Biological Evaluation of Silver-Treated Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Application as Antibacterial and Regenerative Wound Dressings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Silver Deposition Treatment
2.2. Biocompatibility Evaluation
2.3. MTT Assay
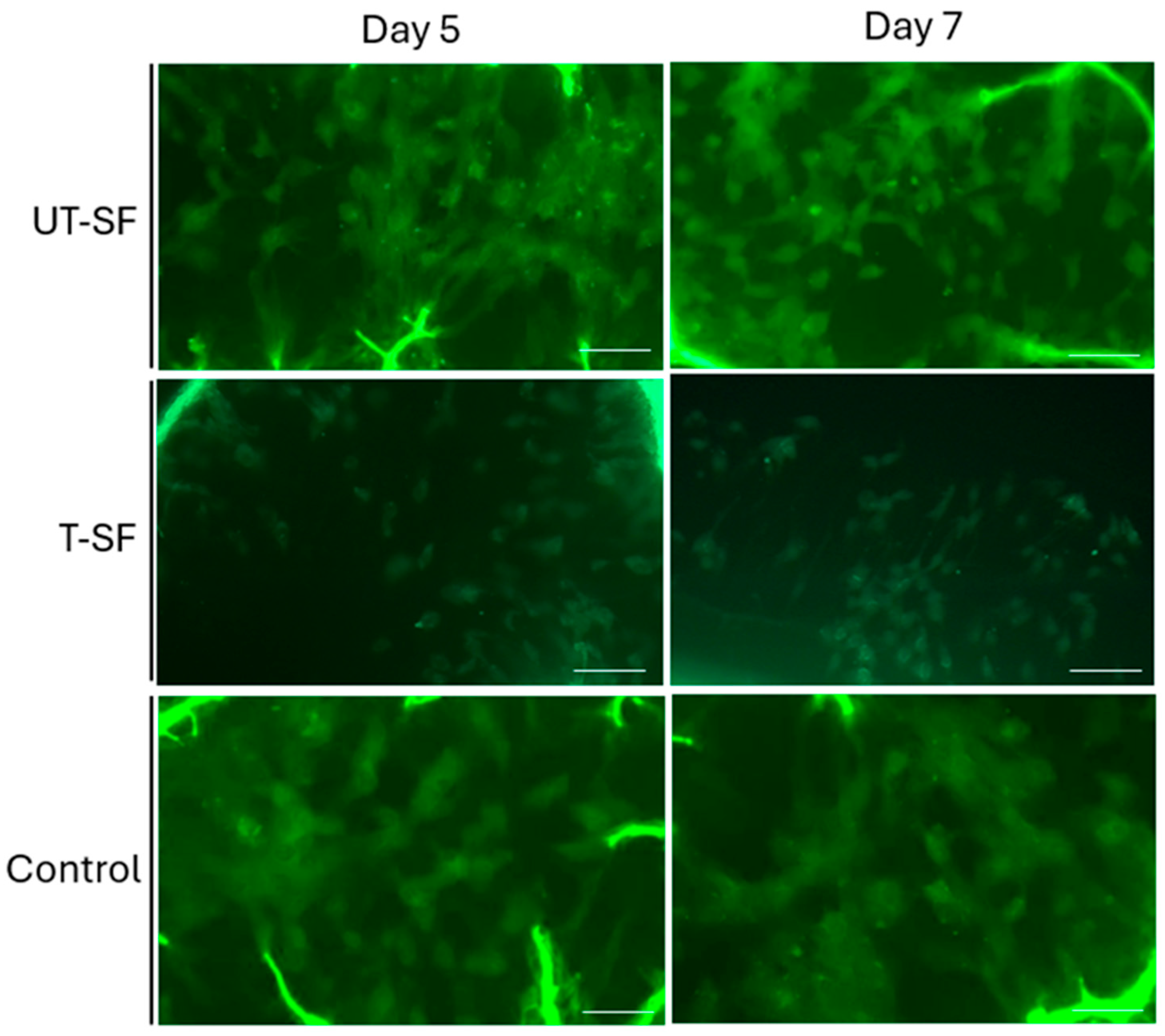
2.4. Live/Dead Assay
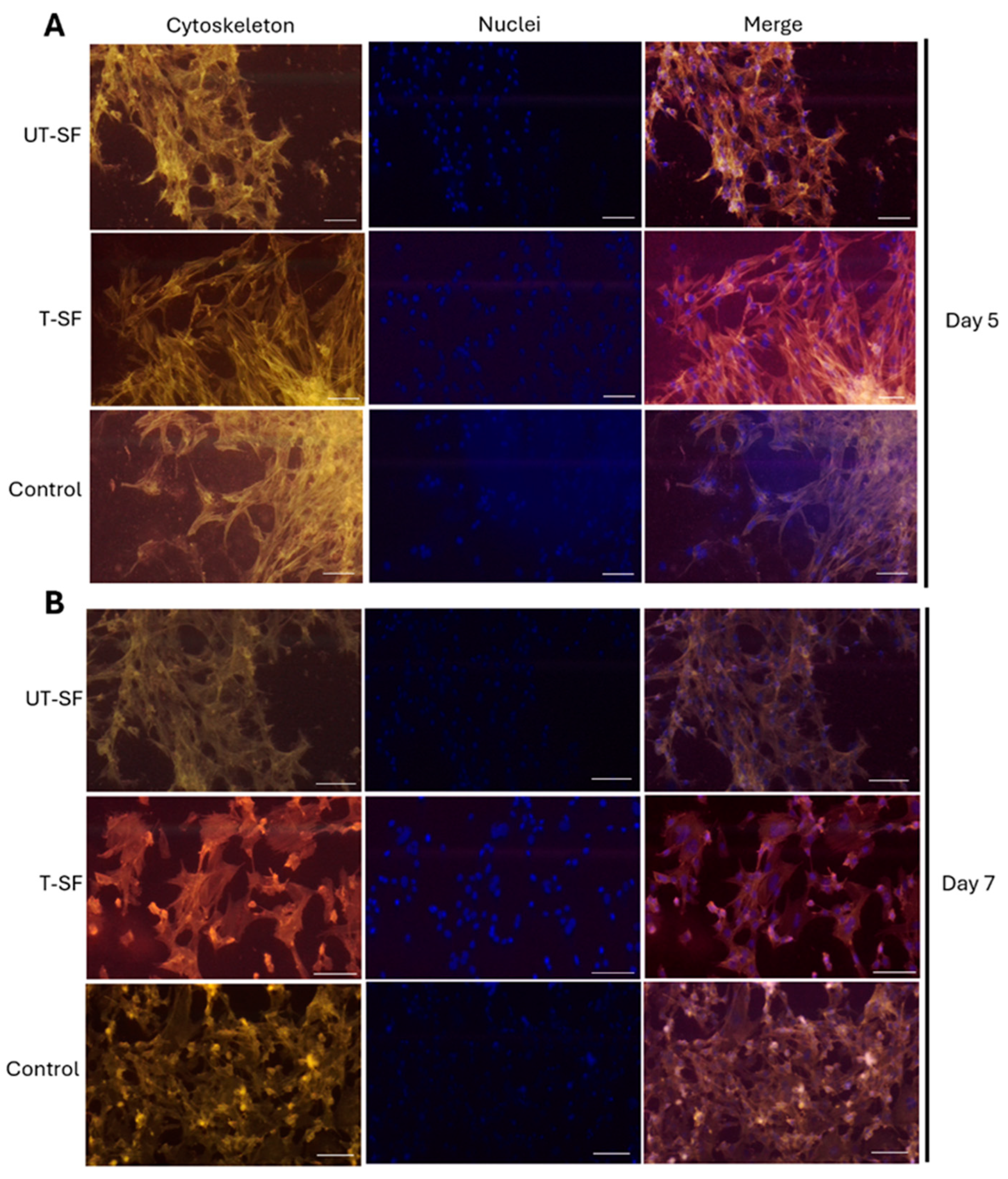
2.5. Cytoskeleton Architecture Analysis
2.6. In Vitro Scratch Assay
- WC: wound closure;
- WAT0: wound area at Time 0;
- WAT1: wound area at Time 1.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biocompatibility of Untreated and Silver-Treated Silk-Fibroin Scaffolds
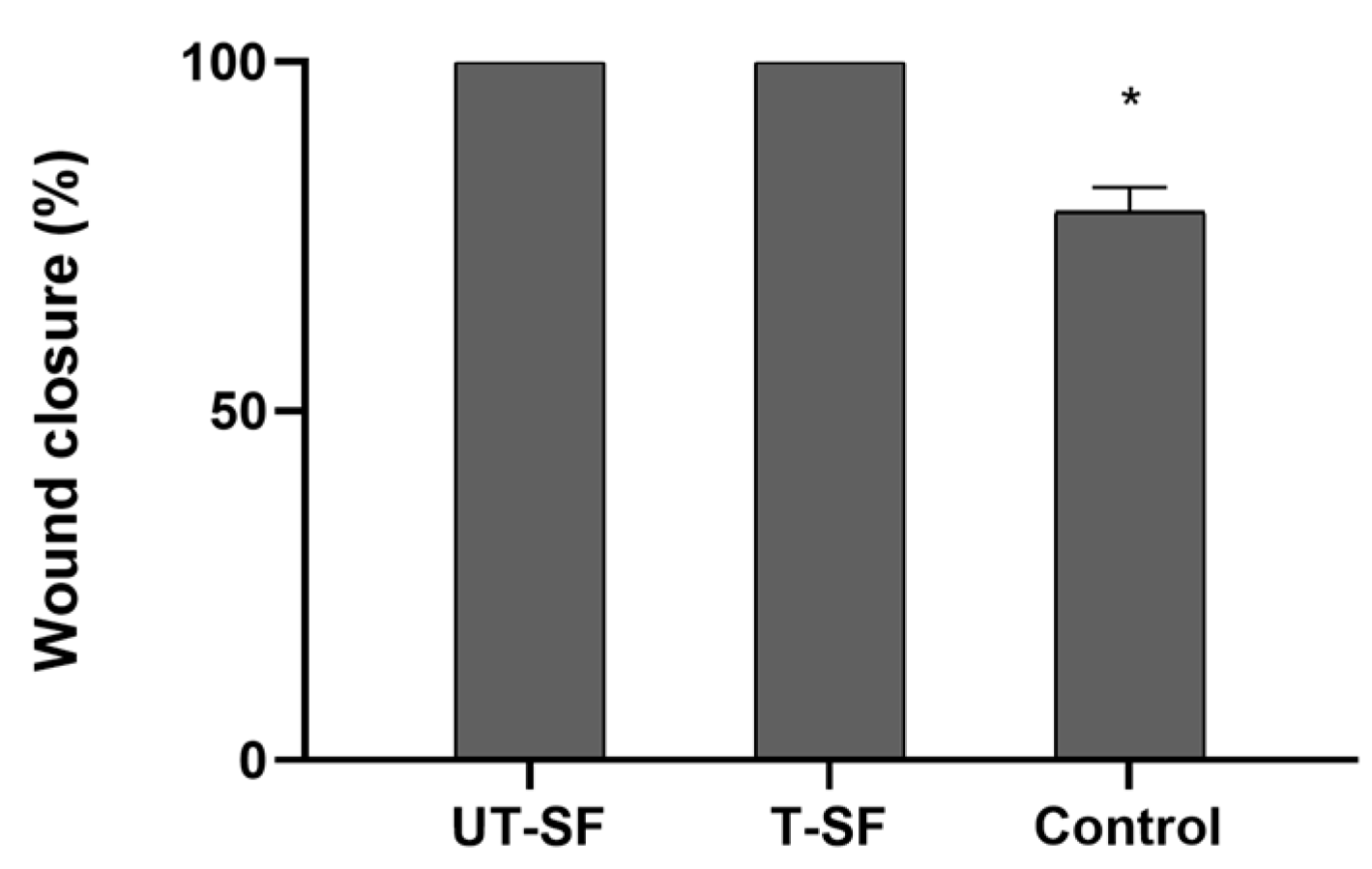
3.2. Wound Healing Properties of Untreated and Silver-Treated Silk-Fibroin Scaffolds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| UT-SF | Untreated silk fibroin scaffold |
| T-SF | Treated silk fibroin scaffold |
| TCPS | Tissue Culture Polystyrene |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| DMSO | Dimetilsolfossido |
| AM | Acetomethoxy |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| TRICT | Tetramethylrhodamine isothiocyanate |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
References
- Falcone, M.; De Angelis, B.; Pea, F.; Scalise, A.; Stefani, S.; Tasinato, R.; Zanetti, O.; Paola, L.D. Challenges in the management of chronic wound infections. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 26, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frykberg, R.G.; Banks, J. Challenges in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 560–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uberoi, A.; McCready-Vangi, A.; Grice, E.A. The wound microbiota: Microbial mechanisms of impaired wound healing and infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrantonaki, E.; Wlaschek, M.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K. Pathogenesis of wound healing disorders in the elderly. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. J. Ger. Soc. Dermatol. 2017, 15, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Dipietro, L.A. Factors affecting wound healing. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, W.-Y.; Yeo, J.C.C.; Soo, X.Y.D.; Thitsartarn, W.; Liu, S.; Tan, B.H.; Suwardi, A.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Responsive hydrogel dressings for intelligent wound management. BMEMat 2023, 1, e12021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, M.; Järbrink, K.; Divakar, U.; Bajpai, R.; Upton, Z.; Schmidtchen, A.; Car, J. The humanistic and economic burden of chronic wounds: A systematic review. Wound Repair Regen. Off. Publ. Wound Health Soc. Eur. Tissue Repair Soc. 2019, 27, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, C.K. Human Wound and Its Burden: Updated 2020 Compendium of Estimates. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, S.; Franco, E. Chronic Wounds: Evaluation and Management. Am. Fam. Physician 2020, 101, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Schilrreff, P.; Alexiev, U. Chronic Inflammation in Non-Healing Skin Wounds and Promising Natural Bioactive Compounds Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, H.A.; Basehore, B.M.; Zito, P.M. Wound Healing Phases. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470443/ (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Goswami, A.G.; Basu, S.; Banerjee, T.; Shukla, V.K. Biofilm and wound healing: From bench to bedside. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mohler, J.; Mahajan, S.D.; Schwartz, S.A.; Bruggemann, L.; Aalinkeel, R. Microbial Biofilm: A Review on Formation, Infection, Antibiotic Resistance, Control Measures, and Innovative Treatment. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Hsu, W.-S.; Chung, W.-Y.; Ko, T.-H.; Lin, J.-H. Silver-based wound dressings reduce bacterial burden and promote wound healing. Int. Wound J. 2016, 13, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, M.H.; Burrell, R.E.; Nadworny, P.L. Evaluating antimicrobial efficacy of new commercially available silver dressings. Int. Wound J. 2010, 7, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, K.; Meshram, S. Biofilm Formation in Chronic Infections: A Comprehensive Review of Pathogenesis, Clinical