The Potential of ICP-MS as a Complementary Tool in Nanoparticle–Protein Corona Analysis
Abstract
1. The Context of the Protein Corona
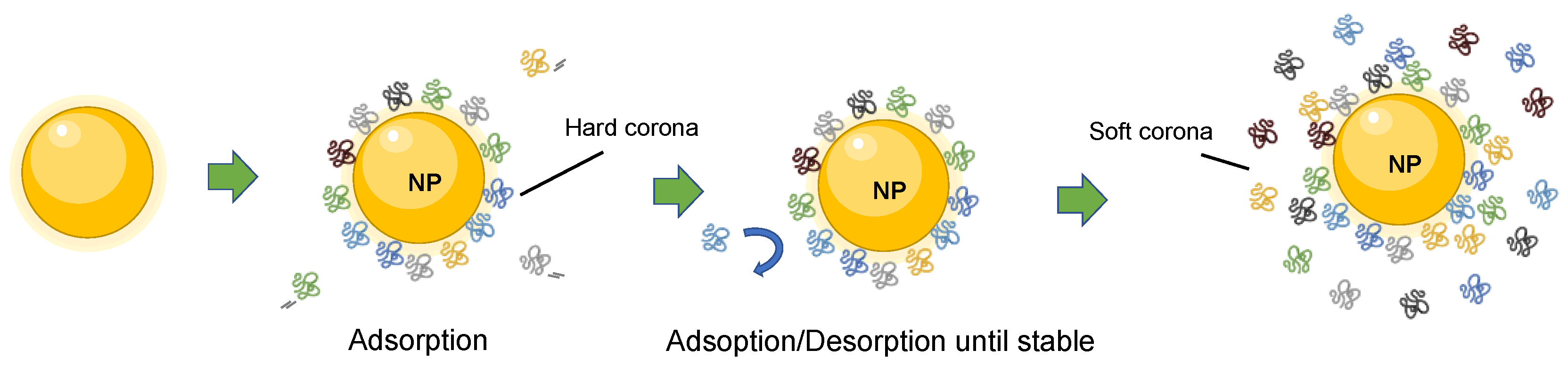
1.1. The Protein Corona Formation
1.2. The Biological Impact of the Protein Corona
2. Traditional Approaches to Study and Characterize the Nanoparticle–Protein Corona Complex
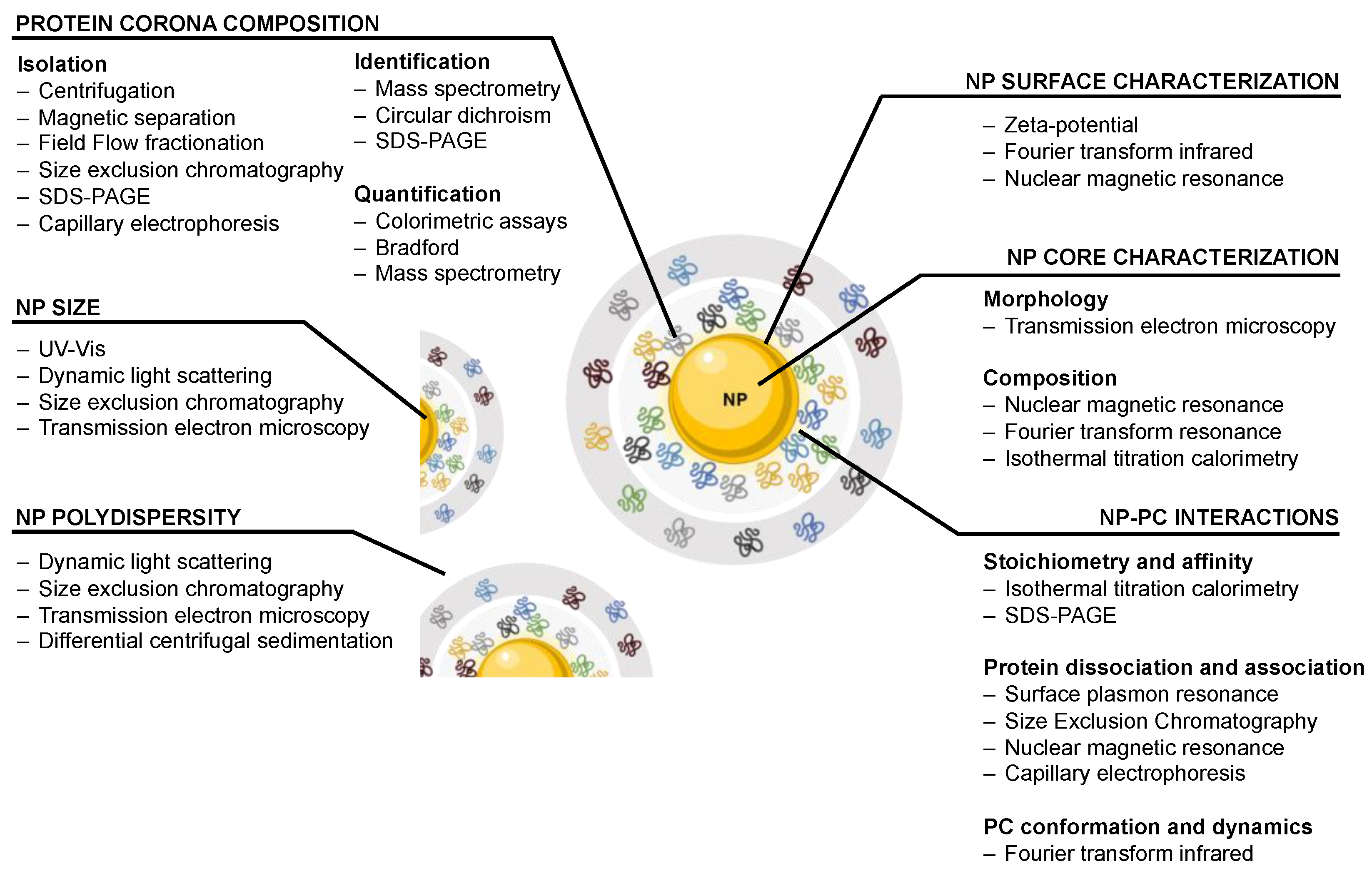
2.1. Nanoparticle Characterization
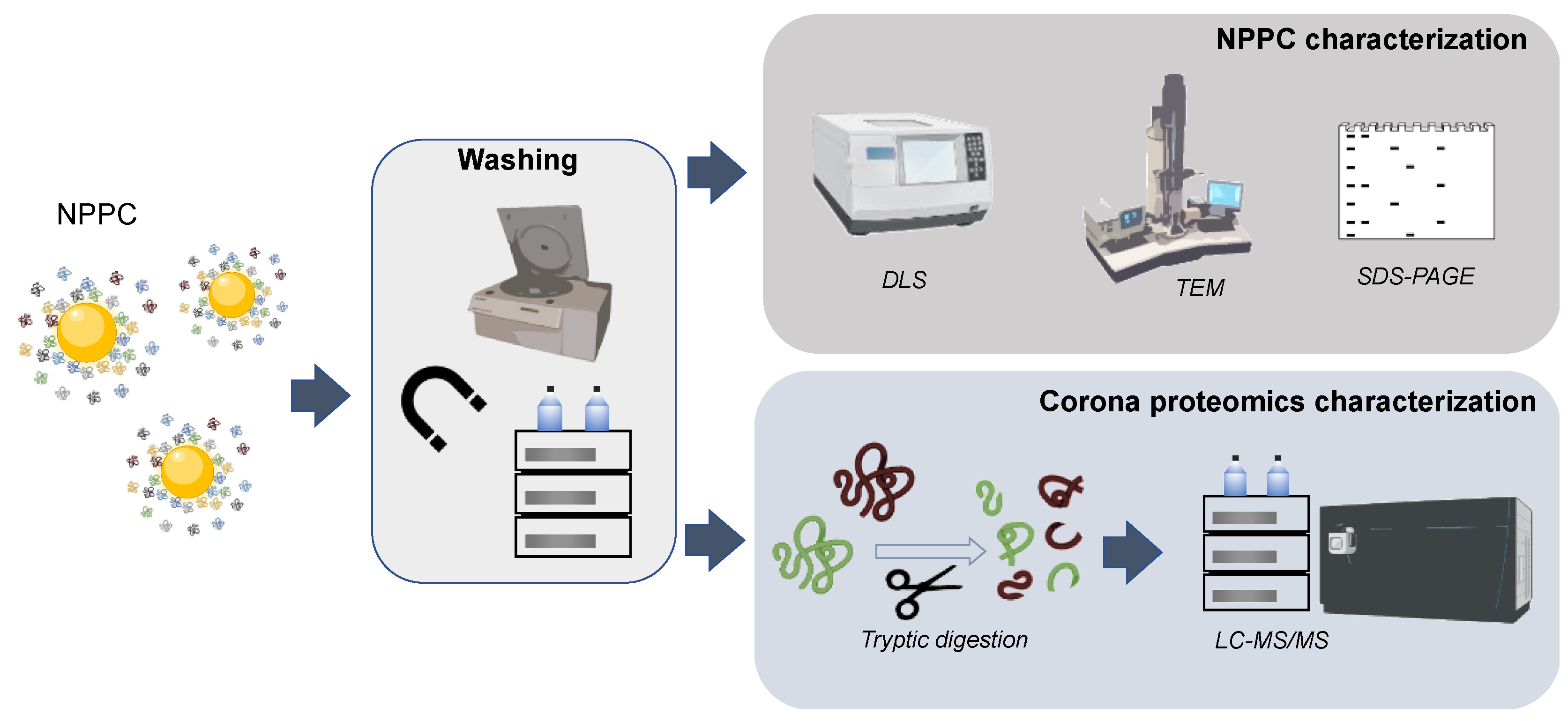
2.2. Protein Corona Composition
2.3. Nanoparticle–Protein Corona Interactions
3. The Need for Improved Methodologies in Nanoparticle–Protein Corona Analysis
3.1. Lack of Standardization in Nanoparticles Synthesis, Production and Characterization
3.2. Irreproducibility and Lack of Standardization in LC-MS Protein Analysis
4. The Potential of ICP-MS in the Study of the Nanoparticle–Protein Corona Complex
4.1. Characterization of Nanoparticle Composition and Functionalization by ICP-MS
4.2. Characterization of NPPC Protein Components by ICP-MS
5. Concluding Remarks and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monopoli, M.P.; Walczyk, D.; Campbell, A.; Elia, G.; Lynch, I.; Bombelli, F.B.; Dawson, K.A. Physical−Chemical Aspects of Protein Corona: Relevance to in Vitro and in Vivo Biological Impacts of Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2525–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakar, A.; Kanel, S.R.; Ray, C.; Snow, D.D.; Nadagouda, M.N. Nanomaterials in the Environment, Human Exposure Pathway, and Health Effects: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lead, J.R.; Batley, G.E.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Croteau, M.-N.; Handy, R.D.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Judy, J.D.; Schirmer, K. Nanomaterials in the Environment: Behavior, Fate, Bioavailability, and Effects—An Updated Review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 2029–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auría-Soro, C.; Nesma, T.; Juanes-Velasco, P.; Landeira-Viñuela, A.; Fidalgo-Gomez, H.; Acebes-Fernandez, V.; Gongora, R.; Almendral Parra, M.J.; Manzano-Roman, R.; Fuentes, M. Interactions of Nanoparticles and Biosystems: Microenvironment of Nanoparticles and Biomolecules in Nanomedicine. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundqvist, M.; Stigler, J.; Cedervall, T.; Berggård, T.; Flanagan, M.B.; Michelle, B.F.; Lynch, I.; Elia, G.; Dawson, K.A. The Evolution of the Protein Corona around Nanoparticles: A Test Study. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7503–7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A. Protein-Nanoparticle Interactions. Nano Today 2008, 3, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.M.; Åberg, C.; Polo, E.; O’Connell, A.; Cookman, J.; Fallon, J.; Krpetić, Ž.; Dawson, K.A. Mapping Protein Binding Sites on the Biomolecular Corona of Nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedervall, T.; Lynch, I.; Lindman, S.; Berggård, T.; Thulin, E.; Nilsson, H.; Dawson, K.A.; Linse, S. Understanding the Nanoparticle-Protein Corona Using Methods to Quantify Exchange Rates and Affinities of Proteins for Nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, W. The Janus of Protein Corona on Nanoparticles for Tumor Targeting, Immunotherapy and Diagnosis. J. Control. Release 2022, 345, 832–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Mao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Du, Z.; Wu, W.; Jiang, L.; Yang, J.; Li, J. Study on the Interaction of Graphene Oxide-silver Nanocomposites with Bovine Serum Albumin and the Formation of Nanoparticle-Protein Corona. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, P.C.; Lin, S.; Parak, W.J.; Davis, T.P.; Caruso, F. A Decade of the Protein Corona. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11773–11776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Orco, D.; Lundqvist, M.; Oslakovic, C.; Cedervall, T.; Linse, S. Modeling the Time Evolution of the Nanoparticle-Protein Corona in a Body Fluid. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczyk, D.; Bombelli, F.B.; Monopoli, M.P.; Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A. What the Cell “Sees” in Bionanoscience. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5761–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenzer, S.; Docter, D.; Kuharev, J.; Musyanovych, A.; Fetz, V.; Hecht, R.; Schlenk, F.; Fischer, D.; Kiouptsi, K.; Reinhardt, C.; et al. Rapid Formation of Plasma Protein Corona Critically Affects Nanoparticle Pathophysiology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mout, R.; Moyano, D.F.; Rana, S.; Rotello, V.M. Surface Functionalization of Nanoparticles for Nanomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopac, T. Protein Corona, Understanding the Nanoparticle–Protein Interactions and Future Perspectives: A Critical Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkey, C.D.; Olsen, J.B.; Song, F.; Liu, R.; Guo, H.; Guo, H.; Olsen, D.W.H.; Cohen, Y.; Emili, A.; Chan, W.C.W. Protein Corona Fingerprinting Predicts the Cellular Interaction of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2439–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkarran, A.A.; Gharibi, H.; Voke, E.; Landry, M.P.; Saei, A.A.; Mahmoudi, M. Measurements of Heterogeneity in Proteomics Analysis of the Nanoparticle Protein Corona across Core Facilities. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesniak, A.; Fenaroli, F.; Monopoli, M.P.; Åberg, C.; Dawson, K.A.; Salvati, A. Effects of the Presence or Absence of a Protein Corona on Silica Nanoparticle Uptake and Impact on Cells. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5845–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Ahmad, A.; Vyawahare, A.; Alam, P.; Khan, T.H.; Khan, R. Biological Effects of Formation of Protein Corona onto Nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 175, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Khan, F.; Mishra, R.K.; Khan, R. Precision Cancer Nanotherapy: Evolving Role of Multifunctional Nanoparticles for Cancer Active Targeting. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 10475–10496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hühn, D.; Kantner, K.; Geidel, C.; Brandholt, S.; De Cock, I.; Soenen, S.J.; Gil, P.R.; Montenegro, J.-M.; Braeckmans, K.; Müllen, K.; et al. Polymer-Coated Nanoparticles Interacting with Proteins and Cells: Focusing on the Sign of the Net Charge. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3253–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monopoli, M.P.; Pitek, A.S.; Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A. Formation and Characterization of the Nanoparticle-Protein Corona. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1025, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.E.; Zia, R.N. Sticky, Active Microrheology: Part 1. Linear-Response. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 554, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galmarini, S.; Hanusch, U.; Giraud, M.; Cayla, N.; Chiappe, D.; Von Moos, N.R.; Hofmann, H.; Maurizi, L. Beyond Unpredictability: The Importance of Reproducibility in Understanding the Protein Corona of Nanoparticles. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 3385–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, I.; Cedervall, T.; Lundqvist, M.; Cabaleiro-Lago, C.; Linse, S.; Dawson, K.A. The Nanoparticle–Protein Complex as a Biological Entity; a Complex Fluids and Surface Science Challenge for the 21st Century. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 134–135, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Alvarez, B.; Cid-Barrio, L.; Ferreira, H.S.; Costa-Fernández, J.M.; Encinar, J.R. Integrated Analytical Platforms for the Comprehensive Characterization of Bioconjugated Inorganic Nanomaterials Aiming at Biological Applications. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 1518–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöttler, S.; Becker, G.; Winzen, S.; Steinbach, T.; Mohr, K.; Landfester, K.; Mailänder, V.; Wurm, F.R. Protein Adsorption Is Required for Stealth Effect of Poly(Ethylene Glycol)- and Poly(Phosphoester)-Coated Nanocarriers. Nat. Nanotechol. 2016, 11, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzas-Ramos, D.; García-Alonso, J.I.; Costa-Fernández, J.M.; Ruiz Encinar, J. Quantitative Assessment of Individual Populations Present in Nanoparticle–Antibody Conjugate Mixtures Using AF4-ICP-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3567–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundqvist, M.; Stigler, J.; Elia, G.; Lynch, I.; Cedervall, T.; Dawson, K.A. Nanoparticle Size and Surface Properties Determine the Protein Corona with Possible Implications for Biological