Nanobioengineered Sensing Technologies Based on Cellulose Matrices for Detection of Small Molecules, Macromolecules, and Cells
Abstract
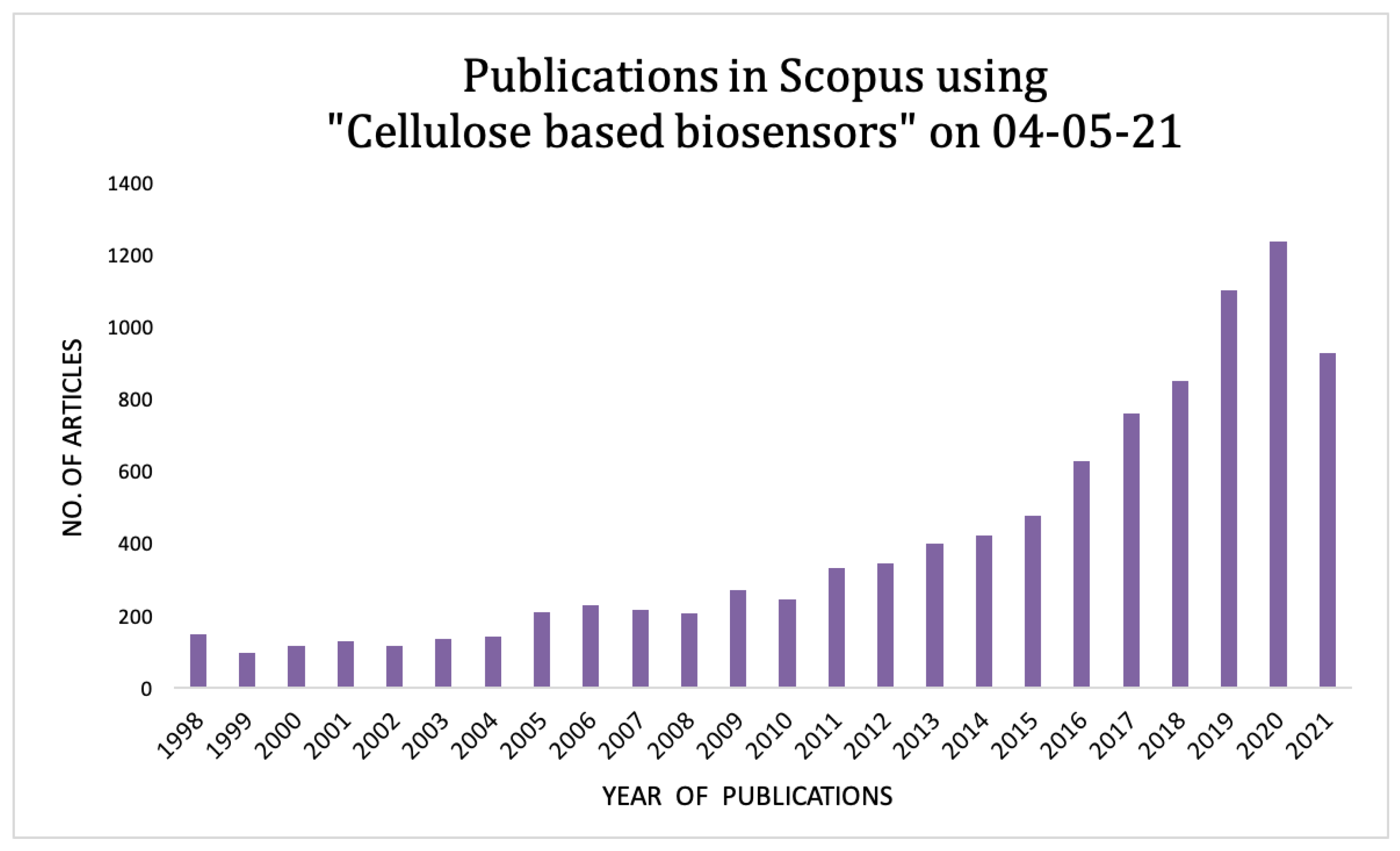
1. Introduction
2. Cellulose: Structure and Biosensing Design Aspects
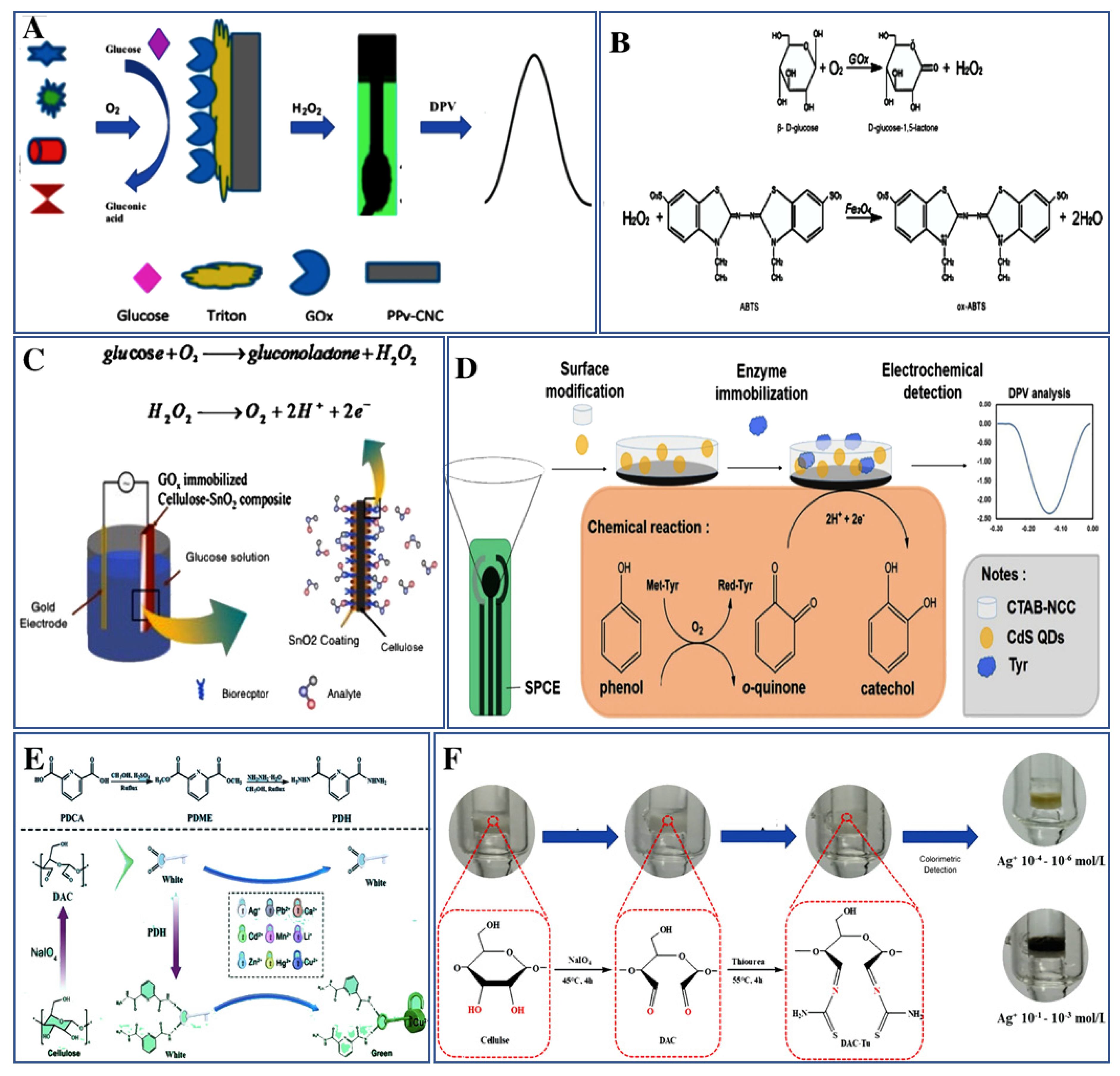
3. Biosensors for the Detection of Small Molecules and Metals
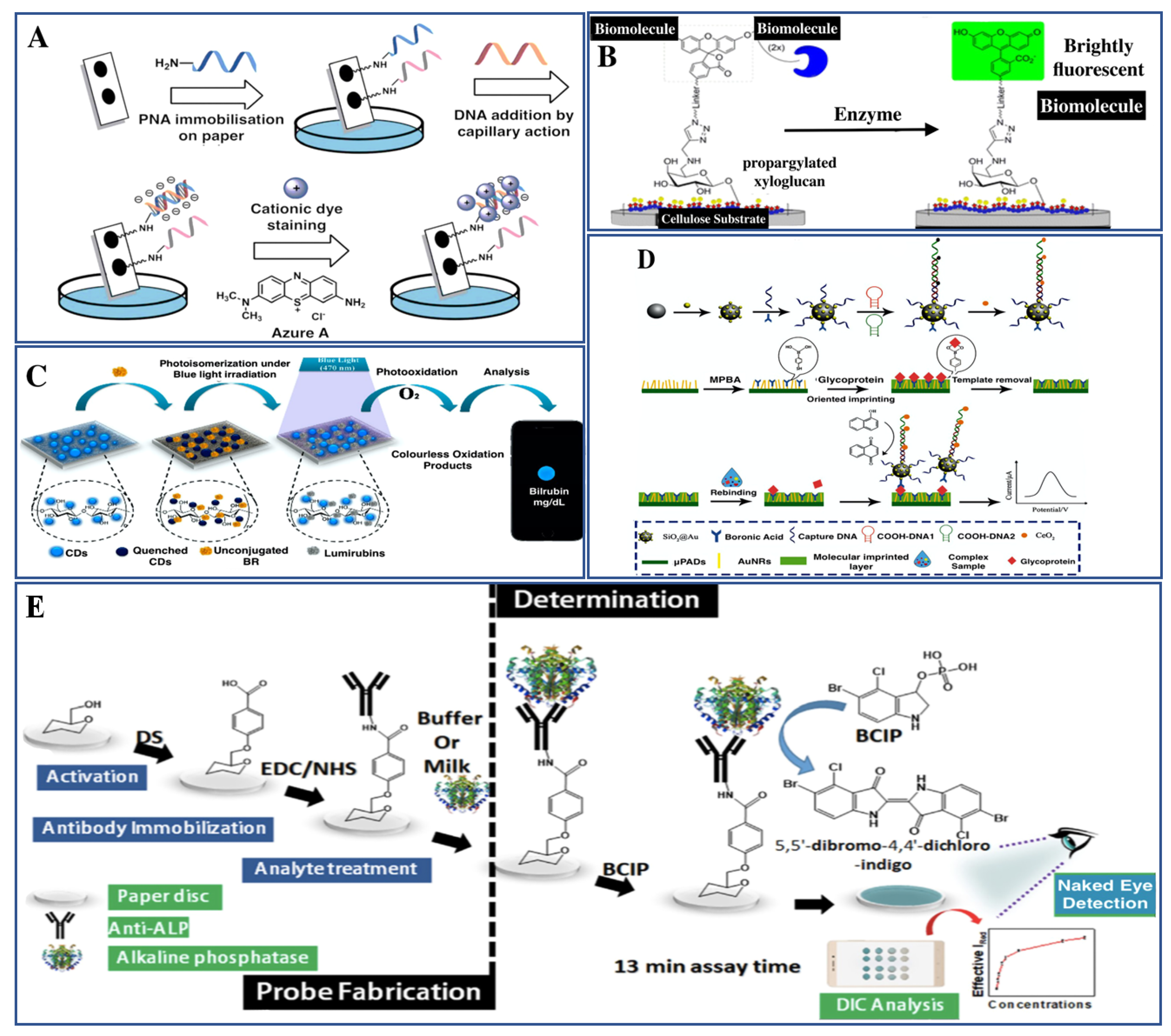
4. Biosensors for Detection of Macromolecules
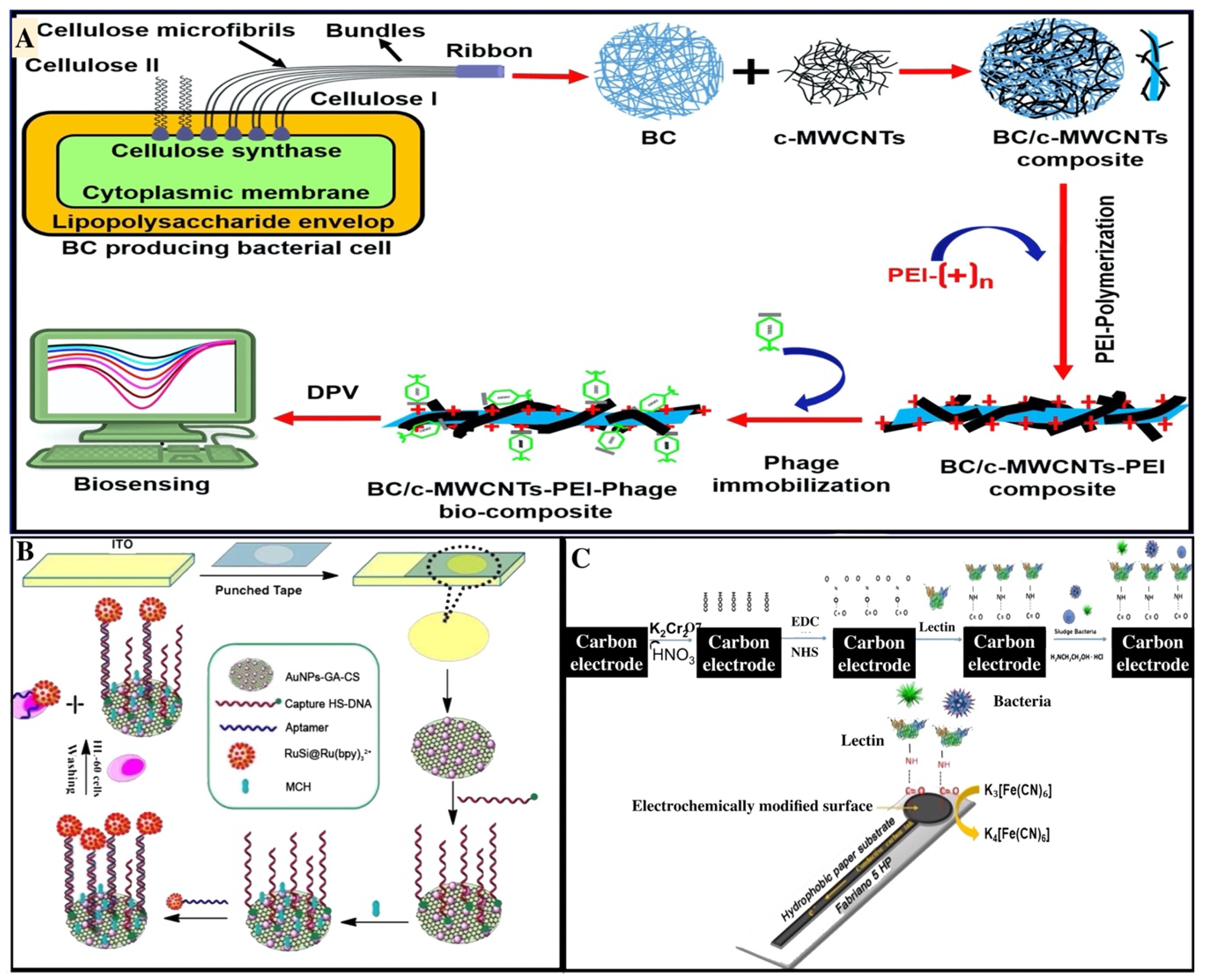
5. Biosensors for Detection of Cells
6. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hallac, B.B.; Ragauskas, A.J. Analyzing cellulose degree of polymerization and its relevancy to cellulosic ethanol. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2011, 5, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Bashline, L.; Lei, L.; Gu, Y. Cellulose synthesis and its regulation. Arab. Book 2014, 12, e0169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, S.S.; Mohammadi, K.; Ji, K.S. Characterization of cellulose synthesis in plant cells. Sci. World J. 2016, 2016, 8641373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangaswamy, B.E.; Vanitha, K.P.; Hungund, B.S. Microbial cellulose production from bacteria isolated from rotten fruit. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 280784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghozali, M.; Meliana, Y.; Chalid, M. Synthesis and characterization of bacterial cellulose by Acetobacter xylinum using liquid tapioca waste. Mater. Today 2021, 44, 2131–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Shen, J.; Li, L. Characterization of cellulose synthase complexes in Populus xylem differentiation. New Phytol. 2010, 187, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Narváez, E.; Golmohammadi, H.; Naghdi, T.; Yousefi, H.; Kostiv, U.; Horak, D.; Pourreza, N.; Merkoçi, A. Nanopaper as an optical sensing platform. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7296–7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, S.; Khattab, A.T. Recent advances in cellulose-based biosensors for medical diagnosis. Biosensors 2020, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, K.; Stobiecka, M. High-performance modified cellulose paper-based biosensors for medical diagnostics and early cancer screening: A concise review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, S.; Li, T.; Jin, S.; Shao, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, D.; Dai, S.; Lu, Y.; Chen, S.; et al. Flexible capacitive humidity sensors based on ionic conductive wood-derived cellulose nanopapers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 41896–41904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, S.; Ali, N.; Jahangir, K.; Shah, S.M.; El-Gendy, A.A. Pharmaceutical significance of cellulose: A review. Express Polym. Lett. 2008, 2, 758–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, D.; Kulkarni, P.; Dixit, M.; Raavi, P.K.; Krishna, L.N.V. Sources of cellulose and their applications—A review. Int. J. Drug Formul. Res. 2011, 2, 19–38. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.-J.; Yu, S.J.; Yang, K.; Jin, Y.; Cho, A.-N.; Kim, J.; Lee, B.; Yang, H.S.; Im, S.G.; Cho, S.-W. Based bioactive scaffolds for stem cell-mediated bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9811–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.Y.; Goh, B.T.; Khor, S.M. Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for potential use in quantitative and direct detection of disease biomarkers in clinical analysis. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1060, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prathapan, R.; McLiesh, H.; Garnier, G.; Tabor, R.F. Surface engineering of transparent cellulose nanocrystal coatings for biomedical applications. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Yin, X.; Jin, D.; Zhang, B.; Gu, Y.; An, Y. Paper-based immunosensors: Current trends in the types and applied detection techniques. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopakumar, D.A.; Thomas, S.; Owolabi, F.; Thomas, S.; Nzihou, A.; Rizal, S.; Khalil, H.A. Nanocellulose based aerogels for varying engineering applications. Encycl. Renew. Sustain. Mater. 2020, 2, 155–165. [Google Scholar]
