AI-Driven Comprehensive SERS-LFIA System: Improving Virus Automated Diagnostics Through SERS Image Recognition and Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
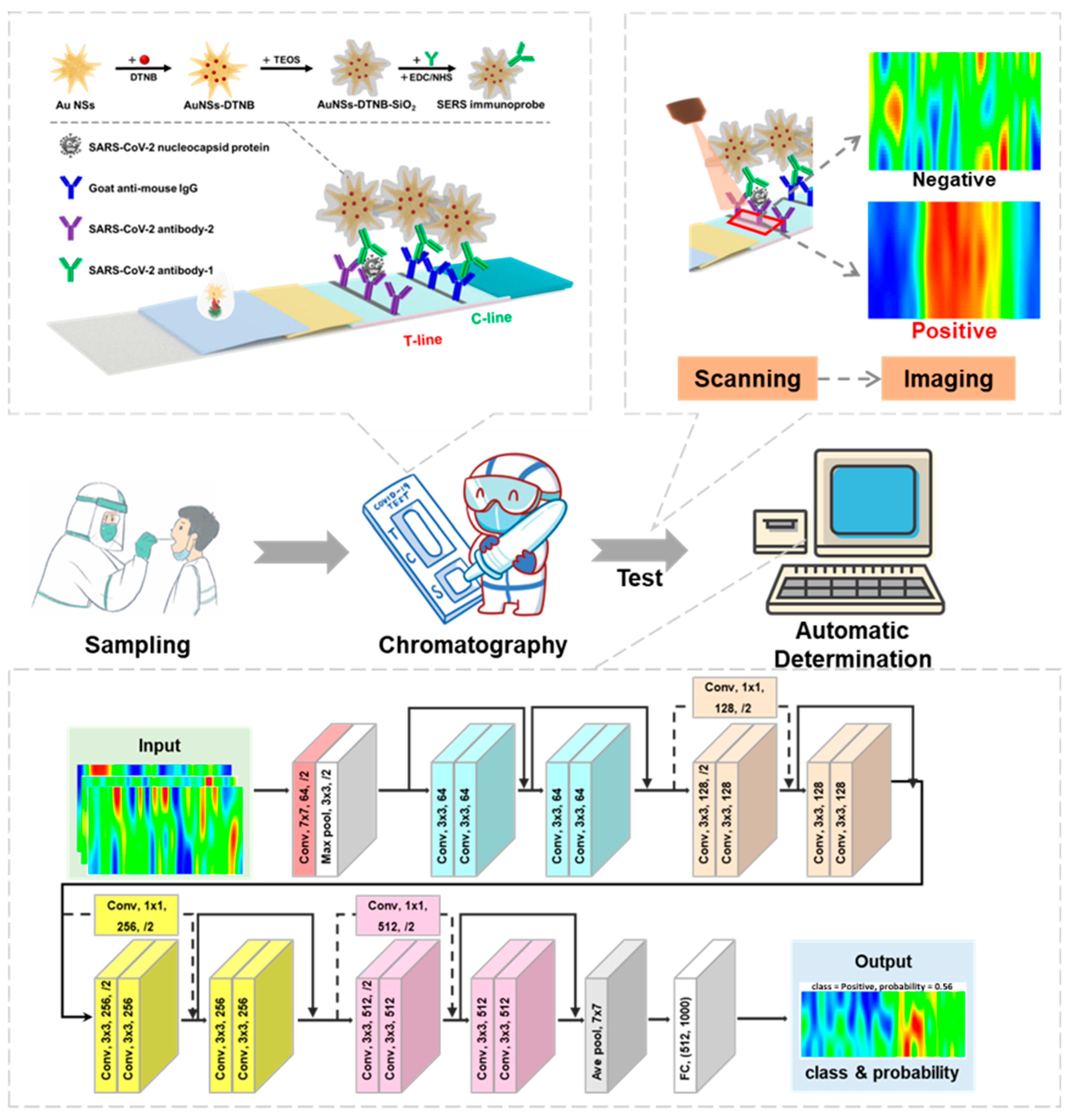
2.2. Synthesis of Au NSs and Au NSs-DTNB-SiO2 Immunoprobe
2.3. Fabrication of LFIA Strip
2.4. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 NP
2.5. Signal Recognition Based on SERS Imaging
2.5.1. Imaging Area Specifications
2.5.2. Scanning Step Size Control
2.5.3. SERS Imaging Mode
2.6. SERS Image Identification Based on Residual Neural Network
2.6.1. Overview of ResNet-18 Architecture
2.6.2. SERS Image Classification:
2.6.3. Model Training and Testing:
3. Results and Discussion
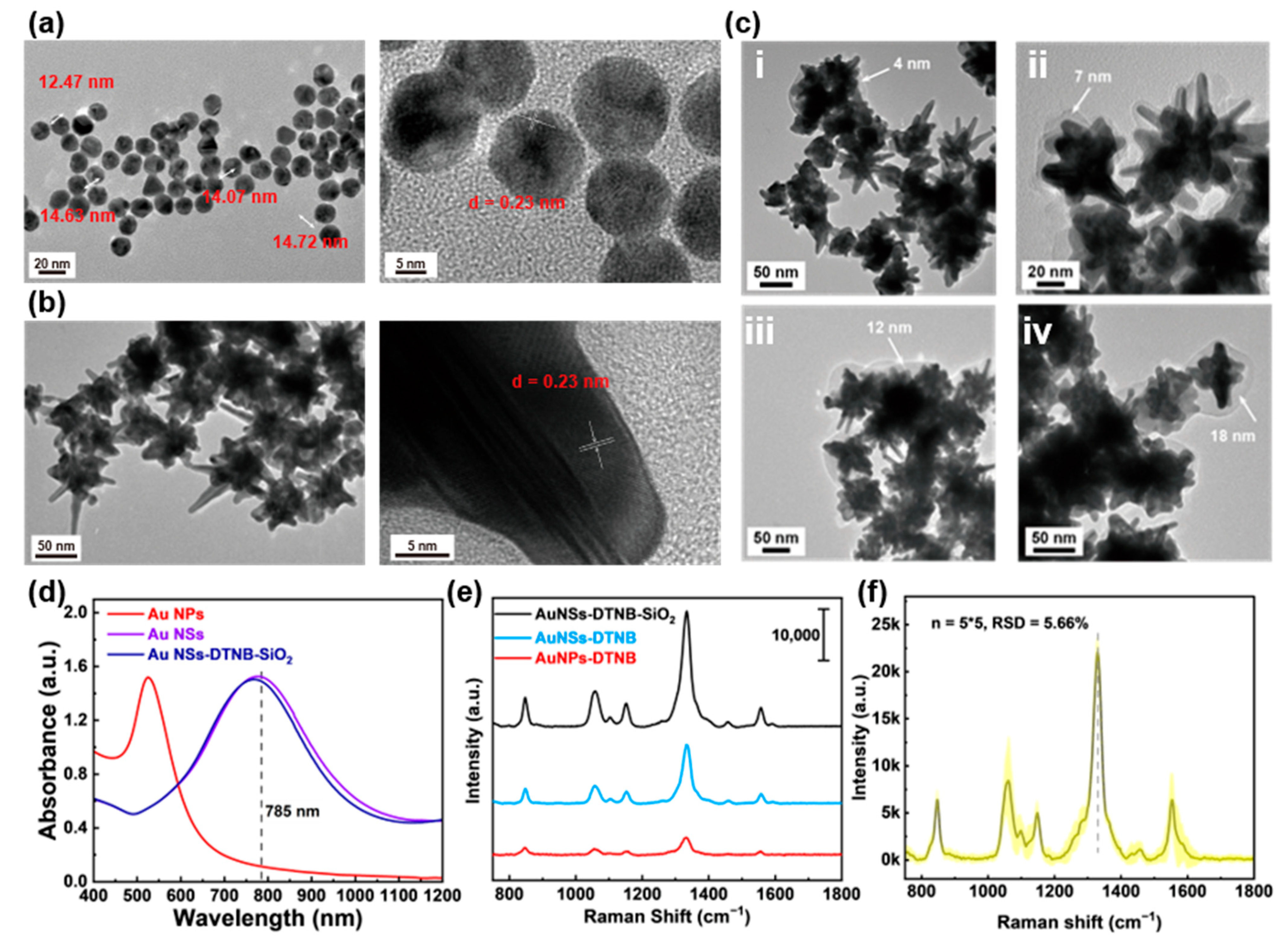
3.1. Characterization of Au NSs-DTNB-SiO2 Immunoprobes
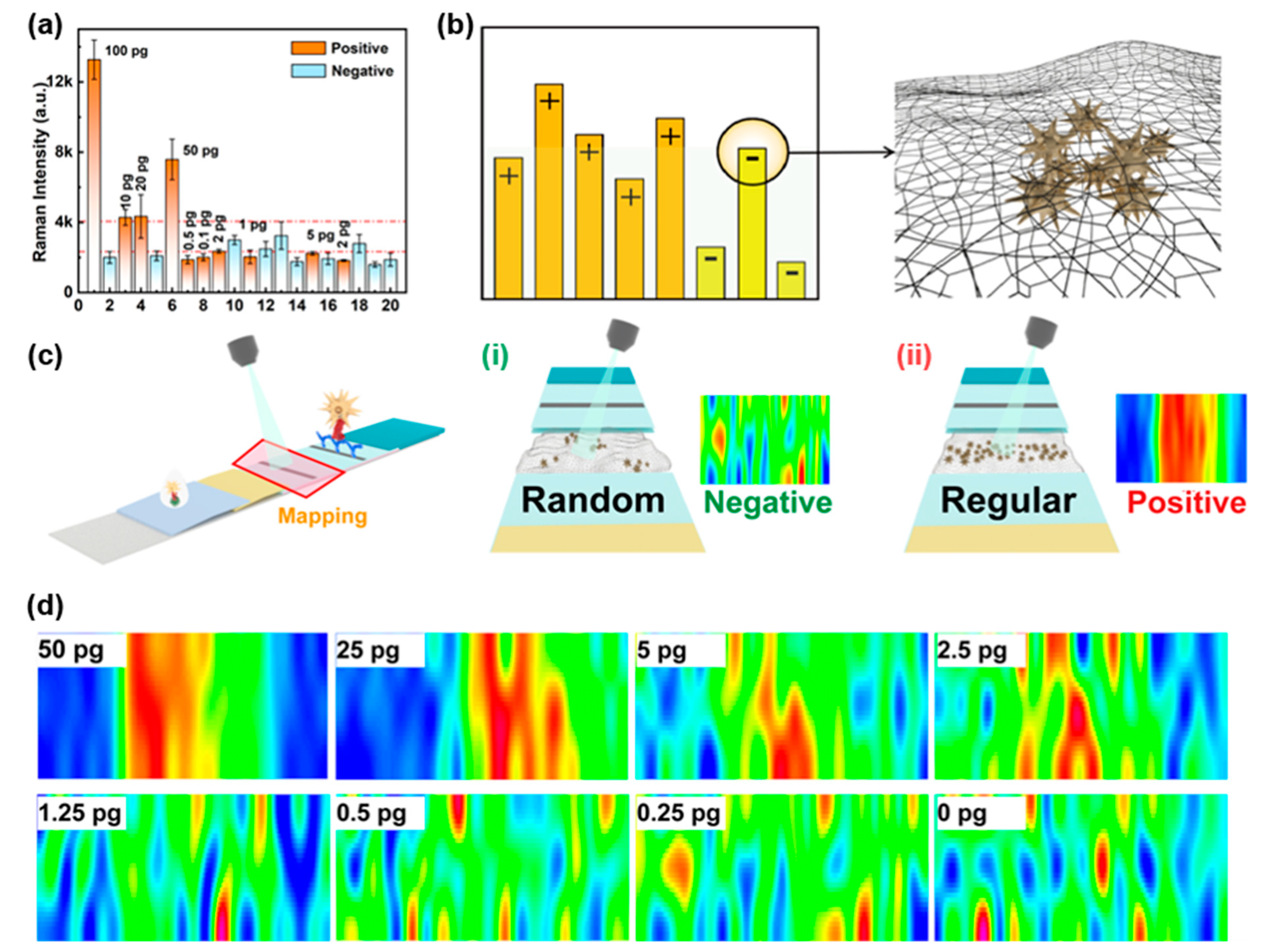
3.2. Performance Evaluation of Au NSs-DTNB-SiO2 Immunoprobe-Based SERS-LFIA Strips
3.3. Recognition of T Line Signals Based on the Distribution of Nanoprobes
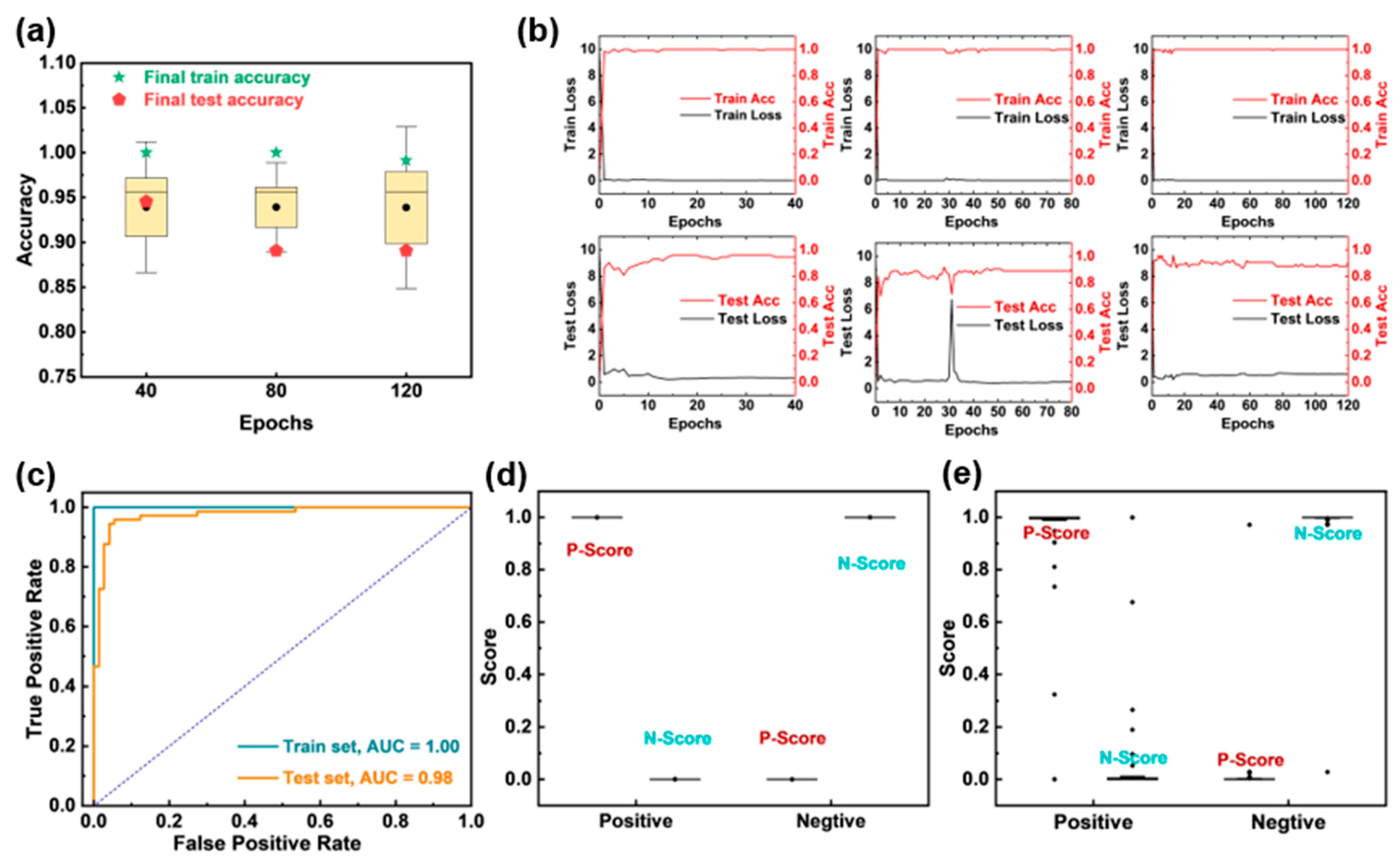
3.4. Automatic SERS Imaging Recognition Based on Residual Neural Networks
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, W.Y.; Wu, H.; Tan, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, D.C.; Li, S. Mechanisms and treatments of myocardial injury in patients with corona virus disease 2019. Life Sci. 2020, 262, 118496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleghani, N.; Taghipour, F. Diagnosis of COVID-19 for controlling the pandemic: A review of the state-of-the-art. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 174, 112830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.Z.; Li, D.Y.; Ramadan, S.; Li, Y.B.; Klein, N. Facile biosensors for rapid detection of COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 170, 112673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.Y.; Cao, C.Y.; You, M.L.; Han, S.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; He, W.H.; Liu, C.; Peng, P.; Xue, Z.R.; et al. Artificial intelligence-assisted colorimetric lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive and quantitative detection of COVID-19 neutralizing antibody. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 213, 114449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Dang, X.; Chen, R.; Li, Y.; Cui, N.; Yang, H. A universal three-dimensional hydrogel electrode for electrochemical detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein and hydrogen peroxide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 259, 116355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, B.L.; Xiong, Q.R.; Duan, H.W.; Xiong, Y.H.; Lai, W.H. Tailored quantum dots for enhancing sensing performance of lateral flow immunoassay. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhao, S.; Lin, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Peng, Y.; Xiao, R.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Y. Dual-Mode Lateral Flow Immunoassay Based on “Pompon Mum”-Like Fe3O4@MoS2@Pt Nanotags for Sensitive Detection of Viral Pathogens. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 11172–11184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khlebtsov, B.; Khlebtsov, N. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering-Based Lateral-Flow Immunoassay. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, J.; Jimenez de Aberasturi, D.; Aizpurua, J.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Auguié, B.; Baumberg, J.J.; Bazan, G.C.; Bell, S.E.J.; Boisen, A.; Brolo, A.G.; et al. Present and Future of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 28–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khlebtsov, B.N.; Bratashov, D.N.; Byzova, N.A.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Khlebtsov, N.G. SERS-based lateral flow immunoassay of troponin I by using gap-enhanced Raman tags. Nano Res. 2018, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Zheng, S.; Yang, X.; Han, H.; Dai, Y.; Xiao, R. Simultaneously ultrasensitive and quantitative detection of influenza A virus, SARS-CoV-2, and respiratory syncytial virus via multichannel magnetic SERS-based lateral flow immunoassay. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2023, 47, 102624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Liu, Z.; Fang, F.; Zhao, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, M.; Peng, Y.; Chen, H.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, W.; et al. Next-Generation Rapid and Ultrasensitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Variants. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 3733–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Lin, C.L.; Xu, M.M.; Zhang, W.D.; Li, D.; Peng, Y.S.; Huang, Z.R.; Yang, Y. Comprehensive SERS-LFIA Platform for Ultrasensitive Detection and Automated Discrimination of Chloramphenicol Residues in Aquatic Products. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 19368–19376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J.; Yi, Z.; Hong, H.; Xie, X.; Huang, Q.-a.; Fu, J.; Ouyang, J.; Zhao, X.; et al. A computer vision and residual neural network (ResNet) combined method for automated and accurate yeast replicative aging analysis of high-throughput microfluidic single-cell images. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 244, 115807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-L.; Chen, C.-H.; Huang, M.H. Seed-Mediated Synthesis of Branched Gold Nanocrystals Derived from the Side Growth of Pentagonal Bipyramids and the Formation of Gold Nanostars. Chem. Mater. 2008, 21, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Huang, Y.F.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Z.L.; Li, S.B.; Zhou, X.S.; Fan, F.R.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Wu, D.Y.; et al. Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nature 2010, 464, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.C.; Chen, S.Q.; Guo, J.H.; Ma, X. Nanomaterial Labels in Lateral Flow Immunoassays for Point-of-Care-Testing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 60, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.F.; Dai, E.H.; Xiao, R.; Zhou, Z.H.; Zhang, M.L.; Bai, Z.K.; Shao, Y.; Qi, K.Z.; Tu, J.; Wang, C.W.; et al. Development of a SERS-based lateral flow immunoassay for rapid and ultra-sensitive detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG in clinical samples. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2021, 329, 129196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, J.W.F.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H. Rapid methods for the detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens: Principles, applications, advantages and limitations. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 00770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, Z.; Pounds, J.G.; Lin, Y. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Protein Biomarker Using a Portable Fluorescence Biosensor Based on Quantum Dots and a Lateral Flow Test Strip. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7008–7014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.; Chouhan, R.S.; Shahdeo, D.; Shrikrishna, N.S.; Kesarwani, V.; Horvat, M.; Gandhi, S. A Recent Update on Advanced Molecular Diagnostic Techniques for COVID-19 Pandemic: An Overview. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 732756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, W.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Lin, T.C.; Lin, C.H.; Chang, H.F.; Tsai, C.H.; Wu, H.T.; Lin, C.S. Development and Efficacy of Lateral Flow Point-of-Care Testing Devices for Rapid and Mass COVID-19 Diagnosis by the Detections of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen and Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmalek, S.; Hamed, W.; Nagy, N.; Shokry, K.; Abdelrahman, H. Evaluation of the diagnostic performance and the utility of stool antigen lateral immunochromatography assay. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukana, N.; Park, J.; Silva Junior, G.J.; Malsick, L.E.; Gallichotte, E.N.; Ebel, G.D.; Geiss, B.J.; Dandy, D.S.; Bertotti, M.; Nacapricha, D.; et al. Magnetophoretic slider assay for electrochemical detection of SARS-cov-2 nucleocapsid protein in nasal swab samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 271, 117048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobysh, M.; Ratautaite, V.; Brazys, E.