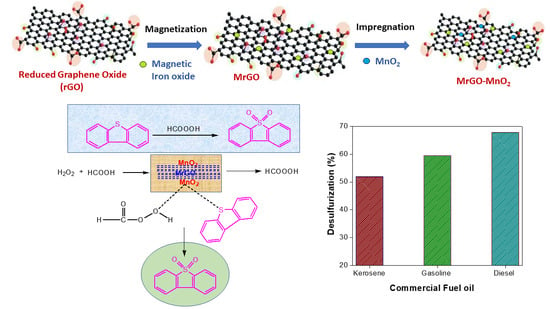
Oxidative Desulfurization of Petroleum Distillate Fractions Using Manganese Dioxide Supported on Magnetic Reduced Graphene Oxide as Catalyst
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of MnO2/MrGO Composite Catalyst
2.3. Characterization of the Catalyst
2.4. ODS Activity of the Catalyst
2.5. Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
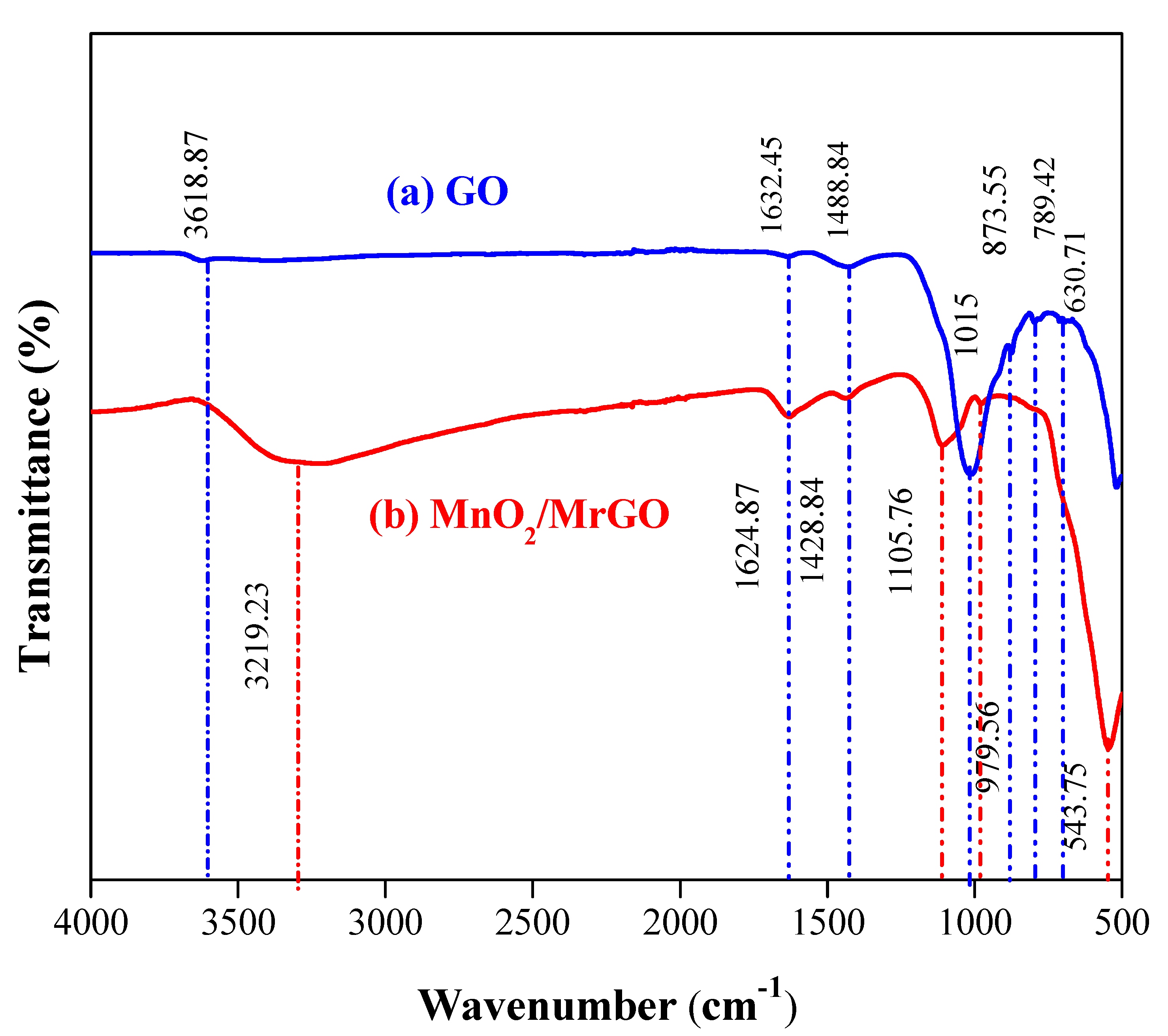
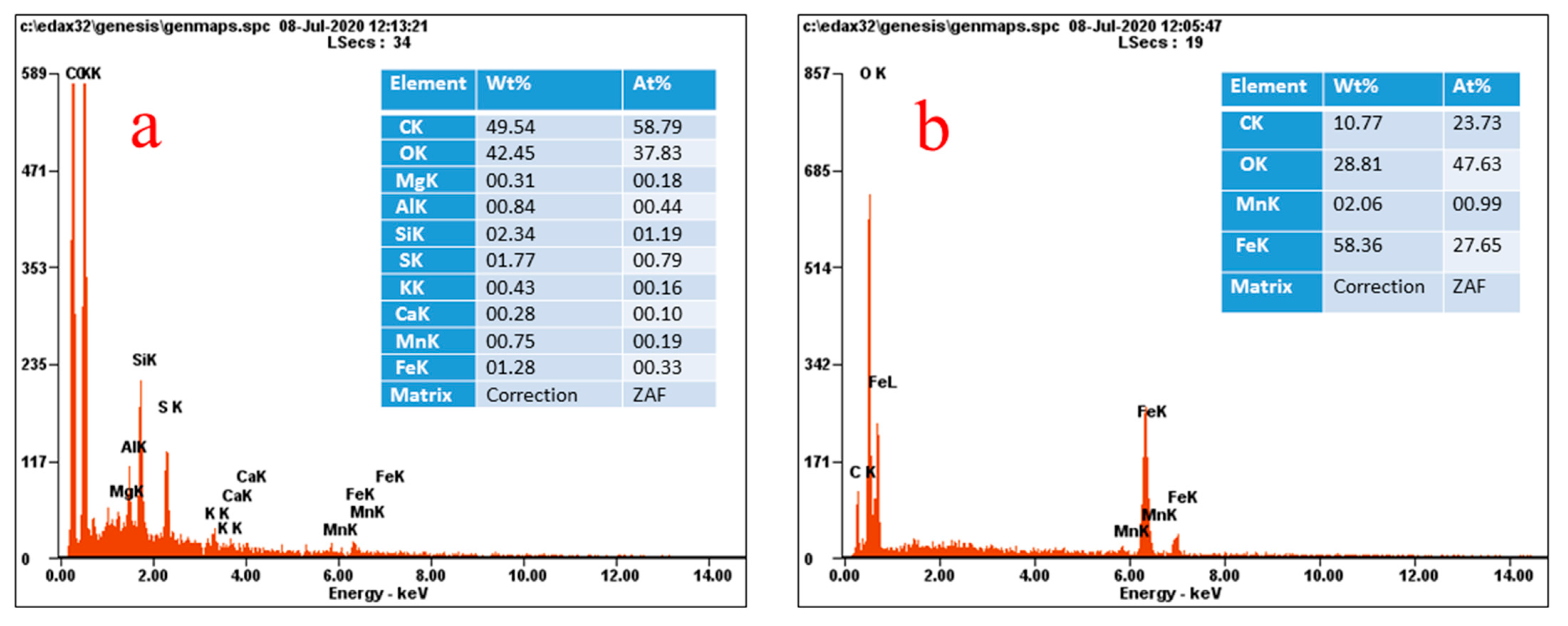
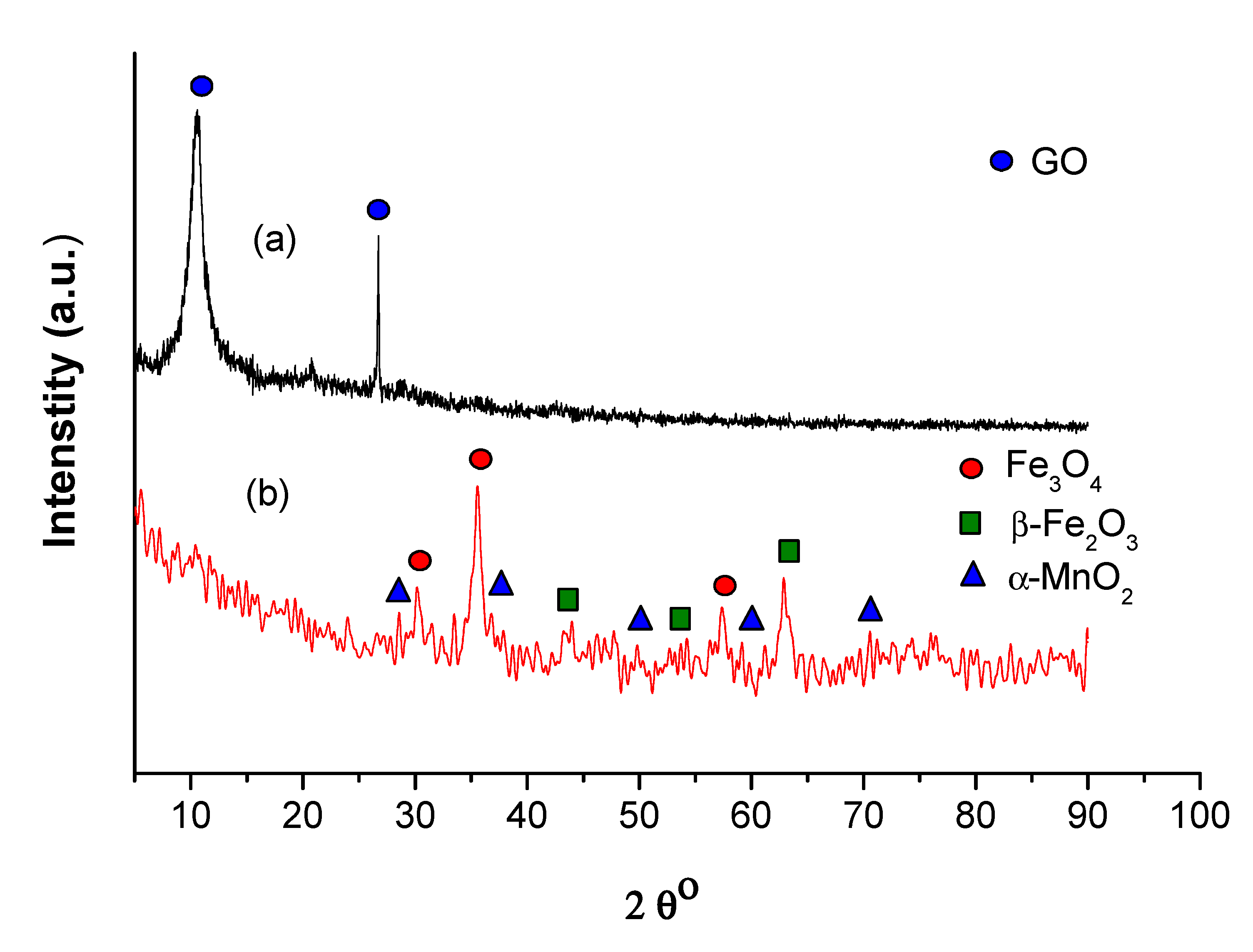
3.1. Characterization of the Catalyst
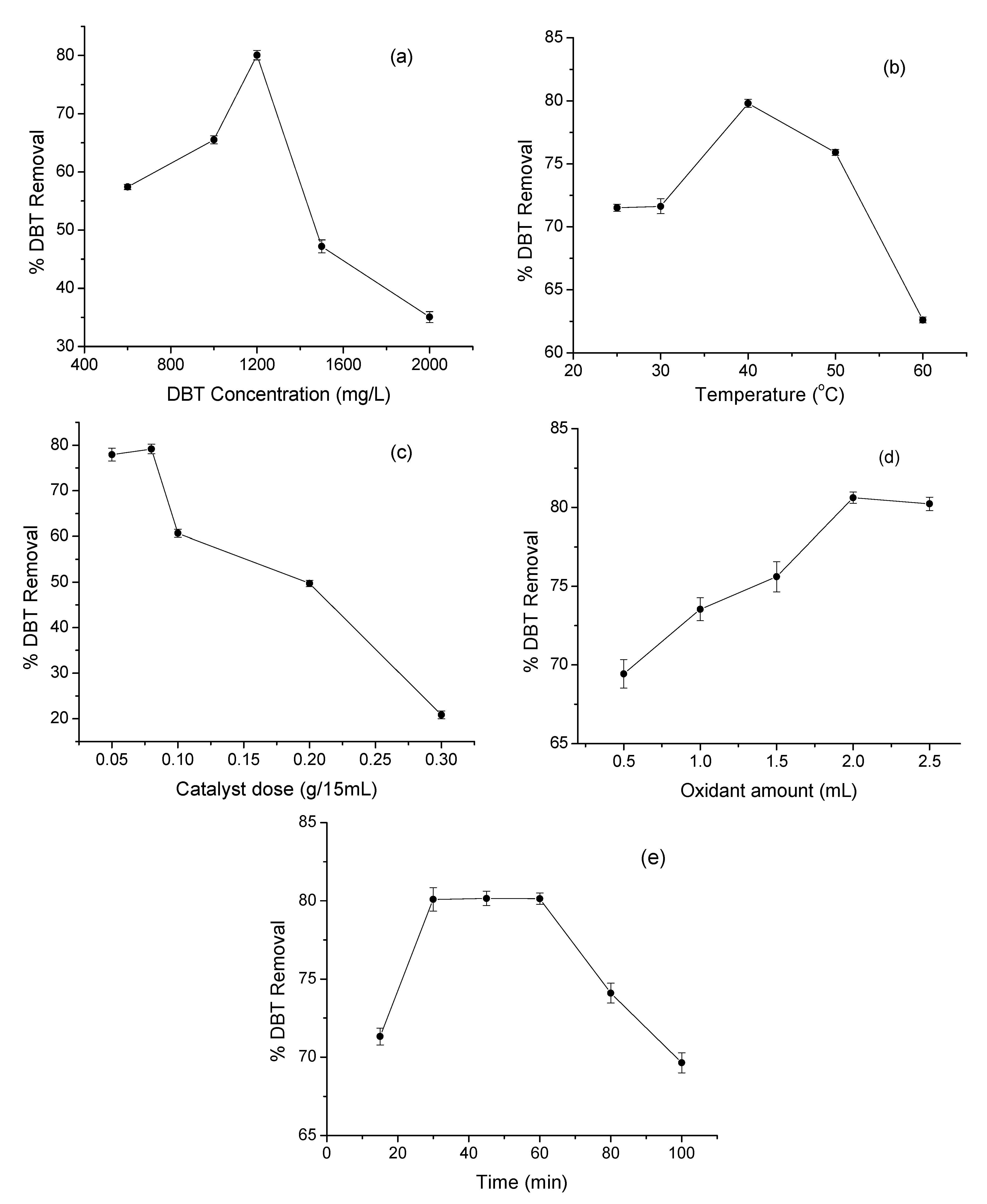
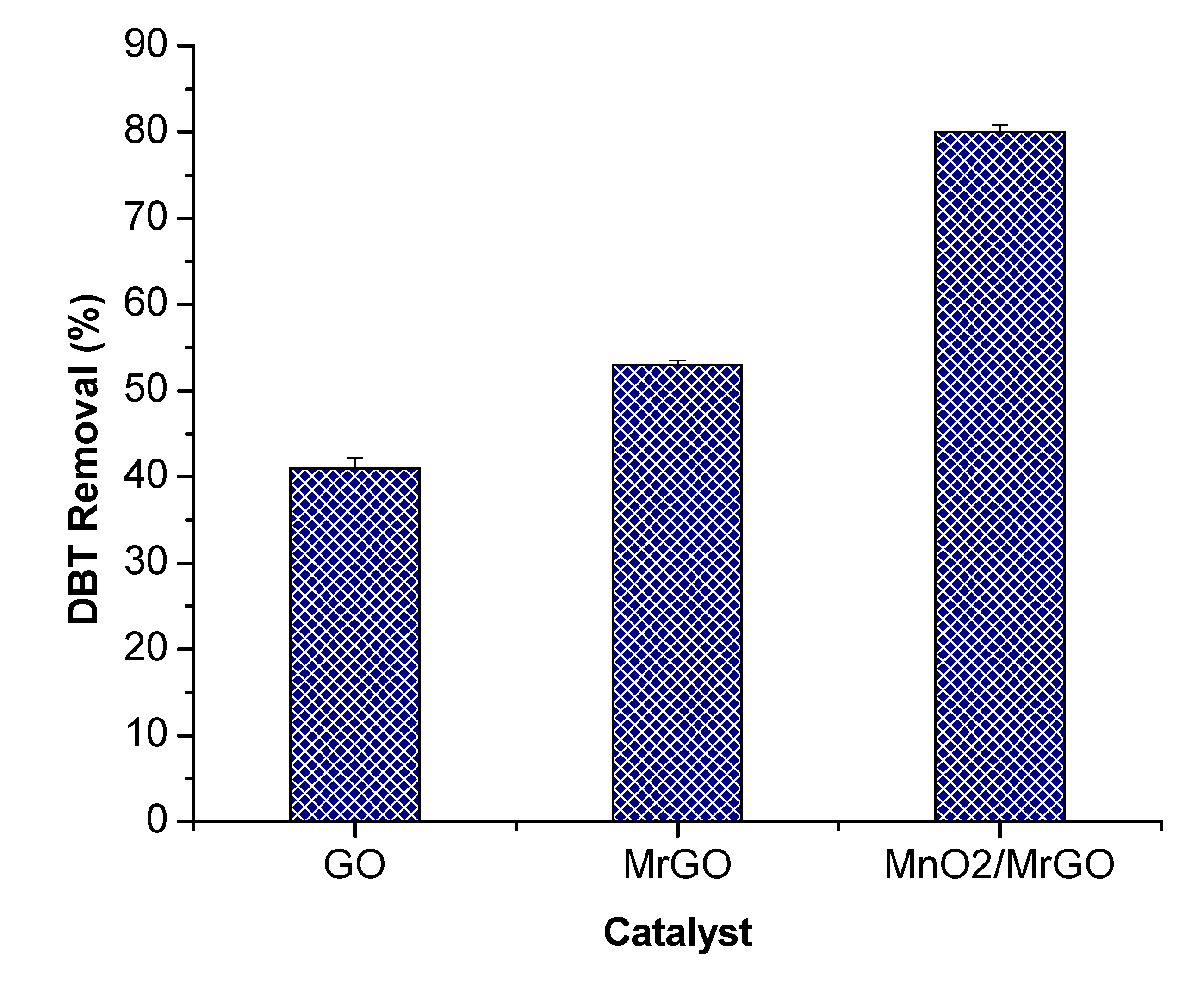
3.2. ODS Activity of MnO2/MrGO
3.3. Effect of Temperature and Kinetic Study
3.4. Regeneration and Recycling of the Catalyst
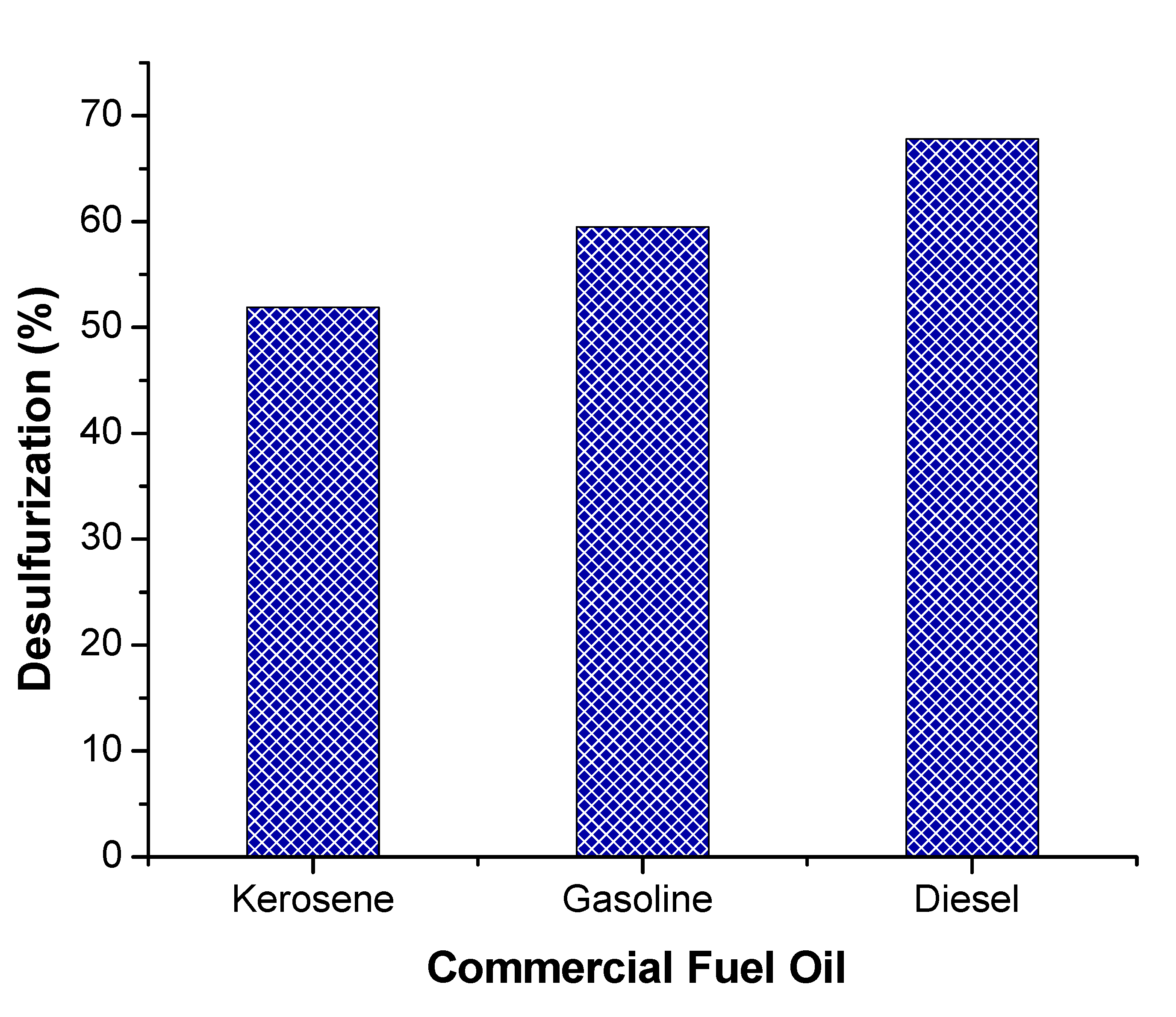
3.5. Catalytic ODS of Commercial Oil Sample
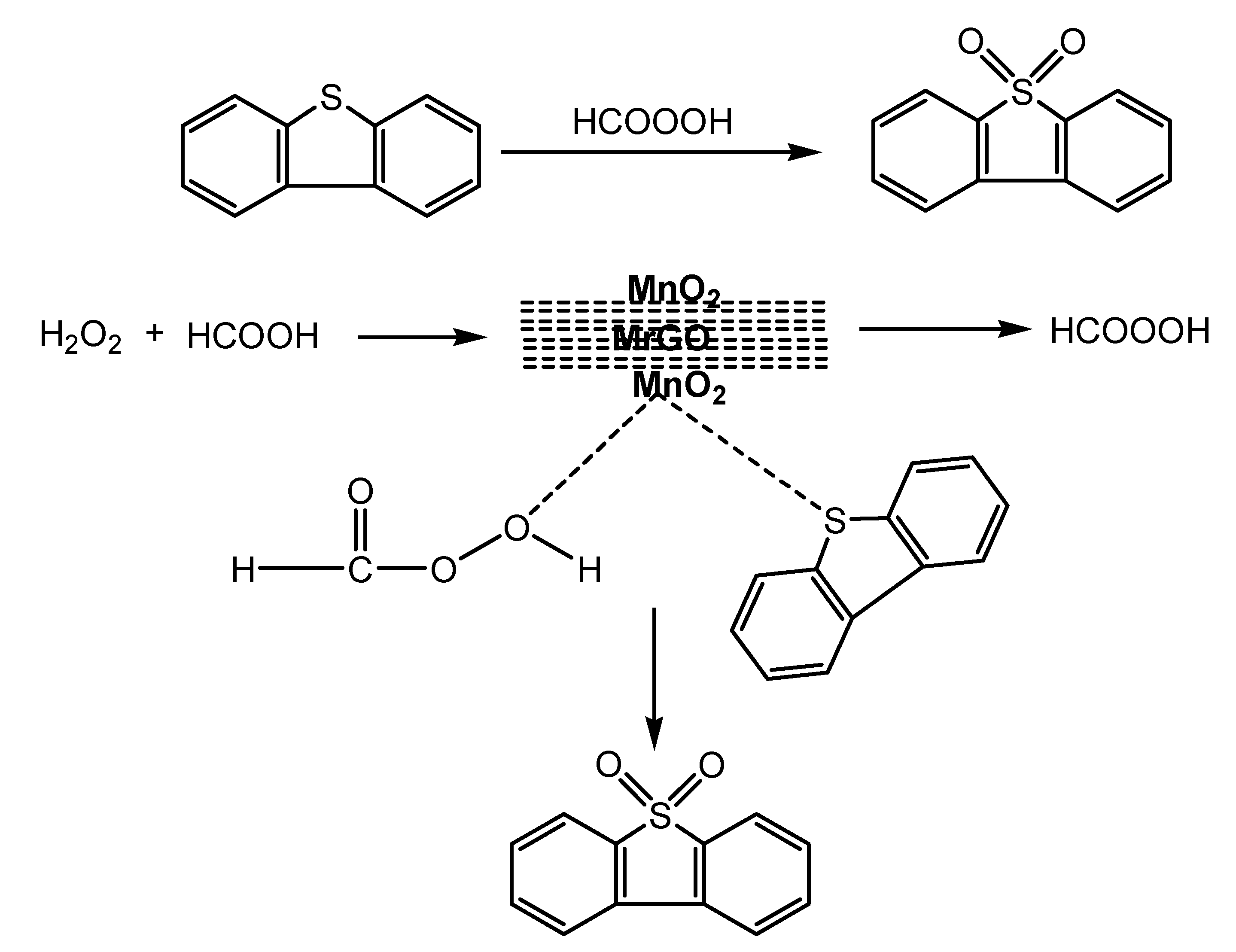
3.6. Suggested Mechanism for ODS of DBT by MnO2/MrGO
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| rGO | reduced Graphene oxide |
| MrGO | Magnetic reduce graphene oxide |
| TBHP | Tertiary butyl hydroperoxide |
| SRGO | Straight run gas oil |
| MMT | Montmorillonite |
| RON | Research Octane Number |
References
- Farshi, A.; Shiralizadeh, P. Sulfur reduction of heavy fuel oil by oxidative desulfurization (ODS) method. Pet. Coal 2015, 57, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, Y.; Shoukat, A.; Rahman, A.U.; Rashid, H.U.; Ahmad, W. Oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene over Fe promoted Co–Mo/Al2O3 and Ni–Mo/Al2O3 catalysts using hydrogen peroxide and formic acid as oxidants. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, P.S.; Kittrell, J.R.; Eldridge, J.W. Desulfurization of fuel oil by oxidation and extraction 1. Enhancement of extraction oil yield. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1990, 29, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, W.A.; Ali, R.; Kadir, A.; Mokhtar, W.N.A.W. Effect of transition metal oxides catalysts on oxidative desulfurization of model diesel. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 101, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhai, Z.; Lu, Y.; Yang, L.; Luo, G. Optimization of composition of a directly combined catalyst in dibenzothiophene oxidation for deep desulfurization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, A.; Cui, T.Y.; Fan, H.X.; Yang, Z.F.; Feng, J.; Li, W.Y. A comprehensive review on oxidative desulfurization catalysts targeting clean energy and environment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 