Neuro-Transistor Based on UV-Treated Charge Trapping in MoTe2 for Artificial Synaptic Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
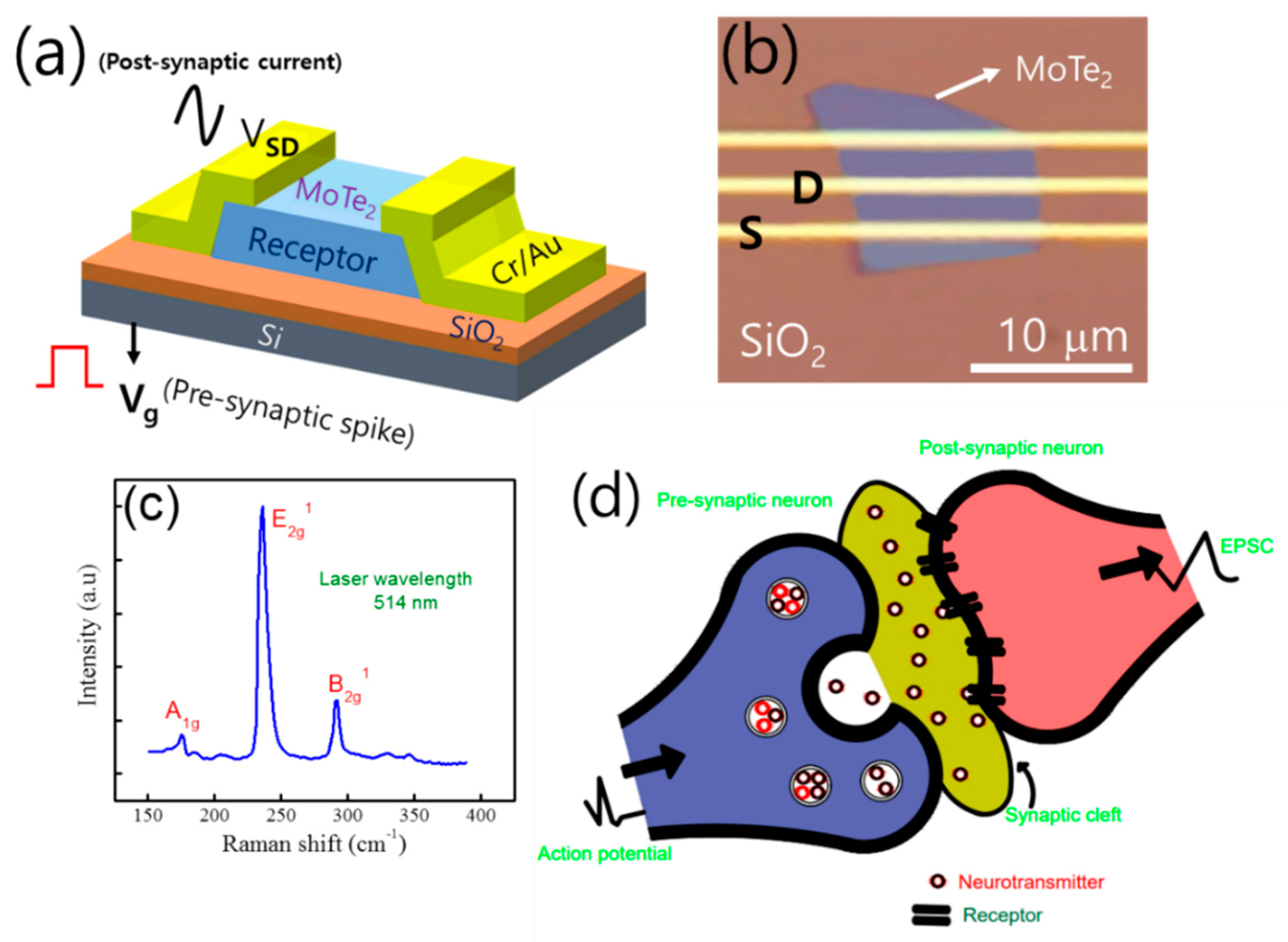
2. Materials and Methods
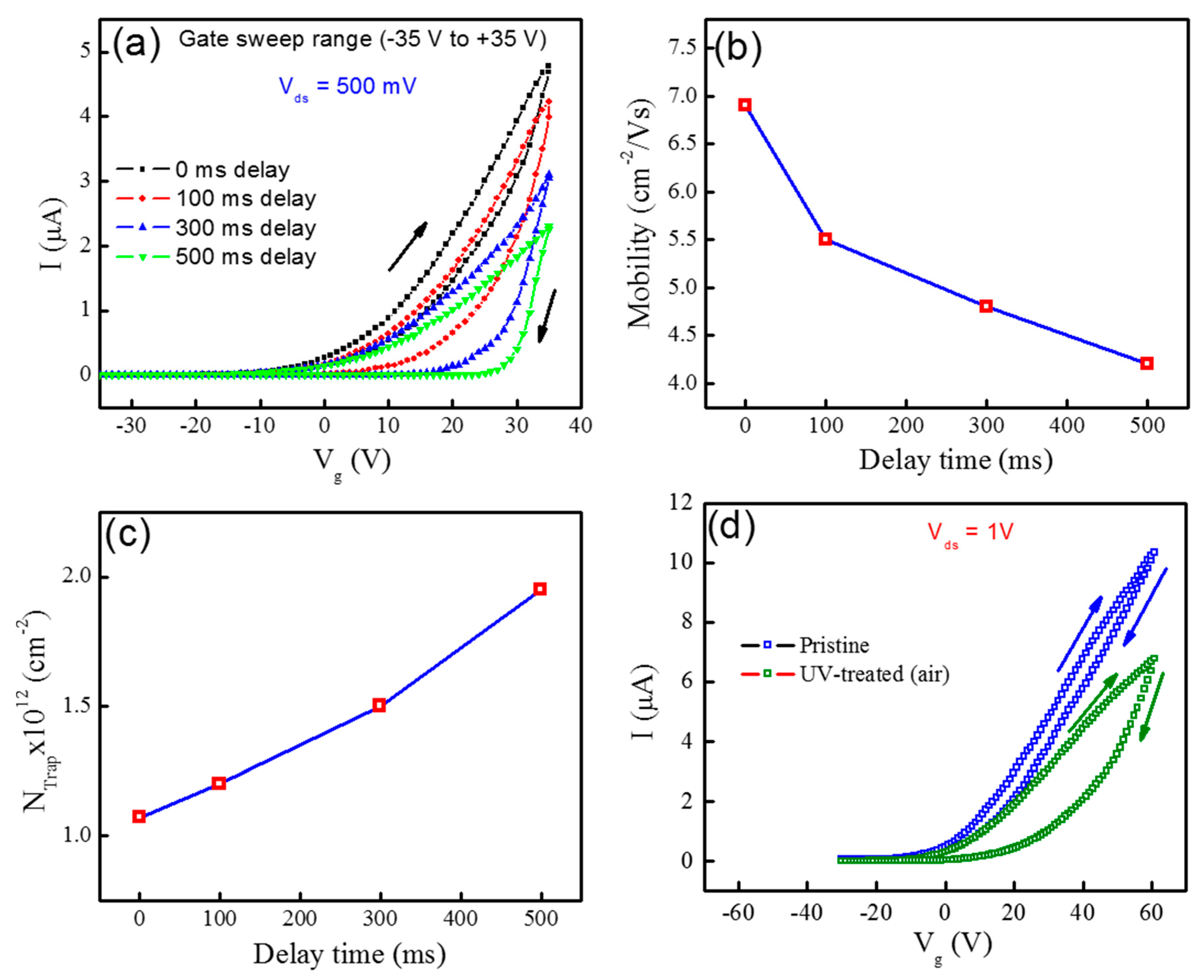
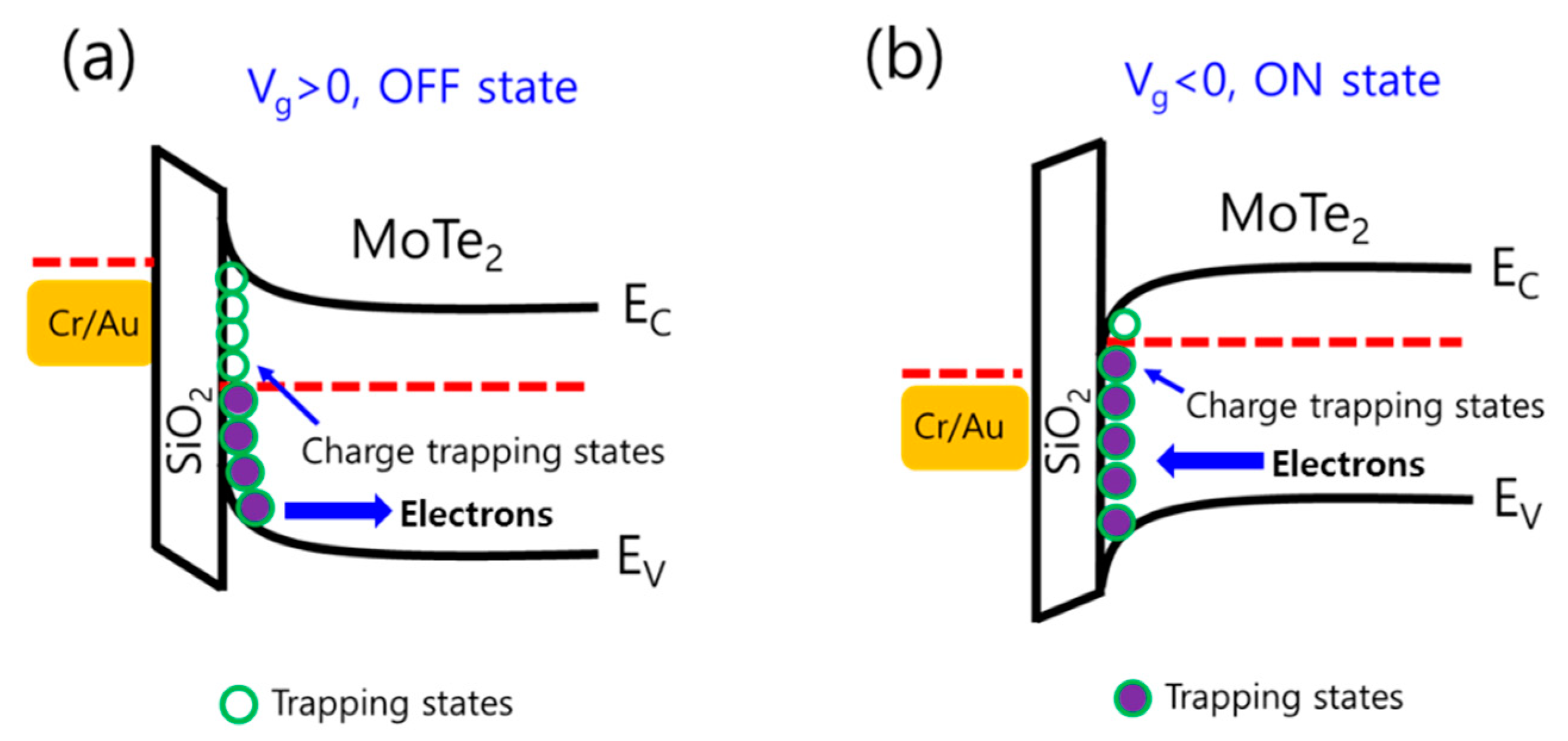
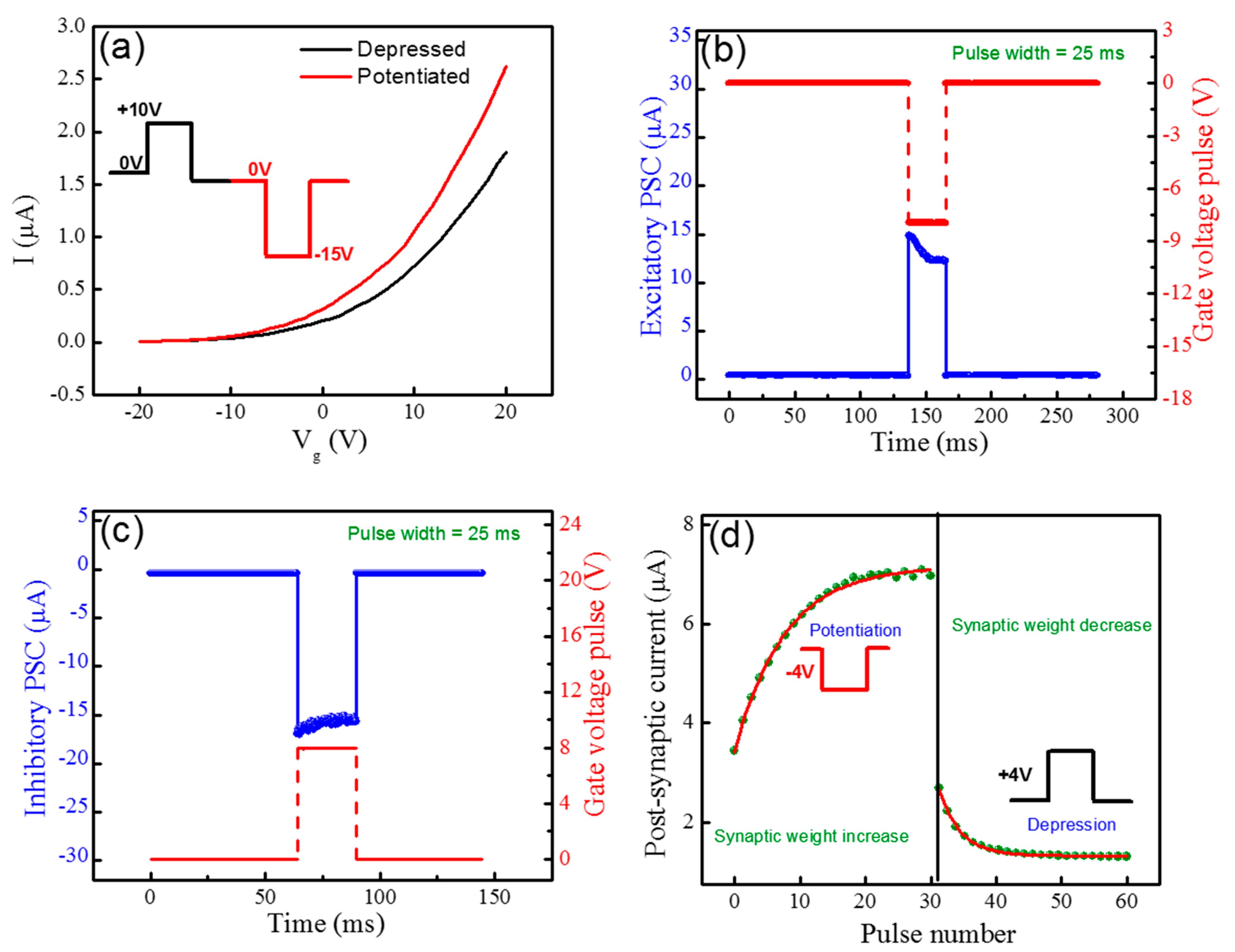
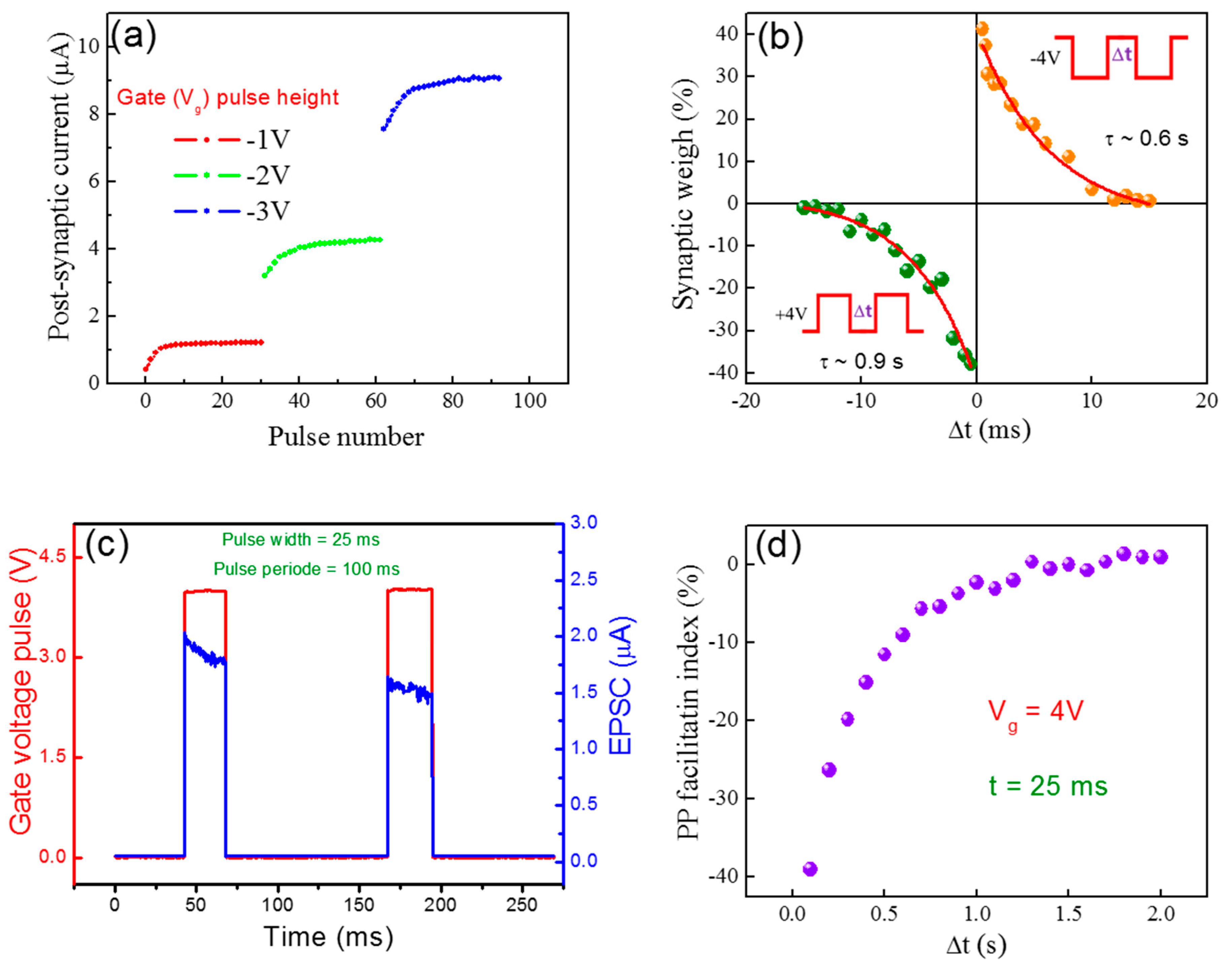
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Indiveri, G.; Douglas, R. Neuromorphic vision sensors. Science 2000, 288, 1189–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lou, Z.; Chen, D.; Shen, G. An artificial flexible visual memory system based on an UV-motivated Memristor. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.J.; Choi, C.; Kim, D.H.; Song, Y.M. Bioinspired artificial eyes: Optic components, digital cameras, and visual prostheses. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Oh, S.; Choi, Y.; Seo, S.; Oh, M.J.; Lee, M.; Lee, W.B.; Yoo, P.J.; Cho, J.H.; Park, J.H. Optoelectronic Synapse Based on IGZO-Alkylated Graphene Oxide Hybrid Structure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taur, Y.; Buchanan, D.A.; Chen, W.; Frank, D.J.; Ismail, K.E.; Lo, S.-H.; Sai-Halasz, G.A.; Viswanathan, R.G.; Wann, H.-J.; Wind, S.J. CMOS scaling into the nanometer regime. Proc. IEEE 1997, 85, 486–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, R.A. Intelligence without representation. Artif. Intell. 