Exploratory Evaluation of EGFR-Targeted Anti-Tumor Drugs for Lung Cancer Based on Lung-on-a-Chip
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. 3D Printing Manufacturing of Chip Templates
2.2. Microchip Fabrication
2.3. Diffusion Characterization of Porous Membrane
2.4. Isolation of Primary Lung Cancer Cells
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. Cell Staining
2.7. Data Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
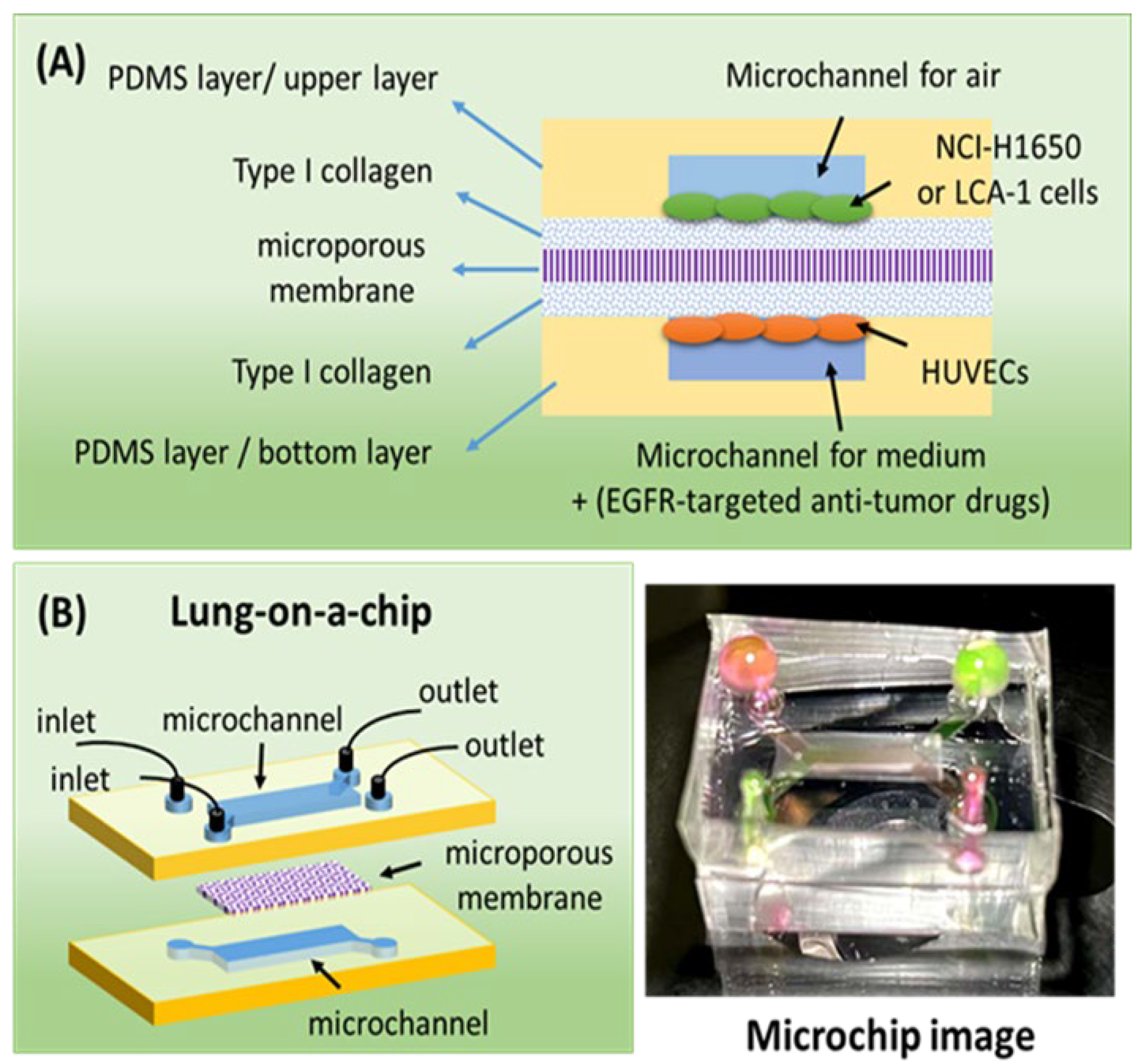
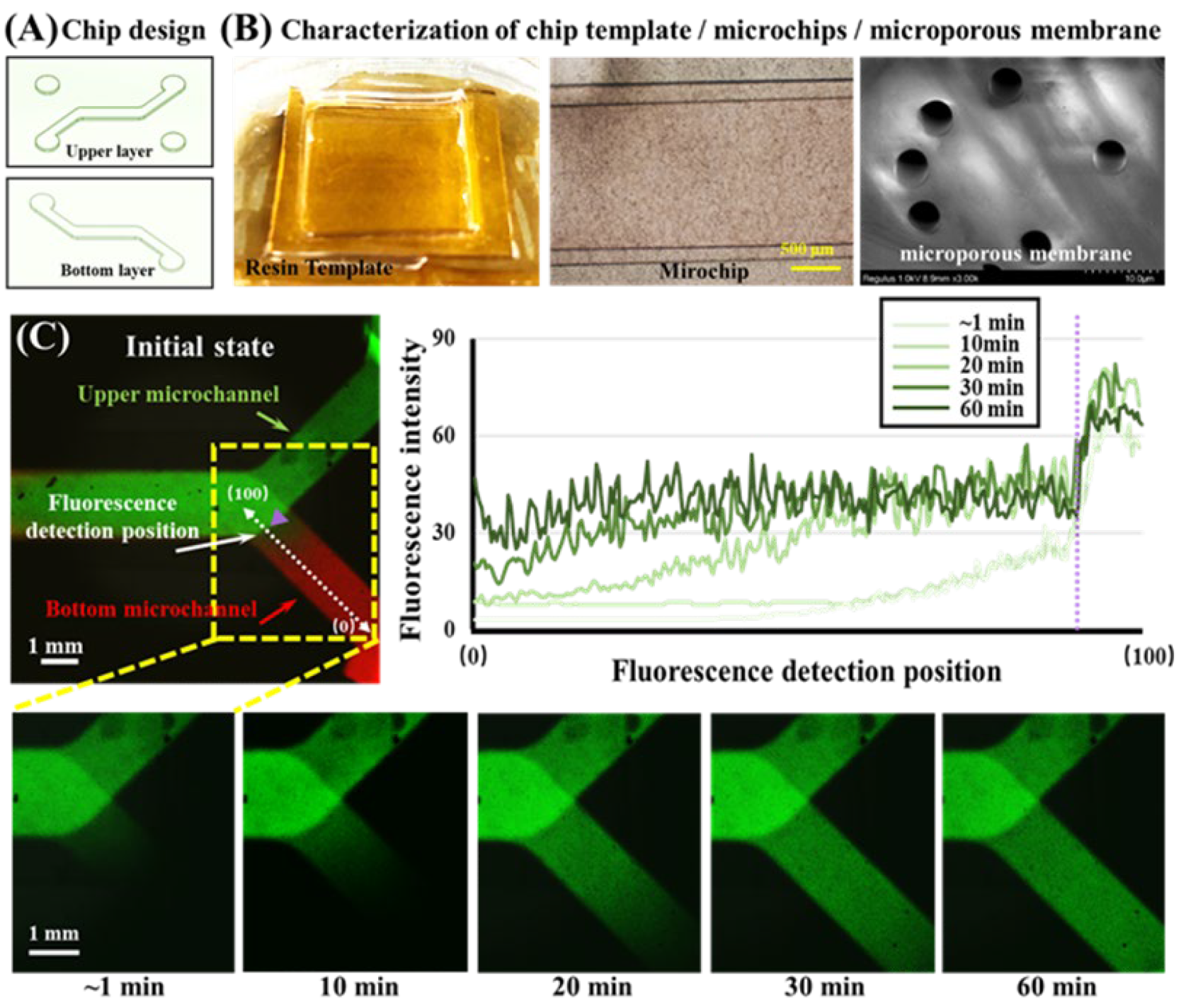
3.1. Evaluation of 3D Printing Chip Templates and Microchip
3.2. Diffusion Characterization of Small Molecules in Chips
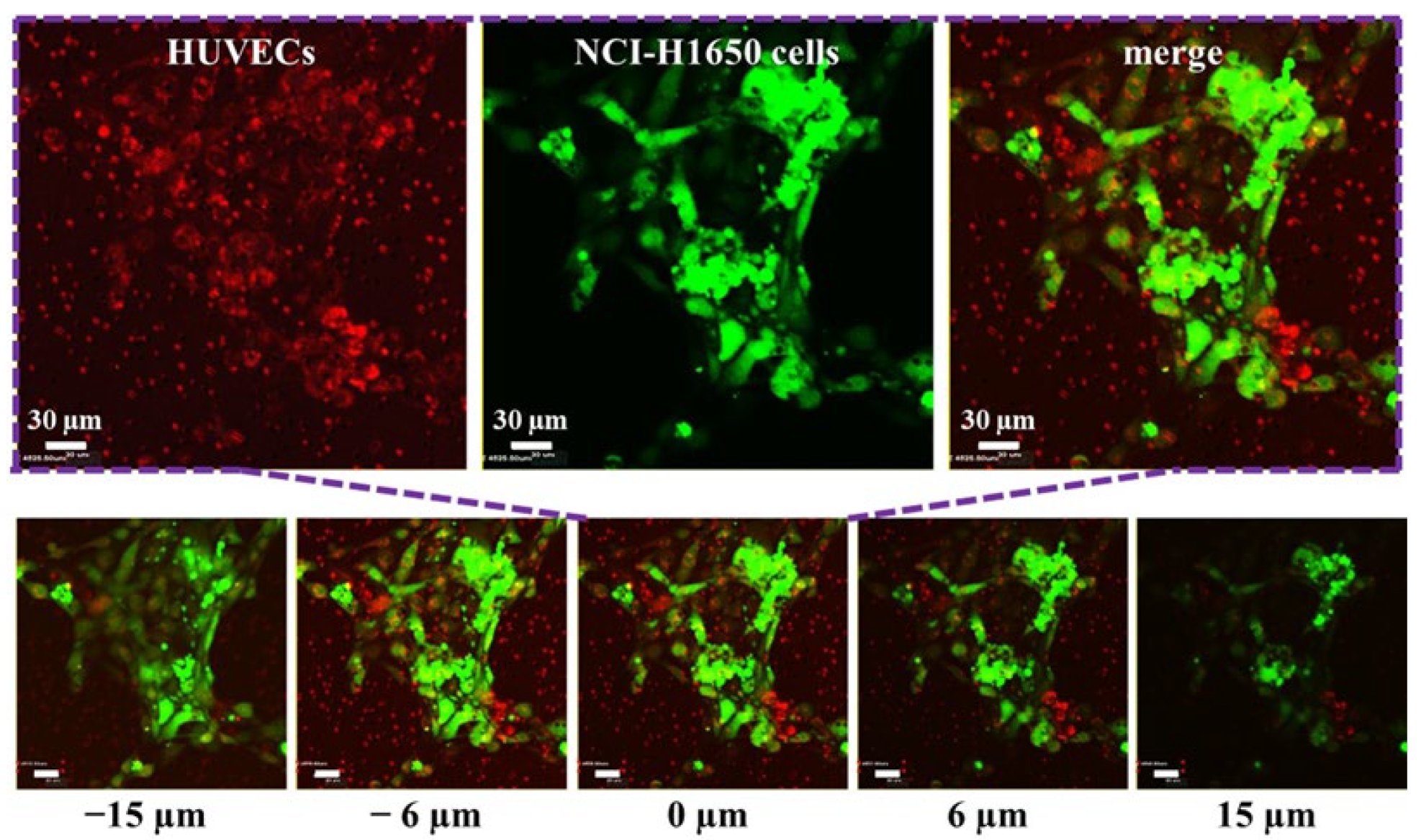
3.3. Stratified Co-Culture of HUVEC and NCI-H1650 Cells
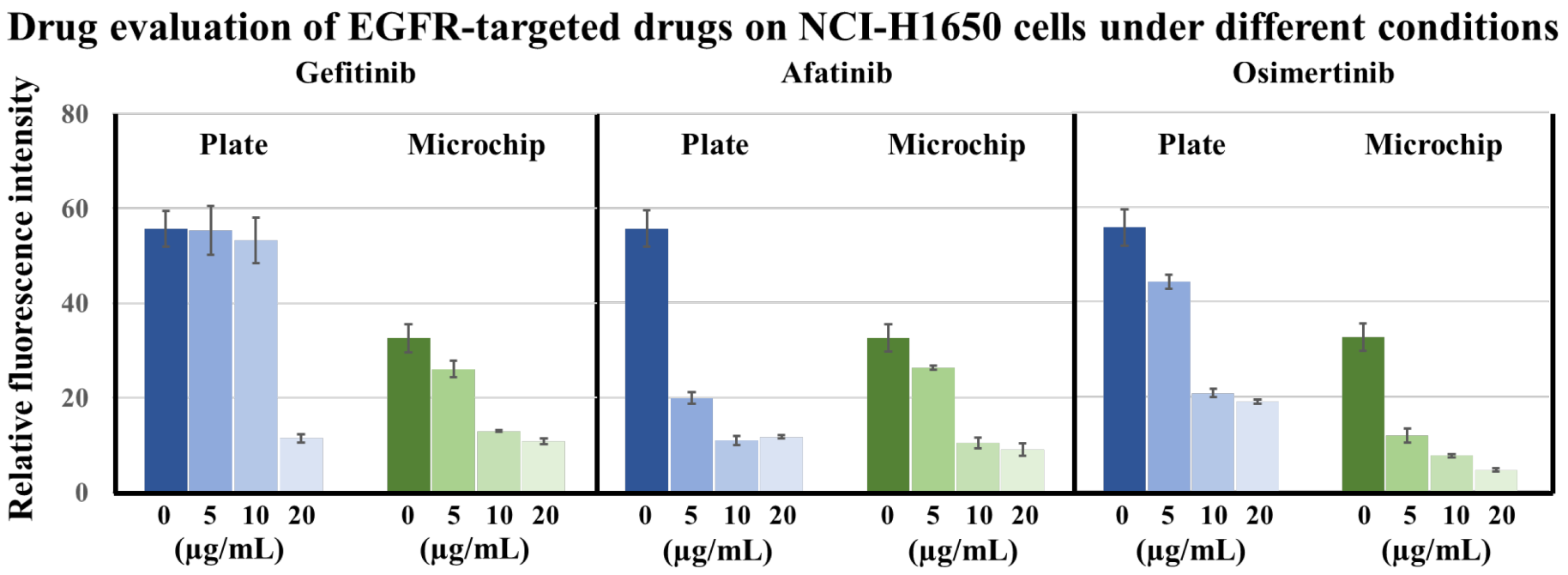
3.4. Evaluation of EGFR-Targeted Drugs for NCI-H1650 Cell
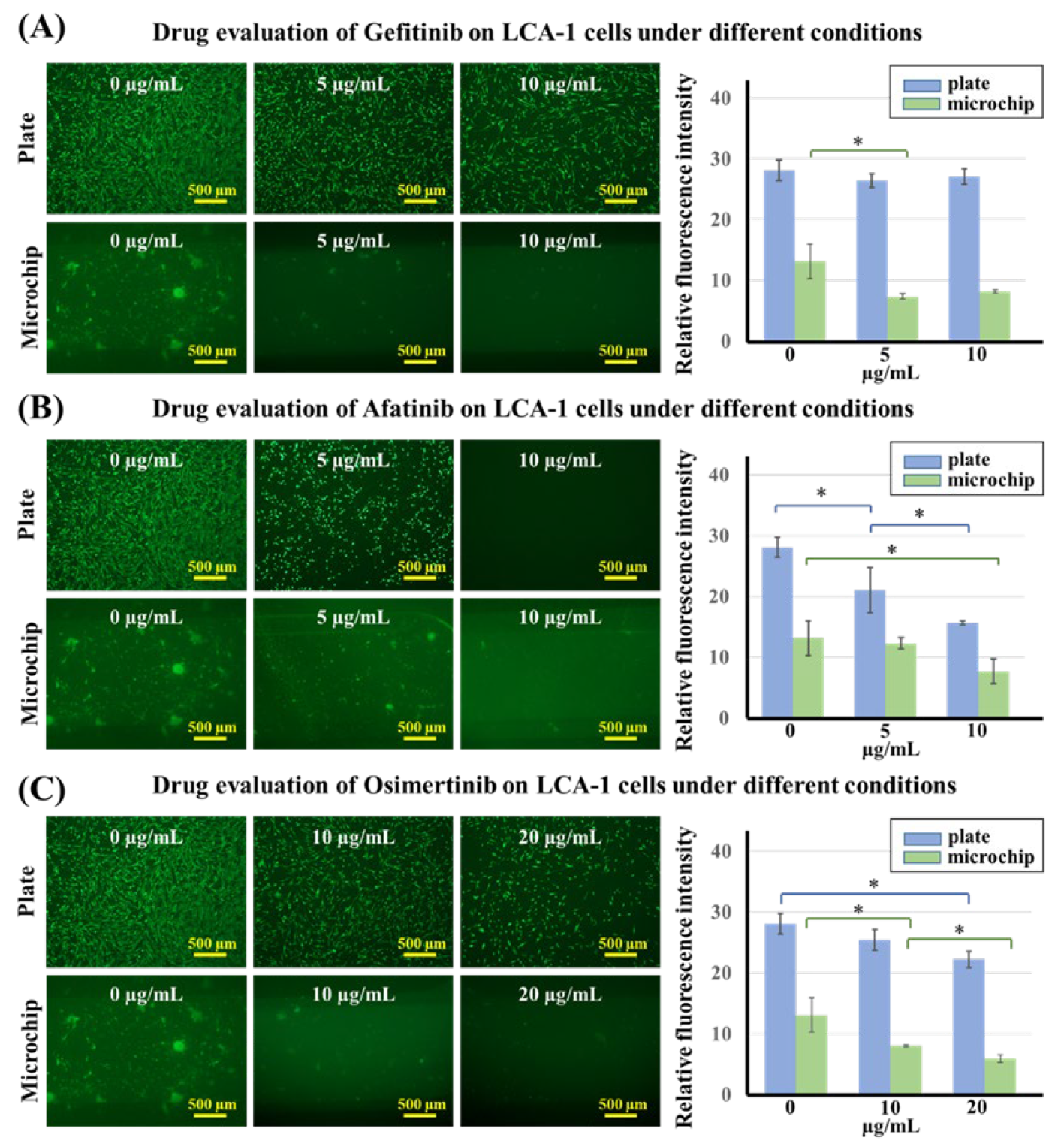
3.5. Evaluation of EGFR-Targeted Drugs for Primary Lung Cancer Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: Globocan Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; Yang, S.; Li, N.; Wu, G.; Liu, W.; Liao, G.; Cai, K.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of EGFR Mutations in Asian Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer of Adenocarcinoma Histology—Mainland China Subset Analysis of the PIONEER study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Thongprasert, S.; Yang, C.H.; Chu, D.T.; Saijo, N.