Microwave-Assisted Preparation of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Aerogels Derived from Food Wastes for Supercapacitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
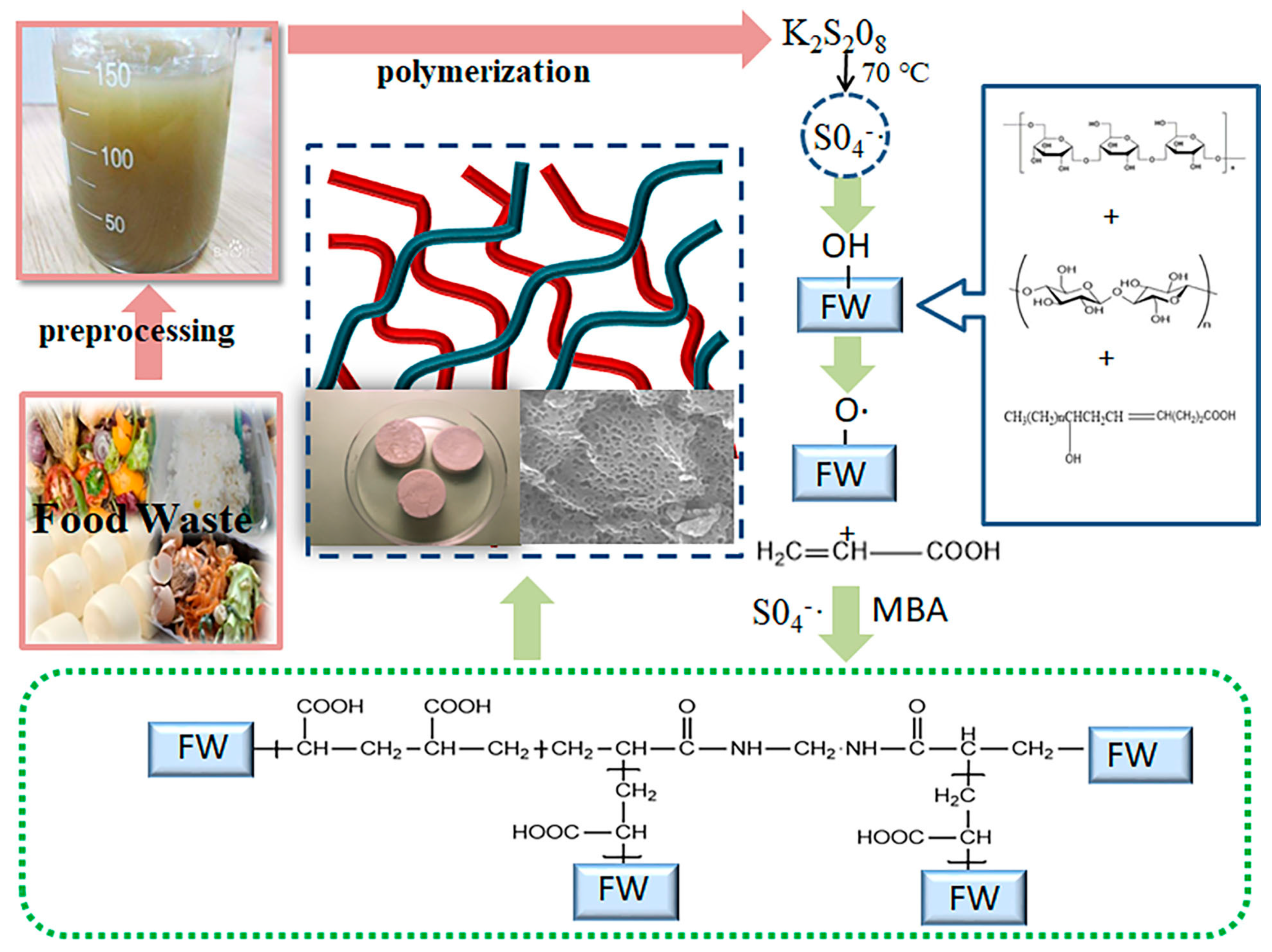
2.1. Preparation of Carbon Aerogel
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
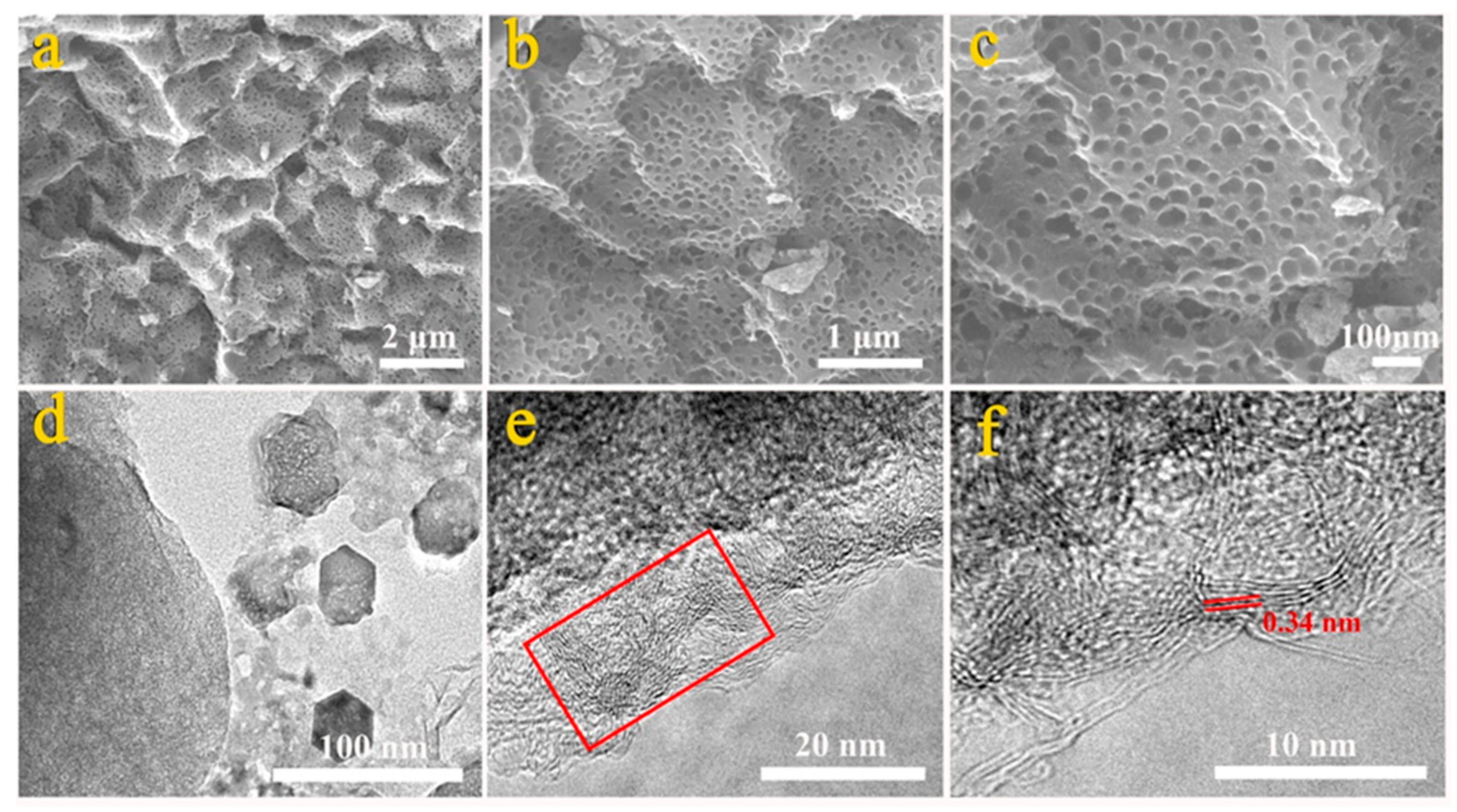
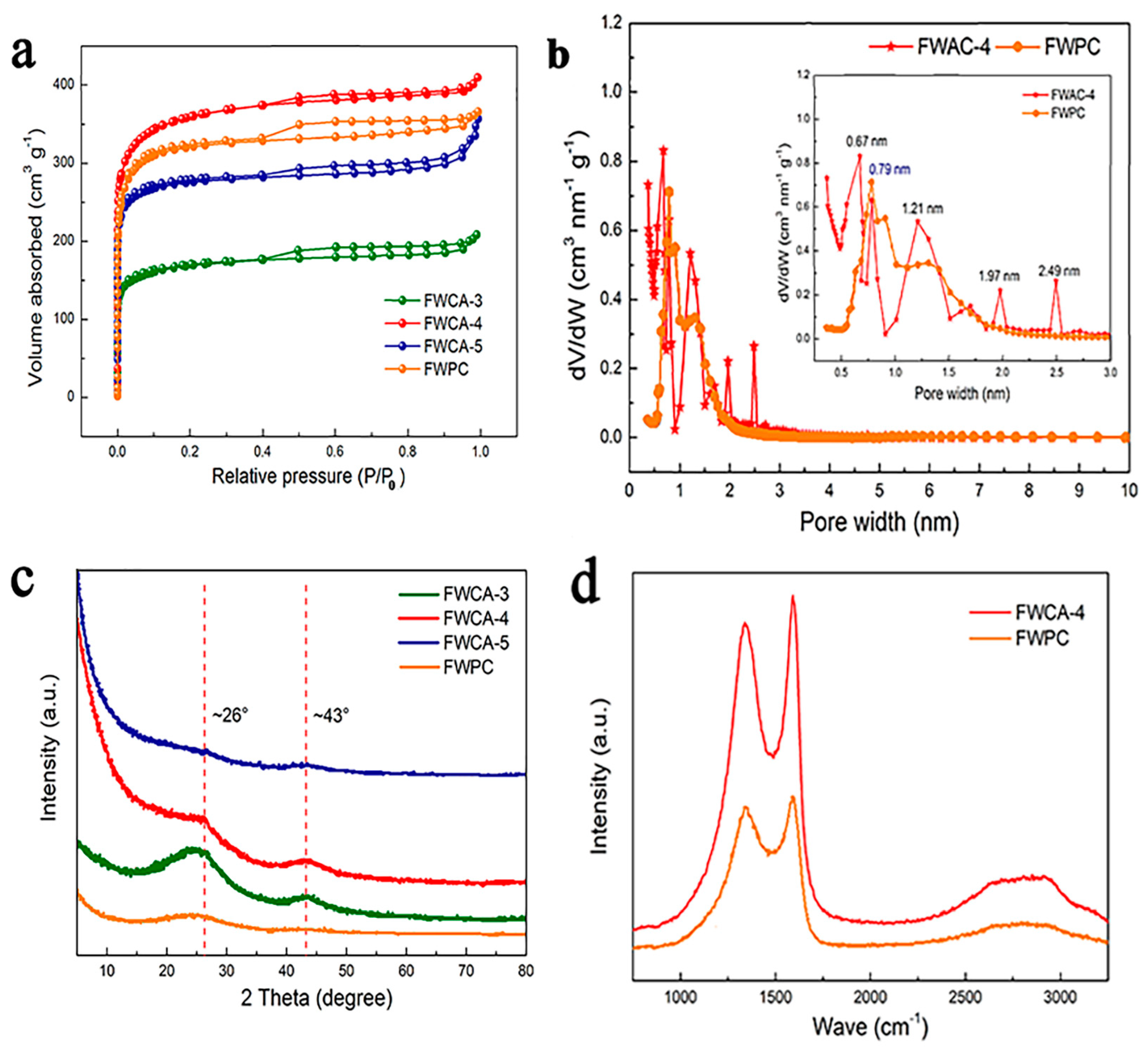
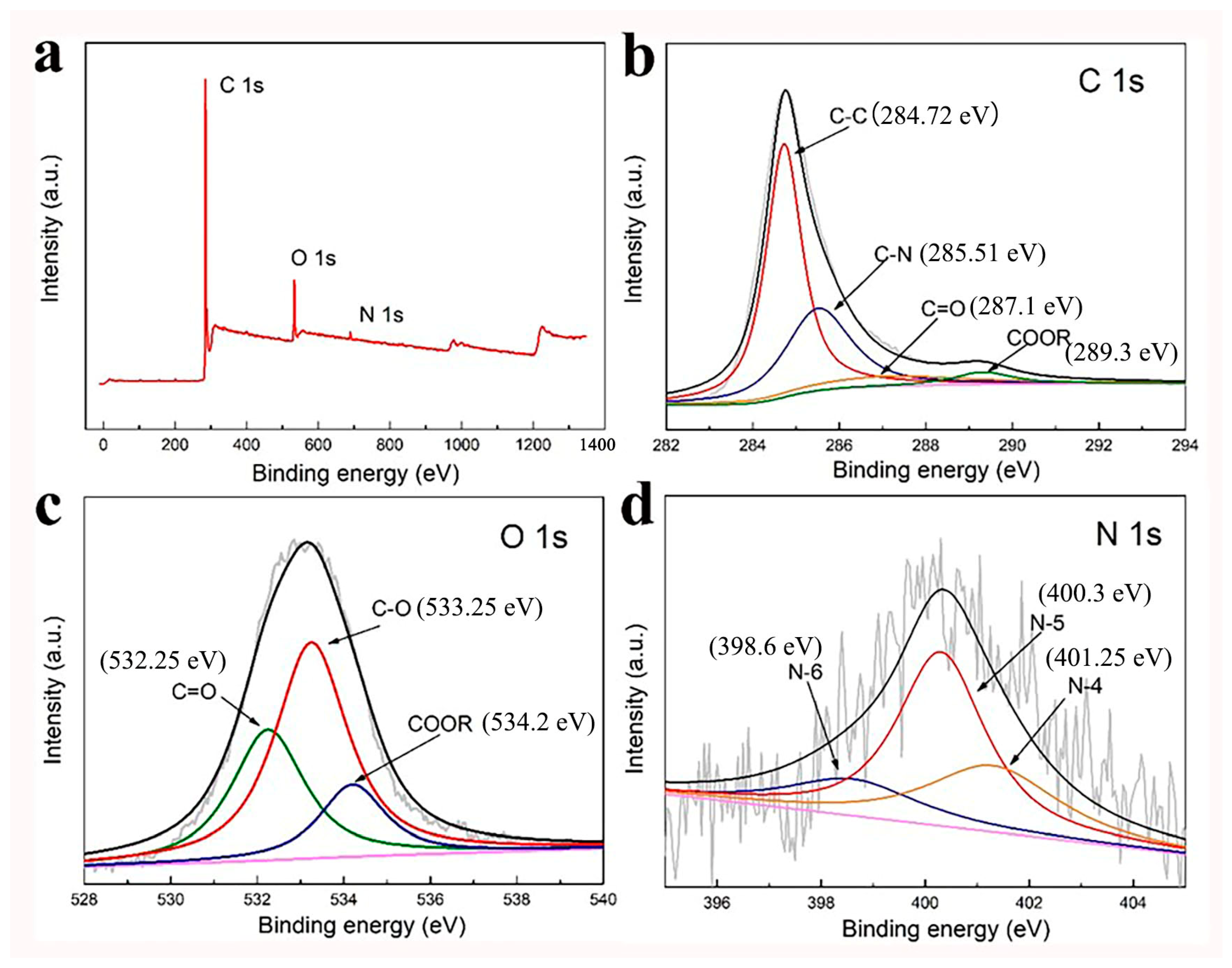
3.1. Morphological and Structural Characterization
3.2. Electrochemical Performance
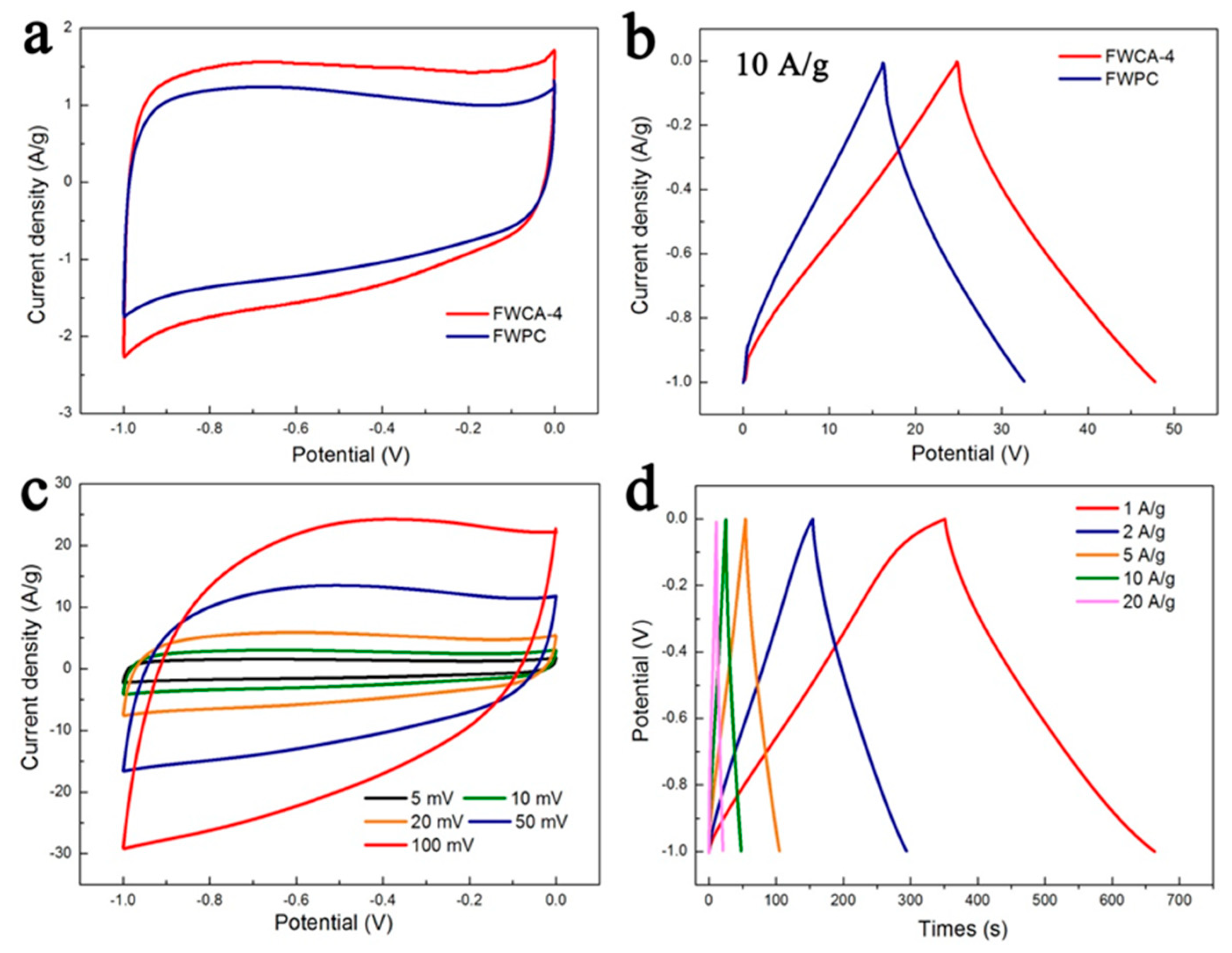
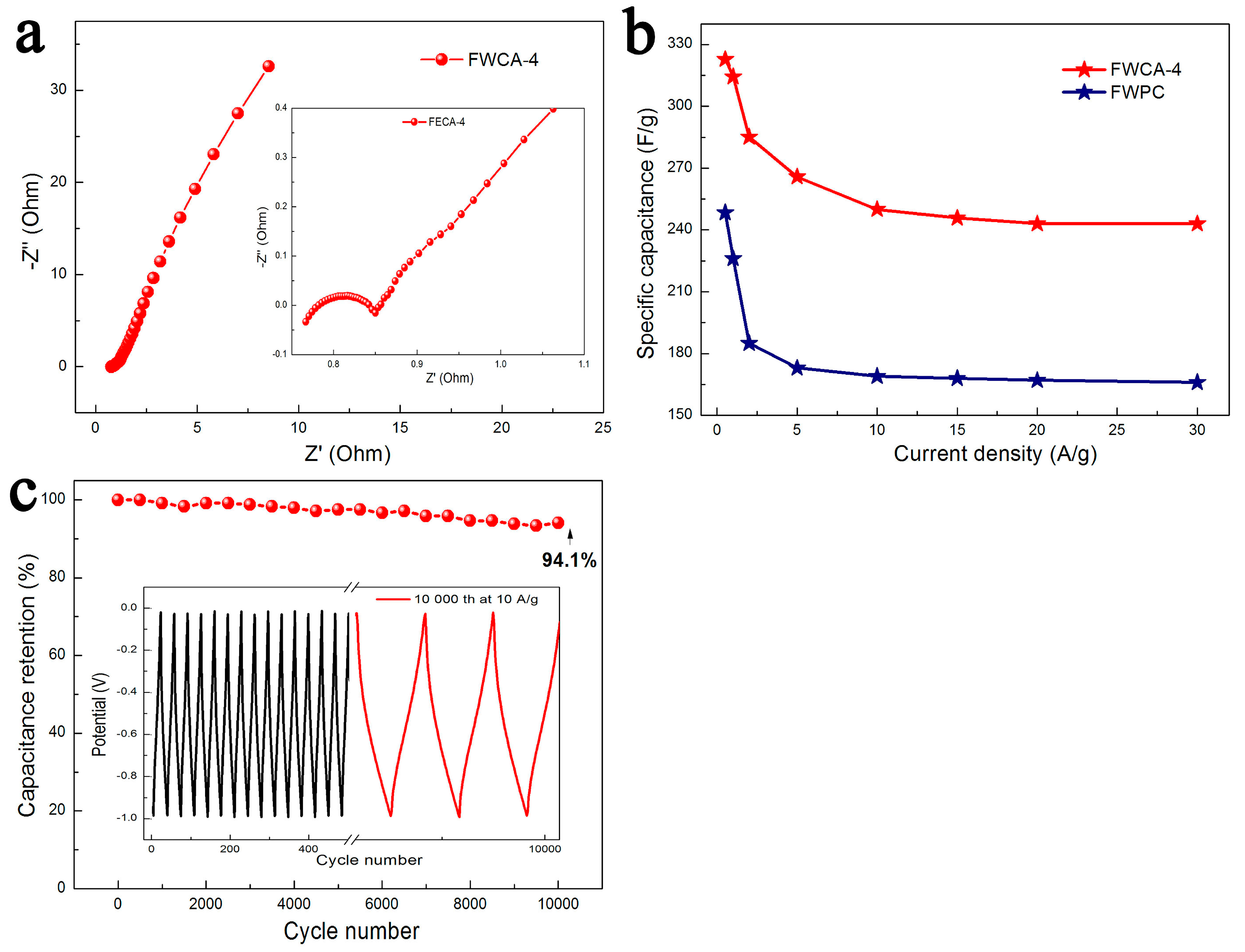
3.2.1. Electrochemical Properties in Three-Electrode System
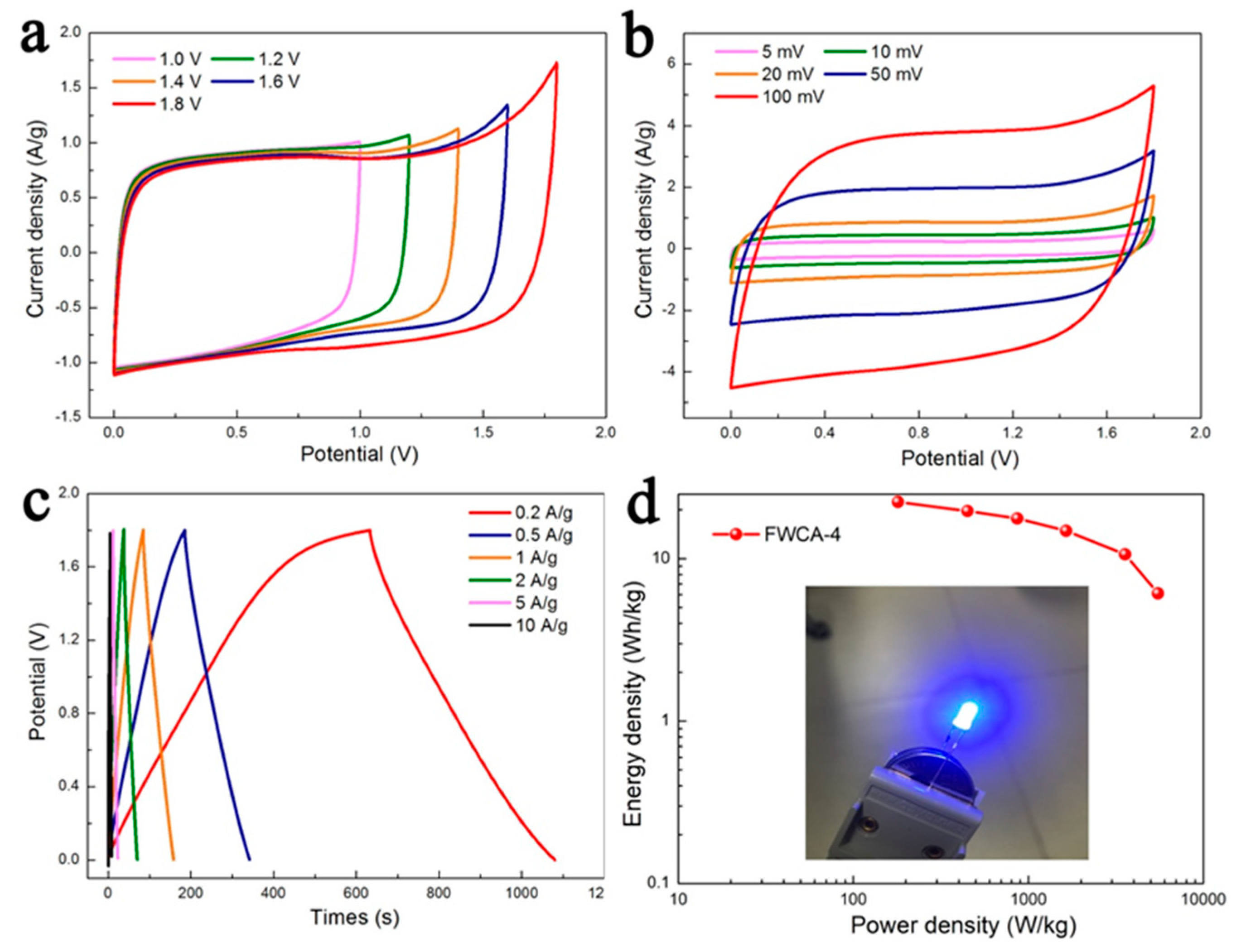
3.2.2. Electrochemical Properties in Symmetrical System
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, Z.; Lyu, J.; Ding, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X. Aerogel fibers made via generic sol-gel centrifugal spinning strategy enable dynamic removal of volatile organic compounds from high-flux gas. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2407221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Lee, W.; Choi, H.; Parale, V.G.; Patil, U.M.; Kanamori, K.; Seo, J.G.; Bae, Y.-S.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, H.-H.; et al. Sol–gel synthesized nickel-doped ruthenium oxide aerogel for highly efficient acidic hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Energy Res. 2024, 2024, 1457751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X. Polyimide aerogel fibers with superior flame resistance, strength, hydrophobicity, and flexibility made via a universal sol–gel confined transition strategy. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 4759–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekala, R.W.; Farmer, J.C.; Alviso, C.T.; Tran, T.D.; Mayer, S.T.; Miller, J.M.; Dunn, B.J. Carbon aerogels for electrochemical applications. Non-Cryst. Solids 1998, 225, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pröbstle, H.; Wiener, M.; Fricke, J.J. Carbon aerogels for electrochemical double layer capacitors. Porous Mater. 