- Tortorella, S.; Buratti, V.V.; Maturi, M.; Sambri, L.; Franchini, M.C.; Locatelli, E. Surface-modified nanocellulose for application in biomedical engineering and nanomedicine: A review. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Kramer, F.; Moritz, S.; Lindstrom, T.; Ankerfors, M.; Gray, D.; Dorris, A. Nanocelluloses: A new family of nature-based materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 5438–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, R.J.; Martini, A.; Nairn, J.; Simonsen, J.; Youngblood, J. Cellulose nanomaterials review: Structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3941–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuek Lawrence, C.S.; Tan, S.N.; Floresca, C.Z. A “green” cellulose paper based glucose amperometric biosensor. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 193, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, W.; Chen, W.; Wu, Y.; Yu, H. Cellulose-based flexible functional materials for emerging intelligent electronics. Adv. Mater. 2020, 2000619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, Y.; Nakaya, M.; Matsui, E.; Hotta, A. Structural and mechanical properties of cellulose composites made of isolated cellulose nanofibers and poly (vinyl alcohol). Compos. Part A 2015, 73, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.G.; Golchinfar, B. Mechanical properties of cellulose nanocrystal (cnc) bundles: Coarse-grained molecular dynamic simulation. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranwal, A.; Mahato, K.; Srivastava, A.; Maurya, P.K.; Chandra, P. Phytofabricated metallic nanoparticles and their clinical applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 105996–106010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, B.; Vernekar, P.R.; Shetti, N.P.; Chandra, P. Biosensor nanoengineering: Design, operation, and implementation for biomolecular analysis. Sens. Int. 2020, 1, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.; Prasad, A.; Maurya, P.; Chandra, P. Nanobiosensors: Next generation point-of-care biomedical devices for personalized diagnosis. J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. 2016, 7, e125. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, P. Advances in clinical diagnosis through electrochemical aptamer sensors. J. Bioanal. Biomed. 2013, 5, e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.; Maurya, P.K.; Chandra, P. Fundamentals and commercial aspects of nanobiosensors in point-of-care clinical diagnostics. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, B.; Kumar, A.; Mahato, K.; Chandra, P. Smartphone-assisted personalized diagnostic devices and wearable sensors. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 13, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P. Miniaturized multiplex electrochemical biosensor in clinical bioanalysis. J. Bioanal. Biomed. 2013, 5, e122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, V.X.T.; Wong, T.I.; Zheng, X.T.; Tan, Y.N.; Zhou, X. Colorimetric biosensors for point-of-care virus detections. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020, 3, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Abas, Z.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J. Recent progress on cellulose-based electro-active paper, its hybrid nanocomposites and applications. Sensors 2016, 16, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.A.; Abbas, M.N.; Singh, B.; Abou-Zeid, R.E.; Kamel, S. Cellulose nanocrystals decorated with gold nanoparticles immobilizing GOx enzyme for non-invasive biosensing of human salivary glucose. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 6073–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Khare, S.K. Immobilization of Aspergillus Niger cellulase on multiwall carbon nanotubes for cellulose hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 252, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Min, D.H. Biosensors based on graphene oxide and its biomedical application. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 105, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Li, C.C.; Zhang, C.Y. Development of quantum dot-based biosensors: Principles and applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6173–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, P.; Das, D.; Abdelwahab, A.A. Gold nanoparticles in molecular diagnostics and therapeutics. Digest J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2010, 5, 363–367. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, W.C.A.; Chandra, P.; Kim, D.-M.; Shim, Y.-B. Electropolymerized self-assembled layer on gold nanoparticles: Detection of inducible nitric oxide synthase in neuronal cell culture. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6177–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobiecka, M.; Chalupa, A. Modulation of plasmon-enhanced resonance energy transfer to gold nanoparticles by protein survivin channeled-shell gating. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 13227–13235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purohit, B.; Kumar, A.; Mahato, K.; Chandra, P. Electrodeposition of metallic nanostructures for biosensing applications in health care. J. Sci. Res. 2020, 64, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.; Nagpal, S.; Shah, M.A.; Srivastava, A.; Maurya, P.K.; Roy, S.; Jaiswal, A.; Singh, R.; Chandra, P. Gold nanoparticle surface engineering strategies and their applications in biomedicine and diagnostics. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valizadeh, A.; Mikaeili, H.; Samiei, M.; Farkhani, S.M.; Zarghami, N.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Davaran, S. Quantum dots: Synthesis, bioapplications, and toxicity. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Wahid, F.; Santos, H.A.; Khan, T. Advances in biomedical and pharmaceutical applications of functional bacterial cellulose-based nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 330–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, N.O.; Carrilho, E.; Machado, S.A.S.; Sgobbi, L.F. Bacterial cellulose-based electrochemical sensing platform: A smart material for miniaturized biosensors. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 349, 136341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Mahato, K.; Chandra, P.; Srivastava, A.; Joshi, S.N.; Maurya, P.K. Bioinspired composite materials: Applications in diagnostics and therapeutics. J. Mol. Eng. Mater. 2016, 4, 1640004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.; Kumar, A.; Purohit, B.; Mahapatra, S.; Srivastava, A.; Chandra, P. Nanomaterial functionalization strategies in bio-interface development for modern diagnostic devices. In Biointerface Engineering: Prospects in Medical Diagnostics and Drug Delivery; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 195–214. [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadayyala, S.R.; Park, J.; Le, H.T.N.; Santhosh, M.; Kadam, A.N.; Cho, S. Recent advances in microfluidic paper-based electrochemiluminescence analytical devices for point-of-care testing applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyazi, T.; Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Benito-Lopez, F. Review on microfluidic paper-based analytical devices towards commercialisation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1001, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahato, K.; Chandra, P. Paper-based miniaturized immunosensor for naked eye ALP detection based on digital image colorimetry integrated with smartphone. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 128, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Hens, A.; Arun, R.K.; Chatterjee, M.; Mahato, K.; Layek, K.; Chanda, N. A paper based microfluidic device for easy detection of uric acid using positively charged gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2015, 140, 1817–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, A.; Donato, N.; Saitta, G.; Bonavita, A.; Rizzo, G.; Neri, G. Flexible ethanol sensors on glossy paper substrates operating at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B 2010, 145, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Mazzaracchio, V.; Cacciotti, I.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. Carbon black-modified electrodes screen-printed onto paper towel, waxed paper and parafilm M((R)). Sensors 2017, 17, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Kim, J. Conductometric glucose biosensor made with cellulose and tin oxide hybrid nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B 2011, 157, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, C.T.; Torlopov, M.A.; Martakov, I.S.; Vdovichenko, E.A.; Zhukov, M.; Krivoshapkin, P.V.; Mikhaylov, V.I.; Krivoshapkina, E.F. Hybrid cellulose nanocrystal/magnetite glucose biosensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, W. Encapsulation of tyrosinase within liposome bioreactors for developing an amperometric phenolic compounds biosensor. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2013, 17, 2887–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lei, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ju, H. Highly sensitive amperometric biosensors for phenols based on polyaniline-ionic liquid-carbon nanofiber composite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manan, F.A.A.; Hong, W.W.; Abdullah, J.; Yusof, N.A.; Ahmad, I. Nanocrystalline cellulose decorated quantum dots based tyrosinase biosensor for phenol determination. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 99, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Ding, Q.; Zhao, N.; Gao, A.; Jing, Q. Supramolecular self-assembly system based on naphthalimide boric acid ester derivative for detection of organic amine. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 256, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, H.; Zhang, J.; Tian, W.; Jin, K.; Jia, R.; Yang, T.; Zhang, J. Cellulose-based fluorescent sensor for visual and versatile detection of amines and anions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, N.A.; Dawood, M.F.A.; Wardany, A.A. The phyto-impact of fluazinam fungicide on cellular structure, agro-physiological, and yield traits of pepper and eggplant crops. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 18064–18078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hou, J.; Lan, S.; Shen, C.; Huo, D.; Ji, Z.; Ma, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhang, S.; He, Q.; et al. MoS2 QDs-based sensor for measurement of fluazinam with triple signal output. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1108, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Guan, J.; Wei, W.; Zou, L. Label-free amperometric immunosensor based on versatile carbon nanofibers network coupled with au nanoparticles for aflatoxin B1 detection. Biosensors 2020, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Bui, M.P.; Abbas, A. Paper-based chemical and biological sensors: Engineering aspects. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahato, K.; Srivastava, A.; Chandra, P. Paper based diagnostics for personalized health care: Emerging technologies and commercial aspects. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, H.L.; Sarkissian, C.N.; Scriver, C.R. Phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL): From discovery to enzyme substitution therapy for phenylketonuria. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 124, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Qiu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Cui, J.; Jia, S. Paper-based biosensor based on phenylalnine ammonia lyase hybrid nanoflowers for urinary phenylalanine measurement. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, C.; Abdi, M.M.; Mathew, A.P.; Jonoobi, M.; Oksman, K.; Rezayi, M. Synergy effect of nanocrystalline cellulose for the biosensing detection of glucose. Sensors 2015, 15, 24681–24697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.J.; Zhang, L.W.; Liu, R.; Liu, L.; Yao, J.M. Ultra-fast and probe-free cellulose biosensor for visual detection of Cu(2+) ions in biological samples. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; He, H.; Zhu, H.; Guo, W.; Zhou, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.R.; Zhang, J. Cellulose-based colorimetric sensor with N, S sites for Ag(+) detection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.-C.; Wang, B.-B.; Xu, Z.-Q.; He, X.-H.; Zou, H.-F.; Yang, Q.-Q.; Jiang, F.-L.; Liu, Y. A novel method for the detection of silver ions with carbon dots: Excellent selectivity, fast response, low detection limit and good applicability. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 267, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniyal, W.M.E.M.M.; Fen, Y.W.; Anas, N.A.A.; Omar, N.A.S.; Ramdzan, N.S.M.; Nakajima, H.; Mahdi, M.A. Enhancing the sensitivity of a surface plasmon resonance-based optical sensor for zinc ion detection by the modification of a gold thin film. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 41729–41736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wei, L.; Duan, L.; Yang, F.; Huang, G.; Xiao, T.; Wei, M.; Liang, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, Z.; et al. Rapid field testing of mercury pollution by designed fluorescent biosensor and its cells-alginate hydrogel-based paper assay. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 106, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerapandian, M.; Seo, Y.T.; Shin, H.; Yun, K.; Lee, M.H. Functionalized graphene oxide for clinical glucose biosensing in urine and serum samples. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 6123–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, T.J.; Zhang, D.W.; Li, H.Y.; Ma, Y.R.; Qi, L.M.; Zhou, Y.L.; Zhang, X.X. Amperometric hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on the immobilization of heme proteins on gold nanoparticles-bacteria cellulose nanofibers nanocomposite. Talanta 2011, 84, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Basso, M.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. A paper-based nanomodified electrochemical biosensor for ethanol detection in beers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 960, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scognamiglio, V.; Antonacci, A.; Arduini, F.; Moscone, D.; Campos, E.V.R.; Fraceto, L.F.; Palleschi, G. An eco-designed paper-based algal biosensor for nanoformulated herbicide optical detection. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaweera, S.; Yin, K.; Hu, X.; Ng, W.J. Fluorescent N/Al Co-doped carbon dots from cellulose biomass for sensitive detection of manganese (VII). J. Fluoresc. 2019, 29, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, P.; Yao, Y.; Li, D.; Zhou, H.; Naeem, M.A.; Feng, Q.; Huang, J.; Cai, Y.; Wei, Q. Self-assembly of nitrogen-doped carbon dots anchored on bacterial cellulose and their application in iron ion detection. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 172, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagkaris, A.S.; Pulkrabova, J.; Hajslova, J.; Filippini, D. A hybrid lab-on-a-chip injector system for autonomous carbofuran screening. Sensors 2019, 19, 5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Moghazy, A.Y.; Amaly, N.; Istamboulie, G.; Nitin, N.; Sun, G. A signal-on electrochemical aptasensor based on silanized cellulose nanofibers for rapid point-of-use detection of ochratoxin A. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirakittiwut, N.; Panyain, N.; Nuanyai, T.; Vilaivan, T.; Praneenararat, T. Pyrrolidinyl peptide nucleic acids immobilised on cellulose paper as a DNA sensor. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24110–24114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, J.; Durgalakshmi, D.; Rakkesh, R.A.; Balakumar, S.; Rajendran, S.; Karimi-Maleh, H. Facile synthesis of paper based graphene electrodes for point of care devices: A double stranded DNA (dsDNA) biosensor. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2020, 566, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Li, F. Equipment-free and visualized biosensor for transcription factor rapid assay based on dopamine-functionalized cellulose paper. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 5461–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.B.; Kohler, J.J. Regulation of intracellular signaling by extracellular glycan remodeling. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010, 5, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Jian, Y.; Wang, H.; Ge, S.; Yan, M.; Yu, J. Ultrasensitive microfluidic paper-based electrochemical biosensor based on molecularly imprinted film and boronate affinity sandwich assay for glycoprotein detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 16198–16206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaee, R.S.; Golmohammadi, H.; Ahmadi, S.H. Easy diagnosis of jaundice: A smartphone-based nanosensor bioplatform using photoluminescent bacterial nanopaper for point-of-care diagnosis of hyperbilirubinemia. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, A.; Michelini, E.; Zangheri, M.; Di Fusco, M.; Calabria, D.; Simoni, P. Smartphone-based biosensors: A critical review and perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derikvand, F.; Yin, D.T.; Barrett, R.; Brumer, H. Cellulose-based biosensors for esterase detection. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2989–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Z.; Xu, F.; Edwards, J.V.; Prevost, N.T.; Nam, S.; Condon, B.D.; French, A.D. Nanocellulose as a colorimetric biosensor for effective and facile detection of human neutrophil elastase. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 216, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, M.; Sweeney, R.E.; Hamilton, T.A.; Lockridge, O.; Duysen, E.G.; Purcell, A.L.; Deshpande, S.S. Role of acetylcholinesterase on the structure and function of cholinergic synapses: Insights gained from studies on knockout mice. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 31, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Guo, W.; Zhu, H.; He, H.; Wang, S. Preparation and properties of a dual-function cellulose nanofiber-based bionic biosensor for detecting silver ions and acetylcholinesterase. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moccia, M.; Caratelli, V.; Cinti, S.; Pede, B.; Avitabile, C.; Saviano, M.; Imbriani, A.L.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. Paper-based electrochemical peptide nucleic acid (PNA) biosensor for detection of miRNA-492: A pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma biomarker. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Jian, Y.; Lan, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. Ultrasensitive microfluidic paper-based electrochemical/visual biosensor based on spherical-like cerium dioxide catalyst for miR-21 detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 105, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrover-Jaume, C.; Alba-Patino, A.; Clemente, A.; Santopolo, G.; Vaquer, A.; Russell, S.M.; Baron, E.; Gonzalez Del Campo, M.D.M.; Ferrer, J.M.; Berman-Riu, M.; et al. Paper biosensors for detecting elevated IL-6 levels in blood and respiratory samples from COVID-19 patients. Sens. Actuators B 2021, 330, 129333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbakan, B.; Kemal Sezginturk, M. An impedimetric biosensor system based on disposable graphite paper electrodes: Detection of ST2 as a potential biomarker for cardiovascular disease in human serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1144, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Ahmed, S.R.; Neethirajan, S. A nanocomposite-based biosensor for bovine haptoglobin on a 3D paper-based analytical device. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 265, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennekinne, J.A.; De Buyser, M.L.; Dragacci, S. Staphylococcus aureus and its food poisoning toxins: Characterization and outbreak investigation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 815–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.; Sarker, M.R.; Hossain, A. Microbiological food safety: A dilemma of developing societies. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 40, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Ullah, M.W.; Yang, Q.; Aziz, A.; Xu, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S. High-density phage particles immobilization in surface-modified bacterial cellulose for ultra-sensitive and selective electrochemical detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 157, 112163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bintsis, T. Foodborne pathogens. AIMS Microbiol. 2017, 3, 529–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Liu, H.; Liao, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhou, X.; Xing, D. Multiplex detection and genotyping of pathogenic bacteria on paper-based biosensor with a novel universal primer mediated asymmetric PCR. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.-M.; Jeong, K.-B.; Luo, K.; Park, J.-S.; Park, J.-W.; Kim, Y.-R. Paper-based colorimetric detection of pathogenic bacteria in food through magnetic separation and enzyme-mediated signal amplification on paper disc. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1151, 338252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xiao, W.; Xu, T.; Chen, H.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Q.; Tang, Y. Miniaturized paper-based smartphone biosensor for differential diagnosis of wild-type pseudorabies virus infection versus vaccination immunization. Sens. Actuators B 2021, 327, 128893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P. Electrochemical nanobiosensors for cancer diagnosis. J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. 2015, 6, e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.; Noh, H.-B.; Shim, Y.-B. Cancer cell detection based on the interaction between an anticancer drug and cell membrane components. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 1900–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, P.; Suman, P.; Mukherjee, M.; Kumar, P. HER2 protein biomarker based sensor systems for breast cancer diagnosis. J. Mol. Biomark. Diagn. 2013, 5, e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chandra, P.; Shim, Y.-B. Ultrasensitive and selective electrochemical diagnosis of breast cancer based on hydrazine-AuNP-aptamer bioconjugate. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purohit, B.; Kumar, A.; Mahato, K.; Roy, S.; Chandra, P. Cancer cytosensing approaches in miniaturized settings based on advanced nanomaterials and biosensors. In Nanotechnology in Modern Animal Biotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Umar, M.; Saifi, A.; Kumar, S.; Augustine, S.; Srivastava, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Electrochemical paper based cancer biosensor using iron oxide nanoparticles decorated PEDOT:PSS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1056, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Su, M.; Li, L.; Lan, F.; Yang, G.; Ge, S.; Yu, J.; Song, X. Aptamer-based fluorescent and visual biosensor for multiplexed monitoring of cancer cells in microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 229, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.; Zaidi, S.A.; Noh, H.-B.; Shim, Y.-B. Separation and simultaneous detection of anticancer drugs in a microfluidic device with an amperometric biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Shi, S.; Ma, J.; Guo, Y. A paper-based electrochemical immunosensor with reduced graphene oxide/thionine/gold nanoparticles nanocomposites modification for the detection of cancer antigen 125. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 135, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujahid, A.; Dickert, F.L. Blood group typing: From classical strategies to the application of synthetic antibodies generated by molecular imprinting. Sensors 2015, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.-M.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.-Y.; Xu, J.-J. Paper-based electrochemiluminescence biosensor for cancer cell detection. Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 49, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengaraj, S.; Cruz-Izquierdo, Á.; Scott, J.L.; Di Lorenzo, M. Impedimetric paper-based biosensor for the detection of bacterial contamination in water. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 265, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.; Chandra, P. Clinically practiced and commercially viable nanobio engineered analytical methods for COVID-19 diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, P. Miniaturized label-free smartphone assisted electrochemical sensing approach for personalized COVID-19 diagnosis. Sens. Int. 2020, 1, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.; Baranwal, A.; Purohit, B.; Roy, S.; Mahto, S.K.; Chandra, P. Advanced biosensing methodologies for ultrasensitive detection of human coronaviruses. In Diagnostic Strategies for COVID-19 and Other Coronaviruses; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 19–36. [Google Scholar]
