Continuous Long-Term Exposure to Low Concentrations of MWCNTs Induces an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in BEAS-2B Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Carbon Nanotubes and Dispersion Protocol
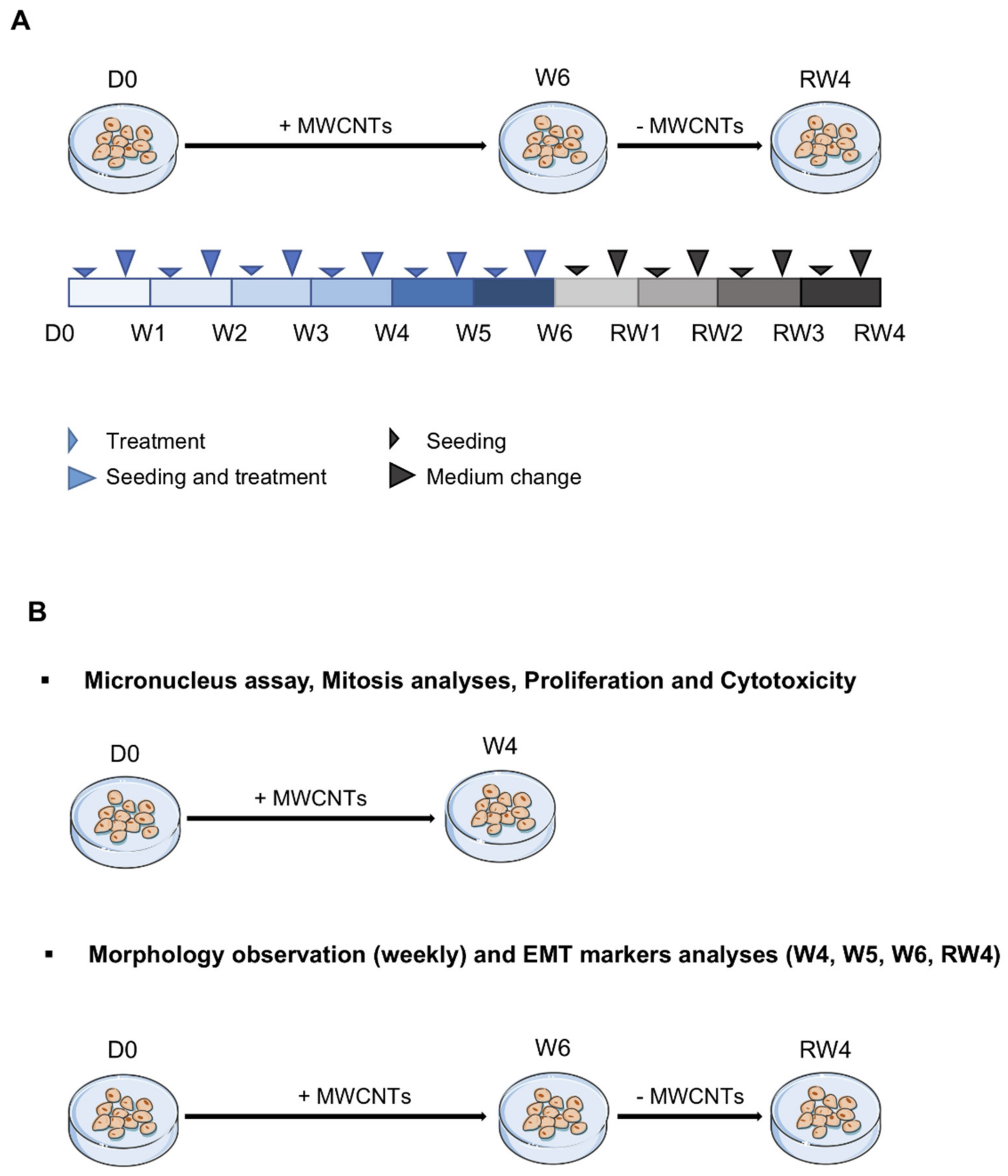
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
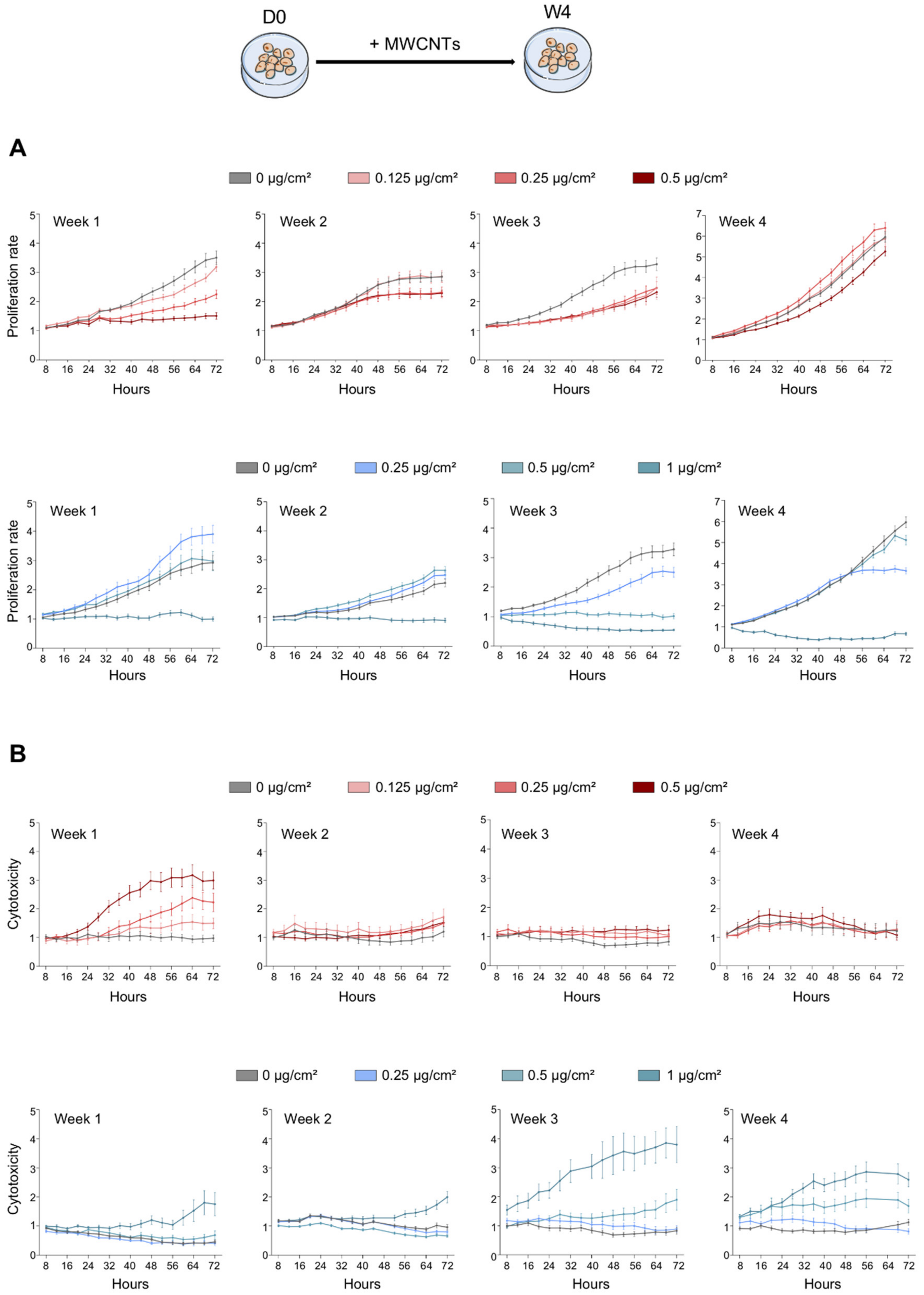
2.3. Proliferation and Cytotoxicity
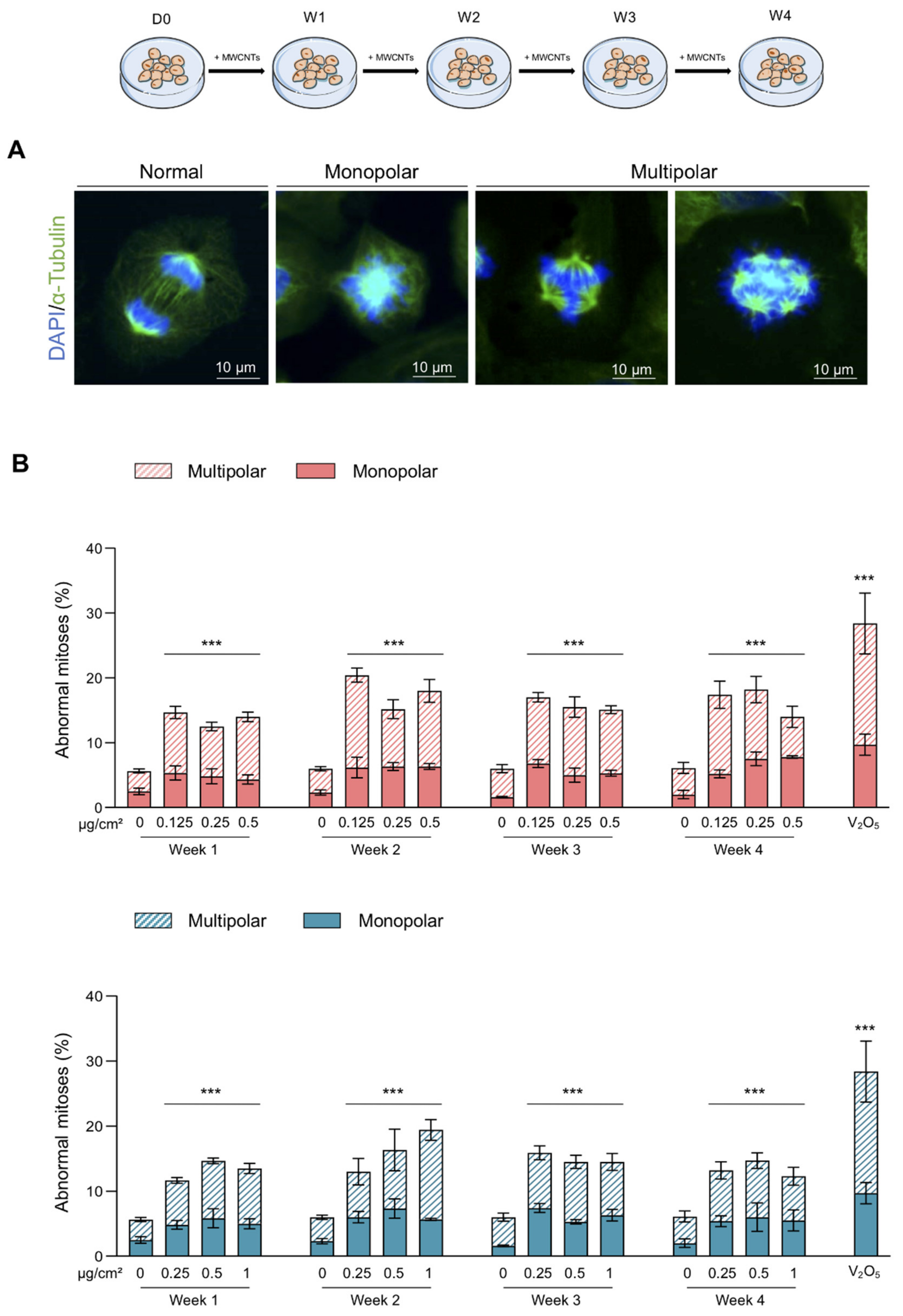
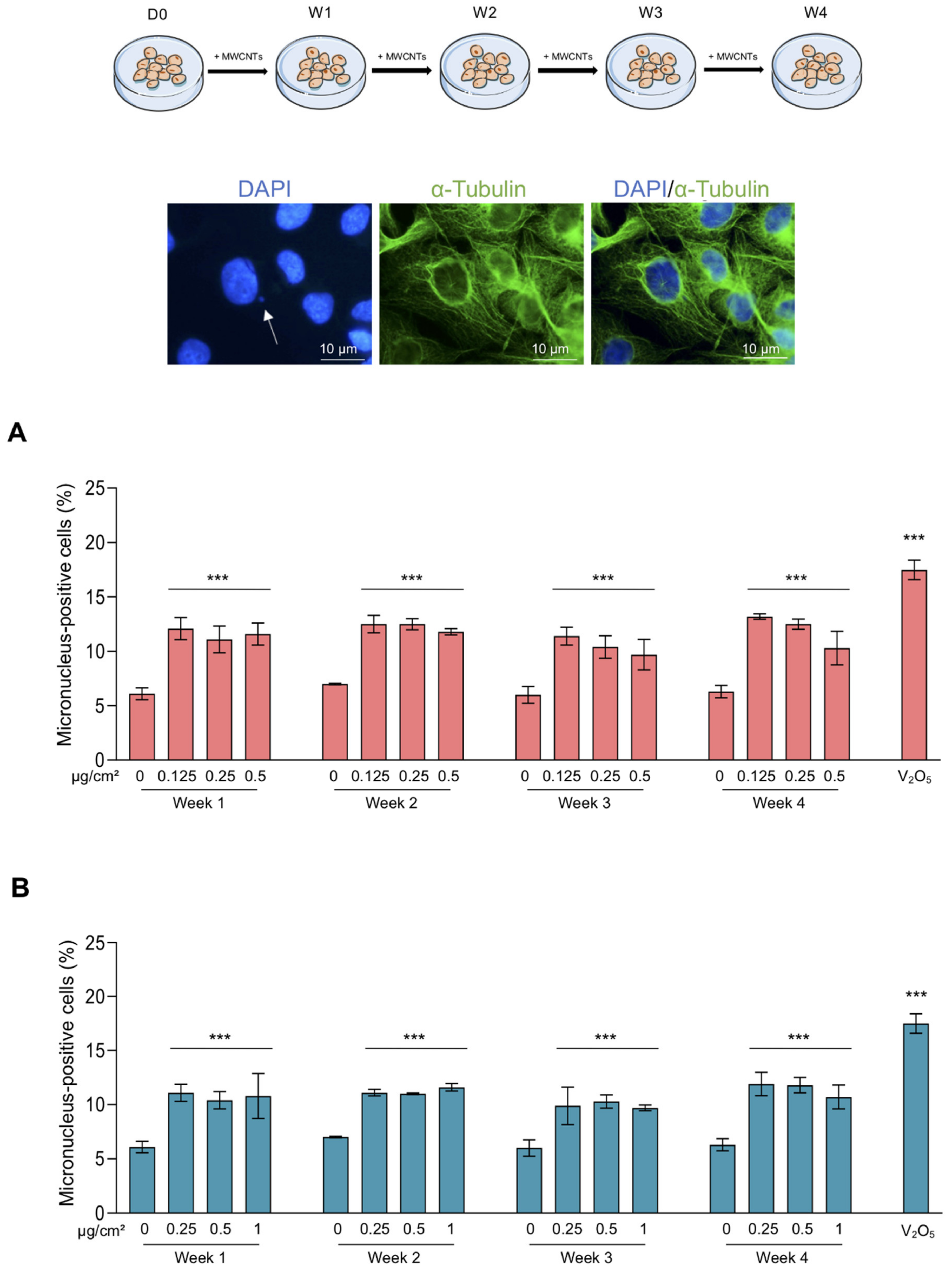
2.4. Abnormal Mitosis and Micronucleus Analysis
2.5. Morphological Observations
2.6. Analysis of Cell Populations
2.7. Total RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR
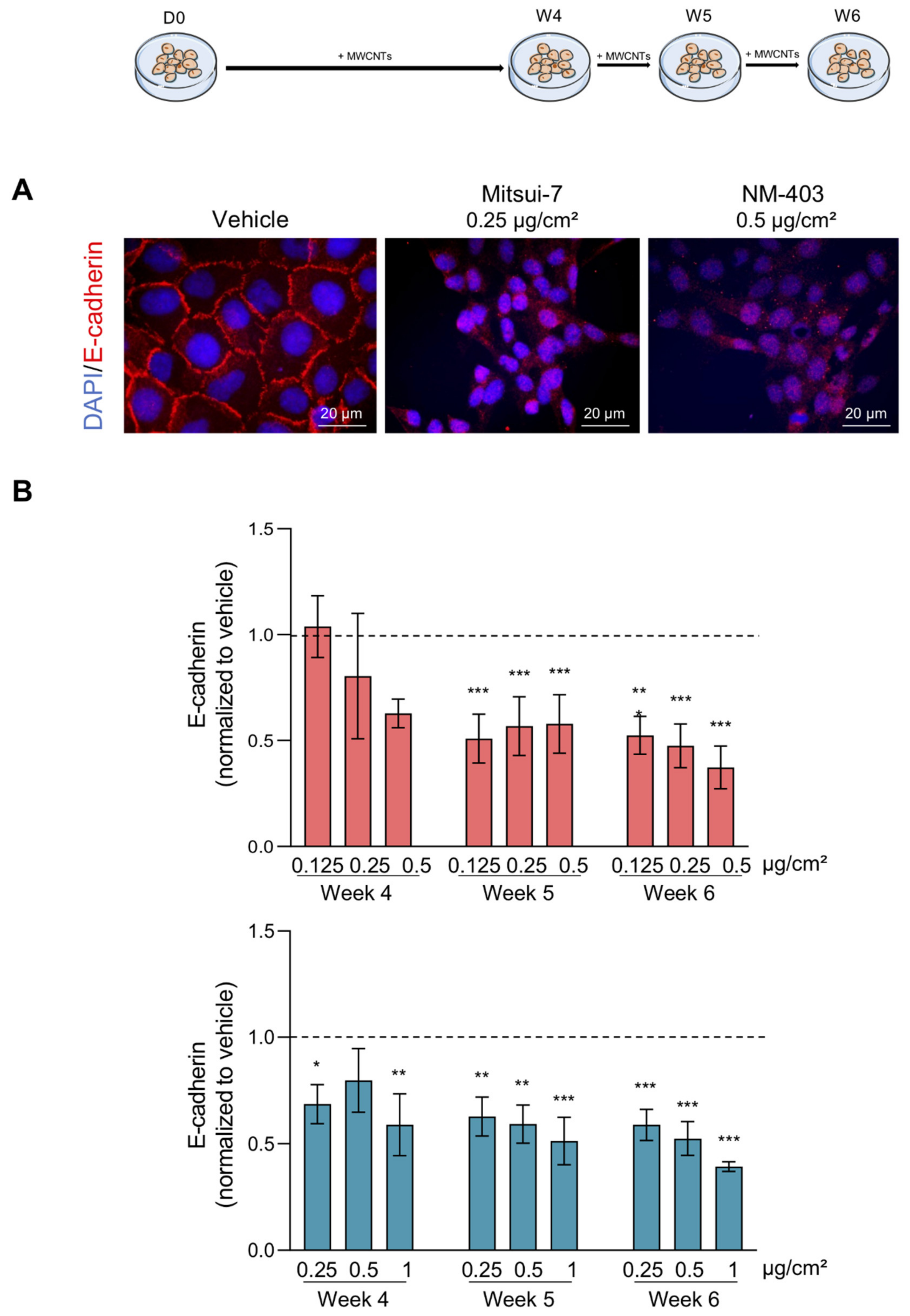
2.8. EMT Markers Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antiproliferative and Cytotoxic Effect of MWCNTs
3.2. Abnormal Mitoses and Genotoxicity
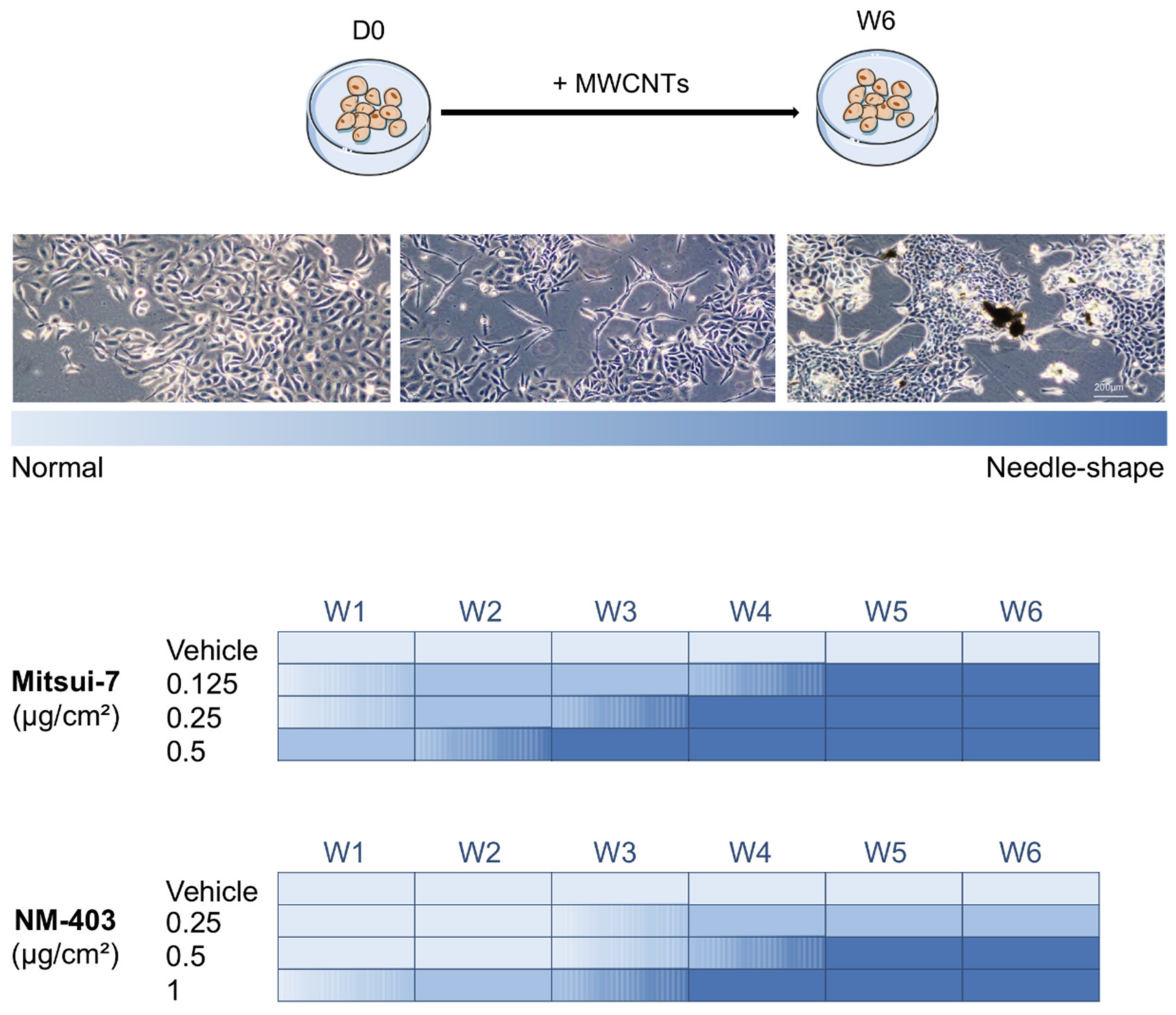
3.3. MWCNTs Altered the Cellular Morphology of BEAS-2B Cells
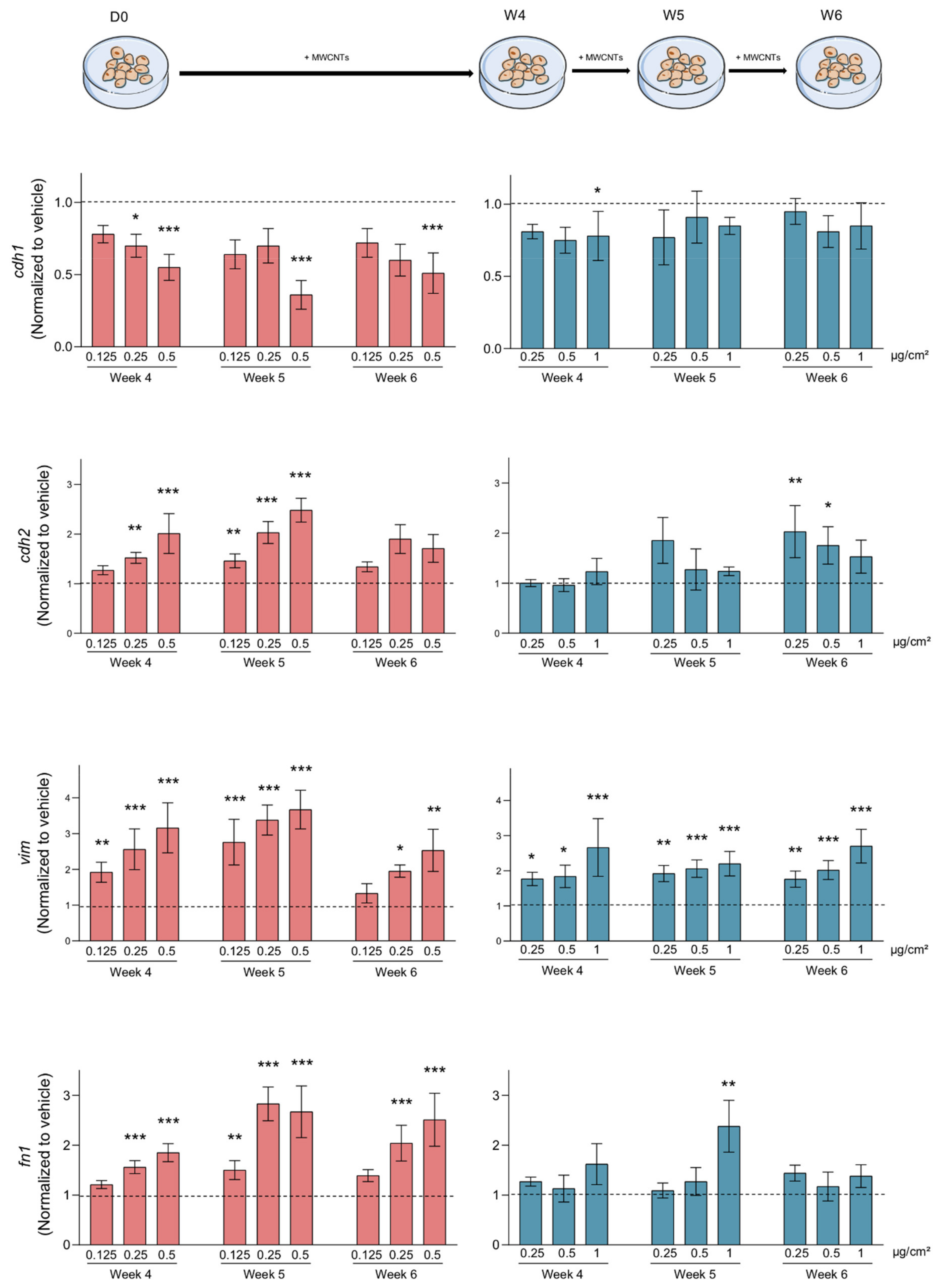
3.4. MWCNTs Are Responsible for the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
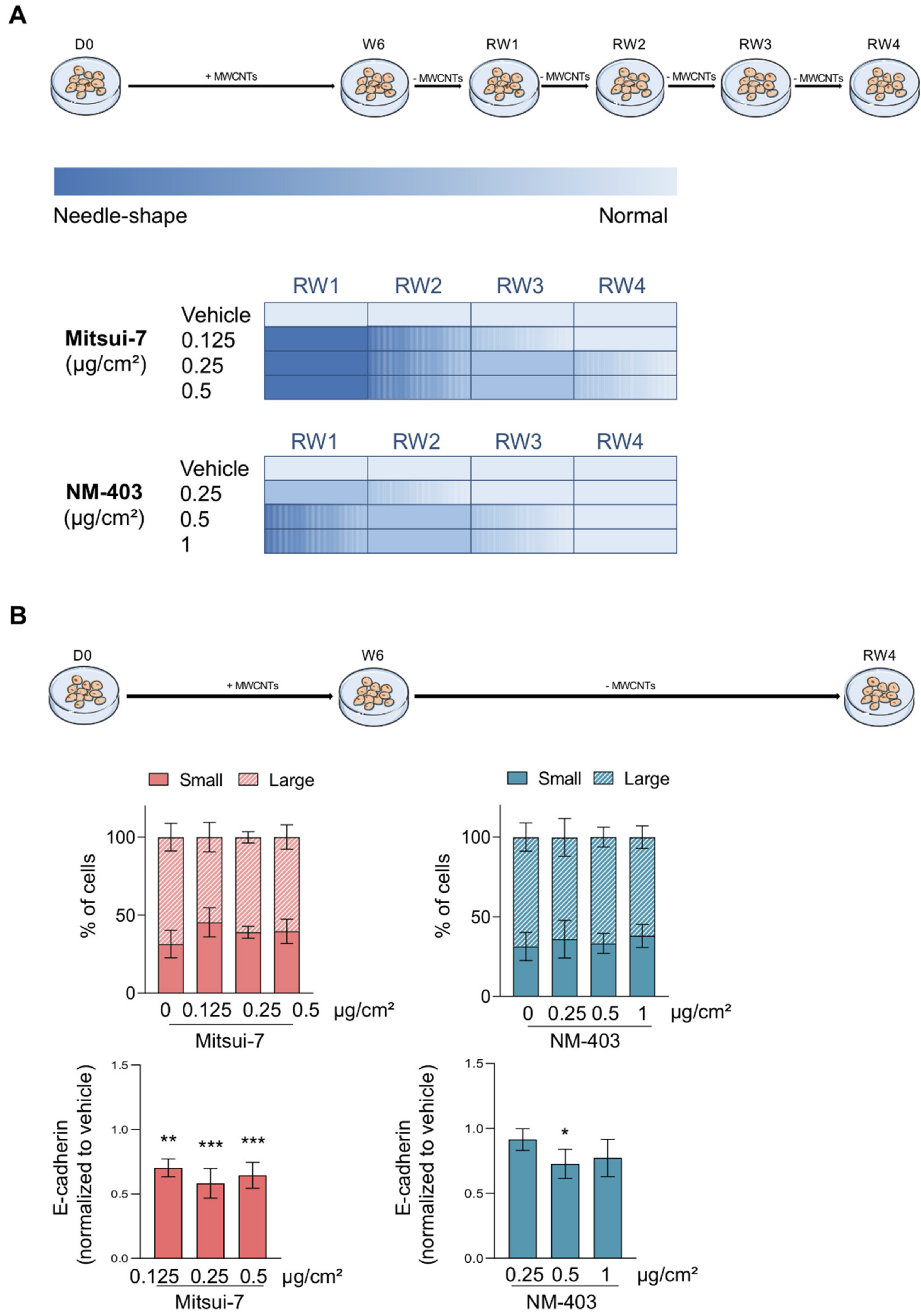
3.5. Reversibility of the Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aqel, A.; Abou El-Nour, K.M.; Ammar, R.A.; Al-Warthan, A. Carbon nanotubes, science and technology part (I) structure, synthesis and characterisation. Arab. J. Chem. 2012, 5, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baughman, R.H.; Zakhidov, A.A.; de Heer, W.A. Carbon nanotubes—the route toward applications. Science 2002, 297, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eatemadi, A.; Daraee, H.; Karimkhanloo, H.; Kouhi, M.; Zarghami, N.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Abasi, M.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Joo, S.W. Carbon nanotubes: Properties, synthesis, purification, and medical applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norizan, M.N.; Moklis, M.H.; Demon, S.Z.N.; Halim, N.A.; Samsuri, A.; Mohamad, I.S.; Knight, V.F.; Abdullah, N. Carbon nanotubes: Functionalisation and their application in chemical sensors. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 43704–43732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitranshi, M.; Pujari, A.; Ng, V.; Chen, D.; Chauhan, D.; Hudepohl, R.; Saleminik, M.; Kim, S.Y.; Kubley, A.; Shanov, V.; et al. Carbon Nanotube Sheet-Synthesis and Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinazze, A.; Zellino, C.; Borghi, F.; Campagnolo, D.; Rovelli, S.; Keller, M.; Fanti, G.; Cattaneo, A.; Cavallo, D.M. Carbon Nanotubes: Probabilistic Approach for Occupational Risk Assessment. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Ma, Q. Advances in mechanisms and signaling pathways of carbon nanotube toxicity. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 658–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasai, T.; Umeda, Y.; Ohnishi, M.; Kondo, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Aiso, S.; Nishizawa, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Fukushima, S. Thirteen-week study of toxicity of fiber-like multi-walled carbon nanotubes with whole-body inhalation exposure in rats. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, T.; Umeda, Y.; Ohnishi, M.; Mine, T.; Kondo, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Fukushima, S. Lung carcinogenicity of inhaled multi-walled carbon nanotube in rats. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzui, M.; Futakuchi, M.; Fukamachi, K.; Numano, T.; Abdelgied, M.; Takahashi, S.; Ohnishi, M.; Omori, T.; Tsuruoka, S.; Hirose, A.; et al. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes intratracheally instilled into the rat lung induce development of pleural malignant mesothelioma and lung tumors. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, N.; Izumi, H.; Morimoto, Y. Review of toxicity studies of carbon nanotubes. J. Occup. Health 2017, 59, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arnoldussen, Y.J.; Skaug, V.; Aleksandersen, M.; Ropstad, E.; Anmarkrud, K.H.; Einarsdottir, E.; Chin-Lin, F.; Granum Bjørklund, C.; Kasem, M.; Eilertsen, E.; et al. Inflammation in the pleural cavity following injection of multi-walled carbon nanotubes is dependent on their characteristics and the presence of IL-1 genes. Nanotoxicology 2018, 12, 522–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gate, L.; Knudsen, K.B.; Seidel, C.; Berthing, T.; Chézeau, L.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Valentino, S.; Wallin, H.; Bau, S.; Wolff, H.; et al. Pulmonary toxicity of two different multi-walled carbon nanotubes in rat: Comparison between intratracheal instillation and inhalation exposure. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 375, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Ma, Q. Integration of inflammation, fibrosis, and cancer induced by carbon nanotubes. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 1244–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindberg, H.K.; Falck, G.C.M.; Suhonen, S.; Vippola, M.; Vanhala, E.; Catalán, J.; Savolainen, K.; Norppa, H. Genotoxicity of nanomaterials: DNA damage and micronuclei induced by carbon nanotubes and graphite nanofibres in human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 186, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.F.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.Q. Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of multi-wall carbon nanotubes on human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2011, 721, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisin, E.R.; Murray, A.R.; Sargent, L.; Lowry, D.; Chirila, M.; Siegrist, K.J.; Schwegler-Berry, D.; Leonard, S.; Castranova, V.; Fadeel, B.; et al. Genotoxicity of carbon nanofibers: Are they potentially more or less dangerous than carbon nanotubes or asbestos? Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 252, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vales, G.; Rubio, L.; Marcos, R. Genotoxic and cell-transformation effects of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) following in vitro sub-chronic exposures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 306, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganem, N.J.; Pellman, D. Linking abnormal mitosis to the acquisition of DNA damage. J. Cell. Biol. 2012, 199, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, B.; Gnawali, N.; Hinman, A.W.; Mattingly, A.J.; Osimani, A.; Cimini, D. Chromosomes missegregated into micronuclei contribute to chromosomal instability by missegregating at the next division. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2660–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, J.C.; Davis, C.; Deshpande, C.; Hwang, W.T.; Jeffries, S.; Huang, A.; Mitchell, T.C.; Langer, C.J.; Albelda, S.M. Gene signature of antigen processing and presentation machinery predicts response to checkpoint blockade in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and melanoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacovelli, M.; Frezza, C. Metabolic reprogramming and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 3132–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, J. The Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, M.A. Context-specific roles of EMT programmes in cancer cell dissemination. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 416–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, S.; Morales, A.V.; Ocaña, O.H.; Valdés, F.; Fabregat, I.; Nieto, M.A. Snail blocks the cell cycle and confers resistance to cell death. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Nie, H.; Gao, X.; Yang, J.; Pu, J.; Chen, Z.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Jia, G. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition involved in pulmonary fibrosis induced by multi-walled carbon nanotubes via TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 226, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.W.; Wang, Q.; Asmani, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, C.; Lippmann, J.M.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, R. Lung Microtissue Array to Screen the Fibrogenic Potential of Carbon Nanotubes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Nie, X.; Braïni, C.; Bai, R.; Chen, C. Multiwall carbon nanotubes directly promote fibroblast-myofibroblast and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions through the activation of the TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Small 2015, 11, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polimeni, M.; Gulino, G.R.; Gazzano, E.; Kopecka, J.; Marucco, A.; Fenoglio, I.; Cesano, F.; Campagnolo, L.; Magrini, A.; Pietroiusti, A.; et al. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes directly induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human bronchial epithelial cells via the TGF-beta-mediated Akt/GSK-3beta/SNAIL-1 signalling pathway. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Some Nanomaterials and Some Fibres; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2017; pp. 35–214. [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen, K.B.; Berthing, T.; Jackson, P.; Poulsen, S.S.; Mortensen, A.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Skaug, V.; Szarek, J.; Hougaard, K.S.; Wolff, H.; et al. Physicochemical predictors of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-induced pulmonary histopathology and toxicity one year after pulmonary deposition of 11 different Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in mice. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryman-Rasmussen, J.P.; Tewksbury, E.W.; Moss, O.R.; Cesta, M.F.; Wong, B.A.; Bonner, J.C. Inhaled multiwalled carbon nanotubes potentiate airway fibrosis in murine allergic asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 40, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, P.; Kling, K.; Jensen, K.A.; Clausen, P.A.; Madsen, A.M.; Wallin, H.; Vogel, U. Characterization of genotoxic response to 15 multiwalled carbon nanotubes with variable physicochemical properties including surface functionalizations in the FE1-Muta(TM) mouse lung epithelial cell line. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2015, 56, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiato, H.; Logarinho, E. Mitotic spindle multipolarity without centrosome amplification. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui, M.; Kamoshita, N.; Nishimura, T.; Honma, M. Mechanism of induction of binucleated cells by multiwalled carbon nanotubes as revealed by live-cell imaging analysis. Genes Environ. 2015, 37, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asakura, M.; Sasaki, T.; Sugiyama, T.; Takaya, M.; Koda, S.; Nagano, K.; Arito, H.; Fukushima, S. Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity of multi-wall carbon nanotubes in cultured Chinese hamster lung cells in comparison with chrysotile A fibers. J. Occup. Health 2010, 52, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sargent, L.M.; Hubbs, A.F.; Young, S.H.; Kashon, M.L.; Dinu, C.Z.; Salisbury, J.L.; Benkovic, S.A.; Lowry, D.T.; Murray, A.R.; Kisin, E.R.; et al. Single-walled carbon nanotube-induced mitotic disruption. Mutat. Res. 2012, 745, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegrist, K.J.; Reynolds, S.H.; Kashon, M.L.; Lowry, D.T.; Dong, C.; Hubbs, A.F.; Young, S.H.; Salisbury, J.L.; Porter, D.W.; Benkovic, S.A.; et al. Genotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes at occupationally relevant doses. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fenoglio, I.; Greco, G.; Tomatis, M.; Muller, J.; Raymundo-Pinero, E.; Béguin, F.; Fonseca, A.; Nagy, J.B.; Lison, D.; Fubini, B. Structural defects play a major role in the acute lung toxicity of multiwall carbon nanotubes: Physicochemical aspects. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cveticanin, J.; Joksic, G.; Leskovac, A.; Petrovic, S.; Sobot, A.V.; Neskovic, O. Using carbon nanotubes to induce micronuclei and double strand breaks of the DNA in human cells. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 015102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyret-Lalle, C.; Pommier, R.; Bouard, C.; Nouri, E.; Richard, G.; Puisieux, A. Cancer cell plasticity and metastatic dissemination. Med. Sci. 2016, 32, 725–731. [Google Scholar]
- Chae, Y.K.; Woo, J.; Kim, M.J.; Kang, S.K.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.K.; Gong, G.; Kim, Y.H.; Soria, J.C.; et al. Expression of Aquaporin 5 (AQP5) Promotes Tumor Invasion in Human Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinwald, A.; Murphy, F.A.; Prina-Mello, A.; Poland, C.A.; Byrne, F.; Movia, D.; Glass, J.R.; Dickerson, J.C.; Schultz, D.A.; Jeffree, C.E.; et al. The threshold length for fiber-induced acute pleural inflammation: Shedding light on the early events in asbestos-induced mesothelioma. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 128, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, F.A.; Poland, C.A.; Duffin, R.; Al-Jamal, K.T.; Ali-Boucetta, H.; Nunes, A.; Byrne, F.; Prina-Mello, A.; Volkov, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Length-dependent retention of carbon nanotubes in the pleural space of mice initiates sustained inflammation and progressive fibrosis on the parietal pleura. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 2587–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbarino, M.; Giordano, A. Assessment of the Carcinogenicity of Carbon Nanotubes in the Respiratory System. Cancers 2021, 13, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Ong, S.L.; Tran, L.M.; Jing, Z.; Liu, B.; Park, S.J.; Huang, Z.L.; Walser, T.C.; Heinrich, E.L.; Lee, G.; et