2003, 10, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahbakhsh, A.; Bahramian, A.R. Self-assembled and pyrolyzed carbon aerogels: An overview of their preparation mechanisms, properties and applications. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 14139–14158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Niu, W.; Zhang, S. Extremely stretchable, sticky and conductive double-network ionic hydrogel for ultra-stretchable and compressible supercapacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 124105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ma, R.; Luo, J.; Sun, S.; Cui, C.; Fang, L.; Huang, H. Microwave pyrolysis of food waste for high-quality syngas production: Positive effects of a CO2 reaction atmosphere and insights into the intrinsic reaction mechanisms. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 206, 112490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Xu, W.; Zheng, J.; Kong, F.; Cui, P.; Wu, D.; Qian, B.; Chen, S.; Song, L. Soybean roots-derived N, P Co-doped mesoporous hard carbon for boosting sodium and potassium-ion batteries. Carbon 2021, 178, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, R.; Menéndez, J.A.; Arenillas, A.; Cot, J. Microwave-assisted pyrolysis of biomass feedstocks: The way forward? Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5481–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, F.; Wu, J.; Zhao, L. Leakage-proof phase change composites supported by biomass carbon aerogels from succulents. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1858–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhan, Y.; Guo, F.; Du, S.; Tian, B.; Dong, Y.; Qian, L. Synthesis of biomass-derived carbon aerogel/MnO composite as electrode material for high-performance supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 390, 138817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Yang, T.; Tong, Y.; Wang, J.; Luan, J.H.; Jiao, Z.B.; Chen, D.; Yang, Y.; Hu, A.; Liu, C.T.; et