Synthesis, Characterization, and Application of Magnetic Zeolite Nanocomposites: A Review of Current Research and Future Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
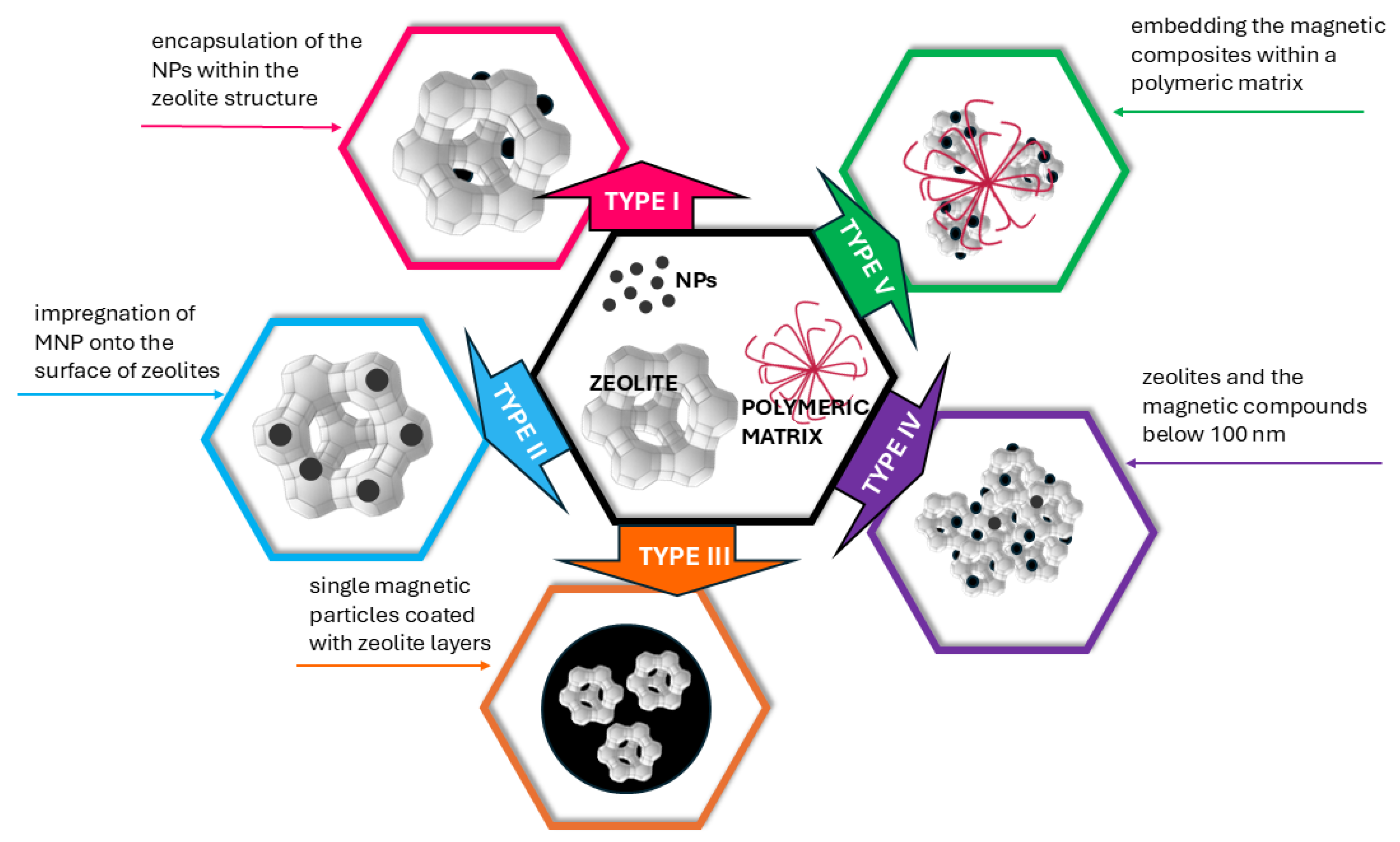
2. Magnetic Zeolite Nanocomposites
- •
- Acid treatment (commonly using HCl, HNO3, or HF) is employed to remove aluminum and create larger mesopores.
- •
- Alkaline treatment with NaOH or KOH promotes the formation of additional pores and increases the specific surface area.
- A magnetic core, which determines the particle’s magnetic properties.
- A protective coating, which stabilizes the NPs and prevents oxidation and agglomeration.
- A functionalized surface, which incorporates chemical groups or coatings that enhance interaction with zeolites and improve adsorption properties.
- •
- Magnetite (Fe3O4) exhibits high saturation magnetization and is superparamagnetic at small sizes (<20 nm), meaning it does not retain magnetization after the external field is removed. However, it readily oxidizes into maghemite when exposed to air.
- •
- Maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) is structurally similar to magnetite but is more oxidation-resistant, making it widely used in environmental and biomedical applications.
- •
- Iron (Fe) NPs have very high magnetization but are prone to oxidation, requiring protective coatings such as SiO2 or polymers.
- •
- Cobalt (Co) and nickel (Ni) NPs are strong magnets, but their high toxicity and lower chemical stability limit their applications.
- •
- •
- •
- •
- Ferromagnetic materials (Fe, Co, Ni) retain magnetization even in the absence of an external magnetic field.
- •
- •
- Van der Waals forces arise due to temporary dipoles between molecules and the NC surface. These forces contribute to the adsorption of non-polar molecules and certain pollutants, such as organic contaminants and oils.
- •
- Electrostatic interactions [59], where zeolites, due to their negatively charged framework resulting from exchangeable cations (Na+, K+, Ca2+), attract positively charged ions and cationic compounds. On the other hand, MNPs (Fe3O4, γ-Fe2O3) possess a surface charge that can change with pH, affecting interactions with other components. These electrostatic interactions can be enhanced by adjusting pH or ionic strength of the solution.
- •
- •
- Covalent bonds: These play a crucial role in surface functionalization. A key example is the silanization of MNPs (Fe3O4) with APTES, which introduces -NH2 groups [61]. These groups can further form covalent bonds with contaminants or catalytic centers, enhancing the nanocomposite’s reactivity.
- •
- Complexation with metal ions [31]: Zeolites and MNPs can form coordination complexes with metal ions, improving their adsorption capacity. For instance, Fe3O4 NPs functionalized with carboxyl (-COOH) or amino (-NH2) groups can selectively complex Cu2+ and Pb2+ ions, increasing their removal efficiency.
- •
- Ion exchange: Zeolites facilitate the exchange of cations within their structure, enhancing the removal of heavy metals. A notable example is magnetic zeolite NCs functionalized with amino groups (-NH2), which exhibit improved adsorption of heavy metal ions (Pb2+, Hg2+) due to their ability to bind metal ions through complexation [38,57].
