Biodegradable Double-Layer Hydrogels with Sequential Drug Release for Multi-Phase Collaborative Regulation in Scar-Free Wound Healing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
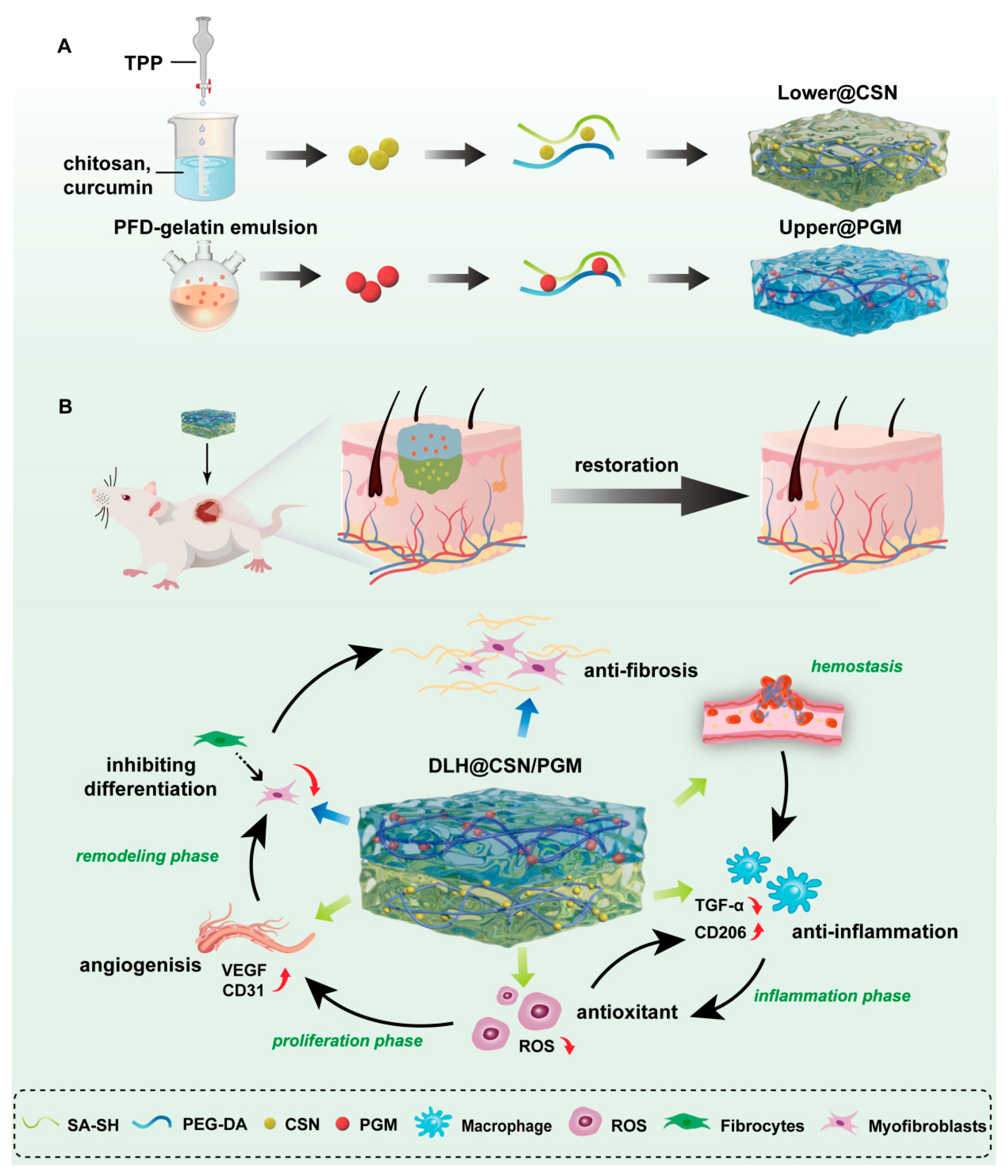
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of (DLH@CSN/PGM)
2.1.1. Lower@CSN Hydrogel
2.1.2. Upper@PGM Hydrogel
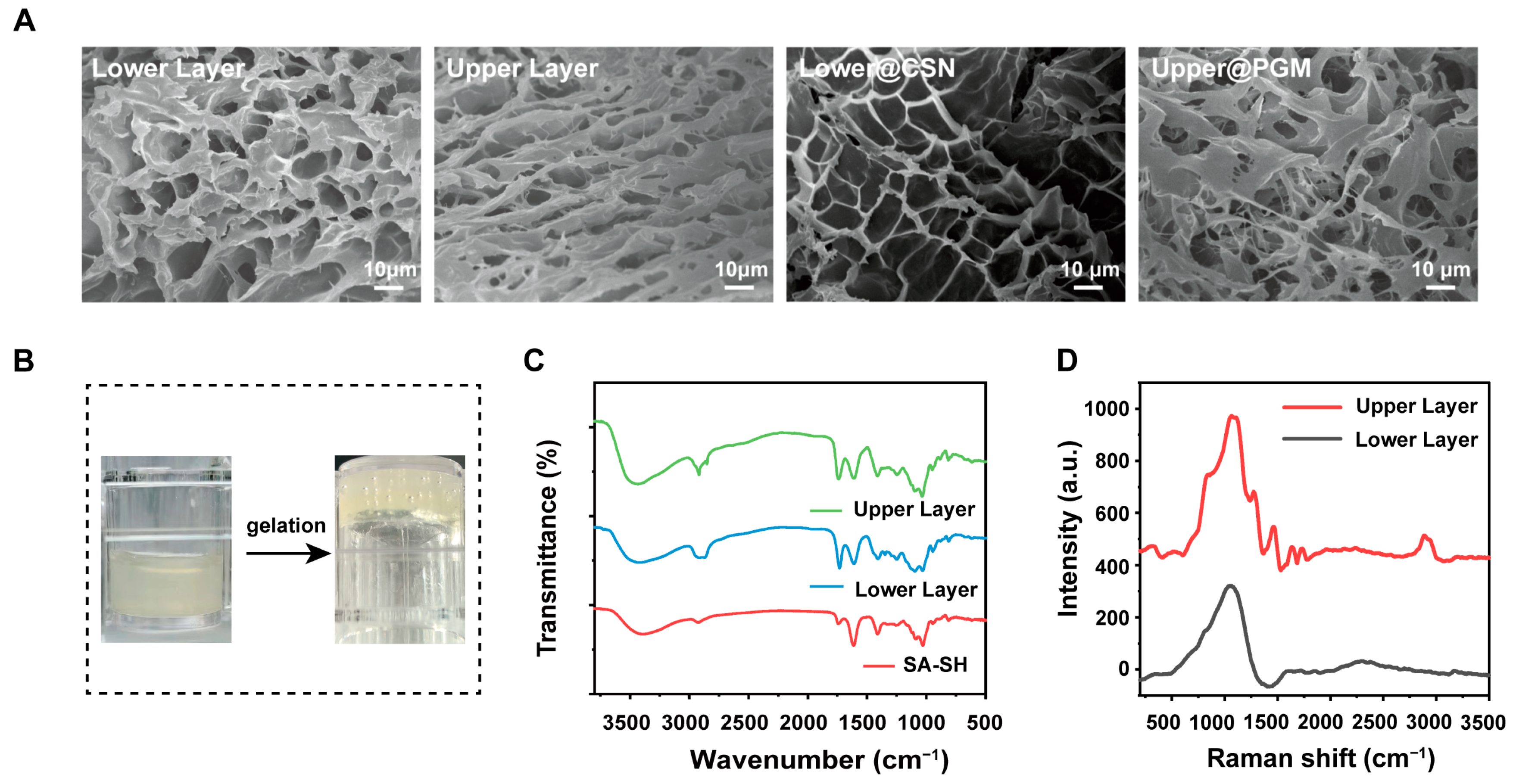
2.1.3. Characterization
2.2. In Vitro Drug Release Study
2.3. Cell Proliferation and Migration Assay
2.4. Tube Formation Assay
2.5. Antioxidant Activity
2.6. In Vivo Wound Healing
2.7. Histological Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of DLH@CSN/PGM
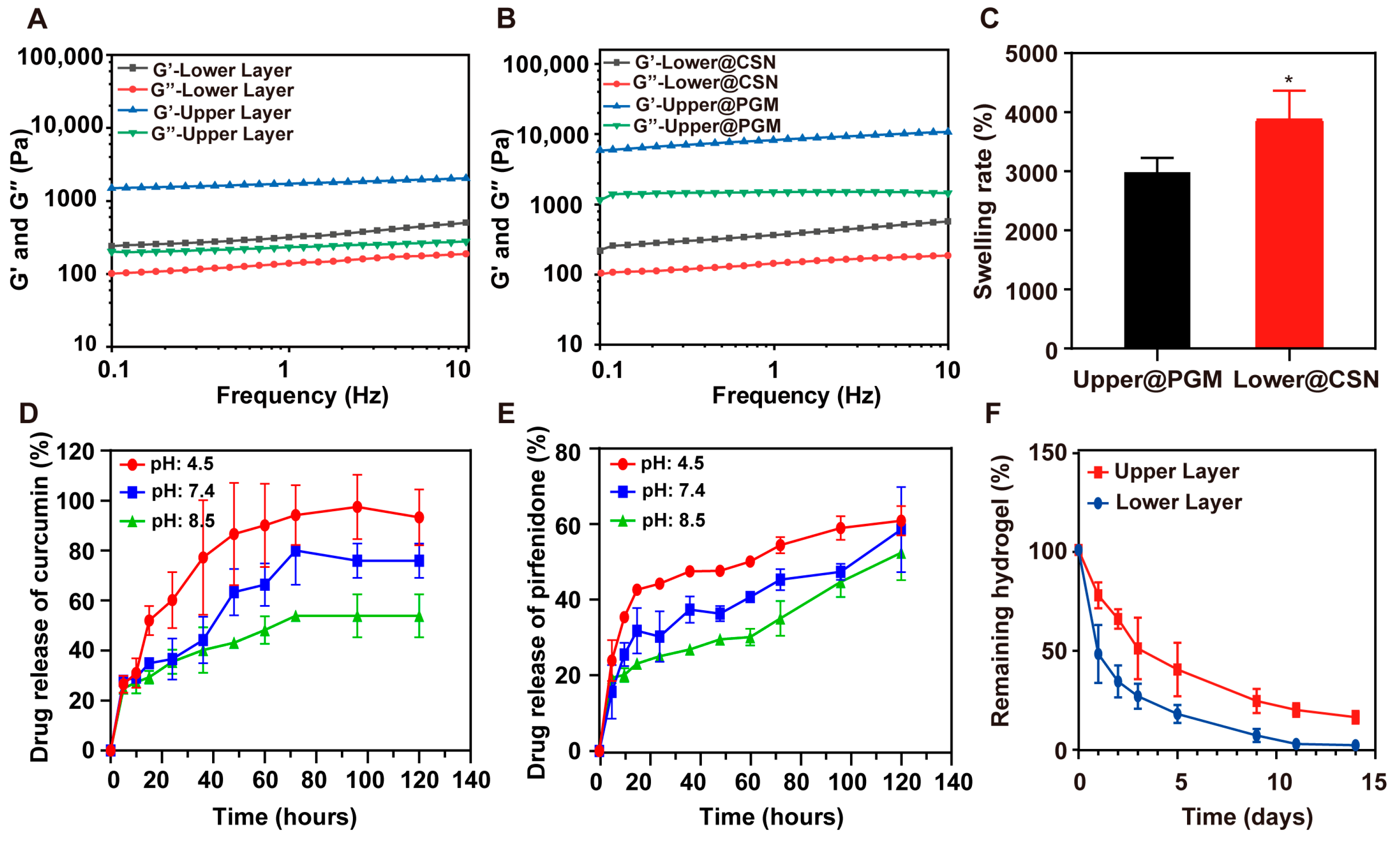
3.2. Mechanical Properties and Swelling Behavior
3.3. Degradation Profiles and Sequential Drug Release
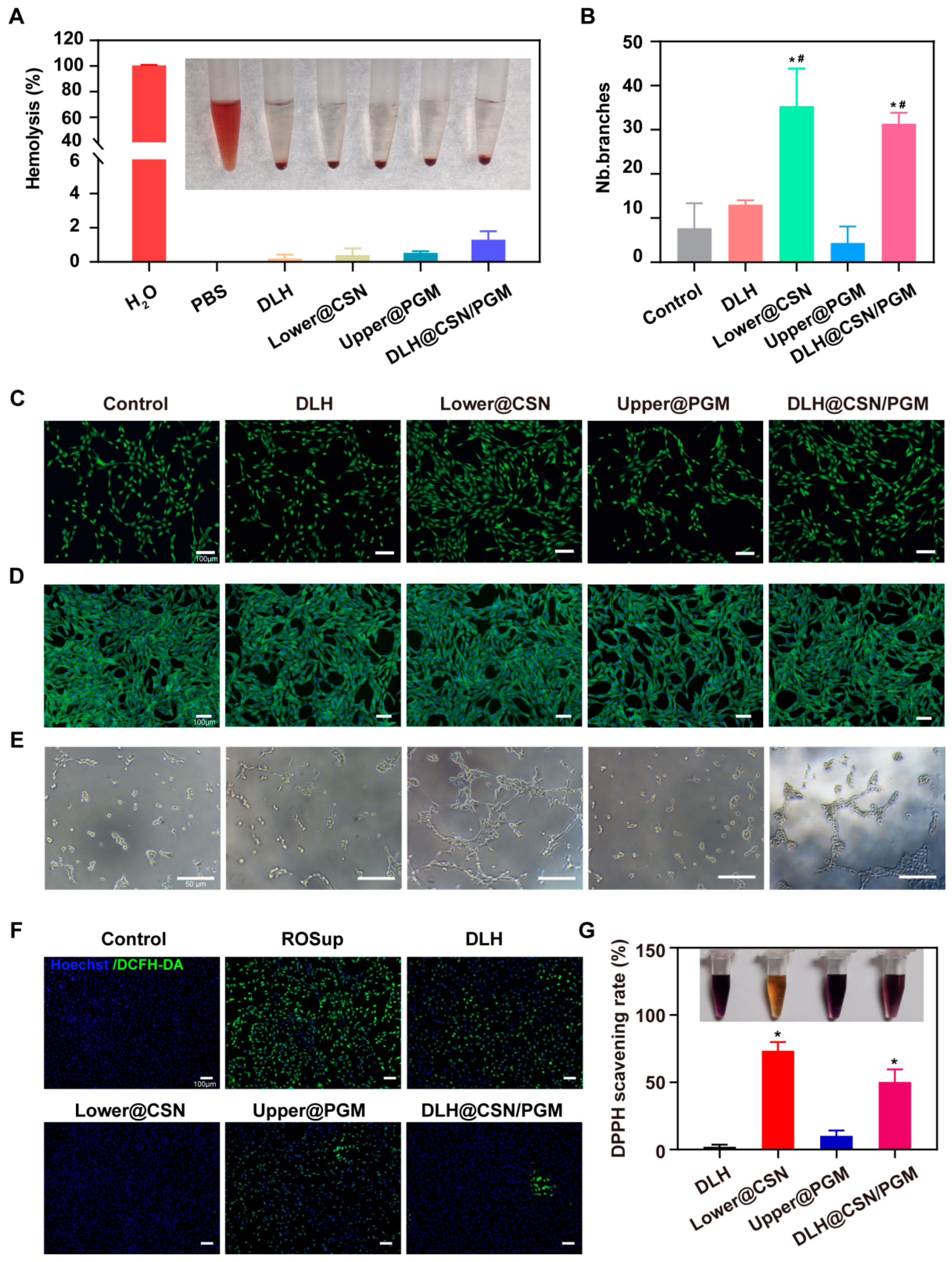
3.4. Biocompatibility and Hemostatic Ability of the Hydrogels
3.5. In Vitro Antioxidant Capacity
3.6. In Vitro Angiogenesis Capacity
3.7. In Vitro Cell Proliferation and Migration
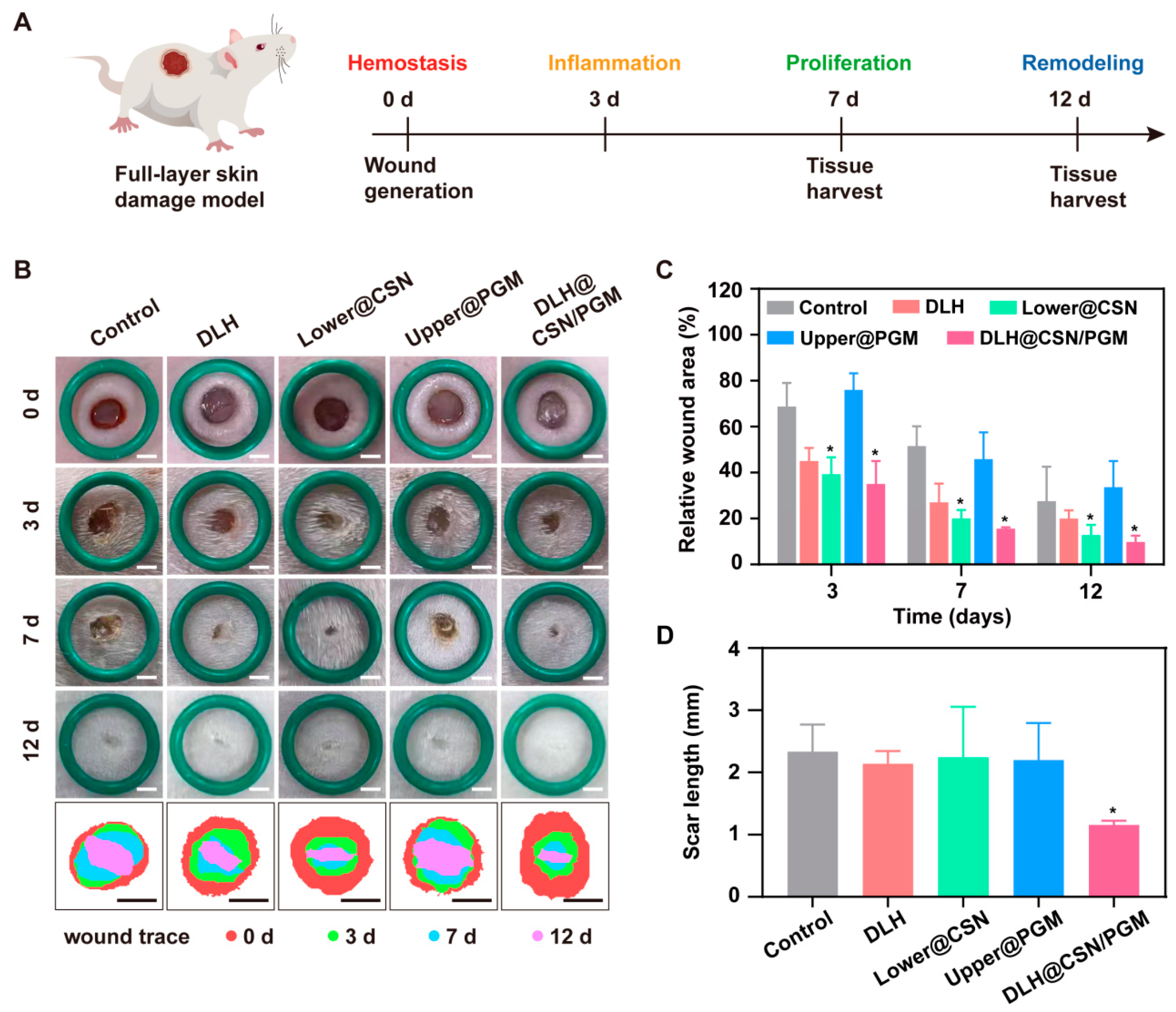
3.8. DLH@CSN/PGM Accelerates Wound Healing and Enhances Scar Quality
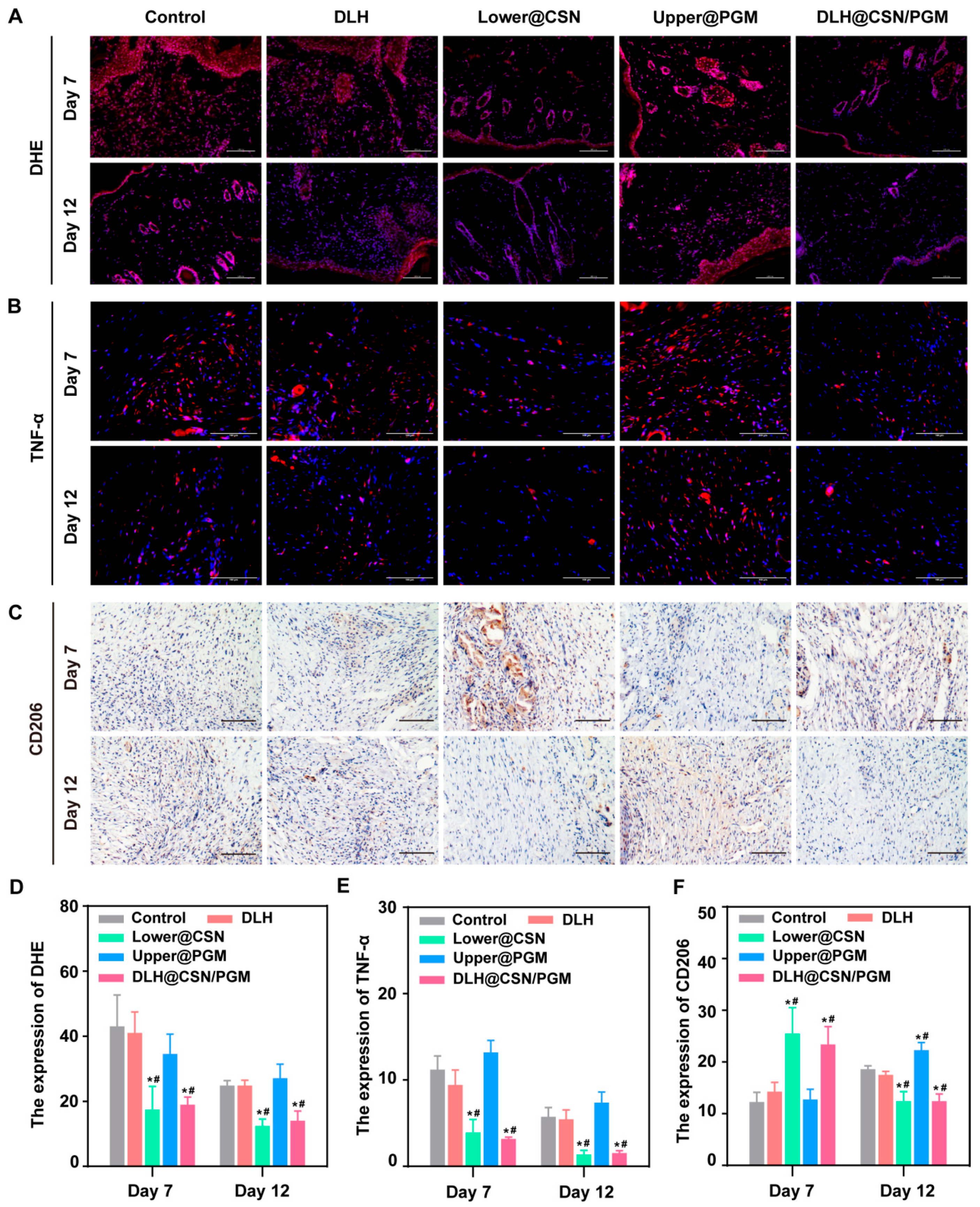
3.9. DLH@CSN/PGM Modulates Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Vivo
3.10. In Vivo Angiogenesis Enhancement by DLH@CSN/PGM
3.11. DLH@CSN/PGM Promotes Reepithelialization and Collagen Deposition
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lv, J.; Ma, H.; Ye, G.; Jia, S.; He, J.; Jiaduo, W.; Ma, J.; Qu, Y.; Gou, K.; Zeng, R. Bilayer Microneedles Based on Bletilla Striata Polysaccharide Containing Asiaticoside Effectively Promote Scarless Wound Healing. Mater. Des. 2023, 226, 111655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerty, C.C.; Jeschke, M.G.; Branski, L.K.; Barret, J.P.; Dziewulski, P.; Herndon, D.N. Hypertrophic Scarring: The Greatest Unmet Challenge after Burn Injury. Lancet 2016, 388, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F.; Luo, L.; Shen, K.