Ultrastructural Features of Gold Nanoparticles Interaction with HepG2 and HEK293 Cells in Monolayer and Spheroids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Preparation of AuNPs, AuBSA-NPs and AuPEI-NPs
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization of Nanoparticles
2.4. Cell Cultures and Spheroid Production
2.5. Incubation of Cells and Spheroids with the NPs
2.6. TEM Studies of NPs
2.7. TEM studies of Cell Cultures and Spheroids
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of the NPs
3.2. Cell Experimental Models
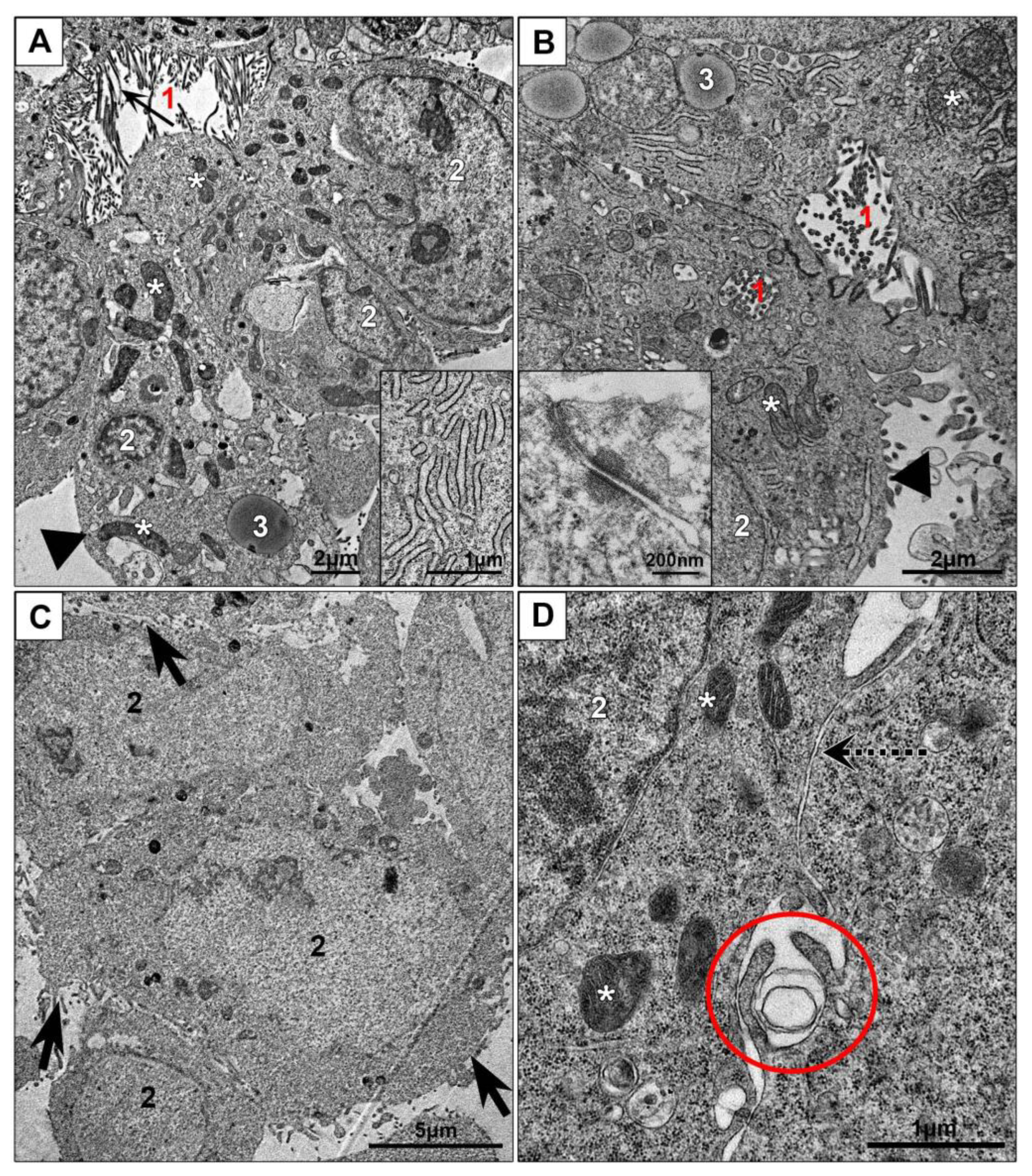
3.2.1. Monolayer Cell Cultures
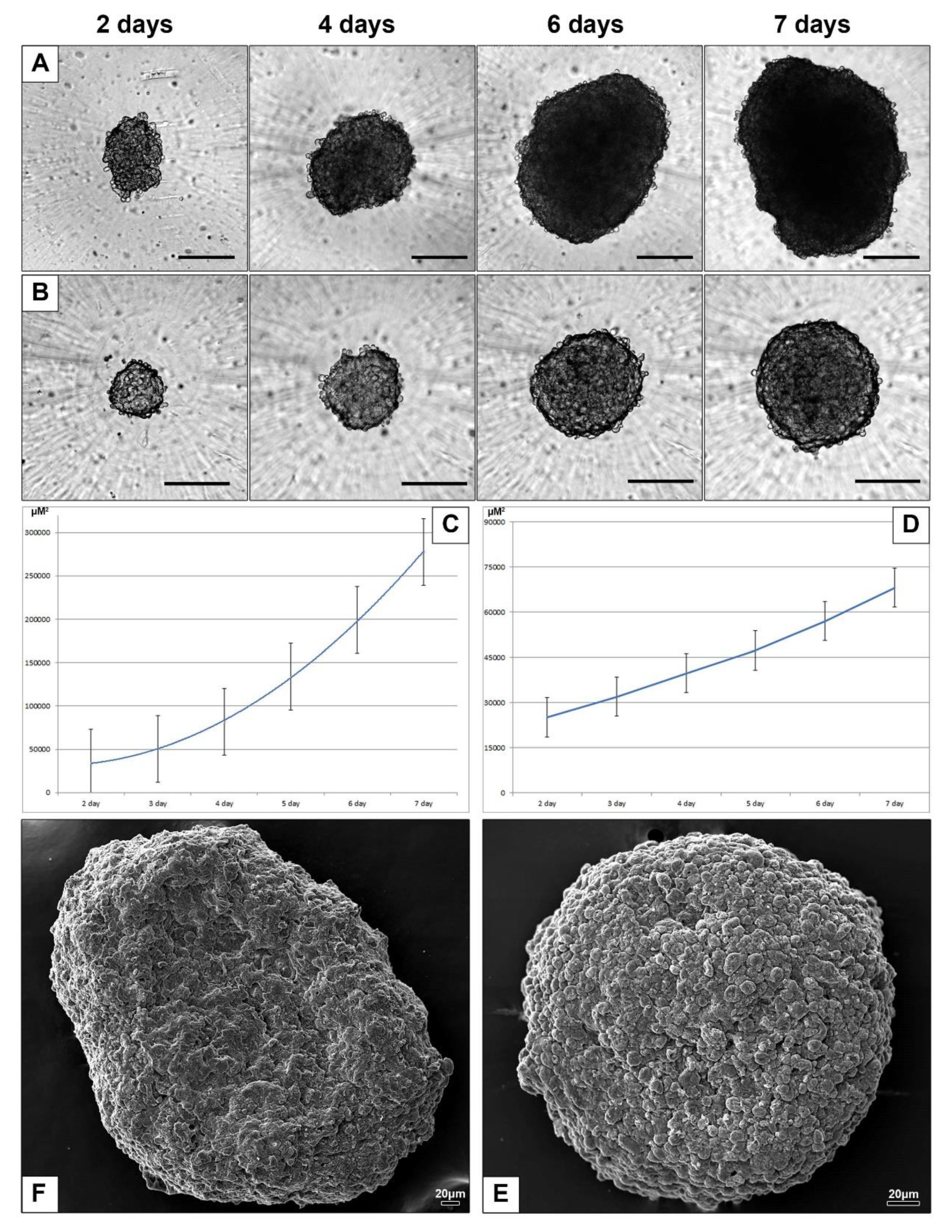
3.2.2. Spheroids of HepG2 and HEK293 Cells
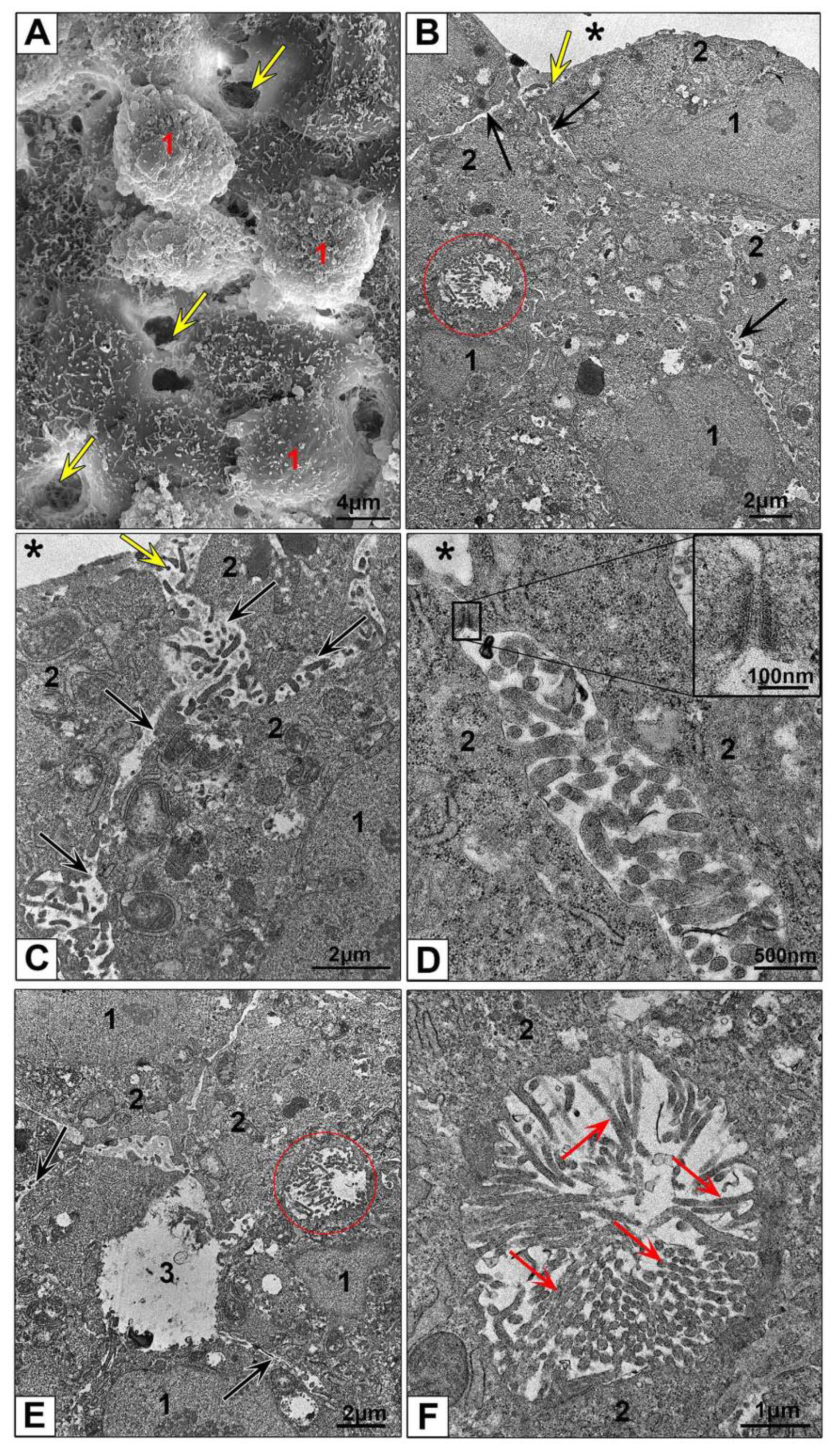
3.2.3. Electron Microscopic Features of HepG2 and HEK293 Spheroids
3.3. Interaction of AuNPs, AuPEI-NPs and AuBSA-NPs with HepG2 and HEK293 Cells
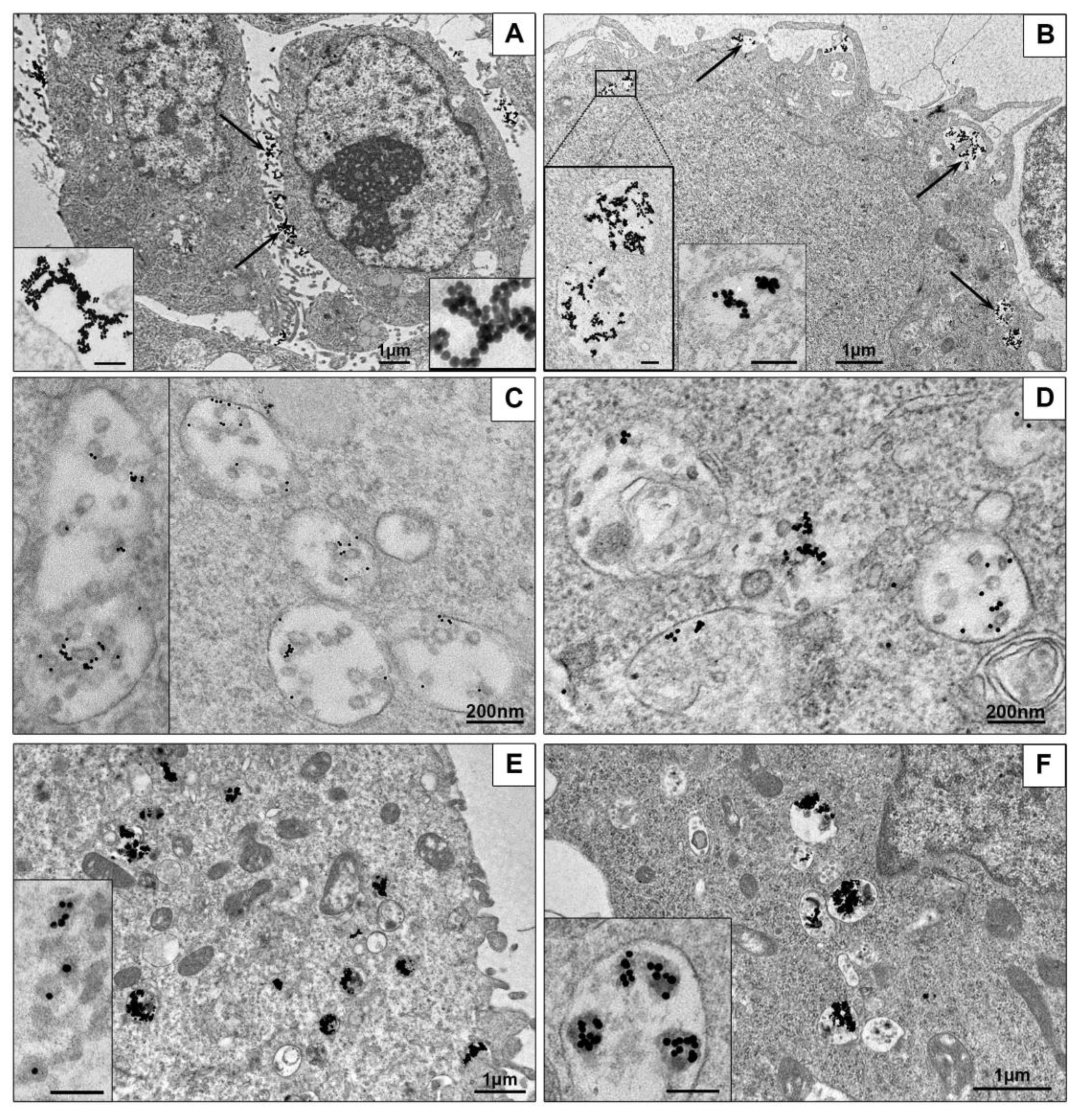
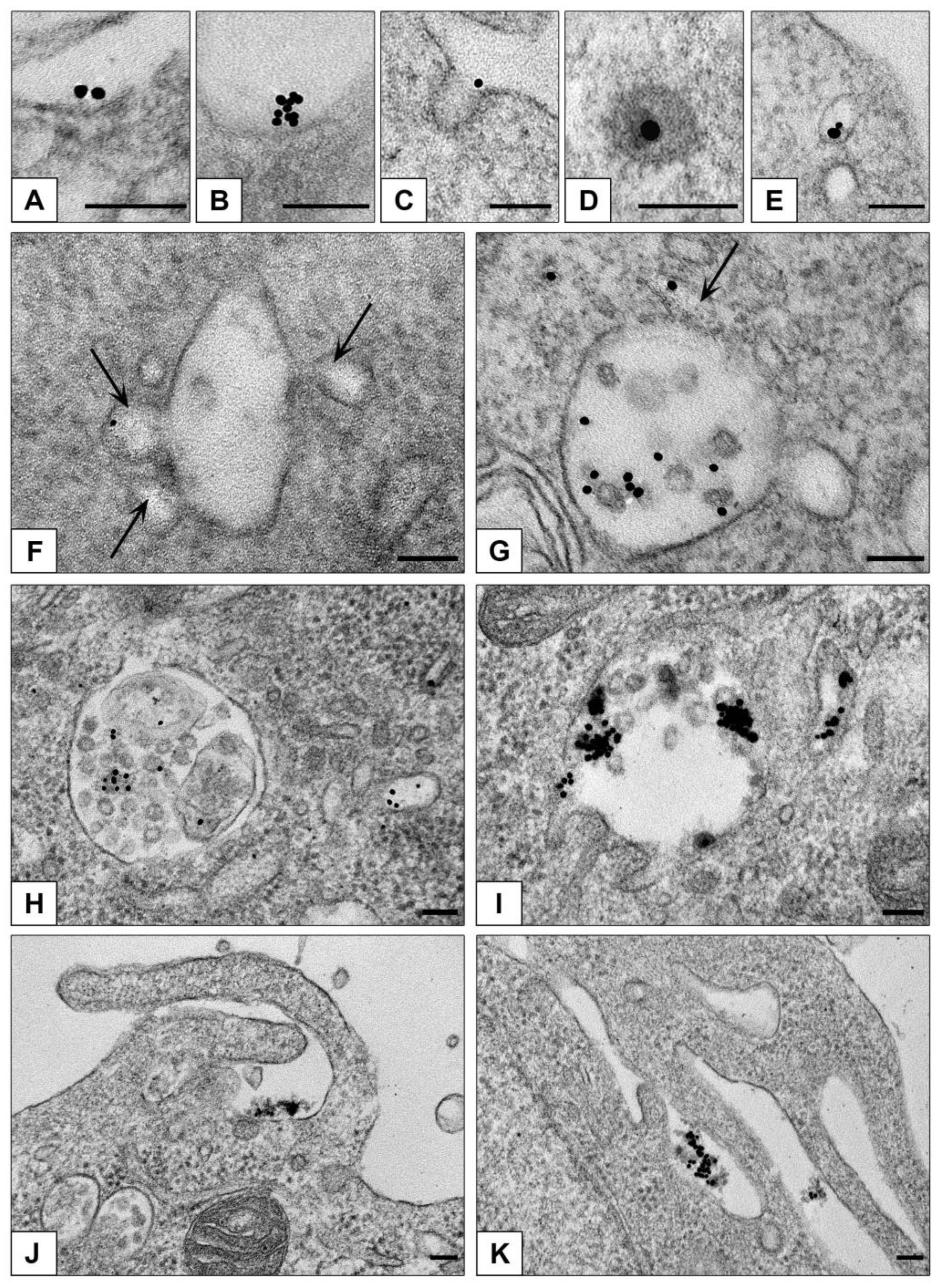
3.3.1. Ultrastructural Features of NPs Interaction with the Cells in Monolayer
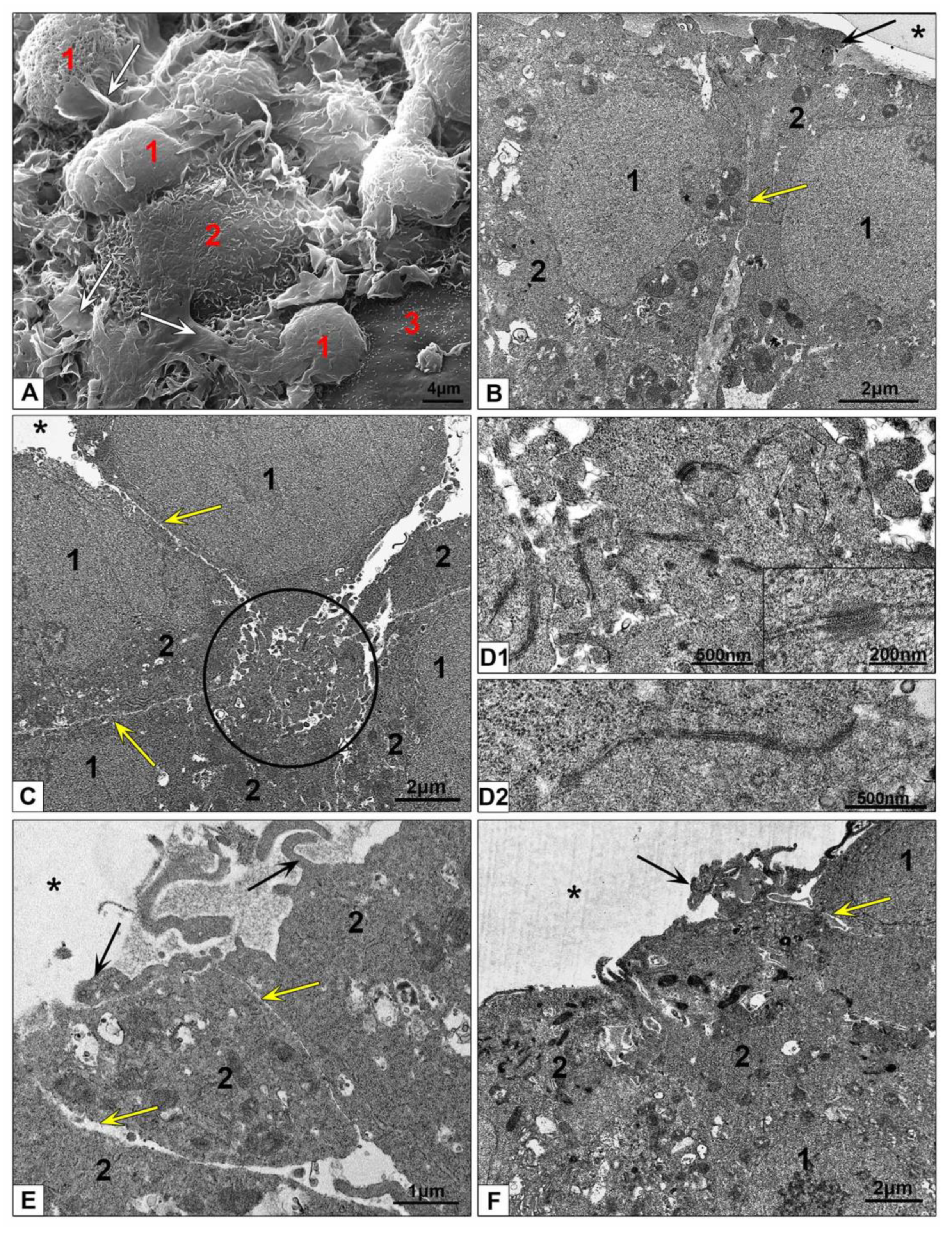
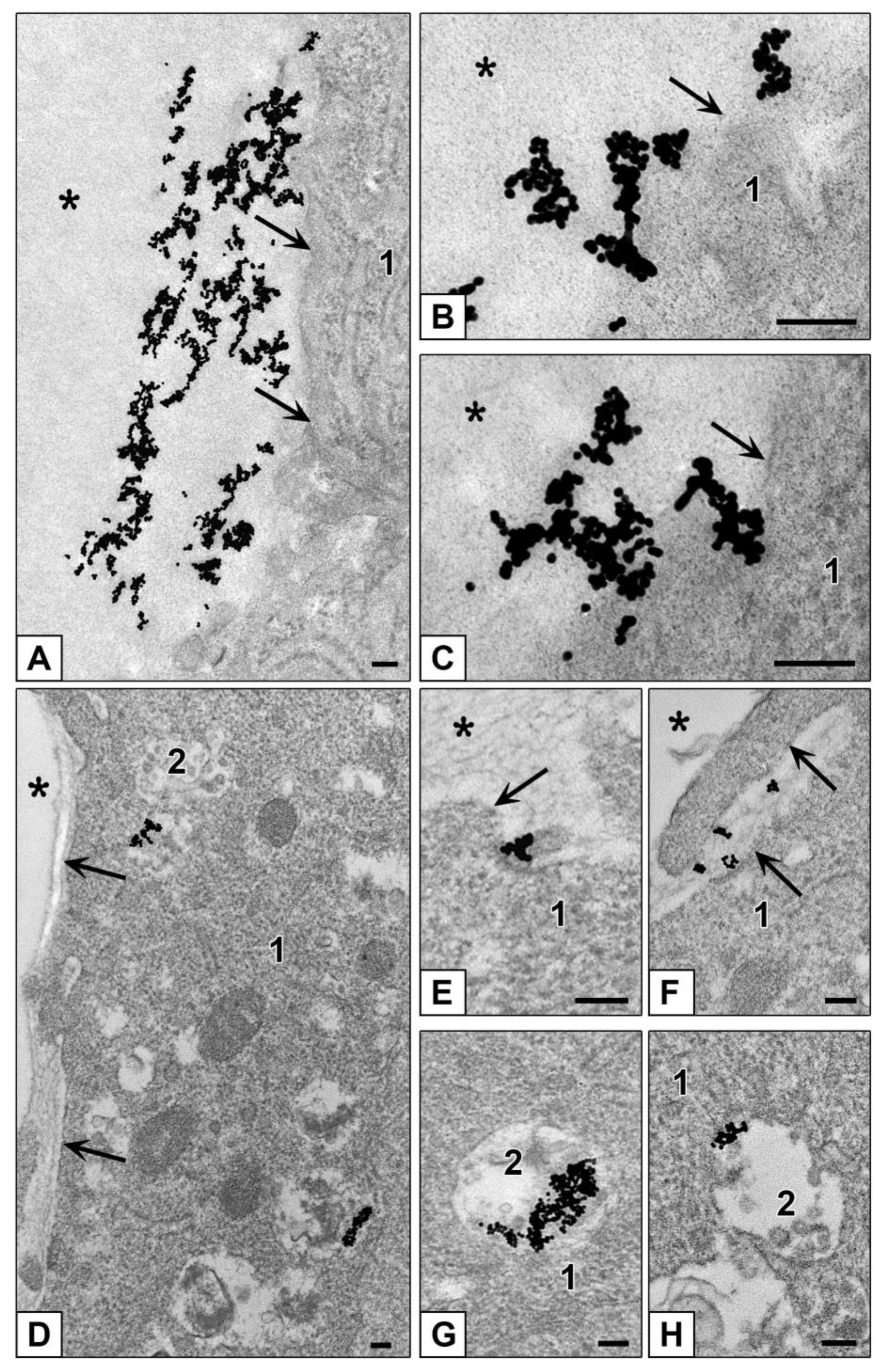
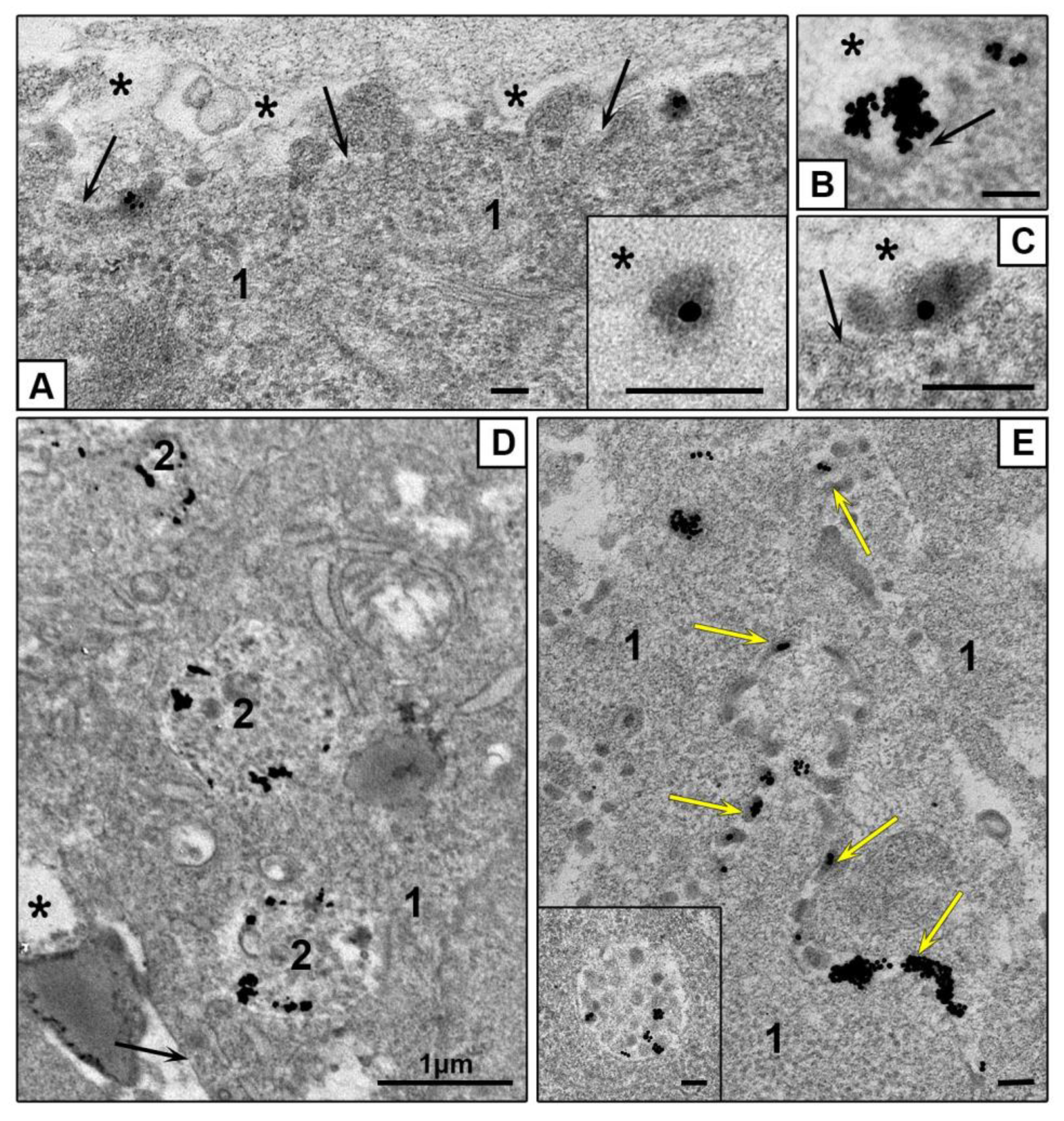
3.3.2. Features of NPs Interaction with Spheroids Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Capek, I. Polymer decorated gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine conjugates. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 249, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durymanov, M.; Reineke, J. Non-viral Delivery of Nucleic Acids: Insight into mechanisms of overcoming intracellular barriers. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, T.; Hamdan, D.; Leboeuf, C.; El Bouchtaoui, M.; Gapihan, G.; Nguyen, T.T.; Meles, S.; Angeli, E.; Ratajczak, P.; Lu, H.; et al. Targeting cancer stem cells to overcome chemoresistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzarini, E.; Mariano, S.; Carata, E.; Mura, F.; Rossi, M.; Dini, L. Intracellular transport of silver and gold nanoparticles and biological responses: An update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artiga, Á.; Serrano-Sevilla, I.; De Matteis, L.; Mitchell, S.G.; De La Fuente, J.M. Current status and future perspectives of gold nanoparticle vectors for siRNA delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 876–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Liang, X. Progress