Stimulus-Responsive Afterglow Carbon Dots from Internal Mechanism to Potential Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
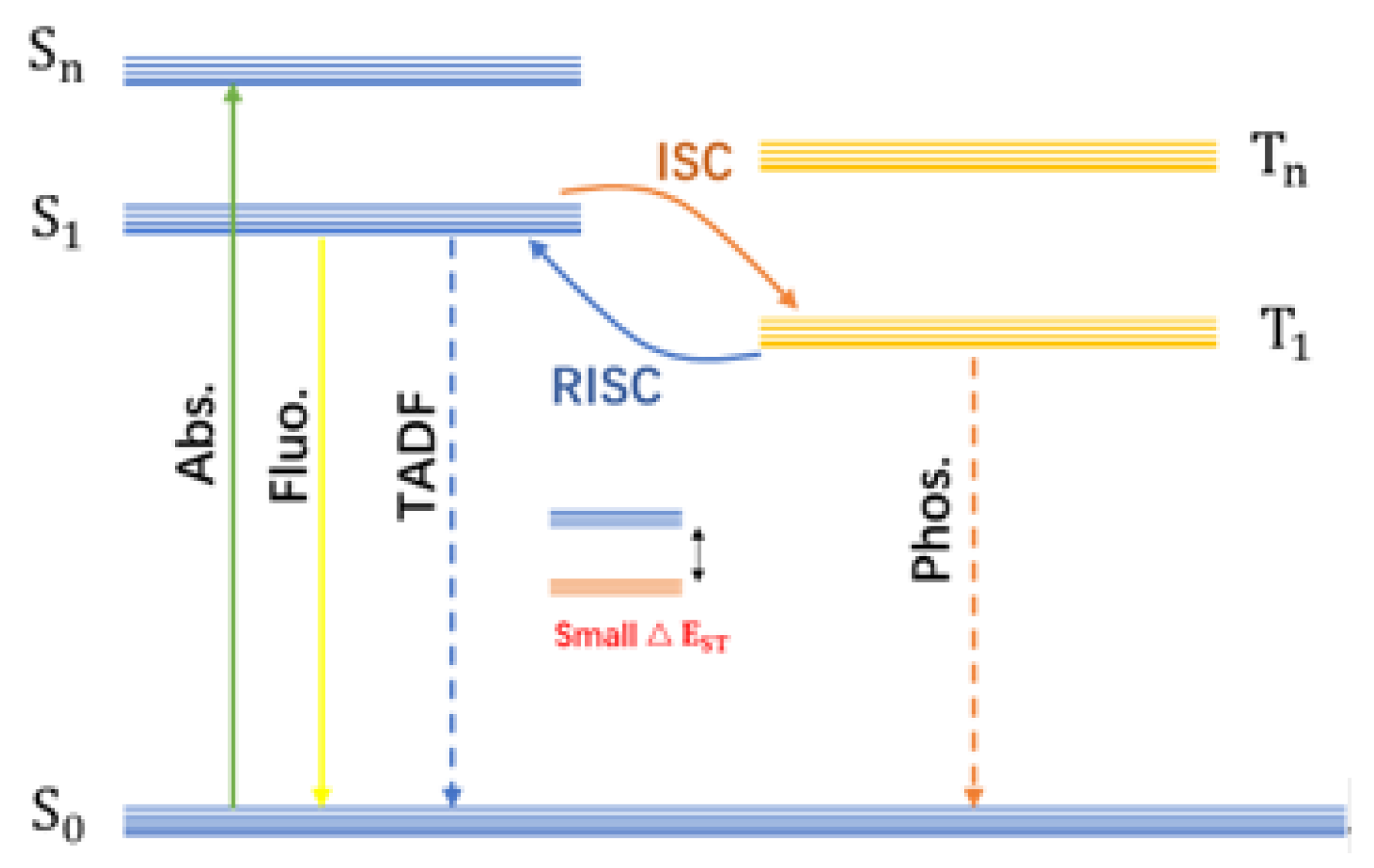
2. Mechanism and Preparation Methods for Afterglow CDs
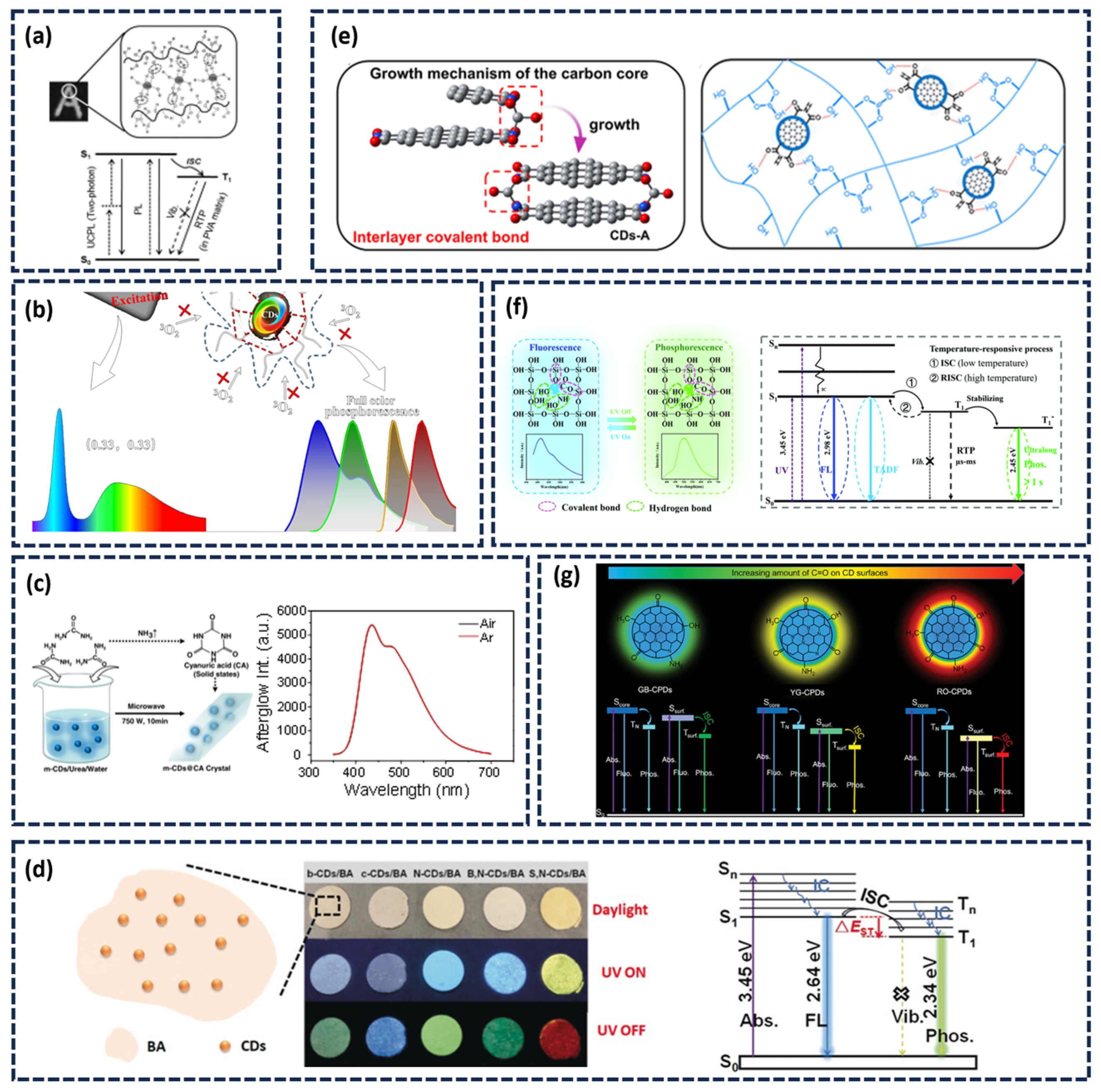
2.1. Construction of the Afterglow Luminescence Center
2.2. Stability of the Afterglow Emission Center
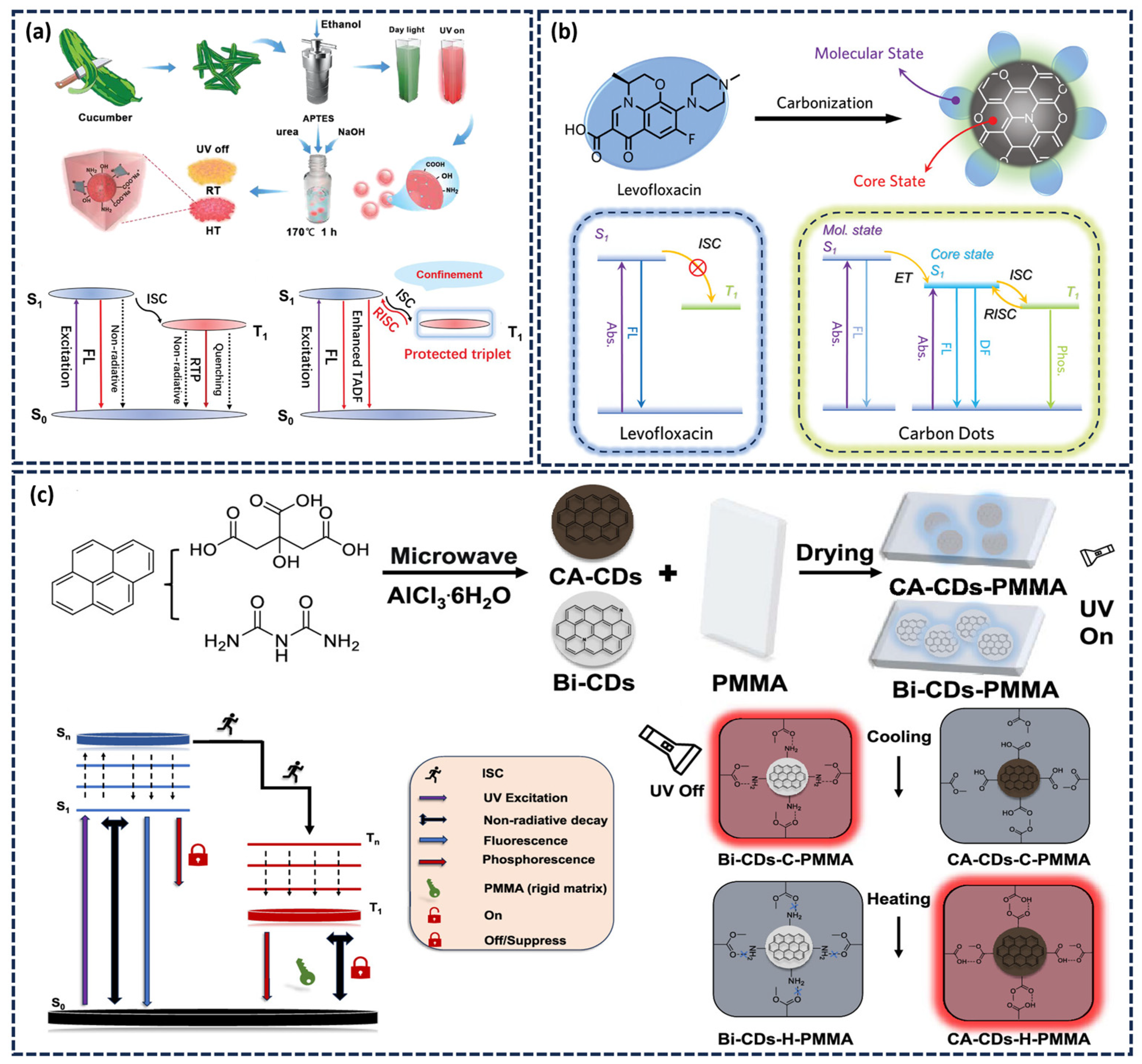
2.2.1. Matrix-Assisted Method
2.2.2. Matrix-Free (Self-Protected) Afterglow CDs
3. Stimulus-Responsive Types and Their Impact on Afterglow Performance