Implications, and Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Cureus 2024, 16, e70629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, I.; Sivori, F.; Mastrofrancesco, A.; Abril, E.; Pontone, M.; Di Domenico, E.G.; Pimpinelli, F. Bacterial Biofilm in Chronic Wounds and Possible Therapeutic Approaches. Biology 2024, 13, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, P.R.; Pandit, S.; Filippis, A.D.; Franci, G.; Mijakovic, I.; Galdiero, M. Silver Nanoparticles: Bactericidal and Mechanistic Approach against Drug Resistant Pathogens. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaarup, I.C.; Iversen, A.K.S.; Lichtenberg, M.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Jakobsen, T.H. Biofilm Survival Strategies in Chronic Wounds. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picca, R.A.; Paladini, F.; Sportelli, M.C.; Pollini, M.; Giannossa, L.C.; Di Franco, C.; Panico, A.; Mangone, A.; Valentini, A.; Cioffi, N. Combined Approach for the Development of Efficient and Safe Nanoantimicrobials: The Case of Nanosilver-Modified Polyurethane Foams. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sportelli, M.C.; Picca, R.A.; Paladini, F.; Mangone, A.; Giannossa, L.C.; Franco, C.D.; Gallo, A.L.; Valentini, A.; Sannino, A.; Pollini, M.; et al. Spectroscopic Characterization and Nanosafety of Ag-Modified Antibacterial Leather and Leatherette. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, D.G.; Bowler, P.G. Biofilm delays wound healing: A review of the evidence. Burns Trauma 2013, 1, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versey, Z.; da Cruz Nizer, W.S.; Russell, E.; Zigic, S.; DeZeeuw, K.G.; Marek, J.E.; Overhage, J.; Cassol, E. Biofilm-Innate Immune Interface: Contribution to Chronic Wound Formation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 648554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diban, F.; Di Lodovico, S.; Di Fermo, P.; D’Ercole, S.; D’Arcangelo, S.; Di Giulio, M.; Cellini, L. Biofilms in Chronic Wound Infections: Innovative Antimicrobial Approaches Using the In Vitro Lubbock Chronic Wound