Sustainable One-Step Solid-State Synthesis of Antibacterially Active Silver Nanoparticles Using Mechanochemistry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mechanochemical Synthesis
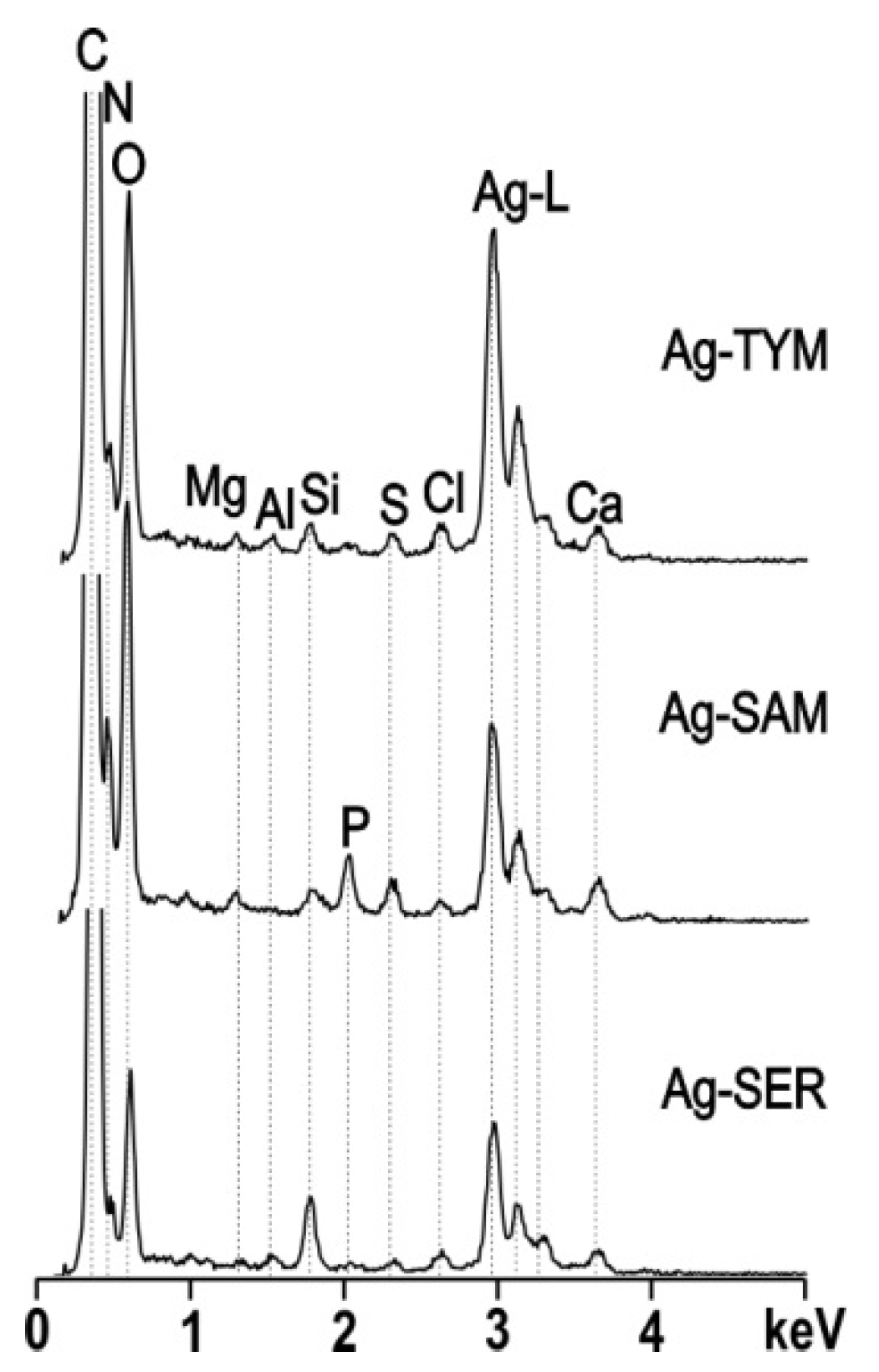
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Antibacterial Activity
3. Results and Discussion
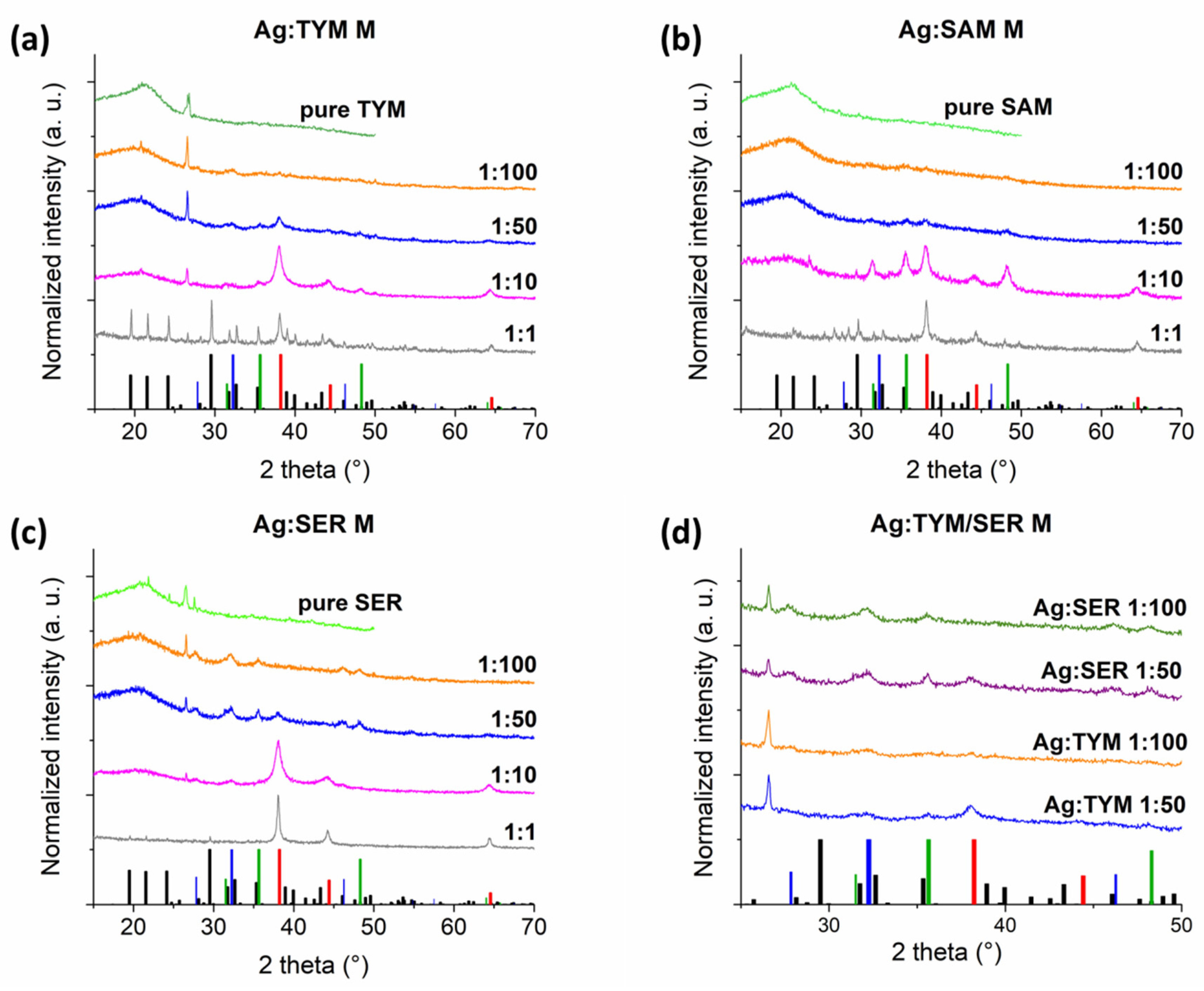