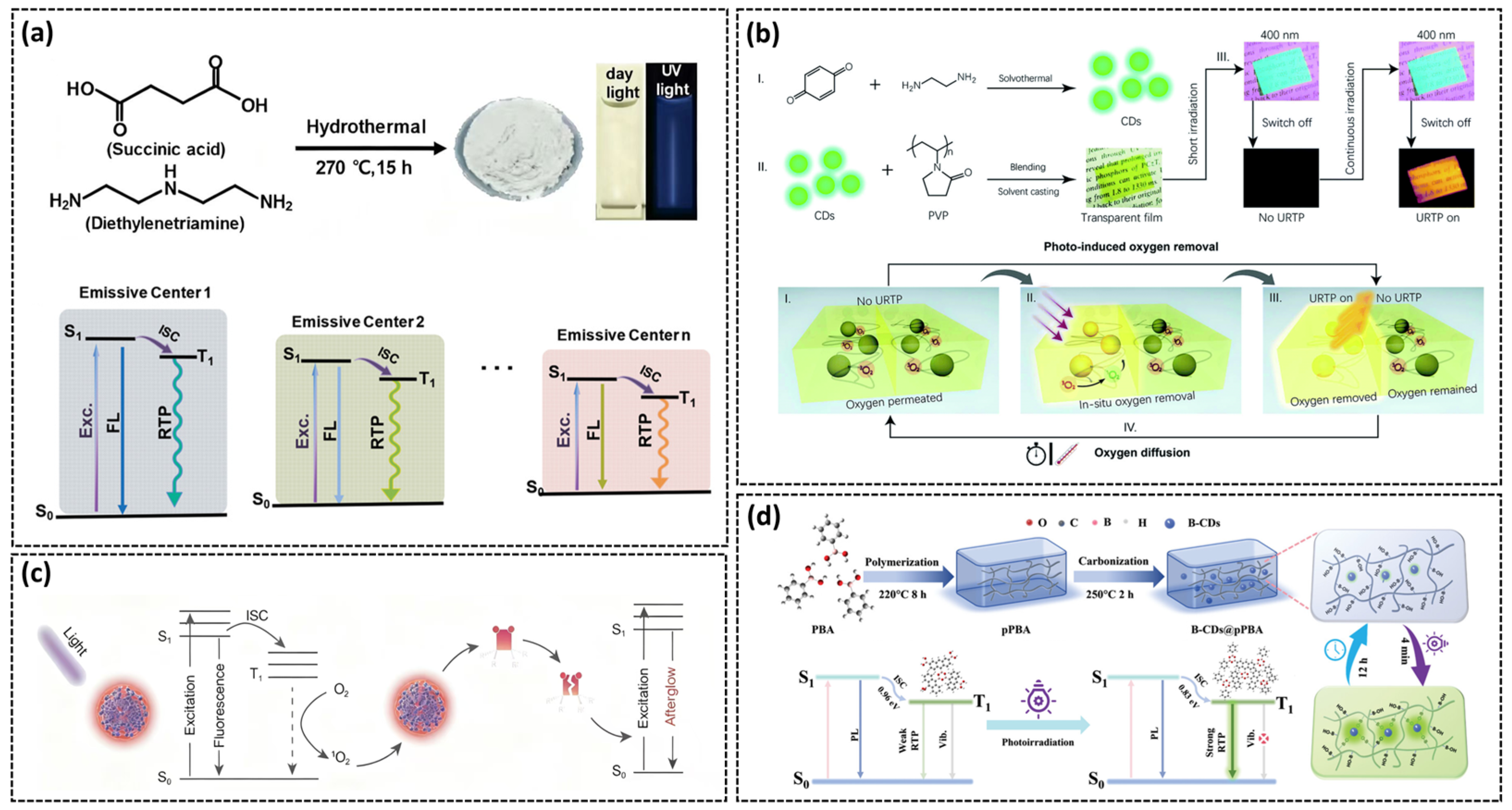
3.1. Temperature-Responsive Afterglow
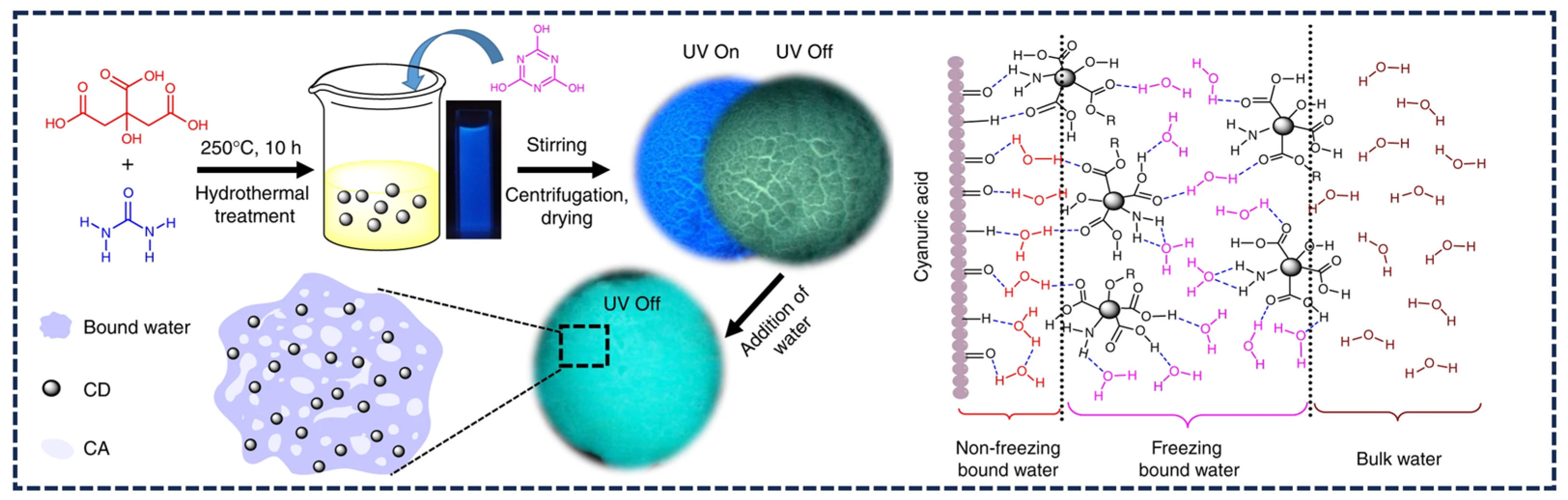
3.2. Moisture-Responsive Afterglow
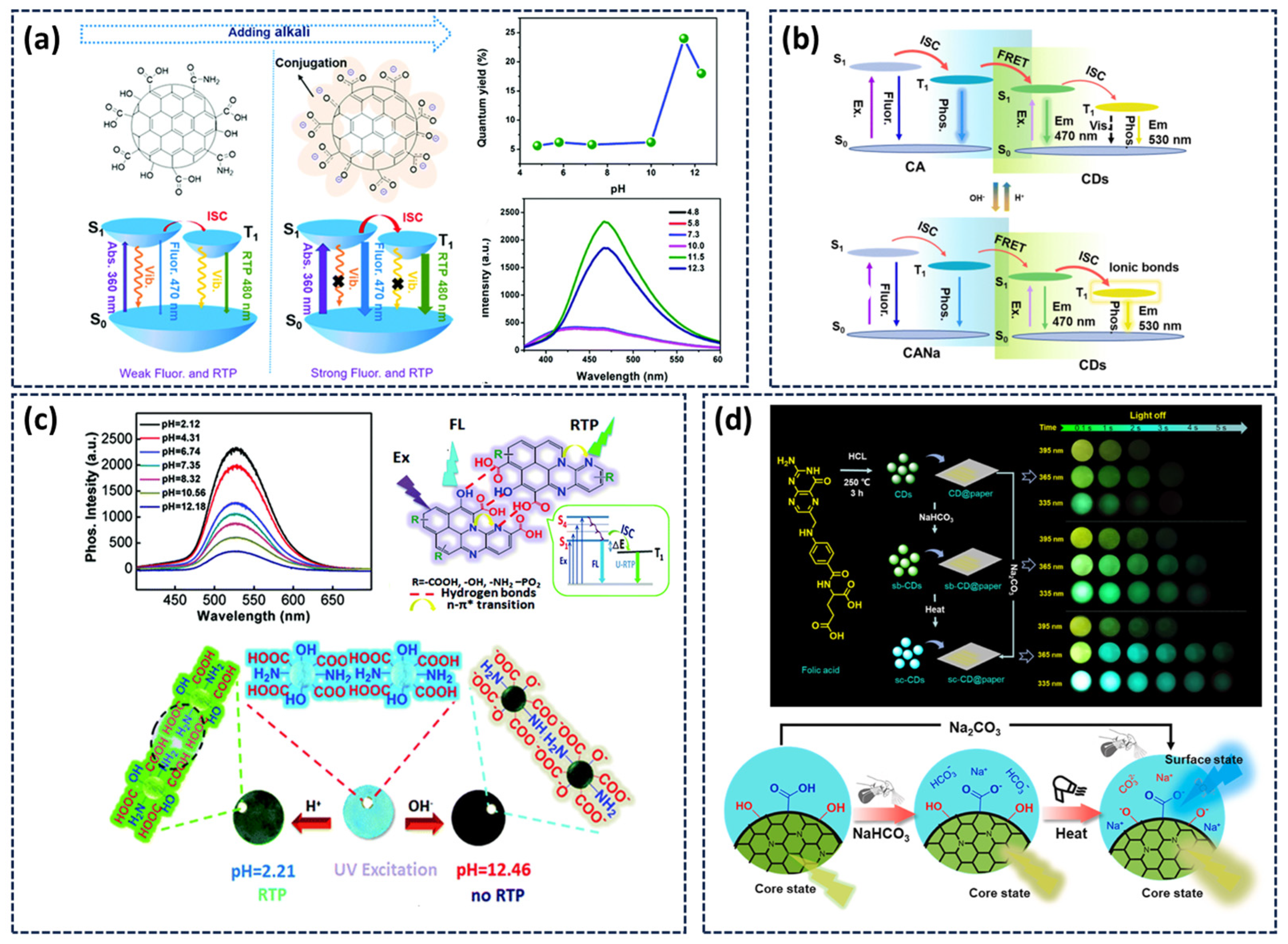
3.3. pH-Responsive Afterglow
3.4. Light-Responsive Afterglow
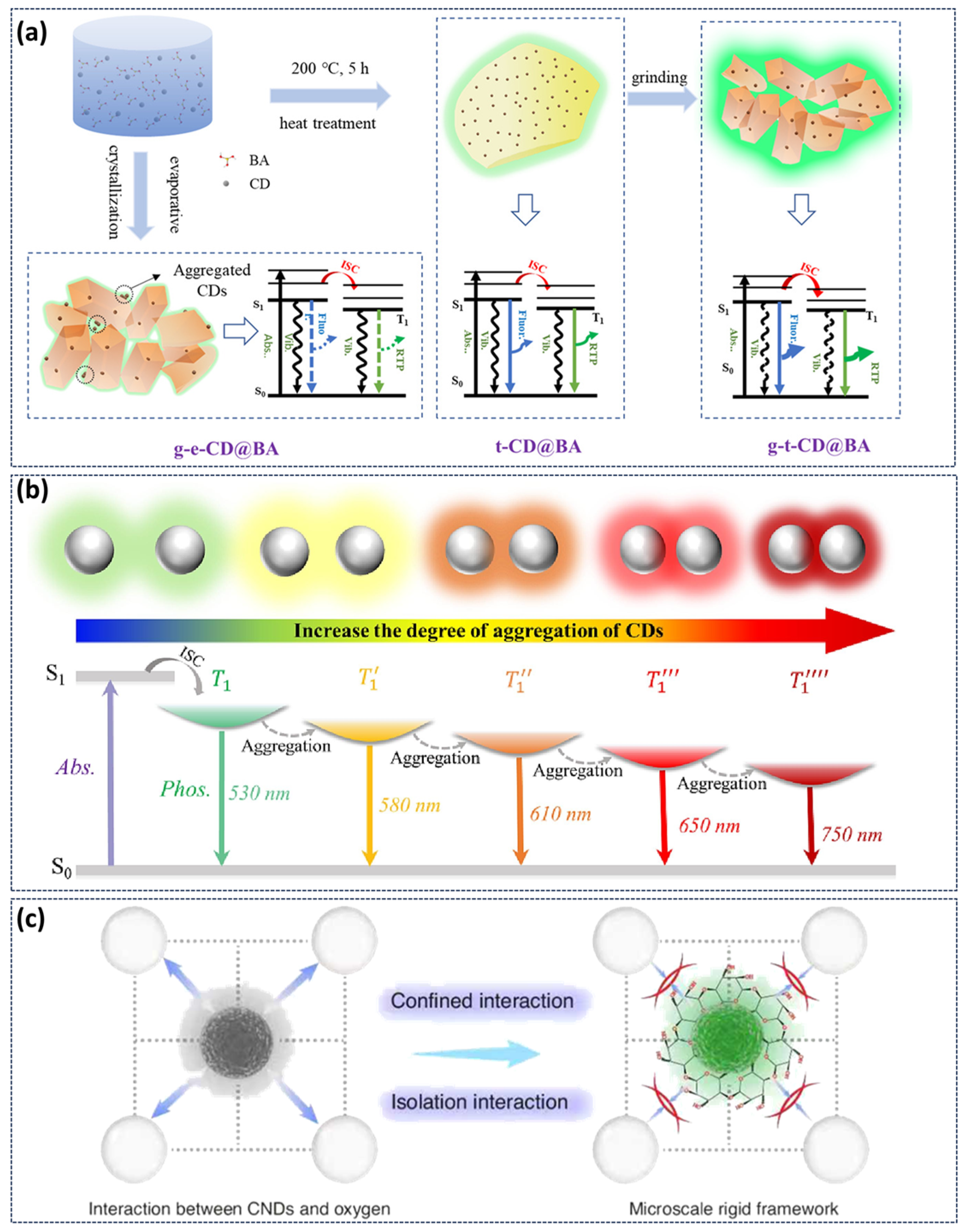
3.5. Other Responses to the Afterglow
4. Application
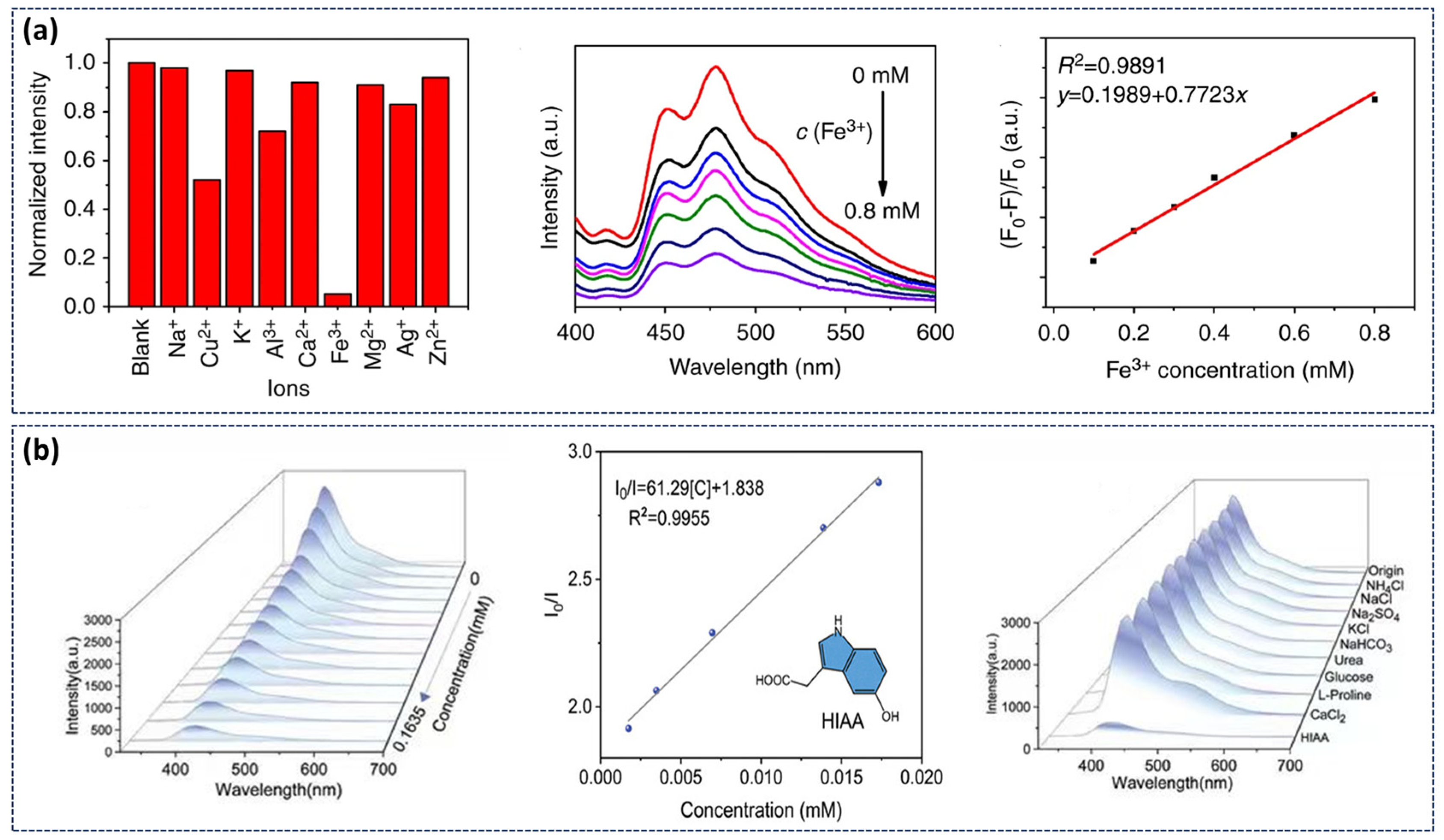
4.1. Sensing
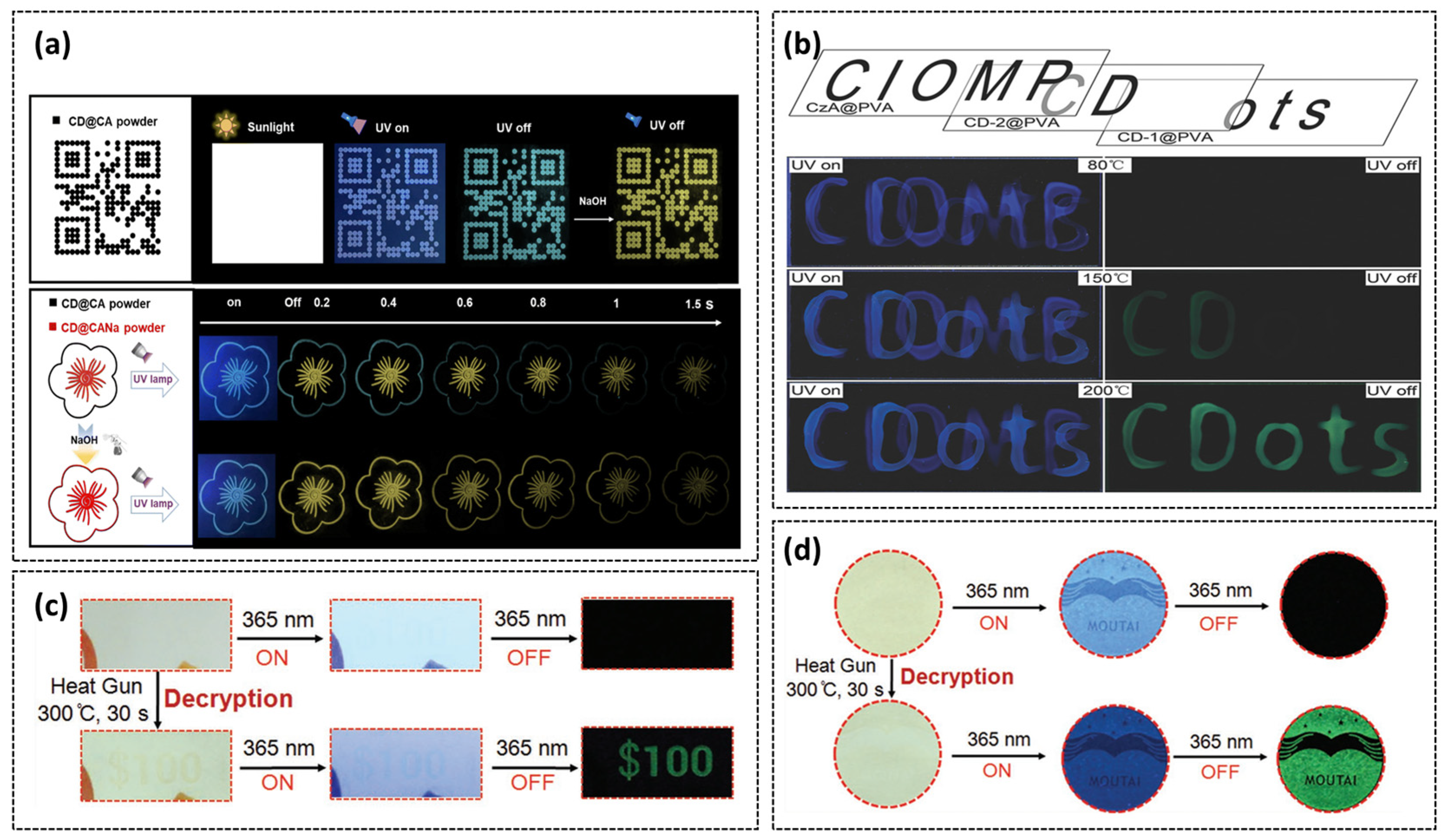
4.2. Information Anti-Counterfeiting Encryption
5. Summary and Outlook