al. Heterogeneous precipitation behavior and stacking-fault-mediated deformation in a CoCrNi-based medium-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2017, 138, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Sahu, J.N.; Ganesan, P. Effect of process parameters on production of biochar from biomass waste through pyrolysis: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ma, R.; Xu, X.; Sun, S.; Micropor, J.L. Microwave-induced preparation of porous graphene nanosheets derived from biomass for supercapacitors. Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 324, 111277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Jiménez, G.; Stevens, L.A.; Kostas, E.T.; Hernández-Montoya, V.; Robinson, J.P.; Binner, E.R. Rapid, simple and sustainable synthesis of ultra-microporous carbons with high performance for CO2 uptake, via microwave heating. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Ling, P.; Qiu, J.; Yu, M.; Zhang, X.; Yu, C.; Zheng, M. Efficient preparation of biomass-based mesoporous carbons for supercapacitors with both high energy density and high. power density. J. Power Sources 2013, 240, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, K.E.; Han, S.S.; Lim, N.; Kang, J.; Park, C.G.; Kim, K. Solvent-responsive polymer nanocapsules with controlled permeability: Encapsulation and release of a fluorescent dye by swelling and deswelling. Chem. Commun. 2009, 12, 1472–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Carey, T.; Chen, K.; Yin, Y.; Torrisi, F. Environmentally-friendly conductive cotton fabric as flexible strain sensor based on hot press reduced graphene oxide. Carbon 2017, 111, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Kong, L.; Xie, M.; Lu, W.; Liu, H.; Li, N.; Feng, Z.; Zhan, J. Carbon aerogel from forestry biomass as a peroxymonosulfate activator for organic contaminants degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Y. Synthesis composite hydrogels from inorganic-organic hybrids based on leftover rice for environment-friendly controlled-release urea fertilizers. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Xing, H. Combination of Fe (II)-induced oxygen deficiency and metal doping strategy for construction of high efficiency water oxidation electrocatalysts under industrial-scale current density. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 135048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, X.; Li, L.; Hu, Z.; Guo, P.; Jiang, Y. The catalytic pyrolysis of food waste by microwave heating. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 166, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneroso, D.; Bermúdez, J.M.; Arenillas, A.; Menéndez, J.A. Influence of the microwave absorbent and moisture content on the microwave pyrolysis of an organic municipal solid waste. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 105, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, R.; Oliva, J. Rodriguez-Gonzalez, Effect of the micro-, meso- and macropores on the electrochemical performance of supercapacitors: A review. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 6989–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.-Q.; Yuan, L.-Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Z.-R.; Chu, S.-Q.; Zheng, L.-R.; Zhang, J.; Chai, Z.-F.; Shi, W.-Q. Introduction of amino groups into acid-resistant MOFs for enhanced U(vi) sorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagiello, J.; Chojnacka, A.; Pourhosseini, S.E.M.; Wang, Z.; Beguin, F. A dual shape pore model to analyze the gas adsorption data of hierarchical micro-mesoporous carbons. Carbon 2021, 178, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Wei, X. A versatile biomass derived carbon material for oxygen reduction reaction, supercapacitors and oil/water separation. Nano Energy 2017, 33, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Chen, C.; Yu, D.; Sun, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Besenbacher, F.; Yu, M. One-step production of O-N-S co-doped three-dimensional hierarchical porous carbons for high-performance supercapacitors. Nano Energy 2018, 47, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Hourcade, M.; Reis, G.S.D.; Grimm, A.; Dinh, V.M.; Lima, E.C.; Larsson, S.H.; Gentili, F.G. Microalgae biomass as a sustainable precursor to produce nitrogen-doped biochar for efficient removal of emerging pollutants from aqueous media. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 348, 131280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talreja, N.; Jung, S.; Yen, L.T.H.; Kim, T. Phenol-formaldehyde-resin-based activated carbons with controlled pore size distribution for high-performance supercapacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Tanaka, S.; Nishiyama, Y.E.N. KOH activation of ordered mesoporous carbons prepared by a soft-templating method and their enhanced electrochemical properties. Carbon 2010, 48, 1985–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yang, J.; Bai, T.; Long, B.; Zhou, X. Facile synthesis of few-layer graphene from biomass waste and its application in lithium ion batteries. J. Electronal. Chem. 2016, 768, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Tian, C.; Li, M.; Meng, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Yin, J.; Fu, H.J. From coconut shell to porous graphene-like nanosheets for high-power supercapacitors. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 6462–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Yu, G.; Lu, L.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; Dai, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, H. Controllable thickness carbon sheet under anion and cation co-doping for supercapacitors and capacitive deionization. Carbon 2024, 225, 119097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Kil, H.-S.; Kim, J.; Mochida, I.; Nakabayashi, K.; Rhee, C.K.; Miyawaki, J.; Yoon, S.-H. Highly graphitized carbon from non-graphitizable raw material and its formation mechanism based on domain theory. Carbon 2017, 121, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-X.; He, D.; Zhu, M.; Wu, L.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.