Effects of Surface Epitope Coverage on the Sensitivity of Displacement Assays that Employ Modified Nanoparticles: Using Bisphenol A as a Model Analyte
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Modification of AuNPs
2.4. Preparation of BPA Standard
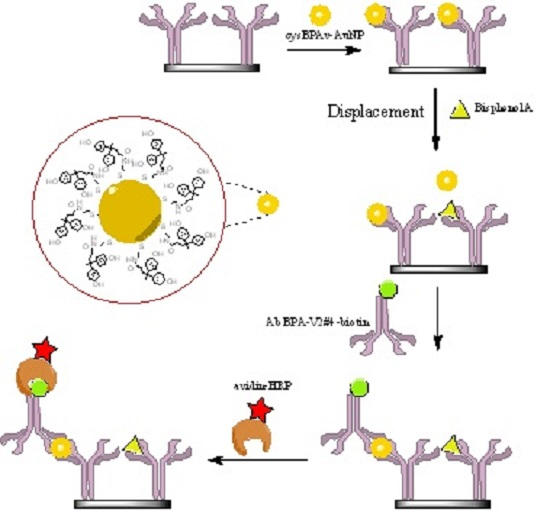
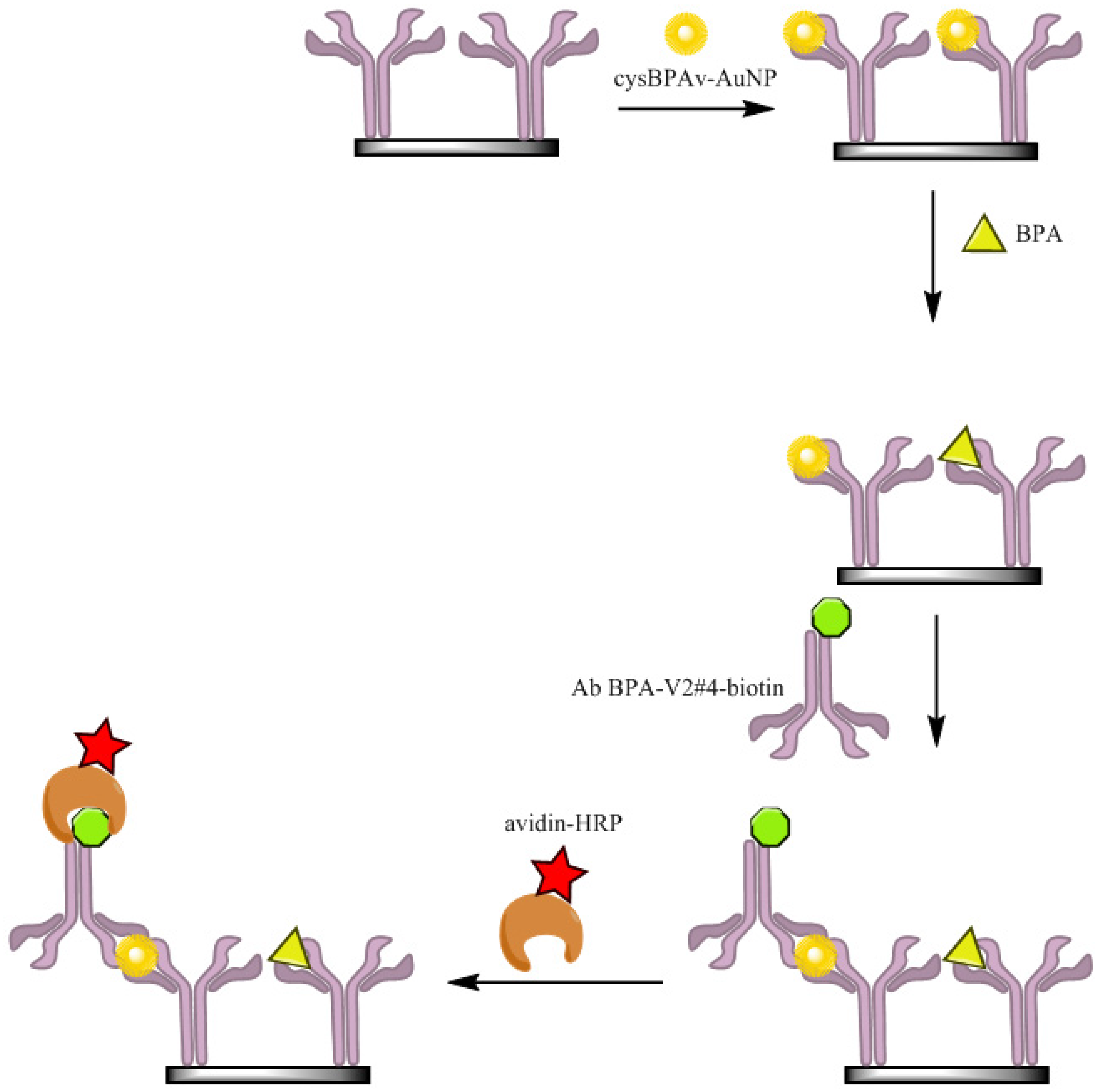
2.5. ELISA via the Displacement Format (d-ELISA)
2.6. Percent Relative Saturation (%RS)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. d-ELISA with Different Displacement Time
3.2. d-ELISA with Different Molar Concentrations of cysBPAv-AuNP-265
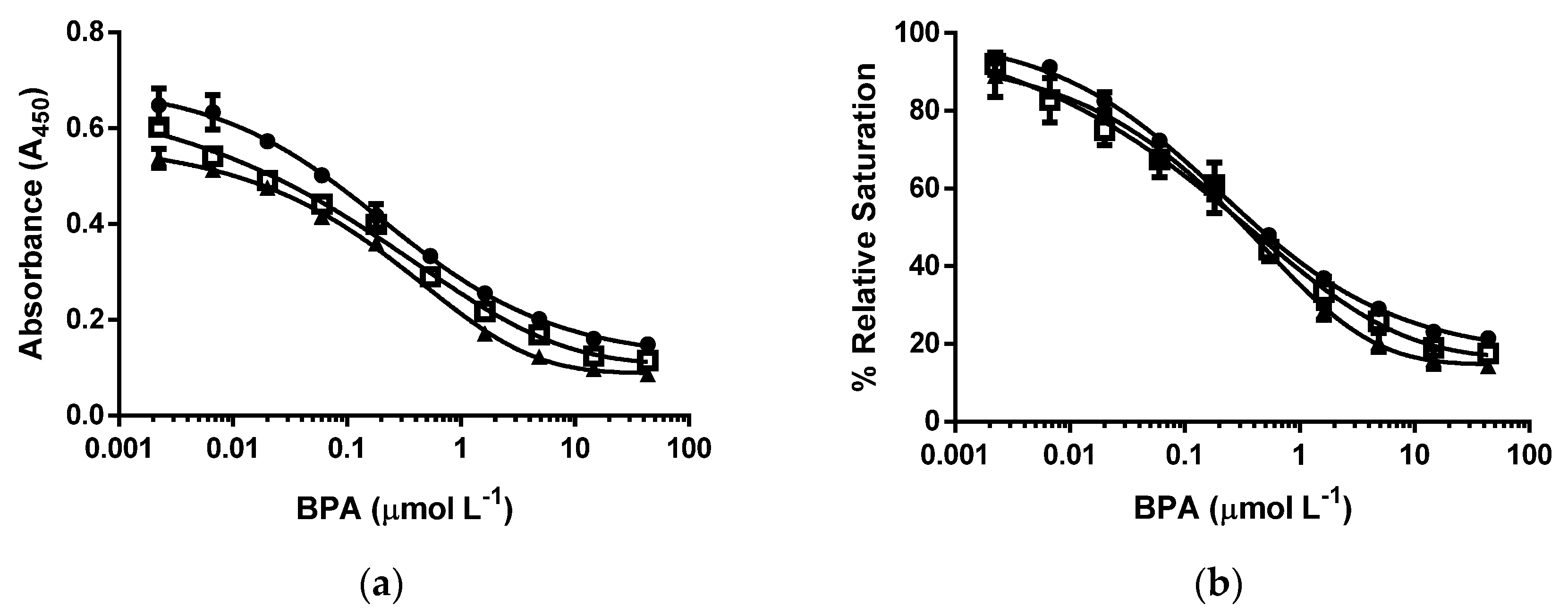
3.3. d-ELISA with the Same Molar Concentration of cysBPAv-AuNP-190, cysBPAv-AuNP-396, and cysBPAv-AuNP-801
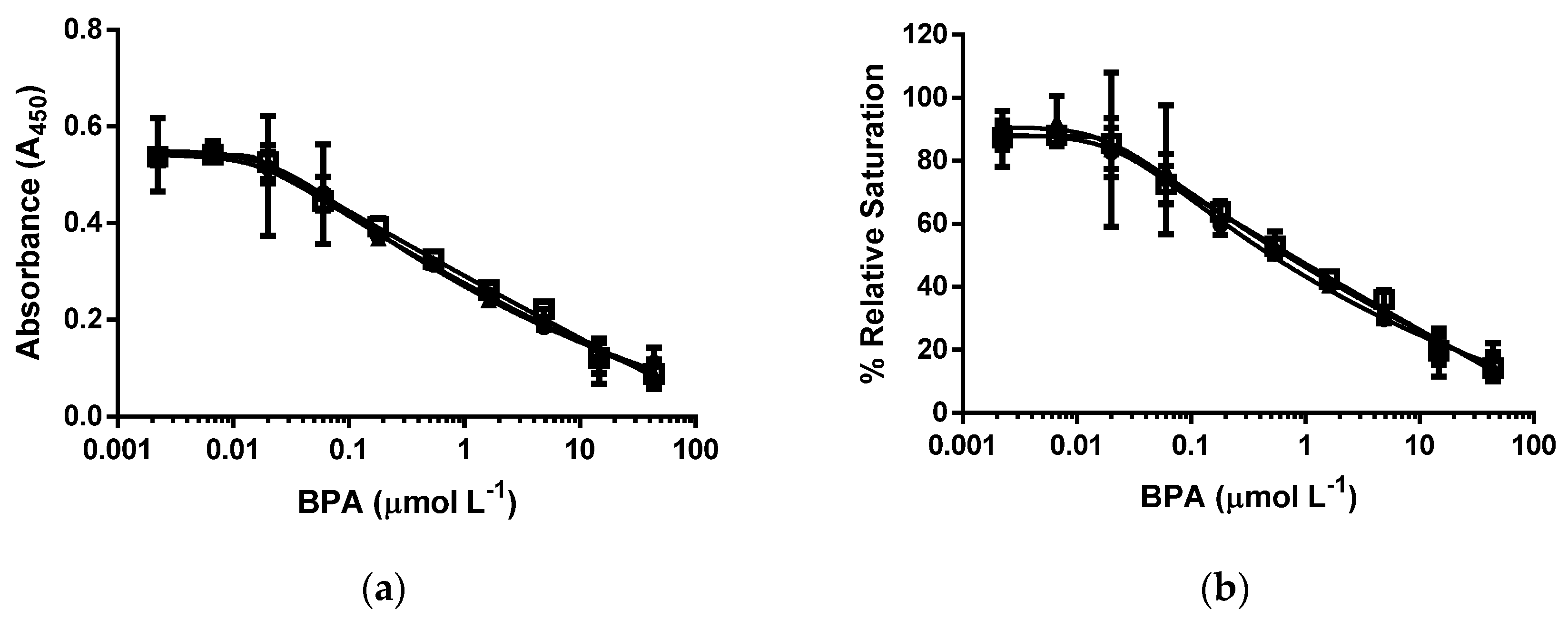
3.4. d-ELISA with the Same Molar Concentration of Epitope in an Assay of cysBPAv-AuNP-190, cysBPAv-AuNP-396, and cysBPAv-AuNP-801
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahmoudi, M.; Lynch, I.; Ejtehadi, M.R.; Monopoli, M.P.; Bombelli, F.B.; Laurent, S. Protein-nanoparticle interactions: Opportunities and challenges. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5610–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.S.; Smith, G.T.; Seo, F.; Ellerbee, A.K. Label-free and non-contact optical biosensing of glucose with quantum dots. Biosen. Bioelectron. 