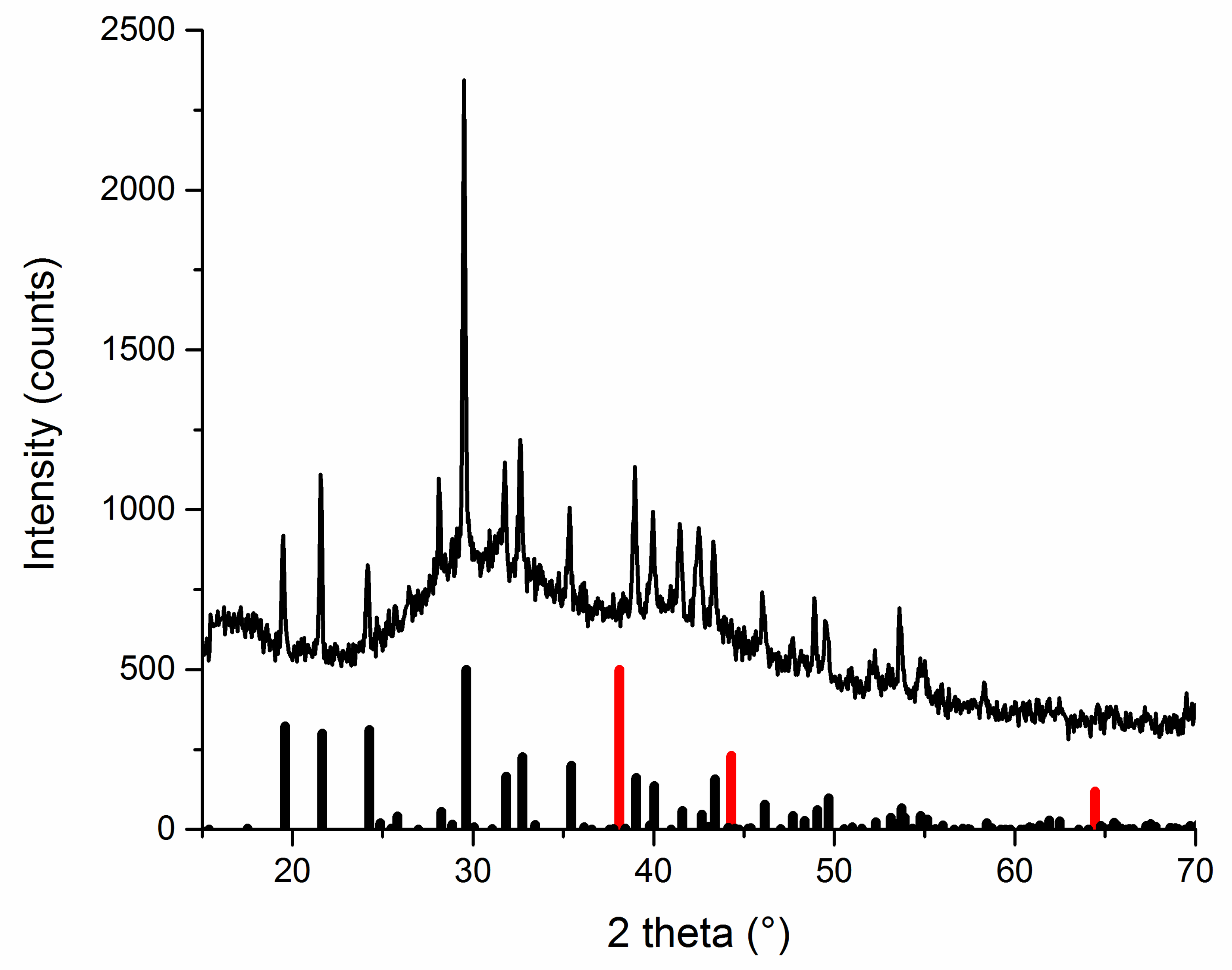
3.1. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
3.1.1. As-Received Powders
3.1.2. Washed Powders Subjected to Rietveld Refinement
3.2. Atomic Absorption Spectrometry Analysis
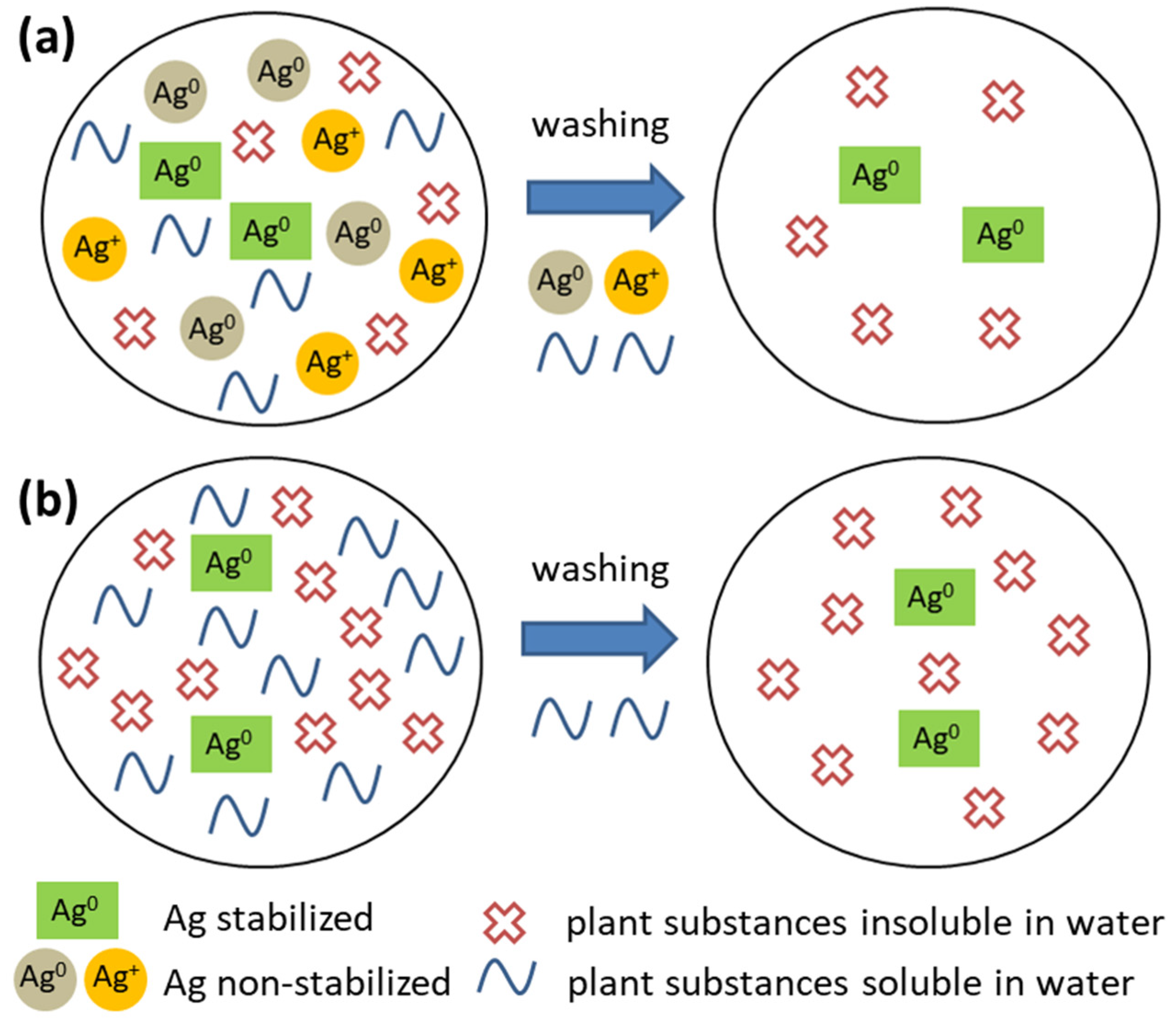
- In the Ag:plant 1:1 samples, the concentration and subsequent dissolution (into distilled water) of non-stabilized Ag0 and Ag+ is relatively high (Figure 3a). The water-soluble plant substances are washed away with the unstabilized Ag species (meaning not retained in the powder, but they are stabilized by the water-soluble components of the plant) as well, but their dissolution from the Ag:plant 1:1 samples is not as high as in the other cases.