al. Chronic IL-1beta-induced inflammation regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition memory phenotypes via epigenetic modifications in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Product Code | Length (µm) | Diameter (nm) | SBET * (m2/g) | Purity (%) | Metal Content (wt%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitsui-7 | MWNT-7 | 5.7 (±0.49) | 74 (29–173) | 26 | >99 | P2O5 0.14, Fe2O3 0.08, SO3 0.08, CaO 0.03, MgO 0.01, SiO 0.006, ZnO 0.001, CuO 0.0003 |
| NM-403 | JRCNM4003a | 0.4 (±0.03) | 12 (5–37) | 135 | >90 | Al2O3 0.24, MgO 0.19, MnO 0.16, P2O5 0.14, CoO 0.12, CaO 0.03, CuO 0.003, Fe2O3 0.002, NiO 0.0018, ZnO 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barthel, H.; Darne, C.; Gaté, L.; Visvikis, A.; Seidel, C. Continuous Long-Term Exposure to Low Concentrations of MWCNTs Induces an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in BEAS-2B Cells. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071742
Barthel H, Darne C, Gaté L, Visvikis A, Seidel C. Continuous Long-Term Exposure to Low Concentrations of MWCNTs Induces an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in BEAS-2B Cells. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(7):1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071742
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarthel, Hélène, Christian Darne, Laurent Gaté, Athanase Visvikis, and Carole Seidel. 2021. "Continuous Long-Term Exposure to Low Concentrations of MWCNTs Induces an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in BEAS-2B Cells" Nanomaterials 11, no. 7: 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071742
APA StyleBarthel, H., Darne, C., Gaté, L., Visvikis, A., & Seidel, C. (2021). Continuous Long-Term Exposure to Low Concentrations of MWCNTs Induces an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in BEAS-2B Cells. Nanomaterials, 11(7), 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071742






