Flower-like SnO2 Nanoparticle Biofabrication Using Pometia pinnata Leaf Extract and Study on Its Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
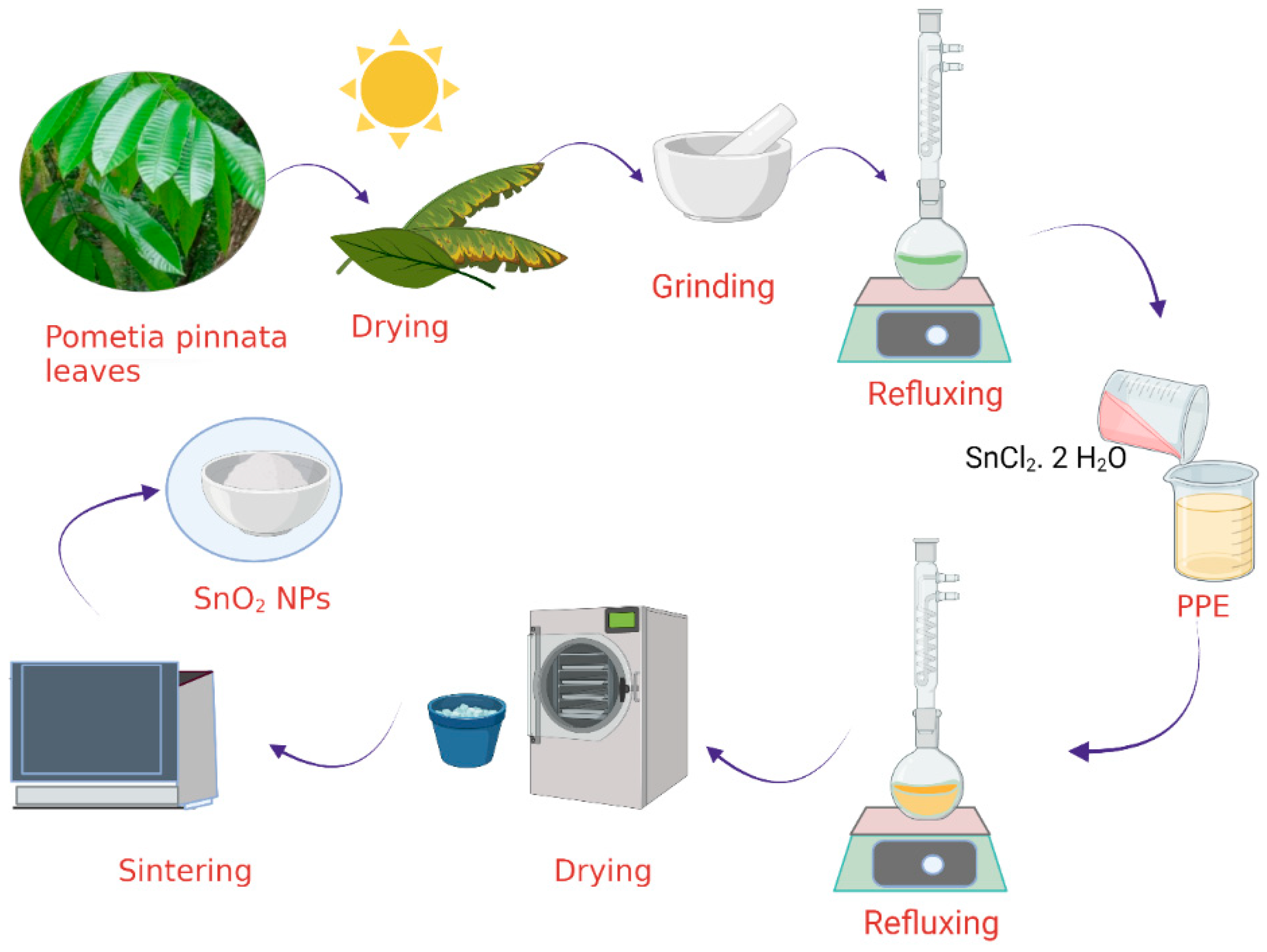
2.2. Extraction of Pometia pinnata Leaves
2.3. Synthesis of SnO2 NPs
2.4. Characterization of SnO2 NPs
2.5. Photocatalytic Activity of SnO2 NPs
2.6. Antibacterial Assay of SnO2 NPs
3. Results
3.1. SnO2 NP Synthesis and Characterization
3.2. Optical Properties of SnO2 NPs
3.3. Photocatalytic Activity
3.4. Identification on Oxidation Mechanism
3.5. Effect of Scavenger
3.6. Reusability of Photocatalysts
3.7. Antibacterial Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frenzilli, G. Nanotechnology for environmental and biomedical research. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsi, I.; Winther-Nielsen, M.; Sethi, R.; Punta, C.; Della Torre, C.; Libralato, G.; Lofrano, G.; Sabatini, L.; Aiello, M.; Fiordi, L.; et al. Ecofriendly nanotechnologies and nanomaterials for environmental applications: Key issue and consensus recommendations for sustainable and ecosafe nanoremediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 154, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Dutta, T.; Kim, K.H.; Rawat, M.; Samddar, P.; Kumar, P. “Green” synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: Applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnology 2018, 16, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Nam Ong, C.; Xie, J. Emerging nanotechnology for environmental applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2016, 5, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, X.L.; Gu, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, G.W. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Potential Applications to Treat Cancer. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Sabouri, Z.; Hosseini, H.A.; Hashemzadeh, A.; Khatami, M.; Darroudi, M. Effect of nickel oxide nanoparticles as a photocatalyst in dyes degradation and evaluation of effective parameters in their removal from aqueous environments. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 115, 107867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Kumar, J.; Thakur, S.; Sharma, S.; Shrivastava, V. Antibacterial study of silver doped zinc oxide nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis. Drug Invent. Today 2013, 5, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.M.; Ahmed, A.I.; Mannaa, M.A. Preparation and characterization of SnO2 doped TiO2 nanoparticles: Effect of phase changes on the photocatalytic and catalytic activity. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2019, 4, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezrianjoo, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.-H.; Kumar, V. Eco-Toxicological and Kinetic Evaluation of TiO2 and ZnO Nanophotocatalysts in Degradation of Organic Dye. Catalysts 2019, 9, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suresh, K.C.; Balamurugan, A. Evaluation of structural, optical, and morphological properties of nickel oxide nanoparticles for multi-functional applications. Inorg. Nano-Metal. Chem. 2021, 51, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, A.; Sakthivel, R.; Mallika, J.; Kannusamy, R.; Rajendran, R. Green Synthesis of Antibacterial Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Biopolymer Azadirachta indica Gum. Orient. J. Chem. 2015, 32, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugazhendhi, S.; Sathya, P.; Palanisamy, P.K.; Gopalakrishnan, R. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles through green approach using Dioscorea alata and their characterization on antibacterial activities and optical limiting behavior. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 159, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalithambika, K.C.; Thayumanavan, A.; Ravichandran, K.; Sriram, S. Photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of eco-friendly green synthesized ZnO and NiO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 2062–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, I.; Hidayat, H.; Nugroho, B.H.; Husein, S. Ultrasound-assisted biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Clitoria ternatea flower. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 34, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritha, E.; Roopan, S.M.; Madhavi, G.; Elango, G.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Arasu, M.V. Green chemical approach towards the synthesis of SnO2 NPs in argument with photocatalytic degradation of diazo dye and its kinetic studies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 162, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, S.; Ahmaruzzaman, M. Green synthesis of SnO2 quantum dots using Parkia speciosa Hassk pods extract for the evaluation of anti-oxidant and photocatalytic properties. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 184, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, M.S.; Aqeel, M.; Haider, A.; Naz, S.; Ikram, M.; Ul-Hamid, A.; Haider, J.; Aslam, I.; Nazir, A.; Butt, A.R. Photocatalytic, Bactericidal and Molecular Docking Analysis of Annealed Tin Oxide Nanostructures. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matussin, S.; Harunsani, M.H.; Tan, A.L.; Khan, M.M. Plant-Extract-Mediated SnO2 Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 3040–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prihanti, G.S.; Katjasungkana, R.M.K.; Novitasari, B.R.; Amalia, S.R.; Nurfajriana, A.; Agustini, S.M.; Cakrawati, H.; Andari, D. Antidiabetic potential of matoa bark extract (pometia pinnata) in alloxan-induced diabetic male rat strain wistar (rattus norvegicus). Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauriasari, R.A.N.I.; Azizah, N.; Basah, K. Tyrosinase Inhibition 2,2-Diphenul-1-picrylhydraxyl Radical Scavening Activity, and Phytochemical Screening of Fractions and Ethanol Extract from Leaves and Steam Bark of Matoa (Pometia Pinnata). Asian J. Pharmacetical Clin. Res. 2017, 10, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Handayani, W.; Ningrum, A.S.; Imawan, C. The Role of pH in Synthesis Silver Nanoparticles Using Pometia pinnata (Matoa) Leaves Extract as Bioreductor. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1428, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujatmiko, F.; Sahroni, I.; Fadillah, G.; Fatimah, I. Visible light-responsive photocatalyst of SnO2/rGO prepared using Pometia pinnata leaf extract. Open Chem. 2021, 19, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suedee, A.; Tewtrakul, S.; Panichayupakaranant, P. Anti-HIV-1 integrase compound from Pometia pinnata leaves. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purwidyaningrum, I.; Sukandar, E.Y.; Fidrianny, I. Diuretic activity of matoa leaves extracts and fractions (Pometia pinnata J.R. Forster & J.G Forster) and its influence on potassium and sodium levels. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2017, 10, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bibi, I.; Kamal, S.; Ahmed, A.; Iqbal, M.; Nouren, S.; Jilani, K.; Nazar, N.; Amir, M.; Abbas, A.; Ata, S.; et al. Nickel nanoparticle synthesis using Camellia Sinensis as reducing and capping agent: Growth mechanism and photo-catalytic activity evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, H.Q.; Yu, H.W. Synthesis of Monodisperse Walnut-Like SnO2 Spheres and Their Photocatalytic Performances. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhosale, T.T.; Shinde, H.M.; Gavade, N.L.; Babar, S.B.; Gawade, V.V.; Sabale, S.R.; Kamble, R.J.; Shirke, B.S.; Garadkar, K.M. Biosynthesis of SnO2 nanoparticles by aqueous leaf extract of Calotropis gigantea for photocatalytic applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 6826–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, I.; Sahroni, I.; Muraza, O.; Doong, R.A. One-pot biosynthesis of SnO2 quantum dots mediated by Clitoria ternatea flower extract for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwoka, M.; Lyson-Sypien, B.; Kulis, A.; Zappa, D.; Comini, E. Surface properties of SnO2 nanowires deposited on Si substrate covered by Au catalyst studies by XPS, TDS and SEM. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.P.; Choi, M.Y.; Choi, H.C. Photocatalytic activity of SnO2 nanoparticles in methylene blue degradation. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 74, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Luo, P.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, L. One-step facile synthesis of hierarchically porous nitrogen-doped SnO2 nanoparticles with ultrahigh surface area for enhanced lithium storage performance. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 5667–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebreslassie, Y.T.; Gebretnsae, H.G. Green and Cost-Effective Synthesis of Tin Oxide Nanoparticles: A Review on the SYnthesis Methodologies, Mechanism of Formation, and Their Potential Applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awoke, N.; Pandey, D.; Habtemariam, A.B. Synthesis of Tin(IV) Oxide Nanoparticles Using Plant Leaf Extracts of Vernonia amygdalina and Mentha spicata. Regen. Eng. Transl. Med. 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomathi, E.; Jayapriya, M.; Arulmozhi, M. Environmental benign synthesis of tin oxide (SnO2) nanoparticles using Actinidia deliciosa (Kiwi) peel extract with enhanced catalytic properties. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 130, 108670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Enazi, N.M.; Ameen, F.; Alsamhary, K.; Dawoud, T.; Al-Khattaf, F.; AlNadhari, S. Tin oxide nanoparticles (SnO2-NPs) synthesis using Galaxaura elongata and its anti-microbial and cytotoxicity study: A greenery approach. Appl. Sci. 2021, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J. Biosynthesis of SnO2 nanoparticles by fig (Ficus Carica) leaf extract for electrochemically determining Hg(II) in water samples. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 10668–10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wicaksono, W.P.; Sahroni, I.; Saba, A.K.; Rahman, R.; Fatimah, I. Biofabricated SnO2 nanoparticles using Red Spinach (Amaranthus tricolor L.) extract and the study on photocatalytic and electrochemical sensing activity. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 075009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.B.; Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W. A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: Synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjati, F.; Citradewi, P.W.; Purwiandono, G.; Fatimah, I. Green synthesis of hematite/TUD-1 nanocomposite as efficient photocatalyst for bromophenol blue and methyl violet degradation. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 8395–8410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.M.; Hong, G.B.; Lee, S.C. Facile synthesis of tin dioxide nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of Congo red dye in aqueous solution. Catalysts 2020, 10, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsaprom, K.; Winyayong, A.; Maensiri, S. Synthesis and room-temperature ferromagnetism in flower-like SnO2 nanostructures. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1144, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, E.; Nadjia, L.; Rose-noe, V. Adsorption of Congo red azo dye on nanosized SnO2 derived from sol-gel method. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2016, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, K.Y.; Muralidhara, H.B.; Nayaka, Y.A.; Balasubramanyam, J.; Hanumanthappa, H. Low-cost synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles and their application in adsorption of commercial dye and heavy metal ion in aqueous solution. Powder Technol. 2013, 246, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houas, A.; Lachheb, H.; Ksibi, M.; Elaloui, E.; Guillard, C.; Herrmann, J.M. Photocatalytic degradation pathway of methylene blue in water. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 31, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, T.; Gul, T.; Saeed, K. Photodegradation of bromophenol blue in aqueous medium using graphene nanoplates-supported TiO2. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A.; Hushmandrad, S. Solar photodecolorization of methylene blue by CuO/X zeolite as a heterogeneous catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 388, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, I.; Rubiyanto, D.; Sahroni, I.; Putra, R.S.; Nurillahi, R.; Nugraha, J. Physicochemical characteristics and photocatalytic performance of Tin oxide/montmorillonite nanocomposites at various Sn/montmorillonite molar to mass ratios. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 193, 105671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A.; Zabihi-Mobarakeh, H. Heterogeneous photodecolorization of mixture of methylene blue and bromophenol blue using CuO-nano-clinoptilolite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarkodi, C.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Paulkumar, K.; Vanaja, M.; Gnanajobitha, G.; Annadurai, G. Biosynthesis and antimicrobial activity of semiconductor nanoparticles against oral pathogens. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2014, 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burdușel, A.C.; Gherasim, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoantă, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Biomedical applications of silver nanoparticles: An up-to-date overview. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wikaningtyas, P.; Sukandar, E.Y. The antibacterial activity of selected plants towards resistant bacteria isolated from clinical specimens. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhavana, S.; Gubbiveeranna, V.; Kusuma, C.G.; Ravikumar, H.; Sumachirayu, C.K.; Nagabhushana, H.; Nagaraju, S. Facile Green Synthesis of SnO2 NPs Using Vitex altissima (L.) Leaves Extracts: Characterization and Evaluation of Antibacterial and Anticancer Properties. J. Clust. Sci. 2019, 30, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizaj, S.M.; Lotfipour, F.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Zarrintan, M.H.; Adibkia, K. Antimicrobial activity of the metals and metal oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 44, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, N.; Somaraj, M.; Tharayil, N.J. Synthesis, Characterization and Anti—Bacterial Activities of SnO2 Nanoparticles Using Biological Molecule. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 360, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, M.; Chitra, S.; Nalini Jayanthi, N. Synthesis and Characterization of Tin Oxide Nanoparticles Using Plant Extract. Pharma Chem. 2018, 10, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Naikoo, G.A.; Mustaqeem, M.; Hassan, I.U.; Awan, T.; Arshad, F.; Salim, H.; Qurashi, A. Bioinspired and green synthesis of nanoparticles from plant extracts with antiviral and antimicrobial properties: A critical review. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidhu, V.K.; Philip, D. Materials Characterization Phytosynthesis and applications of bioactive SnO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Charact. 2015, 101, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.; Mishra, N.; Gadani, K.; Solanki, P.S.; Shah, N.A. Mechanism of Anti-bacterial Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Against Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]














| Bioreductor. | Morphology | Particle Size (nm) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camellia sinensis flower extract | spherical | 5–30 | [32] |
| Vernonia amygdalina leaf extract | nanorod | 6.45 | [33] |
| Menta spicata leaf extract | nanorod | 7.35 | [33] |
| Actinidia deliciosa (Kiwi) peel extract. | spherical | 20 | [34] |
| Galaxaura elongata | spherical | 35 | [35] |
| Ficus Carica leaf | spherical | 128 | [36] |
| Calotropis gigantea | irregular | 35 | [27] |
| Vitex altissima (L.) Leaf Extract | spherical | 20 | [27] |
| Red spinach leaf extract | Spherical | 20–40 | [37] |
| Initial Concentration | Light | R2 of the Second Order Kinetics | Kinetics Constant k (L/mg.min) | DE at 120 min (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | UV | 0.997 | 3.41 | 99.93 |
| 5 | UV | 0.993 | 0.72 | 98.52 |
| 10 | UV | 0.995 | 0.60 | 94.50 |
| 25 | UV | 0.994 | 0.21 | 92.85 |
| 2 | Visible | 0.994 | 0.67 | 93.29 |
| 5 | Visible | 0.996 | 0.63 | 95.85 |
| 10 | Visible | 0.996 | 0.60 | 94.50 |
| 25 | Visible | 0.996 | 0.21 | 85.16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fatimah, I.; Purwiandono, G.; Hidayat, H.; Sagadevan, S.; Ghazali, S.A.I.S.M.; Oh, W.-C.; Doong, R.-A. Flower-like SnO2 Nanoparticle Biofabrication Using Pometia pinnata Leaf Extract and Study on Its Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Activities. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113012
Fatimah I, Purwiandono G, Hidayat H, Sagadevan S, Ghazali SAISM, Oh W-C, Doong R-A. Flower-like SnO2 Nanoparticle Biofabrication Using Pometia pinnata Leaf Extract and Study on Its Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Activities. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113012
Chicago/Turabian StyleFatimah, Is, Gani Purwiandono, Habibi Hidayat, Suresh Sagadevan, Sheikh Ahmad Izaddin Sheikh Mohd Ghazali, Won-Chun Oh, and Ruey-An Doong. 2021. "Flower-like SnO2 Nanoparticle Biofabrication Using Pometia pinnata Leaf Extract and Study on Its Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Activities" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113012
APA StyleFatimah, I., Purwiandono, G., Hidayat, H., Sagadevan, S., Ghazali, S. A. I. S. M., Oh, W.-C., & Doong, R.-A. (2021). Flower-like SnO2 Nanoparticle Biofabrication Using Pometia pinnata Leaf Extract and Study on Its Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Activities. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113012