in research on gold nanoparticles in cancer management. Medicine 2019, 98, e15311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Stenzel, M. Multicellular Tumor Spheroids (MCTS) as a 3D in vitro evaluation tool of nanoparticles. Small 2018, 14, e1702858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauschke, V.M.; Shafagh, R.Z.; Hendriks, D.F.G.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. 3D primary hepatocyte culture systems for analyses of liver diseases, drug metabolism, and toxicity: Emerging culture paradigms and applications. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elje, E.; Mariussen, E.; Moriones, O.H.; Bastús, N.G.; Puntes, V.F.; Kohl, Y.; Dusinska, M.; Rundén-Pran, E. Hepato(Geno)Toxicity Assessment of nanoparticles in a HepG2 liver spheroid model. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobańska, Z.; Domeradzka-Gajda, K.; Szparaga, M.; Grobelny, J.; Tomaszewska, E.; Ranoszek-Soliwoda, K.; Celichowski, G.; Zapór, L.; Kowalczyk, K.; Stępnik, M. Comparative analysis of biological effects of molybdenum(IV) sulfide in the form of nano- and microparticles on human hepatoma HepG2 cells grown in 2D and 3D models. Toxicol. Vitro 2020, 68, 104931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, P.; Hewitt, N.J.; Albrecht, U.; Andersen, M.E.; Ansari, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bode, J.G.; Bolleyn, J.; Borner, C.; Böttger, J.; et al. Recent advances in 2D and 3D in vitro systems using primary hepatocytes, alternative hepatocyte sources and non-parenchymal liver cells and their use in investigating mechanisms of hepatotoxicity, cell signaling and ADME. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1315–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millard, M.; Yakavets, I.; Zorin, V.; Kulmukhamedova, A.; Marchal, S.; Bezdetnaya, L. Drug delivery to solid tumors: The predictive value of the multicellular tumor spheroid model for nanomedicine screening. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7993–8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, D.V.D.; Massuger, L.F.; Brock, R.; Verdurmen, W.P.R. Mimicking tumors: Toward more predictive in vitro models for peptide- and protein-conjugated drugs. Bioconjugate Chem. 2017, 28, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilenberger, C.; Rothbauer, M.; Ehmoser, E.