Defect-Engineered Elastic CNC/Chitosan-Based Carbon Aerogel with Wideband Microwave Absorption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
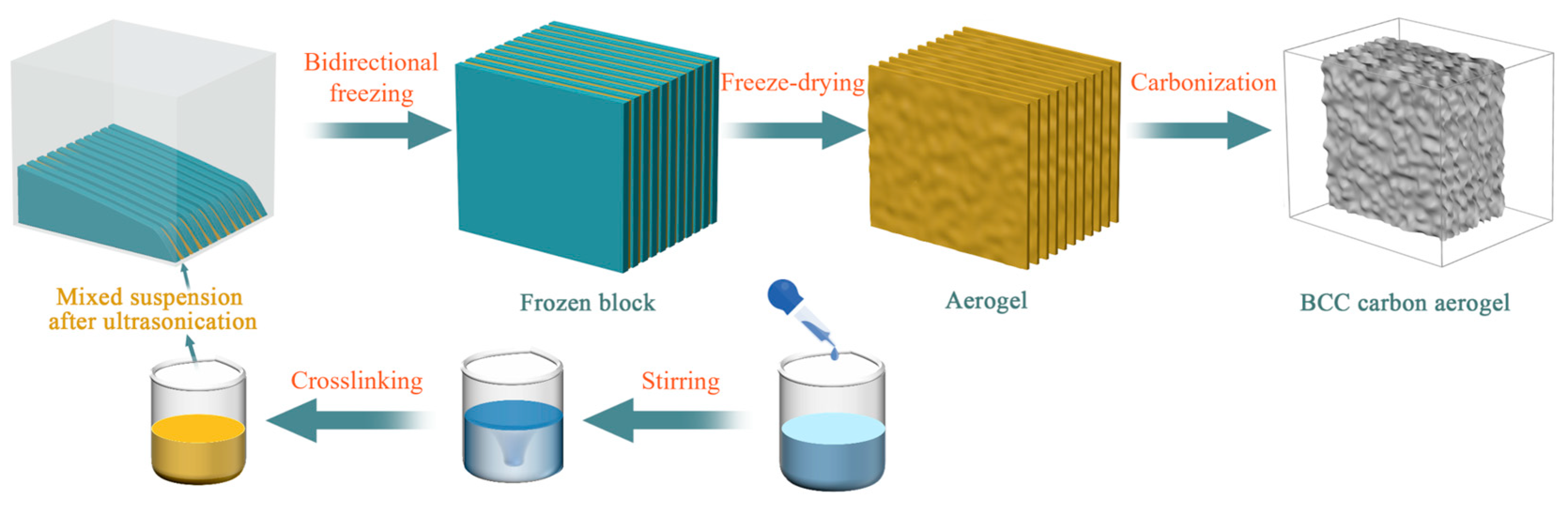
2.2. Fabrication of BCC Aerogels
2.3. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
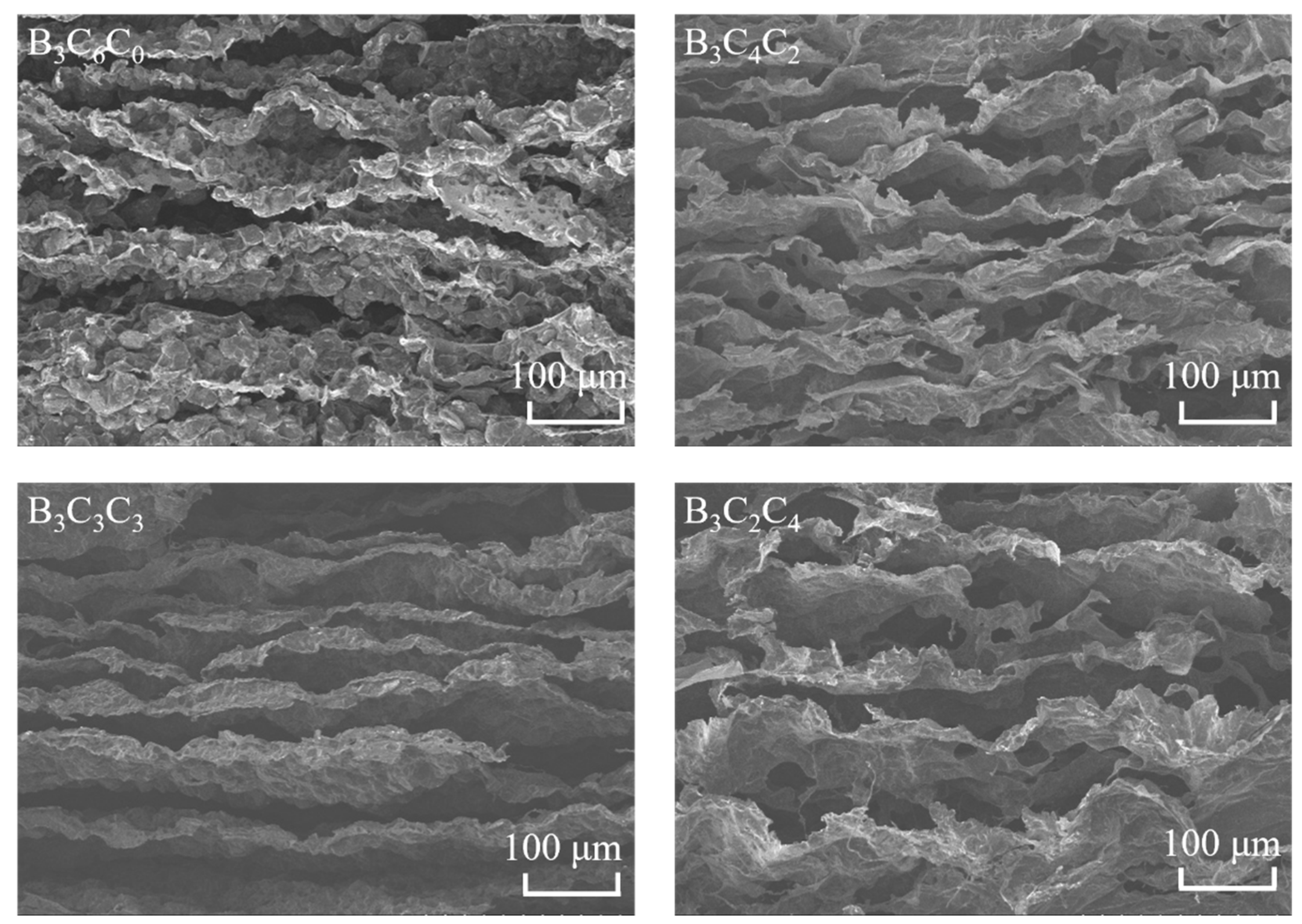
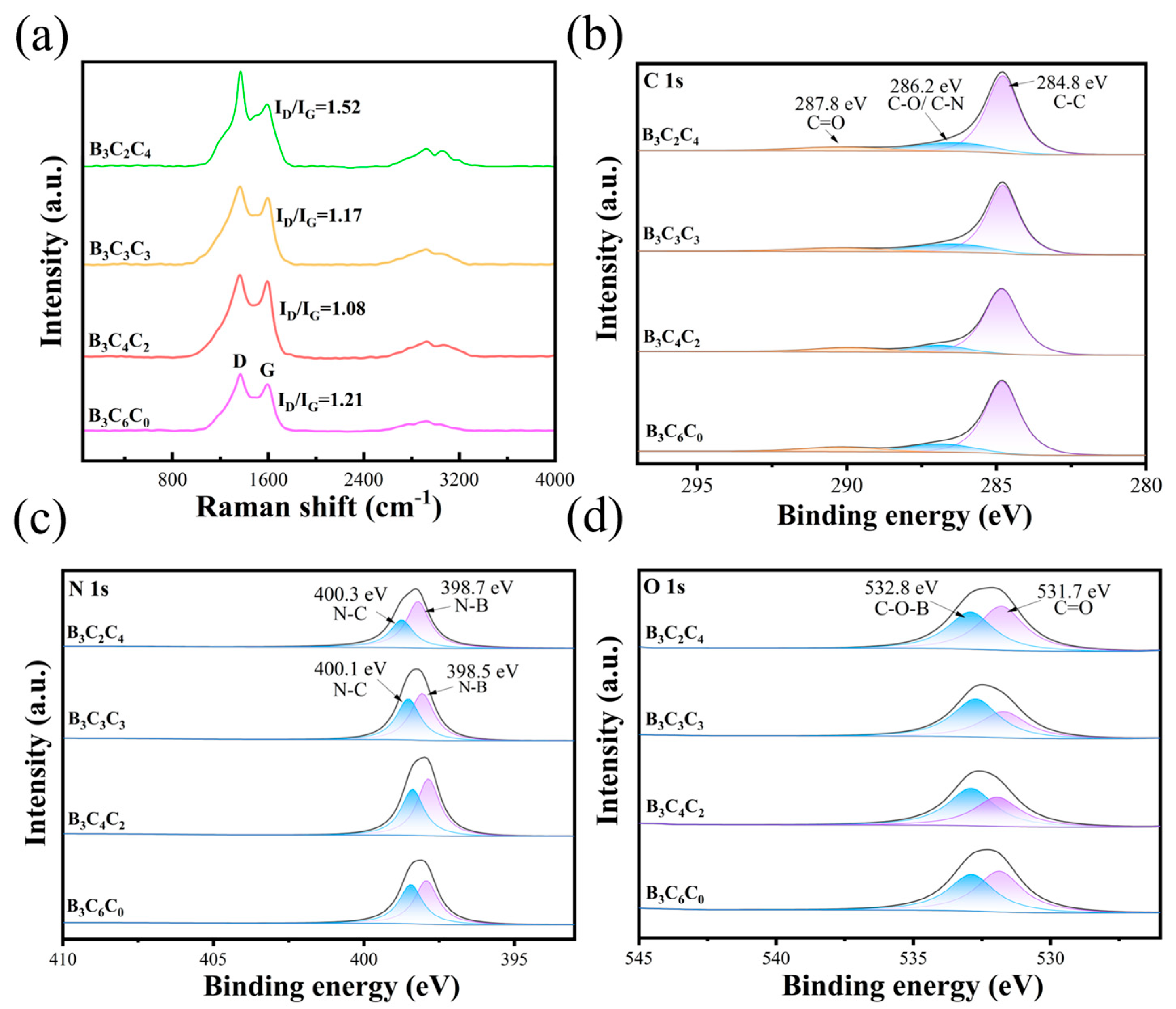
3.1. Microstructural Composition and Morphology of BCC Aerogels
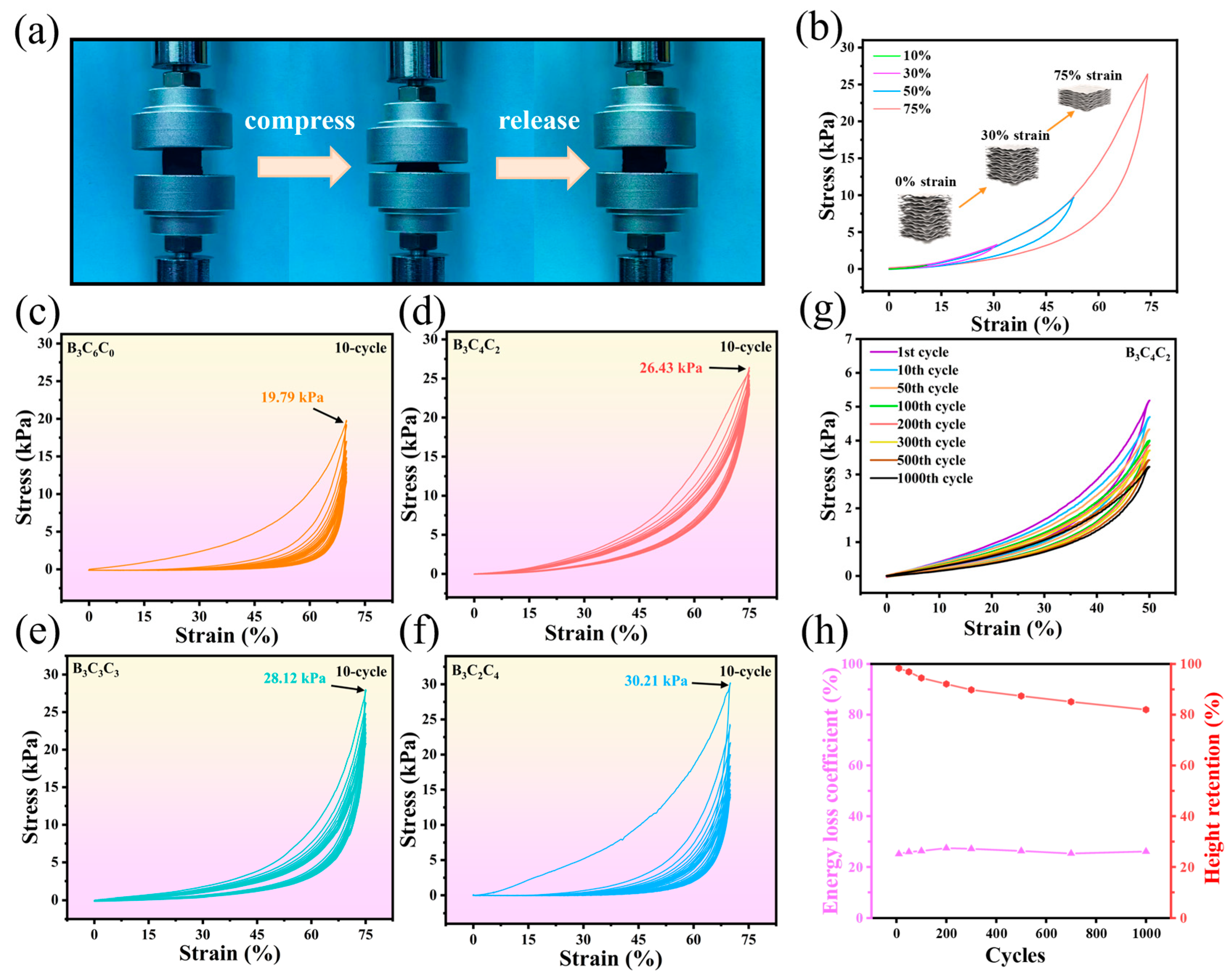
3.2. Elastic Mechanical Properties of BCC Aerogels
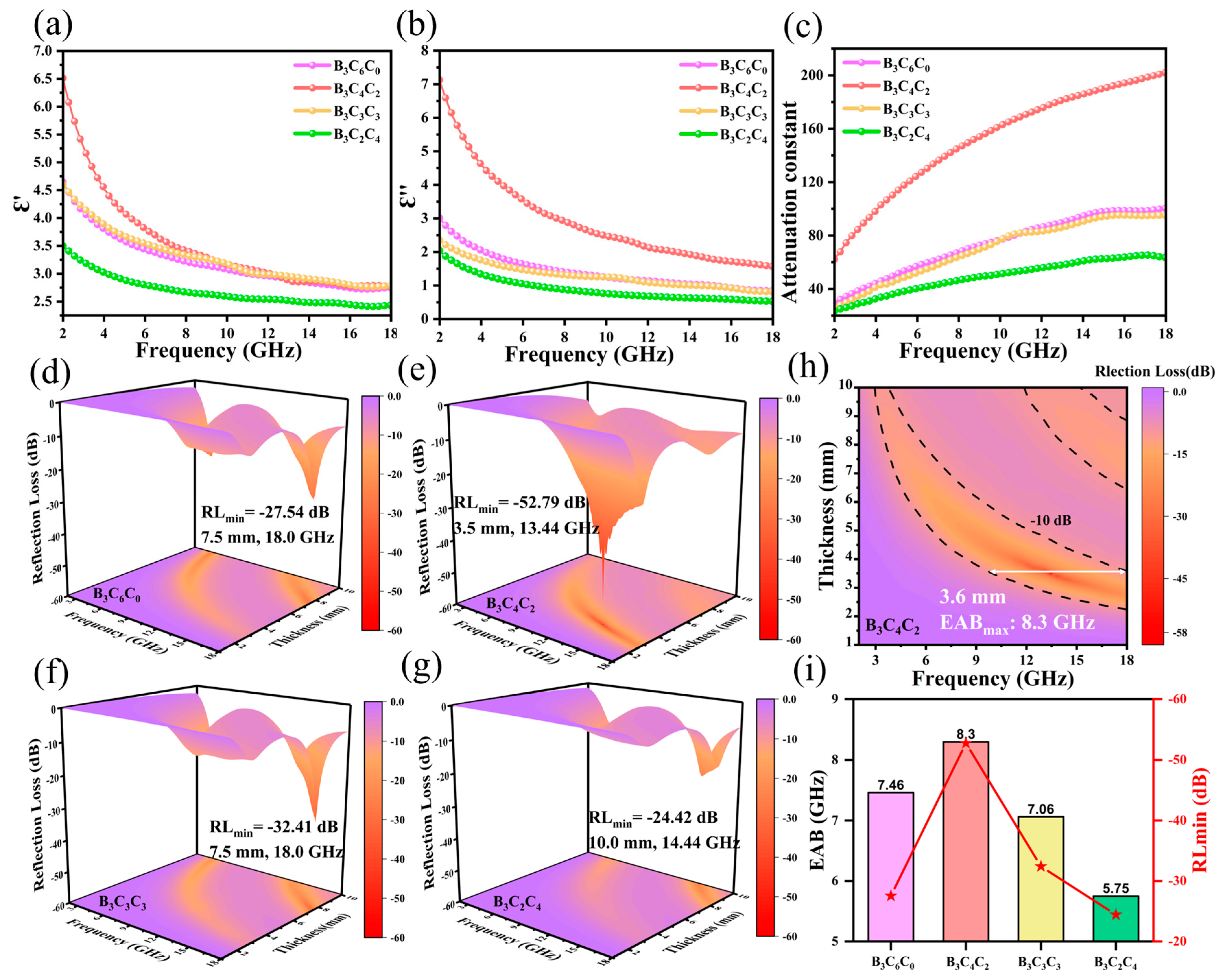
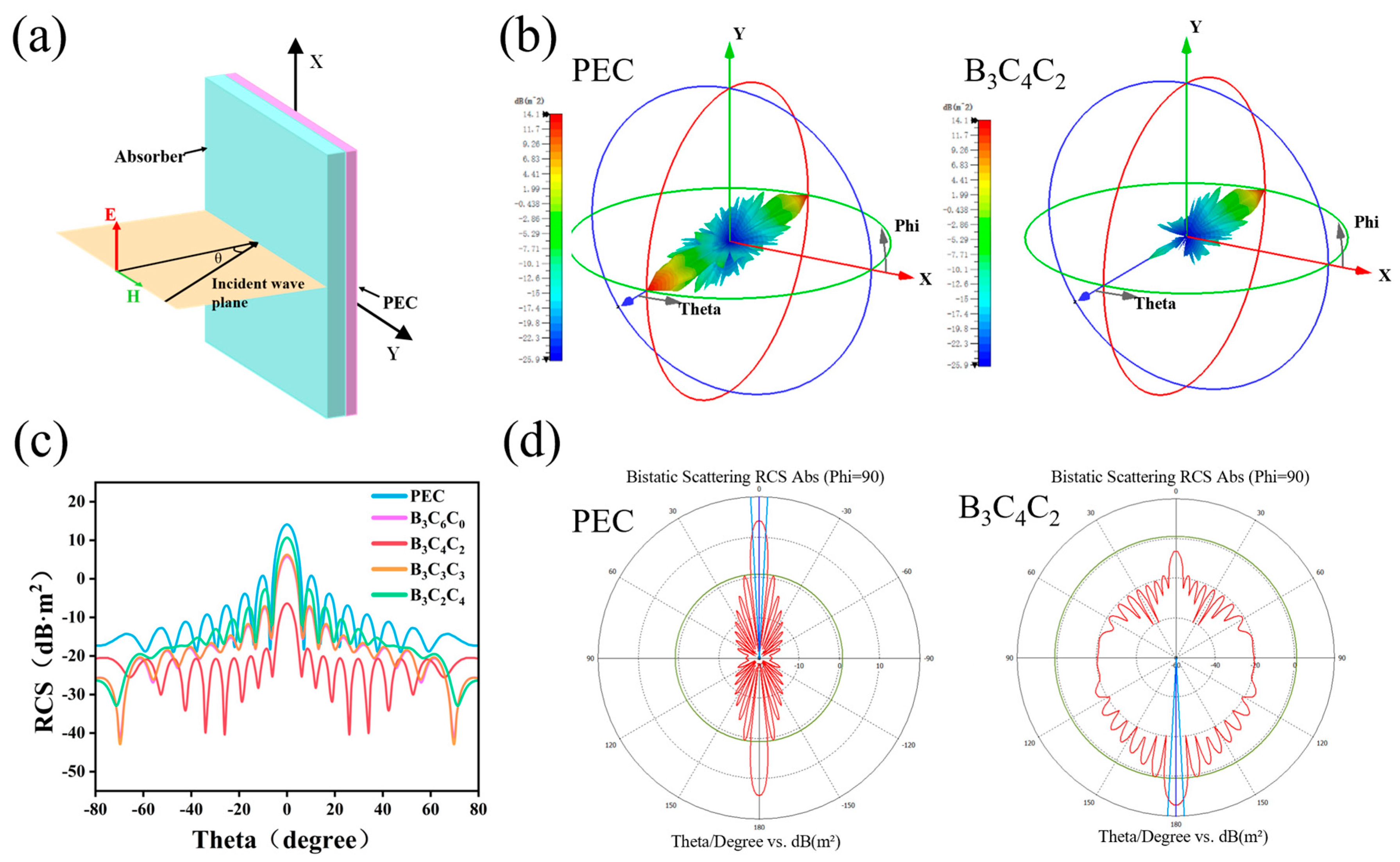
3.3. Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties of BCC Aerogels
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Jiang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Yang, D.; Sun, Y.; Guo, J.; Ding, B.; Dai, S.; Liu, D.; et al. Bamboo-like carbon nanotubes assisted assembly of magnetic-dielectric aerogels to enhance microwave attenuation. Carbon 2025, 234, 119973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkó, M.; Mattsson, M.O. 5G Wireless Communication and Health Effects—A Pragmatic Review Based on Available Studies Regarding 6 to 100 GHz. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meklesh, V.; Kékicheff, P. Bending elastic modulus of a polymer-doped lyotropic lamellar phase. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 582, 1158–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, D.; Kim, B.J.; Nam, I.W. A Comprehensive Study on EMI Shielding Performance of Carbon Nanomaterials-Embedded CFRP or GFRP Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, P.Y.; Peng, H.L.; Hou, Z.L.; Hu, P.; Liu, L.M.; Wang, G.S. Interface-induced dual-pinning mechanism enhances low-frequency electromagnetic wave loss. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, K.; Han, L.; Wu, T.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J. Ultra-strength polyurethane/MOF-derived composites with self-healing and recycling capabilities and highly efficient microwave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 1446–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, P.; Wei, T.; Chen, J.; Lou, J.; Huang, R.; Deng, J. An interpenetrating-network-like structure in cellulose nanocrystal/polyurethane composites and the relative strengthening mechanism. Cellulose 2022, 29, 5007–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.; Hanaor, D.A.H.; Shen, X.; Gurlo, A. Freeze Casting: From Low-Dimensional Building Blocks to Aligned Porous Structures—A Review of Novel Materials, Methods, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1907176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, H.; Hu, Y.J.; Chen, Z.H.; Peng, X.W.; Lai, H.H.; Liu, L.X.; Liu, Q.Z.; Liu, C.F.; Zhong, L.X. Linking Renewable Cellulose Nanocrystal into Lightweight and Highly Elastic Carbon Aerogel. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 11921–11929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, C.; Li, A.; Wang, W.J.; Guo, R.H.; Qin, W.F.; Ren, E.H.; Xiao, H.Y.; Zhou, M. Flexible Waterborne Polyurethane/Cellulose Nanocrystal Composite Aerogels by Integrating Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes for a Highly Sensitive Pressure Sensor. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 14029–14039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, W.; Miao, Y.; Cui, A.; Gao, C.; Wang, C.; Yuan, L.; Tian, Z.; Meng, A.; Li, Z.; et al. Enhancing Defect-Induced Dipole Polarization Strategy of SiC@MoO3 Nanocomposite