Surface Plasmon Resonance Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Film for l-Phenylalanine Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
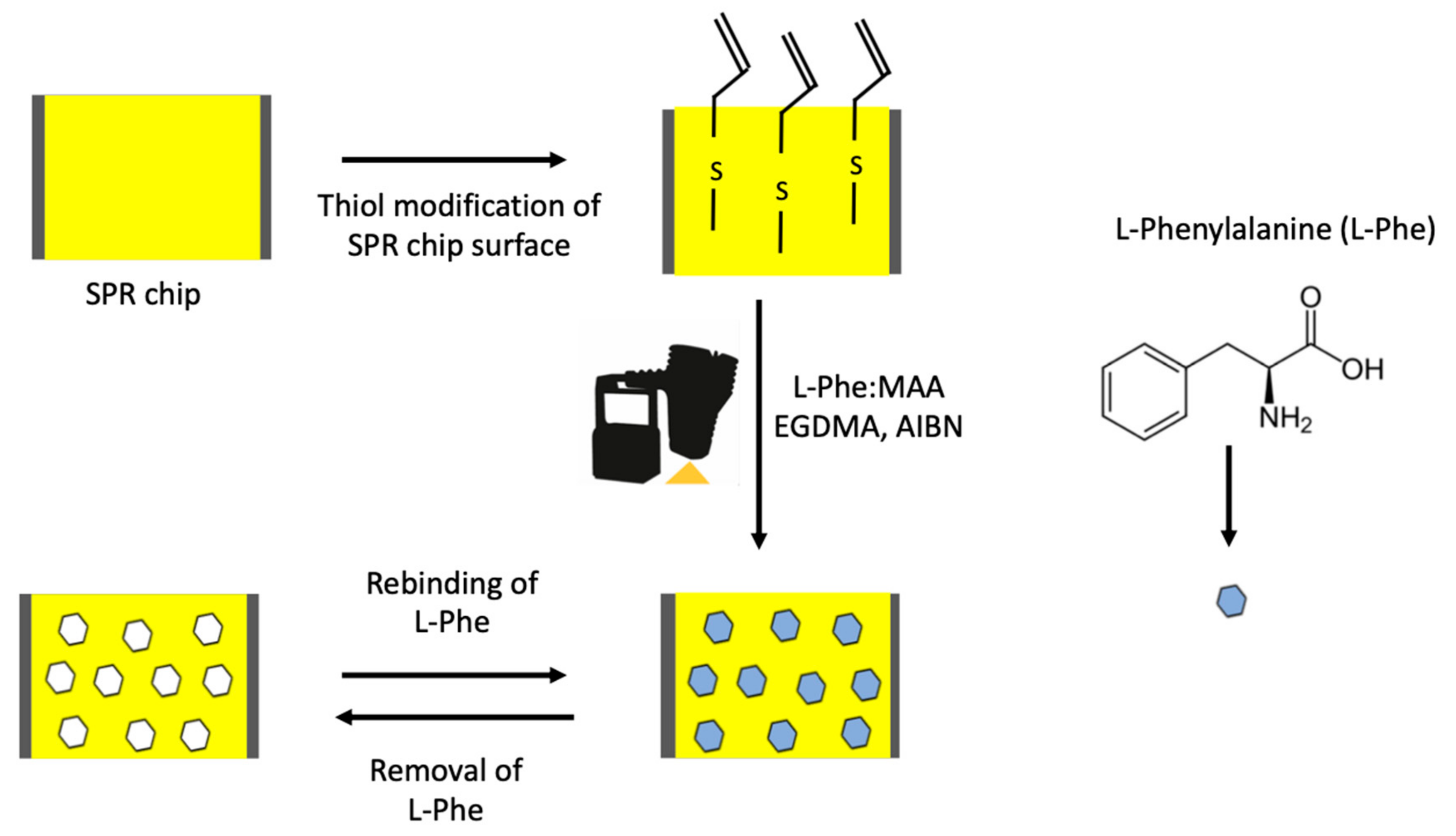
2.2. Preparation of l-Phenylalanine Imprinted and Non-Imprinted SPR Chip
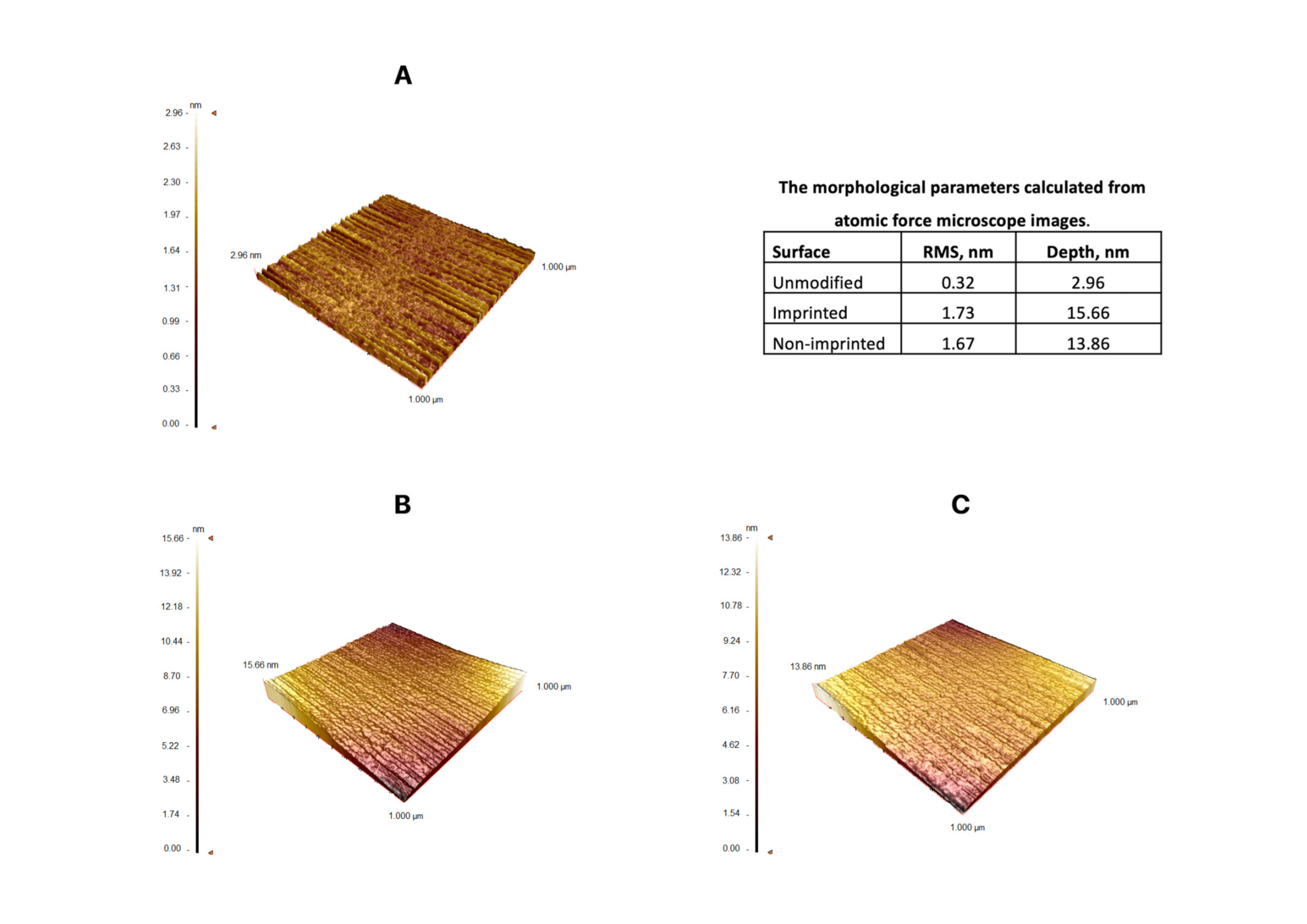
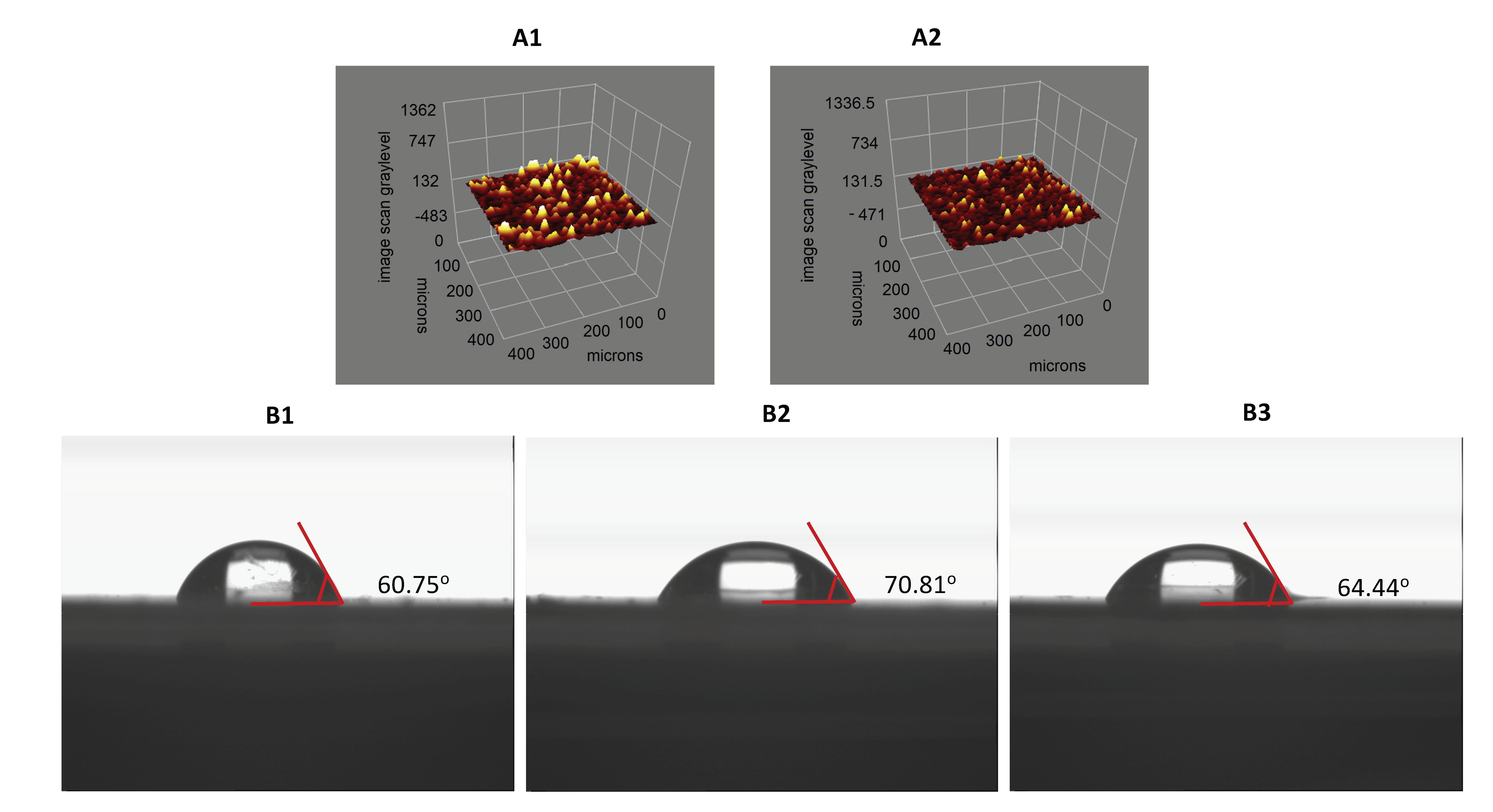
2.3. Characterization Studies
2.4. Kinetic Analysis
2.5. Clinical Analysis
3. Results
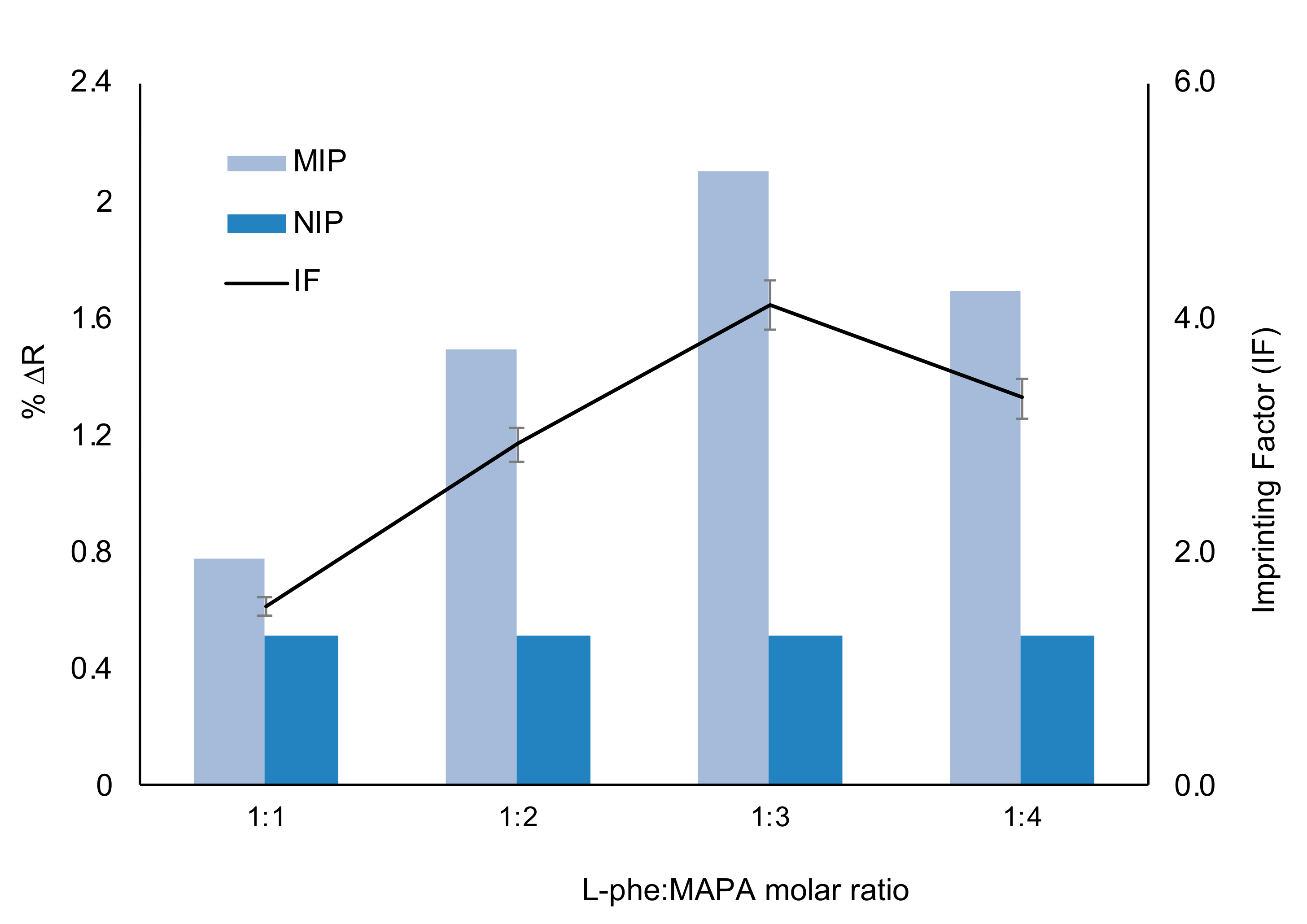
3.1. Characterization Studies
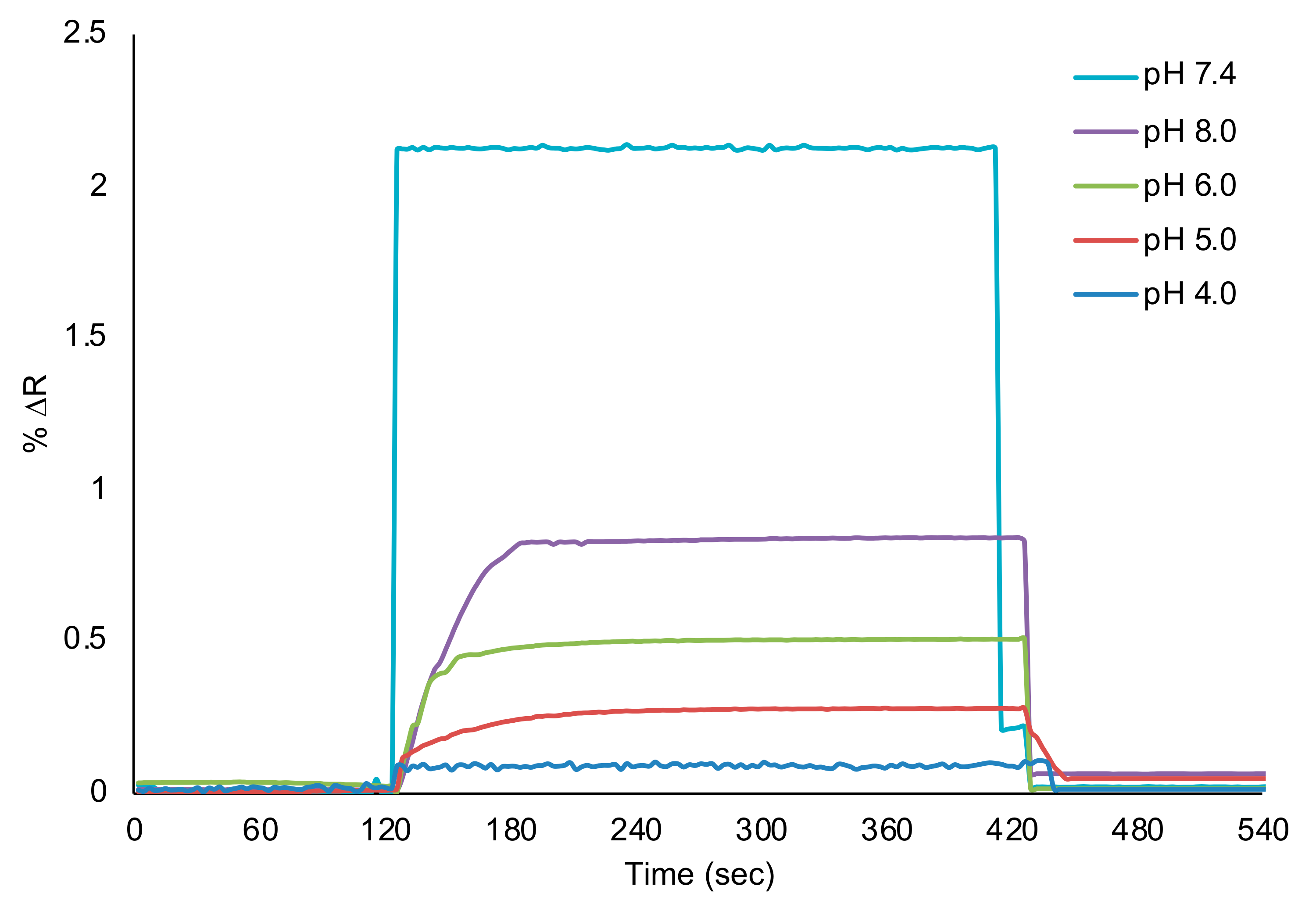
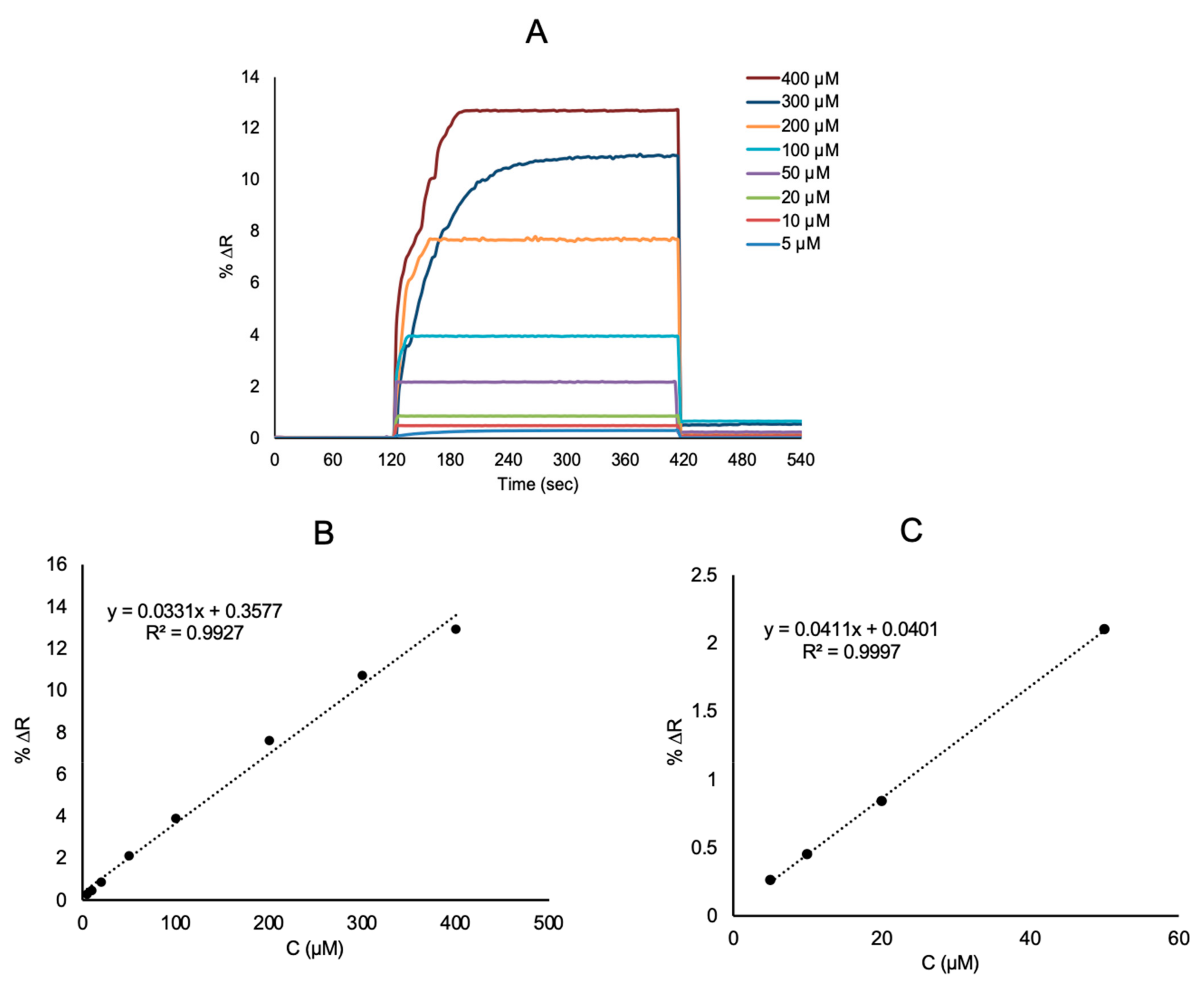
3.2. Real Time Detection of l-Phe with SPR Sensor
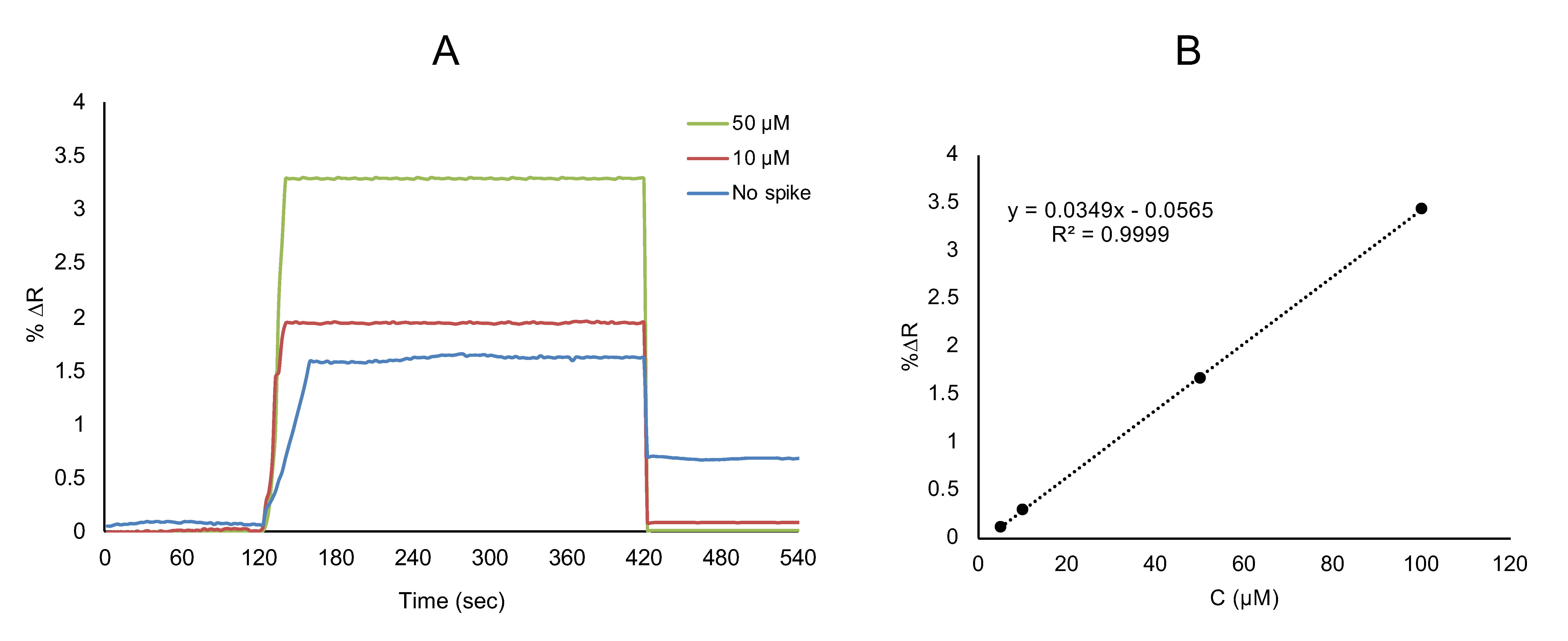
3.3. Clinical Analysis
3.4. Reusability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahalakshmi, R.; Jesuraja, S.X.; Jerome, S. Das Growth and characterization of l-phenylalanine. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2006, 41, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonnesbeck, C.J.; McPheeters, M.L.; Krishnaswami, S.; Lindegren, M.L.; Reimschisel, T. The probability of IQ impairment from blood phenylalanine for phenylketonuria patients: A hierarchical meta-analysis. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2013, 36, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rijn, M.V. Protein metabolism in adult patients with phenylketonuria. Nutrition 2007, 23, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blau, N.; Spronsen, F.J.; Levy, H.L. Phenylketonuria. Lancet 2010, 376, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vockley, J.; Andersson, H.; Antshel, K.; Braverman, N.; Burton, B.; Frazier, D.; Mitchell, J.; Smith, W.; Thompson, B.; Berry, S. Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency: Diagnosis and management guideline. Genet. Med. 2014, 16, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scriver, C.R.; Kaufman, S. Hyperphenylalaninemia. Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. In The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, 8th ed.; Scriver, C.R., Beaudet, A.L., Sly, W.S., Valle, D., Eds.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 1667–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Przyrembel, H.; Bremer, H.J. Nutrition, physical growth, and bone density in treated phenylketonuria. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2000, 159, S129–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilder, D.A.; Burton, B.K.; Coond, H.; Levitonb, L.; Ashworth, J.; Lundy, B.D.; Vespab, H.; Bakiana, A.V.; Longoe, N. Psychiatric symptoms in adults with phenylketonuria. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2013, 108, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Jair, Y.C.; Chou, Y.C.; Chen, P.S.; Yeh, Y.C. Transcription factor-based biosensor for detection of phenylalanine and tyrosine in urine for diagnosis of phenylketonuria. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1041, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idili, A.; Parolo, C.; Ortega, G.; Plaxco, K.W. Calibration-Free Measurement of Phenylalanine Levels in the Blood Using an Electrochemical Aptamer-Based Sensor Suitable for Point-of-Care Applications. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 3227–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermiş, N.; Uzun, L.; Denizli, A. Preparation of molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for l-phenylalanine detection and its application. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 807, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambruschini, N.; Pérez-Dueñas, B.; Vilaseca, M.A.; Mas, A.; Artuch, R.; Gassió, R.; Gómez, L.; Gutiérrez, A.; Campistol, J. Clinical and nutritional evaluation of phenylketonuric patients on tetrahydrobiopterin monotherapy. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2005, 86, S54–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceglarek, U.; Müller, P.; Stach, B.; Bührdel, P.; Thiery, J.; Kiess, W. Validation of the phenylalanine/tyrosine ratio determined by tandem mass spectrometry: Sensitive newborn screening for phenylketonuria. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2002, 40, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peat, J.; Garg, U. Determination of phenylalanine and tyrosine by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1378, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andrensek, S.; Golc-Wondra, A.; Prosek, M. Determination of phenylalanine and tyrosine by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kand’ar, R.; Záková, P. Determination of phenylalanine and tyrosine in plasma and dried blood samples using HPLC with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 3926–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saylan, Y.; Akgönüllü, S.; Yavuz, H.; Ünal, S.; Denizli, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensors for Medical Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 1279. [Google Scholar]
- Justino, C.I.L.; Freitas, A.C.; Pereira, R.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha, S.T.A.P. Recent Developments in Recognition Elements for Chemical Sensors and Biosensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 68, 2–17. [Google Scholar]
- Çimen, D.; Denizli, A. Development of Rapid, Sensitive, and Effective Plasmonic Nanosensor for the Detection of Vitamins in Infact Formula and Milk Samples. Photonic Sens. 2020, 10, 316–332. [Google Scholar]
- Faalnouri, S.; Çimen, D.; Bereli, N.; Denizli, A. Surface Plasmon Resonance Nanosensors for Detecting Amoxicillin in Milk Samples with Amoxicillin Imprinted Poly(hydroxyethylmethacrylate-n-methacryloyl-(l)-glutamicacid). Chemistryselect 2020, 5, 4761–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Akgönüllü, S.; Çimen, D.; Derazshamshir, A.; Bereli, N.; Yılmaz, F.; Denizli, A. Development of surface plasmon resonance sensors based on molecularly imprinted nanofilms for sensitive and selective detection of pesticides. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 241, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilzadeh, M.; Çimen, D.; Özgür, E.; Esen, C.; Denizli, A. Designing and Preparing Imprinted Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Nanosensor for Detection of Zn(II) ions. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2019, 56, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çimen, D.; Bereli, N.; Günaydın, S.; Denizli, A. Detection of cardiac troponin-I by optic biosensors with immobilized anti-cardiac troponin-I monoclonal antibody. Talanta 2020, 219, 121259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertürk, G.; Özen, H.; Tümer, M.A.; Mattiasson, B.; Denizli, A. Microcontact imprinting based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor for real-time and ultrasensitive detection of prostate specific antigen (PSA) from clinical samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 224, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Huang, Y.; Hu, J.; Yuan, C.; Lin, B. Surface Plasmon Resonance Studies on Molecular Imprinting. Sensors 2002, 2, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öncel, Ş.; Uzun, L.; Garipcan, B.; Denizli, A. Synthesis of Phenylalanine-Containing Hydrophobic Beads for Lysozyme Adsorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 7049–7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E.E. Contact angles of rotating sessile droplets. Colloids