-K.; Ertl, P.; Küpcü, S. Effect of spheroidal age on sorafenib diffusivity and toxicity in a 3D HepG2 spheroid model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleddermann, J.; Susewind, J.; Peuschel, H.; Koch, M.; Tavernaro, I.; Kraegeloh, A. Distribution of sio2 nanoparticles in 3d liver microtissues. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1411–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyffin, J.A.; Sharma, P.; Leedale, J.A.; Colley, H.E.; Murdoch, C.; Mistry, P.; Webb, S. Impact of cell types and culture methods on the functionality of in vitro liver systems—A review of cell systems for hepatotoxicity assessment. Toxicol. Vitro 2018, 48, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underhill, G.H.; Khetani, S.R. Bioengineered liver models for drug testing and cell differentiation studies. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 5, 426–439.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shen, J.X.; Lauschke, V.M. Comprehensive evaluation of organotypic and microphysiological liver models for prediction of drug-induced liver injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Ge, R.; Zhang, M.; Xia, J.; Han, S.; Lu, W.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Sun, Y. A triple modality BSA-coated dendritic nanoplatform for NIR imaging, enhanced tumor penetration and anticancer therapy. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 9021–9037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, D.P.N.; Park, D.M.; Schmidt, T.-L.; Werner, C. Modular peptide-functionalized gold nanorods for effective glioblastoma multicellular tumor spheroid targeting. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obinu, A.; Rassu, G.; Corona, P.; Maestri, M.; Riva, F.; Miele, D.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E. Poly (ethyl 2-cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles (PECA-NPs) as possible agents in tumor treatment. Coll. Surf. B Bioint. 2019, 177, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrián, V.; Martín-Saavedra, F.; Yagüe, C.; Arruebo, M.; Santamaría, J.; Vilaboa, N. Size-dependent transfection efficiency of PEI-coated gold nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3645–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, S.; Faria, H.; Soares, M.E.; Duarte, J.A.; Soares, L.; Pereira, E.; Costa-Pereira, C.; Teixeira, J.P.; Bastos, M.D.L.; Carmo, H. Influence of the