- Exploration of Novel Stimulus-Responsive Afterglow CDs: Current research primarily focuses on conventional stimuli including temperature, humidity, pH, and light. Future work should expand toward novel stimulus-responsive systems involving electric fields, magnetic fields, biomolecules, and gases. Such developments would significantly enrich the response dimensions of CDs and broaden their application scope in next-generation intelligent responsive materials and devices.
- Development of Multi-Stimulus Response Afterglow CDs: Single-stimulus responses are increasingly insufficient for complex application scenarios. Future efforts should focus on developing CD systems capable of multi-stimulus coordination or orthogonal responses, enabling simultaneous or sequential recognition and feedback of multiple environmental parameters. This advancement will enhance their utility and security in multimodal sensing and encryption platforms.
- Development of Wide Color Gamut Dynamic Color Afterglow CDs: Most current color-changing devices exhibit limited color-shifting ranges, struggling to cover the entire visible spectrum. By precisely tuning the energy level structure of color-changing devices, the types and distribution of luminescent center, and the interactions between the substrate and color-changing devices, it is anticipated to achieve wide color gamut, high-contrast, and reversible dynamic color-shifting behavior spanning ultraviolet to near-infrared wavelengths. This advancement addresses the demands of high-end display applications and anti-counterfeiting requirements.
