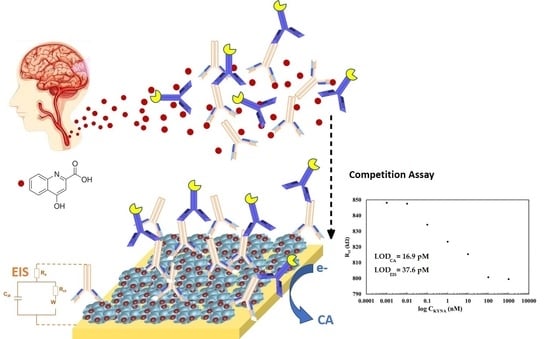
Kynurenic Acid Electrochemical Immunosensor: Blood-Based Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
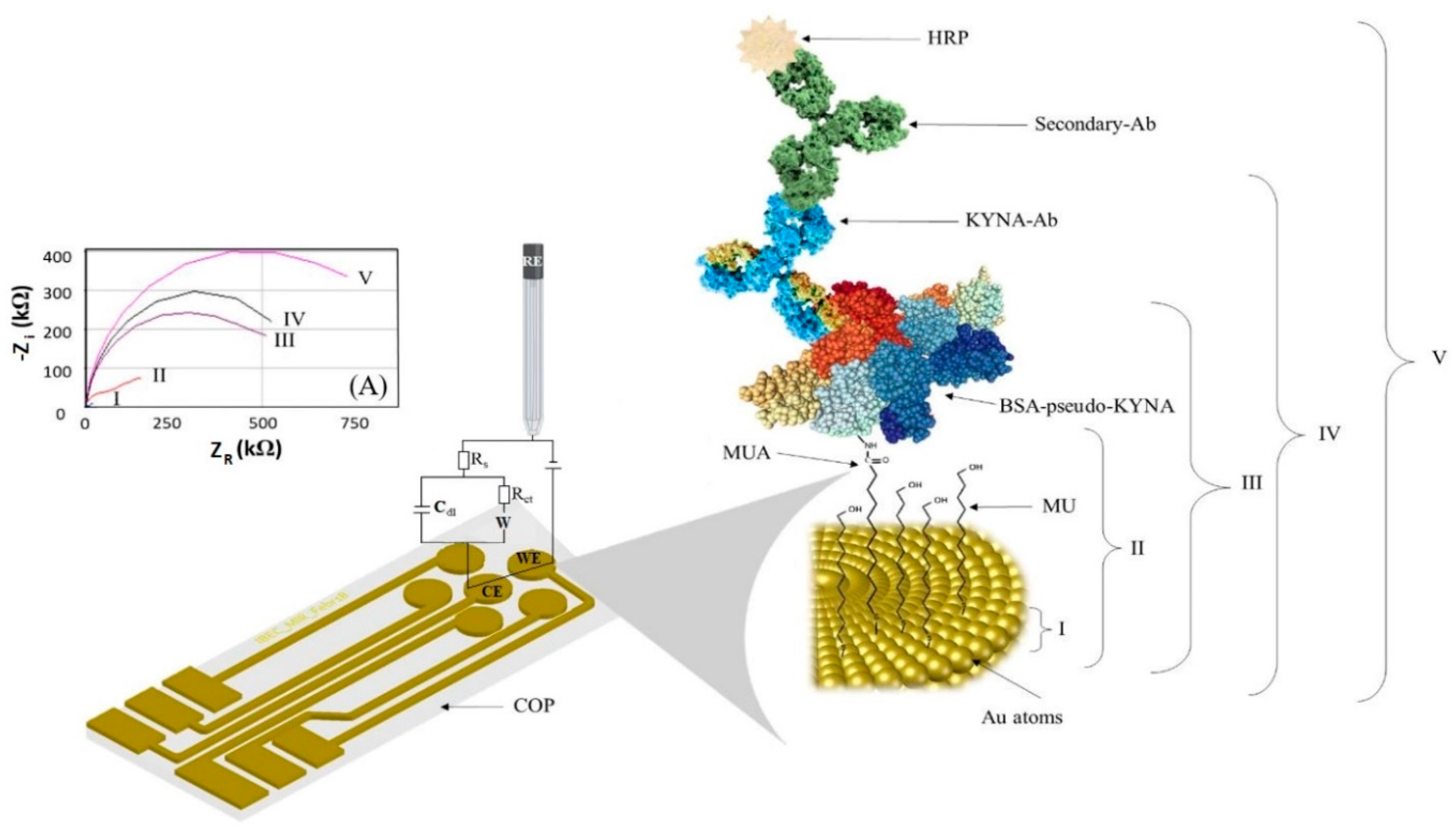
2.2. Multi-Electrode Platform
2.3. Immunosensor Construction
2.3.1. Fabrication of Self-Assembled Monolayer Platform for Competitive Immunosensing
2.3.2. Experimental Setup and Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Functionalization Optimization and Characterization of the Electrochemical Immunosensor

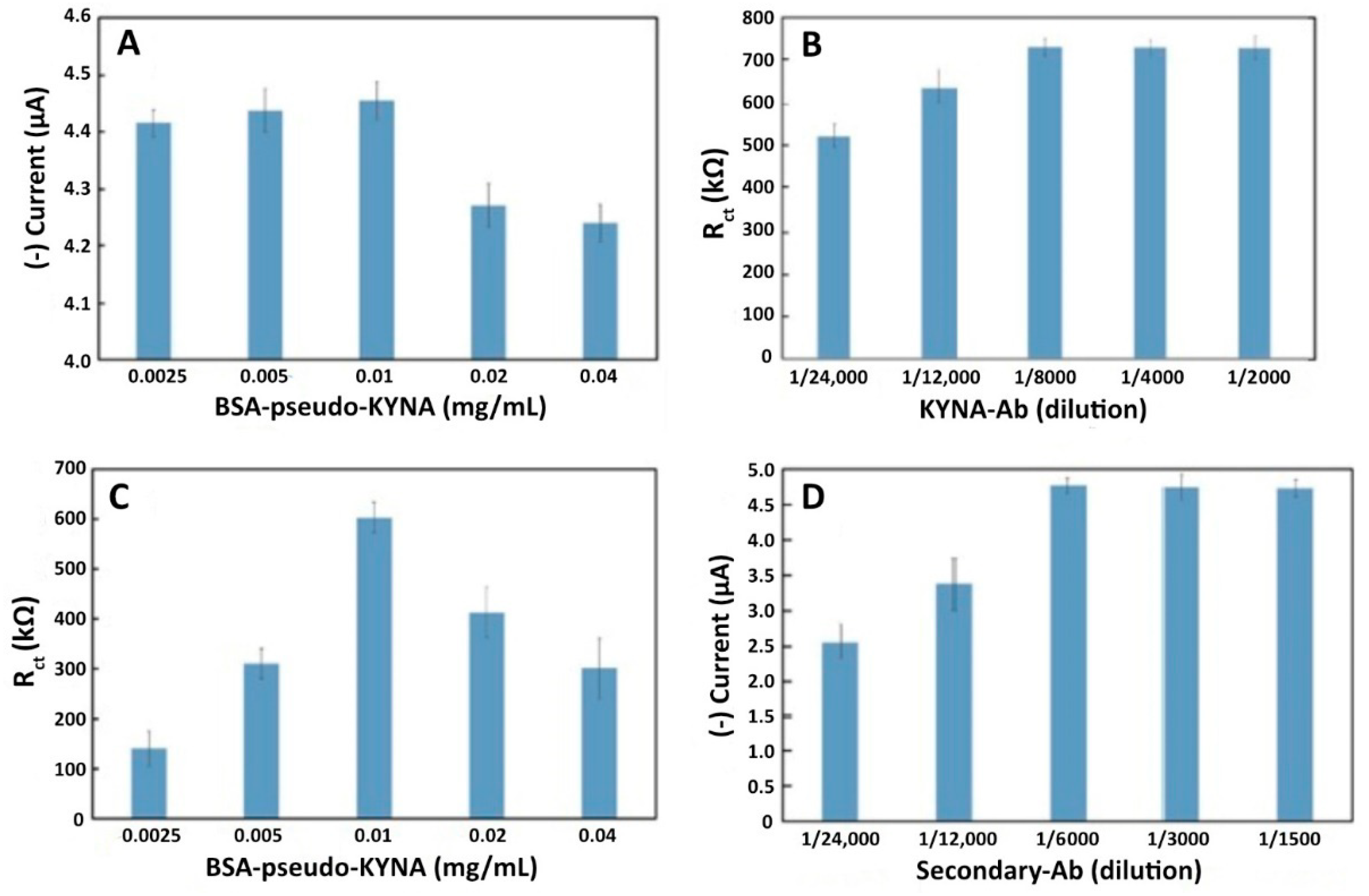
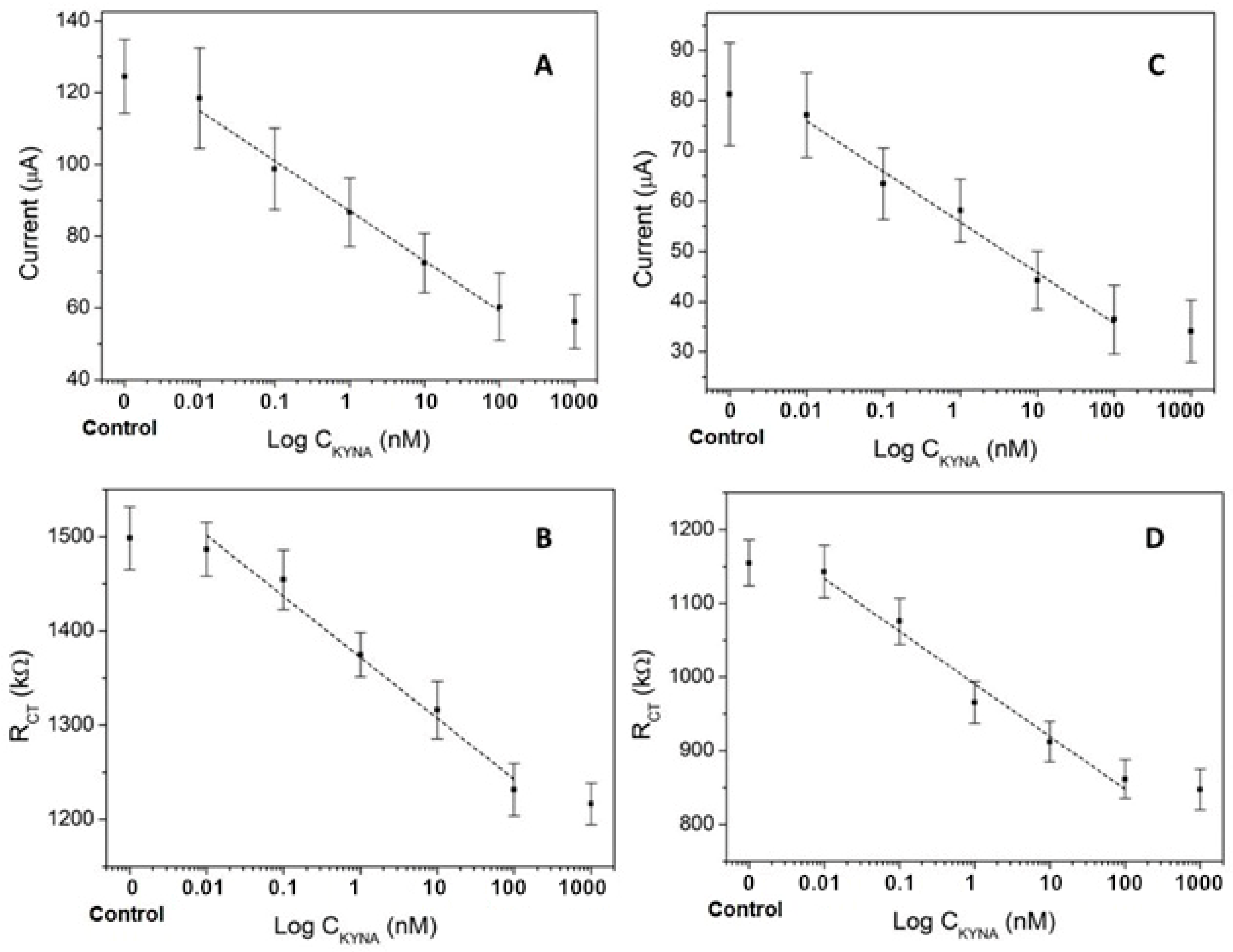
3.1.1. Effect of BSA-Pseudo-KYNA Concentration
3.1.2. Effect of KYNA-Ab Concentration
3.1.3. Effect of Secondary Antibody Concentration
3.2. Study of Biosensor’s Performance
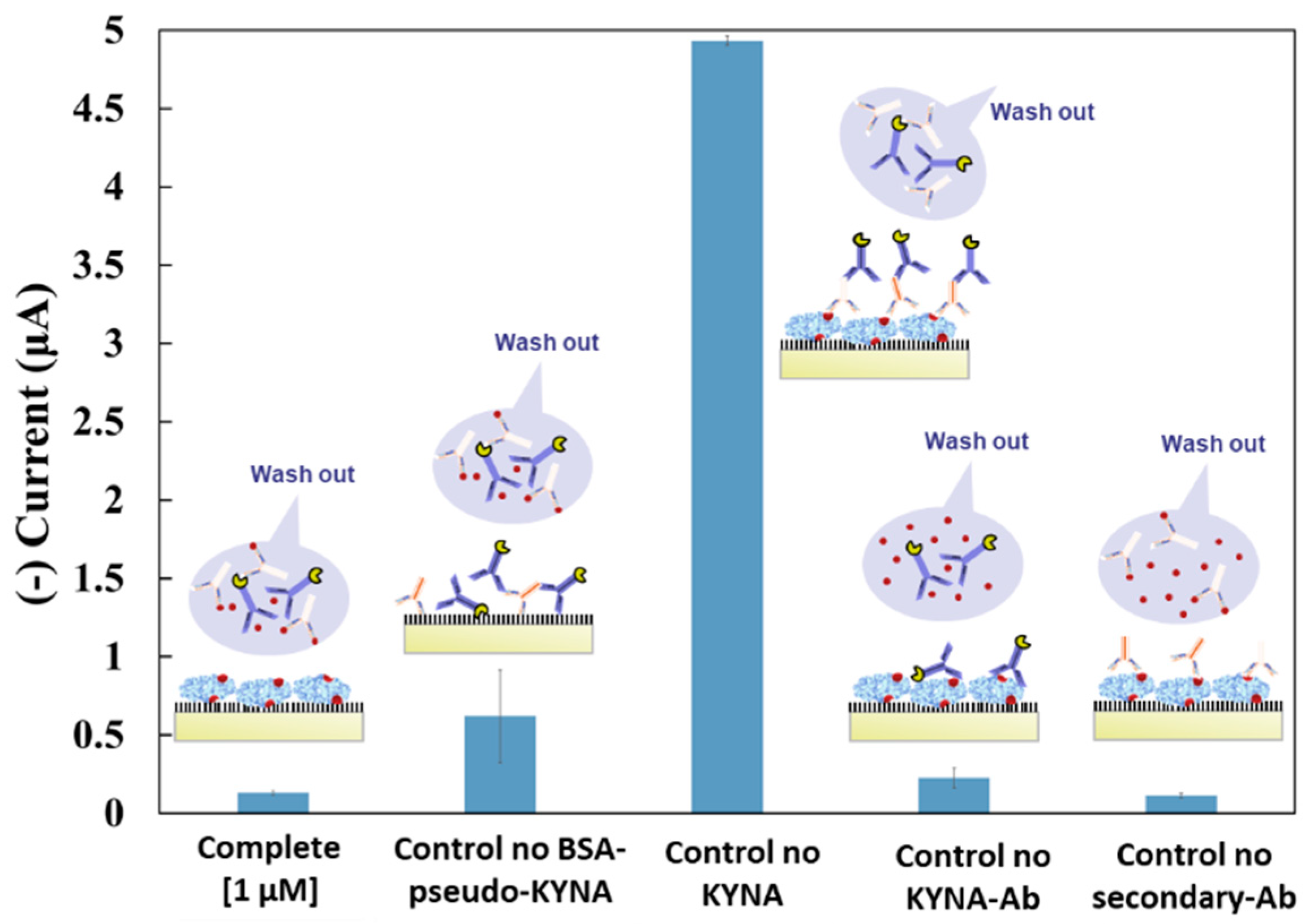
3.2.1. Selectivity Study
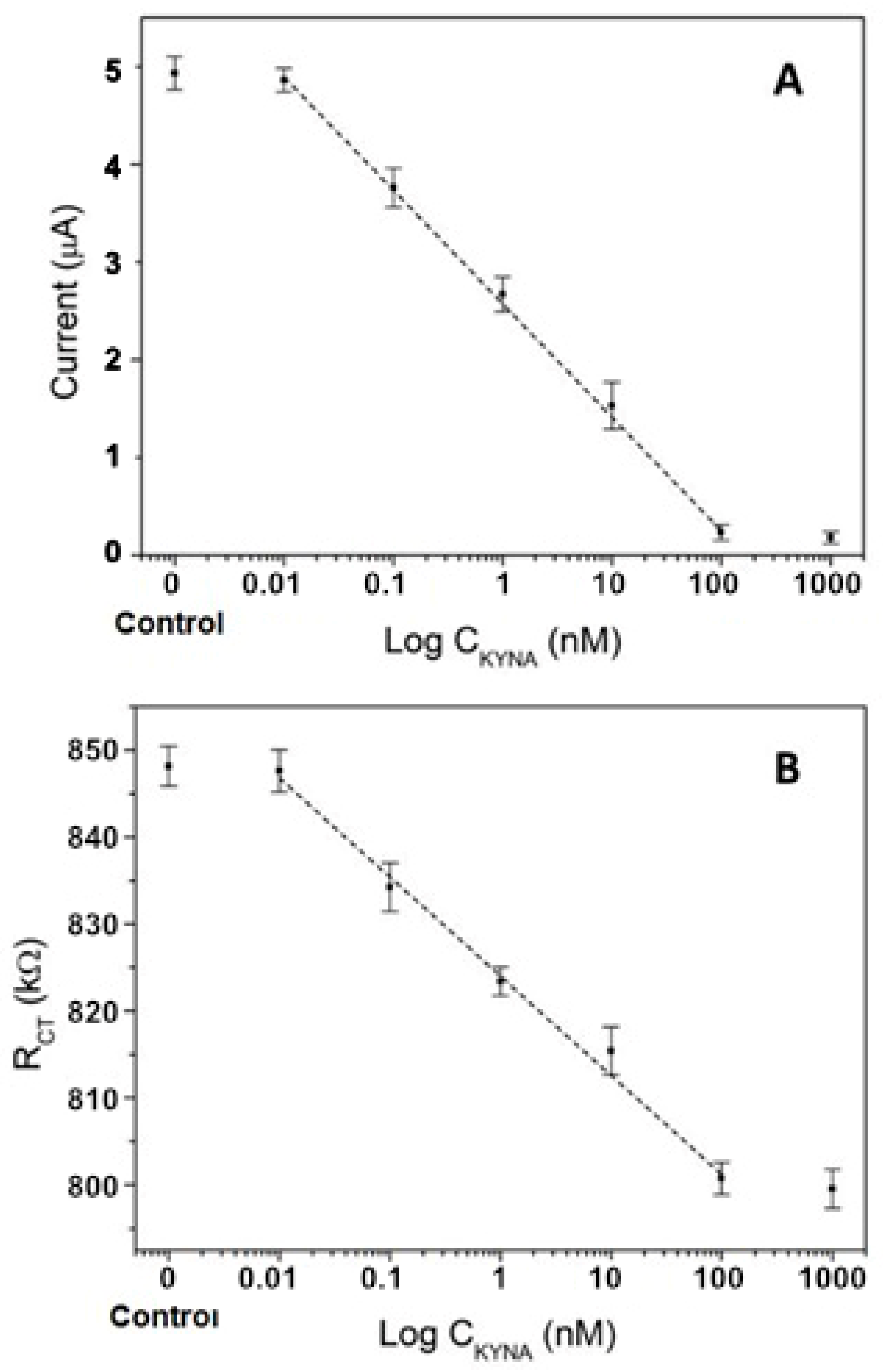
3.2.2. Sensitivity Study
3.2.3. Determination of KYNA in Human Serum Samples
3.2.4. Reproducibility Analysis of the Sensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI), London, The State of the Art of Dementia Research: New Frontiers. September 2018. Available online: https://www.alz.co.uk/research/WorldAlzheimerReport2018.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- World Health Organiztion. Dementia Key Facts. 21 September 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia#:~:text=Worldwide%2C%20around%2050%20million%20people,dependency%20among%20older%20people%20worldwide (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- Selkoe, D.J. Alzheimer’s disease: Genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 