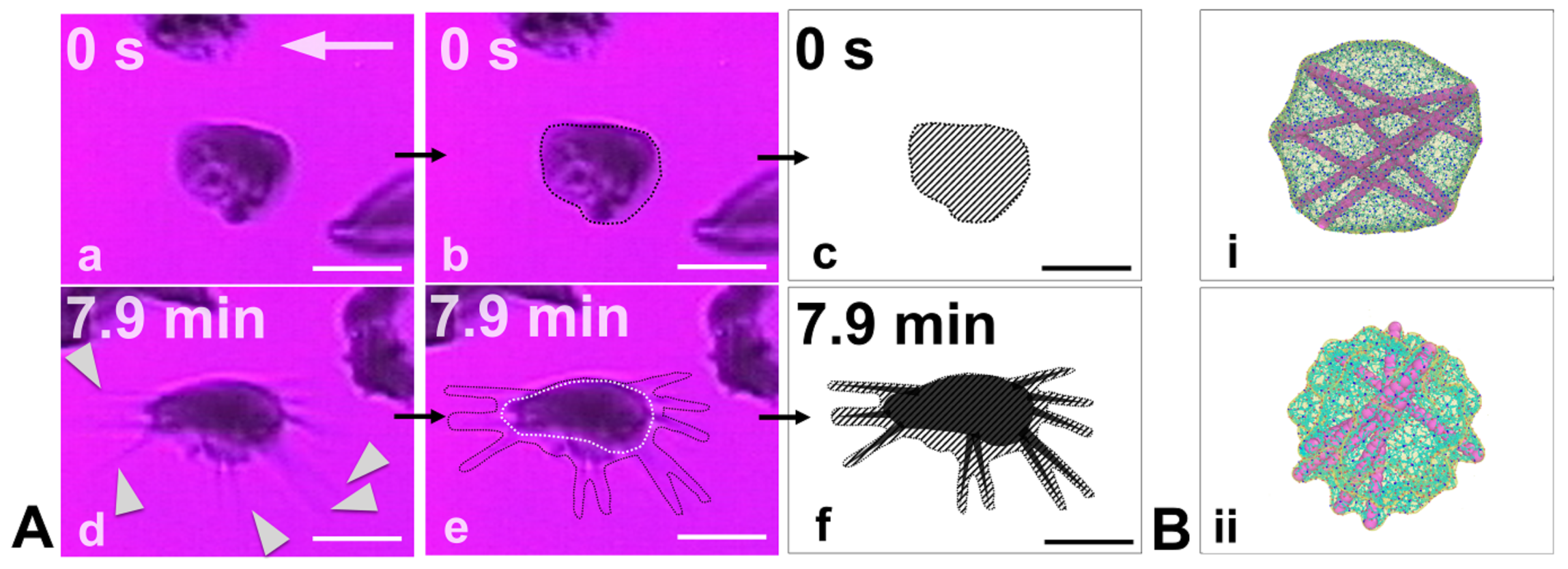
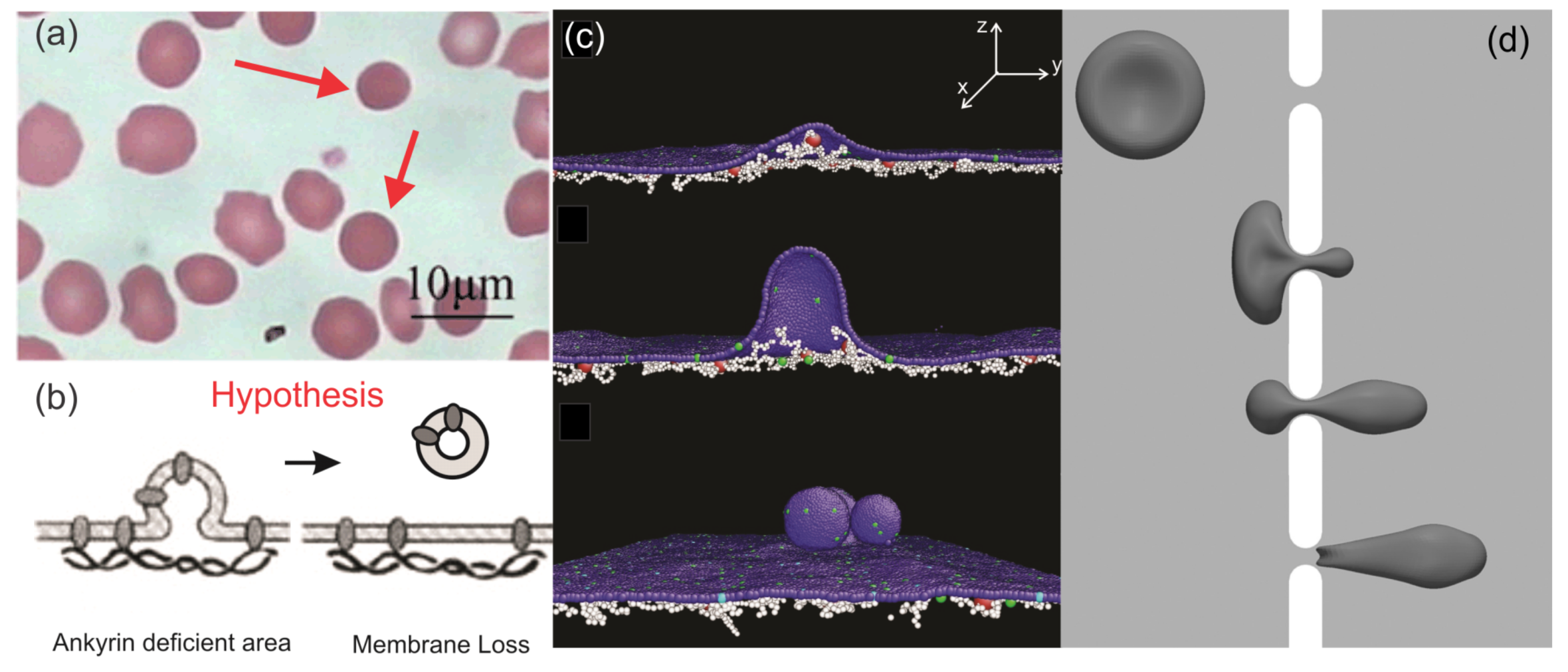
3.1. RBC Vesiculation
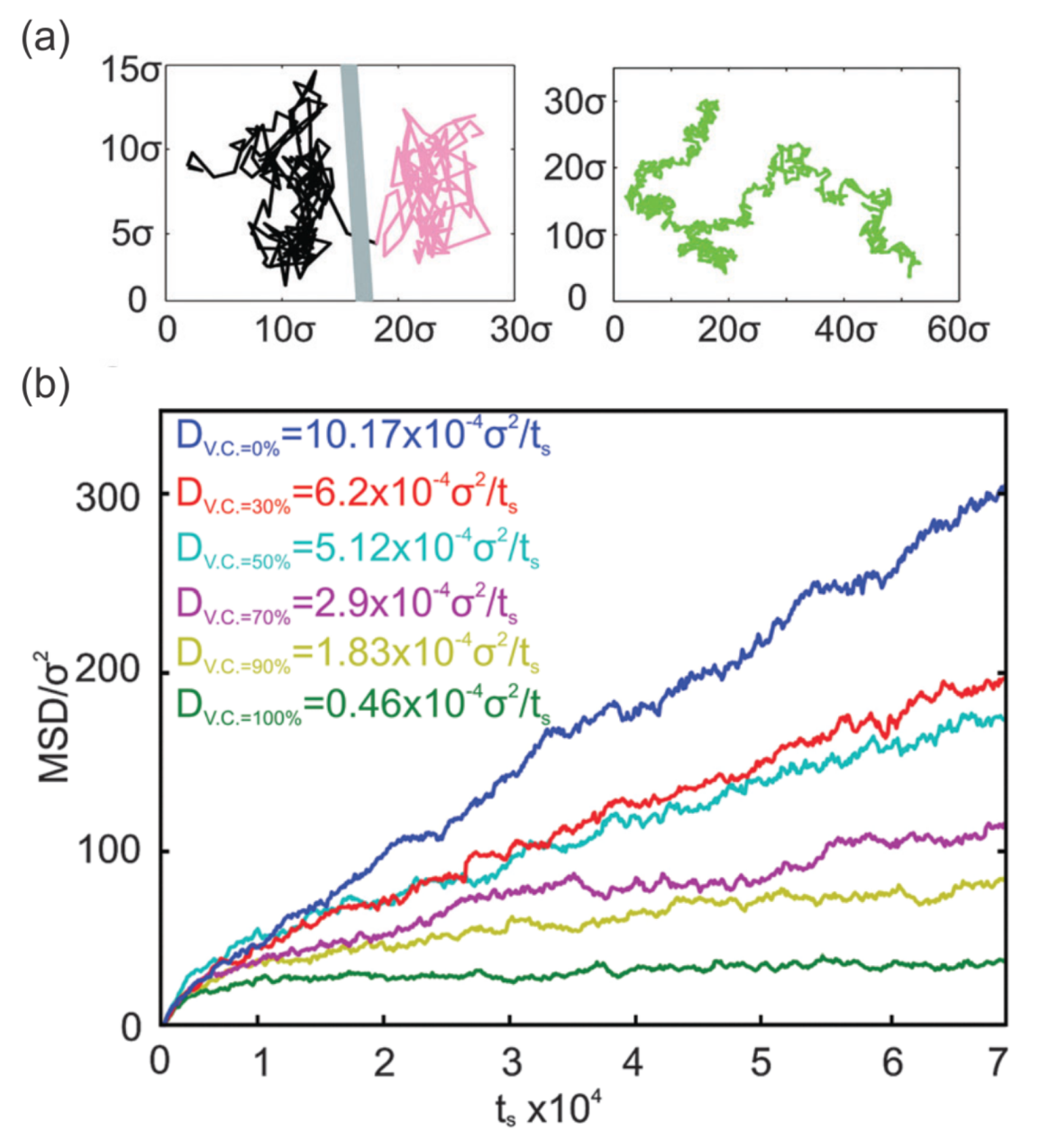
3.2. Membrane Protein Diffusion
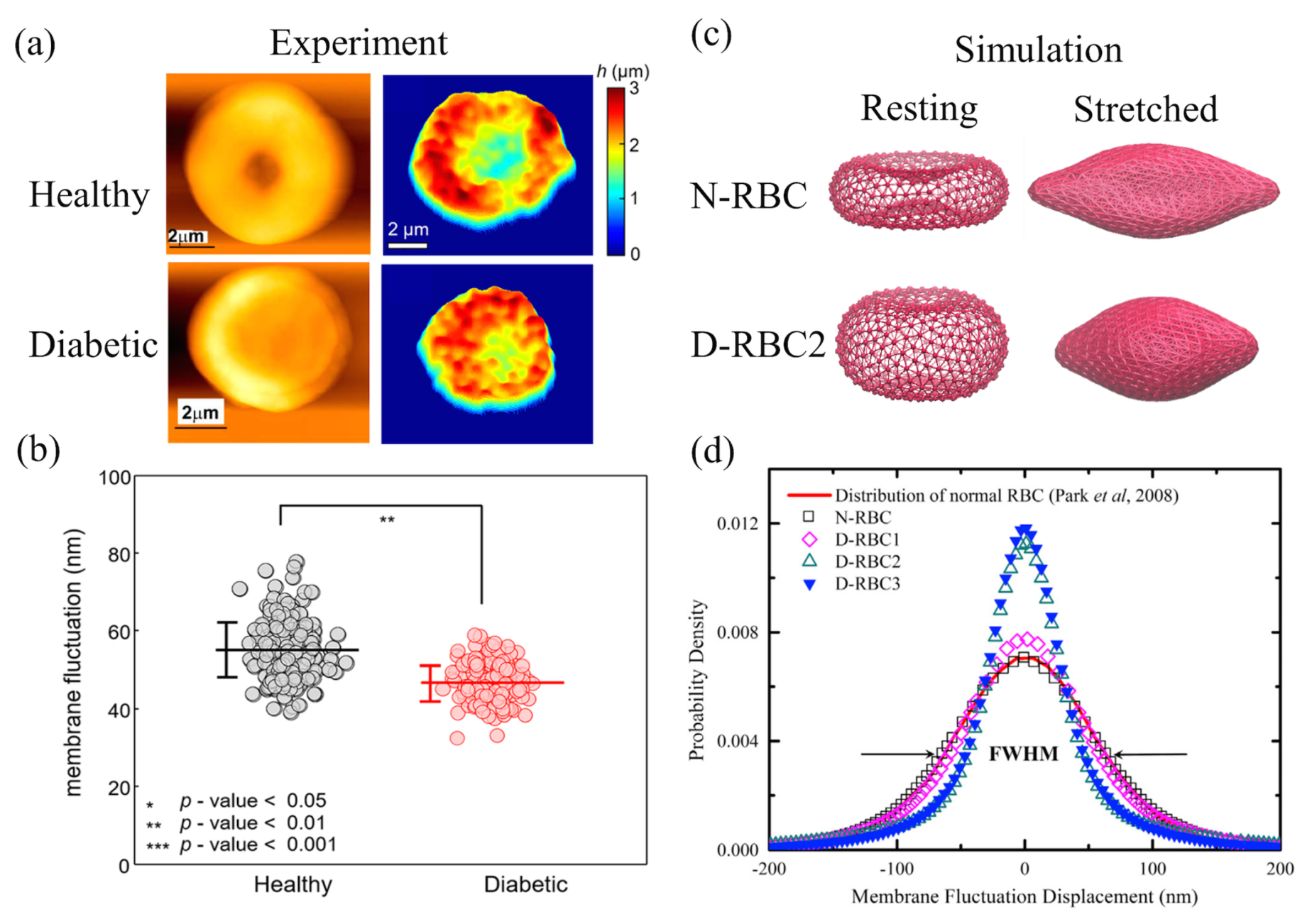
4. Diabetes Mellitus
4.1. Mechanics of Diabetic RBCs
4.2. Biorheology of Diabetic Blood
5. Future Prospectus
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boal, D.H. Mechanics of the Cell; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, G.M.; Hausman, R.E. The Cell: A Molecular Approach; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2000; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Steck, T.L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane: A review. J. Cell Biol. 1974, 62, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohandas, N.; Chasis, J. Red blood cell deformability, membrane material properties and shape: Regulation by transmembrane, skeletal and cytosolic proteins and lipids. Semin. Hematol. 1993, 30, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lykotrafitis, G.; Dao, M.; Suresh, S. Cytoskeletal dynamics of human erythrocyte. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4937–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, W.C.; Waugh, R.E. Energy of dissociation of lipid bilayer from the membrane skeleton of red blood cells. Biophys. J. 1997, 72, 2669–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Mohandas, N. Disorders of red cell membrane. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 141, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohandas, N.; Gallagher, P.G. Red cell membrane: Past, present, and future. Blood 2008, 112, 3939–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauling, L.; Itano, H.A.; Singer, S.; Wells, I.C. Sickle cell anemia, a molecular disease. Science 1949, 110, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingram, V.M. Gene mutations in human haemoglobin: The chemical difference between normal and sickle cell haemoglobin. Nature 1957, 180, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, C.T.; Schechter, A.N. The intracellular polymerization of sickle hemoglobin and its relevance to sickle cell disease. Blood 1981, 58, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eaton, W.A.; Hofrichter, J. Sickle cell hemoglobin polymerization. Adv. Protein Chem. 1990, 40, 63–279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferrone, F.A. Polymerization and sickle cell disease: A molecular view. Microcirculation 2004, 11, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, D.K.; Fabry, M.E. In vivo studies of sickle red blood cells. Microcirculation 2004, 11, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manwani, D.; Frenette, P.S. Vaso-occlusion in sickle cell disease: Pathophysiology and novel targeted therapies. Blood 2013, 122, 3892–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandao, M.; Fontes, A.; Barjas-Castro, M.; Barbosa, L.; Costa, F.; Cesar, C.; Saad, S. Optical tweezers for measuring red blood cell elasticity: Application to the study of drug response in sickle cell disease. Eur. J. Haematol. 2003, 70, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lande, W.M.; Andrews, D.L.; Clark, M.R.; Braham, N.V.; Black, D.M.; Embury, S.H.; Mentzer, W.C. The incidence of painful crisis in homozygous sickle cell disease: Correlation with red cell deformability. Blood 1988, 72, 2056–2059. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chien, S. Red cell deformability and its relevance to blood flow. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1987, 49, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, D.K.; Fabry, M.E.; Nagel, R.L. Microvascular sites and characteristics of sickle cell adhesion to vascular endothelium in shear flow conditions: Pathophysiological implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 3356–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenette, P.S.; Atweh, G.F. Sickle cell disease: Old discoveries, new concepts, and future promise. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eber, S.; Lux, S.E. Hereditary spherocytosis—Defects in proteins that connect the membrane skeleton to the lipid bilayer. Semin. Hematol. 2004, 41, 118–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, P.G. Hematologically important mutations: Ankyrin variants in hereditary spherocytosis. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2005, 35, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrotta, S.; Gallagher, P.G.; Mohandas, N. Hereditary spherocytosis. Lancet 2008, 372, 1411–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, L.; Galimand, J.; Fenneteau, O.; Mohandas, N. Hereditary spherocytosis, elliptocytosis, and other red cell membrane disorders. Blood Rev. 2013, 27, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narla, J.; Mohandas, N. Red cell membrane disorders. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2017, 39, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reliene, R.; Mariani, M.; Zanella, A.; Reinhart, W.H.; Ribeiro, M.L.; del Giudice, E.M.; Perrotta, S.; Iolascon, A.; Eber, S.; Lutz, H.U. Splenectomy prolongs in vivo survival of erythrocytes differently in spectrin/ankyrin-and band 3-deficient hereditary spherocytosis. Blood 2002, 100, 2208–2215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, D.E.; Utterback, N.G.; La Puma, J. Reduced erythrocyte deformability in diabetes. Diabetes 1978, 27, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, R.; Smart, T.; Nobre-Cardoso, J.; Richards, C.; Bhatnagar, R.; Tufail, A.; Shima, D.; Jones, P.H.; Pavesio, C. Assessment of red blood cell deformability in type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic retinopathy by dual optical tweezers stretching technique. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 15873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowluru, R.; Bitensky, M.; Kowluru, A.; Dembo, M.; Keaton, P.; Buican, T. Reversible sodium pump defect and swelling in the diabetic rat erythrocyte: Effects on filterability and implications for microangiopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 3327–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornal, M.; Lekka, M.; Pyka-Fościak, G.; Lebed, K.; Grodzicki, T.; Wizner, B.; Styczeń, J. Erythrocyte stiffness in diabetes mellitus studied with atomic force microscope. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2006, 35, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dulińska, I.; Targosz, M.; Strojny, W.; Lekka, M.; Czuba, P.; Balwierz, W.; Szymoński, M. Stiffness of normal and pathological erythrocytes studied by means of atomic force microscopy. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2006, 66, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, T.T.; Sinha, A.; Malleret, B.; Suwanarusk, R.; Park, J.E.; Naidu, R.; Das, R.; Dutta, B.; Ong, S.T.; Verma, N.K.; et al. Quantitative mass spectrometry of human reticulocytes reveal proteome-wide modifications during maturation. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciaszek, J.L.; Lykotrafitis, G. Sickle cell trait human erythrocytes are significantly stiffer than normal. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henon, S.; Lenormand, G.; Richert, A.; Gallet, F. A new determination of the shear modulus of the human erythrocyte membrane using optical tweezers. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guck, J.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Mahmood, H.; Moon, T.J.; Cunningham, C.C.; Käs, J. The optical stretcher: A novel laser tool to micromanipulate cells. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 767–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, M.; Lim, C.T.; Suresh, S. Mechanics of the human red blood cell deformed by optical tweezers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2003, 51, 2259–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S. Mechanical response of human red blood cells in health and disease: Some structure-property-function relationships. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 21, 1871–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E. New membrane concept applied to the analysis of fluid shear-and micropipette-deformed red blood cells. Biophys. J. 1973, 13, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.; Waugh, R. Osmotic correction to elastic area compressibility measurements on red cell membrane. Biophys. J. 1977, 20, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.; Sung, K.L.; Skalak, R.; Usami, S.; Tözeren, A. Theoretical and experimental studies on viscoelastic properties of erythrocyte membrane. Biophys. J. 1978, 24, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochmuth, R.M. Micropipette aspiration of living cells. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.J.; Telfer, P.; MacKinnon, H.; Langabeer, L.; McMahon, C.; Darbyshire, P.; Dhermy, D. Using the eosin-5-maleimide binding test in the differential diagnosis of hereditary spherocytosis and hereditary pyropoikilocytosis. Cytometry Part B Clin. Cytometry J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2008, 74, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, R.; Mishra, P.; Pati, H. Evaluation of eosin-5-maleimide flow cytometric test in diagnosis of hereditary spherocytosis. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2010, 32, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedar, P.; Colah, R.; Kulkarni, S.; Ghosh, K.; Mohanty, D. Experience with eosin-5-maleimide as a diagnostic tool for red cell membrane cytoskeleton disorders. Clin. Lab. Haematol. 2003, 25, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessis, M.; Mohandas, N.; Feo, C. Automated ektacytometry: A new method of measuring red cell deformability and red cell indices. Blood Cells 1980, 6, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohandas, N.; Clark, M.R.; Jacobs, M.S.; Shohet, S.B. Analysis of factors regulating erythrocyte deformability. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 66, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballas, S.K.; Smith, E. Red blood cell changes during the evolution of the sickle cell painful crisis. Blood 1992, 79, 2154–2163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baskurt, O.K.; Gelmont, D.; Meiselman, H.J. Red blood cell deformability in sepsis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, L.; Suner, L.; Galimand, J.; Bonnel, A.; Pascreau, T.; Couque, N.; Fenneteau, O.; Mohandas, N. Diagnostic tool for red blood cell membrane disorders: Assessment of a new generation ektacytometer. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2016, 56, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, K.; Park, Y. Measurement techniques for red blood cell deformability: Recent advances. In Blood Cell—An Overview of Studies in Hematology; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tomaiuolo, G. Biomechanical properties of red blood cells in health and disease towards microfluidics. Biomicrofluidics 2014, 8, 051501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Shin, S. Advances in the measurement of red blood cell deformability: A brief review. J. Cell. Biotechnol. 2015, 1, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivkin, I.V.; Karniadakis, G.E. Accurate coarse-grained modeling of red blood cells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 118105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedosov, D.A.; Caswell, B.; Karniadakis, G.E. A multiscale red blood cell model with accurate mechanics, rheology, and dynamics. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 2215–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y.; Kondo, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Lim, C.T.; Yamaguchi, T. Modeling of hemodynamics arising from malaria infection. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y.; Nakaaki, K.; Kondo, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Lim, C.T.; Yamaguchi, T. Margination of red blood cells infected by Plasmodium falciparum in a microvessel. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 1553–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedosov, D.; Caswell, B.; Suresh, S.; Karniadakis, G. Quantifying the biophysical characteristics of Plasmodium-falciparum-parasitized red blood cells in microcirculation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Li, X.; Pivkin, I.V.; Dao, M.; Karniadakis, G.E.; Suresh, S. Lipid bilayer and cytoskeletal interactions in a red blood cell. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13356–13361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lykotrafitis, G. Erythrocyte membrane model with explicit description of the lipid bilayer and the spectrin network. Biophys. J. 2014, 107, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.H.; Lu, L.; Li, H.; Evangelinos, C.; Grinberg, L.; Sachdeva, V.; Karniadakis, G.E. OpenRBC: A Fast Simulator of Red Blood Cells at Protein Resolution. Biophys. J. 2017, 112, 2030–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Caswell, B.; Karniadakis, G.E. A low-dimensional model for the red blood cell. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 4366–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, T.; Phan-Thien, N.; Cheong Khoo, B.; Teck Lim, C. Numerical modelling of a healthy/malaria-infected erythrocyte in shear flow using dissipative particle dynamics method. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 224701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Isfahani, A.H.; Olson, L.N.; Freund, J.B. A spectral boundary integral method for flowing blood cells. J. Comput. Phys. 2010, 229, 3726–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanujan, S.; Pozrikidis, C. Deformation of liquid capsules enclosed by elastic membranes in simple shear flow: Large deformations and the effect of fluid viscosities. J. Fluid Mech. 1998, 361, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doddi, S.K.; Bagchi, P. Three-dimensional computational modeling of multiple deformable cells flowing in microvessels. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 046318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Y.; Chew, Y.; Low, H. A lattice Boltzmann study on the large deformation of red blood cells in shear flow. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2007, 18, 993–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Kim, O.; Alber, M. Three-dimensional multi-scale model of deformable platelets adhesion to vessel wall in blood flow. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2014, 372, 20130380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Vlahovska, P.M.; Karniadakis, G.E. Continuum-and particle-based modeling of shapes and dynamics of red blood cells in health and disease. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y.; Omori, T.; Shimogonya, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ishikawa, T. Numerical methods for simulating blood flow at macro, micro, and multi scales. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 2221–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, T.; Phan-Thien, N.; Lim, C.T. Particle-based simulations of red blood cells—A review. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 2255–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Chang, H.Y.; Lykotrafitis, G.; Karniadakis, G.E. Computational biomechanics of human red blood cells in hematological disorders. J. Biomech. Eng. 2017, 139, 021008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chang, H.; Yang, J.; Lu, L.; Tang, Y.; Lykotrafitis, G. Modeling biomembranes and red blood cells by coarse-grained particle methods. Appl. Math. Mech. 2018, 39, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykes, G.; Crepeau, R.H.; Edelstein, S.J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the fibre of sickle cell haemoglobin. Nature 1978, 272, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dykes, G.W.; Crepeau, R.H.; Edelstein, S.J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the 14-filament fibers of hemoglobin S. J. Mol. Biol. 1979, 130, 451–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carragher, B.; Bluemke, D.A.; Gabriel, B.; Potel, M.J.; Josephs, R. Structural analysis of polymers of sickle cell hemoglobin III. Fibers within fascicles. J. Mol. Biol. 1988, 199, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watowich, S.J.; Gross, L.J.; Josephs, R. Intermolecular contacts within sickle hemoglobin fibers. J. Mol. Biol. 1989, 209, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watowich, S.J.; Gross, L.J.; Josephs, R. Analysis of the Intermolecular Contacts within Sickle Hemoglobin Fibers: Effect of Site-Specific Substitutions, Fiber Pitch, and Double-Strand Disorder. J. Struct. Biol. 1993, 111, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cretegny, I.; Edelstein, S.J. Double strand packing in hemoglobin S fibers. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 230, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, D.J.; Adachi, K.; Royer, W.E. The high resolution crystal structure of deoxyhemoglobin S1. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 272, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Li, X.; Vekilov, P.G.; Karniadakis, G.E. Probing the Twisted Structure of Sickle Hemoglobin Fibers via Particle Simulations. Biophys. J. 2016, 110, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lykotrafitis, G. A coarse-grain molecular dynamics model for sickle hemoglobin fibers. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ha, V.; Lykotrafitis, G. Modeling sickle hemoglobin fibers as one chain of coarse-grained particles. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Caswell, B.; Karniadakis, G.E. Effect of chain chirality on the self-assembly of sickle hemoglobin. Biophys. J. 2012, 103, 1130–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Li, H.; Bian, X.; Li, X.; Karniadakis, G.E. Mesoscopic Adaptive Resolution Scheme toward Understanding of Interactions between Sickle Cell Fibers. Biophys. J. 2017, 113, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messmann, R.; Gannon, S.; Sarnaik, S.; Johnson, R.M. Mechanical properties of sickle cell membranes. Blood 1990, 75, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Connes, P.; Lamarre, Y.; Waltz, X.; Ballas, S.K.; Lemonne, N.; Etienne-Julan, M.; Hue, O.; Hardy-Dessources, M.D.; Romana, M. Haemolysis and abnormal haemorheology in sickle cell anaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 165, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, H.; Hillman, T.R.; Higgins, J.M.; Diez-Silva, M.; Peng, Z.; Dao, M.; Dasari, R.R.; Suresh, S.; Park, Y. Optical measurement of biomechanical properties of individual erythrocytes from a sickle cell patient. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 4130–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, P.; Abidi, S.Z.; Du, E.; Papageorgiou, D.P.; Choi, Y.; Park, Y.; Higgins, J.M.; Kato, G.J.; Suresh, S.; Dao, M.; et al. Cellular normoxic biophysical markers of hydroxyurea treatment in sickle cell disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9527–9532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.; Eddington, D.; Bhatia, S.; Mahadevan, L. Sickle cell vasoocclusion and rescue in a microfluidic device. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20496–20500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, E.; Diez-Silva, M.; Kato, G.J.; Dao, M.; Suresh, S. Kinetics of sickle cell biorheology and implications for painful vasoocclusive crisis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciciliano, J.C.; Abbaspour, R.; Woodall, J.; Wu, C.; Bakir, M.S.; Lam, W.A. Probing blood cell mechanics of hematologic processes at the single micron level. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 3804–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, G.B.; Johnson, C.S.; Meiselman, H.J. Influence of oxygen tension on the viscoelastic behavior of red blood cells in sickle cell disease. Blood 1986, 67, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.Y.; Lim, C.T. Biomechanics approaches to studying human diseases. Trends Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bento, D.; Rodrigues, R.O.; Faustino, V.; Pinho, D.; Fernandes, C.S.; Pereira, A.I.; Garcia, V.; Miranda, J.M.; Lima, R. Deformation of Red Blood Cells, Air Bubbles, and Droplets in Microfluidic Devices: Flow Visualizations and Measurements. Micromachines 2018, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, D.K.; Fabry, M.; Windisch, P.; Baez, S.; Nagel, R. Erythrocytes in sickle cell anemia are heterogeneous in their rheological and hemodynamic characteristics. J. Clin. Investig. 1983, 72, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duez, J.; Holleran, J.; Ndour, P.; Pionneau, C.; Diakité, S.; Roussel, C.; Dussiot, M.; Amireault, P.; Avery, V.; Buffet, P. Mechanical clearance of red blood cells by the human spleen: Potential therapeutic applications of a biomimetic RBC filtration method. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2015, 22, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Du, E.; Dao, M.; Suresh, S.; Karniadakis, G.E. Patient-specific modeling of individual sickle cell behavior under transient hypoxia. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebbel, R.P.; Boogaerts, M.A.; Eaton, J.W.; Steinberg, M.H. Erythrocyte adherence to endothelium in sickle-cell anemia: A possible determinant of disease severity. N. Engl. J. Med. 1980, 302, 992–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenette, P.S. Sickle cell vaso-occlusion: Multistep and multicellular paradigm. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2002, 9, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebbel, R. Adhesion of sickle red cells to endothelium: Myths and future directions. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2008, 15, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, C.; Manwani, D.; Frenette, P.S. Neutrophils, platelets, and inflammatory pathways at the nexus of sickle cell disease pathophysiology. Blood 2016, 127, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, M.A.; Tutuncuoglu, E.; Barge, S.; Novelli, E.M.; Sundd, P. Quantitative microfluidic fluorescence microscopy to study vaso-occlusion in sickle cell disease. Haematologica 2015, 100, e390–e393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennewitz, M.F.; Jimenez, M.A.; Vats, R.; Tutuncuoglu, E.; Jonassaint, J.; Kato, G.J.; Gladwin, M.T.; Sundd, P. Lung vaso-occlusion in sickle cell disease mediated by arteriolar neutrophil-platelet microemboli. J. Clin. Investig. Insight 2017, 2, e89761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoover, R.; Rubin, R.; Wise, G.; Warren, R. Adhesion of normal and sickle erythrocytes to endothelial monolayer cultures. Blood 1979, 54, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaul, D.; Fabry, M.; Nagel, R. Erythrocytic and vascular factors influencing the microcirculatory behavior of blood in sickle cell anemia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1989, 565, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, D.; Tsai, H.; Liu, X.; Nakada, M.; Nagel, R.; Coller, B. Monoclonal antibodies to αVβ3 (7E3 and LM609) inhibit sickle red blood cell-endothelium interactions induced by platelet-activating factor. Blood 2000, 95, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spring, F.; An, X.; Mohandas, N.; Anstee, D.; Chasis, J.A. Peptides based on V-binding domains of erythrocyte ICAM-4 inhibit sickle red cell-endothelial interactions and vaso-occlusion in the microcirculation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 291, C922–C930. [Google Scholar]
- Loiseau, E.; Massiera, G.; Mendez, S.; Martinez, P.A.; Abkarian, M. Microfluidic study of enhanced deposition of sickle cells at acute corners. Biophys. J. 2015, 108, 2623–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.; Karniadakis, G.E. Probing vasoocclusion phenomena in sickle cell anemia via mesoscopic simulations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11326–11330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, D.K.; Xue, H. Rate of deoxygenation and rheologic behavior of blood in sickle cell anemia. Blood 1991, 77, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turhan, A.; Weiss, L.A.; Mohandas, N.; Coller, B.S.; Frenette, P.S. Primary role for adherent leukocytes in sickle cell vascular occlusion: A new paradigm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3047–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenette, P.S.; Mayadas, T.N.; Rayburn, H.; Hynes, R.O.; Wagner, D.D. Susceptibility to infection and altered hematopoiesis in mice deficient in both P-and E-selectins. Cell 1996, 84, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeramkumar, V.; Adrover, J.M.; Ballesteros, I.; Cuartero, M.I.; Rossaint, J.; Bilbao, I.; Nácher, M.; Pitaval, C.; Radovanovic, I.; Fukui, Y.; et al. Neutrophils scan for activated platelets to initiate inflammation. Science 2014, 346, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kim, K.; Hahm, E.; Molokie, R.; Hay, N.; Gordeuk, V.R.; Du, X.; Cho, J. Neutrophil AKT2 regulates heterotypic cell-cell interactions during vascular inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, D.P.; Abidi, S.Z.; Chang, H.; Li, X.; Kato, G.J.; Karniadakis, G.E.; Dao, M.; Suresh, S. Simultaneous polymerization and adhesion under hypoxia in sickle cell disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.Y.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Karniadakis, G.E. MD/DPD multiscale framework for predicting morphology and stresses of red blood cells in health and disease. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1005173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safeukui, I.; Buffet, P.A.; Deplaine, G.; Perrot, S.; Brousse, V.; Ndour, A.; Nguyen, M.; Mercereau-Puijalon, O.; David, P.H.; Milon, G.; et al. Quantitative assessment of sensing and sequestration of spherocytic erythrocytes by the human spleen. Blood 2012, 120, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, L.; Lu, L.; Juan, L. Topological Structures and Membrane Nanostructures of Erythrocytes after Splenectomy in Hereditary Spherocytosis Patients via Atomic Force Microscopy. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 74, 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Walensky, L. Disorders of the Red Blood Cell Membrane; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003; pp. 1709–1858. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Lykotrafitis, G. Vesiculation of healthy and defective red blood cells. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 012715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Salehyar, S.; Cabrales, P.; Asaro, R.J. Prospects for Human Erythrocyte Skeleton-Bilayer Dissociation during Splenic Flow. Biophys. J. 2017, 113, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spangler, E.J.; Harvey, C.W.; Revalee, J.D.; Kumar, P.S.; Laradji, M. Computer simulation of cytoskeleton-induced blebbing in lipid membranes. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 051906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lykotrafitis, G. Two-component coarse-grained molecular-dynamics model for the human erythrocyte membrane. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, J.; Chu, T.T.; Naidu, R.; Lu, L.; Chandramohanadas, R.; Dao, M.; Karniadakis, G.E. Cytoskeleton Remodeling Induces Membrane Stiffness and Stability Changes of Maturing Reticulocytes. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 2014–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, L.; Mohandas, N.; Sorette, M.; Grange, M.J.; Tchernia, G.; Cynober, T. Temporal differences in membrane loss lead to distinct reticulocyte features in hereditary spherocytosis and in immune hemolytic anemia. Blood 2001, 98, 2894–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheetz, M.P.; Schindler, M.; Koppel, D.E. Lateral mobility of integral membrane proteins is increased in spherocytic erythrocytes. Nature 1980, 285, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomishige, M.; Sako, Y.; Kusumi, A. Regulation mechanism of the lateral diffusion of band 3 in erythrocyte membranes by the membrane skeleton. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 142, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxton, M.J. The spectrin network as a barrier to lateral diffusion in erythrocytes. A percolation analysis. Biophys. J. 1989, 55, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auth, T.; Gov, N.S. Diffusion in a fluid membrane with a flexible cortical cytoskeleton. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, 818–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumi, A.; Sako, Y. Cell surface organization by the membrane skeleton. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1996, 8, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, J.D.; Agre, P.; Palek, J.; Golan, D.E. Differential control of band 3 lateral and rotational mobility in intact red cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, A.; Ohnishi, S. Restriction of the lateral motion of band 3 in the erythrocyte membrane by the cytoskeletal network: Dependence on spectrin association state. Biochemistry 1986, 25, 6133–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.R.; Eber, S.W.; Liu, S.C.; Lux, S.E.; Golan, D.E. Regulation of band 3 rotational mobility by ankyrin in intact human red cells. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 17828–17835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumi, A.; Sako, Y.; Yamamoto, M. Confined lateral diffusion of membrane receptors as studied by single particle tracking (nanovid microscopy). Effects of calcium-induced differentiation in cultured epithelial cells. Biophys. J. 1993, 65, 2021–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodippili, G.C.; Spector, J.; Sullivan, C.; Kuypers, F.A.; Labotka, R.; Gallagher, P.G.; Ritchie, K.; Low, P.S. Imaging of the diffusion of single band 3 molecules on normal and mutant erythrocytes. Blood 2009, 113, 6237–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spector, J.; Kodippili, G.C.; Ritchie, K.; Low, P.S. Single molecule studies of the diffusion of band 3 in sickle cell erythrocytes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodippili, G.C.; Spector, J.; Kang, G.E.; Liu, H.; Wickrema, A.; Ritchie, K.; Low, P.S. Analysis of the kinetics of band 3 diffusion in human erythroblasts during assembly of the erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 150, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxton, M.J. Single-particle tracking: Effects of corrals. Biophys. J. 1995, 69, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ha, V.; Lykotrafitis, G. Modeling of band-3 protein diffusion in the normal and defective red blood cell membrane. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 3643–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathers, C.D.; Loncar, D. Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration. Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: A collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet 2010, 375, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wautier, J.L.; Paton, R.C.; Wautier, M.P.; Pintigny, D.; Abadie, E.; Passa, P.; Caen, J.P. Increased adhesion of erythrocytes to endothelial cells in diabetes mellitus and its relation to vascular complications. N. Engl. J. Med. 1981, 305, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skovborg, F.; Nielsen, A.; Schlichtkrull, J.; Ditzel, J. Blood-viscosity in diabetic patients. Lancet 1966, 287, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erem, C.; Hacıhasanoğlu, A.; Çelik, Ş.; Ovalı, E.; Ersöz, H.Ö.; Ukinç, K.; Deger, O.; Telatar, M. Coagulation and fibrinolysis parameters in type 2 diabetic patients with and without diabetic vascular complications. Med. Princ. Pract. 2005, 14, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukada, K.; Sekizuka, E.; Oshio, C.; Minamitani, H. Direct measurement of erythrocyte deformability in diabetes mellitus with a transparent microchannel capillary model and high-speed video camera system. Microvasc. Res. 2001, 61, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamitani, H.; Tsukada, K.; Kawamura, T.; Sekizuka, E.; Oshio, C. Analysis of elasticity and deformability of erythrocytes using micro-channel flow system and atomic force microscope. In Proceedings of the 1st Annual International IEEE-EMBS Special Topic Conference on Microtechnologies in Medicine and Biology, Lyon, France, 12–14 October 2000; pp. 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lekka, M.; Fornal, M.; Pyka-Fościak, G.; Lebed, K.; Wizner, B.; Grodzicki, T.; Styczeń, J. Erythrocyte stiffness probed using atomic force microscope. Biorheology 2005, 42, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yeom, E.; Byeon, H.; Lee, S.J. Effect of diabetic duration on hemorheological properties and platelet aggregation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Xing, X.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.; Ma, S.; Ye, H.; Cai, J. Detection of erythrocytes influenced by aging and type 2 diabetes using atomic force microscope. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 1698–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Park, H.; Kim, K.; Sohn, Y.; Jang, S.; Park, Y. Refractive index tomograms and dynamic membrane fluctuations of red blood cells from patients with diabetes mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.Y.; Li, X.; Karniadakis, G.E. Modeling of biomechanics and biorheology of red blood cells in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biophys. J. 2017, 113, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Diez-Silva, M.; Popescu, G.; Lykotrafitis, G.; Choi, W.; Feld, M.S.; Suresh, S. Refractive index maps and membrane dynamics of human red blood cells parasitized by Plasmodium falciparum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13730–13735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokori-Brown, M.; Petrov, P.G.; Khafaji, M.A.; Mughal, M.K.; Naylor, C.E.; Shore, A.C.; Gooding, K.M.; Casanova, F.; Mitchell, T.J.; Titball, R.W.; et al. Red blood cell susceptibility to pneumolysin: Correlation with membrane biochemical and physical properties. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 10210–10227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, J.; Gardner, R.; Boylan, C.; Carroll, G.; Chang, K.; Marvel, J.; Gonen, B.; Kilo, C.; Tran-Son-Tay, R.; Sutera, S. Microrheologic investigation of erythrocyte deformability in diabetes mellitus. Blood 1985, 65, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fischer, T.M. Tank-tread frequency of the red cell membrane: Dependence on the viscosity of the suspending medium. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 2553–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, H.; Dharmadhikari, A.K.; Dharmadhikari, J.A.; Sharma, S.; Mathur, D. Tank treading of optically trapped red blood cells in shear flow. Biophys. J. 2011, 101, 1604–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran-Son-Tay, R.; Sutera, S.; Rao, P. Determination of red blood cell membrane viscosity from rheoscopic observations of tank-treading motion. Biophys. J. 1984, 46, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanotte, L.; Mauer, J.; Mendez, S.; Fedosov, D.A.; Fromental, J.M.; Claveria, V.; Nicoud, F.; Gompper, G.; Abkarian, M. Red cells’ dynamic morphologies govern blood shear thinning under microcirculatory flow conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13289–13294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.I.; Mooney, M.P.; Cho, D.J. Hemorheological disorders in diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingg, W.; Sulev, J.; Morgan, C.; Ehrlich, R. Blood viscosity in diabetic children. Diabetologia 1971, 7, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peduzzi, M.; Melli, M.; Fonda, S.; Codeluppi, L.; Guerrieri, F. Comparative evaluation of blood viscosity in diabetic retinopathy. Int. Ophthalmol. 1984, 7, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’apolito, R.; Tomaiuolo, G.; Taraballi, F.; Minardi, S.; Kirui, D.; Liu, X.; Cevenini, A.; Palomba, R.; Ferrari, M.; Salvatore, F.; et al. Red blood cells affect the margination of microparticles in synthetic microcapillaries and intravital microcirculation as a function of their size and shape. J. Control. Release 2015, 217, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, R.; Grant, P. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: Pathophysiology of a life-threatening epidemic. Herz 2016, 41, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, S.; Ajjan, R. Coagulation and fibrinolysis in diabetes. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2010, 7, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, P. Diabetes mellitus as a prothrombotic condition. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 262, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanas, N.; Symeonidis, G.; Maltezos, E.; Mavridis, G.; Karavageli, E.; Vosnakidis, T.; Lakasas, G. Mean platelet volume in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Platelets 2004, 15, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavil, Y.; Sen, N.; Yazici, H.; Turfan, M.; Hizal, F.; Çengel, A.; Abaci, A. Coronary heart disease is associated with mean platelet volume in type 2 diabetic patients. Platelets 2010, 21, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Graham, M.D. Margination and segregation in confined flows of blood and other multicomponent suspensions. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 10536–10548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, P.A.; van den Broek, S.A.; Prins, G.W.; Kuiken, G.D.; Sixma, J.J.; Heethaar, R.M. Blood platelets are concentrated near the wall and red blood cells, in the center in flowing blood. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1988, 8, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdee, K.; Thompson, A.J.; Charoenphol, P.; Eniola-Adefeso, O. Margination propensity of vascular -targeted spheres from blood flow in a microfluidic model of human microvessels. Langmuir 2013, 29, 2530–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahidkhah, K.; Bagchi, P. Microparticle shape effects on margination, near-wall dynamics and adhesion in a three-dimensional simulation of red blood cell suspension. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 2097–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, K.; Fedosov, D.A.; Gompper, G. Margination of micro-and nano-particles in blood flow and its effect on drug delivery. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesnutt, J.K.; Han, H.C. Platelet size and density affect shear-induced thrombus formation in tortuous arterioles. Phys. Biol. 2013, 10, 056003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yedgar, S.; Koshkaryev, A.; Barshtein, G. The red blood cell in vascular occlusion. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2002, 32, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedosov, D.A.; Pan, W.; Caswell, B.; Gompper, G.; Karniadakis, G.E. Predicting human blood viscosity in silico. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11772–11777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.A. Erythrocyte Metabolism and Enzyme Defects. Lab. Med. 2015, 27, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yachie-Kinoshita, A.; Nishino, T.; Shimo, H.; Suematsu, M.; Tomita, M. A metabolic model of human erythrocytes: Practical application of the E-Cell Simulation Environment. BioMed Res. Int. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapoport, T.A.; Heinrich, R.; Jacobasch, G.; Rapoport, S. A Linear Steady-State Treatment of Enzymatic Chains. FEBS J. 1974, 42, 107–120. [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita, A.; Tsukada, K.; Soga, T.; Hishiki, T.; Ueno, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Tomita, M.; Suematsu, M. Roles of hemoglobin allostery in hypoxia-induced metabolic alterations in erythrocytes simulation and its verification by metabolome analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 10731–10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, T.; Yachie-Kinoshita, A.; Hirayama, A.; Soga, T.; Suematsu, M.; Tomita, M. In silico modeling and metabolome analysis of long-stored erythrocytes to improve blood storage methods. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 144, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cines, D.B.; Lebedeva, T.; Nagaswami, C.; Hayes, V.; Massefski, W.; Litvinov, R.I.; Rauova, L.; Lowery, T.J.; Weisel, J.W. Clot contraction: Compression of erythrocytes into tightly packed polyhedra and redistribution of platelets and fibrin. Blood 2014, 123, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimogonya, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Imai, Y.; Matsuki, N.; Yamaguchi, T. Can temporal fluctuation in spatial wall shear stress gradient initiate a cerebral aneurysm? A proposed novel hemodynamic index, the gradient oscillatory number (GON). J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebral, J.R.; Castro, M.A.; Appanaboyina, S.; Putman, C.M.; Millan, D.; Frangi, A.F. Efficient pipeline for image-based patient-specific analysis of cerebral aneurysm hemodynamics: Technique and sensitivity. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2005, 24, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evju, Ø.; Valen-Sendstad, K.; Mardal, K.A. A study of wall shear stress in 12 aneurysms with respect to different viscosity models and flow conditions. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2802–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valen-Sendstad, K.; Piccinelli, M.; Steinman, D.A. High-resolution computational fluid dynamics detects flow instabilities in the carotid siphon: Implications for aneurysm initiation and rupture? J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 3210–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazilevs, Y.; Hsu, M.C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Kvamsdal, T.; Hentschel, S.; Isaksen, J. Computational vascular fluid–structure interaction: Methodology and application to cerebral aneurysms. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2010, 9, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torii, R.; Oshima, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Takagi, K.; Tezduyar, T.E. Fluid-structure interaction modeling of a patient-specific cerebral aneurysm: Influence of structural modeling. Comput. Mech. 2008, 43, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takizawa, K.; Schjodt, K.; Puntel, A.; Kostov, N.; Tezduyar, T.E. Patient-specific computational analysis of the influence of a stent on the unsteady flow in cerebral aneurysms. Comput. Mech. 2013, 51, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, H.; Jayaraman, M.; Richardson, P.; Karniadakis, G. Flow instability and wall shear stress variation in intracranial aneurysms. J. R. Soc. Interface 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karniadakis, G.; Sherwin, S. Spectral/hp Element Methods for CFD; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gambaruto, A.; João, A. Flow structures in cerebral aneurysms. Comput. Fluids 2012, 65, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimogonya, Y.; Kumamaru, H.; Itoh, K. Sensitivity of the gradient oscillatory number to flow input waveform shapes. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, H.G.; Bonnefous, O. Unraveling the relationship between arterial flow and intra-aneurysmal hemodynamics. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Natarajan, S.K.; Tremmel, M.; Ma, D.; Mocco, J.; Hopkins, L.N.