Impacts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14265–14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.J.; Mortimer, G.; Schiller, T.; Musumeci, A.; Martin, D.; Minchin, R.F. Differential Plasma Protein Binding to Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 455101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, S.; Mahmoud, N.N.; Voke, E.; Landry, M.P.; Mahmoudi, M. Importance of Standardizing Analytical Characterization Methodology for Improved Reliability of the Nanomedicine Literature. Nano Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, A.; Wei, W.; Siddiqui, G.; Tang, H.; Li, Y.; Kakinen, A.; Wan, X.; Koppel, K.; Hoffmann, M.R.; Lin, S.; et al. Dynamic Protein Corona of Gold Nanoparticles with an Evolving Morphology. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 58238–58251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casals, E.; Pfaller, T.; Duschl, A.; Oostingh, G.J.; Puntes, V.F. Time Evolution of the Nanoparticle Protein Corona. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3623–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monopoli, M.P.; Åberg, C.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A. Biomolecular Coronas Provide the Biological Identity of Nanosized Materials. Nat. Nanotechol. 2012, 7, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M. The Need for Improved Methodology in Protein Corona Analysis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Carrion, C.; Carril, M.; Parak, W.J. Techniques for the Experimental Investigation of the Protein Corona. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 46, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, B.J.S.C.; Markwell, J. Assays for Determination of Protein Concentration. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2007, 48, 3.4.1–3.4.29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetti, F.; Fedel, M.; Minati, L.; Speranza, G.; Migliaresi, C. Gold Nanoparticles: Role of Size and Surface Chemistry on Blood Protein Adsorption. J. Nanopartic. Res. 2013, 15, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheibani, S.; Basu, K.; Farnudi, A.; Ashkarran, A.; Ichikawa, M.; Presley, J.F.; Bui, K.H.; Ejtehadi, M.R.; Vali, H.; Mahmoudi, M. Nanoscale Characterization of the Biomolecular Corona by Cryo-Electron Microscopy, Cryo-Electron Tomography, and Image Simulation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Celis, F.; Encinar, J.R.; Sanz-Medel, A. Standardization Approaches in Absolute Quantitative Proteomics with Mass Spectrometry. Mass Spec. Rev. 2018, 37, 715–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampado, R.; Crotti, S.; Caliceti, P.; Pucciarelli, S.; Agostini, M. Recent Advances in Understanding the Protein Corona of Nanoparticles and in the Formulation of “Stealthy” Nanomaterials. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langevin, D.; Lozano, O.; Salvati, A.; Kestens, V.; Monopoli, M.; Raspaud, E.; Mariot, S.; Salonen, A.; Thomas, S.; Driessen, M.; et al. Inter-Laboratory Comparison of Nanoparticle Size Measurements Using Dynamic Light Scattering and Differential Centrifugal Sedimentation. NanoImpact 2018, 10, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, M.; Björnmalm, M.; Thurecht, K.J.; Kent, S.J.; Parton, R.G.; Kavallaris, M.; Johnston, A.P.R.; Gooding, J.J.; Corrie, S.R.; Boyd, B.J.; et al. Minimum Information Reporting in Bio-Nano Experimental Literature. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupree, E.J.; Jayathirtha, M.; Yorkey, H.; Mihasan, M.; Petre, B.A.; Darie, C.C. A Critical Review of Bottom-Up Proteomics: The Good, the Bad, and the Future of This Field. Proteomes 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignjatovic, V.; Geyer, P.E.; Palaniappan, K.K.; Chaaban, J.E.; Omenn, G.S.; Baker, M.S.; Deutsch, E.W.; Schwenk, J.M. Mass Spectrometry-Based Plasma Proteomics: Considerations from Sample Collection to Achieving Translational Data. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 4085–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernemalm, M.; Sandberg, A.; Zhu, Y.; Boekel, J.; Tamburro, D.; Schwenk, J.M.; Björk, A.; Wahren-Herlenius, M.; Åmark, H.; Östenson, C.-G.; et al. In-Depth Human Plasma Proteome Analysis Captures Tissue Proteins and Transfer of Protein Variants across the Placenta. eLife 2019, 8, e41608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meermann, B.; Nischwitz, V. ICP-MS for the Analysis at the Nanoscale—A Tutorial Review. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 1432–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesik, J.W.; Gray, P.J. Considerations for Measurement of Individual Nanoparticles or Microparticles by ICP-MS: Determination of the Number of Particles and the Analyte Mass in Each Particle. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2012, 27, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid-Barrio, L.; Calderón-Celis, F.; Costa-Fernández, J.M.; Encinar, J.R. Assessment of the Potential and Limitations of Elemental Mass Spectrometry in Life Sciences for Absolute Quantification of Biomolecules Using Generic Standards. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 13500–13508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, O.V.; Mokhodoeva, O.B.; Maksimova, V.V.; Dzhenloda, R.K.; Jarosz, M.; Shkinev, V.M.; Timerbaev, A.R. High-Resolution ICP-MS Approach for Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 189, 113479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, O.V.; Jarosz, M.; Keppler, B.K.; Timerbaev, A.R. Toward a Deeper and Simpler Understanding of Serum Protein-Mediated Transformations of Magnetic Nanoparticles by ICP-MS. Talanta 2021, 229, 122287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitkänen, L.; Striegel, A.M. Size-Exclusion Chromatography of Metal Nanoparticles and Quantum Dots. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapiella-Alfonso, L.; Montoro Bustos, A.R.; Encinar, J.R.; Costa-Fernández, J.M.; Pereiro, R.; Sanz-Medel, A. New Integrated Elemental and Molecular Strategies as a Diagnostic Tool for the Quality of Water Soluble Quantum Dots and Their Bioconjugates. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menendez-Miranda, M.; Fernandez-Arguelles, M.T.; Costa-Fernandez, J.M.; Encinar, J.R.; Sanz-Medel, A. Elemental Ratios for Characterization of Quantum-Dots Populations in Complex Mixtures by Asymmetrical Flow Field-Flow Fractionation on-Line Coupled to Fluorescence and Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 839, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzas-Ramos, D.; Cigales Canga, J.; Mayo, J.C.; Sainz, R.M.; Ruiz Encinar, J.; Costa-Fernandez, J.M. Carbon Quantum Dots Codoped with Nitrogen and Lanthanides for Multimodal Imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cortes, M.; Sotelo González, E.; Fernández-Argüelles, M.T.; Encinar, J.R.; Costa-Fernández, J.M.; Sanz-Medel, A. Capping of Mn-Doped ZnS Quantum Dots with DHLA for Their Stabilization in Aqueous Media: Determination of the Nanoparticle Number Concentration and Surface Ligand Density. Langmuir 2017, 33, 6333–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzas-Ramos, D.; García-Cortes, M.; Sanz-Medel, A.; Encinar, J.R.; Costa-Fernández, J.M. Assessment of the Removal of Side Nanoparticulated Populations Generated during One-Pot Synthesis by Asymmetric Flow Field-Flow Fractionation Coupled to Elemental Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1519, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degueldre, C.; Favarger, P.-Y. Colloid Analysis by Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectroscopy: A Feasibility Study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 217, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozhayeva, D.; Engelhard, C. A Critical Review of Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry—A Step towards an Ideal Method for Nanomaterial Characterization. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 1740–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Bi, X.; Reed, R.B.; Ranville, J.F.; Herckes, P.; Westerhoff, P. Nanoparticle Size Detection Limits by Single Particle ICP-MS for 40 Elements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10291–10300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, R.; Herrera-Rivera, Z.; Undas, A.; van der Lee, M.; Marvin, H.; Bouwmeester, H.; Weigel, S. Single Particle ICP-MS Combined with a Data Evaluation Tool as a Routine Technique for the Analysis of Nanoparticles in Complex Matrices. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2015, 30, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, A.R.M.; Purushotham, K.P.; Possolo, A.; Farkas, N.; Vladár, A.E.; Murphy, K.E.; Winchester, M.R. Validation of Single Particle ICP-MS for Routine Measurements of Nanoparticle Size and Number Size Distribution. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 14376–14386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuello-Nuñez, S.; Abad-Álvaro, I.; Bartczak, D.; del Castillo Busto, M.E.; Ramsay, D.A.; Pellegrino, F.; Goenaga-Infante, H. The Accurate Determination of Number Concentration of Inorganic Nanoparticles Using SpICP-MS with the Dynamic Mass Flow Approach. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 1832–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborda, F.; Abad-Álvaro, I.; Jiménez, M.S.; Bolea, E. Catching Particles by Atomic Spectrometry: Benefits and Limitations of Single Particle—Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2023, 199, 106570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, H.E.; Rogers, N.J.; Jarolimek, C.; Coleman, V.A.; Higgins, C.P.; Ranville, J.F. Determining Transport Efficiency for the Purpose of Counting and Sizing Nanoparticles via Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9361–9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Miyashita, S.; Inagaki, K.; Liu, Y.-H.; Hsu, I.-H. Evaluation of Three Different Sample Introduction Systems for Single-Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (SpICP-MS) Applications. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labied, L.; Rocchi, P.; Doussineau, T.; Randon, J.; Tillement, O.; Lux, F.; Hagège, A. Taylor Dispersion Analysis Coupled to Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry for Ultrasmall Nanoparticle Size Measurement: From Drug Product to Biological Media Studies. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degasperi, A.; Labied, L.; Farre, C.; Moreau, E.; Martini, M.; Chaix, C.; Hagège, A. Probing the Protein Corona of Gold/Silica Nanoparticles by Taylor Dispersion Analysis-ICP-MS. Talanta 2022, 243, 123386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosti, A.J.; Barrio, L.C.; Calderón Celis, F.; Soldado, A.; Encinar, J.R. Absolute Quantification of Proteins Using Element Mass Spectrometry and Generic Standards. J. Proteom. 2022, 256, 104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Celis, F.; Encinar, J.R. A Reflection on the Role of ICP-MS in Proteomics: Update and Future Perspective. J. Proteom. 2019, 198, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Celis, F.; Cid-Barrio, L.; Encinar, J.R.; Sanz-Medel, A.; Calvete, J.J. Absolute Venomics: Absolute Quantification of Intact Venom Proteins through Elemental Mass Spectrometry. J. Proteom. 2017, 164, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cid-Barrio, L.; Calderón-Celis, F.; Abásolo-Linares, P.; Fernández-Sánchez, M.L.; Costa-Fernández, J.M.; Encinar, J.R.; Sanz-Medel, A. Advances in Absolute Protein Quantification and Quantitative Protein Mapping Using ICP-MS. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 104, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, D.; Ge, F.; Yang, L.; Wag, Q. Fluorescent and mass spectrometric evaluation of the phagocytic internalization of a CD47-peptide modified drug-nanocarrier. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 4193–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matczuk, M.; Legat, J.; Shtykov, S.N.; Jarosz, M.; Timerbaev, A.R. Characterization of the Protein Corona of Gold Nanoparticles by an Advanced Treatment of CE-ICP-MS Data. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 2257–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Iglesias, N.; Bettmer, J. Complementary Mass Spectrometric Techniques for the Quantification of the Protein Corona: A Case Study on Gold Nanoparticles and Human Serum Proteins. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 14324–14331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legat, J.; Matczuk, M.; Timerbaev, A.; Jarosz, M. CE Separation and ICP-MS Detection of Gold Nanoparticles and Their Protein Conjugates. Chromatographia 2017, 80, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matczuk, M.; Anecka, K.; Scaletti, F.; Messori, L.; Keppler, B.K.; Timerbaev, A.R.; Jarosz, M. Speciation of Metal-Based Nanomaterials in Human Serum Characterized by Capillary Electrophoresis Coupled to ICP-MS: A Case Study of Gold Nanoparticles. Metallomics 2015, 7, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Sanz, S.; Fariñas, N.R.; Martín-Doimeadios, R.d.C.R.; Ríos, Á. Analytical Strategy Based on Asymmetric Flow Field Flow Fractionation Hyphenated to ICP-MS and Complementary Techniques to Study Gold Nanoparticles Transformations in Cell Culture Medium. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1053, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuentes-Cervantes, A.; Ruiz Allica, J.; Calderón Celis, F.; Costa-Fernández, J.M.; Ruiz Encinar, J. The Potential of ICP-MS as a Complementary Tool in Nanoparticle–Protein Corona Analysis. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13061132
Fuentes-Cervantes A, Ruiz Allica J, Calderón Celis F, Costa-Fernández JM, Ruiz Encinar J. The Potential of ICP-MS as a Complementary Tool in Nanoparticle–Protein Corona Analysis. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(6):1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13061132
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuentes-Cervantes, Ana, Julia Ruiz Allica, Francisco Calderón Celis, José M. Costa-Fernández, and Jorge Ruiz Encinar. 2023. "The Potential of ICP-MS as a Complementary Tool in Nanoparticle–Protein Corona Analysis" Nanomaterials 13, no. 6: 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13061132
APA StyleFuentes-Cervantes, A., Ruiz Allica, J., Calderón Celis, F., Costa-Fernández, J. M., & Ruiz Encinar, J. (2023). The Potential of ICP-MS as a Complementary Tool in Nanoparticle–Protein Corona Analysis. Nanomaterials, 13(6), 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13061132








