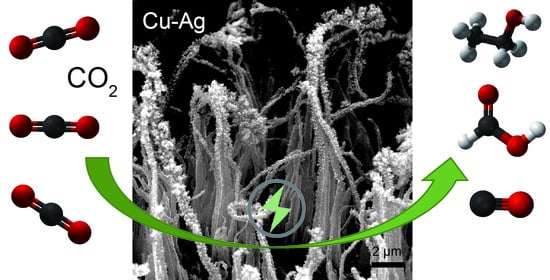
Copper–Silver Bimetallic Nanowire Arrays for Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
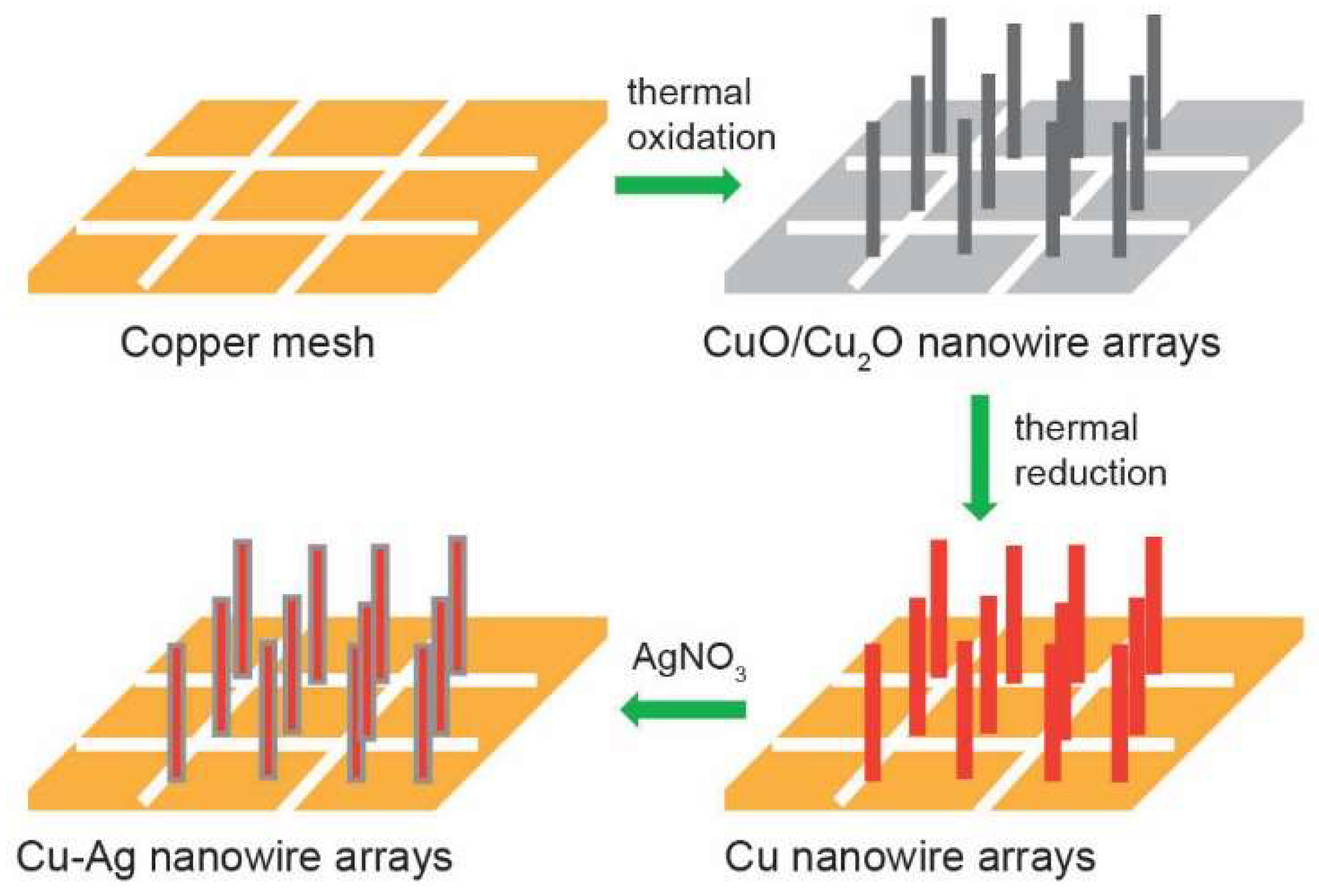
2.2. Copper Nanowire Array Synthesis
2.3. Copper–Silver Nanowire Array Synthesis
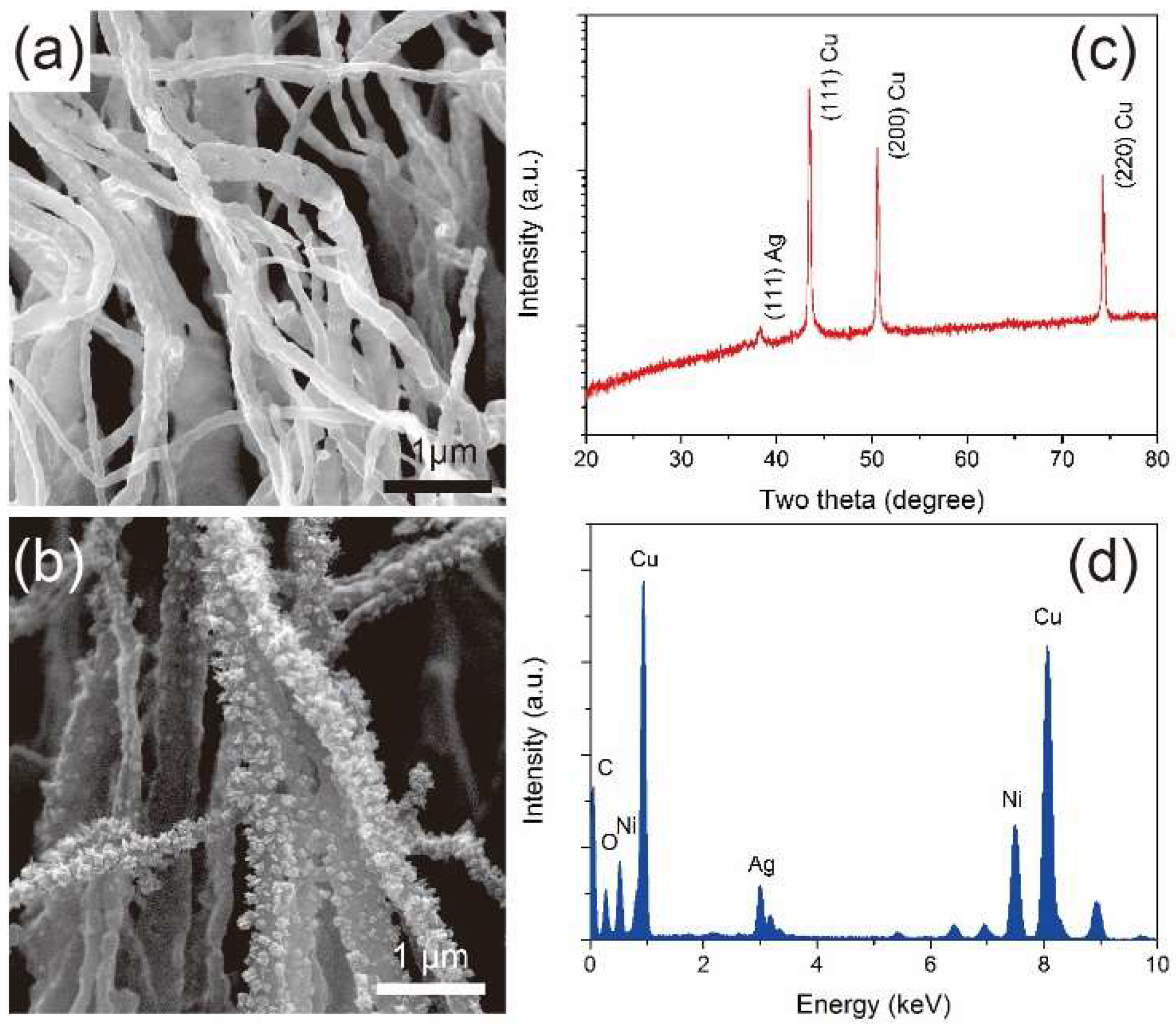
2.4. Material Characterization
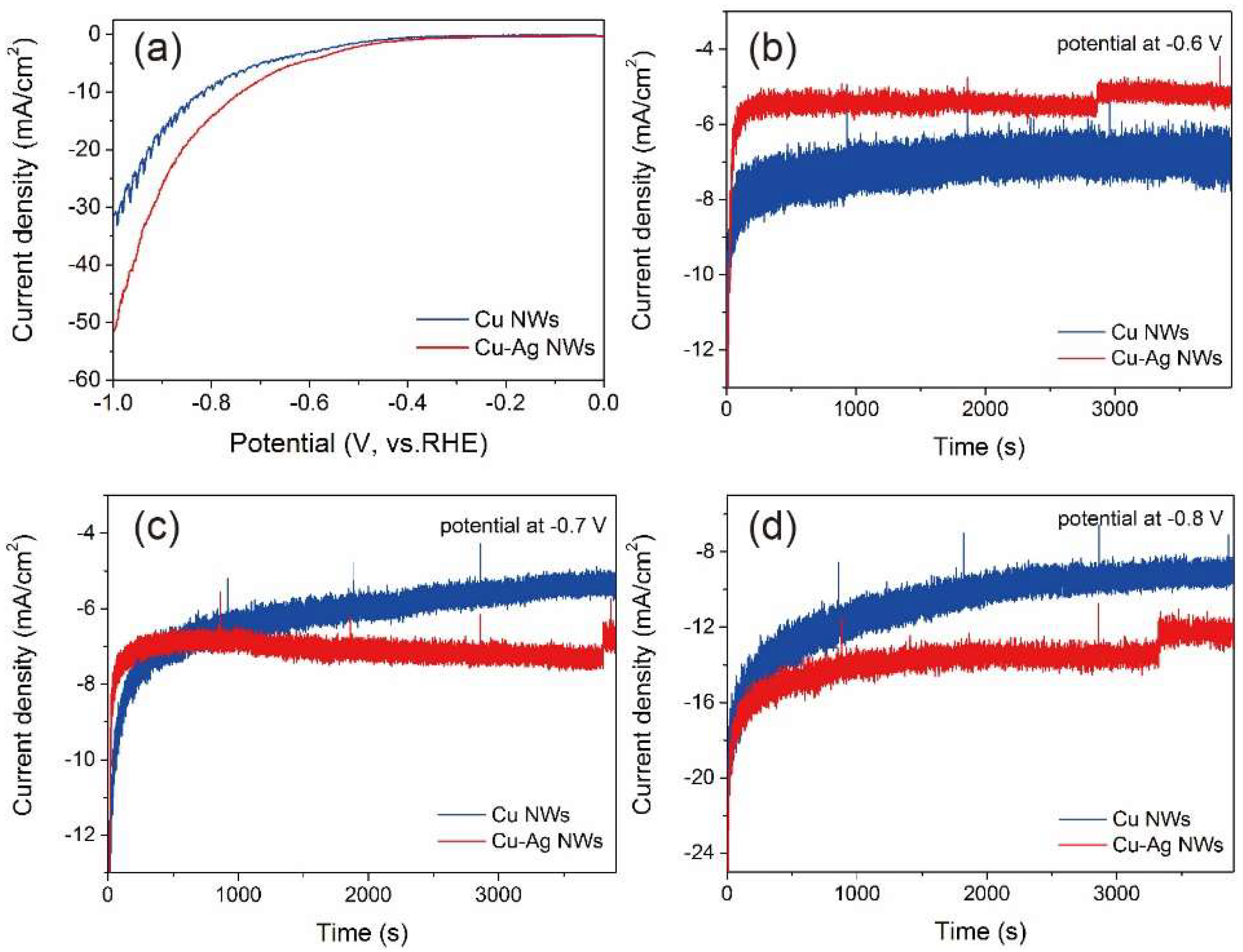
2.5. Electrochemical Studies
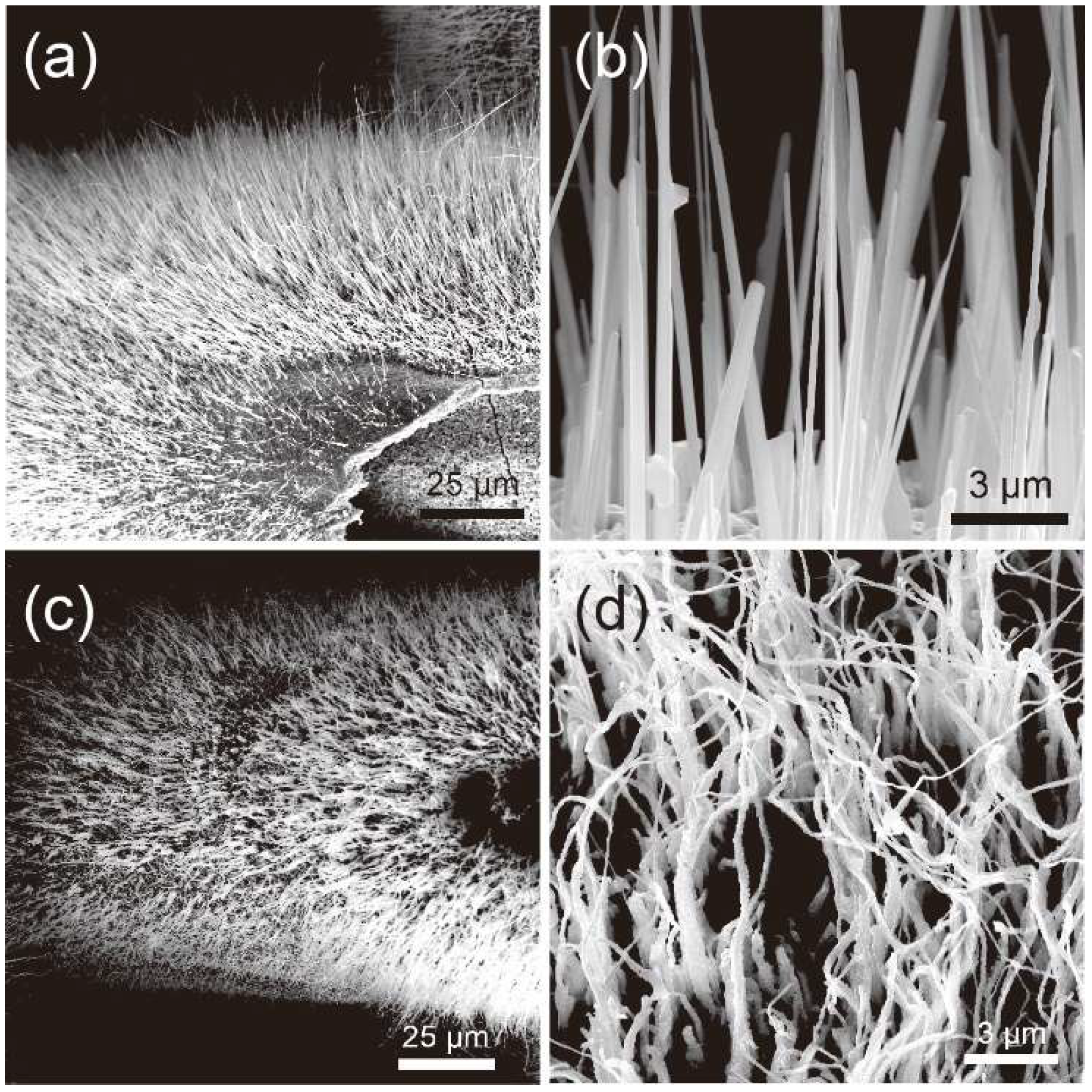
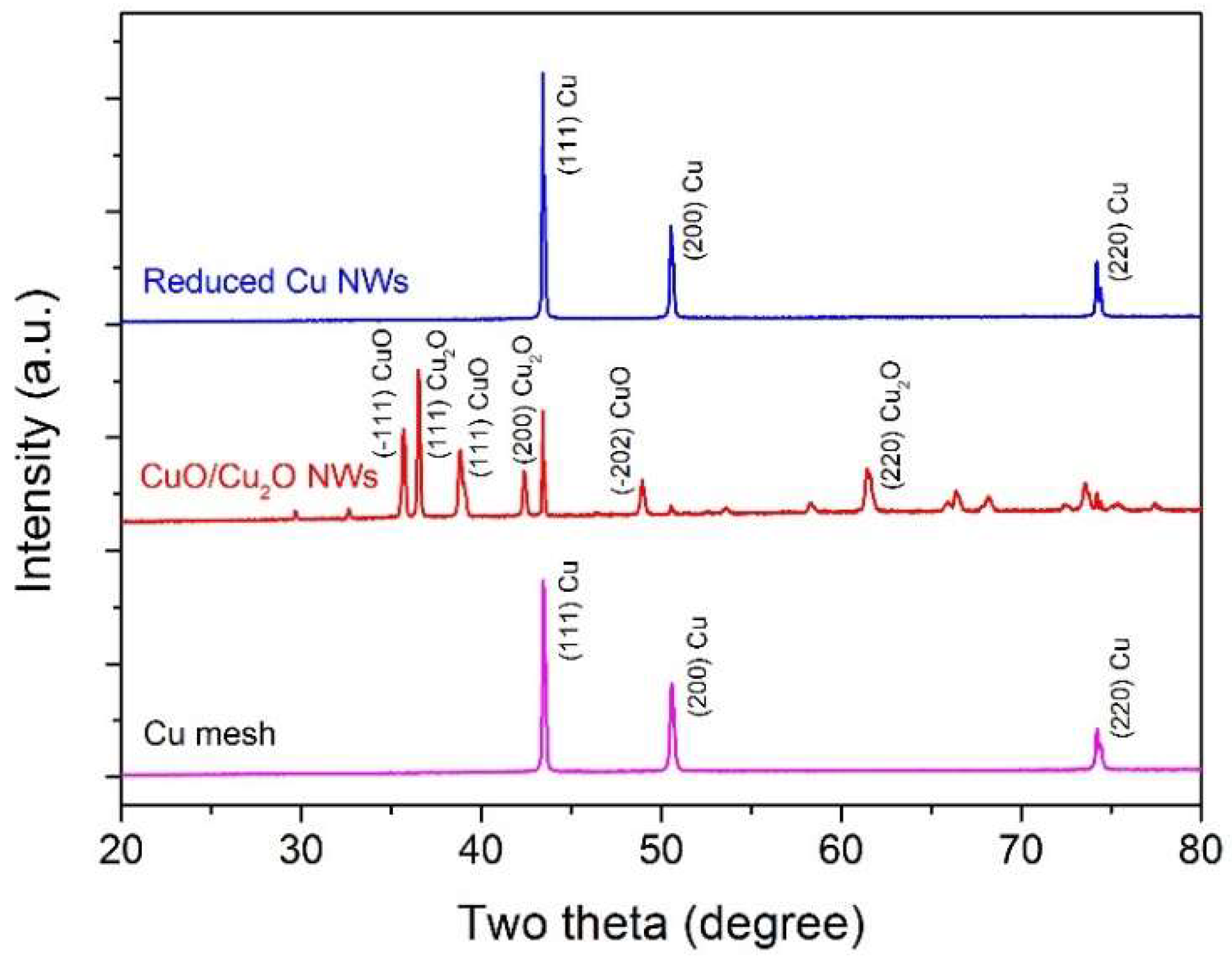
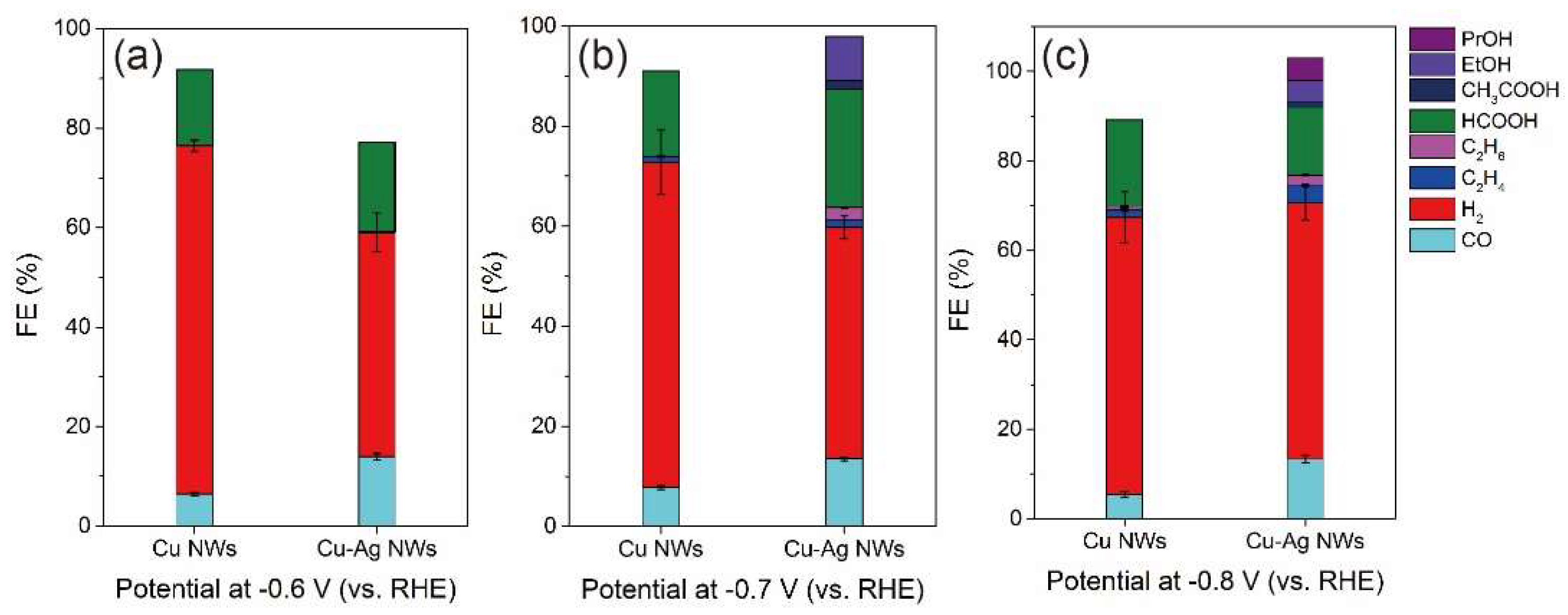
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, W.-H.; Himeda, Y.; Muckerman, J.T.; Manbeck, G.F.; Fujita, E. CO2 Hydrogenation to Formate and Methanol as an Alternative to Photo- and Electrochemical CO2 Reduction. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12936–12973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khezri, B.; Fisher, A.C.; Pumera, M. CO2 Reduction: The Quest for Electrocatalytic Materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 8230–8246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, E.E.; Kubiak, C.P.; Sathrum, A.J.; Smieja, J.M. Electrocatalytic and Homogeneous Approaches to Conversion of CO2 to Liquid Fuels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakowski Dubois, M.; Dubois, D.L. Development of Molecular Electrocatalysts for CO2 Reduction and H2 