- In plant-rich samples, only stabilized Ag0 is present; thus, only water-soluble plant species are washed away, resulting in a larger amount of Ag being identified in the samples (Figure 3b).
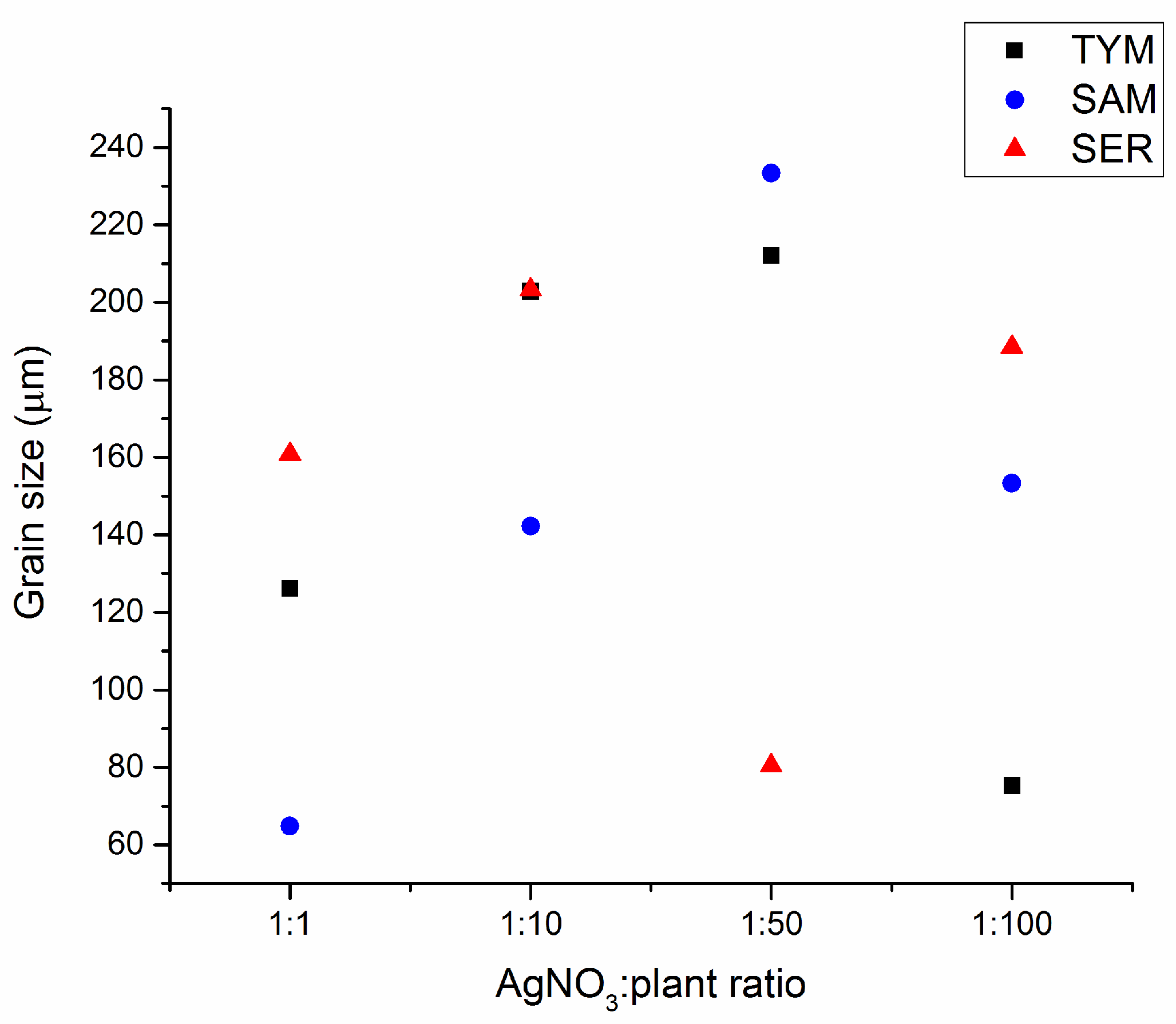
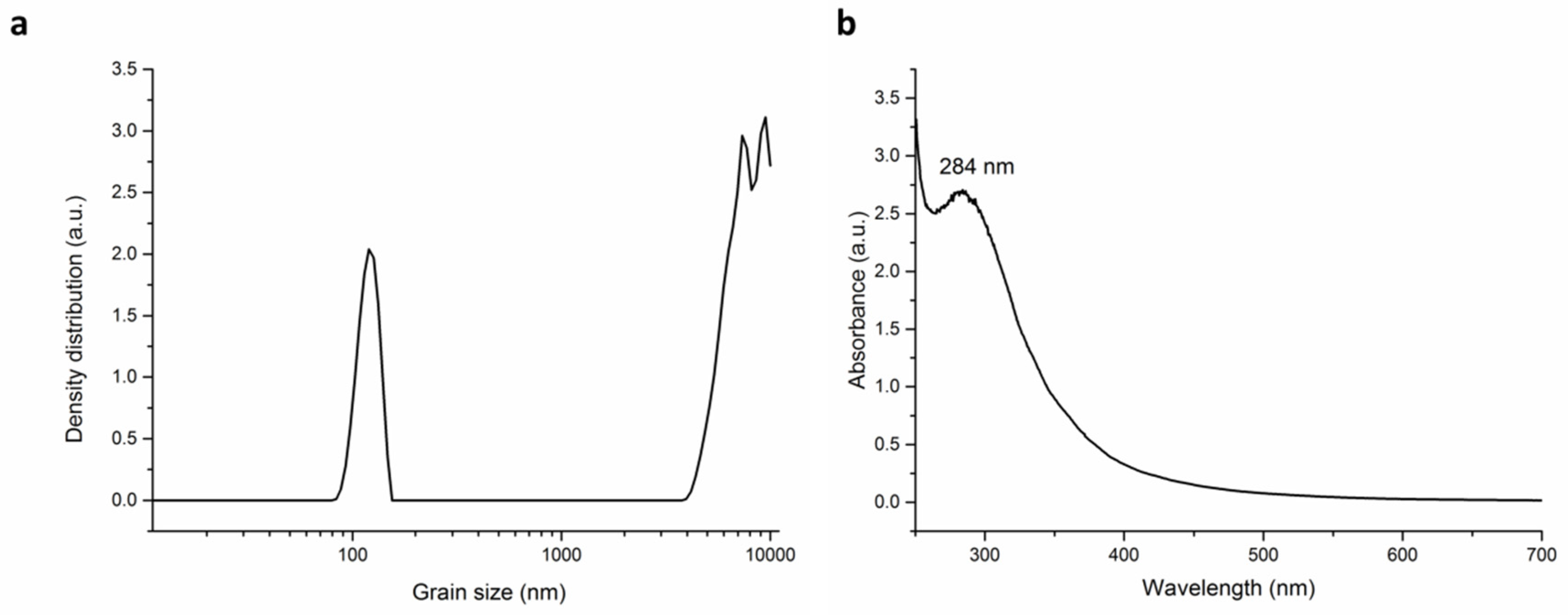
3.3. Grain Size Analysis
3.4. UV-Vis Results
3.5. TEM Analysis
3.6. Characterization of the Filtrate of Ag:SER 1:1 Sample after Washing
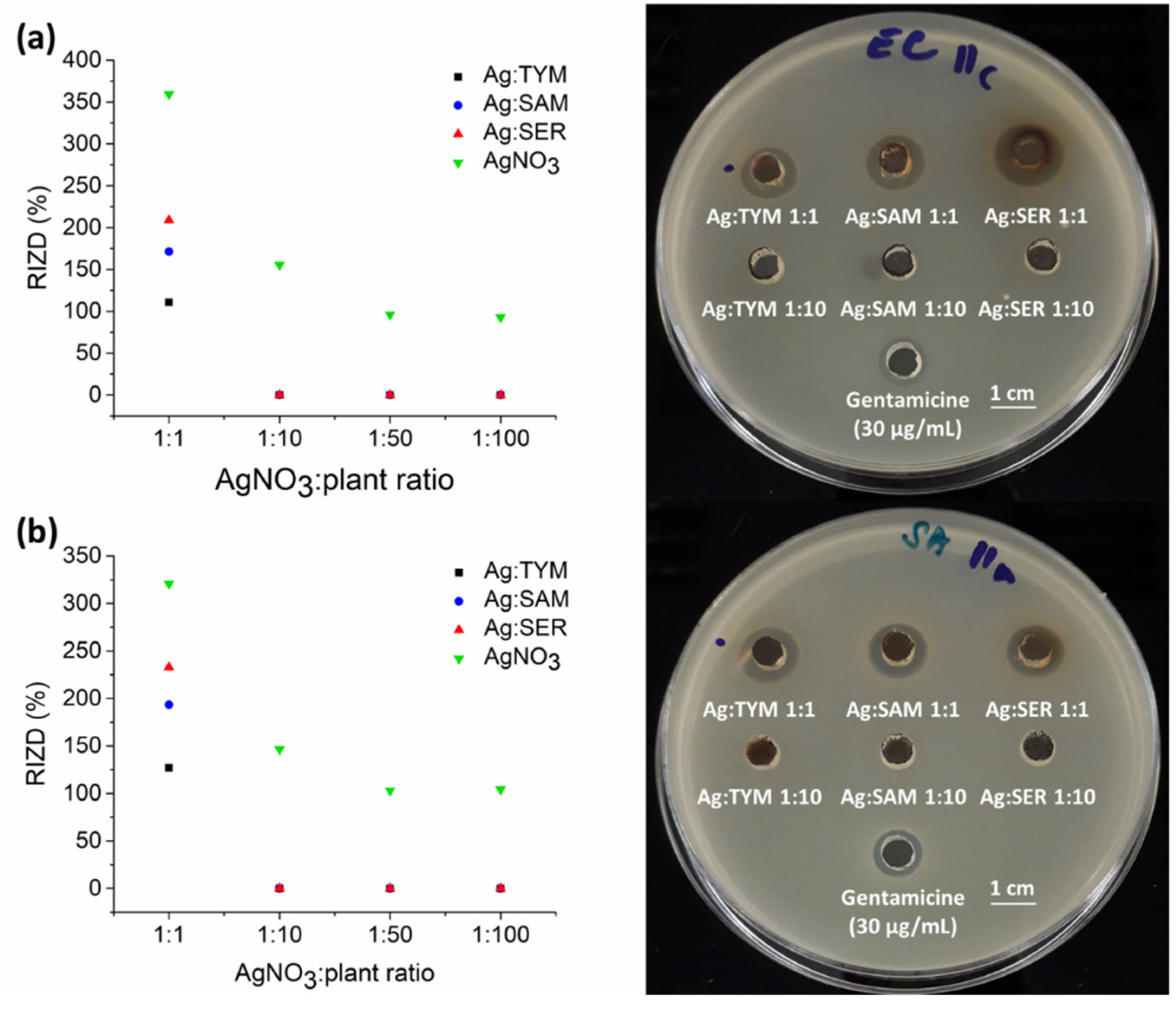
3.7. Antibacterial Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarina, S.; Waclawik, E.R.; Zhu, H.Y. Photocatalysis on supported gold and silver nanoparticles under ultraviolet and visible light irradiation. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 1814–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syafiuddin, A.; Salmiati; Salim, M.R.; Hong Kueh, A.B.; Hadibarata, T.; Nur, H. A Review of Silver Nanoparticles: Research Trends, Global Consumption, Synthesis, Properties, and Future Challenges. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2017, 64, 732–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Jun, B.H. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis and application for nanomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Maheshwari, S.K. Applications of Silver nanoparticles in diverse sectors. Int. J. Nano Dimens. 2019, 10, 18–36. [Google Scholar]
- Marambio-Jones, C.; Hoek, E.M.V. A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, H.H.; Garza-Trevino, E.N.; Ixtepan-Turrent, L.; Singh, D.K. Silver nanoparticles are broad-spectrum bactericidal and virucidal compounds. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Kon, K.; Ingle, A.; Duran, N.; Galdiero, S.; Galdiero, M. Broad-spectrum bioactivities of silver nanoparticles: The emerging trends and future prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 1951–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Liu, Z.G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, properties, applications, and therapeutic approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.Y.; Lu, J.R.; Xu, H.Z.; Patel, A.; Chen, Z.S.; Chen, G.F. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, and therapeutic applications. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Singh, M.; Verma, J.L.; Kumar, N.; Mandal, R.K. Stabilization of nanocrystalline silver by Sella and Mansoori rice starch. Trans. Indian Inst. Metals 2015, 68, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarannum, N.; Divya; Gautam, Y.K. Facile green synthesis and applications of silver nanoparticles: A state-of-the-art review. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 34926–34948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Munir, S.; Zeb, N.; Ullah, A.; Khan, B.; Ali, J.; Bilal, M.; Omer, M.; Alamzeb, M.; Salman, S.M.; et al. Green nanotechnology: A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles—An ecofriendly approach. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5087–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, A.; Pourakbar, L.; Farhadi, K.; Mohamadgolizad, L.; Goosta, Y. Biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of antibacterial and antifungal properties of silver and copper nanoparticles. Turk. J. Biol. 2015, 39, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, Z.; Salehzadeh, A.; Shandiz, S.A.S.; Tajdoost, S. Anti-cancer and anti-oxidant properties of ethanolic leaf extract of Thymus vulgaris and its bio-functionalized silver nanoparticles. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erci, F.; Torlak, E. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles by using aqueous leaf extract of Thymus serpyllum. Sak. Univ. J. Sci. 2019, 23, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.; Moldovan, B.; Vulcu, A.; Olenic, L.; Perde-Schrepler, M.; Fischer-Fodor, E.; Florea, A.; Crisan, M.; Chiorean, I.; Clichici, S.; et al. Green synthesis, characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of silver nanoparticles using European black elderberry fruits extract. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 122, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldovan, B.; David, L.; Achim, M.; Clichici, S.; Filip, G.A. A green approach to phytomediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Sambucus nigra L. fruits extract and their antioxidant activity. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 221, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.; Tang, R.C. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activities using aqueous Eriobotrya japonica leaf extract. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 015014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronavari, A.; Kovacs, D.; Igaz, N.; Vagvolgyi, C.; Boros, I.M.; Konya, Z.; Pfeiffer, I.; Kiricsi, M. Biological activity of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles depends on the applied natural extracts: A comprehensive study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciplak, Z.; Gokalp, C.; Getiren, B.; Yildiz, A.; Yildiz, N. Catalytic performance of Ag, Au and Ag-Au nanoparticles synthesized by lichen extract. Green Process. Synth. 2018, 7, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baláž, M.; Balážová, Ľ.; Kováčová, M.; Daneu, N.; Salayová, A.; Bedlovičová, Z.; Tkáčiková, Ľ. The relationship between precursor concentration and antibacterial activity of biosynthesized Ag nanoparticles. Adv. Nano Res. 2019, 7, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rak, M.J.; Friscic, T.; Moores, A. One-step, solvent-free mechanosynthesis of silver nanoparticle-infused lignin composites for use as highly active multidrug resistant antibacterial filters. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 58365–58370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancon, R.A.D.; Balu, A.M.; Romero, A.A.; Ojeda, M.; Gomez, M.; Blanco, J.; Domingo, J.L.; Luque, R. Mechanochemically synthesized Ag-based nanohybrids with unprecedented low toxicity in biomedical applications. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baláž, M.; Balážová, Ľ.; Daneu, N.; Dutková, E.; Balážová, M.; Bujňáková, Z.; Shpotyuk, Y. Plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their stabilization by wet stirred media milling. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baláž, M.; Daneu, N.; Balážová, Ľ.; Dutková, E.; Tkáčiková, Ľ.; Briančin, J.; Vargová, M.; Balážová, M.; Zorkovská, A.; Baláž, P. Bio-mechanochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 3307–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, J.; Rahimi, M.; Hamezadeh, Z.; Motamedi, E.; Naghavi, M.R. Fulfillment of green chemistry for synthesis of silver nanoparticles using root and leaf extracts of Ferula persica: Solid-state route vs. solution-phase method. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 192, 514–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiczak-Yigitbasi, J.; Lacin, O.; Demir, M.; Ahan, R.E.; Seker, U.O.S.; Baytekin, B. A sustainable preparation of catalytically active and antibacterial cellulose metal nanocomposites via ball milling of cellulose. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baláž, M.; Goga, M.; Hegedüs, M.; Daneu, N.; Kováčová, M.; Tkáčiková, Ľ.; Balážová, Ľ.; Bačkor, M. Biomechanochemical solid-state synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity using lichens. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 13945–13955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, P.F.M.; Torresi, R.M.; Emmerling, F.; Camargo, P.H.C. Challenges and opportunities in the bottom-up mechanochemical synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 16114–16141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baláž, M.; Bedlovičová, Z.; Kováčová, M.; Salayová, A.; Balážová, Ľ. Green and Bio-Mechanochemical Approach to Silver Nanoparticles Synthesis, Characterization and Antibacterial Potential. In Nanostructures for Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Applications; Prasad, R., Siddhardha, B., Dyavaiah, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 145–183. [Google Scholar]
- Goga, M.; Baláž, M.; Daneu, N.; Elečko, J.; Tkáčiková, Ľ.; Marcinčinová, M.; Bačkor, M. Biological activity of selected lichens and lichen-based Ag nanoparticles prepared by a green solid-state mechanochemical approach. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathna, T.C.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Raichur, A.M.; Mukherjee, A. Biomimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Citrus limon (lemon) aqueous extract and theoretical prediction of particle size. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 82, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.M.H.; Ismail, E.H.; El-Baghdady, K.Z.; Mohamed, D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using olive leaf extract and its antibacterial activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khoury, E.; Abiad, M.; Kassaify, Z.G.; Patra, D. Green synthesis of curcumin conjugated nanosilver for the applications in nucleic acid sensing and anti-bacterial activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 127, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Cerda, J.; Alonso-Nunez, G.; Espinoza-Gomez, H.; Flores-Lopez, L.Z. Synthesis, kinetics and photocatalytic study of “ultra-small” Ag-NPs obtained by a green chemistry method using an extract of Rosa ‘Andeli’ double delight petals. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 458, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiriborournand, M.; Montazer, M.; Barani, H. Preparation and characterization of biocompatible silver nanoparticles using pomegranate peel extract. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 179, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, M.R.; Khan, M.; Kuniyil, M.; Al-Warthan, A.; Alkhathlan, H.Z.; Siddiqui, M.R.H.; Shaik, J.P.; Ahamed, A.; Mahmood, A.; Khan, M.; et al. Plant-Extract-Assisted Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Origanum vulgare L. Extract and Their Microbicidal Activities. Sustainability 2018, 10, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathcart, N.; Frank, A.J.; Kitaev, V. Silver nanoparticles with planar twinned defects: Effect of halides for precise tuning of plasmon resonance maxima from 400 to >900 nm. Chem. Commun. 2009, 46, 7170–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.H.; Zhu, H.L.; Shen, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.T.; Zhang, L. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles of different particle size against Vibrio Natriegens. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.A.; Kanwal, Z.; Rauf, A.; Sabri, A.N.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Size- and Shape-Dependent Antibacterial Studies of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Wet Chemical Routes. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, G.A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Antibacterial Activity of Nanosilver Ions and Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, E.; Diaz-Fernandez, Y.A.; Taglietti, A.; Pallavicini, P.; Pasotti, L.; Cucca, L.; Milanese, C.; Grisoli, P.; Dacarro, C.; Fernandez-Hechavarria, J.M.; et al. Synthesis, Characterization and Antibacterial Activity against Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria of Biomimetically Coated Silver Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 9165–9173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallavicini, P.; Dacarro, G.; Taglietti, A. Self-Assembled Monolayers of Silver Nanoparticles: From Intrinsic to Switchable Inorganic Antibacterial Surfaces. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 2018, 4846–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, Y.N.; Asnis, J.; Hafeli, U.O.; Bach, H. Metal nanoparticles: Understanding the mechanisms behind antibacterial activity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | 1:1 | 1:10 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | WC | Ag | WC | AgCl | |
| Ag:TYM | 99.60 ± 0.27 | 0.40 ± 0.27 | 78.0 ± 2.3 | 18.6 ± 2.3 | 3.4 ± 0.7 |
| Ag:SAM | 100 | - | 37.7 ± 6.7 | 62.3 ± 6.7 | - |
| Ag:SER | 100 | - | 93.6 ± 1.6 | - | 6.4 ± 1.6 |
| Sample | 1:1 | 1:10 |
|---|---|---|
| Ag:TYM | 22 ± 4 | 19 ± 2 |
| Ag:SAM | 18 ± 0.3 | 13 ± 0.2 |
| Ag:SER | 27 ± 3 | 19 ± 4 |
| Sample | 1:1 | 1:10 |
|---|---|---|
| Ag:TYM | 68.101 ± 0.043 | 68.304 ± 0.074 |
| Ag:SAM | 68.075 ± 0.059 | 68.329 ± 0.071 |
| Ag:SER | 67.982 ± 0.040 | 68.265 ± 0.078 |
| Sample | Ag Content in the Milled Sample (M) (%) | Ag Content in the Milled Sample after Washing (W) (%) | W/M Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ag:TYM 1:1 | 31.20 | 18.34 | 0.59 |
| Ag:SAM 1:1 | 32.50 | 23.31 | 0.72 |
| Ag:SER 1:1 | 32.10 | 26.06 | 0.81 |
| Ag:TYM 1:10 | 5.64 | 10.95 | 1.94 |
| Ag:SAM 1:10 | 5.40 | 11.33 | 2.10 |
| Ag:SER 1:10 | 4.95 | 12.28 | 2.48 |
| Ag:TYM 1:50 | 0.60 | 2.19 | 3.65 |
| Ag:SAM 1:50 | 0.75 | 2.28 | 3.04 |
| Ag:SER 1:50 | 0.22 | 1.83 | 8.32 |
| Ag:TYM 1:100 | 0.13 | 0.80 | 6.15 |
| Ag:SAM 1:100 | 0.16 | 0.97 | 6.06 |
| Ag:SER 1:100 | 0.15 | 0.63 | 4.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kováčová, M.; Daneu, N.; Tkáčiková, Ľ.; Búreš, R.; Dutková, E.; Stahorský, M.; Bujňáková, Z.L.; Baláž, M. Sustainable One-Step Solid-State Synthesis of Antibacterially Active Silver Nanoparticles Using Mechanochemistry. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112119
Kováčová M, Daneu N, Tkáčiková Ľ, Búreš R, Dutková E, Stahorský M, Bujňáková ZL, Baláž M. Sustainable One-Step Solid-State Synthesis of Antibacterially Active Silver Nanoparticles Using Mechanochemistry. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(11):2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112119
Chicago/Turabian StyleKováčová, Mária, Nina Daneu, Ľudmila Tkáčiková, Radovan Búreš, Erika Dutková, Martin Stahorský, Zdenka Lukáčová Bujňáková, and Matej Baláž. 2020. "Sustainable One-Step Solid-State Synthesis of Antibacterially Active Silver Nanoparticles Using Mechanochemistry" Nanomaterials 10, no. 11: 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112119
APA StyleKováčová, M., Daneu, N., Tkáčiková, Ľ., Búreš, R., Dutková, E., Stahorský, M., Bujňáková, Z. L., & Baláž, M. (2020). Sustainable One-Step Solid-State Synthesis of Antibacterially Active Silver Nanoparticles Using Mechanochemistry. Nanomaterials, 10(11), 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112119







