Large-Scale Production of Silver Nanoplates via Ultrasonic-Assisted Continuous-Flow Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
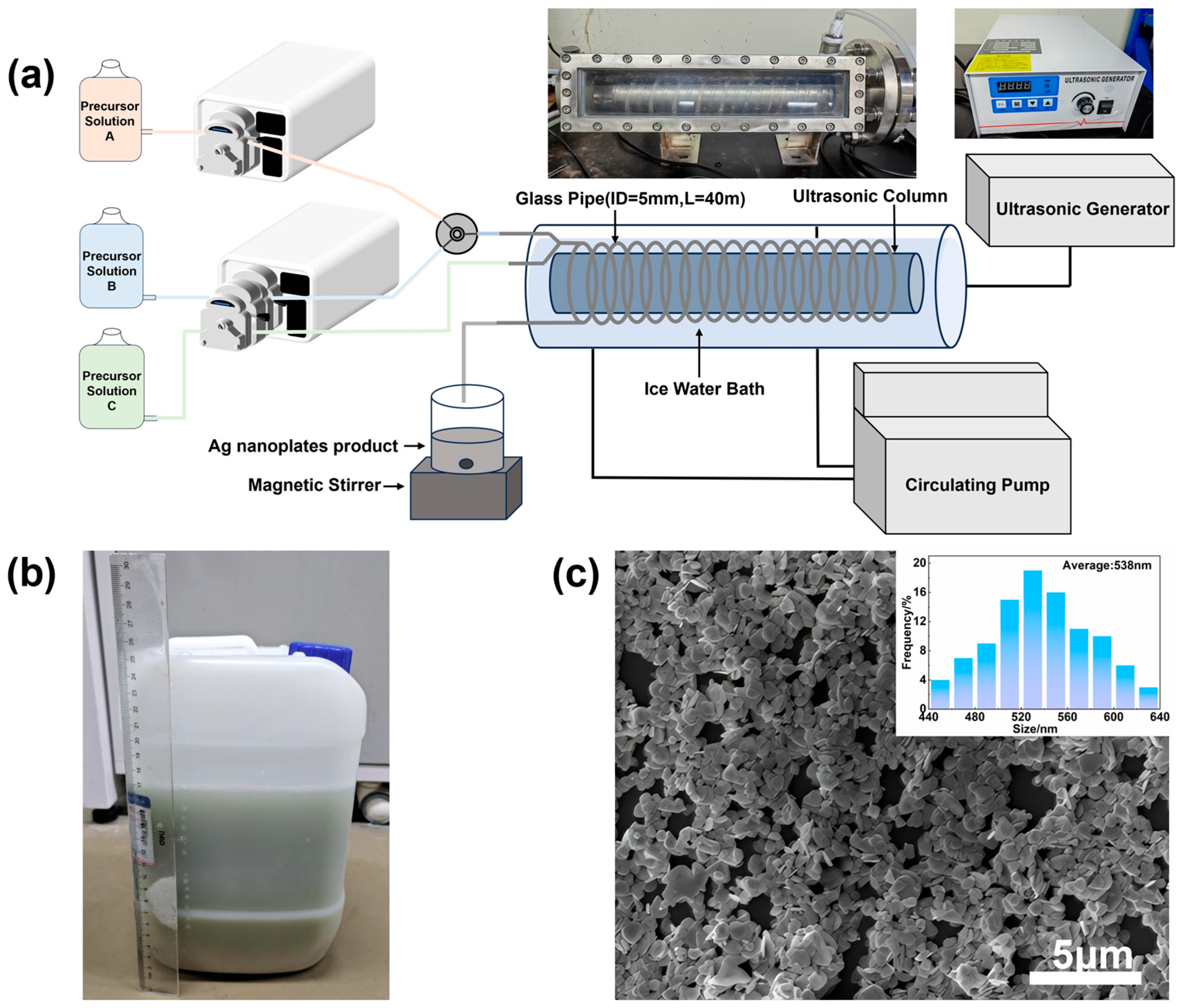
2.2. Methods
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Shape Control of Silver Nanoplates
3.2. Continuous-Flow System and Initial Characterization
3.3. The Role of Ultrasound Assistance
3.4. Optimization of Synthesis Parameters in Continuous Flow
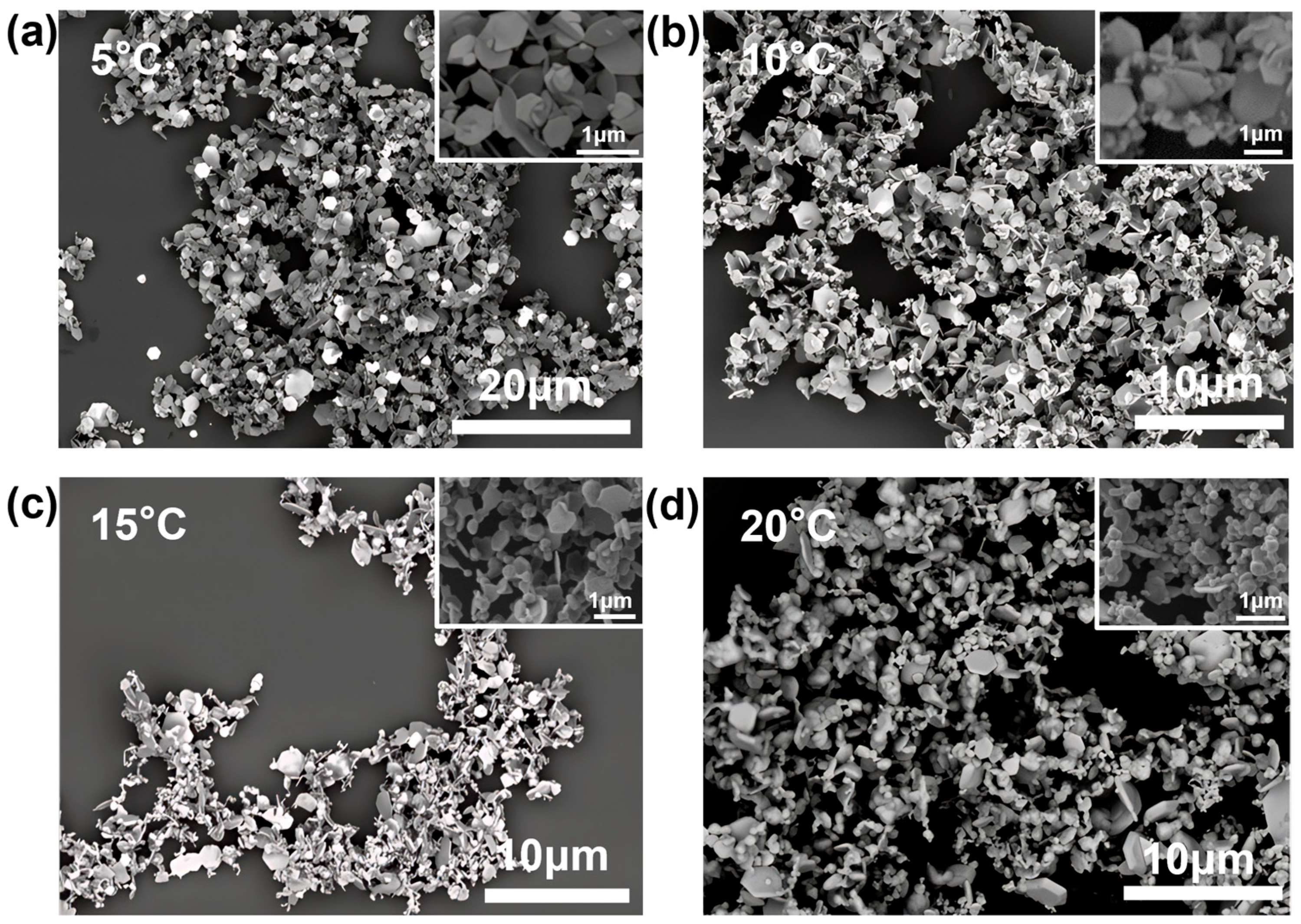
3.4.1. Effect of Temperature
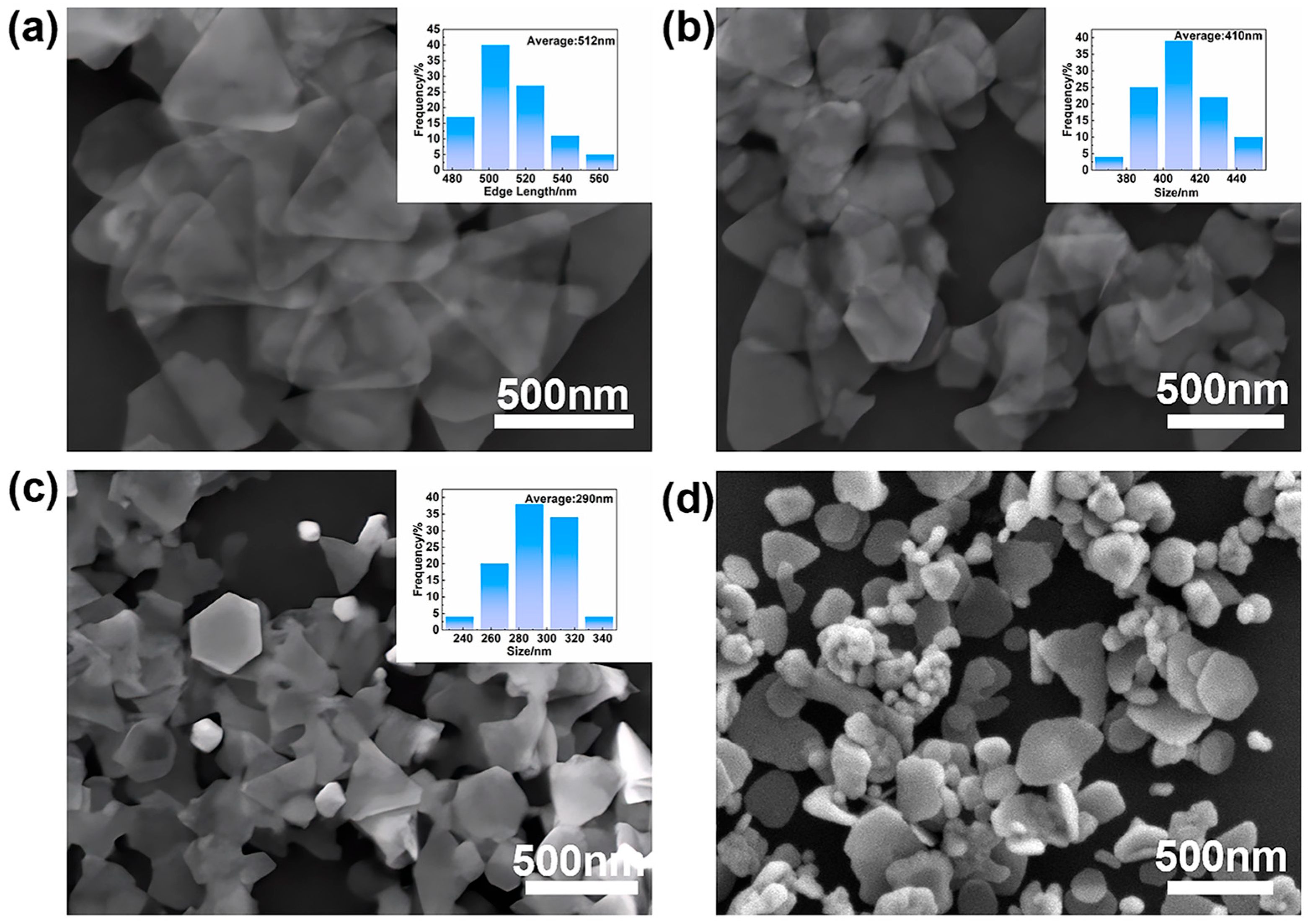
3.4.2. Effect of Flow Rate (Residence Time)
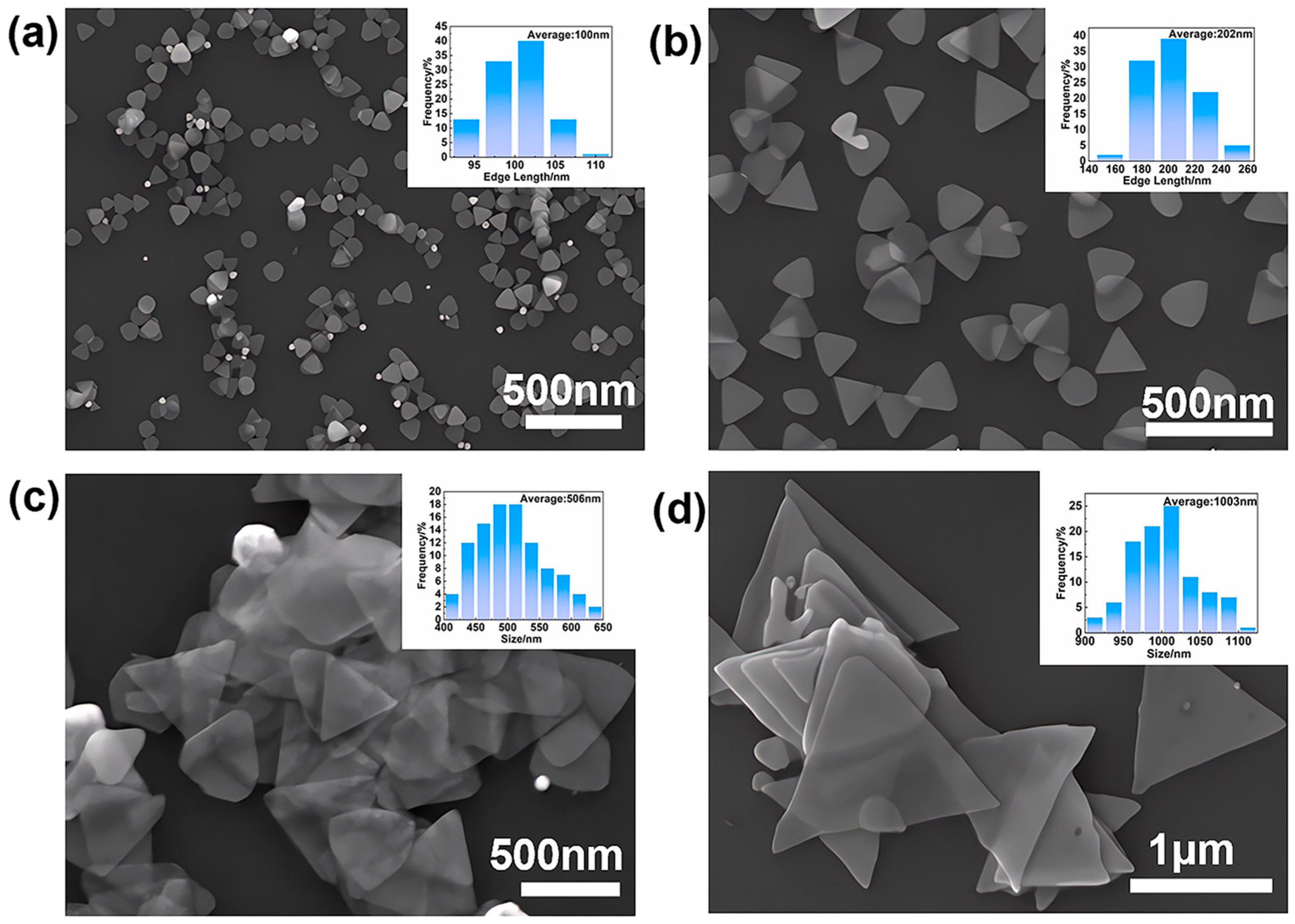
3.4.3. Size Control via Seed Concentration
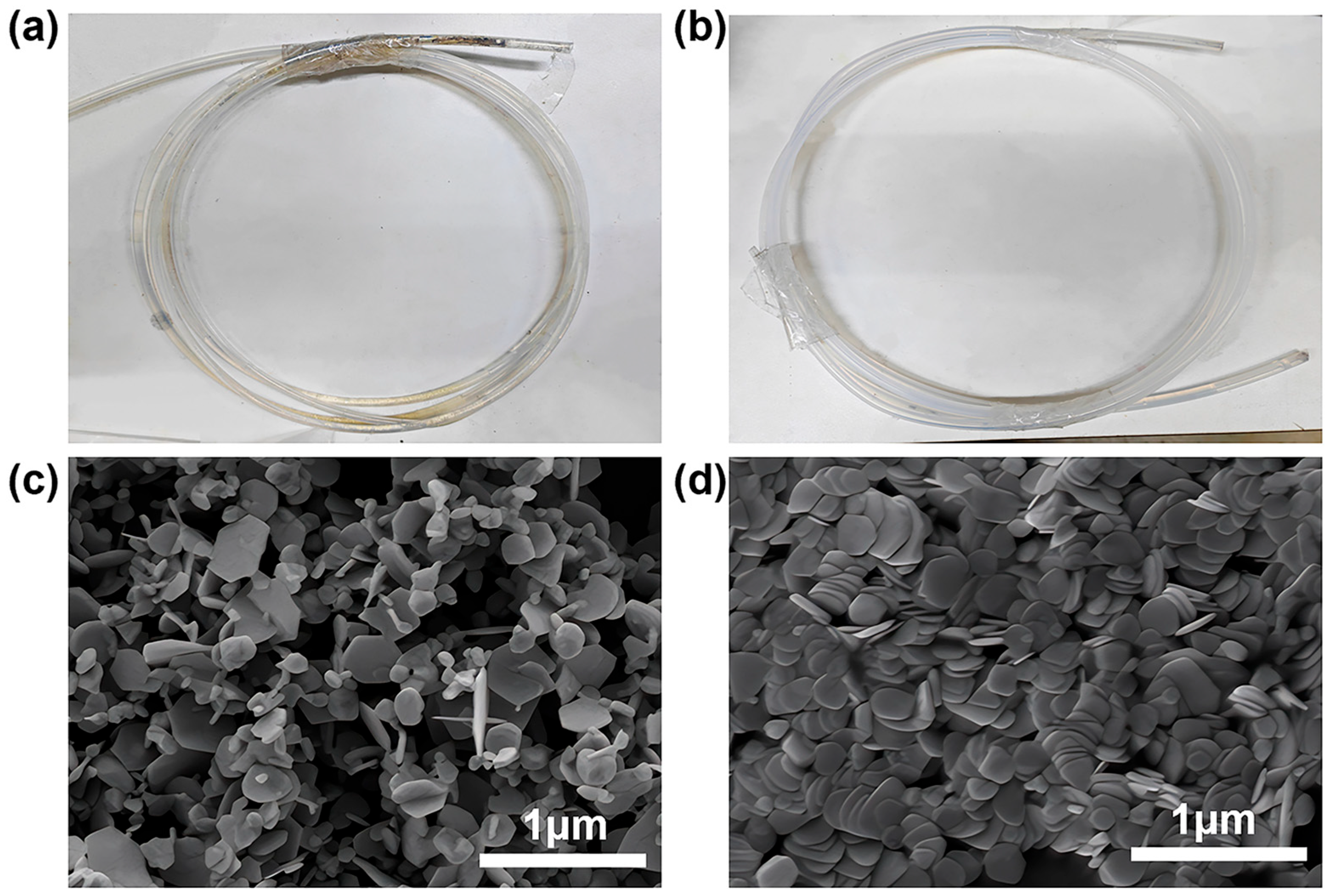
3.5. Electrical Conductivity of Silver Nanoplate Pastes
3.6. Scaled-Up Production and Future Prospects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Sio, L.; Placido, T.; Comparelli, R.; Lucia Curri, M.; Striccoli, M.; Tabiryan, N.; Bunning, T.J. Next-Generation Thermo-Plasmonic Technologies and Plasmonic Nanoparticles in Optoelectronics. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2015, 41, 23–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoubas, L.; Carlberg, M.; Le Rouzo, J.; Pourcin, F.; Ackermann, J.; Margeat, O.; Reynaud, C.; Duche, D.; Simon, J.-J.; Sauvage, R.-M.; et al. Design and Realization of Light Absorbers Using Plasmonic Nanoparticles. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2019, 63, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaud, C.A.; Duché, D.; Simon, J.-J.; Sanchez-Adaime, E.; Margeat, O.; Ackermann, J.; Jangid, V.; Lebouin, C.; Brunel, D.; Dumur, F.; et al. Rectifying Antennas for Energy Harvesting from the Microwaves to Visible Light: A Review. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2020, 72, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, M.; Lu, Y. Polyacrylic Acid Assisted Assembly of Oxide Particles and Carbon Nanotubes for High Performance Flexible Battery Anodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 5, 1401207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.K.; Choo, D.C.; Kang, H.S.; Yoo, K.H.; Kim, T.W. Transparent Ultra-Thin Silver Electrodes Formed via a Maskless Evaporation Process for Applications in Flexible Organic Light-Emitting Devices. Nano Energy 2020, 71, 104649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravljak, R.; Božič, B.; Podlogar, M.; Podgornik, A. Tubular Catalytic polyHIPE Reactor with Deposited Silver Nanoplate Nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 449, 137869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Du, D.X.; Xie, H.; Zhang, X.B.; Lin, K.W.; Wang, K.; Fu, E. Printability and Electrical Conductivity of Silver Nanoparticle-Based Conductive Inks for Inkjet Printing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Tang, B.; Shen, X.; Cui, C.; Zhan, X.; Bi, F.; Bao, X. Synthesis Water-Dispersible Silver Nanoparticles Based on Green Chemistry for Inverted Organic Solar Cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2025, 316, 118088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, R.; Safaiee, R.; Sheikhi, M.H.; Golshan, M.M.; Horastani, Z.K. Graphene Decorated with Silver Nanoparticles as a Low-Temperature Methane Gas Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 21795–21806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Jiao, X.; Chen, D. Size-Controlled and Size-Designed Synthesis of Nano/Submicrometer Ag Particles. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 3378–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wang, W.; Ji, M.; Xing, X.; Lu, Z. Robust Synthesis of Silver Nanocubes in Oil Phase. Cryst. Growth Des. 2023, 23, 2203–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Gao, C. One-Step Growth of Triangular Silver Nanoplates with Predictable Sizes on a Large Scale. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 4513–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mravljak, R.; Podgornik, A. Simple and Tailorable Synthesis of Silver Nanoplates in Gram Quantities. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 2760–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yin, Y.; Mayers, B.T.; Herricks, T.; Xia, Y. Uniform Silver Nanowires Synthesis by Reducing AgNO3 with Ethylene Glycol in the Presence of Seeds and Poly(Vinyl Pyrrolidone). Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 4736–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, G.; Hou, X.; Su, A.; Yang, X.; Wu, K. Streamlined Synthesis of Silver Nanowires Using Multi-Objective Optimization for Electrically Conductive Composite Filaments. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2407999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandak, V.S.; Nagime, P.V. Synthesis, Characterization and Applications of Silver Nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) in the Field of Electronics and Optoelectronics Device—A Review. Hybrid Adv. 2025, 8, 100389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, C.L.; McFarland, A.D.; Zhao, L.; Van Duyne, R.P.; Schatz, G.C.; Gunnarsson, L.; Prikulis, J.; Kasemo, B.; Käll, M. Nanoparticle Optics: The Importance of Radiative Dipole Coupling in Two-Dimensional Nanoparticle Arrays. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 7337–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Colloidal Silver Nanoplates. State of the Art and Future Challenges. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 1724–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.D.; Zhang, S.M.; Jing, H.Y.; Wei, J.; Bu, F.H.; Zhao, L.; Lv, X.Q.; Xu, L.Y. The Fabrication of Highly Conductive and Flexible Ag Patterning through Baking Ag Nanosphere−nanoplate Hybrid Ink at a Low Temperature of 100 °C. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 135301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, G.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, T.; Sun, R.; Zhu, P. Low Temperature Sintered Silver Nanoflake Paste for Power Device Packaging and Its Anisotropic Sintering Mechanism. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 5365–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Raj, N.; Strasser, J.W.; Crooks, R.M. Paper Biosensor for the Detection of NT-proBNP Using Silver Nanodisks as Electrochemical Labels. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Guo, W.; Wu, C. Preparation of micro-size flake silver powder by planetary ball mill. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, A.; Cai, X.; Du, B. A Novel Wet-Chemical Method for Preparation of Silver Flakes. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Cao, Y.; Mirkin, C.; Kelly, K.; Schatz, G.; Zheng, J. Photoinduced conversion of silver nanospheres to nanoprisms. Science 2001, 294, 1901–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Charles Cao, Y.; Hao, E.; Métraux, G.S.; Schatz, G.C.; Mirkin, C.A. Controlling Anisotropic Nanoparticle Growth through Plasmon Excitation. Nature 2003, 425, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoobakht, B.; El-Sayed, M.A. Preparation and Growth Mechanism of Gold Nanorods (NRs) Using Seed-Mediated Growth Method. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Lim, B.; Skrabalak, S. Shape-controlled synthesis of metal nanocrystals: Simple chemistry meets complex physics? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 60–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Xia, X.; Rycenga, M.; Henneghan, P.; Li, Q.; Xia, Y. Successive Deposition of Silver on Silver Nanoplates: Lateral versus Vertical Growth. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Yan, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, K.; Luo, G. Continuous Synthesis of Nanocrystals via Flow Chemistry Technology. Small 2019, 16, 1902828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrea, A.; Sebastian, V.; Ibarra, A.; Arruebo, M.; Santamaria, J. Gas Slug Microfluidics: A Unique Tool for Ultrafast, Highly Controlled Growth of Iron Oxide Nanostructures. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 4254–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chu, G.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, B.; Shao, L. Controllable preparation of nano-CaCO3 in a microporous tube-in-tube microchannel reactor. Chem. Eng. Process 2014, 79, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.H.; Giersig, M. Colloidal Cadmium Sulfide Preparation via Flow Techniques: Ultrasmall Particles and the Effect of a Chromatographic Column. Langmuir 1992, 8, 1475–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.Z.; Terepka, A.D.; Yang, H. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles in a Continuous Flow Tubular Microreactor. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 2227–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akwi, F.M.; Watts, P. Continuous Flow Chemistry: Where Are We Now? Recent Applications, Challenges and Limitations. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 13894–13928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmanuel, N.; Emonds-Alt, G.; Lismont, M.; Eppe, G.; Monbaliu, J.