Towards Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Urso, L.; Compagnini, G.; Puglisi, O. sp/sp2 bonding ratio in sp rich amorphous carbon thin films. Carbon 2006, 44, 2093–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Geng, S.; Sain, M.; Oksman, K. Hetero-Porous, High-Surface Area Green Carbon Aerogels for the Next-Generation Energy Storage Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Sheikhi, A.; van de Ven, T.G. Reusable Green Aerogels from Cross-Linked Hairy Nanocrystalline Cellulose and Modified Chitosan for Dye Removal. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11771–11779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Dang, B.; Li, C.; Sun, Q. A multilevel gradient structural carbon derived from naturally preprocessed biomass. Carbon 2020, 168, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Zhu, M.; Song, H.; Zhang, H. Interfacial Characteristics of Boron Nitride Nanosheet/Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Nishida, Y. Quantitative Analysis of Surface Functional Groups on the Amorphous Carbon in Magnetic Media with XPS Preceded by Chemical Derivatization. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 80, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’eRrico, A.; Schropfer, M.; Mondschein, A.; Safeer, A.A.; Baldus, M.; Wösten, H.A.B. Cross-linking impacts the physical properties of mycelium leather alternatives by targeting hydroxyl groups of polysaccharides and amino groups of proteins. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.J.; Liu, X.; Risen, W.M. Biopolymer-containing aerogels: Chitosan-silica hybrid aerogels. In Aerogels Handbook; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 385–401. [Google Scholar]