Production/Oxidation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1974–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.; Jia, H.; Muckerman, J.T.; Fujita, E. Thermodynamics and Kinetics of CO2, CO, and H+ Binding to the Metal Centre of CO2 Reduction Catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2036–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.-P.; Prakash, G.K.S.; Olah, G.A. Electrochemical CO2 Reduction: Recent Advances and Current Trends. Isr. J. Chem. 2014, 54, 1451–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Jiao, F. Electrochemical CO2 Reduction: Electrocatalyst, Reaction Mechanism, and Process Engineering. Nano Energy 2016, 29, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, C.; Wang, D. Metallic Nanocatalysts for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction in Aqueous Solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 527, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y. Electrochemical CO2 Reduction on Metal Electrodes. In Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 89–189. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Rosen, J.; Jiao, F. Nanostructured Metallic Electrocatalysts for Carbon Dioxide Reduction. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; Zheng, G. Tuning of CO2 Reduction Selectivity on Metal Electrocatalysts. Small 2017, 13, 1701809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, C.W.; Kanan, M.W. Aqueous CO2 Reduction at Very Low Overpotential on Oxide-Derived Au Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19969–19972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Zhang, H.; Lv, H.; Li, Q.; Michalsky, R.; Peterson, A.A.; Sun, S. Active and Selective Conversion of CO2 to CO on Ultrathin Au Nanowires. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16132–16135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Jeon, H.S.; Eom, T.; Jee, M.S.; Kim, H.; Friend, C.M.; Min, B.K.; Hwang, Y.J. Achieving Selective and Efficient Electrocatalytic Activity for CO2 Reduction Using Immobilized Silver Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13844–13850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Trześniewski, B.J.; Xie, J.; Smith, W.A. Selective and Efficient Reduction of Carbon Dioxide to Carbon Monoxide on Oxide-Derived Nanostructured Silver Electrocatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9748–9752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Kang, P.; Meyer, T.J. Nanostructured Tin Catalysts for Selective Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide to Formate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1734–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, X.; Kanan, M.W. Pd-Catalyzed Electrohydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide to Formate: High Mass Activity at Low Overpotential and Identification of the Deactivation Pathway. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 4701–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.W.; Kanan, M.W. CO2 Reduction at Low Overpotential on Cu Electrodes Resulting from the Reduction of Thick Cu2O Films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7231–7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reske, R.; Mistry, H.; Behafarid, F.; Roldan Cuenya, B.; Strasser, P. Particle Size Effects in the Catalytic Electroreduction of CO2 on Cu Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6978–6986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.A.; Abild-Pedersen, F.; Studt, F.; Rossmeisl, J.; Norskov, J.K. How Copper Catalyzes the Electroreduction of Carbon Dioxide into Hydrocarbon Fuels. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortlever, R.; Shen, J.; Schouten, K.J.P.; Calle-Vallejo, F.; Koper, M.T.M. Catalysts and Reaction Pathways for the Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 4073–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.-J.; Gong, J. Nanostructured Materials for Heterogeneous Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction and their Related Reaction Mechanisms. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 11326–11353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Yao, Q.; Cui, P.; Liu, H.; Xie, J.; Yang, J. Tailoring the Selectivity of Bimetallic Copper–Palladium Nanoalloys for Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to CO. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Resasco, J.; Yu, Y.; Asiri, A.M.; Yang, P. Synergistic Geometric and Electronic Effects for Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide using Gold–Copper Bimetallic Nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raciti, D.; Livi, K.J.; Wang, C. Highly Dense Cu Nanowires for Low-Overpotential CO2 Reduction. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6829–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alia, S.M.; Pivovar, B.S.; Yan, Y. Platinum-Coated Copper Nanowires with High Activity for Hydrogen Oxidation Reaction in Base. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13473–13478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Z.; Cui, F.; Yu, Y.; Becknell, N.; Sun, Y.; Khanarian, G.; Kim, D.; Dou, L.; Dehestani, A.; Schierle-Arndt, K.; et al. Ultrathin Epitaxial Cu@Au Core–Shell Nanowires for Stable Transparent Conductors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7348–7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, X.