-C.M. Exploring the Fundamentals of Microreactor Technology with Multidisciplinary Lab Experiments Combining the Synthesis and Characterization of Inorganic Nanoparticles. J. Chem. Educ. 2017, 94, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xue, T.; Qin, M.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Z. Solvothermal Preparation of Crystal Seeds and Anisotropy-Controlled Growth of Silver Nanoplates. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 28659–28665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, W.; Li, K.; Li, G. The Hydrothermal Synthesis of Ultra-High Aspect Ratio Ag Nanoflakes and Their Performance as Conductive Fillers in Heaters and Pastes. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 8937–8943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xia, Y. Triangular Nanoplates of Silver: Synthesis, Characterization, and Use as Sacrificial Templates for Generating Triangular Nanorings of Gold. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.R.; Walter, D.G.; Natan, M.J. Seeding of Colloidal Au Nanoparticle Solutions. 2. Improved Control of Particle Size and Shape. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, N.R.; Gearheart, L.; Murphy, C.J. Seeding Growth for Size Control of 5−40 Nm Diameter Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2001, 17, 6782–6786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, N.R.; Gearheart, L.; Murphy, C.J. Seed-Mediated Growth Approach for Shape-Controlled Synthesis of Spheroidal and Rod-like Gold Nanoparticles Using a Surfactant Template. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, N.; Goebl, J.; Lu, Z.; Yin, Y. A Systematic Study of the Synthesis of Silver Nanoplates: Is Citrate a “Magic” Reagent? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 18931–18939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Guo, S.; Goebl, J.; Yin, Y. Seeded Growth of Uniform Ag Nanoplates with High Aspect Ratio and Widely Tunable Surface Plasmon Bands. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 5037–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Zhang, J.; He, H.; Xu, X.; Luo, B.; Li, X.; Li, K.; Niu, G.; Tan, X.; Luo, J.; et al. Convenient Synthesis of Silver Nanoplates with Adjustable Size through Seed Mediated Growth Approach. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Size (nm) | Resistance (Ω) | Resistivity Value (Ω·m) |
|---|---|---|
| 1003 ± 100 | 0.54 | 1.97 × 10−7 |
| 506 ± 120 | 0.78 | 2.87 × 10−7 |
| 202 ± 40 | 2.53 | 9.3 × 10−7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Yao, Y.; Yan, F.; Pan, J.; Lu, Z. Large-Scale Production of Silver Nanoplates via Ultrasonic-Assisted Continuous-Flow Synthesis. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231770
Hu X, Yao Y, Yan F, Pan J, Lu Z. Large-Scale Production of Silver Nanoplates via Ultrasonic-Assisted Continuous-Flow Synthesis. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(23):1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231770
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xiangting, Yixuan Yao, Fuqiang Yan, Jiahao Pan, and Zhenda Lu. 2025. "Large-Scale Production of Silver Nanoplates via Ultrasonic-Assisted Continuous-Flow Synthesis" Nanomaterials 15, no. 23: 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231770
APA StyleHu, X., Yao, Y., Yan, F., Pan, J., & Lu, Z. (2025). Large-Scale Production of Silver Nanoplates via Ultrasonic-Assisted Continuous-Flow Synthesis. Nanomaterials, 15(23), 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231770






