Smartphone Biosensors for Non-Invasive Drug Monitoring in Saliva
Abstract
1. Introduction
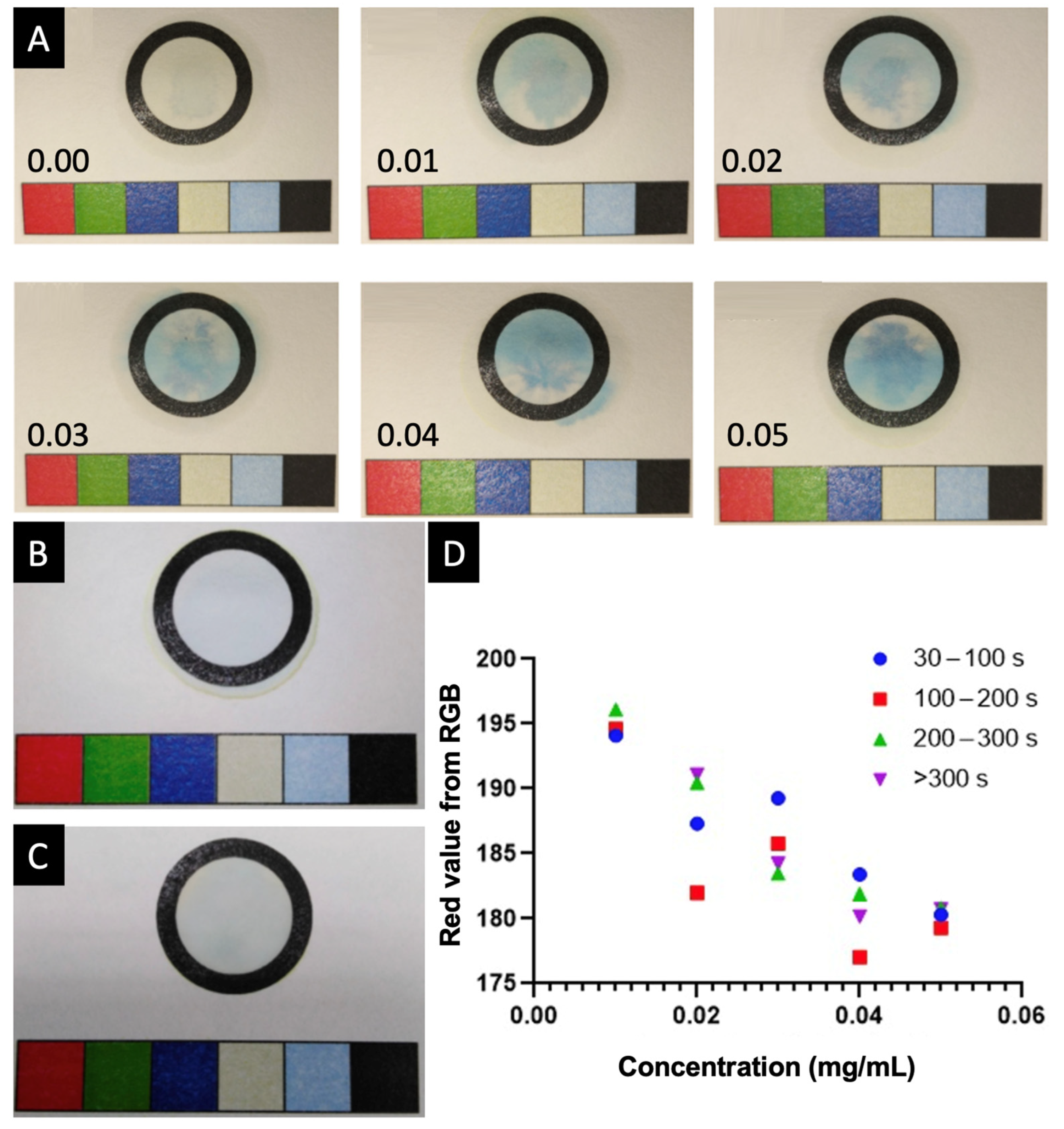
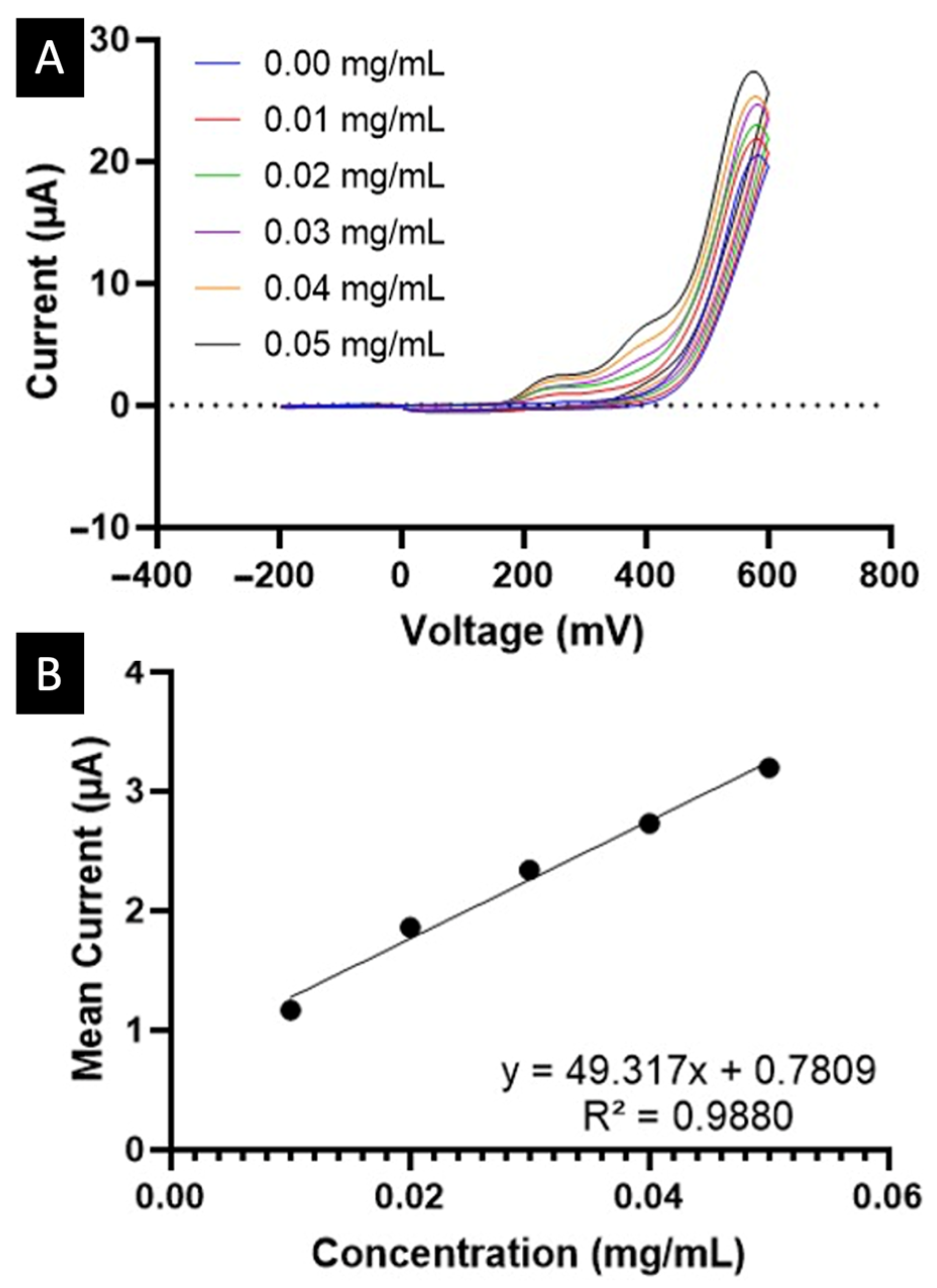
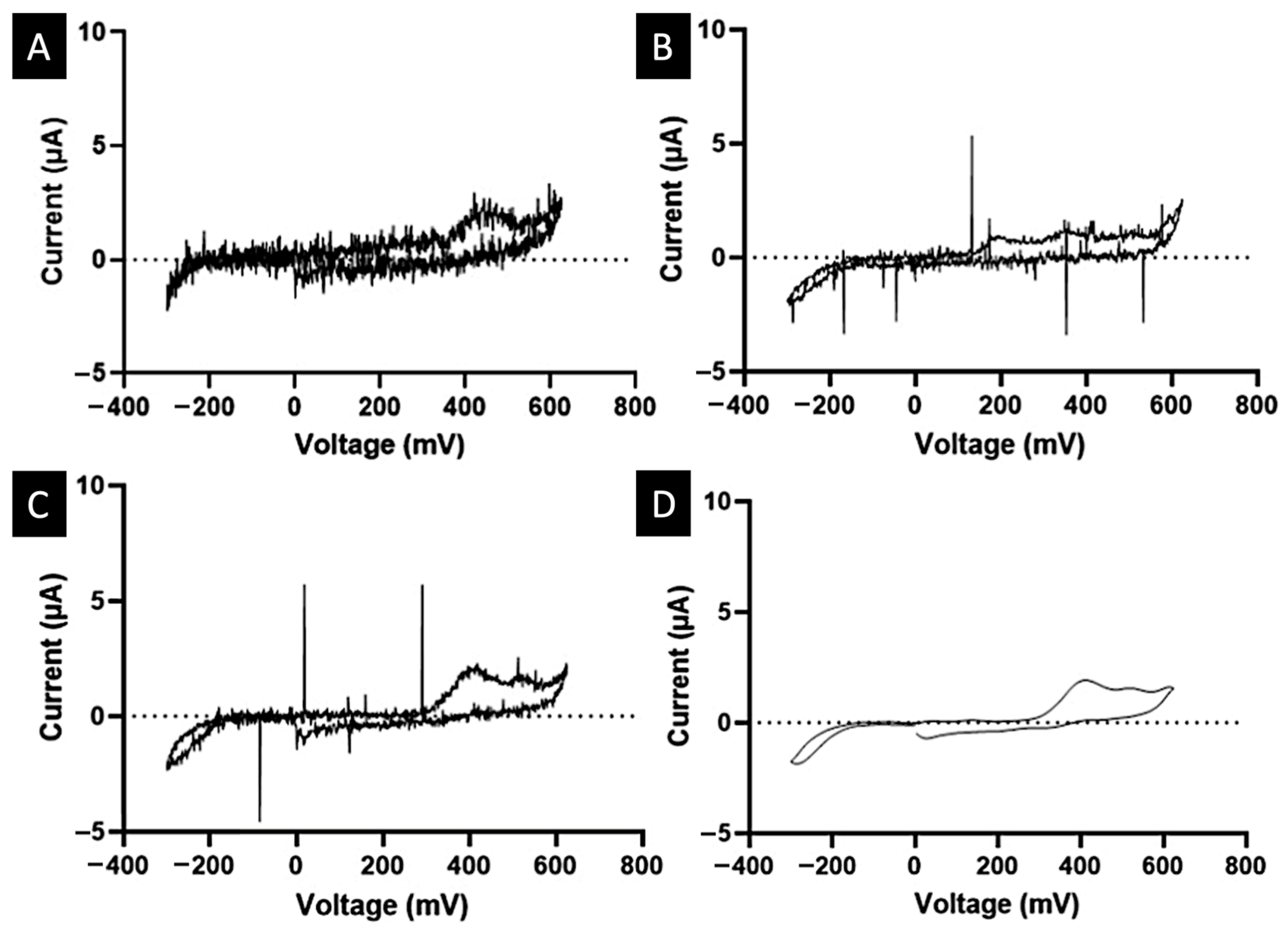
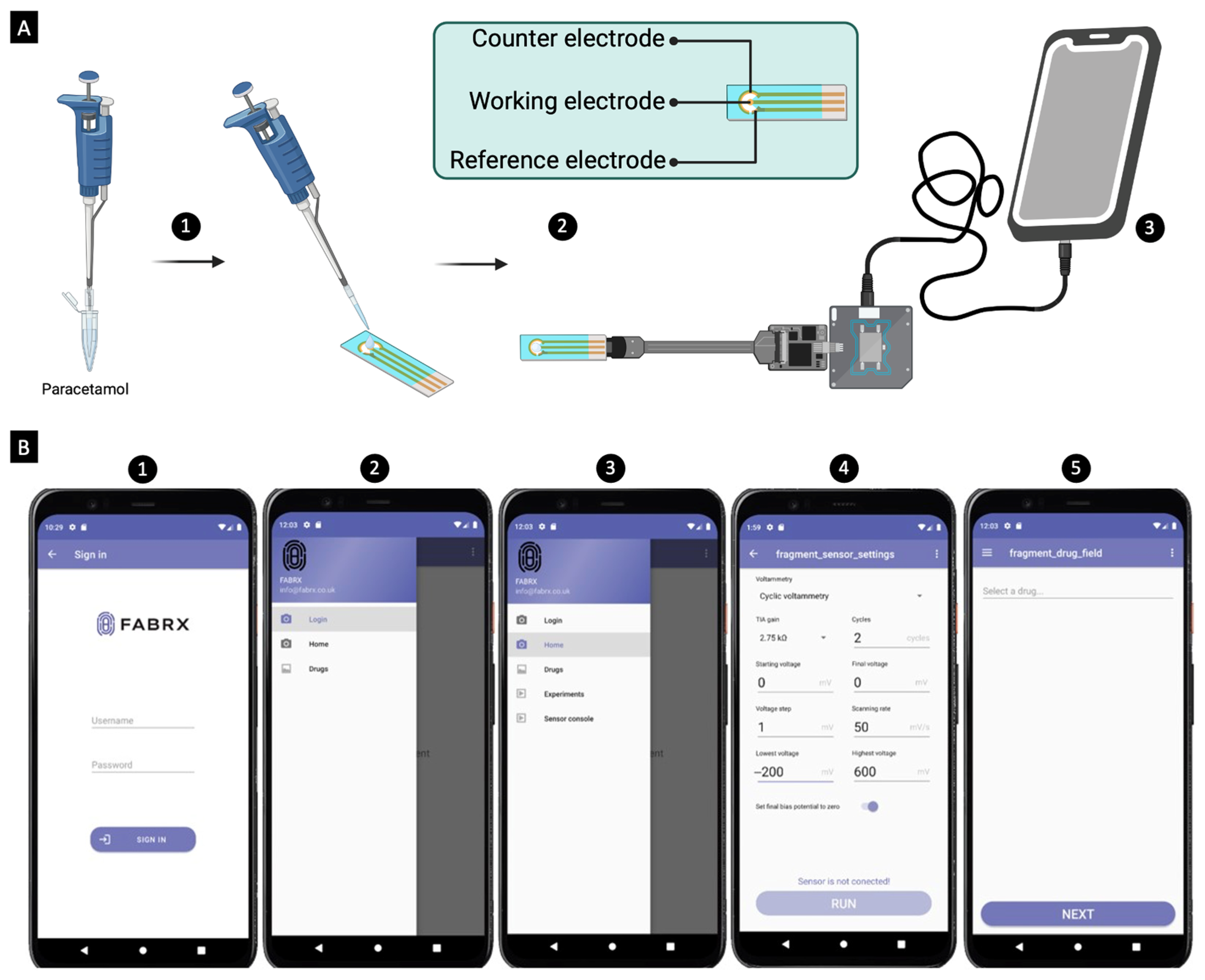
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Artificial Saliva Preparation
3.2.2. Paracetamol Samples Preparation
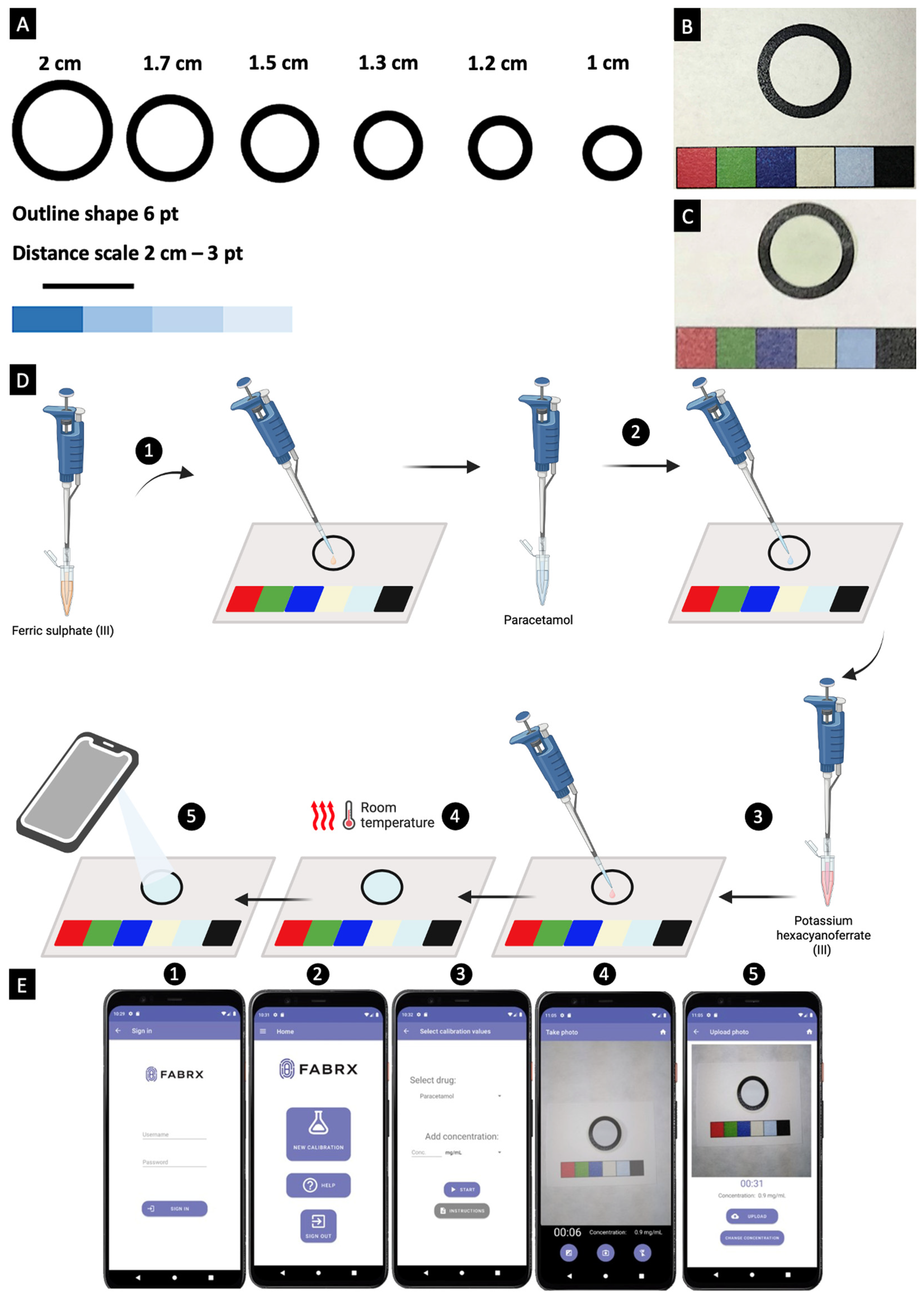
3.2.3. Colour Reagent Preparation
3.2.4. Mobile Application Development
3.2.5. Colourimetric Calibration and Quantification
3.2.6. Electrochemical Calibration and Quantification
3.2.7. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, J.S.; Lee, M.H. Overview of therapeutic drug monitoring. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2009, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.R.; AlOthman, Z.A.; Rahman, N. Analytical techniques in pharmaceutical analysis: A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1409–S1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascali, J.P.; Giorgetti, A.; Barone, R.; Pelletti, G.; Fais, P. Valproic acid determination by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) in whole blood for forensic purposes. Drug Test. Anal. 2023, 15, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, C.; Ramirez, S.; Ramazzotti, E.; Mancini, R.; Muratori, R.; Raggi, M.A.; Conti, M. Multiplexed therapeutic drug monitoring of antipsychotics in dried plasma spots by LC-MS/MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Guo, H.; Ren, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, J. Dried plasma spot–based liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the quantification of methotrexate in human plasma and its application in therapeutic drug monitoring. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Maghsoudlou, P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): The basics. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2016, 77, C98–C101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouton, J.W.A.; Raaijmakers, J.; Botterblom, M.; Toonen, M.; ter Heine, R.; Smeets, R.L.; Brüggemann, R.J.M.; te Brake, L.; Jager, N.G.L. Development and validation of a bioanalytical assay for the measurement of total and unbound teicoplanin in human serum. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 78, 2723–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qriouet, Z.; Qmichou, Z.; Bouchoutrouch, N.; Mahi, H.; Cherrah, Y.; Sefrioui, H. Analytical methods used for the detection and quantification of benzodiazepines. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieddu, M.; Baralla, E.; Pasciu, V.; Rimoli, M.G.; Boatto, G. Cross-reactivity of commercial immunoassays for screening of new amphetamine designer drugs. A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 218, 114868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roda, A.; Mirasoli, M.; Guardigli, M.; Zangheri, M.; Caliceti, C.; Calabria, D.; Simoni, P. Advanced biosensors for monitoring astronauts’ health during long-duration space missions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 111, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Li, Z.; Brown, C.; Galdino, N.M.; Shah, R.; Liu, S.; Hubble, L.J.; Bagot, K.; Tapert, S.; et al. Simultaneous detection of salivary Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol and alcohol using a Wearable Electrochemical Ring Sensor. Talanta 2020, 211, 120757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-M.; Teymourian, H.; De la Paz, E.