Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles as Multifunctional Agents Against Gut Microbiota Imbalance and Inflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
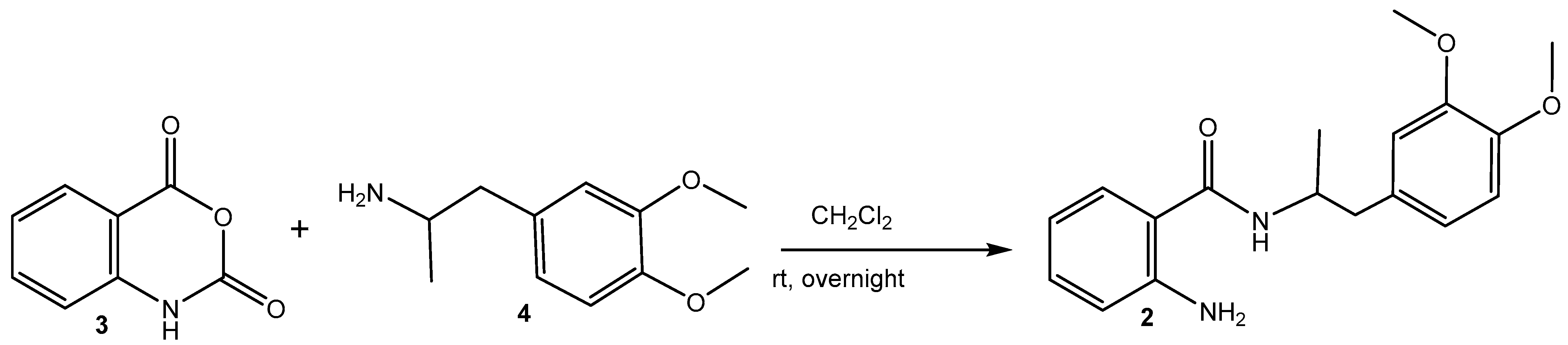
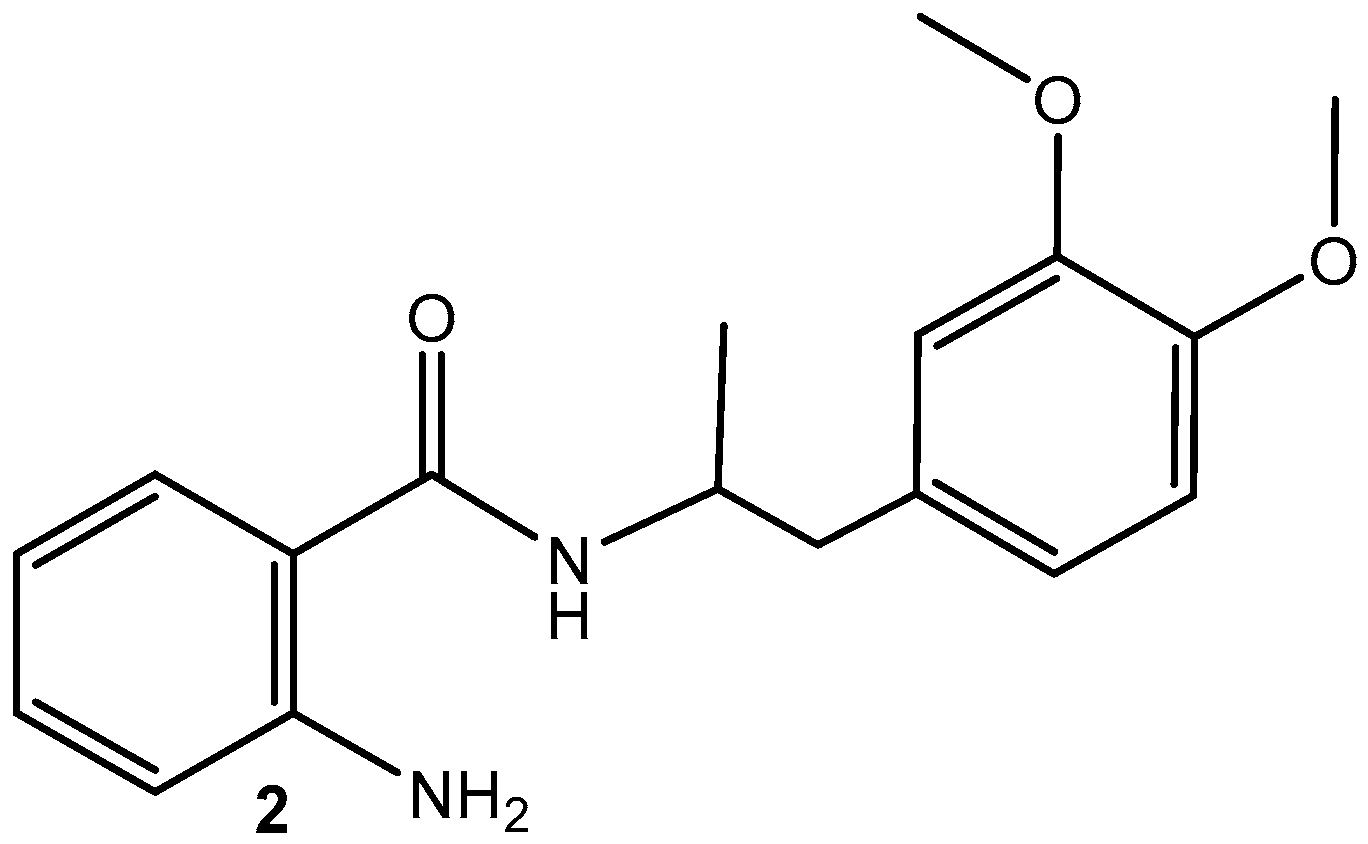
2.1. Synthesis of MA (2) (Scheme 1) [39]
Synthesis of MA-Loaded AgNPs (1)
2.2. Antimicrobial Activity Assay
2.3. Inhibition of Albumin Denaturation
2.4. Ex Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Activity
2.4.1. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.4.2. Histological and Morphometric Analysis
2.5. Ex Vivo Spasmolytic Activity
2.6. DFT Calculations
2.7. Cell Culturing Conditions and IC50 Determination for AgNPs, MA, and AgNPs Loaded with MA
2.8. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) Analysis of HepG2 Cells
2.9. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Antimicrobial Activity
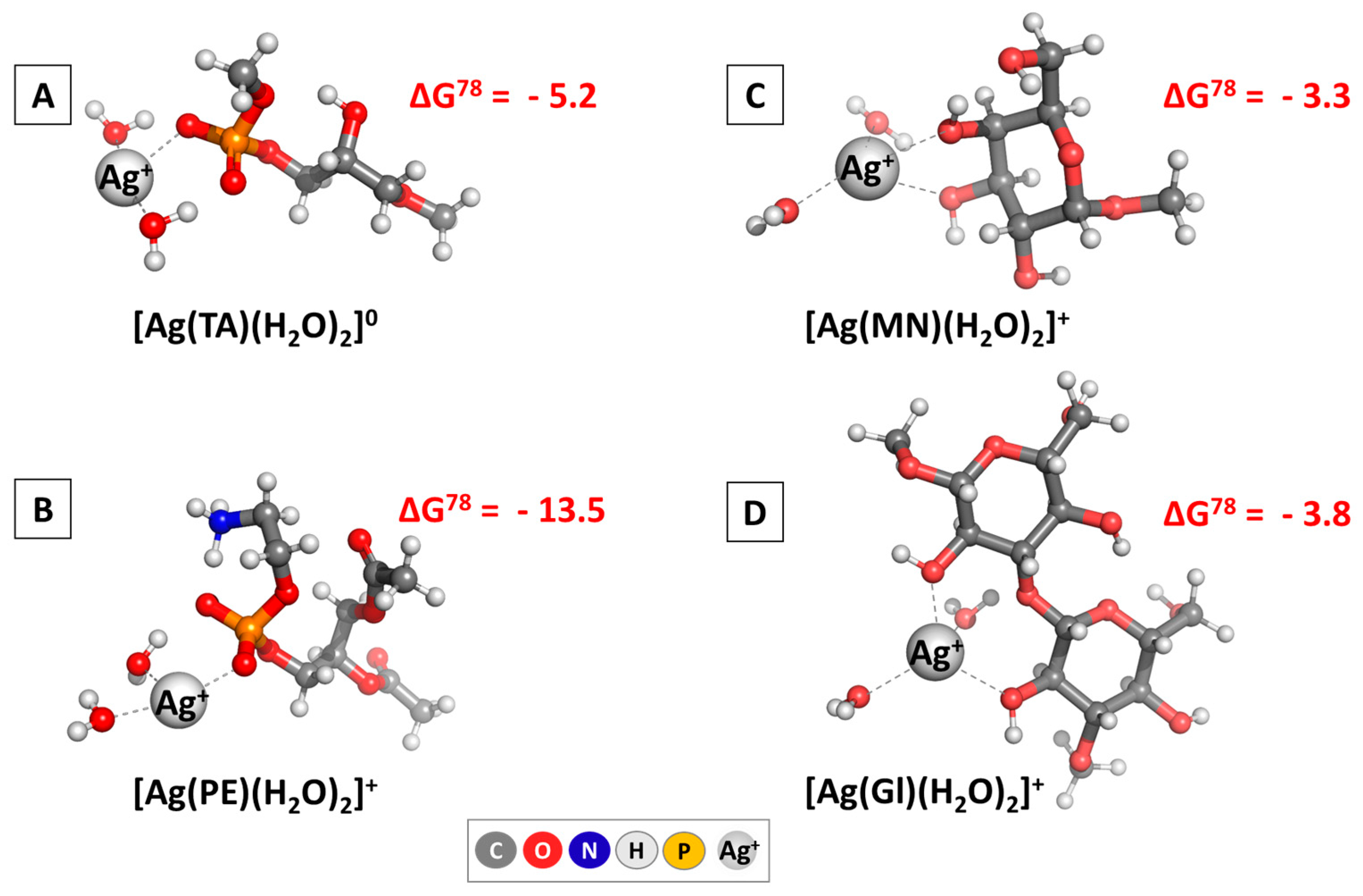
3.1.1. DFT Analysis
3.1.2. Experimental Results
3.2. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3.3. Cell Culturing Conditions and IC₅0 Determination for AgNPs, MA, and AgNPs Loaded with MA
3.4. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) Analysis of HepG2 Cell Morphology
3.5. Immunohistochemistry, Ex Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Effect
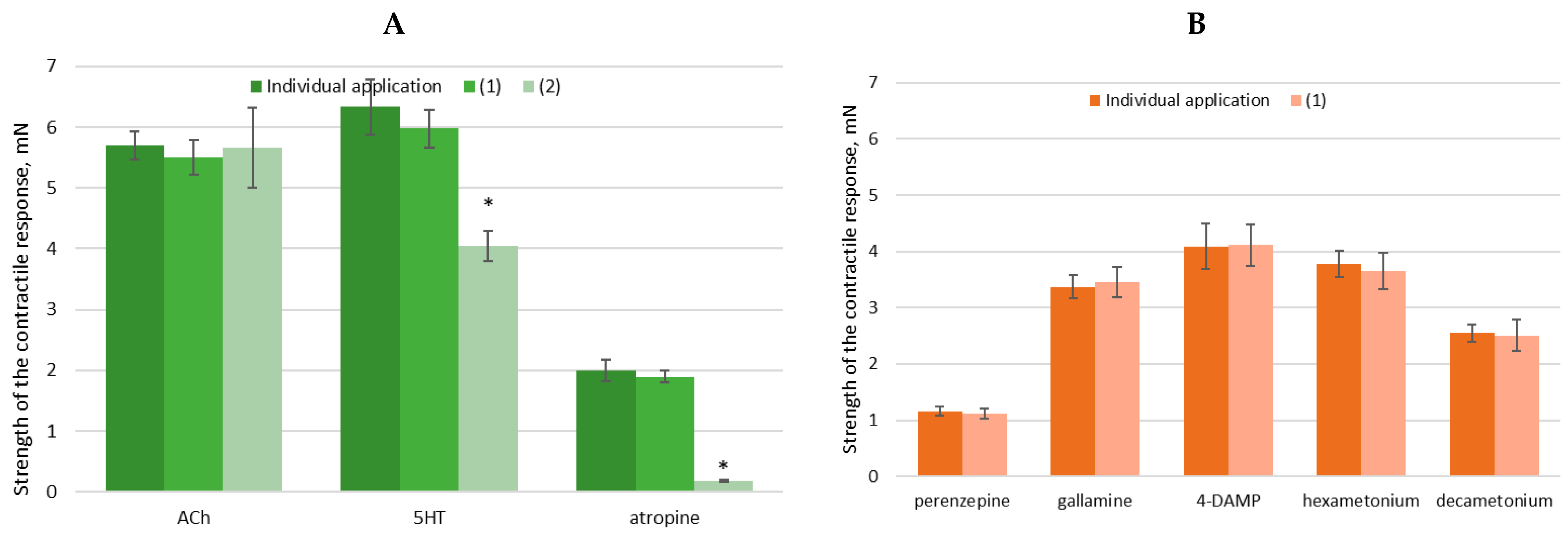
3.6. Evaluation of Ex Vivo Spasmolytic Effect
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bengmark, S. Ecological Control of the Gastrointestinal Tract. The role of probiotic flora. Gut 1998, 42, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.V.; Leonardi, I.; Iliev, I.D. Gut Mycobiota in Immunity and Inflammatory Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 1365–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooks, M.G.; Garrett, W.S. Gut Microbiota, Metabolites and Host Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajinka, O.; Darboe, A.; Tan, Y.; Abdelhalim, K.A.; Cham, L.B. Gut Microbiota and the Human Gut Physiological Changes. Ann. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Tsolis, R.M.; Bäumler, A.J. The Microbiome and Gut Homeostasis. Science 2022, 377, eabp9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siezen, R.J.; Kleerebezem, M. The Human Gut Microbiome: Are We Our Enterotypes? Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markey, L.; Shaban, L.; Green, E.R.; Lemon, K.P.; Mecsas, J.; Kumamoto, C.A. Pre-Colonization with the Commensal Fungus Candida albicans Reduces Murine Susceptibility to Clostridium difficile Infection. Gut Microbes 2018, 9, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Aschenbrenner, D.; Yoo, J.Y.; Zuo, T. The Gut Mycobiome in Health, Disease, and Clinical Applications in Association with the Gut Bacterial Microbiome Assembly. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, e969–e983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey-Klett, P.; Burlinson, P.; Deveau, A.; Barret, M.; Tarkka, M.; Sarniguet, A. Bacterial-Fungal Interactions: Hyphens between Agricultural, Clinical, Environmental, and Food Microbiologists. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 583–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.; Coyte, K.Z.; Bainter, W.; Geha, R.S.; Martin, C.R.; Rakoff-Nahoum, S. Multi-Kingdom Ecological Drivers of Microbiota Assembly in Preterm Infants. Nature 2021, 591, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Wong, S.H.; Cheung, C.P.; Lam, K.; Lui, R.; Cheung, K.; Zhang, F.; Tang, W.; Ching, J.Y.L.; Wu, J.C.Y.; et al. Gut Fungal Dysbiosis Correlates with Reduced Efficacy of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Clostridium difficile Infection. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.T. Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2652–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, C.; Duranti, S.; Bottacini, F.; Casey, E.; Turroni, F.; Mahony, J.; Belzer, C.; Delgado Palacio, S.; Arboleya Montes, S.; Mancabelli, L.; et al. The First Microbial Colonizers of the Human Gut: Composition, Activities, and Health Implications of the Infant Gut Microbiota. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00036-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Brown, M.A.; Qiao, S. Dietary Protein and Gut Microbiota Composition and Function. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 20, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; He, J.; Huang, Z.; Mao, X.; Zheng, P.; Yu, J.; Luo, J.; Tian, G.; et al. The Fungal Community and Its Interaction with the Concentration of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in the Faeces of Chenghua, Yorkshire and Tibetan Pigs. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.; Zuo, T.; Ho, M.; Chan, F.K.L.; Chan, P.K.S.; Ng, S.C. Review Article: Fungal Alterations in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongomin, F.; Gago, S.; Oladele, R.; Denning, D. Global and Multi-National Prevalence of Fungal Diseases—Estimate Precision. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, N.; Caplan, T.; Cowen, L.E. Molecular Evolution of Antifungal Drug Resistance. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 753–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambugala, K.M.; Daranagama, D.A.; Tennakoon, D.S.; Jayatunga, D.P.W.; Hongsanan, S.; Xie, N. Humans vs. Fungi: An Overview of Fungal Pathogens against Humans. Pathogens 2024, 13, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Karhana, S.; Shamsuzzaman, M.; Khan, M.A. Recent Drug Development and Treatments for Fungal Infections. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 1695–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Sulaiman, T.; Al-Ahmed, S.H.; Buhaliqah, Z.A.; Buhaliqah, A.A.; AlYuosof, B.; Alfaresi, M.; Al Fares, M.A.; Alwarthan, S.; Alkathlan, M.S.; et al. Potential Strategies to Control the Risk of Antifungal Resistance in Humans: A Comprehensive Review. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roemer, T.; Krysan, D.J. Antifungal Drug Development: Challenges, Unmet Clinical Needs, and New Approaches. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a019703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Robbins, N.; Cowen, L.E. Molecular Mechanisms Governing Antifungal Drug Resistance. NPJ Antimicrob. Resist. 2023, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavin, Y.N.; Bach, H. Mechanisms of Antifungal Properties of Metal Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Li, X.; Maier, M.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Heath, D.E.; O’Connor, A.J. Using Inorganic Nanoparticles to Fight Fungal Infections in the Antimicrobial Resistant Era. Acta Biomater. 2023, 158, 56–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, S.; Salman, A.; Khan, Z.; Khan, S.; Krishnaraj, C.; Yun, S.I. Metallic Nanoparticles: A Promising Arsenal against Antimicrobial Resistance-Unraveling Mechanisms and Enhancing Medication Efficacy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madkhali, O.A. A Comprehensive Review on Potential Applications of Metallic Nanoparticles as Antifungal Therapies to Combat Human Fungal Diseases. Saudi Pharm. J. 2023, 31, 101733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraji, M.; Thanikachalam, P.V.; Elumalai, K. The Potential of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles in Nanomedicine: A Comprehensive Review. Biotechnol. Notes 2024, 5, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, Z.A.; Raza, M.A.; Alqurashi, A.; Sajid, S.; Ashraf, S.; Imtiaz, K.; Aman, F.; Alessa, A.H.; Shamsi, M.B.; Latif, M. Advances in the Optimization of Fe Nanoparticles: Unlocking Antifungal Properties for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, M.; Lee, D.G. Reactive Oxygen Species-Independent Apoptotic Pathway by Gold Nanoparticles in Candida albicans. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 207, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, J.; Tortella, G.; Seabra, A.B.; Fincheira, P.; Rubilar, O. Potential Antifungal Effect of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Combined with Fungicides against Botrytis cinerea and Fusarium oxysporum. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosquera-Sánchez, L.P.; Arciniegas-Grijalba, P.A.; Patiño-Portela, M.C.; Guerra–Sierra, B.E.; Muñoz-Florez, J.E.; Rodríguez-Páez, J.E. Antifungal Effect of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) on Colletotrichum sp., Causal Agent of Anthracnose in Coffee Crops. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 25, 101579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba, B.; Rai, G.B.; Bhandary, R.; Parajuli, P.; Thapa, N.; Kandel, D.R.; Mulmi, S.; Shrestha, S.; Malla, S. Antifungal Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) on Fusarium Equiseti Phytopathogen Isolated from Tomato Plant in Nepal. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achilonu, C.C.; Kumar, P.; Swart, H.C.; Roos, W.D.; Marais, G.J. Zinc Oxide:Gold Nanoparticles (ZnO:Au NPs) Exhibited Antifungal Efficacy Against Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus candidus. BioNanoScience 2024, 14, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, Z.-e.-H.; Mirza, F.S.; Anjum, T.; Rizwana, H.; Akram, W.; Aftab, M.; Ali, M.D.; Li, G. Antifungal Potential of Biogenic Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Controlling Cercospora Leaf Spot in Mung Bean. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Stevens, S.E. Multiple Parameters for the Comprehensive Evaluation of the Susceptibility of Escherichia coli to the Silver Ion. Biometals 1998, 11, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sütterlin, S.; Tano, E.; Bergsten, A.; Tallberg, A.; Melhus, H. Effects of Silver-Based Wound Dressings on the Bacterial Flora in Chronic Leg Ulcers and Its Susceptibility in Vitro to Silver. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2012, 92, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, M.; Milusheva, M.; Georgieva, M.; Ivanov, P.; Miloshev, G.; Krasteva, N.; Hristova-Panusheva, K.; Feizi-Dehnayebi, M.; Ghodsi, M.Z.; Stojnova, K.; et al. Synthesis, Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Evaluation of Drug-Loaded Silver Nanoparticles with Mebeverine and Its Analog. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, M.; Milusheva, M.; Gledacheva, V.; Stefanova, I.; Todorova, M.; Kircheva, N.; Angelova, S.; Pencheva, M.; Stojnova, K.; Tsoneva, S.; et al. Spasmolytic Activity and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Novel Mebeverine Derivatives. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurul, F.; Turkmen, H.; Cetin, A.E.; Topkaya, S.N. Nanomedicine: How Nanomaterials Are Transforming Drug Delivery, Bio-Imaging, and Diagnosis. Next Nanotechnol. 2025, 7, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, A.; Tandi, A.; Moharana, S.; Chakroborty, S.; Mohapatra, S.S.; Mondal, A.; Dey, S.; Chandra, P. Silver Nanoparticle for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Hybrid. Adv. 2024, 6, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaka, A.; Mali, S.C.; Sharma, S.; Trivedi, R. A Review on Biological Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Potential Applications. Results Chem. 2023, 6, 101108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, Z.; Nemmar, A. Health Impact of Silver Nanoparticles: A Review of the Biodistribution and Toxicity Following Various Routes of Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, M.; Shahzaib, A.; Nishat, N.; Jahan, A.; Bhat, T.A.; Inam, A. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review of Methods, Influencing Factors, and Applications. JCIS Open 2024, 16, 100125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sati, A.; Ranade, T.N.; Mali, S.N.; Yasin, H.K.A.; Pratap, A. Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs): Comprehensive Insights into Bio/Synthesis, Key Influencing Factors, Multifaceted Applications, and Toxicity—A 2024 Update. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 7549–7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milusheva, M.; Gledacheva, V.; Stefanova, I.; Pencheva, M.; Mihaylova, R.; Tumbarski, Y.; Nedialkov, P.; Cherneva, E.; Todorova, M.; Nikolova, S. In Silico, in Vitro, and Ex Vivo Biological Activity of Some Novel Mebeverine Precursors. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milusheva, M.; Gledacheva, V.; Batmazyan, M.; Nikolova, S.; Stefanova, I.; Dimitrova, D.; Saracheva, K.; Tomov, D.; Chaova-Gizdakova, V. Ex Vivo and in Vivo Study of Some Isoquinoline Precursors. Sci. Pharm. 2022, 90, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumbarski, Y.; Lincheva, V.; Petkova, N.; Nikolova, R.; Vrancheva, R.; Ivanov, I. Antimicrobial Activity of Extract from Aerial Parts of Potentilla (Potentilla reptans L.). Acad. J. Ind. Technol. 2017, 4, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milusheva, M.; Todorova, M.; Gledacheva, V.; Stefanova, I.; Feizi-Dehnayebi, M.; Pencheva, M.; Nedialkov, P.; Tumbarski, Y.; Yanakieva, V.; Tsoneva, S.; et al. Novel Anthranilic Acid Hybrids—An Alternative Weapon against Inflammatory Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milusheva, M.; Gledacheva, V.; Stefanova, I.; Feizi-Dehnayebi, M.; Mihaylova, R.; Nedialkov, P.; Cherneva, E.; Tumbarski, Y.; Tsoneva, S.; Todorova, M.; et al. Synthesis, Molecular Docking, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Anthranilic Acid Hybrid and Its Diamides as Antispasmodics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhardt, S.; Brunetto, P.S.; Gagnon, J.; Priebe, M.; Giese, B.; Fromm, K.M. Nanobio Silver: Its Interactions with Peptides and Bacteria, and Its Uses in Medicine. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4708–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.; Trucks, G.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G. Gaussian 09, Revision d. 01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009; p. 201. [Google Scholar]
- Lenardon, M.D.; Sood, P.; Dorfmueller, H.C.; Brown, A.J.P.; Gow, N.A.R. Scalar Nanostructure of the Candida albicans Cell Wall; a Molecular, Cellular and Ultrastructural Analysis and Interpretation. Cell Surf. 2020, 6, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimi, A.; Miyazawa, K.; Abe, K. Cell Wall Structure and Biogenesis in Aspergillus Species. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 1700–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircheva, N.; Dobrev, S.; Nikolova, V.; Angelova, S.; Dudev, T. Theoretical Insight into the Phosphate-Targeted Silver’s Antibacterial Action: Differentiation between Gram (+) and Gram (−) Bacteria. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 10089–10100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, H.; Macquarrie, D.A.; Simon, J.D. Physical Chemistry: A Molecular Approach Problems and Solutions to Accompany McQuarrie and Simon: Physical Chemistry; University Science Books: Sausalito, CA, USA, 1997; ISBN 9780935702439. [Google Scholar]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal Solvation Model Based on Solute Electron Density and on a Continuum Model of the Solvent Defined by the Bulk Dielectric Constant and Atomic Surface Tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.P.