- Loryuenyong, V.; Nakhlo, W.; Srikaenkaew, P.; Yaidee, P.; Buasri, A.; Eiad-Ua, A. Enhanced CO2 Capture Potential of Chitosan-Based Composite Beads by Adding Activated Carbon from Coffee Grounds and Crosslinking with Epichlorohydrin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, L.A.; Da Silva, A.M.; Dos Santos, H.F.; De Almeida, W.B. Oxidized single-walled carbon nanotubes and nanocones: A DFT study. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 13212–13222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, E.; Zakertabrizi, M.; Korayem, A.H.; Chang, Z. Mechanical and electromechanical properties of functionalized hexagonal boron nitride nanosheet: A density functional theory study. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 149, 114701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y.; Saito, S. Impurities Effects on the Electronic Structure of Titanium Dioxide. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 302, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tan, T.; Ji, W.; Zhou, W.; Bao, Y.; Xia, X.; Zeng, Z.; Gao, Y. Remarkably Enhanced Methane Sensing Performance at Room Temperature via Constructing a Self-Assembled Mulberry-Like ZnO/SnO2 Hierarchical Structure. Energy Environ. Mater. 2023, 7, e12624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.L.; Zhu, Y.B.; Mao, L.B.; Wang, F.C.; Luo, X.S.; Liu, Y.Y.; Lu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Ge, J.; Shen, W.; et al. Super-elastic and fatigue resistant carbon material with lamellar multi-arch microstructure. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Luo, J.; Liu, H.C.; Zhang, S.; Park, J.G.; Liang, R.; Kumar, S. Carbon fibers from polyacrylonitrile/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposite fibers. Carbon 2019, 145, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leray, N.; Talantikite, M.; Villares, A.; Cathala, B. Xyloglucan-cellulose nanocrystal-chitosan double network hydrogels for soft actuators. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 293, 119753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rege, A. Constitutive Modeling of the Densification Behavior in Open-Porous Cellular Solids. Materials 2021, 14, 2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H. Dielectric Loss Mechanism in Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Materials. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Liu, N.; Lu, Z. Recent Progress of Iron-Based Magnetic Absorbers and Its Applications in Elastomers: A Review. Materials 2024, 17, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Dong, J.; Abdulkarim, Y.I.; Wu, R.; Muhammadsharif, F.F.; Shi, R.; Howlader, M.M.R. A double negative (DNG) metamaterial based on parallel double-E square split resonators for multi-band applications: Simulation and experiment. Results Phys. 2023, 46, 106203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Tardy, B.L.; Khan, S.A.; Liebner, F.; Rojas, O.J. Expanding the upper limits of robustness of cellulose nanocrystal aerogels: Outstanding mechanical performance and associated pore compression response of chiral-nematic architectures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 15309–15319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, Q.; Song, L.; Lu, H.; Xu, H.; Shao, G.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, C.; Fan, B. Enhancing electromagnetic wave absorption with core-shell structured SiO2@MXene@MoS2 nanospheres. Carbon Energy 2024, 6, e502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, T.; Hosomi, S.; Fujii, S.; Ninomiya, K.; Takahashi, K. Nano-Structural