Biofilm Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Domenico, E.G.; Farulla, I.; Prignano, G.; Gallo, M.T.; Vespaziani, M.; Cavallo, I.; Sperduti, I.; Pontone, M.; Bordignon, V.; Cilli, L.; et al. Biofilm is a Major Virulence Determinant in Bacterial Colonization of Chronic Skin Ulcers Independently from the Multidrug Resistant Phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, M.P. Wound Dressing Materials: Bridging Material Science and Clinical Practice. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, M.M.; Dima, M.B.; Dima, B.; Holban, A.M. Nanomaterials for Wound Healing and Infection Control. Materials 2019, 12, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, F.; Russo, F.; Masi, A.; Lanzillotti, C.; Sannino, A.; Pollini, M. Silver-Treated Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Prevention of Critical Wound Infections. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, A.S.; Dzurny, D.I.; Dees, W.R.; Qin, N.; Rodriguez, C.C.N.; Alt, L.A.; Ellward, G.L.; Best, J.A.; Rudawski, N.G.; Fujii, K.; et al. Silver nanoparticles enhance the efficacy of aminoglycosides against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1064095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, I.X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, I.S.; Mei, M.L.; Li, Q.; Chu, C.H. The Antibacterial Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles and Its Application in Dentistry. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, F.; Pollini, M. Novel Approaches and Biomaterials for Bone Tissue Engineering: A Focus on Silk Fibroin. Materials 2022, 15, 6952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, T.; Vaughn, A.E.; Seal, S.; Liechty, K.W.; Zgheib, C. Silk Fibroin-Based Therapeutics for Impaired Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melke, J.; Midha, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ito, K.; Hofmann, S. Silk fibroin as biomaterial for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2016, 31, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-H.; Ji, S.-C.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Shen, X.