1991, 47, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicca, E.; Badoni, D.; Dante, V.; D’Andreagiovanni, M.; Salina, G.; Carota, L.; Fusi, S.; Del Giudice, P. A VLSI recurrent network of integrate-and-fire neurons connected by plastic synapses with long-term memory. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2003, 14, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indiveri, G.; Liu, S.-C. Memory and information processing in neuromorphic systems. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 1379–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, D.; Huang, A.; Maddison, C.J.; Guez, A.; Sifre, L.; Van Den Driessche, G.; Schrittwieser, J.; Antonoglou, I.; Panneershelvam, V.; Lanctot, M. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 2016, 529, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striedter, G.F. Neurobiology: A Functional Approach; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gerstner, W.; Kistler, W.M.; Naud, R.; Paninski, L. Neuronal Dynamics: From Single Neurons to Networks and Models of Cognition; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nestler, E.J. Molecular basis of long-term plasticity underlying addiction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucker, R.S.; Regehr, W.G. Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2002, 64, 355–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Wigchering, R.; Manning, H.G.; Boland, J.J.; Hurley, P.K. Emulating synaptic response in n-and p-channel MoS 2 transistors by utilizing charge trapping dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Huang, J. Energy-efficient hybrid perovskite memristors and synaptic devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 1600100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; Kim, H.; Khan, M.F.; Hur, J.-H.; Eom, J.; Kim, D.-K. Tunable resistive switching of vertical ReSe2/graphene hetero-structure enabled by Schottky barrier height and DUV light. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 855, 157310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Ahmed, F.; Rehman, S.; Akhtar, I.; Rehman, M.A.; Shinde, P.A.; Khan, K.; Kim, D.-K.; Eom, J.; Lipsanen, H. High performance complementary WS2 devices with hybrid Gr/Ni contacts. Nanoscale 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.F.; Rehman, S.; Rehman, M.A.; Sagar, R.U.R.; Kim, D.-K.; Khalil, H.W.; Shinde, P.A.; ul Hassan, N.; Sharma, P.R.; Eom, J. Multi-heterostructured spin-valve junction of vertical FLG/MoSe. APL Mater. 2020, 8, 071104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Rehman, S.; Rehman, M.A.; Basit, M.A.; Kim, D.-K.; Ahmed, F.; Khalil, H.W.; Akhtar, I.; Jun, S.C. Modulation of Magnetoresistance Polarity in BLG/SL-MoSe 2 Heterostacks. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, J.; Kim, M.; Woo, J.; Koo, S.