Ultrabright Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles for Dual pH and Temperature Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Nanosensors
2.3. Characterization Techniques
3. Results
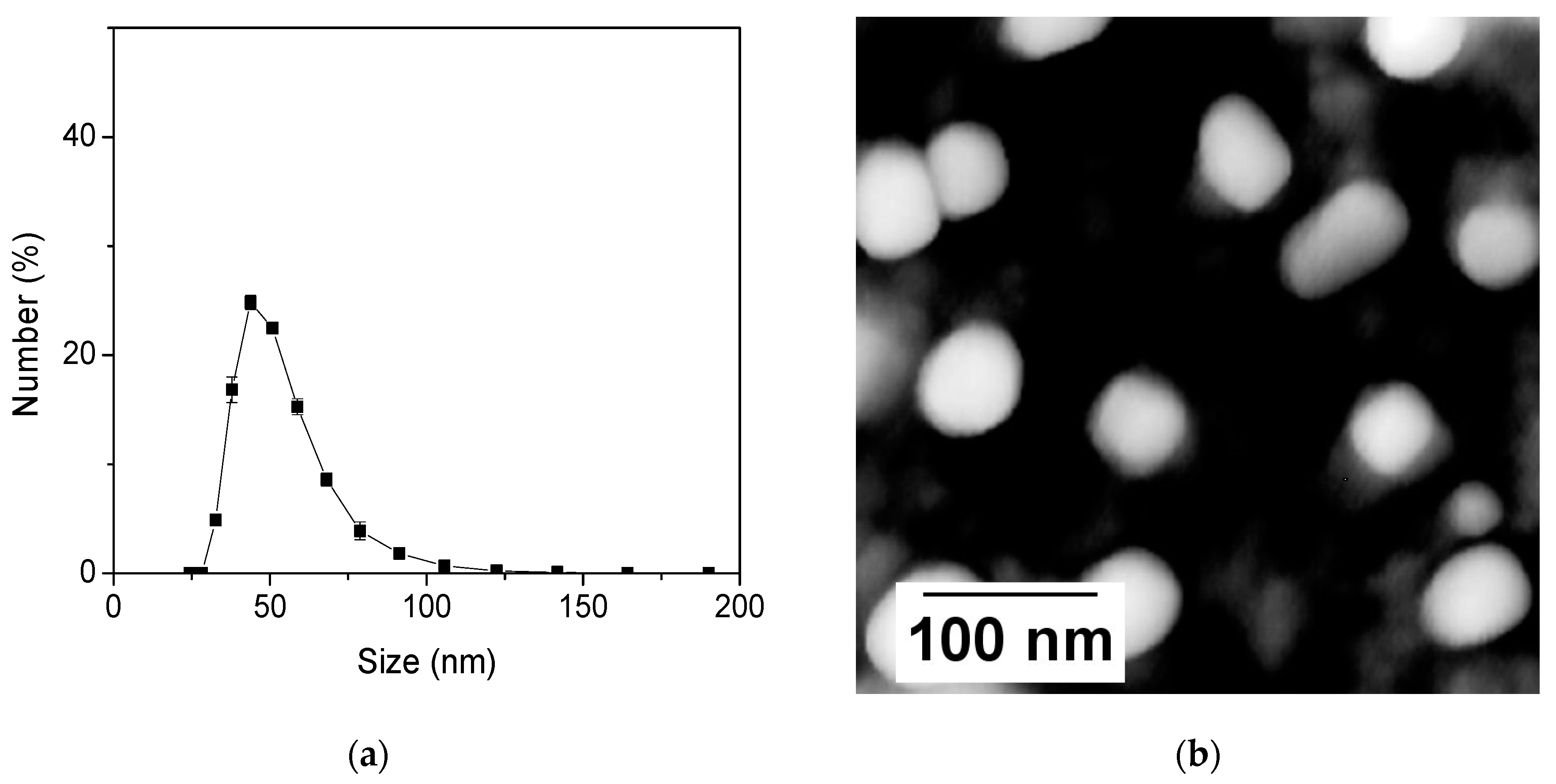
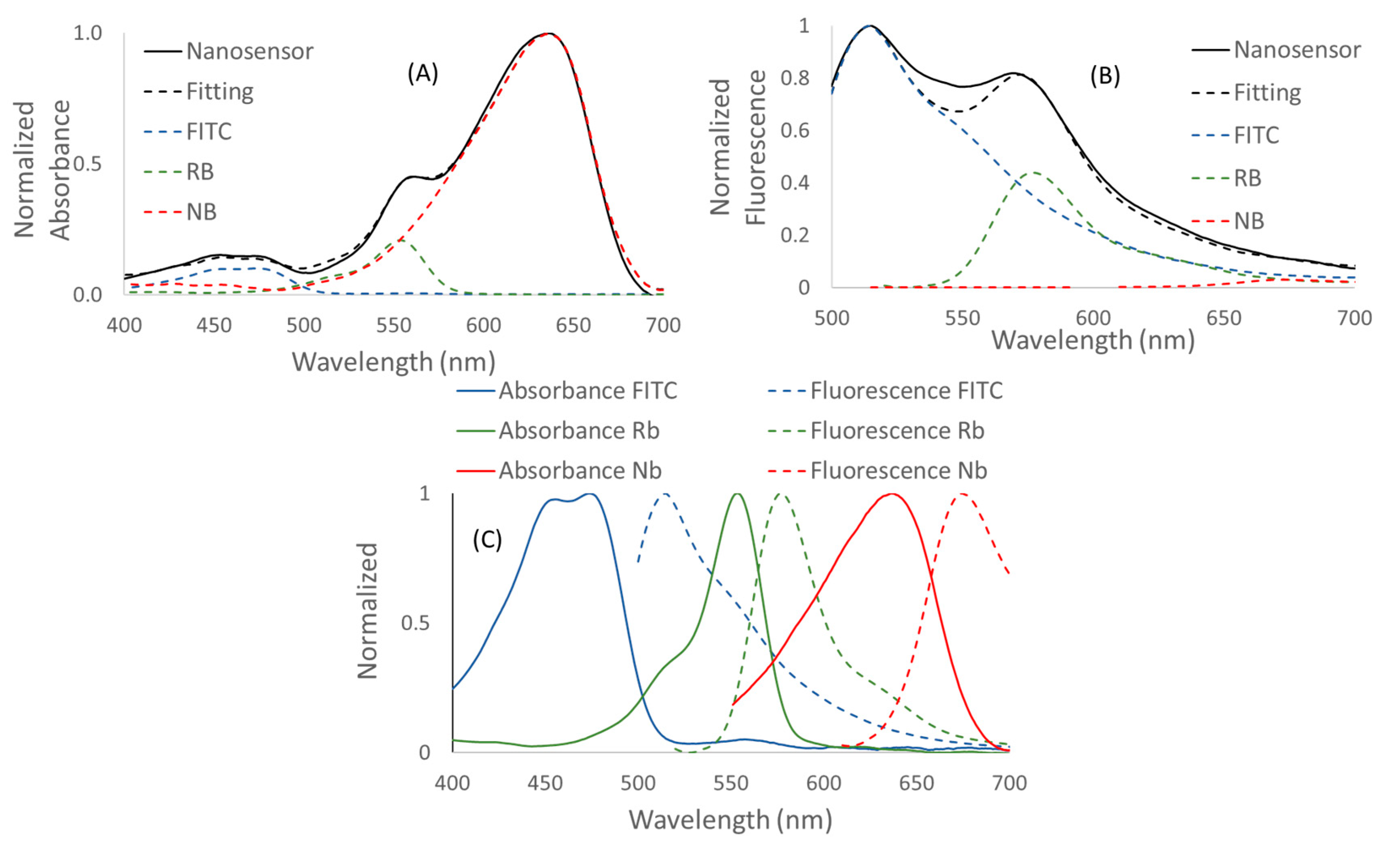
3.1. Characterization of the Nanosensors
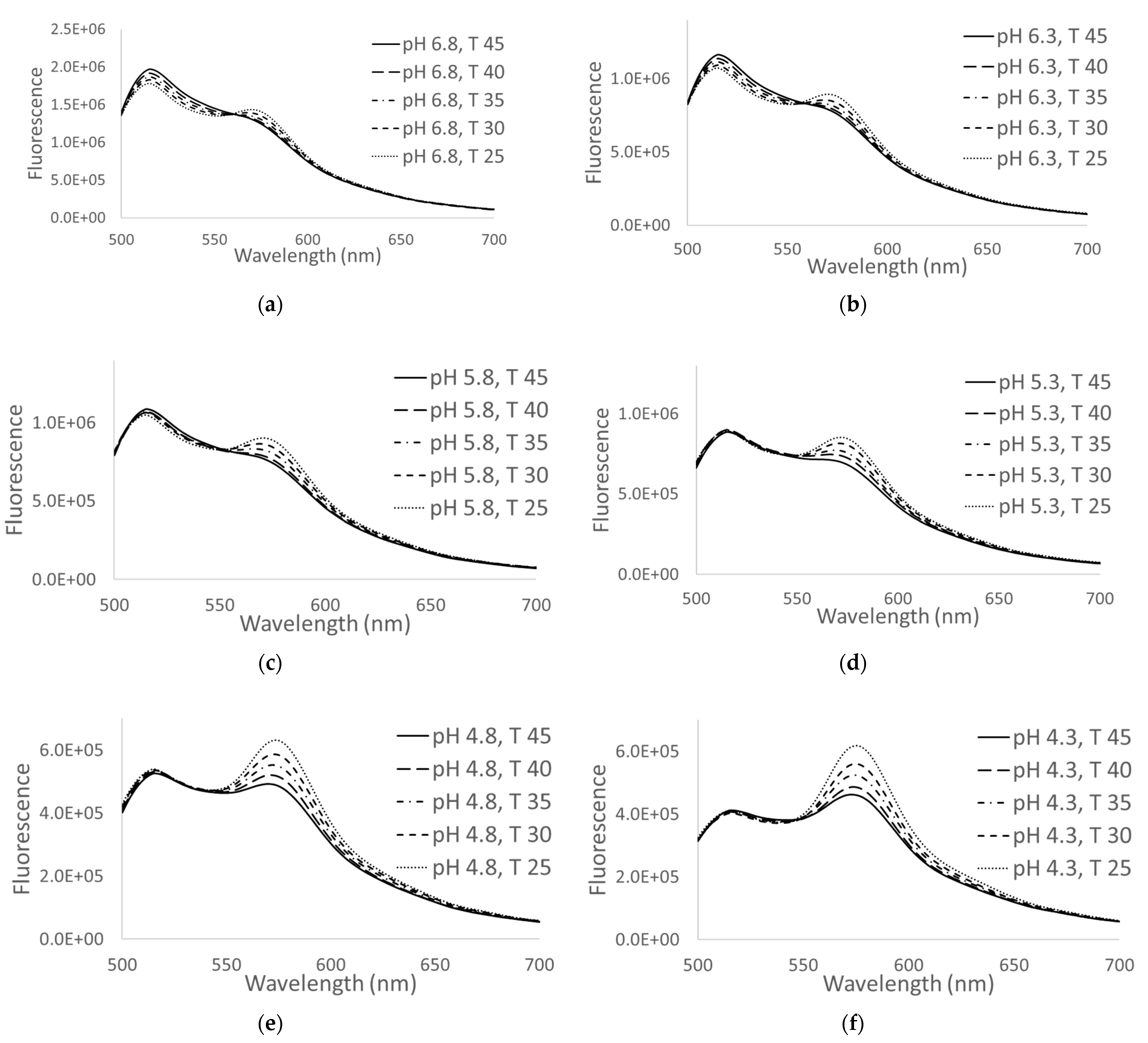
3.2. Temperature and pH Calibration
3.3. Method of Simultaneous Measurements of Temperature and Acidity
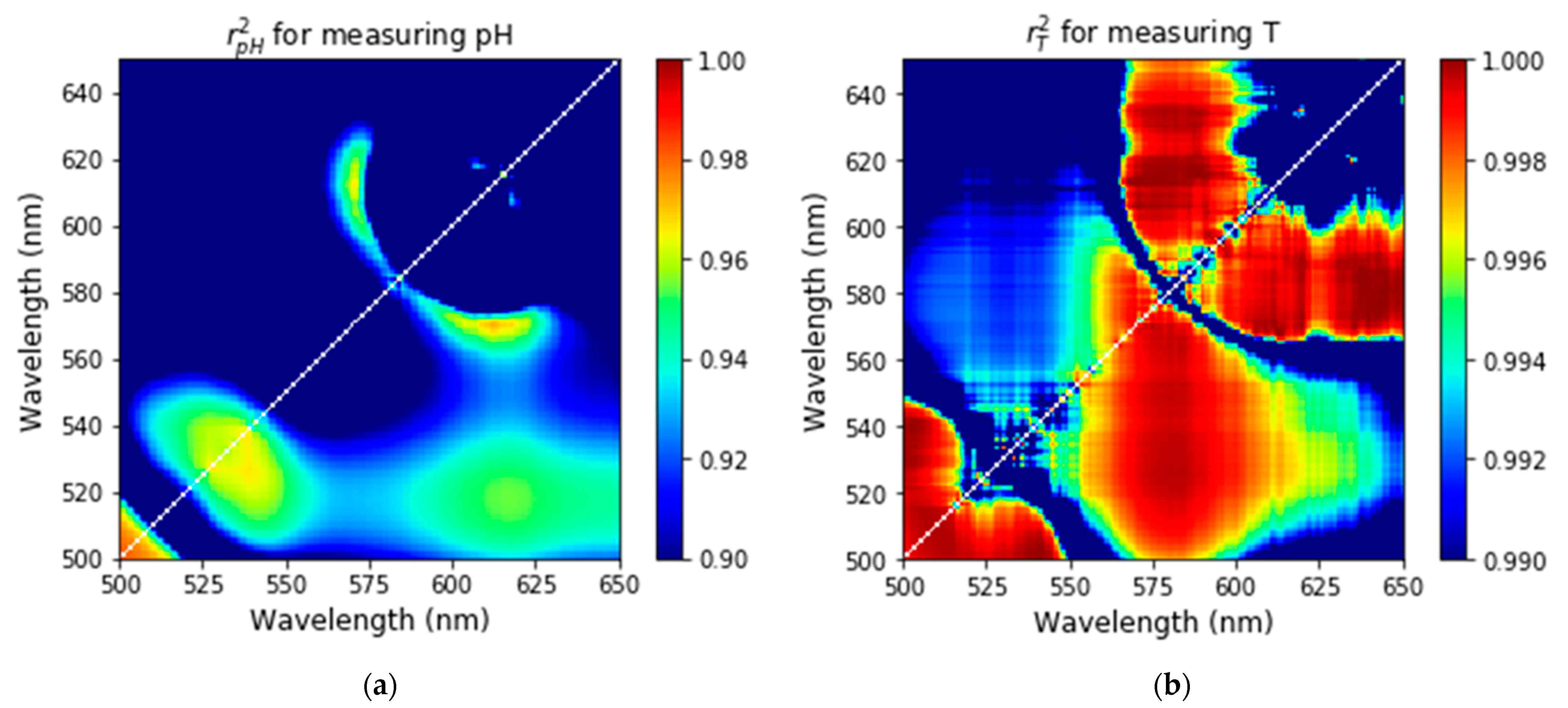
3.4. Finding the Optimal Values of Wavelengths to Measure Temperature and Acidity Simultaneously
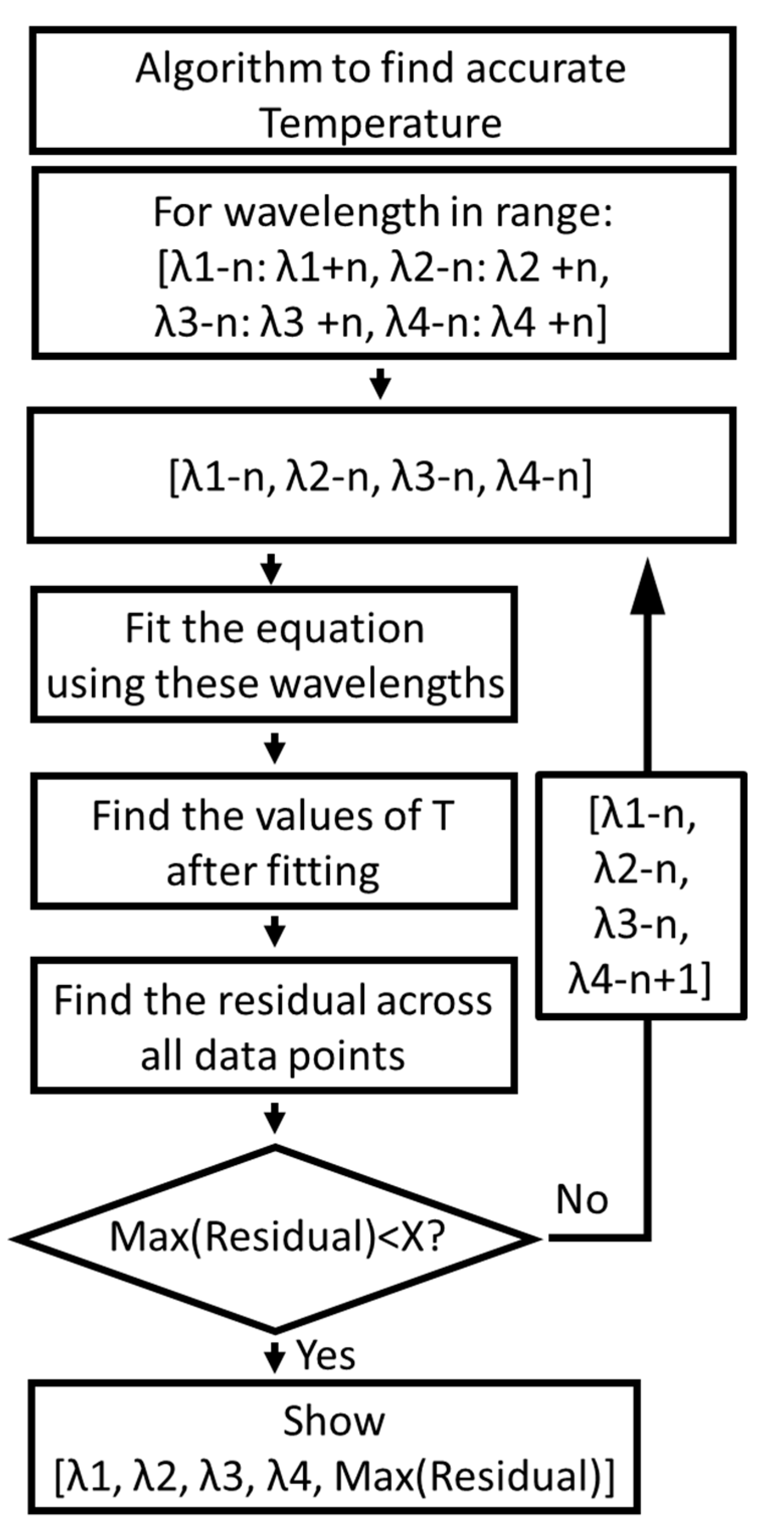
3.5. Algorithm for Further Finding the Optimal Values of Wavelength
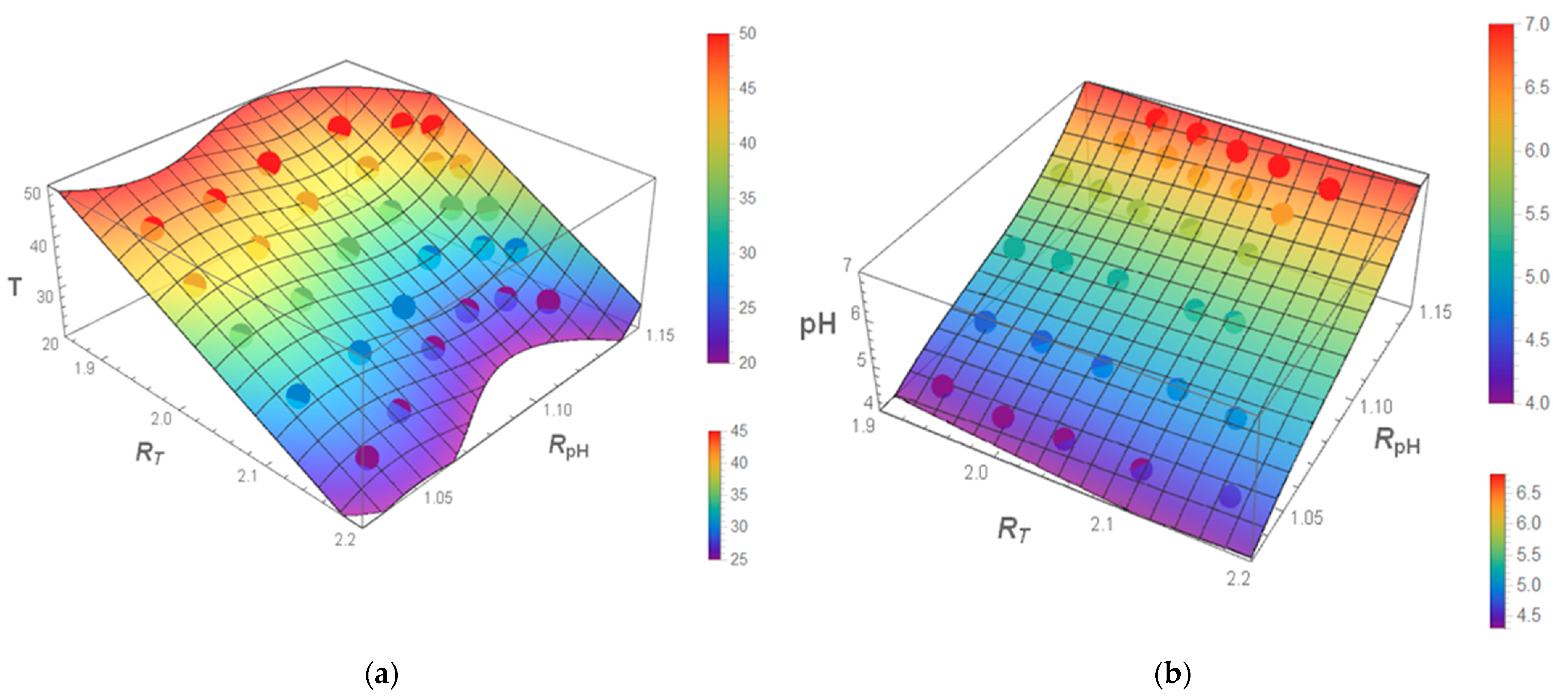
3.6. Multiparametric Fit for pH and Temperature
4. Discussion
4.1. Use of Mesoporous Silica Versus Solid Silica as the Material of the Nanothermometers
4.2. The Problem of Ambiguity of Simultaneous Measurement of Temperature and Acidity
4.3. Multiparametric Sensor
4.4. Stability of the Sensor
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Somero, G.N. Proteins and temperature. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1995, 57, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, C.R.; Singh, M.; Targosinski, S.; Sinha, I.; Sørensen, J.A.; Eriksson, E.; Nuutila, K. The effect of pH on cell viability, cell migration, cell proliferation, wound closure, and wound reepithelialization: In vitro and in vivo study. Wound Repair Regen. 