-H.; Yang, H. Green fabrication of hierarchically porous carbon microtubes from biomass waste via self-activation for high-energy-density supercapacitor. J. Power Sources 2023, 560, 232703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, Y.; Fan, H.; Wei, X.; Hu, C.; Luo, H.; Qu, L. Large scale production of biomass-derivedN-doped porous carbon spheres for oxygen reduction and supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yu, C.; Zhong, W. Facile synthesis of high nitrogen-doped content, mesopore-dominated biomass-derived hierarchical porous graphitic carbon for high performance supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 334, 135615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, D.; Yan, Y.; Guo, T.; Pang, H.; Xue, H. Porous high specific surface area-activated carbon with co-doping N, S and P for high-performance supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 43780–43788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Ding, B.; Liu, S.; Henzie, J.; Amin, M.A.; Yuliarto, B.; Sugahara, Y.; Yamauchi, Y. N-doped hollow carbon nanoplates with mesoporous thin shells towards high-performance supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 2022, 542, 231776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani-Pedram, M.; Retuert, J.; Quijada, R. Hydrogels based on modified chitosan, 1 - Synthesis and swelling behavior of poly(acrylic acid) grafted chitosan. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2000, 201, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zou, H.; Liu, P. Anisotropic and Lightweight Carbon/Graphene Composite Aerogels for Efficient Thermal Insulation and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 45844–45852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frackowiak, E.; Fic, K.; Meller, M.; Lota, G. Electrochemistry Serving People and Nature: High-Energy Ecocapacitors based on Redox-Active Electrolytes. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xi, X.; Xing, X.; Wu, D. A facile biomass based approach towards hierarchically porous nitrogen-doped carbon aerogels. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 83613–83618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Li, T.; Yu, H.; Zhi, L.; Liu, Z.; Lei, Z. Biomass-Derived Carbon Fiber Aerogel as a Binder-Free Electrode for High-Rate Supercapacitors. J. Phys. Chem. C Nanomater. Interfaces 2016, 4, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, G.; Shen, J.; Zou, L.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X. Nanocellulose-derived highly porous carbon aerogels for supercapacitors. Carbon 2016, 99, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Li, D.; Luo, C.; Qiang, F.; Pan, C. Highly porous graphitic biomass carbon as advanced electrode materials for supercapacitors. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 4132–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, W.; Xiao, D.; Wang, X. Oxygen-rich hierarchical porous carbon made from pomelo peel fiber as electrode material for supercapacitor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 416, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, S.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, D.; Yan, H.; Tian, C.; Fu, H. A hierarchical porous carbon material from a loofah sponge network for high performance supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 42430–42437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Cai, Z.; Ma, Z.; Gong, S. Cellulose Nanofibril/Reduced Graphene Oxide/Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Aerogels for Highly Flexible and All-Solid-State Supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 3263–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Lai, X.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. Hierarchical structure N, O-co-doped porous carbon/carbon nanotube composite derived from coal for supercapacitors and CO2 capture. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, C.; Yu, X.; Liang, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Lv, R.; Huang, Z.; Kang, F. Flour food waste derived activated carbon for high-performance supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 89391–89396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Proximate Analysis (wt.%) | Elemental Analysis a (wt.%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | Ash a | Volatiles a | C | H | N | S | O c |