2246–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M. Review on recent patents in sulfur removal from liquid fuels by oxidative desulfurization (ODS) process. Recent Pat. Chem. Eng. 2010, 3, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.W.; Gao, R.M.; Zhang, R.L.; Zhao, J.S. Template method for a hybrid catalyst material POM@ MOF-199 anchored on MCM-41: Highly oxidative desulfurization of DBT under molecular oxygen. Fuel 2016, 184, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeelani, G.G.; Ashrafi, A.; Dhakad, A.; Gupta, G.; Pal, S.L. Catalytic oxidative desulfurization of liquid fuels: A review. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2016, 3, 331–336. [Google Scholar]
- Subhan, S.; Muhammad, Y.; Sahibzada, M.; Subhan, F.; Tong, Z. Studies on the selection of a catalyst–oxidant system for the energy-efficient desulfurization and denitrogenation of fuel oil at mild operating conditions. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 8423–8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gutiérrez, J.L.; Fuentes, G.A.; Hernández-Terán, M.E.; Garcia, P.; Murrieta-Guevara, F.; Jiménez-Cruz, F. Ultra-deep oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuel by the Mo/Al2O3-H2O2 system: The effect of system parameters on catalytic activity. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 334, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueras, F.; Palomeque, J.; Loridant, S.; Fèche, C.; Essayem, N.; Gelbard, G. Influence of the coordination on the catalytic properties of supported W catalysts. J. Catal. 2004, 226, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.E.; Ren, T. Sulfide oxygenation by tert-butyl hydroperoxide with mononuclear (Me3TACN) Mn catalysts. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 6805–6808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.; Jeong, K.-E.; Chae, H.-J.; Kim, C.-U.; Jeong, S.-Y. Oxidative desulfurization of 4, 6-dimethyl dibenzothiophene and light cycle oil over supported molybdenum oxide catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 1966–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, R.; Iruretagoyena, D.; Wang, Y.; Bawaked, S.M.; Mokhtar, M.; Al-Thabaiti, S.A.; Basahel, S.N.; Shaffer, M.S. Graphene oxide/mixed metal oxide hybrid materials for enhanced adsorption desulfurization of liquid hydrocarbon fuels. Fuel 2016, 181, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, M.A.; Khandan, S. Synthesis and characterization of new sandwich-type polyoxometalate/nanoceramic nanocomposite, Fe2W18Fe4@FeTiO3, as a highly efficient heterogeneous nanocatalyst for desulfurization of fuel. Solid State Sci. 2019, 98, 106036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, S.; Yang, N.; Tantai, X.