2017, 25, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, E.P.; Brooks, B.R.; Thirumalai, D. Effects of pH on proteins: Predictions for ensemble and single-molecule pulling experiments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 134, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarkar, T.; Selvakumar, K.; Motiei, L.; Margulies, D. Message in a molecule. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Park, N.; Yi, C.; Han, J.H.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, K.P.; Kang, D.H.; Sessler, J.L.; Kang, C.; Kim, J.S. Mitochondria-Immobilized pH-Sensitive Off–On Fluorescent Probe. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14136–14142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, K.; Inada, N.; Gota, C.; Harada, Y.; Funatsu, T.; Uchiyama, S. Intracellular temperature mapping with a fluorescent polymeric thermometer and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, J.; Ding, C.; Zhu, A.; Tian, Y. An efficient core–shell fluorescent silica nanoprobe for ratiometric fluorescence detection of pH in living cells. Analyst 2016, 141, 4766–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Maruyama, H.; Masuda, T.; Honda, A.; Arai, F. Multi-fluorescent micro-sensor for accurate measurement of pH and temperature variations in micro-environments. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalaparthi, V.; Palantavida, S.; Sokolov, I. The nature of ultrabrightness of nanoporous fluorescent particles with physically encapsulated fluorescent dyes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 2197–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, I.; Volkov, D.O. Ultrabright fluorescent mesoporous silica particles. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4247–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.B.; Volkov, D.O.; Sokolov, I. Ultrabright Fluorescent Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Small 2010, 6, 2314–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaparthi, V.; Peng, B.; Peerzade, S.A.M.; Palantavida, S.; Maloy, B.; Dokukin, M.E.; Sokolov, I. Ultrabright fluorescent nanothermometers for absolute measurements of temperature. 2021; under review. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.-d.; Stolwijk, J.A.; Lang, T.; Sperber, M.; Meier, R.J.; Wegener, J.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Ultra-small, highly stable, and sensitive dual nanosensors for imaging intracellular oxygen and pH in cytosol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17011–17014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Del Rosal, B.; Jaque, D.; Uchiyama, S.; Jin, D. Advances and challenges for fluorescence nanothermometry. Nat Methods 2020, 17, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerzade, S.A.M.A.; Qin, X.; Laroche, F.J.F.; Palantavida, S.; Dokukin, M.; Peng, B.; Feng, H.; Sokolov, I. Ultrabright fluorescent silica nanoparticles for in vivo targeting of xenografted human tumors and cancer cells in zebrafish. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 22316–22327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerzade, S.A.M.A.; Makarova, N.; Sokolov, I. Ultrabright Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles for Multiplexed Detection. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.J.; Zahid, M.U.; Le, P.; Ma, L.; Entenberg, D.; Harney, A.S.; Condeelis, J.; Smith, A.M. Brightness-equalized quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, W.C.W.; Maxwell, D.J.; Gao, X.H.; Bailey, R.E.; Han, M.Y.; Nie, S.M. Luminescent quantum dots for multiplexed biological detection and imaging. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.C.W.; Nie, S.M. Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 1998, 281, 2016–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. Superbright multifluorescent core-shell mesoporous nanospheres as trackable transport carrier for drug. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3447–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medintz, I.L.; Uyeda, H.T.; Goldman, E.R.; Mattoussi, H. Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palantavida, S.; Tang, R.; Sudlow, G.P.; Akers, W.J.; Achilefu, S.; Sokolov, I. Ultrabright NIR fluorescent mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 3107–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, K.; Tapec, R.; Tan, W. Conjugation of Biomolecules with Luminophore-Doped Silica Nanoparticles for Photostable Biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 4988–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigaev, A.; Smagley, Y.; Haynes, M.K.; Ursu, O.; Bologa, C.G.; Halip, L.; Oprea, T.; Waller, A.; Carter, M.B.; Zhang, Y. FRET detection of lymphocyte function–associated antigen-1 conformational extension. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Yu, Z.; Alfano, R.; Gersten, J. Picosecond studies of energy transfer of donor and acceptor dye molecules in solution. Phys. Rev. A 1982, 26, 3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabuchi, M.F.; Hetu, M.M.; Tong, W.G. Sensitive analysis of α-synuclein by nonlinear laser wave mixing coupled with capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 500, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birtalan, E.; Rudat, B.; Kölmel, D.K.; Fritz, D.; Vollrath, S.B.; Schepers, U.; Bräse, S. Investigating rhodamine B-labeled peptoids: Scopes and limitations of its applications. Pept. Sci. 2011, 96, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahavendran, S.V.; Karnes, H.T. A high sensitivity laboratory constructed HPLC-VDLIF detector evaluated with an oxazine reagent. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 1997, 25, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, M.; Kele, P.; Achatz, D.E.