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. KLF4 Alleviates Hypertrophic Scar Fibrosis by Directly Activating BMP4 Transcription. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 3324–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Fan, B.; Shang, P.; Ding, R.; Du, J.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, H.; Yan, X. VR23 and Bisdemethoxycurcumin Enhanced Nanofiber Niche with Durable Bidirectional Functions for Promoting Wound Repair and Inhibiting Scar Formation. Small Methods 2024, 8, 2400273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Shu, J.; Wang, Y.; Deng, H.; Zhang, J.; He, J.; Wu, F. ROS-Scavenging Hydrogel to Accelerate Wound Healing and Reduce Scar Formation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, M.; Järbrink, K.; Divakar, U.; Bajpai, R.; Upton, Z.; Schmidtchen, A.; Car, J. The Humanistic and Economic Burden of Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review. Wound Repair. Regen. 2019, 27, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, M.; Zhu, T.; Xiong, H.; Zhu, L.-M. A Careob-like Nanofibers with a Sustained Drug Release Profile for Promoting Skin Wound Repair and Inhibiting Hypertrophic Scar. Compos. Part B 2022, 236, 109790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lu, R.; Jia, M.; Xiao, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, S. Biological Glue from Only Lipoic Acid for Scarless Wound Healing by Anti-Inflammation and TGF-β Regulation. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 2588–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Teng, L.; Zhang, X.; Dong, C. Multifunctional Single-Component Polypeptide Hydrogels: The Gelation Mechanism, Superior Biocompatibility, High Performance Hemostasis, and Scarless Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2101809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Ju, L.; Saengow, C.; Ren, W.; Ewoldt, R.; Fan, T.; Irudayaraj, J. Nano Oxygen Chamber by Cascade Reaction for Hypoxia Mitigation and Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging in Wound Healing. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 35, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, F.; Whited, J.L. Finding Solutions for Fibrosis: Understanding the Innate Mechanisms Used by Super-Regenerator Vertebrates to Combat Scarring. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2100407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Abdouss, M.; Mazinani, S.; Soltanabadi, A.; Kalaee, M. Modified Nanofiber Containing Chitosan and Graphene Oxide-Magnetite Nanoparticles as Effective Materials for Smart Wound Dressing. Compos. Part B 2022, 231, 109557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wubneh, A.; Tsekoura, E.K.; Ayranci, C.; Uludağ, H. Current State of Fabrication Technologies and Materials for Bone Tissue Engineering. Acta Biomater. 2018, 80, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ding, Z.; Cheng, W.; Lu, Q.; Kong, X.; Zhou, X.; Lu, G.; Kaplan, D.L. Microskin-Inspired Injectable MSC-Laden Hydrogels for Scarless Wound Healing with Hair Follicles. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2020, 9, 2000041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, P.; Wu, L.; Su, Z.; Gui, X.; Gao, C.