2015, 65, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsmar, C.; Yoon, K.Y.; Yu, H.; Ryoo, S.; Barth, J.; Shao, S.; Milner, T.E.; Bryant, S.L.; Huh, C.; Johnston, K.P. Stable Citrate Coated Iron Oxide Superparamagnetic Nanoclusters at High Salinity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 12435–12443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong, W.H.D.; Borm, P.J.A. Drug delivery and nanoparticles: Applications and hazards. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujardin, E.; Mann, S. Bio-inspired Materials Chemistry. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingarrón, J.M.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; González-Cortés, A. Gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical biosensors. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5848–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Patel, V.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Ultrasensitive immunosensor for cancer biomarker proteins using gold nanoparticle film electrodes and multienzyme-particle amplification. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suaifan, G.A.R.Y.; Esseghaier, C.; Ng, A.; Zourob, M. Ultra-rapid colorimetric assay for protease detection using magnetic nanoparticle-based biosensors. Analyst 2013, 138, 3735–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassa, C.; Duffner, J.L.; Lewis, T.A.; Weissleder, R.; Schreiber, S.L.; Koehler, A.N.; Shaw, S.Y. Binding affinity and kinetic analysis of targeted small molecule-modified nanoparticles. Bioconj. Chem. 2010, 21, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, W. Covalent functionalization of gold nanoparticles as electronic bridges and signal amplifiers towards an electrochemical immunosensor for botulinum neurotoxin type A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, E.R.; Lin, A.Y.; Yan, J.; Luo, L.; Foster, A.E.; Drezek, R.A. Optimization of PAMAM-gold nanoparticle conjugation for gene therapy. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Peterson, J.R.; Luais, E.; Gooding, J.J.; Lee, N.A. Surface Epitope Coverage Affects Binding Characteristics of Bisphenol-A Functionalized Nanoparticles in a Competitive Inhibition Assay. J. Nanomater. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Z.; Paddon-Row, M.N.; Gooding, J.J. Protein modulation of electrochemical signals: Application to immunobiosensing. Chem. Commun. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, S.M.; Liu, G.Z.; Peterson, J.R.; Iyengar, S.G.; Gooding, J.J. An electrochemical immunobiosensor for direct detection of veterinary drug residues in undiluted complex matrices. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, S.M.; Liu, G.Z.; Fairman, C.; Iyengar, S.G.; Gooding, J.J. The importance of interfacial design for the sensitivity of a label-free electrochemical immuno-biosensor for small organic molecules. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2038–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, S.M.; Thordarson, P.; Gooding, J.J. The impact of antibody/epitope affinity strength on the sensitivity of electrochemical immunosensors for detecting small molecules. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3889–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Peterson, J.R.; Gooding, J.J.; Lee, N.A. Development of sensitive direct and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) for monitoring bisphenol-A in canned foods and beverages. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, J.R.; Lu, Y.; Luais, E.; Lee, N.A.; Gooding, J.J. Demonstrating the Use of Bisphenol A-functionalised Gold Nanoparticles in Immunoassays. Aust. J. Chem. 2013, 66, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbany, S.Y.; Piervincenzi, R.; Judd, L.; Kusterbeck, A.W.; Bredehorst, R.; Hakansson, K.; Ligler, F.S. Assessment of heterogeneity in antibody-antigen displacement reactions. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
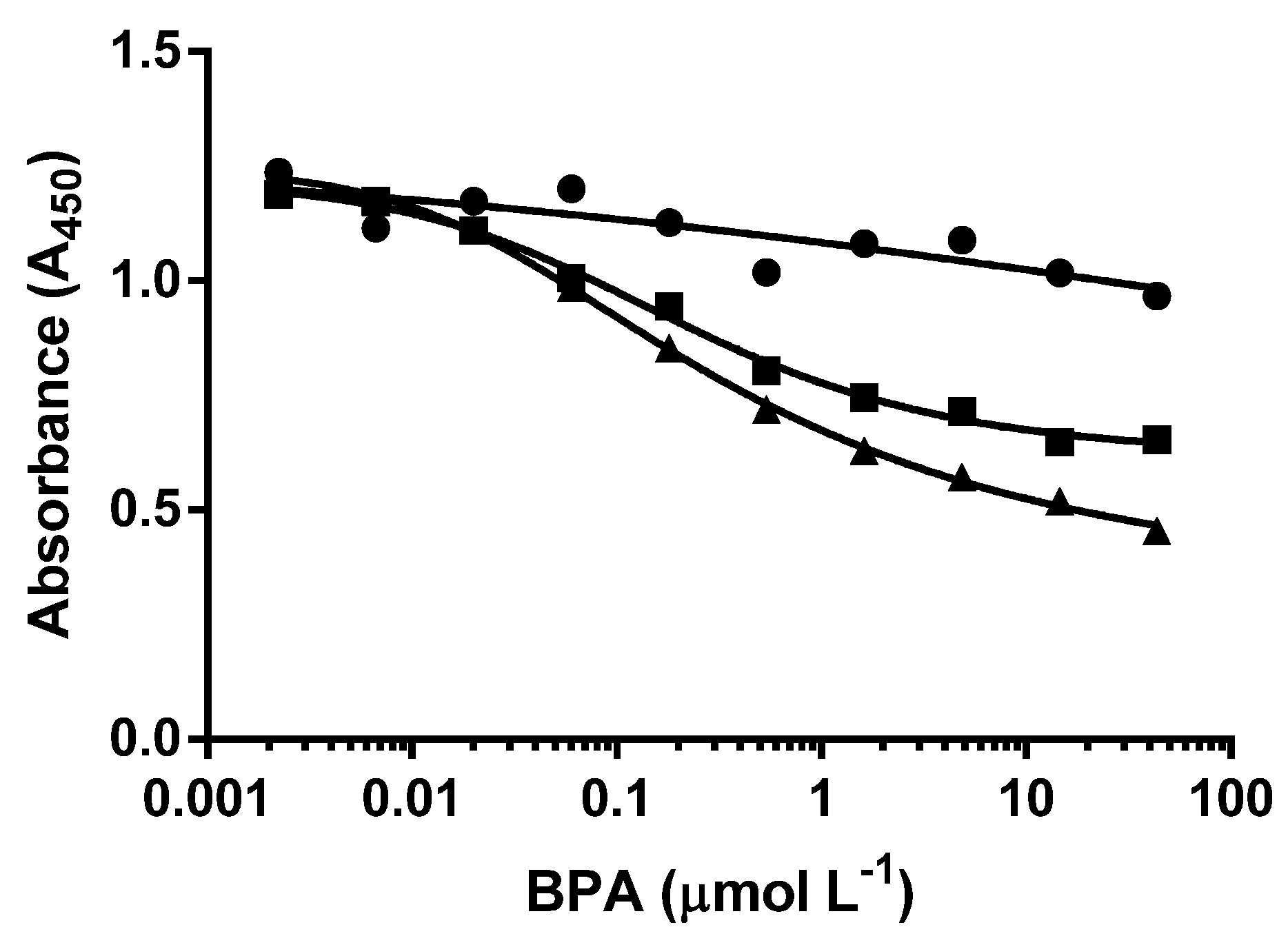
