Biological Effects of Micro-/Nano-Plastics in Macrophages
Abstract
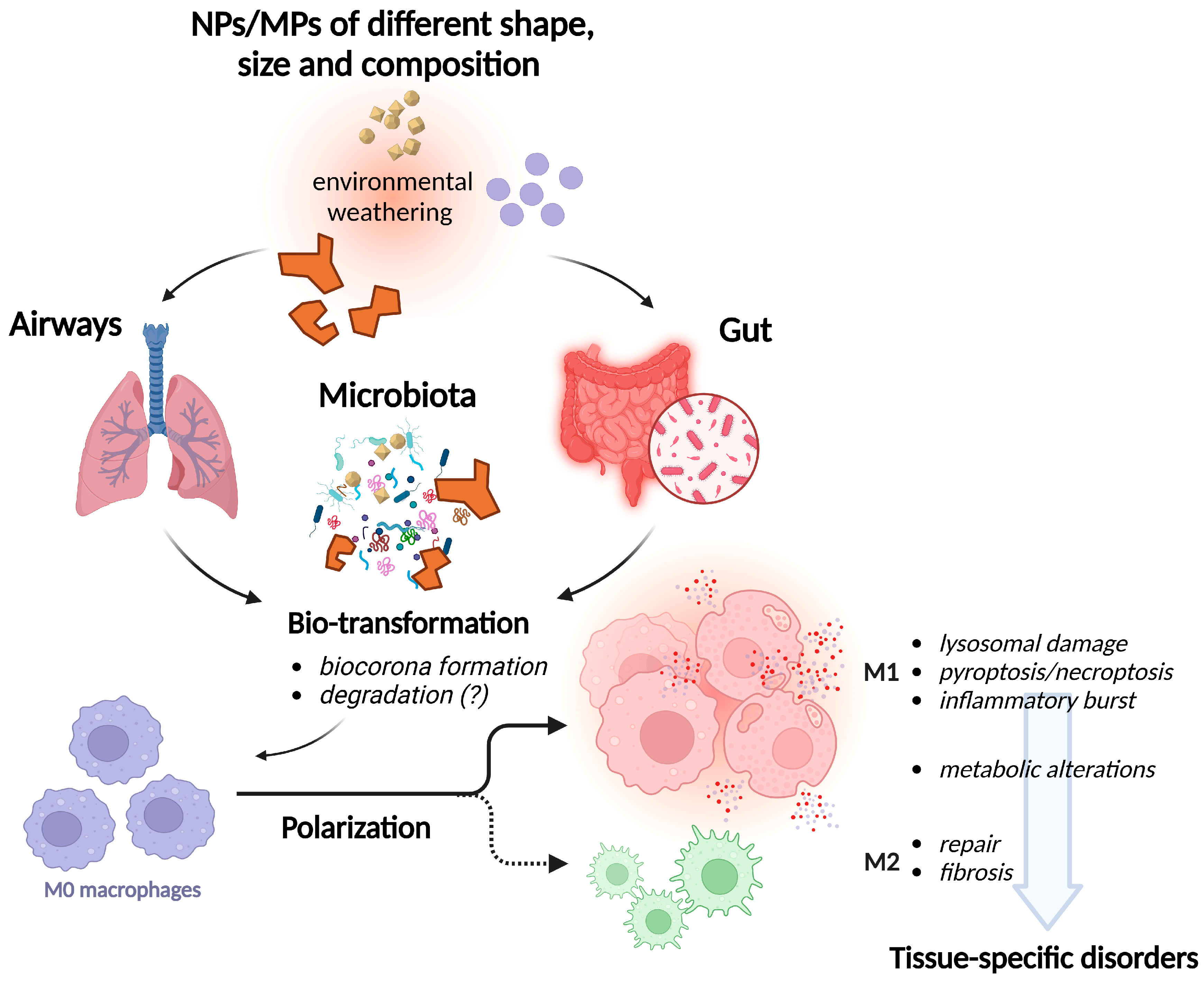
1. Introduction
2. Cytotoxicity
3. Phagocytosis and Intracellular Accumulation
4. Inability to Digest MPs/NPs, Lysosomal Impairment, Autophagy Defect
5. Polarization
6. Metabolism
7. MPs/NPs, Macrophages, and Microbial Communities
8. Inflammation and Inflammation-Related Disease
8.1. Lungs and the Respiratory System
8.2. Gut
8.3. Liver
8.4. Bone
8.5. Cardiovascular System
8.6. Other Organs and Systems
9. Conclusions and Open Issues
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BALF | Bronchoalveolar fluid |
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
| MAFLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease |
| MASH | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis |
| MPs | Plastic microparticles |
| NP | Plastic nanoparticles |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PET | Polyethylene terephthalate |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PVC | Polyvinylchloride |
| ROSs | Reactive oxygen substances |
References
- Hirt, N.; Body-Malapel, M. Immunotoxicity and intestinal effects of nano- and microplastics: A review of the literature. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vethaak, A.D.; Legler, J. Microplastics and human health. Science 2021, 371, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.C.; Courtene-Jones, W.; Boucher, J.; Pahl, S.; Raubenheimer, K.; Koelmans, A.A. Twenty years of microplastic pollution research-what have we learned? Science 2024, 386, eadl2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xie, K.; Chen, J.; He, J.; Gao, J.; Yu, C. Long-term exposure to polystyrene microplastics reduces macrophages and affects the microbiota-gut-brain axis in mice. Toxicology 2024, 509, 153951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, X.M.; He, H.; Li, F.; Liu, K.; Zhao, F.; Hu, H.; Zhang, P.; Huang, B.; Pan, X. Cytotoxicity and pro-inflammatory effect of polystyrene nano-plastic and micro-plastic on RAW264.7 cells. Toxicology 2023, 484, 153391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Pei, W.; Li, J.; Feng, Y.; Gao, X.; Jiang, P.; Wu, Q.; Li, L. Microplastics induced apoptosis in macrophages by promoting ROS generation and altering metabolic profiles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 271, 115970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Baimanov, D.; Yuan, H.; Xie, H.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhao, F.; You, Y.; Guan, Y.; et al. Protein Corona-Directed Cellular Recognition and Uptake of Polyethylene Nanoplastics by Macrophages. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 14158–14168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Jo, J.; Acharya, M.; Maharjan, A.; Lee, D.; K C, P.B.; Kim, C.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.; Heo, Y. Evaluation of potential toxicity of polyethylene microplastics on human derived cell lines. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakolpournegari, A.; Villacorta, A.; Morataya-Reyes, M.; Arribas Arranz, J.; Banaei, G.; Pastor, S.; Velazquez, A.; Marcos, R.; Hernandez, A.; Annangi, B. Harmful effects of true-to-life nanoplastics derived from PET water bottles in human alveolar macrophages. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 348, 123823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijagic, A.; Kotlyar, O.; Larsson, M.; Salihovic, S.; Hedbrant, A.; Eriksson, U.; Karlsson, P.; Persson, A.; Scherbak, N.; Farnlund, K.; et al. Immunotoxic, genotoxic, and endocrine disrupting impacts of polyamide microplastic particles and chemicals. Environ. Int. 2024, 183, 108412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K C, P.B.; Maharjan, A.; Acharya, M.; Lee, D.; Kusma, S.; Gautam, R.; Kwon, J.T.; Kim, C.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.; et al. Polytetrafluorethylene microplastic particles mediated oxidative stress, inflammation, and intracellular signaling pathway alteration in human derived cell lines. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, J.; Volkl, M.; Jerome, V.; Scheibel, T.; Freitag, R. Noxic effects of polystyrene microparticles on murine macrophages and epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Qu, C.; Yi, W.; Yang, J.; Pan, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Bai, C.; Zhou, P.K.; et al. Exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics induces abnormal activation of innate immunity via the cGAS-STING pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 275, 116255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Qu, C.; Yan, Y.; Yi, W.; Yang, J.; Skonieczna, M.; Chen, C.; Miszczyk, J.; Ivanov, D.S.; et al. Metabolomics reveals that PS-NPs promote lung injury by regulating prostaglandin B1 through the cGAS-STING pathway. Chemosphere 2023, 342, 140108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, M.Y.; Issoual, I.; Ruckert, M.; Deloch, L.; Meier, C.; Tschernig, T.; Alexiou, C.; Pfister, F.; Ramsperger, A.F.; Laforsch, C.; et al. Effect of micro- and nanoplastic particles on human macrophages. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 471, 134253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koner, S.; Florance, I.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Cellular response of THP-1 macrophages to polystyrene microplastics exposure. Toxicology 2023, 483, 153385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Mei, A.; Wang, X.; Shi, Q. Cellular absorption of polystyrene nanoplastics with different surface functionalization and the toxicity to RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 252, 114574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, L.; Gazzi, A.; Giro, L.; Schefer, R.B.; D’Almeida, S.M.; Cagliani, R.; Zoccheddu, M.; Uyar, R.; Besbinar, O.; Celik, D.; et al. Nanoplastics: Immune Impact, Detection, and Internalization after Human Blood Exposure by Single-Cell Mass Cytometry. Adv. Mater. 2024, e2413413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Lai, K.P.; Stoeger, T.; Ji, S.; Lin, Z.; Lin, X.; Chan, T.F.; Fang, J.K.; Lo, M.; Gao, L.; et al. Detrimental effects of microplastic exposure on normal and asthmatic pulmonary physiology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, S.; Rodriguez, C.; Sarrett, S.M.; Dayts, E.J.; Zeglis, B.M.; Keinanen, O. Unraveling the in vivo fate of inhaled micro- and nanoplastics with PET imaging. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin-Faure, V.; Vitipon, M.; Torres, A.; Tanyeres, O.; Dalzon, B.; Rabilloud, T. The internal dose makes the poison: Higher internalization of polystyrene particles induce increased perturbation of macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1092743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroiwa, M.; Yamaguchi, S.I.; Kato, Y.; Hori, A.; Toyoura, S.; Nakahara, M.; Morimoto, N.; Nakayama, M. Tim4, a macrophage receptor for apoptotic cells, binds polystyrene microplastics via aromatic-aromatic interactions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasinski, J.; Volkl, M.; Hahn, J.; Jerome, V.; Freitag, R.; Scheibel, T. Polystyrene microparticle distribution after ingestion by murine macrophages. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 457, 131796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkley, S.D.; Moss, H.C.; Goodfellow, S.M.; Ling, C.L.; Meyer-Hagen, J.L.; Weaver, J.; Campen, M.J.; Castillo, E.F. Polystyrene microplastics induce an immunometabolic active state in macrophages. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2022, 38, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Chen, L.; Gu, W.; Liu, S.; Wu, B. Heterogeneity effects of nanoplastics and lead on zebrafish intestinal cells identified by single-cell sequencing. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horonushi, D.; Furumoto, Y.; Nakata, Y.; Azuma, T.; Yoshida, A.; Yasuda, K. On-Chip Free-Flow Measurement Revealed Possible Depletion of Macrophages by Indigestible PM2.5 within a Few Hours by the Fastest Intervals of Serial Phagocytosis. Micromachines 2023, 14, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, H.; Porbahaie, M.; Boeren, S.; Busch, M.; Bouwmeester, H. The in vitro gastrointestinal digestion-associated protein corona of polystyrene nano- and microplastics increases their uptake by human THP-1-derived macrophages. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2024, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Yu, X.; Shao, S.; Li, T.; Xu, S.; Wu, L. Aging of Nanoplastics Significantly Affects Protein Corona Composition Thus Enhancing Macrophage Uptake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 3206–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.G.; Chiu, M.; Taurino, G.; Bergamaschi, E.; Cubadda, F.; Macaluso, G.M.; Bussolati, O. The TLR4/NFkappaB-Dependent Inflammatory Response Activated by LPS Is Inhibited in Human Macrophages Pre-Exposed to Amorphous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florance, I.; Ramasubbu, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Polystyrene nanoplastics dysregulate lipid metabolism in murine macrophages in vitro. Toxicology 2021, 458, 152850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florance, I.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Gopinath, P.M.; Mukherjee, A. Exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics impairs lipid metabolism in human and murine macrophages in vitro. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 238, 113612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingaro, F.; Gianoncelli, A.; Ceccone, G.; Birarda, G.; Cassano, D.; La Spina, R.; Agostinis, C.; Bonanni, V.; Ricci, G.; Pascolo, L. Morphological and lipid metabolism alterations in macrophages exposed to model environmental nanoplastics traced by high-resolution synchrotron techniques. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1247747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfella, R.; Prattichizzo, F.; Sardu, C.; Fulgenzi, G.; Graciotti, L.; Spadoni, T.; D’Onofrio, N.; Scisciola, L.; La Grotta, R.; Frige, C.; et al. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Atheromas and Cardiovascular Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liang, B.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; Du, J.; Ye, R.; Xian, H.; Deng, Y.; Xiu, J.; et al. Long-Chain Acyl Carnitines Aggravate Polystyrene Nanoplastics-Induced Atherosclerosis by Upregulating MARCO. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2205876. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Ibrahim, M.S.; Tan, L.Y.; Yeo, X.Y.; Lee, Y.A.; Park, S.J.; Wustefeld, T.; Park, J.W.; Jung, S.; Cho, N.J. Microplastics released from food containers can suppress lysosomal activity in mouse macrophages. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 128980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, S.; Haga, Y.; Tsujino, H.; Ikuno, Y.; Asahara, H.; Higashisaka, K.; Tsutsumi, Y. Treatment of polyethylene microplastics degraded by ultraviolet light irradiation causes lysosome-deregulated cell death. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24008. [Google Scholar]
- Orecchioni, M.; Ghosheh, Y.; Pramod, A.B.; Ley, K. Macrophage Polarization: Different Gene Signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. Classically and M2(LPS−) vs. Alternatively Activated Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Qin, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, W.; Lin, Y.; Liu, X. Polystyrene microplastics disturb maternal-fetal immune balance and cause reproductive toxicity in pregnant mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, C.M.; Singer, D.; Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S. Immune and inflammatory responses of human macrophages, dendritic cells, and T-cells in presence of micro- and nanoplastic of different types and sizes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, P.; Xu, T.; Wu, M.; Lv, S. Polystyrene nanoplastics of different particle sizes regulate the polarization of pro-inflammatory macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Shi, W.; Hu, F.; Song, X.