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Cen, Y.; et al. In Situ Photo-Crosslinked Adhesive Hydrogel Loaded with Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promotes Diabetic Wound Healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, G.; Huang, H.; Wang, K.; Wang, H.; Lang, M.; Gao, H.; Zhao, S. Sequential Release of Small Extracellular Vesicles from Bilayered Thiolated Alginate/Polyethylene Glycol Diacrylate Hydrogels for Scarless Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6352–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Shen, Y.; Harmon, J.W. Engineering Pro-Regenerative Hydrogels for Scarless Wound Healing. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2018, 7, 1800016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, J.; Zhang, C.; Xing, C.; Bian, H.; Lv, J.; Chen, D.; Xiao, L.; Su, J.; et al. Advanced multilayer composite dressing with co-delivery of gelsevirine and silk fibroin for burn wound healing. Compos. Part B 2023, 253, 110549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, C.; Pradhan, J. A human epidermal growth factor-curcumin bandage bioconjugate loaded with mesenchymal stem cell for in vivo diabetic wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 111, 110751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, C.; Sahoo, S.K. Curcumin and its topical formulations for wound healing applications. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Song, W.; He, Y.; Li, H. Multilayer Injectable Hydrogel System Sequentially Delivers Bioactive Substances for Each Wound Healing Stage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 29787–29806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ji, Z.; Feng, J.; Shu, L.; Xiao, S.; Huang, Z. Wound microenvironment sensing and self-adjusting hydrogel with glucose, ROS, and MMP-9 responsiveness for improving microcirculation of diabetes foot ulcers. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, R.T.; Turner, P.A.; Carson, W.F., 4th; Levi, B.; Kunkel, S. Harnessing macrophage-mediated degradation of gelatin microspheres for spatiotemporal control of BMP2 release. Biomaterials 2018, 161, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Mao, J.; Zhao, B.; Mao, X.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; et al. Secretory Fluid-Aggregated Janus Electrospun Short Fiber Scaffold for Wound Healing. Small 2022, 18, 2200799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B. An Intrinsically Bioactive Hydrogel with On-Demand Drug Release Behaviors for Diabetic Wound Healing. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4592–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Yasothan, U.; Kirkpatrick, P. Pirfenidone. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 489–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiang, L.; Lin, F.; Tang, Y.; Deng, L.; Cui, W. A Biomaterial-Based Hedging Immune Strategy for Scarless Tendon Healing. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, Q.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Shi, J.; Kong, L.; Fu, D.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Z. An Injectable Bioactive Dressing Based on Platelet-Rich Plasma and Nanoclay: Sustained Release of Deferoxamine to Accelerate Chronic Wound Healing. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 4318–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Meng, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, P.; Zhang, H.; Fang, X.; Wang, D.-A.; Fan, C. Progress of Gelatin-Based Microspheres (GMSs) as Delivery Vehicles of Drug and Cell. Biomater. Adv. 2021, 122, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Yin, T.; Jiang, J.; He, Y.; Xiang, T.; Zhou, S. Wound Microenvironment Self-Adaptive Hydrogel with Efficient Angiogenesis for Promoting Diabetic Wound Healing. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 20, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cai, K.; Zhang, J. Combination Wound Healing Using Polymer Entangled Porous Nanoadhesive Hybrids with Robust ROS Scavenging and Angiogenesis Properties. Acta Biomater. 2022, 152, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Ding, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Q.; Kaplan, D.L. Asiaticoside-Laden Silk Nanofiber Hydrogels to Regulate Inflammation and Angiogenesis for Scarless Skin Regeneration. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 5227–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.; Kamalasanan, K. Drug Delivery to Optimize Angiogenesis Imbalance in Keloid: A Review. Control. Release 2021, 329, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daya, R.; Xu, C.; Nguyen, N.-Y.T.; Liu, H.H. Angiogenic Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels with Curcumin-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Tissue Repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 11051–11067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wang, P.; Cao, R.; Wu, J.; Ji, H.; Wang, M.; Hu, C.; Huang, P.; Wang, X. Exudate Absorbing and Antimicrobial Hydrogel Integrated with Multifunctional Curcumin-Loaded Magnesium Polyphenol Network for Facilitating Burn Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 22355–22370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ale, T.; Kehinde, V.; Ale, T.; Wang, H.-C.; Lavik, E. Polyester Nanoparticles and Polyurethane Nanocapsules Deliver Pirfenidone To Reduce Fibrosis and Scarring. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 3348–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, U.; Lee, M.S.; Jeon, J.; Lee, S.; Hwang, M.P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.S.; Kim, K. Coacervate-Mediated Exogenous Growth Factor Delivery for Scarless Skin Regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019, 90, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Tu, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhan, Y.; Ding, J.; Wu, X.; Yang, Z.; Cao, W.; Deng, L.; et al. A ROS-Scavenging Hydrogel Loaded with Bacterial Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Hyperbranched Poly-L-Lysine Promotes the Wound Scar-Free Healing of Infected Skin in Vivo. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 436, 135130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Fu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Gerhard, E.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Guo, J. Anti-Oxidant Anti-Inflammatory and Antibacterial Tannin-Crosslinked Citrate-Based Mussel-Inspired Bioadhesives Facilitate Scarless Wound Healing. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 20, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Xi, K.; Tang, Y.; Bian, J.; Qin, Y.; Xiao, W.; Pan, T.; Cheng, X.; Ge, Z.; Cui, W. Immunized Microspheres Engineered Hydrogel Membrane for Reprogramming Macrophage and Mucosal Repair. Small 2023, 19, 2207030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korntner, S.; Lehner, C.; Gehwolf, R.; Wagner, A.; Grütz, M.; Kunkel, N.; Tempfer, H.; Traweger, A. Limiting Angiogenesis to Modulate Scar Formation. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2019, 146, 170–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Sun, S.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, J.