Surf. A 2013, 432, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, F.; Çimen, D.; Bereli, N.; Denizli, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Quartz Crystal Microbalance Biosensor for the Clinical Detection of Insulin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 111, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payton, B.O.; Champneys, A.R.; Homer, M.E.; Picco, L.; Miles, M.J. Feedback-induced instability in tapping mode atomic force microscopy: Theory and experiment. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 467, 1801–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, E.; Majidi, D.; Ozgur, E.; Denizli, A. Whole cell imprinting based Escherichia coli sensors: A study for SPR and QCM. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 209, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Park, J.; Kang, S.; Kim, M. Surface Plasmon Resonance: A Versatile Technique for Biosensor Applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 10481–10510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X. Modeling of Experimental Adsorption Isotherm Data. Information 2015, 6, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Dai, Z.; Liu, F.; Huang, J. Optical property and adsorption isotherm models of glucose sensitive membrane based on prism SPR sensor. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 237, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Husson, S.M. Adsorption of dansylated amino acids on molecularly imprinted surfaces: A surface plasmon resonance study. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, S.K.; Katsaros, F.K.; Kouvelos, E.P.; Kanellopoulos, N.K. Prediction of binary adsorption isotherms of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ on calcium alginate beads from single adsorption data. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, B.; Uzun, L.; Beşirli, N.; Denizli, A. Microcontact imprinted surface plasmon resonance sensor for myoglobin detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3609–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gao, C.; Guo, C.Y. UV assisted ultrasensitive trace NO2 gas sensing based on few-layer MoS2 nanosheet–ZnO nanowire heterojunctions at room temperature. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 10286–10296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Koshida, T.; Gessei, T.; Miyajima, K.; Takahashi, D.; Kudo, H.; Yano, K.; Mitsubayashi, K. Biosensor for l-phenylalanine based on the optical detection of NADH using a UV light emitting diode. Microchim. Acta 2011, 173, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Luo, L.; Yao, S. Electrochemical determination of L-phenylalanine at polyaniline modified carbon electrode based on cyclodextrin incorporated carbon nanotube composite material and imprinted sol–gel film. Talanta 2011, 84, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Fan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, H.; Yu, J.; Jiang, N.; Zhao, S.; Lai, G.; Yu, A.; Lin, C.; et al. β-Cyclodextrin-Immobilized Ni/Graphene Electrode for Electrochemical Enantiorecognition of Phenylalanine. Materials 2020, 13, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamruzzaman, M.; Alam, A.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, G.; Dang, T.D. Microfluidic chip based chemiluminescence detection of l-phenylalanine in pharmaceutical and soft drinks. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Das, S. Electrochemical detection of l-serine and l-phenylalanine at bamboo charcoal–carbon nanosphere electrode. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2014, 4, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naghib, S.M.; Rabiee, M.; Omidinia, E. Electrochemical Biosensor for l-phenylalanine Based on a Gold Electrode Modified with Graphene Oxide Nanosheets and Chitosan. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, L.W.; Lin, Y.H.; Guo, J.Y.; Chen, C.F.; Chou, Y.J.; Yeh, Y.C. Simultaneous Determination of l-Phenylalanine, Phenylethylamine, and Phenylacetic Acid Using Three-Color Whole-Cell Biosensors within a Microchannel Device. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 5120–5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigi, S.M.; Khurshid, C.A.; Mesgari, F.; Poursaberi, T.; Hosseini, M. Use of an Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Sensor Modified with Sm2O3 Nanoparticles/Chitosan for the Analysis of Phenylalanine. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 2020, 12, 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Zargami, A.; Baghban, H.N.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Shadjou, N.; Mahboob, S. Aptamer-based assay for monitoring genetic disorder phenylketonuria (PKU). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sensor Transducer | Linear Range | Real Sample | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optical biosensor | 10–10,000 μM | - | 5–10 μM | [39] |
| Electrochemical sensor | 0.5–100 μM | blood plasma | 0.001 μM | [40] |
| Electrochemical enantiorecognition biosensors | 0.001–10,000 μM | plasma | 0.001 μM | [41] |
| Chemiluminescence | 0.015–0.12 μM | pharmaceutical and soft drinks | 0.00024 μM | [42] |
| A carbon nanosphere electrode (CN) | 1–100 μM | pharmaceutical products | - | [43] |
| Electrochemical biosensor | 0.5–15,000 μM | human blood and saliva | 0.416 μM | [44] |
| Whole-Cell siosensors | 5−50 μM | - | 4.87 μM | [45] |
| Chemiluminescence sensor | 0.00005–0.5 μM | human plasma | 0.000014 μM | [46] |
| Aptasensor | 0.72 μM–6 μM | human plasma | 0.23 μM | [47] |
