Development of MoSe2 Nano-Urchins as a Sensing Platform for a Selective Bio-Capturing of Escherichia coli Shiga Toxin DNA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
- Capture probe—5′-NH2-AAACTCAAAGGAATTGAC-3′;
- Target probe—3′-TTTGAGTTTCCTTAACTG-5′.
2.2. Apparatus and Methods
2.3. Synthesis of 2D Nanomaterial MoSe2 Nano-Urchins
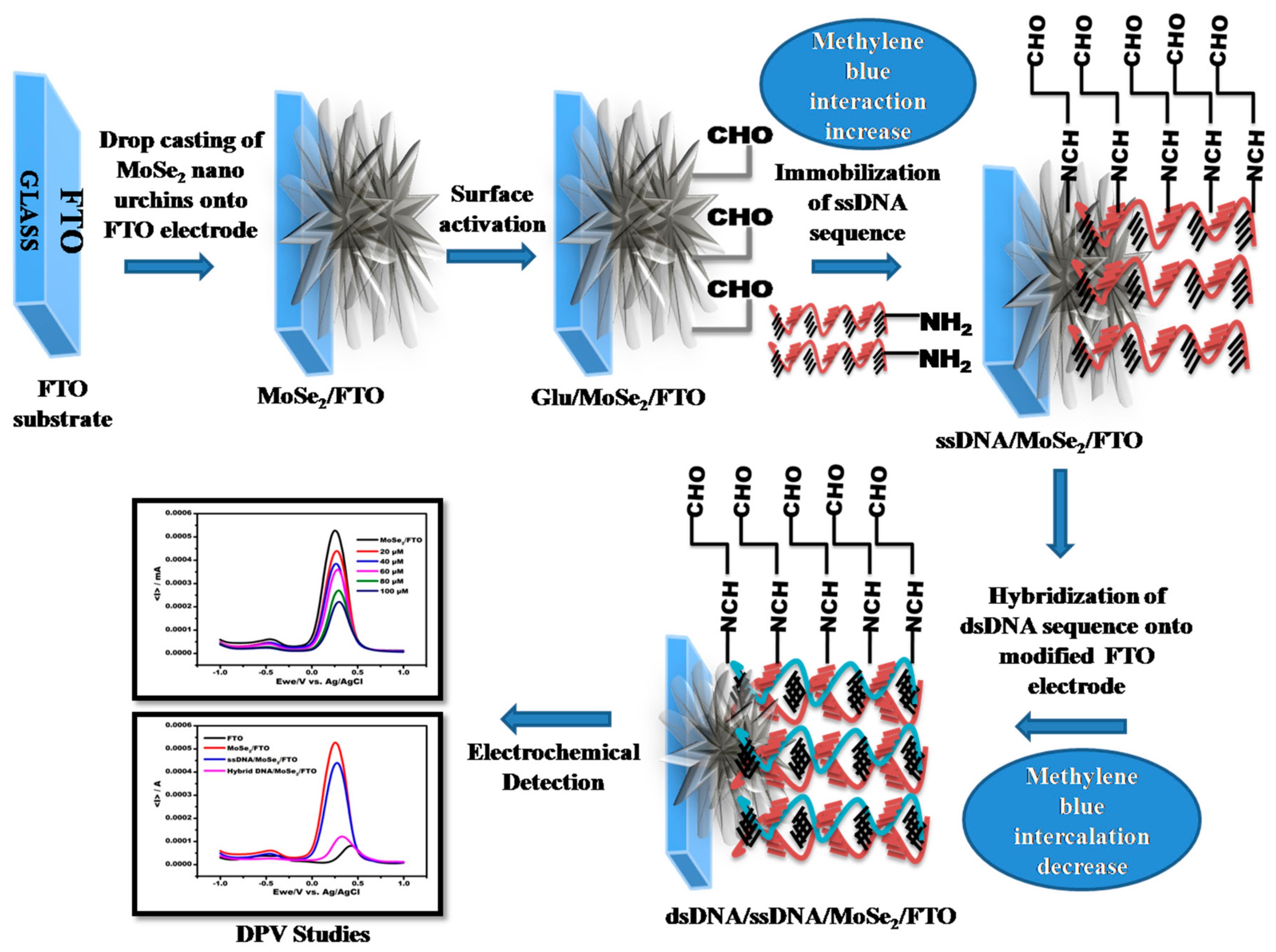
2.4. Preparation of Electrode
2.5. Immobilization of “Amino Modified” Probe DNA onto MoSe2 Modified FTO Electrode
2.6. Electrochemical Characterizations of Modified Electrode
2.7. Application of Fabricated Biosensor in a Real Sample
3. Results and Discussions
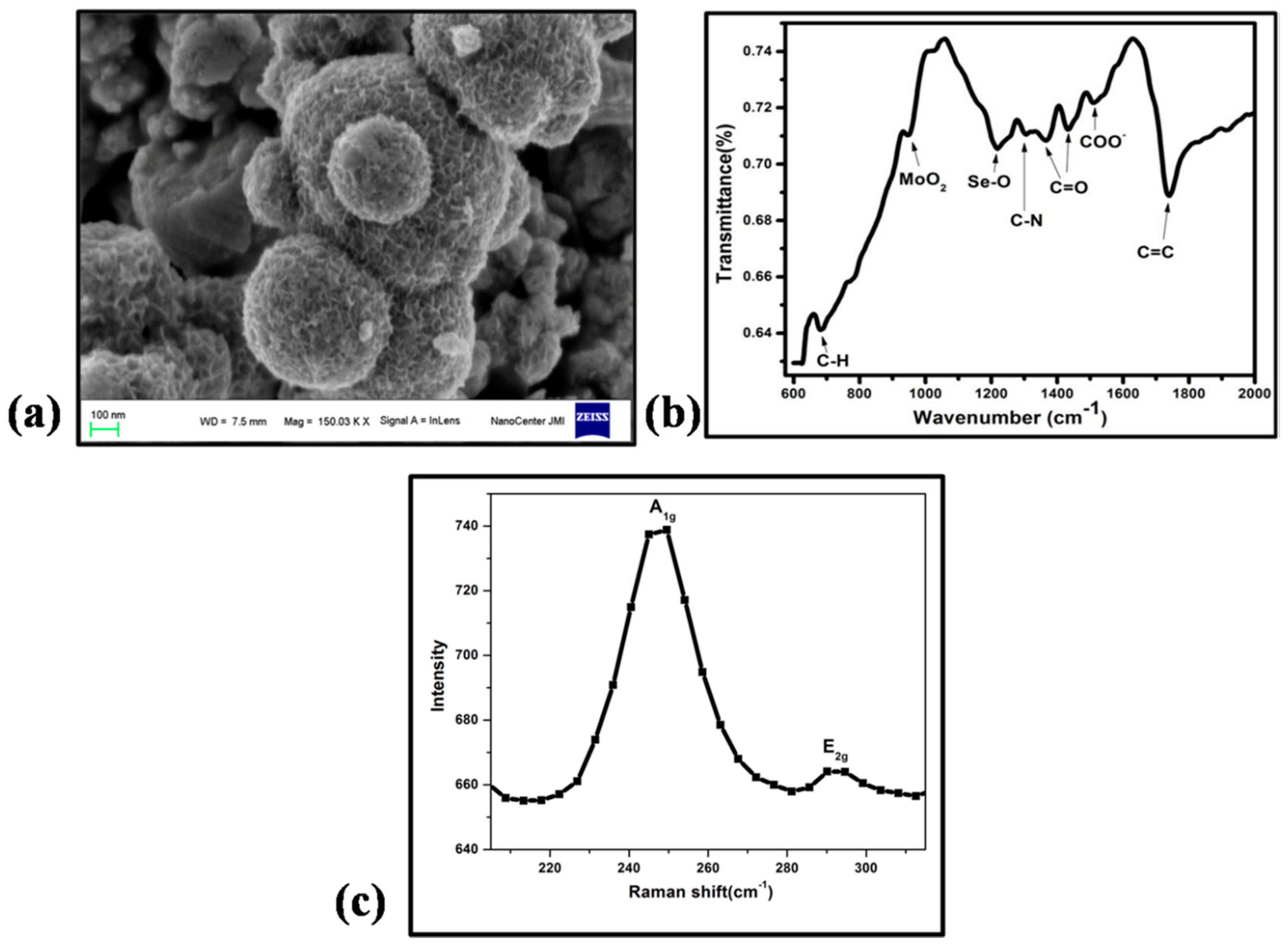
3.1. Physical Characterization of MoSe2 Nano Urchins
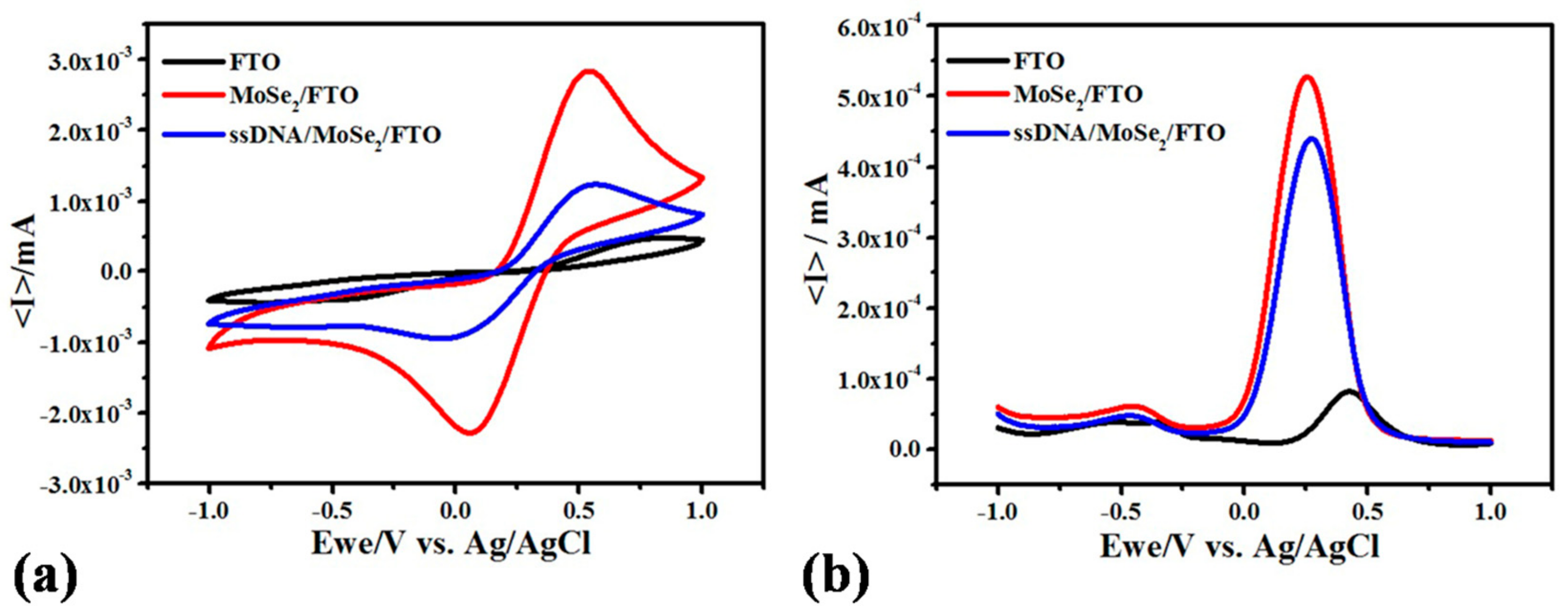
3.2. Electrochemical Characterizations of Various Stages of Electrode
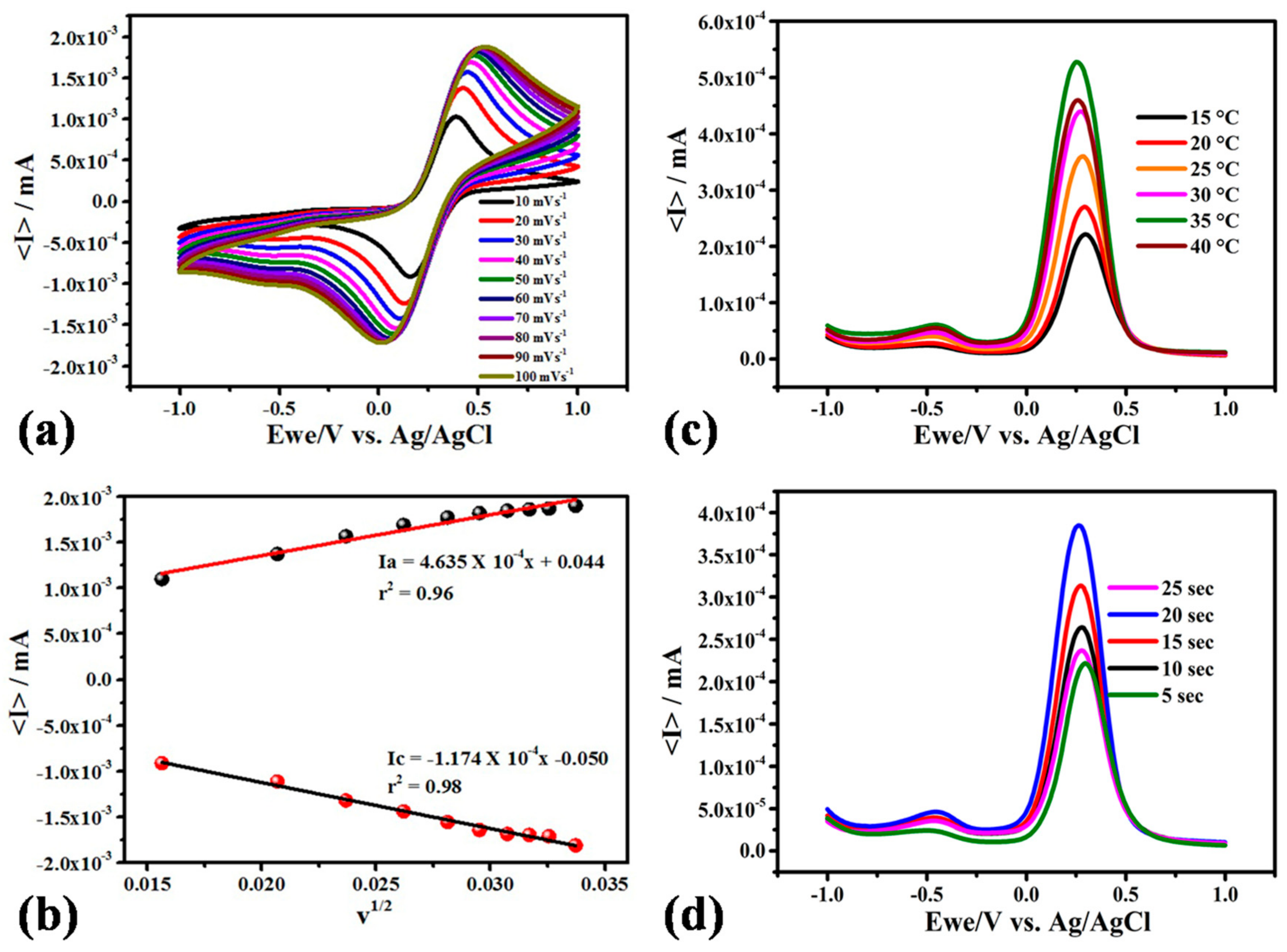
3.3. Optimization of Experimental Variables
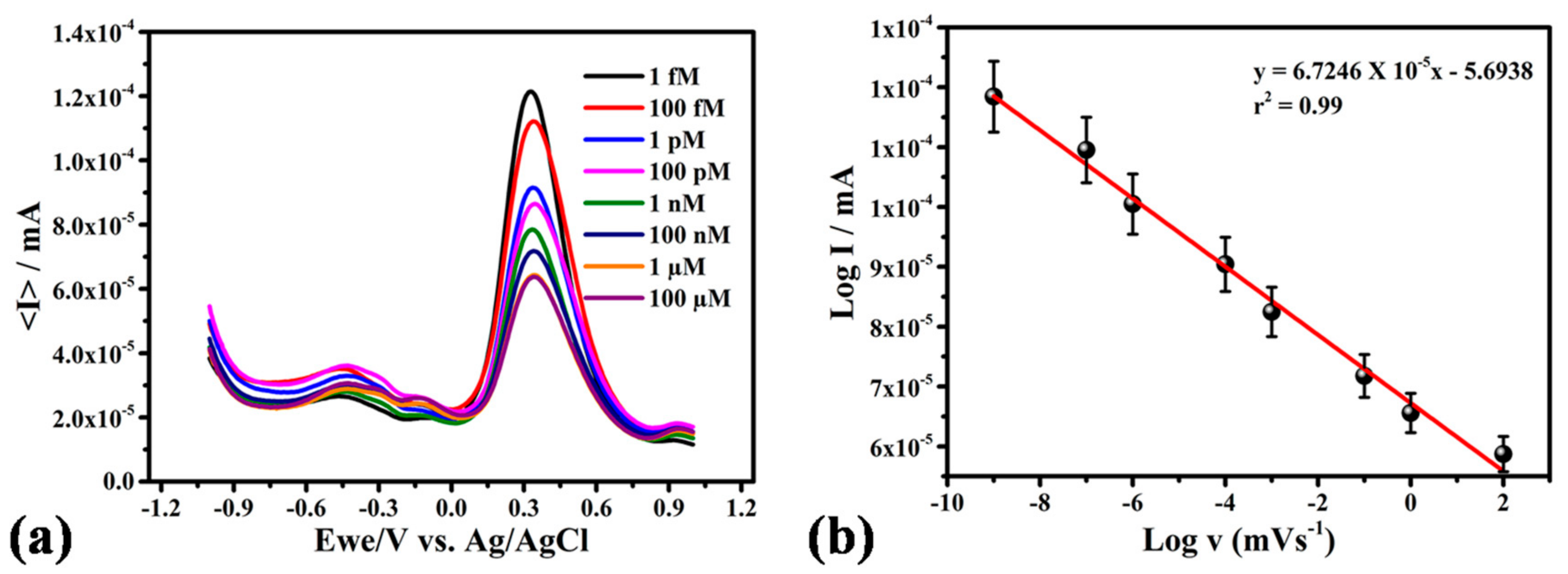
3.4. Analytical Performance of the DNA Biosensor
3.5. Selectivity and Stability of the DNA Biosensor
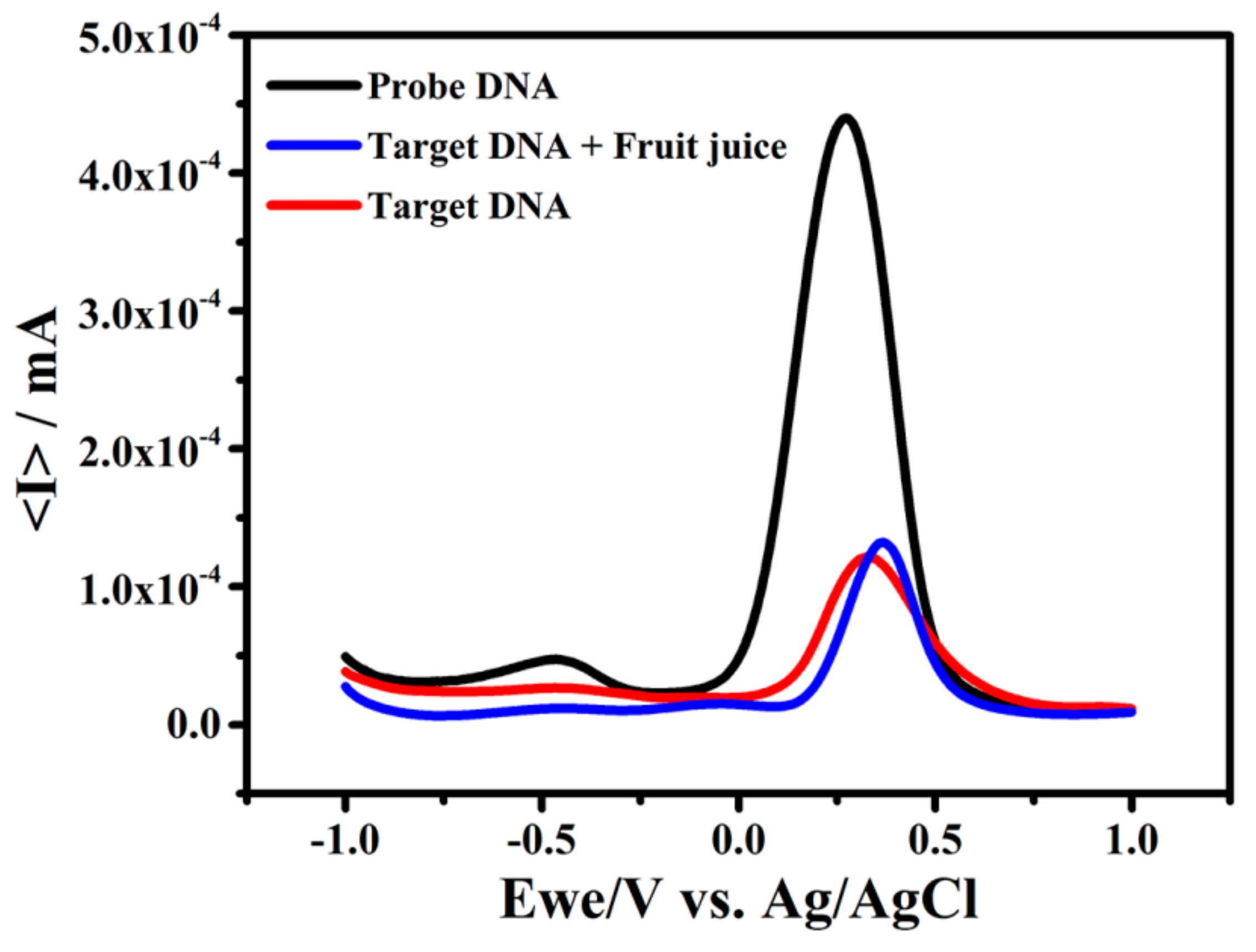