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecularly imprinted composite-based biosensor for the determination of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 251, 116043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Gu, J.; Ren, X.; Ma, H.; Wu, D.; Wei, Q. A sandwich-type photoelectrochemical immunosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 N protein based on CdS:Mn sensitized Bi2MoO6/In2S3 and NaYF4:Yb, Er for signal amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 427, 137210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Gu, C.; Zeng, S.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, T.; Wu, K. In–situ self–reduction preparation of Ti3C2Tx/Ag on flexible PMMA chip for quantitative detection of SARS–CoV–2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 422, 136610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Gu, C.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, T.; Wu, K. Hydrophilic-hydrophobic polymer strip with intrinsic signal and chemical-electromagnetic synergistic enhancement for non-metallic SERS-based identification of SARS-CoV-2 antigen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 399, 134866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Duan, S.; Ji, J.; Wu, M.; Yang, Z.; Cai, M.; Xue, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, R.; Yaron, S.; et al. Structured protein probes modified with selenium nanoparticle for 1-minute measurement of SARS-CoV-2 antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 268, 116878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Training Set (114 Samples) | Testing Set (73 Samples) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Class | Original Class | ||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | ||
| Predicted class | Positive | 54 | 0 | 32 | 1 |
| Negative | 0 | 60 | 3 | 37 | |
| Sensitivity | 100.00% | 91.43% | |||
| Specificity | 100.00% | 97.37% | |||