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Han, B.; Margono, B.; Ichinose, Y.; et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Tan, E.; O’Byrne, K.; Zhang, L.; Boyer, M.; Mok, T.; Hirsh, V.; Yang, J.C.; Lee, K.H.; Lu, S.; et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): A phase 2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; He, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, B.; Liu, C.; Walding, A.; Saggese, M.; Huang, X.; et al. Osimertinib Versus Comparator EGFR TKI as First-Line Treatment for EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC:FLAURA China, A Randomized Study. Targ. Oncol. 2021, 16, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappa, C.; Mousa, S.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Current treatment and future advances. Transl. Lung Cancer R. 2016, 5, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassell, B.A.; Goyal, G.; Lee, E.; Sontheimer-Phelps, A.; Levy, O.; Chen, C.S.; Ingber, D.E. Human Organ Chip Models Recapitulate Orthotopic Lung Cancer Growth, Therapeutic Responses, and Tumor Dormancy In Vitro. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Hao, Y.; Li, E.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Q. Application of a microfluidic chip-based 3D co-culture to test drug sensitivity for individualized treatment of lung cancer. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4109–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Knoblich, J.A. Organogenesis in a dish: Modeling development and disease using organoid technologies. Science 2014, 345, 1247125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeck, H. Modeling human lung development and disease using pluripotent stem cells. Development 2015, 142, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, S.; Lee, S.; Park, J.Y.; Jeon, J.S.; Cho, Y.; Kim, S. Potential of Drug Efficacy Evaluation in Lung and Kidney Cancer Models Using Organ-on-a-Chip Technology. Micromachines 2021, 12, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizgolshani, H.; Coppeta, J.R.; Vedula, E.M.; Marr, E.E.; Cain, B.P.; Luu, R.J.; Lech, M.P.; Kann, S.H.; Mulhern, T.J.; Tandon, V.; et al. High-throughput organ-on-chip platform with integrated programmable fluid flow and real-time sensing for complex tissue models in drug development workflows. Lab. Chip. 2021, 21, 1454–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, F.R.; Valkai, S.; Kincses, A.; Petneházi, A.; Czeller, T.; Veszelka, S.; Ormos, P.; Deli, M.A.; Dér, A. A versatile lab-on-a-chip tool for modeling biological barriers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, P.; Luo, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, M.; Tao, T.; Chen, W.; et al. Biomimetic Human Disease Model of SARS-CoV-2-Induced Lung Injury and Immune Responses on Organ Chip System. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, T.; Kim, S.; You, S.; Jung, Y. Three-Dimensional Vascularized Lung Cancer-on-a-Chip with Lung Extracellular Matrix Hydrogels for In Vitro Screening. Cancers 2021, 13, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, Â.; Ferreira, G.; Seixas, D.; Guimarães-Teixeira, C.; Henrique, R.; Monteiro, F.J.; Jerónimo, C. Emerging Lab-on-a-Chip Approaches for Liquid Biopsy in Lung Cancer: Status in CTCs and ctDNA Research and Clinical Validation. Cancers 2021, 13, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawroth, J.C.; Lucchesi, C.; Cheng, D.; Shukla, A.; Ngyuen, J.; Shroff, T.; Varone, A.; Karalis, K.; Lee, H.; Alves, S.; et al. A Microengineered Airway Lung Chip Models Key Features of Viral-induced Exacerbation of Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 63, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, J.; Razavi, B.S.; Aboulkheyr, E.H.; Yaghobian, A.D.; Thierry, B.; Ebrahimi, W.M.; Ghadiri, M. Lung-on-a-chip: The future of respiratory disease models and pharmacological studies. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yang, X.; Xue, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X. Biomimetic human lung-on-a-chip for modeling disease investigation. Biomicrofluidics 2019, 13, 31501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Barrile, R.; van der Meer, A.D.; Mammoto, A.; Mammoto, T.; De