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Z. Opportunities and Challenges of Nanomaterials in Wound Healing: Advances, Mechanisms, and Perspectives. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, X.; Sun, W.; Zhao, Y. Emerging Biomedical Technologies for Scarless Wound Healing. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 42, 449–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zu, Q.; Deng, C.; Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Jin, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, E. Biodegradable Double-Layer Hydrogels with Sequential Drug Release for Multi-Phase Collaborative Regulation in Scar-Free Wound Healing. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16050164
Zhang X, Zu Q, Deng C, Gao X, Liu H, Jin Y, Yang X, Wang E. Biodegradable Double-Layer Hydrogels with Sequential Drug Release for Multi-Phase Collaborative Regulation in Scar-Free Wound Healing. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2025; 16(5):164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16050164
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinyu, Qianhe Zu, Chunlin Deng, Xin Gao, Hongxu Liu, Yi Jin, Xinjian Yang, and Enjun Wang. 2025. "Biodegradable Double-Layer Hydrogels with Sequential Drug Release for Multi-Phase Collaborative Regulation in Scar-Free Wound Healing" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 16, no. 5: 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16050164
APA StyleZhang, X., Zu, Q., Deng, C., Gao, X., Liu, H., Jin, Y., Yang, X., & Wang, E. (2025). Biodegradable Double-Layer Hydrogels with Sequential Drug Release for Multi-Phase Collaborative Regulation in Scar-Free Wound Healing. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 16(5), 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16050164