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. SM6: A Density Functional Theory Continuum Solvation Model for Calculating Aqueous Solvation Free Energies of Neutrals, Ions, and Solute−Water Clusters. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2005, 1, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, M.T.T.; Wibowo, D.; Rehm, B.H.A. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00181-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Yngard, R.A.; Lin, Y. Silver Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis and Their Antimicrobial Activities. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, A.; Abu-Elghait, M.; Atta, H.M.; Salem, S.S. Antibacterial Activity of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Lawsonia Inermis against Common Pathogens from Urinary Tract Infection. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 196, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.; Kandasamy, R. Nonantibiotics Enhance the Antibacterial Activity of Ceftriaxone against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2018, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, D.; Kandasamy, R. Antibacterial Potentiality of Antiulcer and Antispasmodic Drugs with Selected Antibiotics against Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: In Vitro and in Silico Studies. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2015, 10, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandini, P.; Deepnandan, D. Synthetic Process Study and Pharmacological Evaluation of Antispasmodic Drug as Potential Antimicrobial Agent. Asian J. Res. Chem. 2009, 2, 494. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.; Dayo, M.; Alahmadi, S.; Ali, S. Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Green-Synthesized Using Extracts of Different Plants. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habschied, K.; Krstanović, V.; Zdunić, Z.; Babić, J.; Mastanjević, K.; Šarić, G.K. Mycotoxins Biocontrol Methods for Healthier Crops and Stored Products. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Li, X.; Saleemi, M.K.; He, C. Mycotoxin Contamination and Control Strategy in Human, Domestic Animal and Poultry: A Review. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 142, 104095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Camejo, L.A.; Zuluaga-Montero, A.; Morris, V.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Lázaro-Escudero, M.T.; Bayman, P. Fungal Diversity in Sahara Dust: Aspergillus sydowii and Other Opportunistic Pathogens. Aerobiologia 2022, 38, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedmousavi, S. Aspergillosis in Humans and Animals. In Recent Trends in Human and Animal Mycology; Singh, K., Srivastava, N., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 81–98. ISBN 9789811394348. [Google Scholar]
- Salazar, F.; Bignell, E.; Brown, G.D.; Cook, P.C.; Warris, A. Pathogenesis of Respiratory Viral and Fungal Coinfections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 35, e00094-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kausar, M.A.; Singh, A.B.; Singh, R. Biological Contaminants in the Indoor Air Environment and Their Impacts on Human Health. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 1723–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacrory, S.; Hashem, A.H.; Hasanin, M. Synthesis of Cellulose Based Amino Acid Functionalized Nano-Biocomplex: Characterization, Antifungal Activity, Molecular Docking and Hemocompatibility. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.S.; Wilmott, R.W. The Pulmonary Mycoses; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 507–527.e503. [Google Scholar]