| Electrochemical sensor | 0.01–0.1 μM | egg white and chicken | 0.001 μM | [11] |
| Surface plasmon resonance sensor | 5–400 μM | artificial plasma | 0.172 μM | This study |
| MIP Sensor | NIP Sensor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆R | k | ∆R | k | k’ | |
| l-Phe | 2.11 | − | 0.59 | − | − |
| d-Phe | 0.91 | 2.31 | 0.53 | 1.11 | 2.08 |
| l-Try | 0.78 | 2.71 | 0.51 | 1.16 | 2.34 |
| l-Phe+d-Phe | 1.66 | 1.27 | 0.52 | 1.13 | 1.11 |
| l-Phe+l-Try | 1.55 | 0.59 | 0.51 | 1.04 | 0.56 |
| l-Phe+d-Phe+l-Try | 1.73 | 0.45 | 0.52 | 0.98 | 0.46 |
| Added l-Phe (μM) | Found l-Phe (μM) | Recovery (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPR Sensor | ELISA | SPR Sensor | ELISA | |
| 10 | 10.18 ± 0.005 | 9.79 ± 0.005 | 101.87 ± 0.005 | 97.80 ± 0.049 |
| 50 | 49.24 ± 0.008 | 48.72 ± 0.005 | 98.48 ± 0.016 | 97.46 ± 0.010 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Çimen, D.; Bereli, N.; Denizli, A. Surface Plasmon Resonance Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Film for l-Phenylalanine Detection. Biosensors 2021, 11, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11010021
Çimen D, Bereli N, Denizli A. Surface Plasmon Resonance Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Film for l-Phenylalanine Detection. Biosensors. 2021; 11(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleÇimen, Duygu, Nilay Bereli, and Adil Denizli. 2021. "Surface Plasmon Resonance Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Film for l-Phenylalanine Detection" Biosensors 11, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11010021
APA StyleÇimen, D., Bereli, N., & Denizli, A. (2021). Surface Plasmon Resonance Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Film for l-Phenylalanine Detection. Biosensors, 11(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11010021