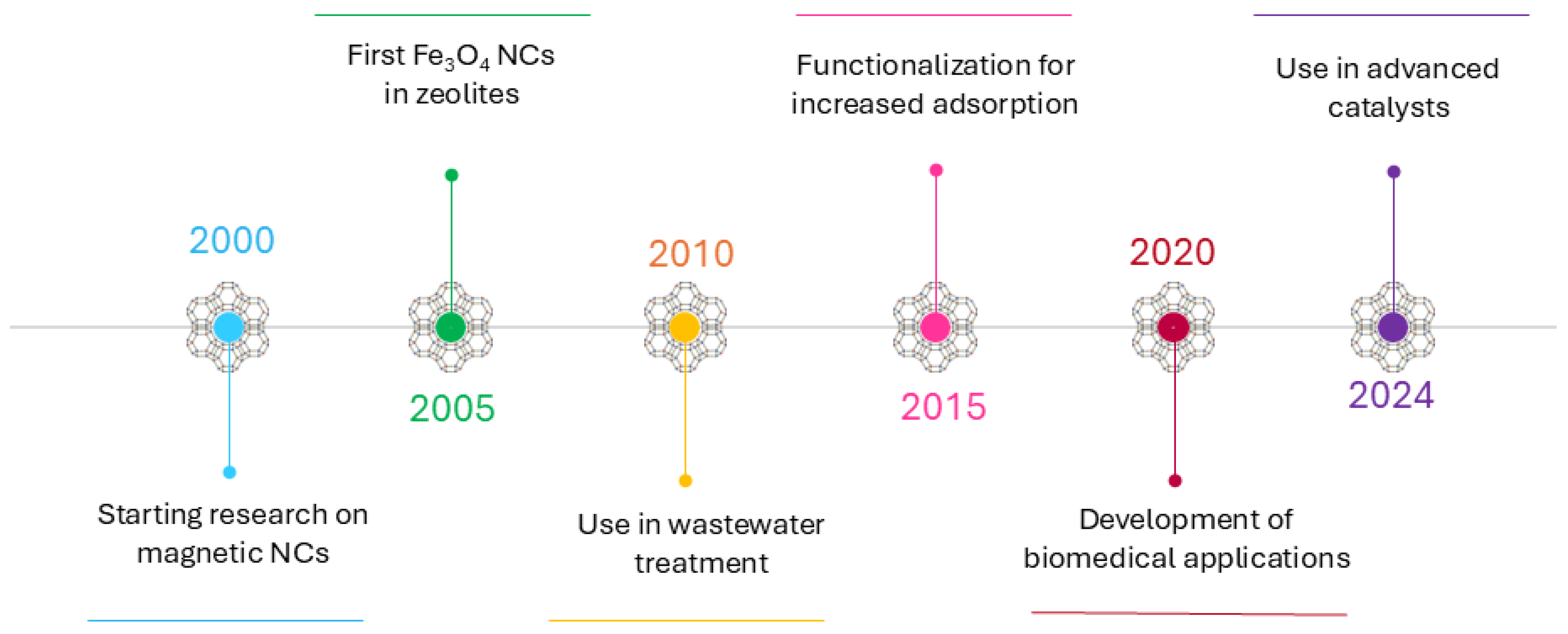
3. The Development of Magnetic Zeolite Nanocomposites over Time
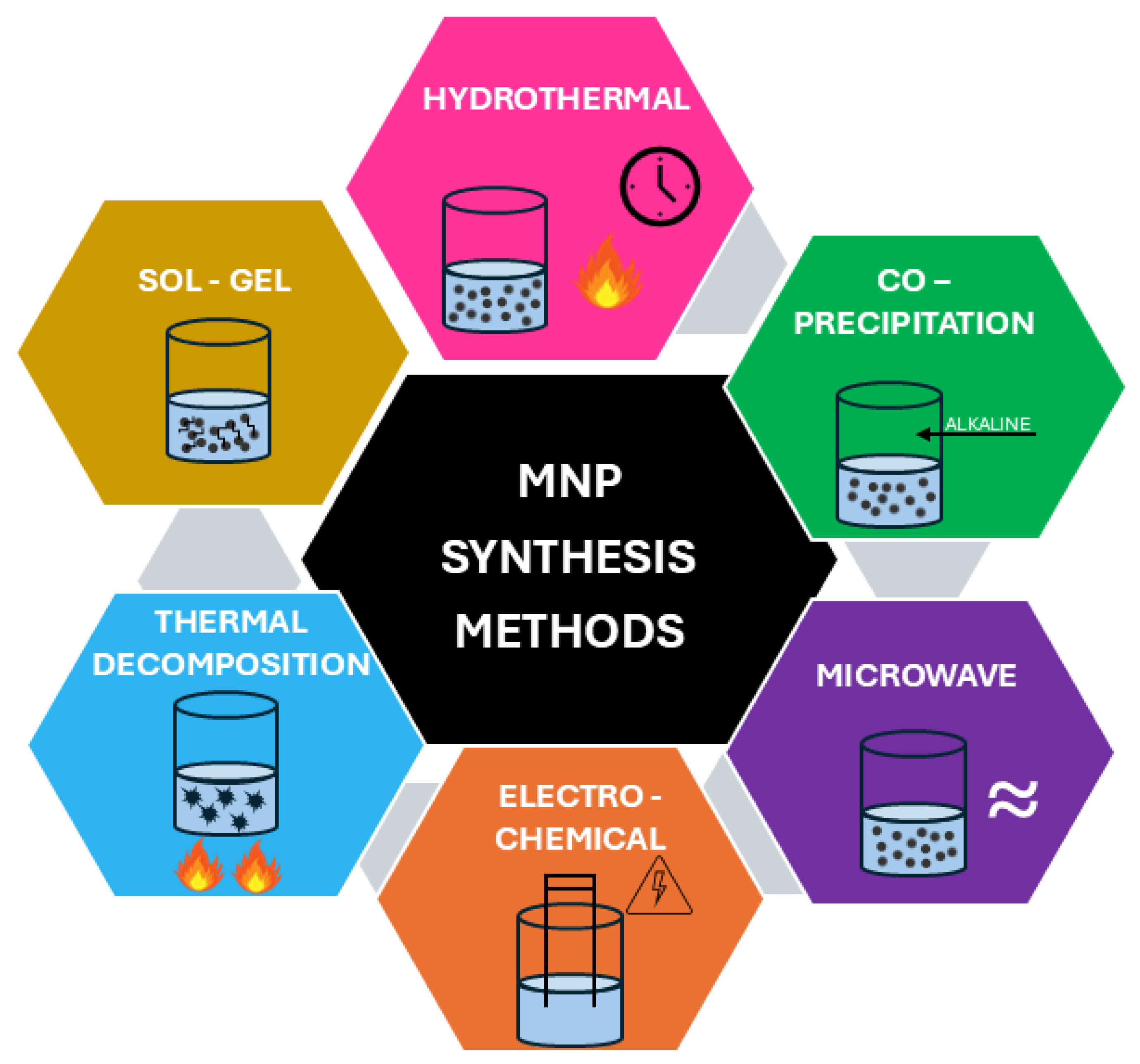
4. Synthesis Methods of Magnetic Zeolite Nanocomposites
- •
- Impregnation method: The zeolite structure is immersed in a solution containing precursors of MNPs, usually iron salts such as FeCl2 or FeCl3. This is followed by a reduction or precipitation process, where iron ions are converted into MNPs, such as magnetite or maghemite [29]. This type of reaction was carried out under mild conditions using low-energy input and inexpensive, non-toxic materials, resulting in inert residues and avoiding hazardous solvents. These features highlight the method’s alignment with green chemistry principles, representing its key advantages.
- •
- A rapid, environmentally friendly impregnation method was also used to prepare MNPs on sodium/potassium zeolite surfaces. Using ferric and ferrous chloride with sodium hydroxide, the zeolite/Fe3O4 NCs was formed in aqueous suspension under ambient conditions, following green chemistry principles [146]. Pescarmona et al. [147] developed a method for the easy separation of heterogeneous catalysts from liquid reaction mixtures in high-throughput experiments (HTEs) using magnetically modified zeolites. Specifically, the zeolites were impregnated with an aqueous solution of an iron precursor, and after reduction in hydrogen, ferromagnetic iron oxide NPs formed on the surface of the zeolites. Vajglova et al. [148] synthesized a series of mono- and bimetallic catalysts by impregnating H–Y-5.1 zeolite with iron and nickel nitrates. These catalysts were prepared with varying Fe/Ni ratios and subsequently calcined.
- •
- In situ synthesis: MNPs are synthesized directly within the porous zeolite structure during the zeolite formation process [149]. Zhang et al. [150] introduced a novel method for synthesizing NaP zeolite adsorbents doped with transition metals (M-NaP) utilizing fly ash as a raw material. The process involves extracting sodium silicate (Na2SiO3) and sodium aluminate (NaAlO2) from fly ash through activation and staged treatment. The in situ synthesis is combined with an organic complexation method to incorporate transition metals such as Co, Ni, Fe, and Ti into the zeolite framework. Nasir et al. [149] presented a straightforward method for the in situ synthesis of magnetic Fe@Si/zeolite Na composites, in which Fe3O4 NPs are incorporated into the zeolite structure during the synthesis process. Natural materials were used, and the Fe3O4 MNPs were prepared via a co-precipitation method, forming core–shell structures with zeolite.
- •
- Co-precipitation: This method involves the simultaneous precipitation of MNPs and zeolite precursors in a solution, leading to the concurrent formation of both components. It is a simple process that allows for the simultaneous synthesis of NPs and zeolites [29]. Nabiyouni et al. [98] synthesized the Fe3O4 NPs and their incorporation into zeolite-Y matrices using a chemical precipitation method. Structural and morphological analyses confirmed the successful formation of NCs, with Fe3O4 particles uniformly distributed within the zeolite framework.
- •
- Microwave-assisted method: Microwave-assisted methods provide a fast and effective route for synthesizing magnetic zeolite NCs, enabling shorter reaction times and often producing materials with improved uniformity and fewer structural defects compared to traditional hydrothermal techniques [151]. Piri et al. [15] presents the development of a magnetic zeolite–hydroxyapatite (MZeo-HAP) NC synthesized via a microwave-assisted method. The process involves reinforcing magnetic hydroxyapatite with zeolite to create an efficient adsorbent.
- •
- Mechanical synthesis (milling): Zeolite and MNPs are mechanically mixed using a milling device, such as a ball mill. The milling process ensures the uniform dispersion of MNPs within the zeolite powder. The method begins by reducing zeolite particles to the nano- or microscale, after which iron oxide nanocrystals are synthesized in their presence. This approach effectively minimizes the agglomeration of magnetite NPs and promotes their uniform integration into the zeolite matrix [152]. Murrieta-Rico et al. [153] explores a solvent-free mechanochemical approach to synthesize iron-modified MFI zeolites. By grinding ammonium-form MFI zeolite with iron(III) chloride, researchers achieved the incorporation of iron into the zeolite framework.