| 80.53 ±3.01 | 15.12 ±0.56 | 84.88 ±3.24 | 54.26 ±1.71 | 8.13 ±0.31 | 4.65 ±0.13 | 0.27 ±0.01 | 32.69 ±2.09 |
| Sample | SBET (m2/g) a | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) b | Micropore Volume (cm3/g) c | Mesopore Volume (cm3/g) | VMi/VT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWCA-3 | 771.26 | 0.512 | 0.23 | 0.086 | 0.449 |
| FWCA-4 | 1470 | 0.634 | 0.40 | 0.11 | 0.631 |
| FWCA-5 | 1070 | 0.54 | 0.29 | 0.14 | 0.537 |
| FWPC | 1240 | 0.56 | 0.49 | 0.07 | 0.875 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Z.; Li, T.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Fu, J.; Sun, S. Microwave-Assisted Preparation of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Aerogels Derived from Food Wastes for Supercapacitors. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050387
Dong Z, Li T, Xu X, Chen Y, Fu J, Sun S. Microwave-Assisted Preparation of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Aerogels Derived from Food Wastes for Supercapacitors. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(5):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050387
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Zijun, Tong Li, Xinghe Xu, Yi Chen, Jiemei Fu, and Shichang Sun. 2025. "Microwave-Assisted Preparation of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Aerogels Derived from Food Wastes for Supercapacitors" Nanomaterials 15, no. 5: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050387
APA StyleDong, Z., Li, T., Xu, X., Chen, Y., Fu, J., & Sun, S. (2025). Microwave-Assisted Preparation of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Aerogels Derived from Food Wastes for Supercapacitors. Nanomaterials, 15(5), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050387