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, J. Prolonged oral ingestion of microplastics induced inflammation in the liver tissues of C57BL/6J mice through polarization of macrophages and increased infiltration of natural killer cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Ding, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Li, D.; Han, X. Chronic exposure to polystyrene microplastics induced LHR reduction and decreased testosterone levels through NF-kappaB pathway. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 358, 124543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, F.; Meng, S.; Li, H.; Song, Y. Polystyrene Microplastics Postpone APAP-Induced Liver Injury through Impeding Macrophage Polarization. Toxics 2022, 10, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paesano, L.; Marmiroli, M.; Bianchi, M.G.; White, J.C.; Bussolati, O.; Zappettini, A.; Villani, M.; Marmiroli, N. Differences in toxicity, mitochondrial function and miRNome in human cells exposed in vitro to Cd as CdS quantum dots or ionic Cd. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, L.; Luo, G.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, D.; Xiao, F. The crosstalk between M1 macrophage polarization and energy metabolism disorder contributes to polystyrene nanoplastics-triggered testicular inflammation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 180, 114002. [Google Scholar]
- Harusato, A.; Seo, W.; Abo, H.; Nakanishi, Y.; Nishikawa, H.; Itoh, Y. Impact of particulate microplastics generated from polyethylene terephthalate on gut pathology and immune microenvironments. iScience 2023, 26, 106474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, B.; Ju, Q.; Sun, B.K. AhR Regulates Peptidoglycan-Induced Inflammatory Gene Expression in Human Keratinocytes. J. Innate Immun. 2022, 14, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.G.; Chiu, M.; Taurino, G.; Bergamaschi, E.; Turroni, F.; Mancabelli, L.; Longhi, G.; Ventura, M.; Bussolati, O. Amorphous silica nanoparticles and the human gut microbiota: A relationship with multiple implications. J. Nanobiotechnology 2024, 22, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawle, D.J.; Dumenil, T.; Tang, B.; Bishop, C.R.; Yan, K.; Le, T.T.; Suhrbier, A. Microplastic consumption induces inflammatory signatures in the colon and prolongs a viral arthritis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 152212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenger, K.J.P.; Ghorbani, Y.; Bharatselvam, S.; Chen, L.; Chomiak, K.M.; Tyler, A.C.; Eddingsaas, N.C.; Fischer, S.E.; Jackson, T.D.; Okrainec, A.; et al. Links between fecal microplastics and parameters related to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) in humans: An exploratory study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fackelmann, G.; Sommer, S. Microplastics and the gut microbiome: How chronically exposed species may suffer from gut dysbiosis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 143, 193–203. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Wan, Z.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induce gut microbiota dysbiosis and hepatic lipid metabolism disorder in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, X.; Sheng, D.; Xu, Z.; Rong, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y. Polyethylene microplastics affect the distribution of gut microbiota and inflammation development in mice. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liao, H.; Zeng, M.; Gao, D.; Kong, C.; Liu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, J. Exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics causes immune damage, oxidative stress and intestinal flora disruption in salamander (Andrias davidianus) larvae. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 175169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, S.; You, Q.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, D.; Sun, J. Polyethylene Terephthalate Hydrolases in Human Gut Microbiota and Their Implications for Human Health. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, M.; Bredeck, G.; Waag, F.; Rahimi, K.; Ramachandran, H.; Bessel, T.; Barcikowski, S.; Herrmann, A.; Rossi, A.; Schins, R.P.F. Assessing the NLRP3 Inflammasome Activating Potential of a Large Panel of Micro- and Nanoplastics in THP-1 Cells. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Jeon, J.H.; Jeong, J.; Kim, G.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Maruthupandy, M.; Lee, K.; Yang, S.I.; Cho, W.S. Size- and oxidative potential-dependent toxicity of environmentally relevant expanded polystyrene styrofoam microplastics to macrophages. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Wei, Y.; Hu, L.J.; Zeng, F.M.; Chen, Y.W.; Xu, D.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.W.; Li, Y.F.; Pang, G.H.; et al. Inhalation of Microplastics Induces Inflammatory Injuries in Multiple Murine Organs via the Toll-like Receptor Pathway. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 18603–18618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, F.; Guo, M.; Gao, D.; Song, Y. Nasal instillation of polystyrene nanoplastics induce lung injury via mitochondrial DNA release and activation of the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-stimulator of interferon genes-signaling cascade. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwabena Danso, I.; Woo, J.H.; Hoon Baek, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, K. Pulmonary toxicity assessment of polypropylene, polystyrene, and polyethylene microplastic fragments in mice. Toxicol. Res. 2024, 40, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xiao, T.; Qin, J.; Song, Y.; Lu, K.; Ding, R.; Shi, W.; Bian, Q. Mechanism of circRNA_SMG6 mediating lung macrophage ECM degradation via miR-570-3p in microplastics-induced emphysema. Environ. Int. 2024, 187, 108701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.H.; Seo, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, I.; Jeon, K.; Kim, B.; Lee, K. Polypropylene nanoplastic exposure leads to lung inflammation through p38-mediated NF-kappaB pathway due to mitochondrial damage. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2023, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzfischer, M.; Ruoss, T.S.; Niechcial, A.; Lee, S.S.; Wawrzyniak, M.; Laimbacher, A.; Atrott, K.; Manzini, R.; Wilmink, M.; Linzmeier, L.; et al. Impact of Nanoplastic Particles on Macrophage Inflammation and Intestinal Health in a Mouse Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolotova, N.; Dzhalilova, D.; Tsvetkov, I.; Makarova, O. Influence of Microplastics on Morphological Manifestations of Experimental Acute Colitis. Toxics 2023, 11, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xuan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhu, M.; Xu, J.; Chen, J. Polystyrene nanoplastics induce intestinal and hepatic inflammation through activation of NF-kappaB/NLRP3 pathways and related gut-liver axis in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Dai, H.; Wang, B.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Q.; Xu, F.; Cheng, H.; Sun, D.; et al. Nanoplastics Shape Adaptive Anticancer Immunity in the Colon in Mice. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 3516–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guraka, A.; Souch, G.; Duff, R.; Brown, D.; Moritz, W.; Kermanizadeh, A. Microplastic-induced hepatic adverse effects evaluated in advanced quadruple cell human primary models following three weeks of repeated exposure. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Adiele, N.; Gomes, D.; Malovichko, M.; Conklin, D.J.; Ekuban, A.; Luo, J.; Gripshover, T.; Watson, W.H.; Banerjee, M.; et al. Obesogenic polystyrene microplastic exposures disrupt the gut-liver-adipose axis. Toxicol. Sci. 2024, 198, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zeng, X.; Li, J.; Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Luan, T. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis reveals heterogeneity of the patterns of responsive genes and cell communications in liver cell populations of zebrafish exposed to polystyrene nanoplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 889, 164082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, M.; Guo, H.; Wei, S.; Xu, W.; Yan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chang, K.; Wei, G.; et al. Single-cell transcriptome analysis of liver immune microenvironment changes induced by microplastics in mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Jin, P.; Fan, K.; Pei, H.; He, Z.; Du, R.; Cao, C.; Yang, Y. Polystyrene microplastics exposure aggravates acute liver injury by promoting Kupffer cell pyroptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 126, 111307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S. Polystyrene microplastics-induced macrophage extracellular traps contributes to liver fibrotic injury by activating ROS/TGF-beta/Smad2/3 signaling axis. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 324, 121388. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, K.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H.; Hou, L.; Guo, T.; Zhao, H.; Xing, M. Polystyrene microplastics promote liver inflammation by inducing the formation of macrophages extracellular traps. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131236. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Liu, L.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Fan, S.; Yang, Y.; Long, Y.; Liu, X. Acute exposure to polystyrene nanoparticles promotes liver injury by inducing mitochondrial ROS-dependent necroptosis and augmenting macrophage-hepatocyte crosstalk. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2024, 21, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Boran, T.; Zengin, O.S.; Seker, Z.; Akyildiz, A.G.; Kara, M.; Oztas, E.; Ozhan, G. An evaluation of a hepatotoxicity risk induced by the microplastic polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) using HepG2/THP-1 co-culture model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 28890–28904. [Google Scholar]
- Giannandrea, D.; Parolini, M.; Citro, V.; De Felice, B.; Pezzotta, A.; Abazari, N.; Platonova, N.; Sugni, M.; Chiu, M.; Villa, A.; et al. Nanoplastic impact on bone microenvironment: A snapshot from murine bone cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 462, 132717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Sun, H.; Yang, B.; Song, E.; Song, Y. Long-term polystyrene nanoplastic exposure disrupt hepatic lipid metabolism and cause atherosclerosis in ApoE(−/−) mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133583. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Dai, H.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, F.; Ma, Q.; Lin, F.; et al. Oral feeding of nanoplastics affects brain function of mice by inducing macrophage IL-1 signal in the intestine. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.G.; Kang, S.; Yoon, H.J.; Im, S.; Oh, S.J.; Pak, Y.K. Polystyrene Microplastics Exacerbate Systemic Inflammation in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ye, S.; Liu, W.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L.; Wei, S.; Anwaier, A.; Chang, K.; Malafaia, G.; Zhang, H.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis decodes the kidney microenvironment induced by polystyrene microplastics in mice receiving a high-fat diet. J. Nanobiotechnology 2024, 22, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, Q.; Gao, L.; Feng, L.; Xiong, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; Huang, L.; Li, L.; Luo, P. Toxicological effects of microplastics in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 2350–2362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Danso, I.K.; Woo, J.H.; Lee, K. Pulmonary Toxicity of Polystyrene, Polypropylene, and Polyvinyl Chloride Microplastics in Mice. Molecules 2022, 27, 7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Gupta, I.; Xia, L.; Pitchai, A.; Shannahan, J.; Mitra, S. Generation of Eroded Nanoplastics from Domestic Wastes and Their Impact on Macrophage Cell Viability and Gene Expression. Molecules 2024, 29, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassano, D.; Bogni, A.; La Spina, R.; Gilliland, D.; Ponti, J. Investigating the Cellular Uptake of Model Nanoplastics by Single-Cell ICP-MS. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Xin, Q.; Tang, L.; Tang, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, L. A quantitative study of nanoplastics within cells using magnetic resonance imaging. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 886, 164033. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, A.; Tannert, A.; Ziller, N.; Eiserloh, S.; Gohrig, B.; Guliev, R.R.; Gonzalez Vazquez, M.J.; Naumann, M.; Mosig, A.S.; Stengel, S.; et al. Quantification of Polystyrene Uptake by Different Cell Lines Using Fluorescence Microscopy and Label-Free Visualization of Intracellular Polystyrene Particles by Raman Microspectroscopic Imaging. Cells 2024, 13, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Jia, H. In Vitro Assessment Reveals the Effects of Environmentally Persistent Free Radicals on the Toxicity of Photoaged Tire Wear Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 1664–1674. [Google Scholar]
- Volkl, M.; Jerome, V.; Weig, A.; Jasinski, J.; Meides, N.; Strohriegl, P.; Scheibel, T.; Freitag, R. Pristine and artificially-aged polystyrene microplastic particles differ in regard to cellular response. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 128955. [Google Scholar]
- Aloi, N.; Calarco, A.; Curcuruto, G.; Di Natale, M.; Augello, G.; Carroccio, S.C.; Cerruti, P.; Cervello, M.; Cuttitta, A.; Colombo, P.; et al. Photoaging of polystyrene-based microplastics amplifies inflammatory response in macrophages. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143131. [Google Scholar]
- Visalli, G.; Lagana, A.; Facciola, A.; Iaconis, A.; Curcio, J.; Pollino, S.; Celesti, C.; Scalese, S.; Libertino, S.; Iannazzo, D.; et al. Enhancement of biological effects of oxidised nano- and microplastics in human professional phagocytes. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 99, 104086. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Ye, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Cui, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L. Hydrogen bonding-mediated interaction underlies the enhanced membrane toxicity of chemically transformed polystyrene microplastics by cadmium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.Z.; Liu, J.H.; Gao, Y.R.; Liang, J.; Tang, C.L. Effect of macrophage polarization on parasitic protection against type 1 diabetes mellitus. Exp. Parasitol. 2024, 256, 108649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lun, H.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Liu, F. The effect of intestinal flora metabolites on macrophage polarization. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35755. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Quan, X.; Shou, D.; Guo, X.; Ouyang, D.; Zhuang, L. New insights into microbial degradation of polyethylene microplastic and potential polyethylene-degrading bacteria in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, South China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 486, 137061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bianchi, M.G.; Casati, L.; Sauro, G.; Taurino, G.; Griffini, E.; Milani, C.; Ventura, M.; Bussolati, O.; Chiu, M. Biological Effects of Micro-/Nano-Plastics in Macrophages. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050394
Bianchi MG, Casati L, Sauro G, Taurino G, Griffini E, Milani C, Ventura M, Bussolati O, Chiu M. Biological Effects of Micro-/Nano-Plastics in Macrophages. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(5):394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050394
Chicago/Turabian StyleBianchi, Massimiliano G., Lavinia Casati, Giulia Sauro, Giuseppe Taurino, Erika Griffini, Christian Milani, Marco Ventura, Ovidio Bussolati, and Martina Chiu. 2025. "Biological Effects of Micro-/Nano-Plastics in Macrophages" Nanomaterials 15, no. 5: 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050394
APA StyleBianchi, M. G., Casati, L., Sauro, G., Taurino, G., Griffini, E., Milani, C., Ventura, M., Bussolati, O., & Chiu, M. (2025). Biological Effects of Micro-/Nano-Plastics in Macrophages. Nanomaterials, 15(5), 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050394