-M.; Oh, J.-M.; Lee, D. Two-terminal structured synaptic device using ionic electrochemical reaction mechanism for neuromorphic system. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2019, 40, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Pseudo-Interface Switching of a Two-Terminal TaOx/HfO2 Synaptic Device for Neuromorphic Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M.K.; Kim, M.-H.; Hussain, F.; Abbas, Y.; Ismail, M.; Hong, K.; Mahata, C.; Choi, C.; Park, B.-G.; Kim, S. Memristive and Synaptic Characteristics of Nitride-Based Heterostructures on Si Substrate. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Ma, W.; Chang, T.; Sheridan, P.; Lu, W.D. Biorealistic implementation of synaptic functions with oxide memristors through internal ionic dynamics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4290–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Chen, C.L.; Truong, Q.; Shen, A.M.; Chen, Y. A carbon nanotube synapse with dynamic logic and learning. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, M.T.; Stephan, S.B.; Bak, P.; Chen, J.; Irvine, D.J. Synapse-directed delivery of immunomodulators using T-cell-conjugated nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5776–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Kim, T.; Kwak, M.; Song, J.; Woo, J.; Jeon, S.; Yoo, I.K.; Hwang, H. HfZrO x-based ferroelectric synapse device with 32 levels of conductance states for neuromorphic applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2017, 38, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, B.; Feng, X.