Ceunynck, K.; Aisiku, O.; Otieno, M.A.; Louden, C.S.; Hamilton, G.A.; et al. Primary Human Lung Alveolus-on-a-chip Model of Intravascular Thrombosis for Assessment of Therapeutics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 103, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulholland, T.; McAllister, M.; Patek, S.; Flint, D.; Underwood, M.; Sim, A.; Edwards, J.; Zagnoni, M. Drug screening of biopsy-derived spheroids using a self-generated microfluidic concentration gradient. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huh, D.; Matthews, B.D.; Mammoto, A.; Montoya-Zavala, M.; Hsin, H.Y.; Ingber, D.E. Reconstituting Organ-Level Lung Functions on a Chip. Science 2010, 328, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huh, D.; Leslie, D.C.; Matthews, B.D.; Fraser, J.P.; Jurek, S.; Hamilton, G.A.; Thorneloe, K.S.; McAlexander, M.A.; Ingber, D.E. A Human Disease Model of Drug Toxicity–Induced Pulmonary Edema in a Lung-on-a-Chip Microdevice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 147r–159r. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Sun, X.; Ji, B.; Yang, X.; Zhou, B.; Lu, Z.; Gao, X. PLGA Nanofiber/PDMS Microporous Composite Membrane-Sandwiched Microchip for Drug Testing. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamprogno, P.; Wuthrich, S.; Achenbach, S.; Thoma, G.; Stucki, J.D.; Hobi, N.; Schneider-Daum, N.; Lehr, C.M.; Huwer, H.; Geiser, T.; et al. Second-generation lung-on-a-chip with an array of stretchable alveoli made with a biological membrane. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Guo, B.; Wen, W.; Gao, X. Nanofiber membrane supported lung-on-a-chip microdevice for anti-cancer drug testing. Lab. Chip. 2018, 18, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Kuang, J.; Xu, L.; Gao, X.; Zhou, C. Exploratory Evaluation of EGFR-Targeted Anti-Tumor Drugs for Lung Cancer Based on Lung-on-a-Chip. Biosensors 2022, 12, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080618
Tan J, Sun X, Zhang J, Li H, Kuang J, Xu L, Gao X, Zhou C. Exploratory Evaluation of EGFR-Targeted Anti-Tumor Drugs for Lung Cancer Based on Lung-on-a-Chip. Biosensors. 2022; 12(8):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080618
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Jianfeng, Xindi Sun, Jianhua Zhang, Huili Li, Jun Kuang, Lulu Xu, Xinghua Gao, and Chengbin Zhou. 2022. "Exploratory Evaluation of EGFR-Targeted Anti-Tumor Drugs for Lung Cancer Based on Lung-on-a-Chip" Biosensors 12, no. 8: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080618
APA StyleTan, J., Sun, X., Zhang, J., Li, H., Kuang, J., Xu, L., Gao, X., & Zhou, C. (2022). Exploratory Evaluation of EGFR-Targeted Anti-Tumor Drugs for Lung Cancer Based on Lung-on-a-Chip. Biosensors, 12(8), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080618