- •
- Hydrothermal synthesis: MNPs are synthesized within the zeolite structure under high temperature and pressure conditions, typically in an autoclave. Aboelfetoh et al. [154] presented a simple one-step hydrothermal synthesis method for a magnetic and porous zeolite/SnFe2O4 NC designed for the removal of both cationic and anionic dyes from wastewater. Characterization confirmed the successful integration of SnFe2O4 NPs into the zeolite structure, resulting in a material with high surface area, strong magnetic properties, and efficient adsorption capabilities.
- •
- Pyrolysis: This process involves heating the precursors of MNPs in the presence of zeolites using a flame or a hot gas stream, leading to the formation of MNPs [155]. Gao et al. [156] explored an innovative method for synthesizing magnetic zeolite composites by utilizing pyrolysis products derived from waste printed circuit boards (WPCBs). The researchers employed the residual heat and carbon-rich gases from the pyrolysis of WPCBs to facilitate the formation of carbon fibers on waste zeolites, resulting in magnetic zeolites coated with carbon fibers.
5. Characterization of Magnetic Zeolite Nanocomposites
5.1. X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)
5.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
5.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
5.4. Transmission and Scanning Electron Microscopy (TEM, SEM)
5.5. Nitrogen Adsorption/Desorption (BET Analysis)
5.6. Vibrating Sample Magnetometry (VSM)
5.7. Zeta Potential (ZP)
5.8. Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES)
5.9. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
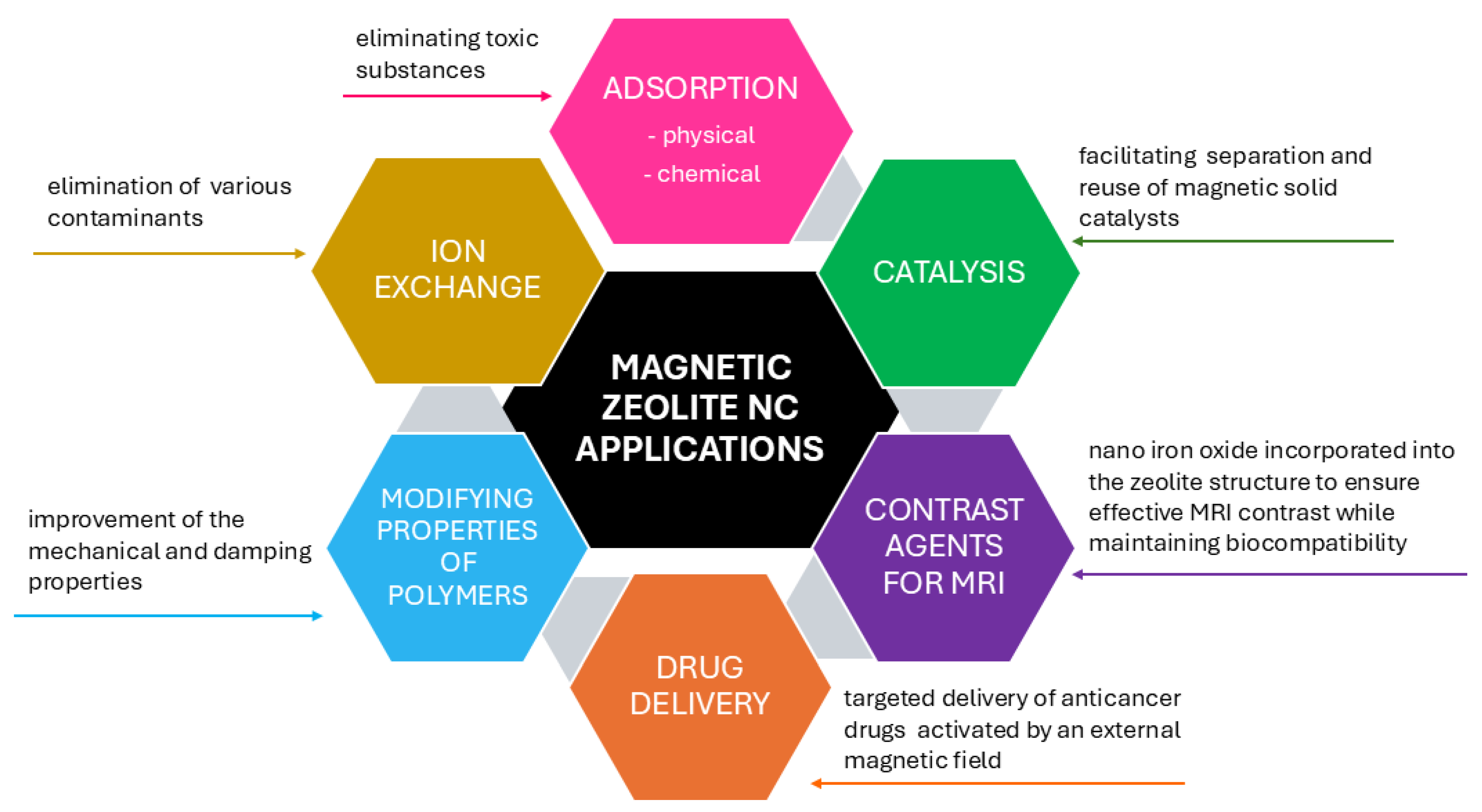
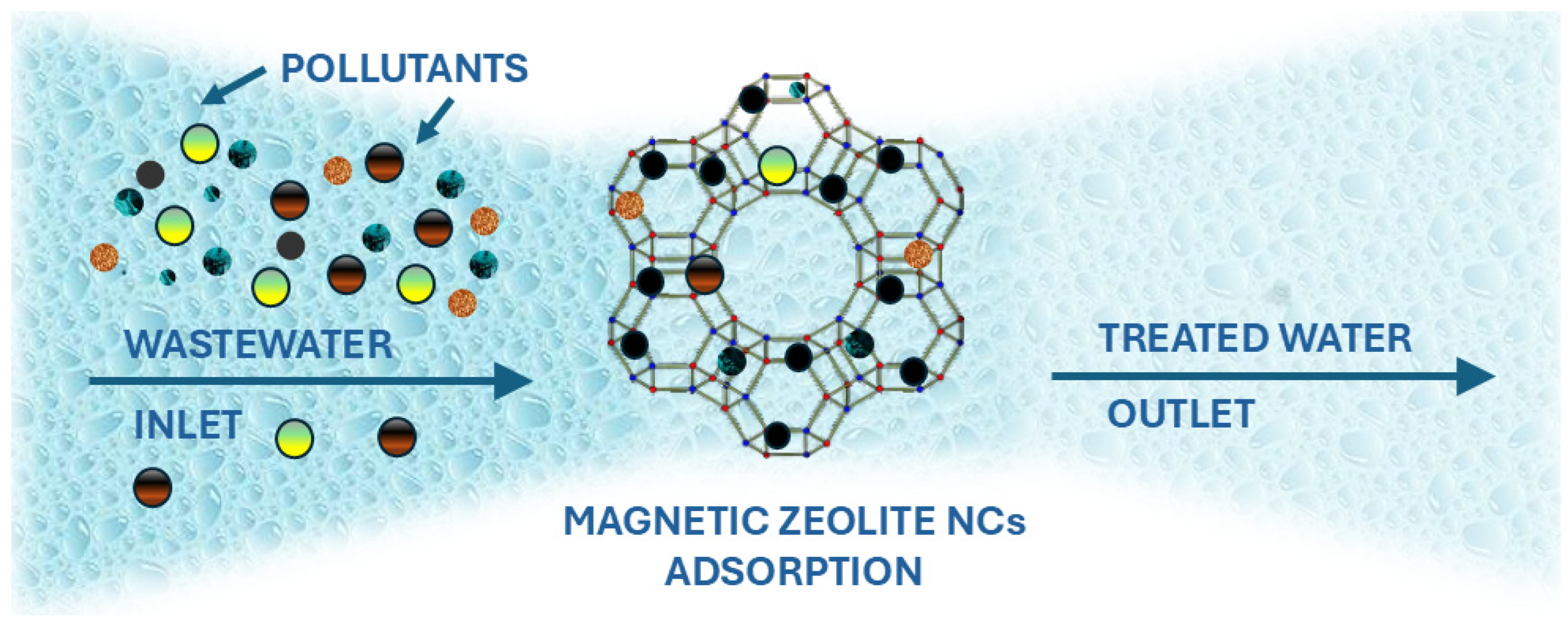
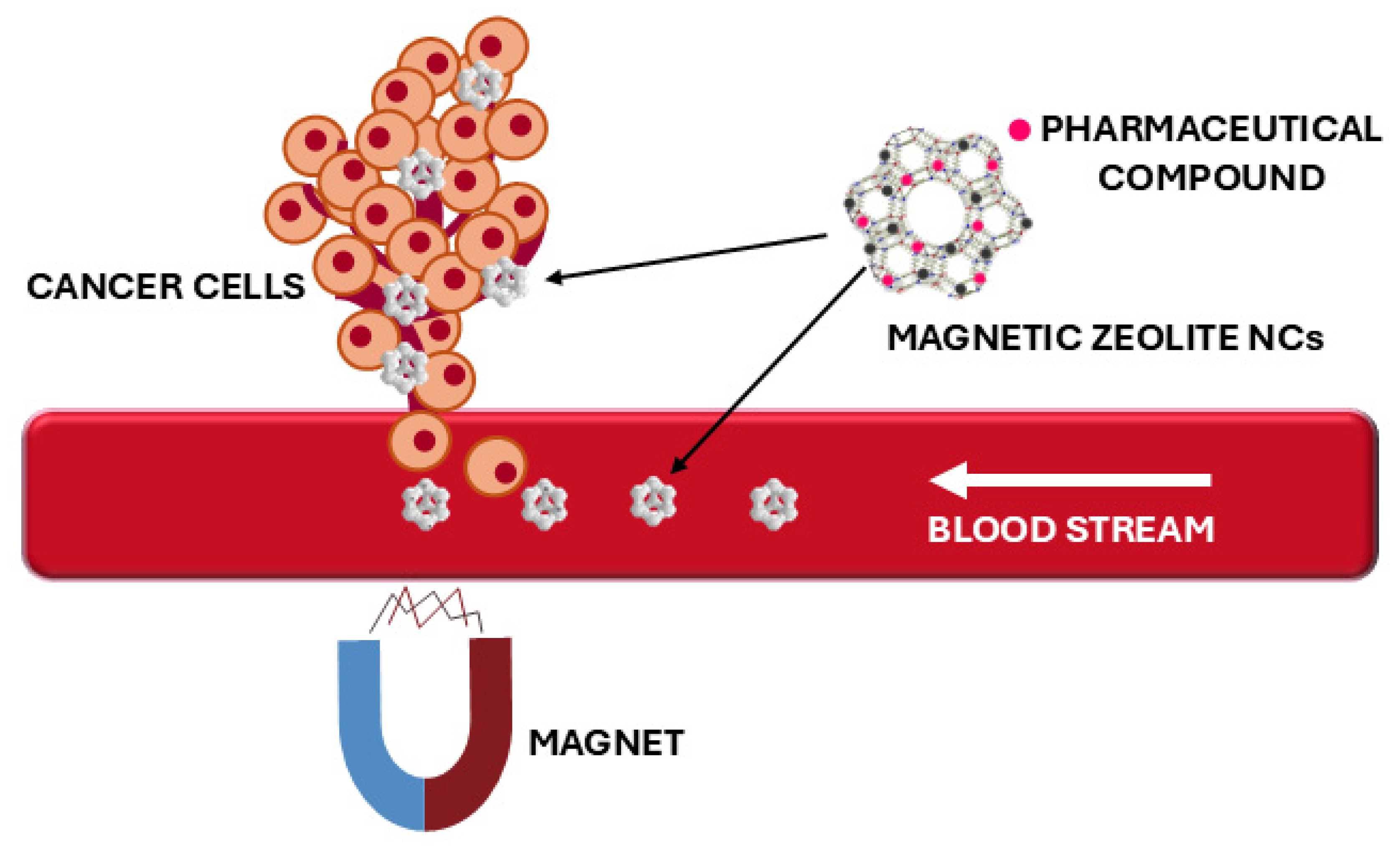
6. Applications of Magnetic Zeolite Nanocomposites
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ulmanu, M. Mineralogy of Natural Zeolites. In Handbook of Natural Zeolites; Bentham Science Publisher: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Weckhuysen, B.M.; Yu, J. Recent advances in zeolite chemistry and catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7022–7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Hu, X.; Song, H.; Xia, G.; Shen, Z.-Y.; Yu, R.; Moskovits, M. Microwave synthesis of zeolites and their related applications. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 323, 111262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordala, N.; Wyszkowski, M. Zeolite Properties, Methods of Synthesis, and Selected Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera, G.; Tiberto, P.; Allia, P.; Bonelli, B.; Esposito, S.; Marocco, A.; Pansini, M.; Leterrier, Y. Magnetic Properties of Nanocomposites. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Introduction to Nanotechnology: History, Status, and Importance of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Education. In Global Perspectives of Nanoscience and Engineering Education; Winkelmann, K., Bhushan, B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, N.H.; Shameli, K.; Etesami, M.; Chan Abdullah, E.; Abdullah, L.C. Facile and green preparation of magnetite/zeolite nanocomposites for energy application in a single-step procedure. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 719, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, B.; Obaidat, I.M.; Albiss, B.A.; Haik, Y. Magnetic nanoparticles: Surface effects and properties related to biomedicine applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21266–21305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Tovar, G.; Salado-Leza, D.; Carreón-Álvarez, C.; Acosta-Ruelas, B.J.; Rodríguez-López, J.L. Chapter 7—Surface functionalization of nanoparticles: Structure determines function. In Antimicrobial Activity of Nanoparticles, Guisbiers, G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 203–248. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, C.J. Properties and applications of Zeolites. Sci. Prog. 2010, 93, 223–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzukashvili, S.; Hu, W.; Sommerville, R.; Brooks, O.; Kökkılıç, O.; Rowson, N.A.; Ouzilleau, P.; Waters, K.E. Magnetic Zeolite: Synthesis and Copper Adsorption Followed by Magnetic Separation from Treated Water. Crystals 2023, 13, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, T.R.; Schildt, L.F.L.; Silva, M.L.L.E.; Vasconcelos, V.V.V.; Di Conzo, C.; Mura, F.; Rossi, M.; Varvaro, G.; Abdolrahimi, M.; Quaranta, S.; et al. Magnetic CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles Immobilized on Modified Rice Husk-Derived Zeolite for Chlorogenic Acid Adsorption. Magnetochemistry 2024, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başkan, G.; Açıkel, Ü.; Levent, M. Investigation of adsorption properties of oxytetracycline hydrochloride on magnetic zeolite/Fe3O4 particles. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, T.; Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Deng, Q.; Chen, G.; Ye, C. Synthesis of a novel magnetic nano-zeolite and its application as an efficient heavy metal adsorbent. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 085007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piri, F.; Mollahosseini, A.; Khadir, A.; Milani Hosseini, M. Enhanced adsorption of dyes on microwave-assisted synthesized magnetic zeolite-hydroxyapatite nanocomposite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharana, M.; Sen, S. Magnetic zeolite: A green reusable adsorbent in wastewater treatment. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitkamp, J. Zeolites and catalysis. Solid State Ion. 2000, 131, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalhor, M.; Zarnegar, Z. Fe3O4/SO3H@zeolite-Y as a novel multi-functional and magnetic nanocatalyst for clean and soft synthesis of imidazole and perimidine derivatives. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 19333–19346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murniati, R.; Rahmayanti, H.D.; Utami, F.D.; Cifriadi, A.; Iskandar, F.; Abdullah, M. Effects of magnetically modified natural zeolite addition on the crosslink density, mechanical, morphological, and damping properties of SIR 20 natural rubber reinforced with nanosilica compounds. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashi, Z.; Divband, B.; Keshtkar, A.; Khatamian, M.; Farahmand-Zahed, F.; Nazarlo, A.K.; Gharehaghaji, N. Synthesis of cytocompatible Fe3O4@ZSM-5 nanocomposite as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 438, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazovskaya, E.Y.; Golubeva, O.Y. Preparation of Magnetic Zeolites for Medicinal Purposes. Pet. Chem. 2023, 63, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divband, B.; Rashidi, M.R.; Khatamian, M.; Eslamian, G.R.K.; Gharehaghaji, N.; Tabriz, F.D. Linde Type A and nano magnetite/NaA zeolites: Cytotoxicity and doxorubicin loading efficiency. Open Chem. 2018, 16, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sossou, K.; Prasad, S.B.; Agbotsou, E.K.; Saidou Souley, H. Evaluation of the performance of magnetic zeolite nanocomposites in removing various water contaminants as heavy metals, organic pollutants, and emerging contaminants: A review. Next Nanotechnol. 2024, 6, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J. Preparation and Properties of Magnetic Zeolite. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2009, 9, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Gaffer, A.; Al Kahlawy, A.A.; Aman, D. Magnetic zeolite-natural polymer composite for adsorption of chromium (VI). Egypt. J. Pet. 2017, 26, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.H.; Pati, S.S.; Coaquira, J.A.H.; Matilla, J.; Guimarães, E.M.; Oliveira, A.C.; Kuzmann, E.; Garg, V.K. Magnetic interactions in cubic iron oxide magnetic nanoparticle bound to zeolite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 416, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.B.T.; Duong, N.B.; Le, N.L. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Fe3O4/Zeolite NaA Nanocomposite for the Adsorption Removal of Methylene Blue Potential in Wastewater Treatment. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 6678588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, T.; Patel, S.; Kulkarni, M.; Singh, Y.R.; Khodakiya, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Prajapati, B.G. Zeolite-based nanoparticles drug delivery systems in modern pharmaceutical research and environmental remediation. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loiola, A.R.; Bessa, R.A.; Oliveira, C.P.; Freitas, A.D.L.; Soares, S.A.; Bohn, F.; Pergher, S.B.C. Magnetic zeolite composites: Classification, synthesis routes, and technological applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 560, 169651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dernaika, F.; Halawy, L.; Zeaiter, J.; Kawrani, S.; Mroue, D.; Lteif, A.; Kourani, S.; Mehanna, M.; Abboud, C.; Mroueh, M.; et al. Development and characterization of a zeolite based drug delivery system: Application to cannabidiol oral delivery. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodha, V.; Shahabuddin, S.; Gaur, R.; Ahmad, I.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Sridewi, N. Comprehensive Review on Zeolite-Based Nanocomposites for Treatment of Effluents from Wastewater. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyankson, E.; Adjasoo, J.; Efavi, J.K.; Amedalor, R.; Yaya, A.; Manu, G.P.; Asare, K.; Amartey, N.A. Characterization and evaluation of zeolite A/Fe3O4 nanocomposite as a potential adsorbent for removal of organic molecules from wastewater. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 8090756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Baltazar, Á.D.J. Advancements in nanoparticle-modified zeolites for sustainable water treatment: An interdisciplinary review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.F.; Loiola, A.R.; Pergher, S.B.C.; Braga, T.P. Challenges, prospects and comprehensive evolution of zeolite-based materials for the catalytic conversion of glycerol: A review. Catal. Today 2025, 444, 114998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Magalhães, L.F.; da Silva, G.R.; Peres, A.E.C.; Kooh, M.R.R. Zeolite Application in Wastewater Treatment. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 4544104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbe, T.; Temesgen, S.; Bitew, M. A Short Review on Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications of Zeolites. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6637898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleque, A.; Alam, M.M.; Hoque, M.; Mondal, S.; Haider, J.B.; Xu, B.; Johir, M.A.H.; Karmakar, A.K.; Zhou, J.L.; Ahmed, M.B.; et al. Zeolite synthesis from low-cost materials and environmental applications: A review. Environ. Adv. 2020, 2, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanfekr Rad, L.; Anbia, M. Zeolite-based composites for the adsorption of toxic matters from water: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Gong, M.; Cai, S.; Zhang, T.; Douglas, J.T.; Chikan, V.; Davies, N.M.; Lee, P.; Choi, I.Y.; Ren, S.; et al. Combining hard and soft magnetism into a single core-shell nanoparticle to achieve both hyperthermia and image contrast. Ther. Deliv. 2015, 6, 1195–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, D.; Freitas, M.; Carvalho, F.; Fernandes, E. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: An Insight into their Biomedical Applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 1808–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, G.G.; Klein, J.J.; Schreiner, W.H.; Mosca, D.H.; de Oliveira, A.J.A.; Zarbin, A.J.G. Nickel nanoparticles obtained by a modified polyol process: Synthesis, characterization, and magnetic properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 311, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; He, Q.; Jiang, C. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis and surface functionalization strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Song, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Han, J. Review on the Use of Magnetic Nanoparticles in the Detection of Environmental Pollutants. Water 2023, 15, 3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, H.; Feng, L. A Review on Advanced FeNi-Based Catalysts for Water Splitting Reaction. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 13491–13522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, D.; Parker, G.; Mosendz, O.; Lyberatos, A.; Mitin, D.; Safonova, N.Y.; Albrecht, M. Review Article: FePt heat assisted magnetic recording media. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2016, 34, 060801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catherine, C.B.; Curtis, A.S.G. Functionalisation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R198. [Google Scholar]
- Kayal, S.; Ramanujan, R.V. Doxorubicin loaded PVA coated iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, L.; Gomaa, H.G.; Ragab, D.; Zhu, J. Magnetic nanoparticles for environmental and biomedical applications: A review. Particuology 2017, 30, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovec, D.; Čampelj, S.; Bele, M.; Maver, U.; Zorko, M.; Drofenik, M.; Jamnik, J.; Gaberšček, M. Nanocomposites containing embedded superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and rhodamine 6G. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 334, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Ji, H.; Yu, P.; Niu, J.; Farooq, M.U.; Akram, M.W.; Udego, I.O.; Li, H.; Niu, X. Surface Modification of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yallapu, M.M.; Foy, S.P.; Jain, T.K.; Labhasetwar, V. PEG-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging applications. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 2283–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Digigow, R.G.; Dechézelles, J.-F.; Dietsch, H.; Geissbühler, I.; Vanhecke, D.; Geers, C.; Hirt, A.M.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Petri-Fink, A. Preparation and characterization of functional silica hybrid magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 362, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleňáková, A.; Zeleňák, V.; Beňová, E.; Kočíková, B.; Király, N.; Hrubovčák, P.; Szűcsová, J.; Nagy, Ľ.; Klementová, M.; Mačák, J.; et al. The surface modification of the silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles and their application in molecular diagnostics of virus infection. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.J.; Kim, M.J.; Choa, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Nam, B.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, K.H. Synthesis and Characterizations of Surface-Coated Superparamagentic Magnetite Nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Su, J.; Chung, T.-S.; Amy, G. Hydrophilic Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Performance in Forward Osmosis Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umejuru, E.C.; Mashifana, T.; Kandjou, V.; Amani-Beni, M.; Sadeghifar, H.; Fayazi, M.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Sithole, N.T. Application of zeolite based nanocomposites for wastewater remediation: Evaluating newer and environmentally benign approaches. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Yang, J.; Dong, S.; Ma, L.; Dai, Q.; Guo, J. Zeolite preparation from industrial solid waste: Current status, applications, and prospects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Chowdhry, J.; Kumar, M.; Chandra Garg, M. Zeolites in wastewater treatment: A comprehensive review on scientometric analysis, adsorption mechanisms, and future prospects. Environ. Res. 2024, 260, 119782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.A.; Suleiman, M.A.; Al-Amrani, W.A.; Usman, A.K.; Onaizi, S.A. Adsorptive removal of organic pollutants from contaminated waters using zeolitic imidazolate framework Composites: A comprehensive and Up-to-date review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 318, 123765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristl, M.; Ostroško, U.; Ban, I.; Petrinić, I.; Stergar, J. Thermal study of APTES-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles with citric acid and polyacrylic acid for advanced forward osmosis systems. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2024, 149, 10449–10463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadughi, M.M.; Mazani, A.; Varnaseri, M.; Barfar, E.; Mengelizadeh, N.; Balarak, D. Synthesis of Magnetic Nanocomposites Based on Imidazole Zeolite-8 Framework Doped with Silver Nanoparticles for Effective Removal of Norfloxacin from Effluents. J. Clust. Sci. 2024, 35, 2991–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntubek, A.; Kinayat, N.; Meiramkulova, K.; Poulopoulos, S.G.; Bear, J.C.; Inglezakis, V.J. Catalytic Oxidation of Methylene Blue by Use of Natural Zeolite-Based Silver and Magnetite Nanocomposites. Processes 2020, 8, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, E.; Song, M.; Kim, J.