- Sugui, J.A.; Kwon-Chung, K.J.; Juvvadi, P.R.; Latgé, J.-P.; Steinbach, W.J. Aspergillus Fumigatus and Related Species. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a019786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Alam, A. Mycotoxins, Mycotoxicosis and Managing Mycotoxin Contamination: A Review. In Bio-management of Postharvest Diseases and Mycotoxigenic Fungi; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, J.A.; Hu, C.; Aitken, S.L.; Beyda, N. Antifungal Resistance: A Concerning Trend for the Present and Future. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2019, 21, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visagie, C.M.; Houbraken, J.; Frisvad, J.C.; Hong, S.-B.; Klaassen, C.H.W.; Perrone, G.; Seifert, K.A.; Varga, J.; Yaguchi, T.; Samson, R.A. Identification and Nomenclature of the Genus Penicillium. Stud. Mycol. 2014, 78, 343–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Chávez, F.; Zwahlen, R.D.; Bovenberg, R.A.L.; Driessen, A.J.M. Engineering of the Filamentous Fungus Penicillium chrysogenum as Cell Factory for Natural Products. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antonio, D.; Violante, B.; Farina, C.; Sacco, R.; Angelucci, D.; Masciulli, M.; Iacone, A.; Romano, F. Necrotizing Pneumonia Caused by Penicillium chrysogenum. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 3335–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, G.; Castillo, S.B.J.; Soto, A.; De Ajanel, M.E.C.; Aguilar, J.; Castellanos, J.L.A.; Cifuentes, J.; Conde-Pereira, C. Acute Respiratory Failure with Fatal Outcome due to Penicillium chrysogenum in a Man from Guatemala with a Seminoma (Germ Cell Tumor). Chest 2021, 160, A307–A308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, E.A.; Cunha, M.; Cunha, F.A. Identificação Preliminar de Algumas Espécies Do Gênero Candida Spp. Em Meio Cromógeno: Resultados de Dois Anos de Um Estudo Multicêntrico Realizado No Ceará. Rev. Patol. Trop. 2012, 40, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallmann, E.J.J.; Cunha, F.A.; Castro, B.N.M.F.; Maciel, A.M.; Menezes, E.A.; Fechine, P.B.A. Antifungal Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Obtained by Green Synthesis. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2015, 57, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.H.; Saied, E.; Amin, B.H.; Alotibi, F.O.; Al-Askar, A.A.; Arishi, A.A.; Elkady, F.M.; Elbahnasawy, M.A. Antifungal Activity of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) against Aspergilli Causing Aspergillosis: Ultrastructure Study. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, V.V.; Chaudhuri, P. Modalities of Protein Denaturation and Nature of Denaturants. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2021, 69, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataesan Kumari, B.; Mani, R.; Asokan, B.R.; Balakrishnan, K.; Ramasamy, A.; Parthasarathi, R.; Kandasamy, C.; Govindaraj, R.; Vijayakumar, N.; Vijayakumar, S. Green Synthesised Silver Nanoparticles Using Anoectochilus elatus Leaf Extract: Characterisation and Evaluation of Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, Antidiabetic, and Antimicrobial Activities. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faedmaleki, F.; Shirazi, F.H.; Salarian, A.-A.; Ahmadi Ashtiani, H.; Rastegar, H. Toxicity Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Mice Liver Primary Cell Culture and HepG2 Cell Line. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2014, 13, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannaraj, G.; Sahi, S.V.; Ravikumar, S.; Venkatachalam, P. Enhanced Cytotoxicity of Biomolecules Loaded Metallic Silver Nanoparticles against Human Liver (HepG2) and Prostate (PC3) Cancer Cell Lines. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 4948–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elson, C.O.; Sartor, R.B.; Tennyson, G.S.; Riddell, R.H. Experimental Models of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 1995, 109, 1344–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traverso, G.; Schoellhammer, C.M.; Schroeder, A.; Maa, R.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Polat, B.; Anderson, D.G.; Blankschtein, D.; Langer, R. Microneedles for Drug Delivery via the Gastrointestinal Tract. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S. Role of Serotonin 5-HT3 Receptors in Intestinal Inflammation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 1406–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, H.; Park, E.; Yun, C.-H.; Sng, N.J.; Lucena-Araujo, A.R.; Yeo, W.-L.; Huberman, M.S.; Cohen, D.W.; Nakayama, S.; Ishioka, K.; et al. Structural, Biochemical and Clinical Characterization of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Exon 20 Insertion Mutations in Lung Cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 216ra177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maehara, A.; Mintz, G.S.; Shimshak, T.M.; Ricotta, J.J.; Ramaiah, V.; Foster, M.T.; Davis, T.P.; Gray, W.A. Intravascular Ultrasound Evaluation of JETSTREAM Atherectomy Removal of Superficial Calcium in Peripheral Arteries. EuroIntervention 2015, 11, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zou, D.; Li, Y.; Gu, S.; Dong, J.; Ma, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, F.; Huang, J.H. Monoamine Neurotransmitters Control Basic Emotions and Affect Major Depressive Disorders. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, S.A.; Helli, P.B.; Janssen, L.J. Ionic Mechanisms and Ca2+ Handling in Airway Smooth Muscle. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 30, 114–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Francesco, E.; Sotgia, F.; Clarke, R.; Lisanti, M.; Maggiolini, M. G Protein-Coupled Receptors at the Crossroad between Physiologic and Pathologic Angiogenesis: Old Paradigms and Emerging Concepts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woll, K.A.; Van Petegem, F. Calcium-Release Channels: Structure and Function of IP3 Receptors and Ryanodine Receptors. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 209–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.X.; Itsuki, K.; Hase, H.; Sawamura, S.; Kurokawa, T.; Mori, Y.; Inoue, R. Dynamics of Receptor-Operated Ca2+ Currents through TRPC Channels Controlled via the PI(4,5)P2-PLC Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill-Eubanks, D.C.; Werner, M.E.; Heppner, T.J.; Nelson, M.T. Calcium Signaling in Smooth Muscle. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, M.R.; Stebbing, M.J.; Furness, J.B. Autonomic Neuromuscular Junctions. Auton. Neurosci. 2021, 234, 102816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touyz, R.M.; Alves-Lopes, R.; Rios, F.J.; Camargo, L.L.; Anagnostopoulou, A.; Arner, A.; Montezano, A.C. Vascular Smooth Muscle Contraction in Hypertension. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, C.; Salazar-García, S.; Palestino, G.; Martínez-Cuevas, P.P.; Ramírez-Lee, M.A.; Jurado-Manzano, B.B.; Rosas-Hernández, H.; Gaytán-Pacheco, N.; Martel, G.; Espinosa-Tanguma, R.; et al. Effect of 45 Nm Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) upon the Smooth Muscle of Rat Trachea: Role of Nitric Oxide. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 207, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zholos, A.V.; Bolton, T.B.; Dresvyannikov, A.V.; Kustov, M.V.; Tsvilovskii, V.V.; Shuba, M.F. Cholinergic Excitation of Smooth Muscles: Multiple Signaling Pathways Linking M2 and M3 Muscarinic Receptors to Cationic Channels. Neurophysiology 2004, 36, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.; Prins, N.H.; Meulemans, A.L.; Lefebvre, R.A. Smooth Muscle 5-HT2A Receptors Mediating Contraction of Porcine Isolated Proximal Stomach Strips. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 137, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Drug-Loaded AgNPs (1) | AgNPs | MA (2) | N * | A * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus subtilis, ATCC 6633 | 10 | ND | ND | n.a. | 16 |