- Expanding the Application Scope of Stimulus-Responsive Afterglow CDs: Beyond conventional sensing and anti-counterfeiting applications, stimulus-responsive afterglow CDs show considerable potential in biomedical applications (e.g., controlled drug delivery, cellular imaging, and pathological microenvironment response imaging), flexible electronics (e.g., wearable sensors and smart labels), and optical information storage and processing. Future efforts should emphasize interdisciplinary collaboration to accelerate the transition of these functional materials from the laboratory to practical implementation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Fang, M.; Li, Z. Stimulus-Responsive Room Temperature Phosphorescence in Purely Organic Luminogens. InfoMat 2020, 2, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Liang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y. Regulating the Aggregation and Dispersion of Carbon Dots to Achieve Stimulus-Responsive Multimodal Luminescence for Dynamic Anti-Counterfeiting. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2025, 13, 2402456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Le, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, T. Stimulus-Responsive Polymer Materials toward Multi-Mode and Multi-Level Information Anti-Counterfeiting: Recent Advances and Future Challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 606–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. Diversity and Tailorability of Photoelectrochemical Properties of Carbon Dots. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 3110–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Lin, Q.; Chang, H.-T. Recent Advances and Sensing Applications of Carbon Dots. Small Methods 2020, 4, 1900387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Kang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X.; Jiang, Z. Carbon-Based Stimuli-Responsive Nanomaterials: Classification and Application. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2023, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Yang, J.; Hu, L.; Cao, Y.; Lai, J.; Cao, F.; Gu, J.; Cao, X. Recent Advances in Room Temperature Phosphorescent Carbon Dots: Preparation, Mechanism, and Applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 4425–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Cheng, D.; Gu, H.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Tan, J.; Li, Q. Mechanical Force-Induced Color-Variable Luminescence of Carbon Dots in Boric Acid Matrix. Molecules 2023, 28, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Meng, Y.; Li, H. Mechanofluorochromic Carbon Dots under Grinding Stimulation. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 16433–16437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Meng, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Tang, Z.; Tan, J.; Qu, S. Ultra-Strong Phosphorescence with 48% Quantum Yield from Grinding Treated Thermal Annealed Carbon Dots and Boric Acid Composite. SmartMat 2022, 3, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Jiang, K.; Jiang, J.; Wang, H.; Lin, H. Achieving Thermal-Stimulus-Responsive Dynamic Afterglow from Carbon Dots by Singlet-Triplet Energy Gap Engineering through Covalent Fixation. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2025, 42, 100169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, N.; Mandal, D. Solvatochromic Response of Carbon Dots: Evidence of Solvent Interaction with Different Types of Emission Centers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 18732–18741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ma, Y.; Yuan, G.; Chen, X.; Mei, J.; Zhang, L.; Ren, L. Solvent-Controlled and Solvent-Dependent Strategies for the Synthesis of Multicolor Carbon Dots for pH Sensing and Cell Imaging. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 9709–9718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Lu, S.; Yu, J. Recent Advances in the Design of Afterglow Materials: Mechanisms, Structural Regulation Strategies and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 8005–8058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Quantum-Sized Carbon Dots for Bright and Colorful Photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, M.; Qiu, J.; Sun, Y.-P. Design and Fabrication of Carbon Dots for Energy Conversion and Storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2315–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Yang, B. Investigation from Chemical Structure to Photoluminescent Mechanism: A Type of Carbon Dots from the Pyrolysis of Citric Acid and an Amine. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 5976–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Lu, S.; Geng, Y.; Zhu, S.; Redfern, S.A.T.; Song, Y.; Feng, T.; Xu, W.; Yang, B. Design of Metal-Free Polymer Carbon Dots: A New Class of Room-Temperature Phosphorescent Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2393–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Lu, S. The Light of Carbon Dots: From Mechanism to Applications. Matter 2022, 5, 110–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. Carbon Dots: A Small Conundrum. Trends Chem. 2019, 1, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, B. Highly Photoluminescent Carbon Dots for Multicolor Patterning, Sensors, and Bioimaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3953–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Song, H.; Li, X.; Tang, L.; Tang, Z.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. Computational Studies on Carbon Dots Electrocatalysis: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2107196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Conti, M.C.M.D.; de Castro, A.A.; Assis, L.C.; Lima, N.M.; Escriba, A.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Ramalho, T.C.; La Porta, F.A. Carbon Dots in the Center of the Spotlight: A Full Evaluation of Their Synthesis and Understanding of Their Fundamental Properties and Applications. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 27, 100937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorai, S.; Sen, K.; Dash, P.S. A Review of First-Principles Studies of Carbon Dot Photoluminescence: Implications for Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 19803–19820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wu, C.; Yang, M.; Li, B.; Yan, X.; Zhu, X.; Yu, H.; Hu, M.; Yang, J. Long-Lived Color-Tunable Room-Temperature Phosphorescence of Boron-Doped Carbon Dots. Langmuir 2022, 38, 2287–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Luo, C.; Quan, Z.; Li, H.; Sun, S.; Xu, Y. A Sequential Dual-Lock Strategy for Generation of Room-Temperature Phosphorescence of Boron Doped Carbon Dots for Dynamic Anti-Counterfeiting. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 632, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Lei, S.; Dong, C. Matrix-Free Room-Temperature Phosphorescent Boron and Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon Dots for Information Encryption and Anticounterfeiting. New J. Chem. 2025, 49, 12568–12575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Sun, S.; Lu, K.; Li, N.; Dong, Z. Boron-Doped Carbon Dots: Doping Strategies, Performance Effects, and Applications. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 109136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Yang, W.; Huang, X.; Lv, J. Preparation and Photodynamic Antibacterial/Anticancer Effects of Ultralong-Lifetime Room-Temperature Phosphorescent N-Doped Carbon Dots. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 20481–20491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, M.; An, S.; Jia, M.; Cao, L.; Li, L.; Ge, M.; Wu, Z.; Mei, Q.; Dong, W.-F. A Facile Strategy to Realize Metal-Free Room-Temperature Phosphorescence by Construct Nitrogen Doped Carbon Dots-Based Nanocomposite. Microchem. J. 2022, 172, 106878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Gan, S.; Cheng, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Xie, G.; Liu, R.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, H. Efficient Tuning of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots Phosphorescence Based on Substrate Regulation for Multicolor and Time-Dependent Anti-Counterfeiting. Dyes Pigments 2024, 224, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Mao, X.; Zhao, X.; Xie, T.; Hu, H.; Li, Z.; Gao, W. Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots with Excitation-Dependent Room Temperature Phosphorescence for Multi-Level Anti-Counterfeiting Applications. J. Lumin. 2024, 275, 120757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Wang, Y.; Pang, C.; Fan, Z. Developing B, P Doped Carbon Dot with Long-Lifetime Aggregation-Induced Room Temperature Phosphorescence for Sensing Metronidazole, Information Encryption and Anticounterfeiting. Microchem. J. 2025, 211, 113155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Wang, Y.; Cai, C.; Lin, H. Conversion of Carbon Dots from Fluorescence to Ultralong Room-Temperature Phosphorescence by Heating for Security Applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Zhu, S.; Feng, T.; Xia, C.; Song, Y.; Yang, B. The Polymeric Characteristics and Photoluminescence Mechanism in Polymer Carbon Dots: A Review. Mater. Today Chem. 2017, 6, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Sharma, S.K.; Peng, Z.; Leblanc, R.M. Polymers in Carbon Dots: A Review. Polymers 2017, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Liu, S.G.; Dong, J.X.; Liang, J.Y.; Li, L.J.; Li, N.B.; Luo, H.Q. Facile Synthesis of Multicolor Photoluminescent Polymer Carbon Dots with Surface-State Energy Gap-Controlled Emission. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 10785–10793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Tao, S.; Yang, B. Polymer–Structure-Induced Room-Temperature Phosphorescence of Carbon Dot Materials. Small Struct. 2023, 4, 2200327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Song, H.; Shen, D. Long Lifetime Pure Organic Phosphorescence Based on Water Soluble Carbon Dots. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5751–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Zhang, L.; Lu, J.; Xu, C.; Cai, C.; Lin, H. Triple-Mode Emission of Carbon Dots: Applications for Advanced Anti-Counterfeiting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7231–7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Sun, X.; Cao, X. Construction and Multifunctional Applications of Visible-Light-Excited Multicolor Long Afterglow Carbon Dots/Boron Oxide Composites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 4477–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Li, D.; Ushakova, E.V.; Maslov, V.G.; Zhou, D.; Jing, P.; Shen, D.; Qu, S.; Rogach, A.L. Multilevel Data Encryption Using Thermal-Treatment Controlled Room Temperature Phosphorescence of Carbon Dot/Polyvinylalcohol Composites. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Ushakova, E.V.; Liu, E.; Zhou, Z.; Li, D.; Zhou, D.; Qu, S.; Rogach, A.L. On–Off Switching of the Phosphorescence Signal in a Carbon Dot/Polyvinyl Alcohol Composite for Multiple Data Encryption. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 14250–14255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Anappara, A.A. Cool White, Persistent Room-Temperature Phosphorescence in Carbon Dots Embedded in a Silica Gel Matrix. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 15137–15144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tan, J.; Liang, P.; Wu, C.; Hou, Z.; Shen, K.; Lei, B.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, J.; et al. Dynamic Room Temperature Phosphorescence of Silane-Functionalized Carbon Dots Confining within Silica for Anti-Counterfeiting Applications. Small 2024, 20, 2306323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Pang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, H.; Hu, C.; Zheng, M.; Lei, B.; Liu, Y. Temperature-Responsive Conversion of Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence and Room-Temperature Phosphorescence of Carbon Dots in Silica. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 5744–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, S.; Xu, X.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, C.; Lei, B.; Kaminski, C.F.; Liu, Y. Carbon Dot-Silica Nanoparticle Composites for Ultralong Lifetime Phosphorescence Imaging in Tissue and Cells at Room Temperature. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 9887–9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lei, M.; Yan, L.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, B. Carbon Dot-Based Afterglow Composite with Tunable Room Temperature Phosphorescence and Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence and Their Anti-Counterfeiting and Encryption Application. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 489, 151245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, R.; Men, W.; Zhao, X. In Situ Confinement Strategy to Achieve High-Stability Room Temperature Phosphorescent Carbon Dots. Inorg. Chem. 2025, 64, 8089–8099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, P. Visible-Light-Excited High Efficiency Multicolor Room Temperature Phosphorescence of Carbon Dots in Boric Acid Matrix. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Xie, Z.; Zheng, M. Colour-Tunable Ultralong-Lifetime Room Temperature Phosphorescence with External Heavy-Atom Effect in Boron-Doped Carbon Dots. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Shang, Y.; Lou, Q.; Zhu, J.; Hu, J.; Xu, W.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, K.; Shan, C.-X.; et al. A Molecular Engineering Strategy for Achieving Blue Phosphorescent Carbon Dots with Outstanding Efficiency above 50%. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Hu, C.; Dong, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Full-Color Room-Temperature Phosphorescent Carbon Dots with Ultrahigh Quantum Yield via Conjugation Regulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; Zheng, L.; Du, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Xie, R.; Li, Z.; Lin, H. Enabling Robust and Hour-Level Organic Long Persistent Luminescence from Carbon Dots by Covalent Fixation. Light Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zou, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Yue, D. Large-Scale Synthesis of N-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots and Their Phosphorescence Properties in a Polyurethane Matrix. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 4742–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Lu, C.; Yang, X. Efficient Room Temperature Phosphorescence Carbon Dots: Information Encryption and Dual-Channel pH Sensing. Carbon 2019, 152, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, M.; Yang, M.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, J. Induction of Long-Lived Room Temperature Phosphorescence of Carbon Dots by Water in Hydrogen-Bonded Matrices. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Li, Q.; Meng, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Ye, Y.; Tang, Z.; Qu, S.; Ren, X. Time-Dependent Phosphorescence Colors from Carbon Dots for Advanced Dynamic Information Encryption. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Meng, S.; Li, Y.; Cheng, D.; Gu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, Z.; Tan, J.; Qu, S. Surface Ionization-Induced Tunable Dynamic Phosphorescence Colors from Carbon Dots on Paper for Dynamic Multimode Encryption. Carbon 2022, 195, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, F.; Feng, N.; Xu, A.; Sun, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, H. Room Temperature Phosphorescence Carbon Dots: Preparations, Regulations, and Applications. Small 2023, 19, 2301240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Gong, X. Evolution and Fabrication of Carbon Dot-Based Room Temperature Phosphorescence Materials. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 3705–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Zheng, J.; Yang, Y.; Yan, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, B. Carbon Dots-Based Delayed Fluorescent Materials: Mechanism, Structural Regulation and Application. iScience 2022, 25, 104884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, H. Afterglow of Carbon Dots: Mechanism, Strategy and Applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Zheng, C.; Tao, Y.; Chen, R.; Shi, H.; Chen, T.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Deng, R.; Liu, X.; et al. Stabilizing Triplet Excited States for Ultralong Organic Phosphorescence. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, T.-L.; Xie, R.-J. Blue, Green, and Red Full-Color Ultralong Afterglow in Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 6584–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhen, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Sun, X.; Xu, B.; Wang, X.; Gao, Z.; Meng, X. Gram-Scale Synthesis of 41% Efficient Single-Component White-Light-Emissive Carbonized Polymer Dots with Hybrid Fluorescence/Phosphorescence for White Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Gao, X.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, H. Carbon Dots with Dual-Emissive, Robust, and Aggregation-Induced Room-Temperature Phosphorescence Characteristics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Luo, Y.; Ran, Z.; Wang, F.; Sun, M.; Luo, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, X.; Lei, B.; Liu, Y.; et al. Calcination Temperature Tuning of RTP and TADF with Wide Range of Emission Color from Carbon Dots Confined in Al2O3. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Liu, Y.; Lei, B.; Hu, C. A Universal Strategy for Activating the Multicolor Room-Temperature Afterglow of Carbon Dots in a Boric Acid Matrix. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7278–7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Shao, R.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Bi, H. High-Temperature Phosphorescence of Carbon Dots by a Synergistic Locking Strategy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 23104–23113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-C.; Shang, Y.; Liu, K.-K.; Liu, Z.; Wu, W.-J.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, X.-Y.; Dong, L.; Shan, C.-X. Water-Induced Ultralong Room Temperature Phosphorescence by Constructing Hydrogen-Bonded Networks. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, J.; Sun, J.; Xu, B.; Gao, Z.; Wang, X.; Yan, L.; Zhu, C.; Meng, X. Ultralong-Lived Room Temperature Phosphorescence from N and P Codoped Self-Protective Carbonized Polymer Dots for Confidential Information Encryption and Decryption. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 4847–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, D.; Dong, X.; Xiu, F.; Huang, W.; Liu, J. Dual-Emission Self-Protective Phosphorescent Carbon Dots with Ultra-Long Lifetime and Time-Dependent Afterglow Colors for Tri-Mode Encryption. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2025, 13, 2403274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Bai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Geng, F.; Qin, J.; Zhou, T.; Feng, F. Ultralong Lifetime Room-Temperature Phosphorescence in Aqueous Medium from Silica Confined Polymer Carbon Dots for Autoluminescence-Free Bioimaging and Multilevel Information Encryption. Dyes Pigments 2022, 197, 109890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, P.; Feng, Y.; Cao, C.; Li, Y.; Han, J.; Li, S.; Peng, C.; Li, Z.; Feng, W. Self-Protective Room-Temperature Phosphorescence of Fluorine and Nitrogen Codoped Carbon Dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Li, Q.; Xiao, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, D.; Wei, J.; Zhang, B. Full-Color Tunable Time-Dependent Room-Temperature Phosphorescence from Self-Protective Carbonized Polymer Dots. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2418722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Shi, B.; Yu, H.; Yang, S.; Nie, G.; Wang, S.; Chen, W. Visible Light-Excited Full-Color Phosphorescent Material Realized by Carbon Dots Dispersed in Polyacrylamide and Applied to Anti-Counterfeiting. Mater. Today Adv. 2023, 20, 100429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Tao, S.; Zhao, X.; Kang, C.; Yang, B. Crosslink-Enhanced Emission-Dominated Design Strategy for Constructing Self-Protective Carbonized Polymer Dots with Near-Infrared Room-Temperature Phosphorescence. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202408516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Q.; Chen, N.; Zhu, J.; Liu, K.; Li, C.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, W.; Chen, X.; Song, Z.; Liang, C.; et al. Thermally Enhanced and Long Lifetime Red TADF Carbon Dots via Multi-Confinement and Phosphorescence Assisted Energy Transfer. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2211858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, D.; Wang, B.; Yang, J.; Hao, Y.; Tan, J.; Li, Q.; Qu, S. Carbon Dots-Inked Paper with Single/Two-Photon Excited Dual-Mode Thermochromic Afterglow for Advanced Dynamic Information Encryption. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2403775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Fu, Q.; Sun, S.; Li, N.; Zhang, K.; Dong, Z.; Yue, M. Temperature-Responsive Red-Phosphorescent Carbon Dots for Anticounterfeiting Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 4465–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Ye, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhao, W.; Yue, D. High pH-Induced Efficient Room-Temperature Phosphorescence from Carbon Dots in Hydrogen-Bonded Matrices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 7890–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Su, Q.; Yang, X. Ultra-Long Room-Temperature Phosphorescent Carbon Dots: pH Sensing and Dual-Channel Detection of Tetracyclines. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 16036–16042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Gu, H.; Cheng, D.; Yang, D.; Xiao, C.; Li, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Qu, S.; Li, Q. Achieving a Colour-Tuneable Afterglow through pH-Responsive Exciton Transfer Channels in a Carbon Dot Matrix System. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 9175–9181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, H. Photo-Stimulated Polychromatic Room Temperature Phosphorescence of Carbon Dots. Small 2020, 16, 2001909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Fu, Q.; Dong, Z.; Yue, M. Photo-Induced Fluorescence Discoloration and Photo-Responsive Room Temperature Phosphorescence Carbon Dot-Based Composites with Excellent Reversibility and Water Resistance. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 155972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Niu, Z.; Wang, D.; Gou, H.; Liao, Q.; Xi, K.; An, Z.; Jia, X. Photo-Induced Ultralong Phosphorescence of Carbon Dots for Thermally Sensitive Dynamic Patterning. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 8199–8206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.-S.; Shen, C.-L.; Niu, C.-Y.; Lou, Q.; Jiang, T.-C.; Li, P.-F.; Shi, X.-J.; Song, R.-W.; Deng, Y.; Lv, C.-F.; et al. Photooxidation Triggered Ultralong Afterglow in Carbon Nanodots. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, M.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Bi, H. Visible-Light Manipulated Reversible and Ultralong Phosphorescence of Carbon Dots Through Dynamic Cross-Linking. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2406672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cheng, D.; Gu, H.; Yang, D.; Li, Y.; Meng, S.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, J.; et al. Aggregation-Induced Color Fine-Tunable Carbon Dot Phosphorescence Covering from Green to near-Infrared for Advanced Information Encryption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 462, 142339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Shao, H.; Liu, K.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Shan, C.; Kuang, L.; Jing, H. Ultrasound-Responsive Phosphorescence in Aqueous Solution Enabled by Microscale Rigid Framework Engineering of Carbon Nanodots. Light Sci. Appl. 2025, 14, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Li, P.; Deng, Y.; Li, H. Reversible and Color-Variable Afterglow Luminescence of Carbon Dots Triggered by Water for Multi-Level Encryption and Decryption. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 128999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.Q.; Xue, N.; Wang, X.R.; Shi, W.Y.; Lu, C. Activating Efficient Room Temperature Phosphorescence of Carbon Dots by Synergism of Orderly Non-Noble Metals and Dual Structural Confinements. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 6658–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Zheng, X.; Gao, L.; Yang, C. Full-Color Long-Lived Room Temperature Phosphorescence in Aqueous Environment. Small 2022, 18, 2201223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Precursors of CDs | Matrix | Heteroatom Type | Quantum Yield | Lifetime | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDTA-2Na | PVA | N, O | — | 380 ms | [39] |
| m-phenylenediamine | PVA | N | — | 456 ms | [40] |
| EDA | SiO2 | N, O | — | 1.62 s | [46] |
| CA and BA | — | B | 23.5% | 1.17 s | [51] |
| m-phenylenediamine | Urea | N | — | 2 h | [54] |
| IPDI | PU | N | 11% | 8.7 ms | [55] |
| levofloxacin | — | N, O | 4.2% | 237 ms, 354 ms | [58] |
| biuret and urea | — | N | 13.9% | 0.53 s | [65] |
| urea and phosphoric acid aqueous solutions | — | N, P | 23% | 320 ms | [66] |
| TA | — | O | 4.2% | 153.6 ms | [67] |
| 1,8-naphthalimide | Al2O3 | N, O | — | 60.6–520.6 ms | [68] |
| CA | BA | O | 8.7% | 1.6 s | [69] |
| imide derivatives | PBA | N, O | 1.98–21.85% | 1.62 s | [70] |
| diethylenetriamine and phosphoric acid | — | N, P | 4.5% | 1.48 s | [71] |
| 1,2,4,5-benzenetetramine and (E)-2-methyl-2-butenedioic acid | — | N | 0.1% | 57.7 ms | [72] |
| 1-butylamine and phosphoric acid aqueous solution | — | N, P | — | 1.25 s, 1.74 s | [73] |
| tetraethylorthosilicate | — | O | 7.4% | 2.19 s | [74] |
| glucose and triethylamine trihydrofluoride | — | N, F | 3.45% | 1045 ms | [75] |
| 1,8-naphthalimide, urea and quinacridone | — | N, O | 13.89%, 27.1%, 8.5% | 407.2 ms, 431.9 ms, 415.4 ms | [76] |
| Stimulus Type | Response Mechanism | Refs. |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Molecular thermal motion | [34,46,79,80,81] |
| pH | Protonation or deprotonation of oxygen-containing groups | [59,82,83] |
| pH | Deprotonation-induced enhancement of conjugation | [84] |
| Light | Selective excitation of different emission centers | [85] |
| Light | Consumption of triplet oxygen via photoexcitation | [86] |
| Light | Reduce oxygen quenching effects | [87] |
| Light | Generation of singlet oxygen | [88] |
| Light | Generation of oxygen free radicals | [89] |
| Moisture | Formation of hydrogen bond networks | [57] |
| Solvent | Aggregation-induced energy level splitting | [90] |
| Grinding | Enhance rigidity and suppress non-radiative transitions | [10] |
| Ultrasound | Enhance the rigidity and suppress non-radiative transitions | [91] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, C.; Gu, X.; Zhu, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q.; Tan, J. Stimulus-Responsive Afterglow Carbon Dots from Internal Mechanism to Potential Application. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231769
Xia C, Gu X, Zhu X, Sun Y, Li Q, Tan J. Stimulus-Responsive Afterglow Carbon Dots from Internal Mechanism to Potential Application. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(23):1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231769
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Chongye, Xingyu Gu, Xingwang Zhu, Yunfei Sun, Qijun Li, and Jing Tan. 2025. "Stimulus-Responsive Afterglow Carbon Dots from Internal Mechanism to Potential Application" Nanomaterials 15, no. 23: 1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231769
APA StyleXia, C., Gu, X., Zhu, X., Sun, Y., Li, Q., & Tan, J. (2025). Stimulus-Responsive Afterglow Carbon Dots from Internal Mechanism to Potential Application. Nanomaterials, 15(23), 1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231769