-Z.; Tao, H.; Li, T.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Fu, X.-Z.; Luo, J.-L. Ultrathin 5-Fold Twinned Sub-25nm Silver Nanowires Enable Highly Selective Electroreduction of CO2 to CO. Nano Energy 2018, 45, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Herricks, T.; Xia, Y. CuO Nanowires Can Be Synthesized by Heating Copper Substrates in Air. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Michalsky, R.; Metin, Ö.; Lv, H.; Guo, S.; Wright, C.J.; Sun, X.; Peterson, A.A.; Sun, S. Monodisperse Au Nanoparticles for Selective Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to CO. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16833–16836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Djanashvili, K.; Smith, W.A. Controllable Hydrocarbon Formation from the Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 over Cu Nanowire Arrays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6680–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; McKiernan, M.; Peng, Z.; Lee, E.P.; Yang, H.; Xia, Y. Noble-Metal Nanotubes Prepared via a Galvanic Replacement Reaction Between Cu Nanowires and Aqueous HAuCl4, H2PtCl6, or Na2PdCl4. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2010, 2, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohl, M.; Dobo, D.; Kukovecz, A.; Konya, Z.; Kordas, K.; Wei, J.; Vajtai, R.; Ajayan, P.M. Formation of CuPd and CuPt Bimetallic Nanotubes by Galvanic Replacement Reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 9403–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, I.E.; Ye, S.; Chen, Z.; Flowers, P.F.; Wiley, B.J. Synthesis of Cu–Ag, Cu–Au, and Cu–Pt Core–Shell Nanowires and Their Use in Transparent Conducting Films. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7788–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Ruditskiy, A.; Xia, Y. 25th Anniversary Article: Galvanic Replacement: A Simple and Versatile Route to Hollow Nanostructures with Tunable and Well-Controlled Properties. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6313–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, W.-L.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Fan, H.-H.; Liao, C.-N. Twin-Mediated Epitaxial Growth of Highly Lattice-Mismatched Cu/Ag Core-Shell Nanowires. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 9862–9866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janáky, C.; Hursán, D.; Endrődi, B.; Chanmanee, W.; Roy, D.; Liu, D.; de Tacconi, N.R.; Dennis, B.H.; Rajeshwar, K. Electro- and Photoreduction of Carbon Dioxide: The Twain Shall Meet at Copper Oxide/Copper Interfaces. ACS Energy Lett. 2016, 1, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, K.P.; Hatsukade, T.; Cave, E.R.; Abram, D.N.; Kibsgaard, J.; Jaramillo, T.F. Electrocatalytic Conversion of Carbon Dioxide to Methane and Methanol on Transition Metal Surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14107–14113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Yan, J.; Mietek, J.; Zhang, Q.S. Advancing the Electrochemistry of the Hydrogen-Evolution Reaction through Combining Experiment and Theory. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 52–65. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Niu, C.; Zhu, Y. Copper–Silver Bimetallic Nanowire Arrays for Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020173
Wang Y, Niu C, Zhu Y. Copper–Silver Bimetallic Nanowire Arrays for Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(2):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020173
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuanxing, Cailing Niu, and Yachuan Zhu. 2019. "Copper–Silver Bimetallic Nanowire Arrays for Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide" Nanomaterials 9, no. 2: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020173
APA StyleWang, Y., Niu, C., & Zhu, Y. (2019). Copper–Silver Bimetallic Nanowire Arrays for Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide. Nanomaterials, 9(2), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020173