741–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šimić, G.; Babić Leko, M.; Wray, S.; Harrington, C.; Delalle, I.; Jovanov-Milošević, N.; Bažadona, D.; Buée, L.; de Silva, R.; Giovanni, G.; et al. Tau protein hyperphosphorylation and aggregation in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies, and possible neuroprotective strategies. Biomolecules 2016, 6, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, B.A.; Blazey, T.M.; Su, Y.; Hari-Raj, A.; Dincer, A.; Flores, S.; Christensen, J.; McDade, E.; Wang, G.; Xiong, C.; et al. Spatial patterns of neuroimaging biomarker change in individuals from families with autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease: A longitudinal study. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Poljak, A.; Valenzuela, M.; Mayeux, R.; Smythe, G.A.; Sachdev, P.S. Meta-analysis of plasma amyloid-β levels in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 26, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, R.; Campbell, B.M.; Strick, C.A.; Horner, W.; Hoffmann, W.E.; Kiss, T.; Chapin, D.S.; McGinnis, D.; Abbott, A.L.; Roberts, B.M.; et al. Reduction of brain kynurenic acid improves cognitive function. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 10592–10602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennström, M.; Nielsen, H.M.; Orhan, F.; Londos, E.; Minthon, L.; Erhardt, S. Kynurenic Acid levels in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with Alzheimer’s disease or dementia with lewy bodies. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2014, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sánchez, M.; Jiménez, J.; Narváez, A.; Antequera, D.; Llamas-Velasco, S.; Martín, A.H.; Arjona, J.; Munain, A.L.; Bisa, A.L.; Marco, M.P.; et al. Kynurenic Acid Levels are Increased in the CSF of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linderholm, K.R.; Skogh, E.; Olsson, S.K.; Dahl, M.L.; Holtze, M.; Engberg, G.; Samuelsson, M.; Erhardt, S. Increased Levels of Kynurenine and Kynurenic Acid in the CSF of Patients with Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2012, 38, 426–432. [Google Scholar]
- Török, N.; Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Searching for Peripheral Biomarkers in Neurodegenerative Diseases: The Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, J.W.; Bemiller, S.M.; Murtishaw, A.S.; Leisgang, A.M.; Salazar, A.M.; Lamb, B.T. Inflammation as a central mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 4, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majláth, Z.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. The potential role of kynurenines in Alzheimer’s disease: Pathomechanism and therapeutic possibilities by influencing the glutamate receptors. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Olsson, S.K.; Samuelsson, M.; Saetre, P.; Lindström, L.; Jönsson, E.G.; Nordin, C.; Engberg, G.; Erhardt, S.; Landén, M. Elevated levels of kynurenic acid in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with bipolar disorder. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2010, 35, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, A.; Hill, M.D.; Rahimi, F.; Warden, L.A.; Halliday, G.M.; Shepherd, C.E. Monocytle chemoattractant protein-1 plays a dominant role in the chronic inflammation observed in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol. 2009, 19, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erabi, H.; Okada, G.; Shibasaki, C.; Setoyama, D.; Kang, D.; Takamura, M.; Yoshino, A.; Fuchikami, M.; Kurata, A.; Kato, T.A.; et al. Kynurenic acid is a potential overlapped biomarker between diagnosis and treatment response for depression from metabolome analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16822–16830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellgren, C.M.; Gracias, J.; Jungholm, O.; Perlis, R.H.; Engberg, G.; Schwieler, L.; Landen, M.; Erhardt, S. Peripheral and central levels of kynurenic acid in bipolar disorder subjects and healthy controls. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, C.R. Reactive astrocytes and α1-antichymotrypsin in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging. 2001, 22, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartai, Z.; Juhász, A.; Rimanóczy, Á.; Janáky, T.; Donkó, T.; Dux, L.; Penke, B.; Tóth, G.K.; Janka, Z.; Kálmán, J. Decreased serum and red blood cell kynurenic acid levels in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Int. 2007, 50, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulaj, E.; Pawlak, K.; Bien, B.; Pawlak, D. Kynurenine and its metabolites in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Adv. Med. Sci. 2010, 55, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.L.; Winefordner, J.D. Limit of detection. A closer look at the IUPAC definition. Anal. Chem. 1983, 55, 713–724. [Google Scholar]