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Brightly fluorescent purple and blue labels for amines and proteins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 5538–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Xu, Q.-H. Separation distance dependent fluorescence enhancement of fluorescein isothiocyanate by silver nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2007, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaigalas, A.K.; Wang, L. Measurement of the fluorescence quantum yield using a spectrometer with an integrating sphere detector. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2008, 113, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Maruyama, H.; Masuda, T.; Arai, F. Sensitivity compensation of multi-fluorescence sensor toward on-chip cell measurement. In Proceedings of the MHS2013, Nagoya, Japan, 10–13 November 2013; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Bewick, V.; Cheek, L.; Ball, J. Statistics review 7: Correlation and regression. Crit. Care 2003, 7, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Ding, C.; Zhou, J.; Tian, Y. 2D ratiometric fluorescent pH sensor for tracking of cells proliferation and metabolism. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, Y.K.; Wu, W.J.; Li, L.; Lin, K.; Sun, K.; Chen, X.Y.; Li, W.W. Magnetic/Fluorescent Barcodes Based on Cadmium-Free Near-Infrared-Emitting Quantum Dots for Multiplexed Detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 7581–7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shi, C.; Yang, X.; Shen, B.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Sun, H.; Yu, K.; Yang, B. pH-and temperature-sensitive hydrogel nanoparticles with dual photoluminescence for bioprobes. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5856–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Fu, S.; Ke, C.; Shum, P.P.; Liu, D. Characterization of fiber Bragg grating inscribed in few-mode silica-germanate fiber. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2014, 26, 1908–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.J.; Morton, S.W.; Bonner, D.K.; Gu, L.; Ow, H.; Hammond, P.T. A plug-and-play ratiometric pH-sensing nanoprobe for high-throughput investigation of endosomal escape. Biomaterials 2015, 51, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, E.B.; Volkov, D.O.; Sokolov, I. Ultrabright Fluorescent Silica Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Control of Particle Size and Dye Loading. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 3129–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Contributing Dye | Excitation | Emission Range | Absolute Brightness (M−1 cm−1) | Relative Brightness (MESF Units) | Number of Dye Molecules Per Particle | Volume Per One Dye Molecule (nm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FITC | 490 nm | 500–700 nm | (10 ± 1) × 106 | 150 ± 10 | 178 ± 12 | 390 |
| Rb | 550 nm | 560–700 nm | (12 ± 1) × 106 | 387 ± 30 | 385 ± 30 | 180 |
| Nb | 630 nm | 640–700 nm | (40 ± 3) × 106 | 1965 ± 135 | 2475 ± 170 | 28 |
| Coefficients for Equation (4) | Value | Coefficients for Equation (5) | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| At | 51,470 | ApH | 2498 |
| Bt | −166,817 | BpH | −8089 |
| Ct | 180,264 | CpH | 8747 |
| Dt | −91.5 | DpH | 1.04 |
| Et | −64,712 | EpH | −3156 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peerzade, S.A.M.A.; Makarova, N.; Sokolov, I. Ultrabright Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles for Dual pH and Temperature Measurements. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061524
Peerzade SAMA, Makarova N, Sokolov I. Ultrabright Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles for Dual pH and Temperature Measurements. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(6):1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061524
Chicago/Turabian StylePeerzade, Saquib Ahmed M. A., Nadezhda Makarova, and Igor Sokolov. 2021. "Ultrabright Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles for Dual pH and Temperature Measurements" Nanomaterials 11, no. 6: 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061524
APA StylePeerzade, S. A. M. A., Makarova, N., & Sokolov, I. (2021). Ultrabright Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles for Dual pH and Temperature Measurements. Nanomaterials, 11(6), 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061524