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Levy, E.I.; Meng, H. Hemodynamic—Morphologic discriminants for intracranial aneurysm rupture. Stroke 2011, 42, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takao, H.; Murayama, Y.; Otsuka, S.; Qian, Y.; Mohamed, A.; Masuda, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Abe, T. Hemodynamic differences between unruptured and ruptured intracranial aneurysms during observation. Stroke 2012, 43, 1436–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y.; Sato, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Yamaguchi, T. Inflow into saccular cerebral aneurysms at arterial bends. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 36, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baharoglu, M.I.; Schirmer, C.M.; Hoit, D.A.; Gao, B.L.; Malek, A.M. Aneurysm inflow-angle as a discriminant for rupture in sidewall cerebral aneurysms: Morphometric and computational fluid dynamic analysis. Stroke 2010, 41, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordasco, D.; Bagchi, P. Orbital drift of capsules and red blood cells in shear flow. Phys. Fluids 2013, 25, 091902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorczewski, T.; Erickson, L.C.; Fogelson, A.L. Platelet motion near a vessel wall or thrombus surface in two-dimensional whole blood simulations. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 1764–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeishi, N.; Imai, Y.; Nakaaki, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ishikawa, T. Leukocyte margination at arteriole shear rate. Physiol. Rep. 2014, 2, e12037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perktold, K.; Rappitsch, G. Computer simulation of local blood flow and vessel mechanics in a compliant carotid artery bifurcation model. J. Biomech. 1995, 28, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, M.; Rappitsch, G.; Perktold, K.; Trubel, W.; Schima, H. Numerical study of wall mechanics and fluid dynamics in end-to-side anastomoses and correlation to intimal hyperplasia. J. Biomech. 1996, 29, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Sugiura, S.; Kafuku, H.; Hisada, T. Multiphysics simulation of left ventricular filling dynamics using fluid-structure interaction finite element method. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 2074–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerbeau, J.F.; Vidrascu, M.; Frey, P. Fluid-structure interaction in blood flows on geometries based on medical imaging. Comput. Struct. 2005, 83, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, S.; Washio, T.; Hatano, A.; Okada, J.; Watanabe, H.; Hisada, T. Multi-scale simulations of cardiac electrophysiology and mechanics using the University of Tokyo heart simulator. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2012, 110, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.; Karniadakis, G.E. Predicting the morphology of sickle red blood cells using coarse-grained models of intracellular aligned hemoglobin polymers. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 4507–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.; Karniadakis, G.E. Quantifying the rheological and hemodynamic characteristics of sickle cell anemia. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Fedosov, D.A.; Caswell, B.; Karniadakis, G.E. Predicting dynamics and rheology of blood flow: A comparative study of multiscale and low-dimensional models of red blood cells. Microvasc. Res. 2011, 82, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foessel, E.; Walter, J.; Salsac, A.V.; Barthès-Biesel, D. Influence of internal viscosity on the large deformation and buckling of a spherical capsule in a simple shear flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2011, 672, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, D.; Imai, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ishikawa, T. Deformation of a spherical capsule under oscillating shear flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2015, 762, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.; Salsac, A.V.; Barthès-Biesel, D.; Le Tallec, P. Coupling of finite element and boundary integral methods for a capsule in a Stokes flow. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2010, 83, 829–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Imai, Y.; Yamaguchi, T. Shear-induced diffusion of red blood cells in a semi-dilute suspension. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 724, 154–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, T.; Hosaka, H.; Imai, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ishikawa, T. Numerical analysis of a red blood cell flowing through a thin micropore. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 013008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nix, S.; Imai, Y.; Matsunaga, D.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ishikawa, T. Lateral migration of a spherical capsule near a plane wall in Stokes flow. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 043009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, J.B. The flow of red blood cells through a narrow spleen-like slit. Phys. Fluids 2013, 25, 110807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Q.; Salsac, A.V.; Barthès-Biesel, D. Flow of a spherical capsule in a pore with circular or square cross-section. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 705, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.M.; Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft lithographic methods for nano-fabrication. J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, L.; Coupier, G.; Dubois, F.; Duperray, A.; Farutin, A.; Minetti, C.; Misbah, C.; Podgorski, T.; Tsvirkun, D.; Vysokikh, M. Blood flow and microgravity. C. R. Mec. 2017, 345, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, R.; Giridharan, G.A.; Nguyen, M.D.; Roussel, T.J.; Shakeri, M.; Parichehreh, V.; Prabhu, S.D.; Sethu, P. Endothelial cell culture model for replication of physiological profiles of pressure, flow, stretch, and shear stress in vitro. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3170–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischel, L.L.; Young, E.W.; Mader, B.R.; Beebe, D.J. Tubeless microfluidic angiogenesis assay with three-dimensional endothelial-lined microvessels. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Craven, M.; Choi, N.W.; Totorica, S.; Diaz-Santana, A.; Kermani, P.; Hempstead, B.; Fischbach-Teschl, C.; López, J.A.; et al. In vitro microvessels for the study of angiogenesis and thrombosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9342–9347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, D.; Matthews, B.D.; Mammoto, A.; Montoya-Zavala, M.; Hsin, H.Y.; Ingber, D.E. Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science 2010, 328, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCain, M.L.; Agarwal, A.; Nesmith, H.W.; Nesmith, A.P.; Parker, K.K. Micromolded gelatin hydrogels for extended culture of engineered cardiac tissues. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 5462–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, R.H.; Weng, S.; Lu, W.; Fu, J. Live-cell subcellular measurement of cell stiffness using a microengineered stretchable micropost array membrane. Integr. Biol. 2012, 4, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiddes, L.K.; Raz, N.; Srigunapalan, S.; Tumarkan, E.; Simmons, C.A.; Wheeler, A.R.; Kumacheva, E. A circular cross-section PDMS microfluidics system for replication of cardiovascular flow conditions. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3459–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, R.W.; Emerson, D.R. Optimal design of microfluidic networks using biologically inspired principles. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2008, 4, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Lee, S.J. Murray’s law and the bifurcation angle in the arterial micro-circulation system and their application to the design of microfluidics. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2010, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosano, J.M.; Tousi, N.; Scott, R.C.; Krynska, B.; Rizzo, V.; Prabhakarpandian, B.; Pant, K.; Sundaram, S.; Kiani, M.F. A physiologically realistic in vitro model of microvascular networks. Biomed. Microdevices 2009, 11, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaiuolo, G.; Barra, M.; Preziosi, V.; Cassinese, A.; Rotoli, B.; Guido, S. Microfluidics analysis of red blood cell membrane viscoelasticity. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Phan, D.T.; Sobrino, A.; George, S.C.; Hughes, C.C.; Lee, A.P. Engineering anastomosis between living capillary networks and endothelial cell-lined microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Du, E.; Lei, H.; Tang, Y.H.; Dao, M.; Suresh, S.; Karniadakis, G.E. Patient-specific blood rheology in sickle-cell anaemia. Interface Focus 2016, 6, 20150065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Jiang, B.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, X. A microfluidic flow-stretch chip for investigating blood vessel biomechanics. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3441–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Nguyen, J.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y. Electrical measurement of red blood cell deformability on a microfluidic device. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 3275–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Shojaei-Baghini, E.; Azad, A.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y. High-throughput biophysical measurement of human red blood cells. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2560–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felton, E.J.; Velasquez, A.; Lu, S.; Murphy, R.O.; ElKhal, A.; Mazor, O.; Gorelik, P.; Sharda, A.; Ghiran, I.C. Detection and quantification of subtle changes in red blood cell density using a cell phone. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3286–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasoglu, S.; Khoory, J.A.; Tekin, H.C.; Thomas, C.; Karnoub, A.E.; Ghiran, I.C.; Demirci, U. Levitational image cytometry with temporal resolution. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3901–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieber, B.B.; Livescu, V.; Hopkins, L.; Wakhloo, A.K. Particle image velocimetry assessment of stent design influence on intra-aneurysmal flow. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 30, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantón, G.; Levy, D.I.; Lasheras, J.C. Hemodynamic changes due to stent placement in bifurcating intracranial aneurysms. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 103, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agati, L.; Cimino, S.; Tonti, G.; Cicogna, F.; Petronilli, V.; De Luca, L.; Iacoboni, C.; Pedrizzetti, G. Quantitative analysis of intraventricular blood flow dynamics by echocardiographic particle image velocimetry in patients with acute myocardial infarction at different stages of left ventricular dysfunction. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 15, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Category | Method | Description | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Computational | Finite Element Method (FEM) and its variants | Suitable for boundary with complex geometry or irregular morphology. The space-time FEM was developed for moving-mesh methods. The Spectral/hp Element Method achieves high-accuracy but sometimes requires intense computation. | FEM [183,184,185,186,187]; space-time [188,189]; Spectral/hp [190,191] |
| Finite Volume Method (FVM) | Easy application for unstructured mesh, which is often used for irregular boundary geometry. | [192,193,194,195]; ANSYS Fluent [196,197,198]. | |
| Immersed Boundary Method (IBM) | A versatile method that easily couples with any existing solvers, like FEM, FVM, and the Lattice Boltzmann Method (LBM). | [66,199,200]; couple LBM [67,68] and FEM [201]. | |
| Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian Method (ALE) | Frequently used for large vessel flow and sometimes coupled with FEM. | [202,203]; couple FEM [187,204,205,206]. | |
| Dissipative Particle Dynamics (DPD) | Particle-based coarse-grained method with artificial viscosity and dissipativity to recover Navier-Stokes equations. | [55,58,110,207,208,209]. | |
| Boundary Element Method (BEM) | The most useful method for infinite flow problems, but limited to the low Reynolds number condition (i.e., Stokes flow). | [65,210,211,212,213,214,215,216,217]. | |
| Experimental | Microchips manufactured by modern material | Deformable materials such as Polydimethylsiloxane-made tubes mimic gas-permeable vessels or other organ tissues. Flexible micro-posts in flow were used to measure shear force of cells. Polymer brushes approximate glycocalyx linings. | [218,219,220,221,222,223,224,225]. |
| Geometry designs of flow system in vitro | Bifurcated or tortuous channels mimic complicated vascular networks. The tapered channel introduces continuously varying shear rates or nutrients. A sudden contracted channel was used to mimic a stenosed arteriole. | [226,227,228,229,230,231,232,233]. | |
| Up-to-date measuring technology | RBCs are divided into different density groups when subjected to magnetic or electrical forces such that the deformability of cells in different groups could be measured. Particle imaging velocimetry (PIV) is introduced to profile the surfaces of blood vessels and measure flow speed. | electrical [234,235]; magnetic [236,237]; PIV [238,239,240]. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Papageorgiou, D.P.; Chang, H.-Y.; Lu, L.; Yang, J.; Deng, Y. Synergistic Integration of Laboratory and Numerical Approaches in Studies of the Biomechanics of Diseased Red Blood Cells. Biosensors 2018, 8, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8030076
Li H, Papageorgiou DP, Chang H-Y, Lu L, Yang J, Deng Y. Synergistic Integration of Laboratory and Numerical Approaches in Studies of the Biomechanics of Diseased Red Blood Cells. Biosensors. 2018; 8(3):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8030076
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, He, Dimitrios P. Papageorgiou, Hung-Yu Chang, Lu Lu, Jun Yang, and Yixiang Deng. 2018. "Synergistic Integration of Laboratory and Numerical Approaches in Studies of the Biomechanics of Diseased Red Blood Cells" Biosensors 8, no. 3: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8030076
APA StyleLi, H., Papageorgiou, D. P., Chang, H.-Y., Lu, L., Yang, J., & Deng, Y. (2018). Synergistic Integration of Laboratory and Numerical Approaches in Studies of the Biomechanics of Diseased Red Blood Cells. Biosensors, 8(3), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8030076