- Moroni, F. Tryptophan metabolism and brain function: Focus on kynurenine and other indole metabolites. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 375, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turski, W.A.; Nakamura, M.; Todd, W.P.; Carpenter, B.K.; Whetsell, W.O.; Schwarcz, R. Identification and quantification of kynurenic acid in human brain tissue. Brain Res. 1988, 454, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezsi, L.; Tuka, B.; Martos, D.; Vecsei, L. Alzheimer’s disease, astrocytes and kynurenines. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2015, 12, 462–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, H.; Jellinger, K.; Deecke, L. Kynurenine metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neural. Transm. 1999, 106, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sas, K.; Robotka, H.; Toldi, J.; Vécsei, L. Mitochondria, metabolic disturbances, oxidative stress and the kynurenine system, with focus on neurodegenerative disorders. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 257, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, T.W. Neuropharmacology of quinolinic and kynurenic acids. Pharmacol. Rev. 1993, 45, 309–379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, M.; Kashiwaguma, Y.; Nagashima, C.; Izumi, M.; Uekusa, A.; Iwasa, S.; Onozato, M.; Ichiba, H.; Fukushima, T. A high-performance liquid chromatography assay with a triazole-bonded column for evaluation of d-amino acid oxidase activity. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016, 30, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flieger, J.; Święch-Zubilewicz, A.; Śniegocki, T.; Dolar-Szczasny, J.; Pizoń, M. Determination of Tryptophan and Its Major Metabolites in Fluid from the Anterior Chamber of the Eye in Diabetic Patients with Cataract by Liquid Chromotography Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Molecules 2018, 23, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.; Homs, A.; Samitier, J. Integrated electrochemical DNA biosensors for lab-on-a-chip devices. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 3386–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, G.I.; Collins, C.A.; Stone, T.W.; Jacob, C. Electrochemical and in vitro evaluation of the redox-properties of kynurenine species. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 300, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, J.E.B. Kinetics of rapid electrode reactions. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1947, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janek, R.P.; Fawcett, W.R.; Ulman, A. Impedance spectroscopy of self-assembled monolayers on Au (111): Sodium ferrocyanide charge transfer at modified electrodes. Langmuir 1998, 14, 3011–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesig, S.T.; Jhan, S.; Hiepe, F.; Volk, H.D.; Fietze, E.; Zugohör, M.; Porstmann, T.; Baehr, R. Multireactive human monoclonal antibodies. Allerg. Immunol. 1990, 36, 163–177. [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson, L.; Baxter, G.A.; Crooks, S.R.H.; Brandon, D.L.; Elliott, C.T. Reduction of sample matrix effects-The analysis of benzimidazole residues in serum by immunobiosensor. Food Agric. Immunol. 