Investigation on Cellulose Highly Dissolved in Ionic Liquid: A Small Angle X-ray Scattering Study. Molecules 2017, 22, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.J.; Guo, A.P.; Wang, G.S.; Yin, P.G. Recent progress in microwave absorption of nanomaterials: Composition modulation, structural design, and their practical applications. IET Nanodielectr. 2018, 2, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-de la Rosa, J.; Bou-Comas, A.; Manel Hernàndez, J.; Marín, P.; Lopez-Villegas, J.M.; Tejada, J.; Chudnovsky, E.M. New Approach to Designing Functional Materials for Stealth Technology: Radar Experiment with Bilayer Absorbers and Optimization of the Reflection Loss. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2308819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Yang, X.; Shu, T.; Yang, X.; Qiao, M.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Rao, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. In Situ Synthesis of C-N@NiFe2O4@MXene/Ni Nanocomposites for Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorption at an Ultralow Thickness Level. Molecules 2022, 28, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Gao, S.; Chen, C.; Zhou, F.; Meng, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y. Vacancies-engineered and heteroatoms-regulated N-doped porous carbon aerogel for ultrahigh microwave absorption. Carbon 2020, 169, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Q. Lightweight and efficient microwave absorbing materials based on walnut shell-derived nano-porous carbon. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 7408–7418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zuo, X.; Guo, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T.; Wen, N.; Chen, H.; Cong, T.; Muhammad, J.; et al. Structural Engineering of Hierarchical Aerogels Comprised of Multi-dimensional Gradient Carbon Nanoarchitectures for Highly Efficient Microwave Absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y. A new flexible and ultralight carbon foam/Ti3C2TX MXene hybrid for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 41038–41049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Zheng, P.; Wang, T.; Yu, X.; Pan, J.; Fan, X.; Zhang, T.; Sun, X.; He, J. MOF-derived multi-interface carbon-based composites with enhanced polarization loss and efficient microwave absorption. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2022, 13, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Xu, C.; Yang, B.; Wang, L.; You, W.; Che, R. Hierarchical Ti3 C2 Tx MXene/Carbon Nanotubes Hollow Microsphere with Confined Magnetic Nanospheres for Broadband Microwave Absorption. Small 2022, 18, e2104380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, P.; Sreemathy, R.; Turuk, M. Radar Cross Section Modelling and Analysis of Static and Dynamic Targets using MATLAB. J. Aircr. Spacecr. Technol. 2022, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Feng, Y.; Shen, C. Understanding interfacial engineering of surface functionalized boron nitride nanosheets within thermal interface materials. Sci. China Mater. 2025, 68, 1300–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample Label | Mass Ratio (CS:CNC:BNNS) | Composition Description |
|---|---|---|
| B3C6C0 | 6:0:3 | CS-dominated |
| B3C4C2 | 4:2:3 | Balanced CS/CNC with BNNS |
| B3C3C3 | 3:3:3 | Equal CS/CNC with BNNS |
| B3C2C4 | 2:4:3 | CNC-dominated |