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, L.; Gong, X.; Fong, X.; Ang, K.-W. Gradual Resistive Switching in Electron Beam Irradiated ReS 2 Transistor and its Application as Electronic Synapse. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Symposium on VLSI Technology, Systems and Applications (VLSI-TSA), Hsinchu, Taiwan, 10–13 August 2020; pp. 157–158. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, A.J.; Razavieh, A.; Nasr, J.R.; Schulman, D.S.; Eichfeld, C.M.; Das, S. Mimicking neurotransmitter release in chemical synapses via hysteresis engineering in MoS2 transistors. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3110–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, S.; Khan, M.F.; Gautam, P.; Noh, H.; Eom, J. MoTe2 van der Waals homojunction p-n diode with low resistive metal contacts. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.B.; Ku, C.H.; Lim, S.C.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Hysteresis and threshold voltage shift of pentacene thin-film transistors and inverters with Al2O3 gate dielectric. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 133503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Nazir, G.; Lermolenko, V.M.; Eom, J. Electrical and photo-electrical properties of MoS2 nanosheets with and without an Al2O3 capping layer under various environmental conditions. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2016, 17, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illarionov, Y.Y.; Waltl, M.; Rzepa, G.; Knobloch, T.; Kim, J.-S.; Akinwande, D.; Grasser, T. Highly-stable black phosphorus field-effect transistors with low density of oxide traps. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 2017, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullmann, D.M.; Lamsa, K.P. Long-term synaptic plasticity in hippocampal interneurons. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Yang, Y.; Feng, P.; Shi, Y.; Wan, Q. Short-term plasticity and synaptic filtering emulated in electrolyte-gated IGZO transistors. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2016, 37, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, Y.; Poo, M.-M. Spike timing-dependent plasticity: From synapse to perception. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.Y.; Ge, C.; Riahi, H.; Guo, E.J.; He, M.; Wang, C.; Yang, G.Z.; Jin, K.J. Dual-Gated MoS2 Transistors for Synaptic and Programmable Logic Functions. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 1901408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Mao, J.Y.; Ren, Y.; Yang, J.Q.; Zhang, S.R.