-C.; Kwon, D.-i.; Rainer, D.N.; Gołąbek, K.; Nam, S.C.; Ryoo, R.; Mazur, M.; Jo, C. Confining Gold Nanoparticles in Preformed Zeolites by Post-Synthetic Modification Enhances Stability and Catalytic Reactivity and Selectivity. JACS Au 2022, 2, 2327–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, V.; Moodley, K.G.; Dass, A.; Gengan, R.M.; Ali, D.; Alarifi, S.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Gao, Y. Ionic liquid covered iron-oxide magnetic nanoparticles decorated zeolite nanocomposite for excellent catalytic reduction and degradation of environmental toxic organic pollutants and dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 342, 117492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghali, M.A.; Abo-Aly, M.M.; Salaheldin, T.A. Modified mesoporous zeolite-A/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for dual removal of methylene blue and Pb2+ ions from wastewater. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 126, 108487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, M.K.; Ifrahim, M.; Rashid, M.; Ul Haq, I.; Asghar, R.; Uthappa, U.T.; Selvaraj, M.; Kurkuri, M. Chemistry of zeolites and zeolite based composite membranes as a cutting-edge candidate for removal of organic dyes & heavy metal ions: Progress and future directions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsova, T.; Ivanets, A.; Prozorovich, V.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Tran, H.N.; Srivastava, V.; Sillanpää, M. Sorption and mechanism studies of Cu2+, Sr2+ and Pb2+ ions on mesoporous aluminosilicates/zeolite composite sorbents. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 984–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serati-Nouri, H.; Jafari, A.; Roshangar, L.; Dadashpour, M.; Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi, Y.; Zarghami, N. Biomedical applications of zeolite-based materials: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 116, 111225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhatib, E.A.; Moharem, M.L.; Saad, A.F.; Abdelhamed, S. A novel nanocomposite-based zeolite for efficient remediation of Cd-contaminated industrial wastewater. Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magyarová, Z.; Králik, M.; Soták, T. Utilization of zeolite catalysts in biomass exploitation: A minireview. Monatshefte Für Chem. Chem. Mon. 2023, 154, 815–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.; Jia, X.; Wu, Z.; Choi, J.; Yip, A.C.K. Incorporating Hierarchy into Conventional Zeolites for Catalytic Biomass Conversions: A Review. Catalysts 2019, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmodi, G.; Dangwal, S.; Zarrintaj, P.; Zhu, M.; Mao, Y.; McLlroy, D.N.; Reza Saeb, M.; Vatanpour, V.; Ramsey, J.D.; Kim, S.-J. NaA zeolite-coated meshes with tunable hydrophilicity for oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshvardoostchokami, M.; Majidi, M.; Zamani, A.; Liu, B. Adsorption of phenol on environmentally friendly Fe3O4/chitosan/zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanocomposite: Optimization by experimental design methodology. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 323, 115064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, Q.A.P.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167. [Google Scholar]
- Mornet, S.; Vasseur, S.; Grasset, F.; Veverka, P.; Goglio, G.; Demourgues, A.; Portier, J.; Pollert, E.; Duguet, E. Magnetic nanoparticle design for medical applications. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2006, 34, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zeng, H. Size-Controlled Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 8204–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.M.; Zheng, W.T.; Jiang, Q. Saturation magnetization of ferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic nanocrystals at room temperature. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaelides, P. Application of natural zeolites in environmental remediation: A short review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 144, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Kuang, Y.; Dai, Q.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, A.; Wang, X.; Song, K.; Lu, Z.; Yuan, C. Growth of carbon nanotubules on Fe-loading zeolites and investigation of catalytic active center. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 1999, 8–9, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakoczy, R.A.; Traa, Y. Nanocrystalline zeolite A: Synthesis, ion exchange and dealumination. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 60, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, A.S.T.; Chao, K.-J. Membranes and films of zeolite and zeolite-like materials. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2001, 62, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukatskaya, M.R.; Vyacheslavov, A.S.; Lukashin, A.V.; Tretyakov, Y.D.; Zhigalina, O.M.; Eliseev, A.A. Cobalt-containing nanocomposites based on zeolites of MFI framework type. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 3866–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Lin, C.; Zhou, C.; Beltramini, J.; Tong, D.; Yu, W. A magnetic zeolitic nanocomposite from occlusion of silica-coated iron species by crystalline titanosilicate-1. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 2752–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.; Zorpas, A. Heat of adsorption, adsorption energy and activation energy in adsorption and ion exchange systems. Desalination Water Treat. 2012, 39, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doocey, D.J.; Sharratt, P.N.; Cundy, C.S.; Plaisted, R.J. Zeolite-Mediated Advanced Oxidation of Model Chlorinated Phenolic Aqueous Waste: Part 2: Solid Phase Catalysis. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2004, 82, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.C.A.; Petkowicz, D.I.; Smaniotto, A.; Pergher, S.B.C. Magnetic zeolites: A new adsorbent for removal of metallic contaminants from water. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3699–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, M.S.; Pourahmad, A.; Sohrabnezhad, S.; Zare, K. Formation of NiS and CoS semiconductor nanoparticles inside mordenite-type zeolite. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 2923–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavati-Niasari, M. Template synthesis and characterization of hexaaza nickel(II) complex nanoparticles entrapped within the zeolite-Y. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2009, 362, 3738–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Din, T.S.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Aldhayan, D.M.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; Al-Deyab, S.S. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetite Zeolite Nano Composite. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 6177–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem Attia, T.M.; Hu, X.L.; Yin, D.Q. Synthesized magnetic nanoparticles coated zeolite for the adsorption of pharmaceutical compounds from aqueous solution using batch and column studies. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2076–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davar, F.; Fereshteh, Z.; Shoja Razavi, H.; Razavi, R.S.; Loghman-Estarki, M.R. Synthesis and characterization of cobalt oxide nanocomposite based on the Co3O4–zeolite Y. Superlattices Microstruct. 2014, 66, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padervand, M.; Janatrostami, S.; Karanji, A.K.; Gholami, M.R. Incredible antibacterial activity of noble metal functionalized magnetic core-zeolitic shell nanostructures. Mater Sci. Eng. C 2014, 35, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihian, H.; Moayed, M.; Firooz, A.; Iravani, M. Synthesis of a novel magnetic zeolite nanocomposite for removal of Cs+ and Sr2+ from aqueous solution: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 393, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Terdkiatburana, T.; Tadé, M.O. Adsorption of Cu(II), Pb(II) and humic acid on natural zeolite tuff in single and binary systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Deng, C.; Qi, D.; Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, D. Synthesis of Core/Shell Colloidal Magnetic Zeolite Microspheres for the Immobilization of Trypsin. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Peng, S.; Shu, L.; Chen, T.; Bao, T.; Frost, R.L. Magnetic zeolite NaA: Synthesis, characterization based on metakaolin and its application for the removal of Cu2+, Pb2+. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabiyouni, G.; Shabani, A.; Karimzadeh, S.; Ghasemi, J.; Ramazani, H. Synthesis, characterization and magnetic investigations of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and zeolite-Y nanocomposites prepared by precipitation method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 5677–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xiao, X.; Yan, B.; Yang, L. Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions by using natural Chinese (Chende) zeolite as adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Han, Z.; Zhang, W.; Song, L.; Li, H. Synthesis of zeolite-supported microscale zero-valent iron for the removal of Cr6+ and Cd2+ from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 169, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sağir, T.; Huysal, M.; Durmus, Z.; Kurt, B.Z.; Senel, M.; Isık, S. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of 5-flourouracil loaded magnetite–zeolite nanocomposite (5-FU-MZNC) for cancer drug delivery applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 77, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mthombeni, N.H.; Mbakop, S.; Ray, S.C.; Leswifi, T.; Ochieng, A.; Onyango, M.S. Highly efficient removal of chromium (VI) through adsorption and reduction: A column dynamic study using magnetized natural zeolite-polypyrrole composite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4008–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, S.-H.; Park, S.-M.; An, J.; Park, C.-G. Adsorption behavior of poly(methacrylic acid)/iron-oxide-coated zeolite for the removal of Mn(II), Fe(II), and As(III) from aqueous solution. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 123, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, E.; Kakavandi, B.; Azari, A.; Izanloo, H.; Gharibi, H.; Mahvi, A.H.; Javid, A.; Hashemi, S.Y. The performance of mesoporous magnetite zeolite nanocomposite in removing dimethyl phthalate from aquatic environments. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 27768–27782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, M.; Javanbakht, V.; Esmaili, J. Synthesis of zeolite/nickel ferrite/sodium alginate bionanocomposite via a co-precipitation technique for efficient removal of water-soluble methylene blue dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesdaghinia, A.; Azari, A.; Nodehi, R.N.; Yaghmaeian, K.; Bharti, A.K.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Sharafi, K. Removal of phthalate esters (PAEs) by zeolite/Fe3O4: Investigation on the magnetic adsorption separation, catalytic degradation and toxicity bioassay. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 233, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, Z.; Younesi, H.; Zinatizadeh, A.A. Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic application of TiO2/Fe-ZSM-5 nanocomposite for the treatment of petroleum refinery wastewater: Optimization of process parameters by response surface methodology. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 552–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatamian, M.; Divband, B.; Jodaei, A. Degradation of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) using ZnO nanoparticles supported on zeolites and modeling of experimental results by artificial neural networks. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 134, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Gao, Q.; Yan, X.; Yang, Y. Facile construction of Fe@ zeolite imidazolate Framework-67 to selectively remove uranyl ions from aqueous solution. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 91, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; McPherson, M.J.; Wheatley, P.S.; Morris, R.E. Ionic Liquid assisted Synthesis of Zeolite-TON. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2014, 640, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharehaghaji, N.; Divband, B.; Zareei, L. Nanoparticulate NaA zeolite composites for MRI: Effect of iron oxide content on image contrast. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 456, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Gao, J.; Qian, J.; Cai, D.; Zheng, K.; Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhong, K.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z. A Multifunctional Magnetic Composite Material as a Drug Delivery System and a Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agent. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 31, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servatan, M.; Zarrintaj, P.; Mahmodi, G.; Kim, S.-J.; Ganjali, M.R.; Saeb, M.R.; Mozafari, M. Zeolites in drug delivery: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraljević Pavelić, S.; Simović Medica, J.; Gumbarević, D.; Filošević, A.; Pržulj, N.; Pavelić, K. Critical Review on Zeolite Clinoptilolite Safety and Medical Applications in vivo. Front. Pharmacol 2018, 9, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suazo-Hernández, J.; Sepúlveda, P.; Manquián-Cerda, K.; Ramírez-Tagle, R.; Rubio, M.A.; Bolan, N.; Sarkar, B.; Arancibia-Miranda, N. Synthesis and characterization of zeolite-based composites functionalized with nanoscale zero-valent iron for removing arsenic in the presence of selenium from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Niu, L.; Yu, W.; Yang, C.; Fang, M.; Lv, H.; et al. Application of solid-phase extraction based on magnetic nanoparticle adsorbents for the analysis of selected persistent organic pollutants in environmental water: A review of recent advances. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 44–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdoust, S.; Arabkhani, P.; Ghaderi, S.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A. Rapid microwave-assisted synthesis of a magnetic biochar@ZIF-67: An efficient nanocomposite-based adsorbent for the dye-contaminated water cleanup. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 9257–9270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasanen, F.; Fuller, R.O.; Maya, F. Fast and simultaneous removal of microplastics and plastic-derived endocrine disruptors using a magnetic ZIF-8 nanocomposite. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmohammad, M.; Ghadi, A.; Beni, A.A. Response surface methodology for adsorption of propylparaben using zeolitic imidazolate-67 modified by Fe3O4 nanoparticles from aqueous solutions. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 304, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohl, S.; Kristl, M.; Stergar, J. Harnessing Magnetic Nanoparticles for the Effective Removal of Micro- and Nanoplastics: A Critical Review. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaça, N.; Gallo, J.; Fernandes, R.; Figueiredo, F.; Fonseca, A.M.; Baltazar, F.; Neves, I.C.; Bañobre-López, M. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro validation of a magnetic zeolite nanocomposite with T2-MRI properties towards theranostic applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 3351–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswini, R.; Hartati, S.; Jothimani, K.; Pothu, R.; Shanmugam, P.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Masimukku, S.; Boddula, R.; Selvaraj, M.; Al-Qahtani, N. Revolutionizing microorganism inactivation: Magnetic nanomaterials in sustainable photocatalytic disinfection. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meirelles, M.R.; Malafatti, J.O.D.; Escote, M.T.; Pinto, A.H.; Paris, E.C. Magnetic Adsorbent Based on Faujasite Zeolite Decorated with Magnesium Ferrite Nanoparticles for Metal Ion Removal. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidi, S.; Fatemeh, Z.S.; Mussa, F.S.; Mehdi, S.G.; and Akbarzadeh, A. Current methods for synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraji, M.; Yamini, Y.; Rezaee, M. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, functionalization, characterization, and applications. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2010, 7, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.; Hong, J.; Choi, S.; Lee, H.-W.; Ahn, J.