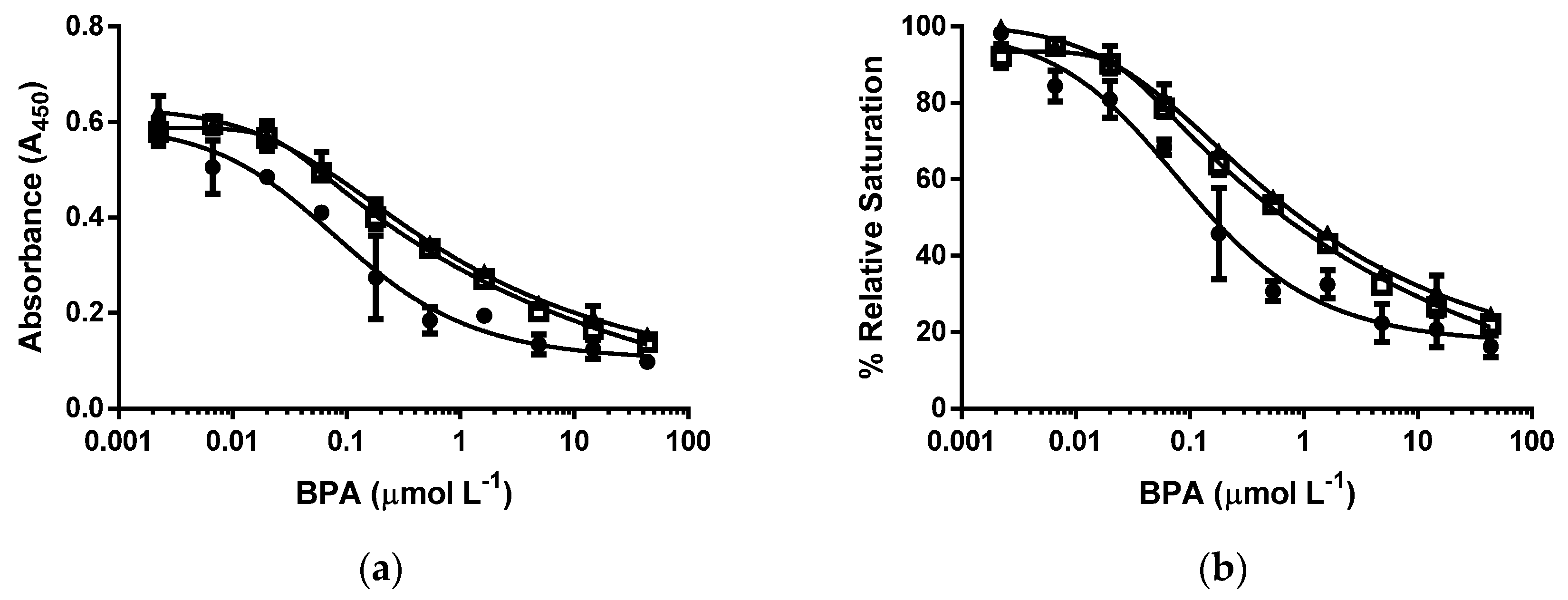
| Surface Epitope | 265 (●) | 265 (□) | 265 (▲) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle number (×10−10 mol·L−1) | 6.6 | 3.3 | 1.3 |
| Molar concentration of epitope (×10−7 mol·L−1) | 1.7 | 0.9 | 0.3 |
| D50 (µmol·L−1) | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Limit of Detection (µmol·L−1) | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Dynamic range (µmol·L−1) | 0.03–42.7 | 0.02–12.0 | 0.01–4.0 |
| Surface Epitope | 190 (●) | 396 (□) | 801 (▲) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle number (×10−10 mol·L−1) | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 |
| Molar concentration of epitope (×10−7 mol·L−1) | 0.4 | 0.8 | 1.6 |
| D50 (µmol·L−1) | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Limit of Detection (µmol·L−1) | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Dynamic range (µmol·L−1) | 0.01–2.3 | 0.02–20.0 | 0.02–39.8 |
| Surface Epitope | 190 (●) | 396 (□) | 801 (▲) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle number (×10−10 mol·L−1) | 5.3 | 2.6 | 1.3 |
| Molar concentration of epitope (×10−7 mol·L−1) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| D50 (µmol·L−1) | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Limit of Detection (µmol·L−1) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Dynamic range (µmol·L−1) | 0.01–39.8 | 0.01–39.8 | 0.01–39.8 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Peterson, J.R.; Luais, E.; Gooding, J.J.; Lee, N.A. Effects of Surface Epitope Coverage on the Sensitivity of Displacement Assays that Employ Modified Nanoparticles: Using Bisphenol A as a Model Analyte. Biosensors 2016, 6, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6030043
Lu Y, Peterson JR, Luais E, Gooding JJ, Lee NA. Effects of Surface Epitope Coverage on the Sensitivity of Displacement Assays that Employ Modified Nanoparticles: Using Bisphenol A as a Model Analyte. Biosensors. 2016; 6(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6030043
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yang, Joshua Richard Peterson, Erwann Luais, John Justin Gooding, and Nanju Alice Lee. 2016. "Effects of Surface Epitope Coverage on the Sensitivity of Displacement Assays that Employ Modified Nanoparticles: Using Bisphenol A as a Model Analyte" Biosensors 6, no. 3: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6030043
APA StyleLu, Y., Peterson, J. R., Luais, E., Gooding, J. J., & Lee, N. A. (2016). Effects of Surface Epitope Coverage on the Sensitivity of Displacement Assays that Employ Modified Nanoparticles: Using Bisphenol A as a Model Analyte. Biosensors, 6(3), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6030043