-C.; Liang, H. Silk fibroin-based scaffolds for tissue engineering. Front. Mater. Sci. 2013, 7, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomherun, N.; Kriangsaksri, R.; Tanticharakunsiri, W.; Foongsawat, N.; Phoolcharoen, W.; Tawinwung, S.; Keeratihattayakorn, S.; Ratanavaraporn, J. Silk fibroin-based hydrogel as injectable carrier for prolonged immunization of plant-based COVID-19 subunit vaccine. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 95, 105574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, I.R.; Pollini, M.; Paladini, F. The potential of photo-deposited silver coatings on Foley catheters to prevent urinary tract infections. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 69, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollini, M.; Paladini, F.; Licciulli, A.; Maffezzoli, A.; Sannino, A. Engineering Nanostructured Silver Coatings for Antimicrobial Applications. In Nano-Antimicrobials: Progress and Prospects; Cioffi, N., Rai, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirwana, I.; Munadziroh, E.; Yogiartono, R.M.; Thiyagu, C.; Ying, C.S.; Dinaryanti, A. Cytotoxicity and proliferation evaluation on fibroblast after combining calcium hydroxide and ellagic acid. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2021, 12, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzillotti, C.; Iaquinta, M.R.; De Pace, R.; Mosaico, M.; Patergnani, S.; Giorgi, C.; Tavoni, M.; Dapporto, M.; Sprio, S.; Tampieri, A.; et al. Osteosarcoma cell death induced by innovative scaffolds doped with chemotherapeutics. J. Cell. Physiol. 2024, 239, e31256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, Y.K.; Robinson, A.; Zanghi, N.; Kratz, A.; Gustetic, A.; Crow, M.M.; Ritts, T.; Hankey, W.; Segarra, V.A. Introducing Wound Healing Assays in the Undergraduate Biology Laboratory Using Ibidi Plates. J. Microbiol. Biol. Educ. 2022, 23, e00061-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazza, M.; Oton-Gonzalez, L.; Scuderi, V.; Rotondo, J.C.; Lanzillotti, C.; Di Mauro, G.; Tognon, M.; Martini, F.; Borghi, A. Tissue cytokine/chemokine profile in vulvar lichen sclerosus: An observational study on keratinocyte and cultures. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2020, 100, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotta, C.; Badiale, G.; Cervellera, C.F.; Morciano, G.; Di Mauro, G.; Touzé, A.; Pinton, P.; Tognon, M.; Martini, F.; Rotondo, J.C. All-trans retinoic acid exhibits anti-proliferative and differentiating activity in Merkel cell carcinoma cells via retinoid pathway modulation. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Gruber, S.; Nickel, A. Toxic or not toxic? The specifications of the standard ISO 10993-5 are not explicit enough to yield comparable results in the cytotoxicity assessment of an identical medical device. Front. Med. Technol. 2023, 5, 1195529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaper, D.J.; Schultz, G.; Carville, K.; Fletcher, J.; Swanson, T.; Drake, R. Extending the TIME concept: What have we learned in the past 10 years?(*). Int. Wound J. 2012, 2 (Suppl. 9), 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tottoli, E.M.; Dorati, R.; Genta, I.; Chiesa, E.; Pisani, S.; Conti, B. Skin Wound Healing Process and New Emerging Technologies for Skin Wound Care and Regeneration. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuutila, K.; Eriksson, E. Moist Wound Healing with Commonly Available Dressings. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Manna, S.; Roy, S.; Nandi, S.K.; Basak, P. Polymeric biomaterials-based tissue engineering for wound healing: A systemic review. Burns Trauma 2023, 11, tkac058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.L.; Pollini, M.; Paladini, F. A combined approach for the development of novel sutures with antibacterial and regenerative properties: The role of silver and silk sericin functionalization. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Dip, T.M.; Nur, M.G.; Padhye, R.; Houshyar, S. Fabrication of Silk Fibroin-Derived Fibrous Scaffold for Biomedical Frontiers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2024, 309, 2300422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, P.J.; Suamte, L. Applications of silk-based biomaterials in biomedicine and biotechnology. Eng. Regen. 