-P.; Kim, C.S.; Lee, S.W. Easy synthesis and magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 2814–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, M.; Gutiérrez, G.; Noriega, S.; Moyano, A.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Matos, M. Microemulsion Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles for Bioapplications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.; Feldmann, C. Microemulsions: Options To Expand the Synthesis of Inorganic Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 15728–15752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, I.; Zamanian, A.; Behnamghader, A. A Simple Thermal Decomposition Method for Synthesis of Co0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles. J. Ultrafine Grained Nanostructured Mater. 2016, 49, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xie, J.; Bai, T.; Zou, J.; Gu, N. Ultrafast Preparation of Monodisperse Fe3O4 Nanoparticles by Microwave-Assisted Thermal Decomposition. Chemistry 2016, 22, 11807–11815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Gómez, N.; Nava, O.; Argueta-Figueroa, L.; García-Contreras, R.; Baeza-Barrera, A.; Vilchis-Nestor, A.R. Shape tuning of magnetite nanoparticles obtained by hydrothermal synthesis: Effect of temperature. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 7921273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theerdhala, S.; Alhat, D.; Vitta, S.; Bahadur, D. Synthesis of shape controlled ferrite nanoparticles by sonochemical technique. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 4268–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girardet, T.; Bianchi, E.; Henrionnet, C.; Pinzano, A.; Bouguet-Bonnet, S.; Boulogne, C.; Leclerc, S.; Cleymand, F.; Fleutot, S. SPIONs magnetic nanoparticles for MRI applications: Microwave synthesis and physicochemical, magnetic and biological characterizations. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikan, V.; McLaurin, E.J. Rapid Nanoparticle Synthesis by Magnetic and Microwave Heating. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasany, S.; Ahmed, I.; Rajan, J.; Rehman, A. Systematic review of the preparation techniques of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 2, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimdad, N.; Khalaj, A.; Azarian, G.; Nematollahi, D. Electrochemical device for the synthesis of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roostaee, M.; Sheikhshoaie, I. Magnetic nanoparticles; synthesis, properties and electrochemical application: A review. Curr. Biochem. Eng. 2020, 6, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Li, X.; Peng, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Monodisperse magnetic single-crystal ferrite microspheres. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2005, 44, 2782–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, N.O.; Tartaj, P.; Morales, M.P.; Bonville, P.; Serna, C.J. Yttria-coated FeCo magnetic nanoneedles. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 3119–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirani, B.; Goyal, P.S.; Sagare, S.S.; Deulkar, S.H.; Dsouza, A.; Rayaprol, S. Magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles having several different coatings. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2023, 46, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Businova, P.; Chomoucka, J.; Prasek, J.; Hrdy, R.; Drbohlavova, J.; Sedlacek, P.; Hubalek, J. Polymer coated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles: Preparation and characterization. Nanocon 2011, 9, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences, and Uses; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; Volume 664. [Google Scholar]
- Barratt, G. Colloidal drug carriers: Achievements and perspectives. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2003, 60, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, V.; Goldstein, A.; Alivisatos, A. Semiconductor nanocrystals covalently bound to metal surfaces with self-assembled monolayers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 5221–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.B.; Ellis, B.L.; Sharma, H.L.; Frost, W.; Caps, V.; Shields, R.A.; Tsang, S.C. Carbon-encapsulated radioactive 99mtc nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangirian, H.; Ismail, M.H.S.; Haron, M.J.; Rafiee-Moghaddam, R.; Shameli, K.; Hosseini, S.; Kalantari, K.; Khandanlou, R.; Gharibshahi, E.; Soltaninejad, S. Synthesis and characterization of zeolite/Fe3O4 nanocomposite by green quick precipitation method. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2013, 8, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar]
- Pescarmona, P.P.; Gagea, B.C.; Van der Aa, P.; Jacobs, P.A.; Martens, J.A. Ferromagnetically modified zeolite catalysts for liquid-phase High–Throughput Experimentation. Catal. Today 2011, 159, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajglová, Z.; Gauli, B.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Kumar, N.; Eränen, K.; Wärnå, J.; Lassfolk, R.; Simakova, I.L.; Prosvirin, I.P.; Peurla, M.; et al. Interactions between Iron and Nickel in Fe–Ni Nanoparticles on Y Zeolite for Co-Processing of Fossil Feedstock with Lignin-Derived Isoeugenol. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 10064–10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Faaizatunnisa, N.; Ariesta, M.N.; Rohmawati, L.; Nurazizah, R.A. Facile in situ synthesis and characterization of Fe@ Si/zeolite Na composites with magnetic core–shell structures from natural materials for enhanced curcumin loading capacity. Nanotechnol. Precis. Eng. 2024, 7, 023008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, W.; Han, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Gong, X.; Zhai, C.; Song, H. In-situ synthesis of NaP zeolite doped with transition metals using fly ash. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 102, 7665–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompsett, G.A.; Conner, W.C.; Yngvesson, K.S. Microwave synthesis of nanoporous materials. Chemphyschem A Eur. J. Chem. Phys. Phys. Chem. 2006, 7, 296–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, L.; Kheiri, F. Synthesis, Characteristics and Kinetic Study of Magnetic-Zeolite Nano Composite for Adsorption of Zirconium. Chem. Technol. Indian J. 2018, 13, 126. [Google Scholar]
- Murrieta-Rico, F.N.; Antúnez-García, J.; Yocupicio-Gaxiola, R.I.; Zamora, J.; Reyes-Serrato, A.; Pestryakov, A.; Petranovskii, V. Study of Electric and Magnetic Properties of Iron-Modified MFI Zeolite Prepared by a Mechanochemical Method. Materials 2022, 15, 7968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboelfetoh, E.F.; El-Attar, H.G.; Okba, E.A. Facile synthesis of magnetic and porous zeolite/SnFe2O4 nanocomposite for cationic and anionic dyes deterioration. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2023, 357, 112611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phakatkar, A.H.; Saray, M.T.; Rasul, M.G.; Sorokina, L.V.; Ritter, T.G.; Shokuhfar, T.; Shahbazian-Yassar, R. Ultrafast Synthesis of High Entropy Oxide Nanoparticles by Flame Spray Pyrolysis. Langmuir 2021, 37, 9059–9068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Liu, B.; Xu, Z. Fabrication of magnetic zeolite coated with carbon fiber using pyrolysis products from waste printed circuit boards. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquist, K.; Larsen, S.C. Chromate adsorption on bifunctional, magnetic zeolite composites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 130, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rando, G.; Sfameni, S.; Galletta, M.; Drommi, D.; Cappello, S.; Plutino, M.R. Functional Nanohybrids and Nanocomposites Development for the Removal of Environmental Pollutants and Bioremediation. Molecules 2022, 27, 4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes Villegas, V.A.; De León Ramirez, J.I.; Pérez-Cabrera, L.; Pérez-Sicairos, S.; Yocupicio-Gaxiola, R.I.; Chávez-Méndez, J.R.; Huerta-Arcos, L.; Petranovskii, V. Sonochemical post-synthesis modification of Y zeolite with iron species. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2025, 331, 130199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpelane, S.; Mpupa, A.; Mlambo, M.; Bingwa, N.; Mketo, N.; Nomngongo, P.N. Magnetic zeolite@β-cyclodextrin-gum Arabic nanocomposite for adsorptive removal of levofloxacin. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 11, 100354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Zuo, X.; Wang, C. Mechanism, application, influencing factors and environmental benefit assessment of steel slag in removing pollutants from water: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaqarbeh, M. Adsorption Phenomena: Definition, Mechanisms, and Adsorption Types: Short Review. Rhazes Green Appl. Chem. 2021, 13, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bruch, L.W.; Cole, M.W.; Zaremba, E. Physical Adsorption: Forces and Phenomena; Courier Dover Publications: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Phouthavong, V.; Hagio, T.; Park, J.-H.; Nijpanich, S.; Duangkhai, K.; Rujiravanit, R.; Thaveemas, P.; Chounlamany, V.; Kong, L.; Li, L.; et al. Removal of heavy metals by BEA zeolite/Fe3O4 composite prepared via dry-gel conversion method using agrowaste-derived raw material. Solid State Sci. 2024, 149, 107473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-X.; Wang, J.-L.; Chai, T.-Q.; Li, J.-X.; Li, P.; Yang, F.-Q. A hierarchical porous Fe3O4-COOH@H-ZIF-67 composite as magnetic solid-phase extraction adsorbent for benzimidazole pesticides. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 111870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Xu, W.; Yu, J.; Zang, Y.; Hu, G.; Hu, T.; Jiang, J.; Mao, P.; et al. A novel and cost-effective synthesis of magnetic zeolite 4A using kaolinite and red mud for Sr(II) removal. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2024, 370, 113069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatamian, M.; Afshar No, N.; Hosseini Nami, S.; Fazli-Shokouhi, S. Synthesis and characterization of zeolite A, Fe3O4/zeolite A, and Fe2O3/zeolite A nanocomposites and investigation of their arsenic removal performance. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2023, 20, 1657–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Marquina, C.; Han, W.; Kwan, J.K.C.; Ricardo Ibarra, M.; Yeung, K.L. Insight into the molecular mechanism of organic pollutants’ adsorption on magnetic ZIF-8 synthesized via a transformational route. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 356, 130006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Přech, J.; Ioannou, E.; Roussis, V.; Kuncser, V.; Podolean, I.; Coman, S.M.; Valtchev, V.; Parvulescu, V.I. Magnetic Fe@Y Composites as Efficient Recoverable Catalysts for the Valorization of the Recalcitrant Marine Sulfated Polysaccharide Ulvan. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubeva, O.Y.; Brazovskaya, E.Y.; Alikina, Y.A.; D’yachenko, S.V.; Zhernovoi, A.I. Synthesis and Study of Nanocomposites Based on Beta Zeolite and Magnetite for Targeted Drug Delivery. Glass Phys. Chem. 2019, 45, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yu, X.; Sun, J.; Han, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, G.; Ma, Q.; Li, Q.; Xiang, H. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework (ZIF-8) Decorated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Loaded Doxorubicin Hydrochloride for Osteosarcoma Treatment–in vitro and in vivo Preclinical Studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 7985–7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruebo, M.; Fernández-Pacheco, R.; Irusta, S.; Arbiol, J.; Ibarra, M.R.; Santamaría, J. Sustained release of doxorubicin from zeolite–magnetite nanocomposites prepared by mechanical activation. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimina, T.M.; Sitkov, N.O.; Gareev, K.G.; Fedorov, V.; Grouzdev, D.; Koziaeva, V.; Gao, H.; Combs, S.E.; Shevtsov, M. Biosensors and Drug Delivery in Oncotheranostics Using Inorganic Synthetic and Biogenic Magnetic Nanoparticles. Biosensors 2022, 12, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricco, R.; Malfatti, L.; Takahashi, M.; Hill, A.J.; Falcaro, P. Applications of magnetic metal–organic framework composites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 13033–13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Type of Functionalization | Main Effect | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Ion Exchange | Selective adsorption of metals | Removal of heavy metals from wastewater [4] |
| Acid Treatment | Increased specific surface area | Catalysis, dye adsorption [38,39] |
| Alkaline Treatment | Formation of mesopores | Removal of large organic molecules [40,41] |
| Silanization | Hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity | Separation of oil pollutants [42] |
| Metal Oxides | Magnetic/photocatalytic properties | Water purification, catalysis [43] |
| Polymer Coating | Stabilization, dispersion | Biomedical applications [44] |
| Synthesis Method | Description | Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-precipitation | MNPs are prepared from aqueous salt solutions, by the addition of a base at room temperature or at high temperatures. By selecting the type of salt, the Fe3+/M2+ stoichiometric ratio, temperature, and pH value, we can significantly influence the size, shape, and composition of the particles. |
|
| [39,124,125] |
| Microemulsion | Within the water droplets of one reverse microemulsion, there is a solution of metal ions, while in the water droplets of another reverse microemulsion, there is a solution of the precipitating reagent. Upon collision, the micelles merge, bringing the reactants into contact and allowing them to react and form a product. This is followed by nucleation and the growth of the newly formed particles. |
|
| [124,126,127,128] |
| Thermal decomposition | High-temperature decomposition of organometallic precursors in high-boiling organic solvents containing stabilizing surfactants. |
|
| [39,124,129,130] |
| Hydrothermal | Includes various wet-chemical techniques for crystallizing materials in a sealed container from an aqueous solution at high temperatures (130 °C to 250 °C) and elevated vapor pressures (0.3 to 4 MPa). |
|
| [39,124,131] |
| Sonochemical | Ultrasound induces cavitation to create extreme reaction conditions, including high temperatures, pressures, and cooling rates. |
|
| [124,132] |
| Microwave-assisted | The reagents absorb microwave energy, leading to uniform heating and a rapid chemical reaction. |
|
| [133,134] |
| Sol–gel | This method involves hydroxylation and condensation of molecular precursors, forming a “sol” of NPs. Further polymerization creates a 3D metal oxide network (wet gel), requiring heat treatment for crystallization. |
|
| [124,135] |
| Electro-chemical | By using electric current, metal ions in solution are reduced, leading to the formation of NPs on the electrode. |
|
| [136,137] |
| Pollutant | Matrix | MNPs | Zeolite | Removal Efficiency | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co2+, Mn2+ | Aqueous solutions | MgFe2O4 | Faujasite (FAU) | 94% | [123] |
| Heavy metals (Pb2+, Cu2+, Zn2+) | Aqueous solutions | Fe3O4 | BEA | 70–90% | [164] |
| Benzimidazole pesticides (BZD) | Simulated pesticides wastewater | Fe3O4-COOH | H-ZIF-67 | 82.76–96.18% | [165] |
| 5-Fluorouracil antitumor drug | Human blood cells | Fe3O4 | BetaBeta | 45% | [21] |
| Sr2+ | Radioactive wastewater | Fe3O4 | 4A | 96.4% | [166] |
| As | Contaminated water | Fe2O3/Fe3O4 | A | 95.39%/98.52% | [167] |
| Methylene blue (MB) and Diclofenac sodium (DCF) | MB and DCF water solution | Fe3O4 | Zeolite Imidazolate Framework-8 (ZIF-8) | 98% | [168] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vohl, S.; Ban, I.; Stergar, J.; Slemnik, M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Application of Magnetic Zeolite Nanocomposites: A Review of Current Research and Future Applications. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120921
Vohl S, Ban I, Stergar J, Slemnik M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Application of Magnetic Zeolite Nanocomposites: A Review of Current Research and Future Applications. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(12):921. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120921
Chicago/Turabian StyleVohl, Sabina, Irena Ban, Janja Stergar, and Mojca Slemnik. 2025. "Synthesis, Characterization, and Application of Magnetic Zeolite Nanocomposites: A Review of Current Research and Future Applications" Nanomaterials 15, no. 12: 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120921
APA StyleVohl, S., Ban, I., Stergar, J., & Slemnik, M. (2025). Synthesis, Characterization, and Application of Magnetic Zeolite Nanocomposites: A Review of Current Research and Future Applications. Nanomaterials, 15(12), 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120921