surface coating on the cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and uptake of gold nanoparticles in human HepG2 cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Koshidaka, Y.; Noguchi, H.; Oishi, K.; Saito, H.; Yukawa, H.; Kaji, N.; Ikeya, T.; Suzuki, S.; Iwata, H.; et al. Observation of positively charged magnetic nanoparticles inside hepg2 spheroids using electron microscopy. Cell Med. 2013, 5, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.C.; Xie, J.; Wurm, P.A.; Xia, Y. Understanding the role of surface charges in cellular adsorption versus internalization by selectively removing gold nanoparticles on the cell surface with a i2/ki etchant. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Huang, J.; Feng, Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Xiao, S.; Li, H.; Zhong, Z.; et al. Size- and cell type-dependent cellular uptake, cytotoxicity and in vivo distribution of gold nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6957–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frens, G. Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Atwater, M.; Wang, J.; Huo, Q. Extinction coefficient of gold nanoparticles with different sizes and different capping ligands. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2007, 58, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epanchintseva, A.V.; Vorobjev, P.; Pyshnyi, D.V.; Pyshnaya, I. Fast and strong adsorption of native oligonucleotides on citrate-coated gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 2017, 34, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, S.; Banerjee, P.; Sarkar, A.; Bhattacharya, S.C. Size-dependent interaction of gold nanoparticles with transport protein: A spectroscopic study. J. Lumin. 2008, 128, 1969–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbakry, A.; Zaky, A.; Liebl, R.; Rachel, R.; Goepferich, A.; Breunig, M. Layer-by-layer assembled gold nanoparticles for sirna delivery. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2059–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyshnaya, I.A.; Razum, K.; Poletaeva, J.E.; Pyshnyi, D.V.; Zenkova, M.A.; Ryabchikova, E.I. Comparison of Behaviour in Different liquids and in cells of gold nanorods and spherical nanoparticles modified by linear polyethyleneimine and bovine serum albumin. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 908175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyshnaya, I.A.; Razum, K.V.; Dolodoev, A.S.; Shashkova, V.V.; Ryabchikova, E.I. Surprises of electron microscopic imaging of proteins and polymers covering gold nanoparticles layer by layer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 150, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.J.; Bey, E.M.; Geddes, E.W.; Lecatsas, G. Establishment of a continuously growing cell line from primary carcinoma of the liver. S. Afr. Med J. 1976, 50, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Lin, Y.; O-Lee, T.W.; Chou, C.K.; Lee, T.S.; Liu, T.J.; P’Eng, F.K.; Chen, T.Y.; Hu, C.P. Induction of plasma protein secretion in a newly established human hepatoma cell line. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1983, 3, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Wang, M.; Ren, Q.; Han, T.; Li, Y.; Sun, S.; Li, X.; Feng, F. Experimental observation of mitochondrial oxidative damage of liver cells induced by isonicotinic acid hydrazide. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 4289–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Męczyńska-Wielgosz, S.; Wojewódzka, M.; Matysiak-Kucharek, M.; Czajka, M.; Jodłowska-Jędrych, B.; Kruszewski, M.; Kapka-Skrzypczak, L. Susceptibility of HepG2 cells to silver nanoparticles in combination with other metal/metal oxide nanoparticles. Materials 2020, 13, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, J.-H.; Hu, C.-P.; Lui, W.-Y.; Lo, S.J.; Chang, C. The formation of bile canaliculi in human hepatoma cell lines. Hepatology 1990, 11, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gissen, P.; Arias, I.M. Structural and functional hepatocyte polarity and liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehlen, N.; Suarez, A.A.R.; El Saghire, H.; Saviano, A.; Schuster, C.; Lupberger, J.; Baumert, T.F. Tight junction proteins and the biology of hepatobiliary disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müsch, A. The unique polarity phenotype of hepatocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 328, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, F.L.; Russell, W.C.; Smiley, J.; Nairn, R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by dna from human adenovirus type 5. J. Gen. Virol. 