| Bacillus cereus NCTC 11145 | 12 | ND | ND | n.a. | 20 |
| Staphylococcus aureus, ATCC 25923 | 8 | ND | ND | n.a. | 35 |
| Listeria monocytogenes, NBIMCC 8632 | 11 | ND | ND | n.a. | 40 |
| Enterococcus faecalis, ATCC 29212 | 9 | ND | 10 | n.a. | 38 |
| Salmonella typhimurium, NBIMCC 1672 | 12 | ND | ND | n.a. | 40 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae, ATCC 13883 | 11 | 8 | 10 | n.a. | 25 |
| Escherichia coli, ATCC 25922 | 12 | 9 | ND | n.a. | 16 |
| Proteus vulgaris, ATCC 6380 | 11 | 11 | 10 | n.a. | 30 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa, ATCC 9027 | 12 | 8 | ND | n.a. | 16 |
| Candida albicans, NBIMCC 74 | 15 | ND | 12 | 21 | n.a. |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae, ATCC 9763 | 15 | ND | ND | 18 | n.a. |
| Aspergillus niger, ATCC 1015 | 15 | 14 | ND | 18 | n.a. |
| Penicillium chrysogenum | 16 | 11 | ND | n.a. | n.a. |
| Fusarium moniliforme, ATCC 38932 | 14 | ND | ND | 15 | n.a. |
| Samples | IC50 at 24th h [µg/mL] | IC50 at 72nd h [µg/mL] |
|---|---|---|
| MA | 24.69 | 29.39 |
| AgNPs | 6.35 | 17.79 |
| AgNPs with MA | 8.88 | 13.93 |
| Concentration, M | Drug-Loaded AgNPs (1) | Volume, µL | MA (2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tonus, mN | Amplitude, mN | Frequency, mN | Tonus, mN | Amplitude, mN | Frequency, mN | ||
| 10−7 | 2.2 | 4 | 4.7 | 2.5 | 2 | 5 | 4 |
| 5 × 10−6 | 2.2 | 4 | 4.8 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 3.8 |
| 2.5 × 10−6 | 2 | 3.8 | 4.8 | 7.5 | 1.8 | 4.3 | 3.8 |
| 10−6 | 2 | 3.7 | 4.6 | 10 | 1.5 | 4 | 3.9 |
| 2.5 × 10−5 | 2 | 3.6 | 4.7 | 12.5 | 1.3 | 3.2 | 3.7 |
| 5 × 10−5 | 1.8 | 3.7 | 4.7 | 15 | 1 | 3 | 3.7 |
| 10−5 | 1.8 | 3.7 | 4.8 | 17.5 | 0.5 | 2 | 3.6 |
| 5 × 10−4 | 1.7 | 3.6 | 4.5 | 20 | 0.2 | 1 | 3.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stoyanova, M.; Gledacheva, V.; Milusheva, M.; Todorova, M.; Kircheva, N.; Angelova, S.; Stefanova, I.; Pencheva, M.; Tumbarski, Y.; Vasileva, B.; et al. Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles as Multifunctional Agents Against Gut Microbiota Imbalance and Inflammation. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110815
Stoyanova M, Gledacheva V, Milusheva M, Todorova M, Kircheva N, Angelova S, Stefanova I, Pencheva M, Tumbarski Y, Vasileva B, et al. Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles as Multifunctional Agents Against Gut Microbiota Imbalance and Inflammation. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(11):815. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110815
Chicago/Turabian StyleStoyanova, Mihaela, Vera Gledacheva, Miglena Milusheva, Mina Todorova, Nikoleta Kircheva, Silvia Angelova, Iliyana Stefanova, Mina Pencheva, Yulian Tumbarski, Bela Vasileva, and et al. 2025. "Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles as Multifunctional Agents Against Gut Microbiota Imbalance and Inflammation" Nanomaterials 15, no. 11: 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110815
APA StyleStoyanova, M., Gledacheva, V., Milusheva, M., Todorova, M., Kircheva, N., Angelova, S., Stefanova, I., Pencheva, M., Tumbarski, Y., Vasileva, B., Hristova-Panusheva, K., Gospodinova, Z., Krasteva, N., Miloshev, G., Georgieva, M., & Nikolova, S. (2025). Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles as Multifunctional Agents Against Gut Microbiota Imbalance and Inflammation. Nanomaterials, 15(11), 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110815