- Baranwal, A.; Mahapatra, S.; Purohit, B.; Roy, S.; Chandra, P. Insights into novel coronavirus and COVID-19 outbreak. In Diagnostic Strategies for COVID-19 and Other Coronaviruses; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, P.; Roy, S. Diagnostic Strategies for COVID-19 and Other Coronaviruses; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yakoh, A.; Pimpitak, U.; Rengpipat, S.; Hirankarn, N.; Chailapakul, O.; Chaiyo, S. Paper-based electrochemical biosensor for diagnosing COVID-19: Detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 176, 112912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, C. A novel paper-based microfluidic enhanced chemiluminescence biosensor for facile, reliable and highly-sensitive gene detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 209, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teengam, P.; Siangproh, W.; Tuantranont, A.; Henry, C.S.; Vilaivan, T.; Chailapakul, O. Electrochemical paper-based peptide nucleic acid biosensor for detecting human papillomavirus. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 952, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sr. No | Analyte | Detection | Sensor Configuration | Response Time | Real Sample | Detection Range | Limit of Detection | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Glucose | Amperometric, CV | GOx immobilized on cellulose paper | NR | Soda beverages | 1 to 5 mM | 0.18 mM | [21] |
| 2 | Glucose | Conductometric | GOx immobilized on nanocomposite of cellulose–tin oxide | NR | NR | 0.5 to 12 mM | NR | [54] |
| 3 | Glucose | Colorimetric | Sulphated and non-sulfated cellulose nanocrystal/magnetite film | NR | Sweat and saliva | low as 5 mM | NR | [55] |
| 4 | Glucose | Voltammetric | Polypyrrole-cellulose nanocrystal-based composites with GOx | NR | NR | 1.0 to 20 mM | (50 ± 10) μM | [68] |
| 5 | Glucose | Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) | Ag@ SiO2-PEG metalloid polymer nanoparticle functionalized with graphene oxide | NR | Urine, Serum | 0.1 to 20 mM | NR | [75] |
| 6 | Phenol | Voltammetric | Nanocrystalline cellulose CdS QDs tyrosine-based biosensor | NR | Water | 5 to 40 μM | 0.082 μM | [58] |
| 7 | Triethylamine | Fluorescence | Cellulose-based Phen-MDI-CA sensor | NR | NR | NR | 0.90 μM | [60] |
| 8 | Ethylenediamine | Fluorescence | Cellulose-based Phen-MDI-CA sensor | NR | NR | NR | 0.99 μM | [60] |
| 9 | Fluazinam | Fluorescence | Disulfide quantum dots (MoS2 QDs) cross-linked into cellulose membrane | NR | Food | 10 to 800 μM | 2.26 μM | [62] |
| 10 | Aflatoxin B1 | Amperometric | Carbon nanofibers derived from BC and coupled with AuNPs | NR | Wheat | 0.05 to 25 ng mL−1 | 0.027 ngmL−1 | [63] |
| 11 | Phenylalanine (Phe) | Colorimetric | Paper-based detection of Phe using phenylalanine ammonia-lyase hybrid nanoflowers | 10 min | Urine | 60 to 2400 μM | NR | [67] |
| 12 | H2O2 | Amperometric | Gold nanoparticles–bacterial cellulose nanofibers (Au–BC)-based sensor | 1 s | Disinfector | 0.3 μM to 1.00 mM | 0.1 μM | [76] |
| 13 | Ethanol | Amperometric | Paper-based sensor modified with CB/PBNPs nanocomposite | NR | Beer | up to 10 mM | 0.52 mM | [77] |
| 14 | Atrazine | Optical | Paper-based algal sensor for nanoencapsulated atrazine | NR | Water | 0.5 to 200 nM | 4 pM | [78] |
| 15 | Cu2+ | Colorimetric | Liquid cellulose biosensor using a facile one-pot process | 10 s | Urine and serum | NR | 1.9309 and 1.9154 ppm | [69] |
| 16 | Ag+ | Colorimetric | Cellulose modified to DAC-Tu biosensor | 10 min | Water | NR | 10−6 mol/L | [70] |
| 17 | Zn2+ | SPR optical | Gold thin film modified with a nanocrystalline cellulose | NR | NR | low as 0.01 ppm | NR | [73] |
| 18 | Hg2+ | Fluorescent | Cells-alginate hydrogel paper-based sensor | 5 min | Wastewater | NR | NR | [74] |
| 19 | Mn7+ | Fluorescence | Nitrogen, aluminium co-doped cellulose-based carbon dots (N/Al-CDs) | NR | Water | 0 to 100 μM | 46.8 nM | [79] |
| 20 | Fe3+ | Fluorescence | Nitrogen-doped carbon dots anchored on BC | 10 min | NR | 0.5 to 600 μM | 84 nM | [80] |
| 21 | Carbonfuran | Colorimetric | Whatman paper used in ULOC device | 3 min | Apple | 0.01–5.00 mg L−1 | 0.05 mg Kg−1 | [81] |
| 22 | Ochratoxin A | CV, EIS | Cellulose nanofibrous matrix labelled with aptamer probe | NR | Coffee | 0.002–2 ng mL−1 | 0.81 pg mL−1 | [82] |