2002, 14, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyprianou, D.; Chianella, I.; Guerreiro, A.; VPiletska, E.; Piletsky, S.A. Development of optical immunosensors for detection of proteins in serum. Talanta 2013, 103, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.; Goozee, K.; Lim, C.K.; James, I.; Shen, K.; Jacobs, K.R.; Sohrabi, H.R.; Shah, T.; Asih, P.R.; Dave, P.; et al. Alterations in serum kynurenine pathway metabolites in individuals with high neocortical amyloid-β load: A pilot study. Scient. Rep. 2018, 8, 8008–8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marrugo-Ramírez, J.; Rodríguez-Núñez, M.; Marco, M.-P.; Mir, M.; Samitier, J. Kynurenic Acid Electrochemical Immunosensor: Blood-Based Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biosensors 2021, 11, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11010020
Marrugo-Ramírez J, Rodríguez-Núñez M, Marco M-P, Mir M, Samitier J. Kynurenic Acid Electrochemical Immunosensor: Blood-Based Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biosensors. 2021; 11(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarrugo-Ramírez, Jose, Montserrat Rodríguez-Núñez, M.-Pilar Marco, Mónica Mir, and Josep Samitier. 2021. "Kynurenic Acid Electrochemical Immunosensor: Blood-Based Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease" Biosensors 11, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11010020
APA StyleMarrugo-Ramírez, J., Rodríguez-Núñez, M., Marco, M.-P., Mir, M., & Samitier, J. (2021). Kynurenic Acid Electrochemical Immunosensor: Blood-Based Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biosensors, 11(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11010020