| Sensor Type | Immunoprobe | LOD (pg/mL) | Detection Time | Usability | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical | PPG | 42 | Hours | labs | [5] |
| MeSA-eMeSA | screen-printed carbon electrodes | 8890 | 10–15 min | labs | [25] |
| MIP systems | polypyrrole | 51.2 | Not mentioned | labs | [26] |
| PEC | CdS: Mn sensitized Bi2MoO6/In2S3 and NaYF4: Yb, Er for signal amplification | 0.0036 | Not mentioned | labs | [27] |
| SERS | Ti3C2Tx@Ag | 3.24 | Not mentioned | labs | [28] |
| SERS | BP/ZIF-67 | 6400 | ~30 min | labs | [29] |
| LFIA | PEG-SeNP | 10 | 1 min | POCT | [30] |
| catalytic colorimetric-LFIA | Fe3O4@MoS2@Pt | 80 | 10–15 min | POCT | [7] |
| photothermal-LFIA | 10 | 10–15 min | |||
| SERS-LFIA | Ag/BP | 0.5 | 10–15 min | POCT | [12] |
| SERS-LFIA | SiO2-Au NSs | 1.8~2.5 | 10–15 min | Automated POCT | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, S.; Xu, M.; Lin, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, D.; Peng, Y.; Tanemura, M.; Yang, Y. AI-Driven Comprehensive SERS-LFIA System: Improving Virus Automated Diagnostics Through SERS Image Recognition and Deep Learning. Biosensors 2025, 15, 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070458
Zhao S, Xu M, Lin C, Zhang W, Li D, Peng Y, Tanemura M, Yang Y. AI-Driven Comprehensive SERS-LFIA System: Improving Virus Automated Diagnostics Through SERS Image Recognition and Deep Learning. Biosensors. 2025; 15(7):458. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070458
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Shuai, Meimei Xu, Chenglong Lin, Weida Zhang, Dan Li, Yusi Peng, Masaki Tanemura, and Yong Yang. 2025. "AI-Driven Comprehensive SERS-LFIA System: Improving Virus Automated Diagnostics Through SERS Image Recognition and Deep Learning" Biosensors 15, no. 7: 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070458
APA StyleZhao, S., Xu, M., Lin, C., Zhang, W., Li, D., Peng, Y., Tanemura, M., & Yang, Y. (2025). AI-Driven Comprehensive SERS-LFIA System: Improving Virus Automated Diagnostics Through SERS Image Recognition and Deep Learning. Biosensors, 15(7), 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15070458