1977, 36, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, J.; Euwart, D.; Mei, B.; Estes, S.; Kshirsagar, R. Human cell lines for biopharmaceutical manufacturing: History, status, and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2015, 36, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, A.D.; Tran, M.Y.; Kamen, A.A. Lentiviral vector production in suspension culture using serum-free medium for the transduction of car-t cells. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2020, 2086, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskell, H.; Sharma, P.; Colley, H.E.; Murdoch, C.; Williams, D.P.; Webb, S.D. Characterization of a functional C3A liver spheroid model. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 5, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, A.; Couvet, M.; Coll, J.-L. Unsuccessful mitosis in multicellular tumour spheroids. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28769–28784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuchi, K.; Oya, K.; Hosoya, K.; Sasaki, K.; Sakurada, Y.; Nakano, T.; Hisatomi, H. Different morphologies of human embryonic kidney 293T cells in various types of culture dishes. Cytotechnology 2019, 72, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelm, J.M.; Timmins, N.E.; Brown, C.J.; Fussenegger, M.; Nielsen, L.K. Method for generation of homogeneous multicellular tumor spheroids applicable to a wide variety of cell types. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003, 83, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slim, C.L.; Van Ijzendoorn, S.C.D.; Lázaro-Diéguez, F.; Müsch, A. The special case of hepatocytes. BioArchitecture 2014, 4, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.R.; Shrivastava, A.; Gallet, B.; Karepina, E.; Charbonnier, P.; Chevallet, M.; Jouneau, P.-H.; Deniaud, A. Canalicular domain structure and function in matrix-free hepatic spheroids. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cording, J.; Berg, J.; Käding, N.; Bellmann, C.; Tscheik, C.; Westphal, J.K.; Milatz, S.; Günzel, R.; Wolburg, H.; Piontek, J.; et al. In tight junctions, claudins regulate the interactions between occludin, tricellulin and marveld3, which, inversely, modulate claudin oligomerization. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 126, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutel, O.; Maraspini, R.; Pombo-García, K.; Martin-Lemaitre, C.; Honigmann, A. Phase separation of zonula occludens proteins drives formation of tight junctions. Cell 2019, 179, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inada, M.; Izawa, G.; Kobayashi, W.; Ozawa, M. 293 cells express both epithelial as well as mesenchymal cell adhesion molecules. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischer, C.C.; Payne, C.K. Nanoparticle–cell interactions: Molecular structure of the protein corona and cellular outcomes. Accounts Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2651–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francia, V.; Montizaan, D.; Salvati, A. Interactions at the cell membrane and pathways of internalization of nano-sized materials for nanomedicine. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Kim, J.; Herrera, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Kabanov, A.V.; Sahay, G. Brief update on endocytosis of nanomedicines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 144, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, M.C.; Teasdale, R.D. Defining macropinocytosis. Traffic 2009, 10, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poussin, C.; Foti, M.; Carpentier, J.-L.; Pugin, J. CD14-dependent endotoxin internalization via a macropinocytic pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 20285–20291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stow, J.L.; Hung, Y.; Wall, A.A. Macropinocytosis: Insights from immunology and cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2020, 65, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neutra, M.R.; Ciechanover, A.; Owen, L.S.; Lodish, H.F. Intracellular transport of transferrin- and asialoorosomucoid-colloidal gold conjugates to lysosomes after receptor-mediated endocytosis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1985, 33, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Ma, H.; Liu, J.; Huo, S.; Kumar, A.; Wei, T.; Zhang, X.; Jin, S.; Gan, Y.; Wang, P.C.; et al. Size-Dependent Localization and Penetration of Ultrasmall Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Cells, Multicellular Spheroids, and Tumors in Vivo. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4483–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, S.; Ma, H.; Huang, K.; Liu, J.; Wei, T.; Jin, S.; Zhang, J.; He, S.; Liang, X.-J. Superior penetration and retention behavior of 50 nm gold nanoparticles in tumors. Cancer Res. 2012, 73, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minchinton, A.I.; Tannock, I.F. Drug penetration in solid tumours. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sujai, P.T.; Joseph, M.M.; Saranya, G.; Nair, J.B.; Murali, V.P.; Maiti, K.K.; T, S.P. Surface charge modulates the internalization vs. penetration of gold nanoparticles: Comprehensive scrutiny on monolayer cancer cells, multicellular spheroids and solid tumors by SERS modality. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 6971–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Lin, C.; Cheng, J.; Su, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, T.; Wen, X.; Zhao, P. Generation of multicellular tumor spheroids with microwell-based agarose scaffolds for drug testing. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | Zeta-Potential (mV) | Polydipersity Index | Hydrodynamic Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AuNPs | −33.6 ± 2.0 | 0.145 ± 0.006 | 17.4 ± 0.4 |
| AuMUA-NPs | −53.8 ± 3.4 | 0.288 ± 0.001 | 46.0 ± 2.2 |
| AuMUA-PEI-NPs | 39.9 ± 1.3 | 0.258 ± 0.008 | 125.9 ± 2.8 |
| AuBSA-NPs | −35.7 ± 1.8 | 0.212 ± 0.008 | 35.9 ± 0.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chelobanov, B.; Poletaeva, J.; Epanchintseva, A.; Tupitsyna, A.; Pyshnaya, I.; Ryabchikova, E. Ultrastructural Features of Gold Nanoparticles Interaction with HepG2 and HEK293 Cells in Monolayer and Spheroids. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102040
Chelobanov B, Poletaeva J, Epanchintseva A, Tupitsyna A, Pyshnaya I, Ryabchikova E. Ultrastructural Features of Gold Nanoparticles Interaction with HepG2 and HEK293 Cells in Monolayer and Spheroids. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(10):2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102040
Chicago/Turabian StyleChelobanov, Boris, Julia Poletaeva, Anna Epanchintseva, Anastasiya Tupitsyna, Inna Pyshnaya, and Elena Ryabchikova. 2020. "Ultrastructural Features of Gold Nanoparticles Interaction with HepG2 and HEK293 Cells in Monolayer and Spheroids" Nanomaterials 10, no. 10: 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102040
APA StyleChelobanov, B., Poletaeva, J., Epanchintseva, A., Tupitsyna, A., Pyshnaya, I., & Ryabchikova, E. (2020). Ultrastructural Features of Gold Nanoparticles Interaction with HepG2 and HEK293 Cells in Monolayer and Spheroids. Nanomaterials, 10(10), 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10102040