2024, 5, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldahish, A.; Shanmugasundaram, N.; Vasudevan, R.; Alqahtani, T.; Alqahtani, S.; Asiri, A.M.; Devanandan, P.; Thamaraikani, T.; Vellapandian, C.; Jayasankar, N. Silk Fibroin Nanofibers: Advancements in Bioactive Dressings through Electrospinning Technology for Diabetic Wound Healing. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hamid, M.I.A.; Ibrahim, D.; Abdelfattah-Hassan, A.; Mohammed, O.B.; Pet, I.; Khalil, S.S.; El-Badry, S.M.; Metwally, A.S.; Azouz, A.A.; Elnegiry, A.A.; et al. Silver nanoparticles loaded with pomegranate peel extract and hyaluronic acid mediate recovery of cutaneous wounds infected with Candida albicans. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1469493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.E.; Wilgus, T.A. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Angiogenesis in the Regulation of Cutaneous Wound Repair. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilgus, T.A. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Cutaneous Scarring. Adv. Wound Care 2019, 8, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.K.; Sheppard, D.; Chapman, H.A. TGF-β1 Signaling and Tissue Fibrosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a022293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Hu, M.; Shi, S.; Li, Z.; Wu, G.; Cui, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Silver nanoparticles/chitosan oligosaccharide/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofiber promotes wound healing by activating TGFβ1/Smad signaling pathway. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.M.C.; Castillo, J.M.Q.; Del Castillo Castro, T.; Felix, D.E.R.; Ortega, H.D.C.S.; Manero, O.; Gastelum, K.A.L.; Chan, L.H.C.; Martinez, D.H.; Hernández, J.A.T.; et al. Aloe vera mucilage loaded gelatin electrospun fibers contained in polylactic acid coaxial system and polylactic acid and poly(e-caprolactone) tri-layer membranes for tissue engineering. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2024, 35, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markandeywar, T.S.; Narang, R.K. Collagen and chitosan-based biogenic sprayable gel of silver nanoparticle for advanced wound care. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 5543–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolimi, P.; Narala, S.; Nyavanandi, D.; Youssef, A.A.A.; Dudhipala, N. Innovative Treatment Strategies to Accelerate Wound Healing: Trajectory and Recent Advancements. Cells 2022, 11, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
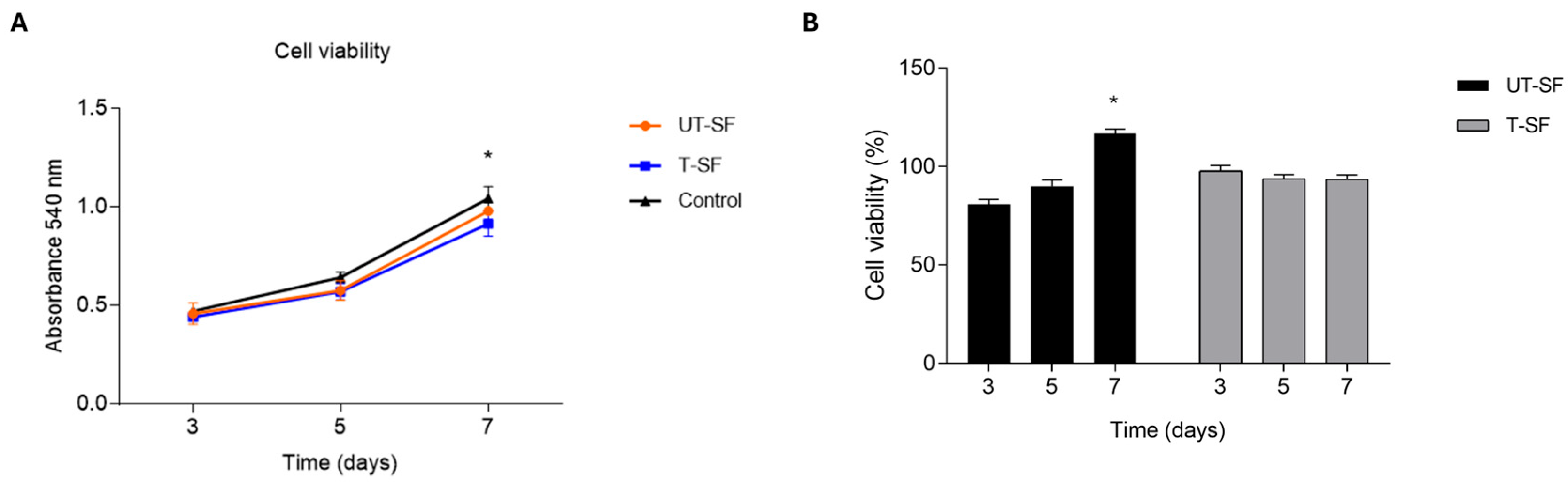
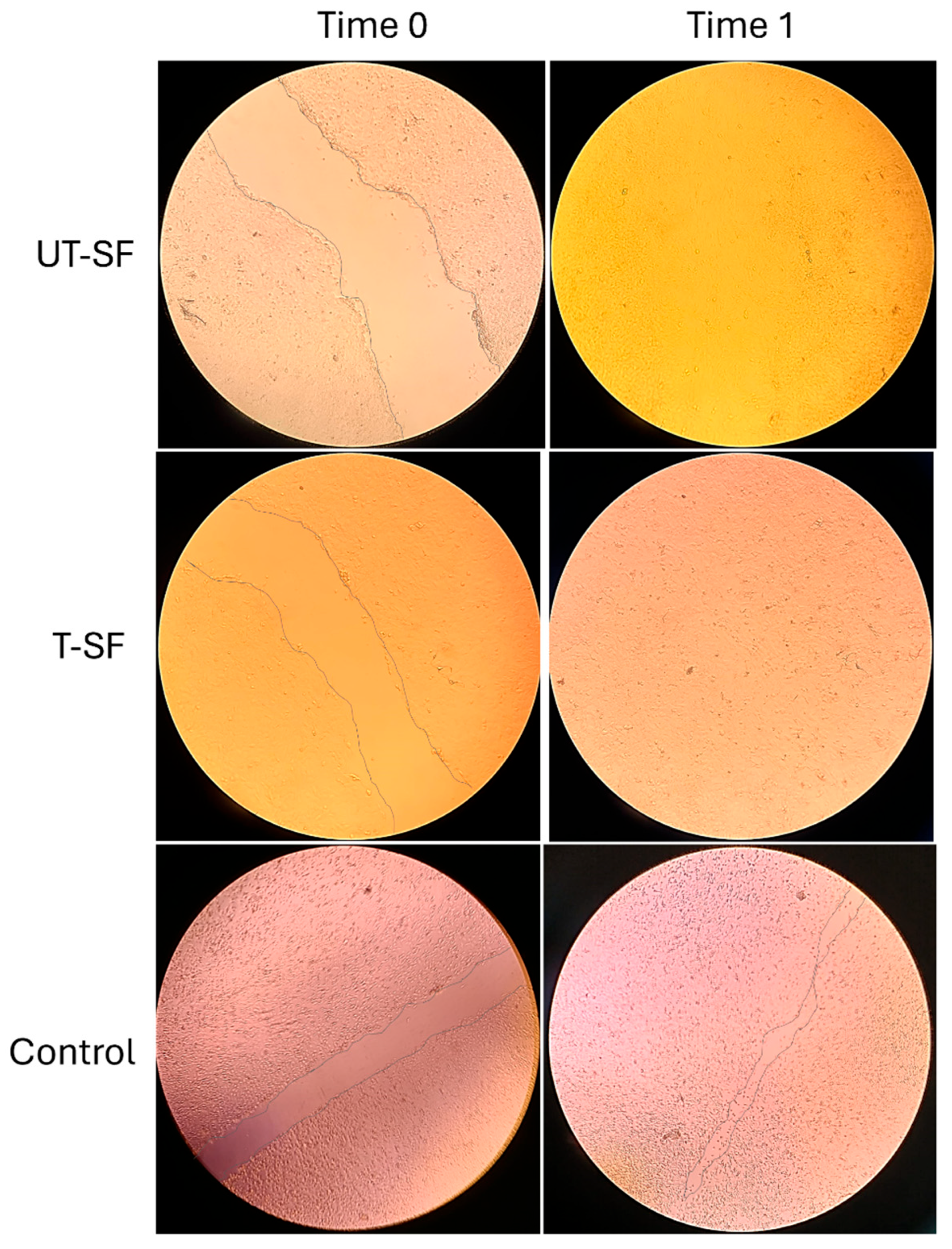
| Sample | Cell Viability (%—Day 3) | Cell Viability (%—Day 5) | Cell Viability (%—Day 7) | Wound Closure Rate (%—Time 1) | Observed Bioactivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UT-SF | 81 | 90 | 116 | 100 | Biocompatible; regenerative |
| T-SF | 98 | 94 | 94 | 100 | Biocompatible; regenerative; synergistic effect of silver and fibroin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paladini, F.; Lanzillotti, C.; Panico, A.; Pollini, M. Biological Evaluation of Silver-Treated Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Application as Antibacterial and Regenerative Wound Dressings. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120919
Paladini F, Lanzillotti C, Panico A, Pollini M. Biological Evaluation of Silver-Treated Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Application as Antibacterial and Regenerative Wound Dressings. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(12):919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120919
Chicago/Turabian StylePaladini, Federica, Carmen Lanzillotti, Angelica Panico, and Mauro Pollini. 2025. "Biological Evaluation of Silver-Treated Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Application as Antibacterial and Regenerative Wound Dressings" Nanomaterials 15, no. 12: 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120919
APA StylePaladini, F., Lanzillotti, C., Panico, A., & Pollini, M. (2025). Biological Evaluation of Silver-Treated Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Application as Antibacterial and Regenerative Wound Dressings. Nanomaterials, 15(12), 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120919