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, B.; Sun, Y. Porous hybrid nanoflower self-assembled from polyoxometalate and polyionene for efficient oxidative desulfurization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 3618–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Ahmad, I. Mechanisms of desulfurization by nanomaterials. In Nanotechnology in Oil and Gas Industries; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 211–243. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Guzman, M.I. CO2 reduction under periodic illumination of ZnS. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 11649–11656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-F.; Kou, S.-C. Sulfur dioxide degradation by composite photocatalysts prepared by recycled fine aggregates and nanoscale titanium dioxide. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Wu, P.; Zhu, L.; He, J.; Tao, D.; Lu, L.; He, M.; Hua, M.; Li, H.; Zhu, W. High-entropy oxide stabilized molybdenum oxide via high temperature for deep oxidative desulfurization. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 20, 100680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Dai, B.; Xu, C.; Liu, P.; Qi, L.; Ban, L. Deep oxidative desulfurization of model fuel via dielectric barrier discharge plasma oxidation using MnO2 catalysts and combination of ionic liquid extraction. Catal. Today 2013, 211, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, R.; Liu, W.; Fu, G.; Liu, C.; Hu, L.; Wang, H. Linkages between ENSO/PDO signals and precipitation, streamflow in China during the last 100 years. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bineesh, K.V.; Kim, D.K.; Cho, H.J.; Park, D.W. Synthesis of metal-oxide pillared montmorillonite clay for the selective catalytic oxidation of H2S. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2010, 16, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betiha, M.A.; Rabie, A.M.; Ahmed, H.S.; Abdelrahman, A.A.; El-Shahat, M.F. Oxidative desulfurization using graphene and its composites for fuel containing thiophene and its derivatives: An update review. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjar, Z.; Kazemeini, M.; Rashidi, A.; Bazmi, M. Graphene based catalysts for deep hydrodesulfurization of naphtha and diesel fuels: A physiochemical study. Fuel 2016, 165, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, R. Nanocarbon materials for oxidative-adsorptive desulfurization using air oxygen under mild conditions. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 73, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Wen, G.; Ding, Y.; Wu, K.-H.; Chen, C.; Su, D. Reduced graphene oxide: A metal-free catalyst for aerobic oxidative desulfurization. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Ahmad, W.; Ahmad, I.; Khan, M.; Iqbal Khattak, M.; Hussain, F. Adsorption and recovery of hexavalent chromium from tannery wastewater over magnetic max phase composite. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wang, C.; Luo, S.; Dong, R.; Tu, X.; Zeng, G. Adsorption of as (III) and as (V) from water using magnetite Fe3O4-reduced graphite oxide–MnO2 nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 187, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, V.; Park, J.; Chun, Y.; Lee, J.W.; Hwang, I.-C.; Kim, K.S. Water-dispersible magnetite-reduced graphene oxide composites for arsenic removal. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3979–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumming, J.; Xiangqin, L. Electrochemical synthesis of Fe3O4-PB nanoparticles with core-shell structure and its electrocatalytic reduction toward H2O2. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2009, 13, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Biswas, H.; Dutta, J.; Ray, N.R.; Ghosh, U.C. Ceria associated manganese oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and arsenic (V) sorption behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizaji, A.K.; Mokhtarani, B.; Mortaheb, H.R. Deep and fast oxidative desulfurization of fuels using graphene oxide-based phosphotungstic acid catalysts. Fuel 2019, 236, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Huang, C.J.; Lin, C.H.; Huang, C.P. Catalytic degradation of chlorpheniramine over GO-Fe3O4 in the presence of H2O2 in water: The synergistic effect of adsorption. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anyika, C.; Asri, N.A.M.; Majid, Z.A.; Yahya, A.; Jaafar, J. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic activated carbon developed from palm kernel shells. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2017, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, V.P.; Le, N.C.; Nguyen, T.P.T.; Nguyen, N.T. Synthesis of α-MnO2 Nanomaterial from a Precursor γ-MnO2: Characterization and Comparative Adsorption of Pb(II) and Fe(III). J. Chem. 2016, 2016, 8285717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhan, S.; Rahman, A.U.; Yaseen, M.; Rashid, H.U.; Ishaq, M.; Sahibzada, M.; Tong, Z. Ultra-fast and highly efficient catalytic oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene at ambient temperature over low Mn loaded Co-Mo/Al2O3 and Ni-Mo/Al2O3 catalysts using NaClO as oxidant. Fuel 2019, 237, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikarwar, P.; Kumar, U.A.; Gosu, V.; Subbaramaiah, V. Catalytic oxidative desulfurization of DBT using green catalyst (Mo/MCM-41) derived from coal fly ash. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Ahmad, W.; Ahmad, I.; Guo, S. Enhanced and Facile Desulfurization of Commercial Oil Using Air-Assisted Performic Acid Oxidation System. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 36, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, Z.; Jeon, J.; Jhung, S.H. Oxidative desulfurization of benzothiophene and thiophene with WOx/ZrO2 catalysts: Effect of calcination temperature of catalysts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 205, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.P.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.H.; Liu, H.P.; Qiao, C.Z. Immobilization of acidic ionic liquid on silica gel for catalytic oxidative desulfurization of fuel oils (II): Desulfurization. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Freienbach, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.; Benxian, S.; Zhou, X. An improved desulfurization process based on H2O2/formic acid oxidation system followed by liquid-liquid extraction. Part 1. Coker gas oil feedstocks. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2005, 23, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, A.; Waqas, A.; Muhammad, I. Desulfurization of liquid fuels using air-assisted performic acid oxidation and emulsion catalyst. Chin. J. Catal. 2013, 34, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.J.; Li, H.Q.; Zhang, H.X.; Lu, Y.Z.; Meng, H.; Li, C.X. Removal mechanism of thiophenic compounds in model oil by inorganic Lewis acids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 4682–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Xia, Q.; Yu, M. Adsorption of benzothiophene and dibenzothiophene on ion-impregnated activated carbons and ion-exchanged Y zeolites. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 3858–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat Mamaghani, A.; Fatemi, S.; Asgari, M. Investigation of influential parameters in deep oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene with hydrogen peroxide and formic acid. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2013, 951045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Liu, Z.; Dong, L.; Miao, G.; Liao, N.; Li, Z.; Xiao, J. Dynamic catalytic adsorptive desulfurization of real diesel over ultra-stable and low-cost silica gel-supported TiO2. AICHE J. 2018, 64, 2146–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomeque-Santiago, J.F.; López-Medina, R.; Oviedo-Roa, R.; Navarrete-Bolaños, J.; Mora-Vallejo, R.; Montoya-de la Fuente, J.A.; Martínez-Magadán, J.M. Deep oxidative desulfurization with simultaneous oxidative denitrogenation of diesel fuel and straight run gas oil. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 236, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, Y.; Duan, E. Oxidative desulfurization of fuel oil by pyridinium-based ionic liquids. Molecules 2009, 14, 4351–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Li, F.T.; Liu, J.X.; Kou, C.G.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, Y.J.; Zhao, D. Preparation of TiO2 in ionic liquid via microwave radiation and in situ photocatalytic oxidative desulfurization of diesel oil. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 6777–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted oxidative desulfurization of gasoline and crude oil. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2020, 147, 107789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jibrin, I.; Zeng, X. Catalytic oxidative desulfurization of gasoline using phosphotungstic acid supported on MWW zeolite. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2019, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svinterikos, E.; Zuburtikudis, I.; Al-Marzouqi, M. Carbon nanomaterials for the adsorptive desulfurization of fuels. J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismagilov, Z.; Yashnik, S.; Kerzhentsev, M.; Parmon, V.; Bourane, A.; Al-Shahrani, F.; Hajji, A.; Koseoglu, O. Oxidative desulfurization of hydrocarbon fuels. Catal. Rev. 2011, 53, 199–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutto, A.W.; Abro, R.; Gao, S.; Abbas, T.; Chen, X.; Yu, G. Oxidative desulfurization of fuel oils using ionic liquids: A review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 62, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Ahmad, I. Desulphurization of transportation fuels by per-formic acid oxidant using MoOx loaded on ZSM-5 catalyst. J. Power Energy Eng. 2017, 5, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.H.; Zaera, F. Kinetic study on the selective catalytic oxidation of 2-propanol to acetone over nickel foils. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2002, 177, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, M. Mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride as photo-catalyst for oxidative desulfurization with oxygen. Catal. Commun. 2016, 85, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, S.Y.; Wang, R. Ultradeep desulfurization of model oil through the oxidative adsorption process using Dawson-type polyoxometalates and graphene oxide multifunctional composites. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, B.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, J. Graphene wrapped phthalocyanine: Enhanced oxidative desulfurization for dibenzothiophene in fuel. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mominou, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, L. Ultra-deep desulfurization of gasoline with cuw/tio2–go through photocatalytic oxidation. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julião, D.; Mirante, F.; Ribeiro, S.O.; Gomes, A.C.; Valenca, R.; Ribeiro, J.C.; Pillinger, M.; de Castro, B.; Gonçalves, I.S.; Balula, S.S. Deep oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuels using homogeneous and SBA-15-supported peroxophosphotungstate catalysts. Fuel 2019, 241, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, G.; Ashokkumar, M.; Alizadeh, A. Ultrasound-assisted oxidative-adsorptive desulfurization using highly acidic graphene oxide as a catalyst-adsorbent. Fuel 2017, 210, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Leus, K.; Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Depauw, H.; Wang, A.; Zhang, J.; Van Der Voort, P. Catalytic oxidative desulfurization of model and real diesel over a molybdenum anchored metal-organic framework. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 277, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Meng, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Zang, S. Extractive and catalytic oxidative desulfurization of gasoline by methyltrioxorhenium in ionic liquids. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Lu, S.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Z. Diesel fuel desulfurization with hydrogen peroxide promoted by formic acid and catalyzed by activated carbon. Carbon 2005, 43, 2285–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

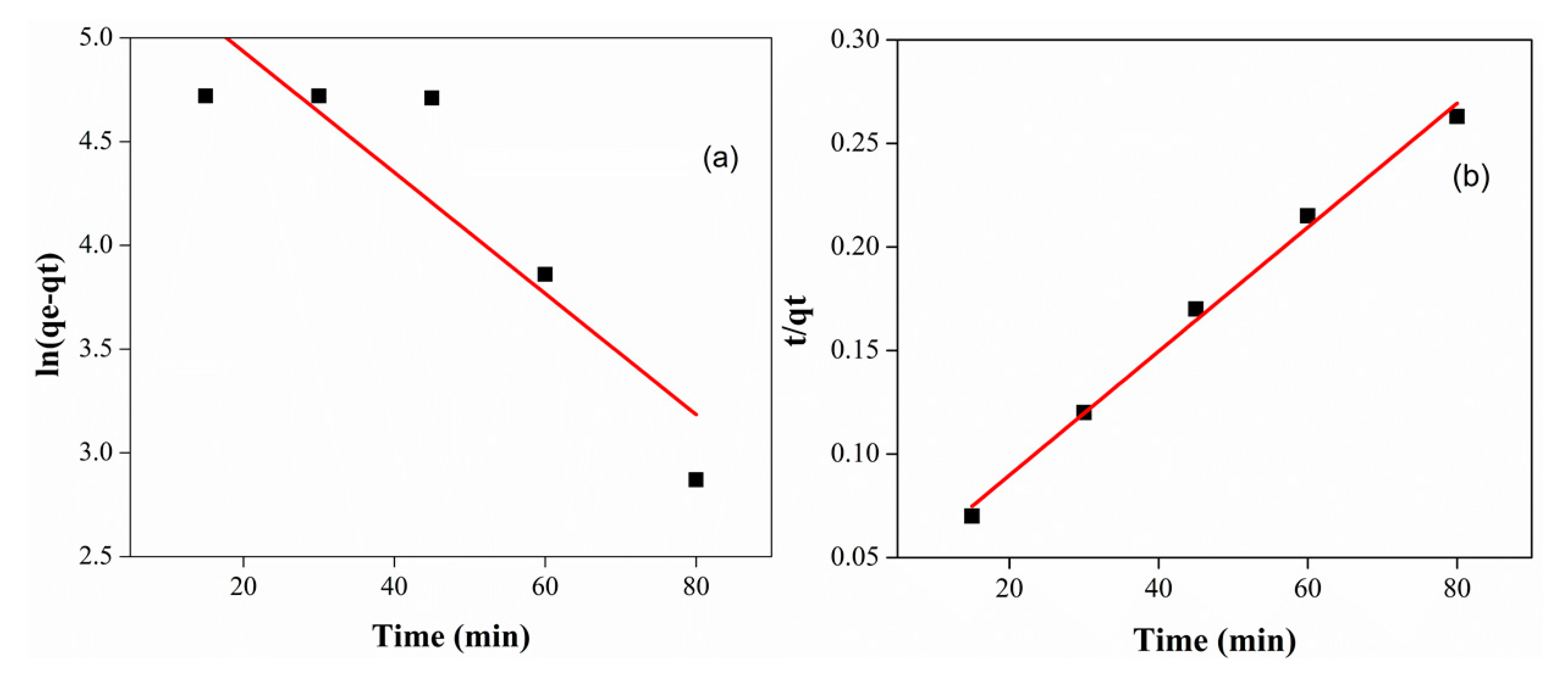

| Order of Reaction | qe (Experimental) | qe (Calculated) | K (min−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | 326.54 | 247.15 | 0.029 | 0.75 |