| Material/Sample | RLmin (dB) | Freq.@RLmin (GHz) | EABmax (GHz) | Thickness@EABmax (mm) | Ref./Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This work: B3C4C2 | −52.79 | 13.44 | 8.30 | 3.6 | (Optimal) |
| This work: B3C6C0 | −27.54 | 18.00 | 7.46 | 8.8 | |
| This work: B3C3C3 | −32.41 | 18.00 | 7.06 | 8.7 | |
| This work: B3C2C4 | −24.42 | 14.44 | 5.75 | 9.5 | |
| N-doped porous carbon aerogel | −49.30 | 9.60 | 4.50 | 2.7 | [38] |
| Walnut shell-derived porous carbon | −42.40 | 8.88 | 2.24 | 1.5 | [39] |
| RGO/CNC/M-NP aerogels | −55.10 | 13.80 | 5.00 | 1.9 | [40] |
| CF/MXene-N2 | −45.00 | 7.50 | 5.00 | 4.5 | [41] |
| NiFe/CoFe@C composites | −43.60 | 13.76 | 7.16 | 2.7 | [42] |
| Fe3O4@Ti3C2Tx/CNT composite | −40.1 | 11.40 | 5.8 | 2.0 | [43] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y.; Feng, J.; Feng, J. Defect-Engineered Elastic CNC/Chitosan-Based Carbon Aerogel with Wideband Microwave Absorption. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15161233
Zhan W, Hu Y, Li L, Jiang Y, Feng J, Feng J. Defect-Engineered Elastic CNC/Chitosan-Based Carbon Aerogel with Wideband Microwave Absorption. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(16):1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15161233
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Weikai, Yijie Hu, Liangjun Li, Yonggang Jiang, Junzong Feng, and Jian Feng. 2025. "Defect-Engineered Elastic CNC/Chitosan-Based Carbon Aerogel with Wideband Microwave Absorption" Nanomaterials 15, no. 16: 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15161233
APA StyleZhan, W., Hu, Y., Li, L., Jiang, Y., Feng, J., & Feng, J. (2025). Defect-Engineered Elastic CNC/Chitosan-Based Carbon Aerogel with Wideband Microwave Absorption. Nanomaterials, 15(16), 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15161233