3.6. Application of Geno-Sensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, F.; Han, X.; Liu, S. Development of an electrochemical DNA biosensor with a high sensitivity of fM by dendritic gold nanostructure modified electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2619–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivnitski, D.; Hamid, I.A.; Atanasov, P.; Wilkins, E. Biosensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1999, 14, 599–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukyanenko, V.; Malyukova, I.; Hubbard, A.; Delannoy, M.; Boedeker, E.; Zhu, C.; Cebotaru, L.; Kovbasnjuk, O. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli infection stimulates Shiga toxin 1 macropinocytosis and transcytosis across intestinal epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandvig, K.; Van Deurs, B. Entry of ricin and Shiga toxin into cells: Molecular mechanisms and medical perspectives. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 5943–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christaki, E. New technologies in predicting, preventing and controlling emerging infectious diseases. Virulence 2015, 6, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bawa, A.S.; Anilakumar, K.R. Genetically modified foods: Safety, risks & public concerns—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, C.A. Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC) Detection Strategies with Formalin-Fixed STEC Cells. Master’s Thesis, University of Arkansas, Fort Smith, AR, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Law, J.W.F.; Mutalib, N.S.A.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H. Rapid methods for the detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens: Principles, applications, advantages and limitations. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ch’ng, A.C.W.; Choong, Y.S.; Lim, T.S. Phage Display-Derived Antibodies: Application of Recombinant Antibodies for Diagnostics. In Proof and Concepts in Rapid Diagnostic Tests and Technologies; Saxena, S.K., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-953-51-2581-5. [Google Scholar]
- Sin, M.L.Y.; Mach, K.E.; Wong, P.K.; Liao, J.C. Advances and challenges in biosensor-based diagnosis of infectious diseases. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salah, K.M.A.; Zourab, M.M.; Mouffouk, F.; Alrokayan, S.A.; Alaamery, M.A.; Ansari, A.A. DNA-Based Nanobiosensors as an Emerging Platform for Detection of Disease. Sensors 2015, 15, 14539–14568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, B.; Tung, S. Development and Applications of Portable Biosensors. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 365–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bora, U.; Sett, A.; Singh, D. Nucleic Acid Based Biosensors for Clinical Applications. Biosens. J. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors Based on Nanomaterials and Nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathakoti, K.; Manubolu, M.; Hwang, H.M. Nanostructures: Current uses and future applications in food science. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhu, H. Two-dimensional MoS2: Properties, preparation, and applications. J. Materiomics 2015, 1, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, Y. Dual signal-amplification electrochemical detection of DNA sequence based on molybdenum selenide nanorod and hybridization chain reaction. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 5234–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setterington, E.B.; Alocilja, E. Electrochemical Biosensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Magnetically Extracted Bacterial Pathogens. Biosensors 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedecky, B.R.; Kudr, J.; Nejdl, L.; Maskova, D.; Kizek, R.; Adam, V. G-Quadruplexes as Sensing Probes. Molecules 2013, 18, 14760–14779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Luo, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Lin, S. Rapid Detection of Shigella Species in Environmental Sewage by an Immunocapture PCR with Universal Primers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2580–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, M.; Gupta, V.; Tomar, M. Flower-like ZnO nanostructure-based electrochemical DNA biosensor for bacterial meningitis detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xue, M.; Yang, X.; Luo, G.; Yang, F. Hydrothermal synthesis and tribological properties of MoSe2 nanoflowers. Micro Nano Lett. 2015, 10, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, J.; Singhal, C.; Mathur, A.; Sharma, S.; Singla, V.; Pundir, C.S. Portable bioactive paper-based geno-sensor incorporated with Zn-Ag nanoblooms for herpes detection at the point-of-care. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talan, A.; Mishra, A.; Eremin, S.A.; Narang, J.; Kumar, A.; Gandhi, S. Ultrasensitive electrochemical immuno-sensing platform based on gold nanoparticles triggering chlorpyrifos detection in fruits and vegetables. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 105, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narang, J.; Malhotra, N.; Pundir, C.S. Electrochemical Techniques. In Biosensors: An Introductory Textbook; Narang, J., Pundir, C.S., Eds.; Pan Stanford Publishing Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2017; pp. 1–155. ISBN 978-1-315-15652-1. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Dong, S. Nucleic Acid Biosensors: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paton, J.C.; Paton, A.W. Pathogenesis and Diagnosis of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 450–479. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Narang, J.; Mishra, A.; Pilloton, R.; VV, A.; Wadhwa, S.; Pundir, C.S.; Khanuja, M. Development of MoSe2 Nano-Urchins as a Sensing Platform for a Selective Bio-Capturing of Escherichia coli Shiga Toxin DNA. Biosensors 2018, 8, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8030077
Narang J, Mishra A, Pilloton R, VV A, Wadhwa S, Pundir CS, Khanuja M. Development of MoSe2 Nano-Urchins as a Sensing Platform for a Selective Bio-Capturing of Escherichia coli Shiga Toxin DNA. Biosensors. 2018; 8(3):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8030077
Chicago/Turabian StyleNarang, Jagriti, Annu Mishra, Roberto Pilloton, Alekhya VV, Shikha Wadhwa, Chandra Shekhar Pundir, and Manika Khanuja. 2018. "Development of MoSe2 Nano-Urchins as a Sensing Platform for a Selective Bio-Capturing of Escherichia coli Shiga Toxin DNA" Biosensors 8, no. 3: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8030077
APA StyleNarang, J., Mishra, A., Pilloton, R., VV, A., Wadhwa, S., Pundir, C. S., & Khanuja, M. (2018). Development of MoSe2 Nano-Urchins as a Sensing Platform for a Selective Bio-Capturing of Escherichia coli Shiga Toxin DNA. Biosensors, 8(3), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8030077