| Sr. No | Analyte | Detection | Sensor Configuration | Response Time | Real Sample | Detection Range | Limit of Detection | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DNA | Colorimetric | Acpc PNA on cellulose paper by DVS conjugation | NR | Human leukocyte antigen alleles | low as 200 nm | NR | [83] |
| 2 | dsDNA | CV, EIS | Paper-based modified electrode sensor | NR | NR | 0.2 pg/mL to 5 pg/mL | 680 fg mL−1 | [84] |
| 3 | miRNA | Voltammetric | PNA-based paper biosensor | <1 h | Serum | up to 100 nm | 6 nm | [94] |
| 4 | miR-21 | Voltammetric | Cerium dioxide—Au@ glucose oxidase paper-based sensor | NR | Serum | 0.001 pm to 1 pm | 0.434 fm | [95] |
| 5 | ALP | Colorimetric | Paper-based naked eye detection | NR | Milk | 10 to 1000 U/mL | 0.87 (±0.07) U/mL | [50] |
| 6 | Esterase | Fluorescence | Chemoenzymatic method used for modification of cellulose matrix | NR | NR | NR | NR | [90] |
| 7 | Transcription factor | Colorimetric | Dopamine coated on the surface of cellulose paper | 20 s | NF-κB p50 in biological fluids | NR | NR | [85] |
| 8 | Glycoprotein | Voltammetric | Paper-based biosensor for glycoprotein based on boronate affinity tag | NR | Ovalbumin | 0.001 ng/mL to 1 μg/mL | 870 fg/mL | [87] |
| 9 | Bilirubin | Photoluminescence | BC nanopaper-based biosensor through embedding of carbon dot sensing probes | NR | Infant’s blood | 2 to 20 mg dL−1 | NR | [88] |
| 10 | Human neutrophil elastase (HNE) | Colorimetric | Immobilizing HNE peptide to the cotton and wood nanocellulose | NR | Chronic wound fluid | Less than 0.005 U/mL | NR | [91] |
| 11 | Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) | Fluorescence | DNA aptamer immobilized on the surface of cellulose nanofiber | NR | NR | NR | NR | [93] |
| 12 | Interleukin-6 | Colorimetric | Paper sensor for IL-6 detection in COVID-19 patients | 10 min | Respiratory | up to 10−1 ng mL−1 | 1 fg mL−1 | [96] |
| 13 | Suppression of Tumorigenicity 2 | CV, EIS | Graphite paper-based disposable sensor through modification of fullerene C60 | NR | Serum | as low as 414 ag mL−1 | 124 ag mL−1 | [97] |
| 14. | Bovine haptoglobin | Colorimetric | AuNP/MWCNT-anti-Hpnanobioconjugate paper-based sensor | NR | Serum | 0.01 to 0.9 mg/mL | 28 μg/mL | [98] |
| Sr. No | Analyte | Detection | Sensor Configuration | Response Time | Real Sample | Detection Range | Limit of Detection | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Staphylococcus aureus | Voltammetric | Immobilization of bacteriophage onto BC | 30 min | Milk, PBS | 5 CFU mL−1, 3 CFU mL−1 | NR | [101] |
| 2 | Staphylococcus aureus | Optical | Paper-based biosensor using a primer-based asymmetric PCR | NR | nuc gene | low as 1 pg/μL | NR | [103] |
| 3 | Listeria monocytogenes | Optical | Paper-based biosensor using a primer-based asymmetric PCR | NR | Hlya gene | low as 1 pg/μL | NR | [103] |
| 4 | Escherichia coli | Optical | Paper-based biosensor using a primer-based asymmetric PCR | NR | rbfE gene | low as 1 pg/μL | NR | [103] |
| 5 | Escherichia coli | Colorimetric | PLL@SMPs-based paper sensor | NR | Food | NR | 30.8 CFU/mL | [104] |
| 6 | Pseudorabies virus | Colorimetric | Latex beads paper-based sensor using PRV gE-mAb | 15 min | Pig serum | NR | NR | [105] |
| 7 | HL-60 cancer cell | Electrochemiluminescence | Ru(bpy)2 3+-conjugated silica nanoparticle-based | NR | NR | 56–5.6 × 106 cells/mL | NR | [116] |
| 8 | SARS-CoV-2 | Voltammetric | Label-free paper-based biosensor | 30 min | Serum | 1 ng/mL | NR | [123] |
| 9 | Listeria monocytogenes | Chemiluminescence | Paper-based sensing device with an immobilized DNA probe | NR | hlyAgene | 0.194 pmol/L to 19.4 × 103 pmol/L | 6.3 × 10−2 pmol/L | [124] |
| 10 | Papillomavirus | Voltammetric | acpcPNA and graphene-polyaniline modified paper-based biosensor | NR | SiHa cells | 10 to 200 nM | 2.3 nM | [125] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Divya; Mahapatra, S.; Srivastava, V.R.; Chandra, P. Nanobioengineered Sensing Technologies Based on Cellulose Matrices for Detection of Small Molecules, Macromolecules, and Cells. Biosensors 2021, 11, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060168
Divya, Mahapatra S, Srivastava VR, Chandra P. Nanobioengineered Sensing Technologies Based on Cellulose Matrices for Detection of Small Molecules, Macromolecules, and Cells. Biosensors. 2021; 11(6):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060168
Chicago/Turabian StyleDivya, Supratim Mahapatra, Vinish Ranjan Srivastava, and Pranjal Chandra. 2021. "Nanobioengineered Sensing Technologies Based on Cellulose Matrices for Detection of Small Molecules, Macromolecules, and Cells" Biosensors 11, no. 6: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060168
APA StyleDivya, Mahapatra, S., Srivastava, V. R., & Chandra, P. (2021). Nanobioengineered Sensing Technologies Based on Cellulose Matrices for Detection of Small Molecules, Macromolecules, and Cells. Biosensors, 11(6), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060168