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Mahato, K.; Sonsa-ard, T.; Huang, N.; Longardner, K.; Litvan, I.; Wang, J. Non-Invasive Sweat-Based Tracking of L-Dopa Pharmacokinetic Profiles Following an Oral Tablet Administration. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 19074–19078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Gomes, N.O.; Machado, S.A.S.; Oliveira, O.N. Wearable glove-embedded sensors for therapeutic drug monitoring in sweat for personalized medicine. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 135047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempionatto, J.R.; Brazaca, L.C.; García-Carmona, L.; Bolat, G.; Campbell, A.S.; Martin, A.; Tang, G.; Shah, R.; Mishra, R.K.; Kim, J.; et al. Eyeglasses-based tear biosensing system: Non-invasive detection of alcohol, vitamins and glucose. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 137, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrotra, P. Biosensors and their applications—A review. J. Oral. Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2016, 6, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, S. Digital 2019: Global Digital Overview—DataReportal–Global Digital Insights. 2019. Available online: https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2019-global-digital-overview#:~:text=There%20are%204.39%20billion%20internet,since%20this%20time%20last%20year (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Quesada-González, D.; Merkoçi, A. Mobile phone-based biosensing: An emerging “diagnostic and communication” technology. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbioli, G.G.; Mazzu-Nascimento, T.; Stockton, A.M.; Carrilho, E. Technical aspects and challenges of colorimetric detection with microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs)—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 970, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.; Kucharska, A.; Erratico, C.; Xu, F.; Den Hond, E.; Koppen, G.; Vanermen, G.; Covaci, A.; Voorspoels, S. Human biomonitoring of emerging pollutants through non-invasive matrices: State of the art and future potential. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 4063–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmongy, H.; Abdel-Rehim, M. Saliva as an alternative specimen to plasma for drug bioanalysis: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 83, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, R.E.; Huestis, M.A. Oral fluid as a diagnostic tool. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2004, 42, 1273–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yao, Y.; Chen, T.; Shen, W.; Tang, S.; Lee, H.K. Application of smartphone-based spectroscopy to biosample analysis: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Sham, T.-T.; Boisdon, C.; Smith, B.L.; Blair, J.C.; Hawcutt, D.B.; Maher, S. Emergency diagnosis made easy: Matrix removal and analyte enrichment from raw saliva using paper-arrow mass spectrometry. Analyst 2023, 148, 5366–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareeb, M.; Akhlaghi, F. Alternative matrices for therapeutic drug monitoring of immunosuppressive agents using LC-MS/MS. Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 1037–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Chen, X.; Fu, Y. Salivary analysis: An emerging paradigm for non-invasive healthcare diagnosis and monitoring. Interdiscip. Med. 2023, 1, e20230009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goryński, K.; Sobczak, Ł. Quantification of prohibited substances and endogenous corticosteroids in saliva using traditional, alternative microextraction-based, and novel 3D printed sample-preparation methods coupled with LC-MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1291, 342236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlès, L.; Lupon, E.; Sheth, T.; Camuzard, O.; Lellouch, A.G.; Shende, C.; Farquharson, S.; Safa, K.; Cetrulo, C.L. Immunosuppressant Drug Monitor: A non-invasive device to measure tacrolimus level in the saliva of transplanted patients. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 653, 123858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, J.M. Chapter 6—Digital Designs and Scientific Hardware. In Open-Source Lab; Pearce, J.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 165–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyo, S.; Kalcher, K.; Apilux, A.; Chailapakul, O.; Siangproh, W. A novel paper-based colorimetry device for the determination of the albumin to creatinine ratio. Analyst 2018, 143, 5453–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulbul, G.; Eskandarloo, H.; Abbaspourrad, A. A novel paper based colorimetric assay for the detection of TiO2 nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worramongkona, P.; Seeda, K.; Phansomboon, P.; Ratnarathorn, N.; Chailapakul, O.; Dungchai, W. A Simple Paper-based Colorimetric Device for Rapid and Sensitive Urinary Oxalate Determinations. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Listyarini, A.; Sholihah, W.; Imawan, C. A paper-based Colorimetric Indicator Label using Natural Dye for Monitoring Shrimp Spoilage. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 367, 012045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakoh, A.; Rattanarat, P.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakul, O. Simple and selective paper-based colorimetric sensor for determination of chloride ion in environmental samples using label-free silver nanoprisms. Talanta 2018, 178, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatoni, A.; Numnuam, A.; Kanatharana, P.; Limbut, W.; Thammakhet, C.; Thavarungkul, P. A highly stable oxygen-independent glucose biosensor based on a chitosan-albumin cryogel incorporated with carbon nanotubes and ferrocene. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 185, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; A Hagen, J.; Papautsky, I. Point-of-care colorimetric detection with a smartphone. Lab A Chip 2012, 12, 4240–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firdaus, L.M.; Aprian, A.; Meileza, N.; Hitsmi, M.; Elvia, R.; Rahmidar, L.; Khaydarov, R. Smartphone Coupled with a Paper-Based Colorimetric Device for Sensitive and Portable Mercury Ion Sensing. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Moreddu, R.; Seifi, S.; Jiang, N.; Vega, K.; Dong, X.; Dong, J.; Butt, H.; Jakobi, M.; Elsner, M.; et al. Dermal Tattoo Biosensors for Colorimetric Metabolite Detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10506–10513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokrollahi, A.; Mohammadpour, Z.; Abbaspour, A. Colorimetric Determination of Free Salicylic Acid in Aspirin and Urine by Scanometry as a New, Reliable, Inexpensive and Simple Method. Pharm. Chem. J. 2017, 51, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, E.G.; Kendrick, D.; Sayal, K.; Orton, E. Poisoning substances taken by young people: A population-based cohort study. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2018, 68, e703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelikay, G.; Karadurmus, L.; Kaya, S.I.; Bakirhan, N.K.; Ozkan, S.A. A Review: New Trends in Electrode Systems for Sensitive Drug and Biomolecule Analysis. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 50, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, E.; Samiei, M.; Hasanzadeh, A.; Kavetskyy, T.; Jafari, S.; Alipour, M.; Salatin, S.; Rameshrad, M.; Sharifi, S.; Eftekhari, A.; et al. Monitoring of drug resistance towards reducing the toxicity of pharmaceutical compounds: Past, present and future. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 186, 113265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snizhko, D.; Zholudov, Y.; Kukoba, A.; Xu, G. Potentiostat design keys for analytical applications. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 936, 117380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoilett, O.S.; Walker, J.F.; Balash, B.M.; Jaras, N.J.; Boppana, S.; Linnes, J.C. KickStat: A Coin-Sized Potentiostat for High-Resolution Electrochemical Analysis. Sensors 2020, 20, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electronic Medicines Compendium. Paracetamol 500 mg Tablets. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/5164/smpc#gref (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Hawkins, L.C.; Edwards, J.N.; Dargan, P.I. Impact of Restricting Paracetamol Pack Sizes on Paracetamol Poisoning in the United Kingdom. Drug Saf. 2007, 30, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa Bosch, M.; Ruiz Sanchez, A.J.; Sanchez Rojas, F.; Bosch Ojeda, C. Determination of paracetamol: Historical evolution. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 42, 291–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiew, A.L.; Gluud, C.; Brok, J.; Buckley, N.A. Interventions for paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2, CD003328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairney, D.G.; Beckwith, H.K.S.; Al-Hourani, K.; Eddleston, M.; Bateman, D.N.; Dear, J.W. Plasma paracetamol concentration at hospital presentation has a dose-dependent relationship with liver injury despite prompt treatment with intravenous acetylcysteine. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 54, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiew, A.L.; Reith, D.; Pomerleau, A.; Wong, A.; Isoardi, K.Z.; Soderstrom, J.; Buckley, N.A. Updated guidelines for the management of paracetamol poisoning in Australia and New Zealand. Med. J. Aust. 2020, 212, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, H.; McCoubrie, D.L.; Fatovich, D.M.; Ryan, J.; Vasikaran, S.; Daly, F.F. Correlation of paired plasma and saliva paracetamol levels following deliberate self-poisoning with paracetamol (The Salivary Paracetamol In Toxicology [SPIT] study). Clin. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vliegenthart, A.D.B.; Antoine, D.J.; Dear, J.W. Target biomarker profile for the clinical management of paracetamol overdose. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 80, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, A.H.; Whyte, I.M. Therapeutic drug monitoring in drug overdose. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, L.; Roscoe, P.; Wright, N.; Brown, S. Plasma-paracetamol half-life and hepatic necrosis in patients with paracetamol overdosage. Lancet 1971, 297, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Savitha, R.; Renganathan, T.; Pushpavanam, S. Fabrication of laser printed microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (LP-microPADs) for point-of-care applications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Melenbrink, E.L.; Cordonier, G.J.; Boggs, C.; Khan, A.; Isaac, M.K.; Nkhonjera, L.K.; Bahati, D.; Billinge, S.J.; Haile, S.M.; et al. An Easily Fabricated Low-Cost Potentiostat Coupled with User-Friendly Software for Introducing Students to Electrochemical Reactions and Electroanalytical Techniques. J. Chem. Educ. 2018, 95, 1658–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopin, P.; Lopin, K.V. PSoC-Stat: A single chip open source potentiostat based on a Programmable System on a Chip. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.D.; Doeven, E.H.; Quayle, K.; Kouzani, A.Z. MiniStat: Development and Evaluation of a Mini-Potentiostat for Electrochemical Measurements. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 31903–31912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Jha, R.R.; Kumari, A.; Khatri, I. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with digital image colorimetry for paracetamol analysis. Microchem. J. 2021, 162, 105870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswathyamma, B.; Grzybowska, I.; Orlewska, C.; Radecki, J.; Dehaen, W.; Kumar, K.G.; Radecka, H. Electroactive Dipyrromethene-Cu (II) Monolayers Deposited onto Gold Electrodes for Voltammetric Determination of Paracetamol. Electroanal. Int. J. Devoted Fundam. Pract. Asp. Electroanal. 2008, 20, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatibello-Filho, O.; Lupetti, K.O.; Leite, O.D.; Vieira, I.C. Procedure 22 Voltammetric determination of paracetamol in pharmaceuticals using a zucchini (Cucurbita pepo) tissue biosensor. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Alegret, S., Merkoçi, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 49, pp. e157–e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagyashri, B.K.; Tawade, A.K.; Kamble, P.; Padavi, M.N.; Sharma, K.K.K.; Ajalkar, B.D.; Tayade, S.N. Hydrothermal Assisted Synthesis of Micro-Bricks Shaped WO3 for Electrochemical Oxidation of Paracetamol: A Microstructured Paracetamol Sensor. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2020, 56, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatibello-Filho, O.; Lupetti, K.O.; Vieira, I.C. Chronoamperometric determination of paracetamol using an avocado tissue (Persea americana) biosensor. Talanta 2001, 55, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Ye, S.; Iqbal, K.; Liu, L.; Qiu, G.; Ye, W. Pt/NiCo2O4 nanocomposite with extremely low Pt loading as an oxidase-like nanozyme for colorimetric detection of acetaminophen in natural water. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 152, 105183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, S.M.; Moon, B.-S.; Kim, D.-H. Selective and sensitive colorimetric detection of p-aminophenol in human urine and paracetamol drugs based on seed-mediated growth of silver nanoparticles. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jager, L.; Andrews, A.R.J. Development of a screening method for cocaine and cocaine metabolites in saliva using hollow fiber membrane solvent microextraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 458, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campiglia, A.D.; Vo-Dinh, T. Rapid screening method for cocaine and benzoylecgonine in saliva samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 372, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Zapatero-Rodríguez, J.; Estrela, P.; O’Kennedy, R. Point-of-care diagnostics in low resource settings: Present status and future role of microfluidics. Biosensors 2015, 5, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yager, P.; Domingo, G.J.; Gerdes, J. Point-of-care diagnostics for global health. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 10, 107–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, E.T.S.G.; Souto, D.E.P.; Barragan, J.T.C.; de F. Giarola, J.; de Moraes, A.C.M.; Kubota, L.T. Electrochemical Biosensors in Point-of-Care Devices: Recent Advances and Future Trends. Chem. Electron. Chem. 2017, 4, 778–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M. Portable biosensing devices for point-of-care diagnostics: Recent developments and applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Molfetta, S.; Caruso, I.; Cignarelli, A.; Natalicchio, A.; Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. Professional continuous glucose monitoring in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoevelmann, J.; Sliwa, K.; Briton, O.; Ntsekhe, M.; Chin, A.; Viljoen, C. Effectiveness of implantable loop recorder and Holter electrocardiographic monitoring for the detection of arrhythmias in patients with peripartum cardiomyopathy. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2023, 112, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jia, H.; Zhou, J.; Huang, X.; Xu, L.; Jia, S.; Gao, Z.; Yao, K.; Li, D.; Zhang, B.; et al. Thin, soft, wearable system for continuous wireless monitoring of artery blood pressure. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidt, B.; Siqueira, W.F.; Eersels, K.; Diliën, H.; van Grinsven, B.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Cleij, T.J. Point of care diagnostics in resource-limited settings: A review of the present and future of PoC in its most needed environment. Biosensors 2020, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P. Personalized biosensors for point-of-care diagnostics: From bench to bedside applications. Nanotheranostics 2023, 7, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, B.; Kumar, A.; Mahato, K.; Chandra, P. Smartphone-assisted personalized diagnostic devices and wearable sensors. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 13, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.; Chandra, P. based miniaturized immunosensor for naked eye ALP detection based on digital image colorimetry integrated with smartphone. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 128, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.; Trenfield, S.J.; Pollard, T.D.; Jie Ong, J.; Elbadawi, M.; McCoubrey, L.E.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Connected Healthcare: Improving Patient Care using Digital Health Technologies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 178, 113958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trenfield, S.J.; Awad, A.; McCoubrey, L.E.; Elbadawi, M.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Advancing pharmacy and healthcare with virtual digital technologies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 182, 114098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrier, E.; Demazières, A.; Girard, N.; Pross, N.; Osbild, D.; Metzger, D.; Guelinckx, I.; Klein, A. Circadian variation and responsiveness of hydration biomarkers to changes in daily water intake. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 113, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotz, C.; Morton, J.T.; Navarro, P.; Coker, J.; Belda-Ferre, P.; Knight, R.; Zengler, K. Quantifying live microbial load in human saliva samples over time reveals stable composition and dynamic load. Msystems 2021, 6, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyraud, E.; Palicki, O.; Schwartz, C.; Nicklaus, S.; Feron, G. Variability of human saliva composition: Possible relationships with fat perception and liking. Arch. Oral Biol. 2012, 57, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, H.; Bacon, A.; Joseph, K.M.; Gwandaru, W.R.W.; Bhide, A.; Sankhala, D.; Dhamu, V.N.; Prasad, S. A Rapid Response Electrochemical Biosensor for Detecting Thc In Saliva. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellagambi, F.G.; Baraket, A.; Longo, A.; Vatteroni, M.; Zine, N.; Bausells, J.; Fuoco, R.; Di Francesco, F.; Salvo, P.; Karanasiou, G.S.; et al. Electrochemical biosensor platform for TNF-α cytokines detection in both artificial and human saliva: Heart failure. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 251, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamchuea, K.; Batchelor-McAuley, C.; Compton, R.G. Understanding electroanalytical measurements in authentic human saliva leading to the detection of salivary uric acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 262, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Tomoto, K.; Nitta, H.; Toma, K.; Takeuchi, S.; Sekita, T.; Minakuchi, S.; Mitsubayashi, K. A Wearable Cellulose Acetate-Coated Mouthguard Biosensor for In Vivo Salivary Glucose Measurement. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 12201–12207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.R.; Sharma, P.; Anzar, N.; Pundir, C.S.; Pilloton, R.; Narang, J.; Shetti, N.P. Analytical methods for detection of human cytomegalovirus clinched biosensor a cutting-edge diagnostic tool. Biomed. Eng. Adv. 2021, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Fuller, E.; Klug, S.; Lee, F.; Su, F.; Zhang, L.; Chao, S.-h.; Meldrum, D.R. A fluorescent colorimetric pH sensor and the influences of matrices on sensing performances. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudin, V. Advances in biosensor development for the screening of antibiotic residues in food products of animal origin—A comprehensive review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duyen, T.T.M.; Matsuura, H.; Ujiie, K.; Muraoka, M.; Harada, K.; Hirata, K. Paper-based colorimetric biosensor for antibiotics inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 123, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Warden, A.R.; Huang, J.; Wang, W.; Ding, X. Colorimetric and Electrochemical Detection of Escherichia coli and Antibiotic Resistance Based on a p-Benzoquinone-Mediated Bioassay. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7524–7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NF S90-701; Artificial Saliva AFNOR NF S91-141 Standard Procedure. AFNOR: Saint-Denis, France, 1988.
- Giacomelli, F.C.; Giacomelli, C.; Spinelli, A. Behavior of a Co-Cr-Mo biomaterial in simulated body fluid solutions studied by electrochemical and surface analysis techniques. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2004, 15, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagli, K.; Traisnel, M.; Hildebrand, H.F. Electrochemical behaviour of titanium and dental alloys in artificial saliva. Electrochim. Acta 1993, 38, 1769–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, M.M.; Nejem, R.M.; El-Abadla, N.S.; Al-Kholy, M.; Saleh, A.A. Novel atomic absorption spectrometric and rapid spectrophotometric methods for the quantitation of paracetamol in saliva: Application to pharmacokinetic studies. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 70, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desimoni, E.; Brunetti, B. About estimating the limit of detection by the signal to noise approach. Pharm. Anal. Acta 2015, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
| Colourimetric | Electrochemical | |
|---|---|---|
| LOD (mg/mL) | 0.0379 | 0.0070 |
| LOQ (mg/mL) | 0.1148 | 0.0211 |
| (mg/mL) | 4.6164 | 0.1041 |
| CV (%) | 3.8544 | 18.733 |
| Detection time (min) | ~5 | ~1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Awad, A.; Rodríguez-Pombo, L.; Simón, P.E.; Álvarez, A.C.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Basit, A.W.; Goyanes, A. Smartphone Biosensors for Non-Invasive Drug Monitoring in Saliva. Biosensors 2025, 15, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030163
Awad A, Rodríguez-Pombo L, Simón PE, Álvarez AC, Alvarez-Lorenzo C, Basit AW, Goyanes A. Smartphone Biosensors for Non-Invasive Drug Monitoring in Saliva. Biosensors. 2025; 15(3):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030163
Chicago/Turabian StyleAwad, Atheer, Lucía Rodríguez-Pombo, Paula Esteiro Simón, André Campos Álvarez, Carmen Alvarez-Lorenzo, Abdul W. Basit, and Alvaro Goyanes. 2025. "Smartphone Biosensors for Non-Invasive Drug Monitoring in Saliva" Biosensors 15, no. 3: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030163
APA StyleAwad, A., Rodríguez-Pombo, L., Simón, P. E., Álvarez, A. C., Alvarez-Lorenzo, C., Basit, A. W., & Goyanes, A. (2025). Smartphone Biosensors for Non-Invasive Drug Monitoring in Saliva. Biosensors, 15(3), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030163