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, Q.; Zeng, Y.J.; Shan, H.; Xu, Z. Biological spiking synapse constructed from solution processed bimetal core-shell nanoparticle based composites. Small 2018, 14, 1800288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rehman, S.; Khan, M.F.; Rahmani, M.K.; Kim, H.; Patil, H.; Khan, S.A.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, D.-k. Neuro-Transistor Based on UV-Treated Charge Trapping in MoTe2 for Artificial Synaptic Features. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122326
Rehman S, Khan MF, Rahmani MK, Kim H, Patil H, Khan SA, Kang MH, Kim D-k. Neuro-Transistor Based on UV-Treated Charge Trapping in MoTe2 for Artificial Synaptic Features. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(12):2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122326
Chicago/Turabian StyleRehman, Shania, Muhammad Farooq Khan, Mehr Khalid Rahmani, Honggyun Kim, Harshada Patil, Sobia Ali Khan, Moon Hee Kang, and Deok-kee Kim. 2020. "Neuro-Transistor Based on UV-Treated Charge Trapping in MoTe2 for Artificial Synaptic Features" Nanomaterials 10, no. 12: 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122326
APA StyleRehman, S., Khan, M. F., Rahmani, M. K., Kim, H., Patil, H., Khan, S. A., Kang, M. H., & Kim, D.-k. (2020). Neuro-Transistor Based on UV-Treated Charge Trapping in MoTe2 for Artificial Synaptic Features. Nanomaterials, 10(12), 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122326