| Pseudo-second-order | 334.44 | 357 | 0.0028 | 0.99 |
| Catalysts | Oxidant Used | Substrate | Temp | Time | Desulfurization (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyoxometalate K6 [α-P2W18O62]·14H2O and K6P2W18O62/GO | Octanal/air | DBT, BT and 4,6-DMDBT | 60 °C | - | 96.10 | [60] |
| HPW-GO | H2O2 | DBT, BT and 4,6-DMDBT | 60 °C | 30 min | 100% | [34] |
| MPc/RGO | O2 | DBT | 60 °C | 180 min | 97.5% | [61] |
| CuW/TiO2–GO | H2O2 | Gasoline oil | 40 °C | 1 h | 100% | [62] |
| SBA-15-supported peroxophospho-tungstate catalysts | H2O2 | DBT, Gasoline | 70 °C | 2 h | 98%, 89% | [63] |
| GO/COOH | H2O2/HCOOH | DBT | 25 °C | 300 min | 95% | [64] |
| Molybdenum anchored/MOF | TBHP | DBT, diesel fuels | 70 °C | 14.4 h−1 | 85%, 74% | [65] |
| Methyltrioxorhenium in ionic liquid | H2O2 | Thiophene, gasoline | 60 °C | 2 h | 99%, 91% | [66] |
| Activated carbon | H2O2/HCOOH, | DBT, diesel fuels | 60 °C | 1 h | 98% | [67] |
| K6P2W18O62/GO, | Air/n-octanol | DBT | 60 °C | 2 h | 92.99% | [60] |
| MnO2/MrGO | H2O2/HCOOH | DBT Real oil samples | 40 °C | 15 min | 80% | Current study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, W.; Ur Rahman, A.; Ahmad, I.; Yaseen, M.; Mohamed Jan, B.; Stylianakis, M.M.; Kenanakis, G.; Ikram, R. Oxidative Desulfurization of Petroleum Distillate Fractions Using Manganese Dioxide Supported on Magnetic Reduced Graphene Oxide as Catalyst. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010203
Ahmad W, Ur Rahman A, Ahmad I, Yaseen M, Mohamed Jan B, Stylianakis MM, Kenanakis G, Ikram R. Oxidative Desulfurization of Petroleum Distillate Fractions Using Manganese Dioxide Supported on Magnetic Reduced Graphene Oxide as Catalyst. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(1):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010203
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Waqas, Atiq Ur Rahman, Imtiaz Ahmad, Muhammad Yaseen, Badrul Mohamed Jan, Minas M. Stylianakis, George Kenanakis, and Rabia Ikram. 2021. "Oxidative Desulfurization of Petroleum Distillate Fractions Using Manganese Dioxide Supported on Magnetic Reduced Graphene Oxide as Catalyst" Nanomaterials 11, no. 1: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010203
APA StyleAhmad, W., Ur Rahman, A., Ahmad, I., Yaseen, M., Mohamed Jan, B., Stylianakis, M. M., Kenanakis, G., & Ikram, R. (2021). Oxidative Desulfurization of Petroleum Distillate Fractions Using Manganese Dioxide Supported on Magnetic Reduced Graphene Oxide as Catalyst. Nanomaterials, 11(1), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010203