Encapsulation of Snail Slime in Metal–Organic Framework ZIF-8
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
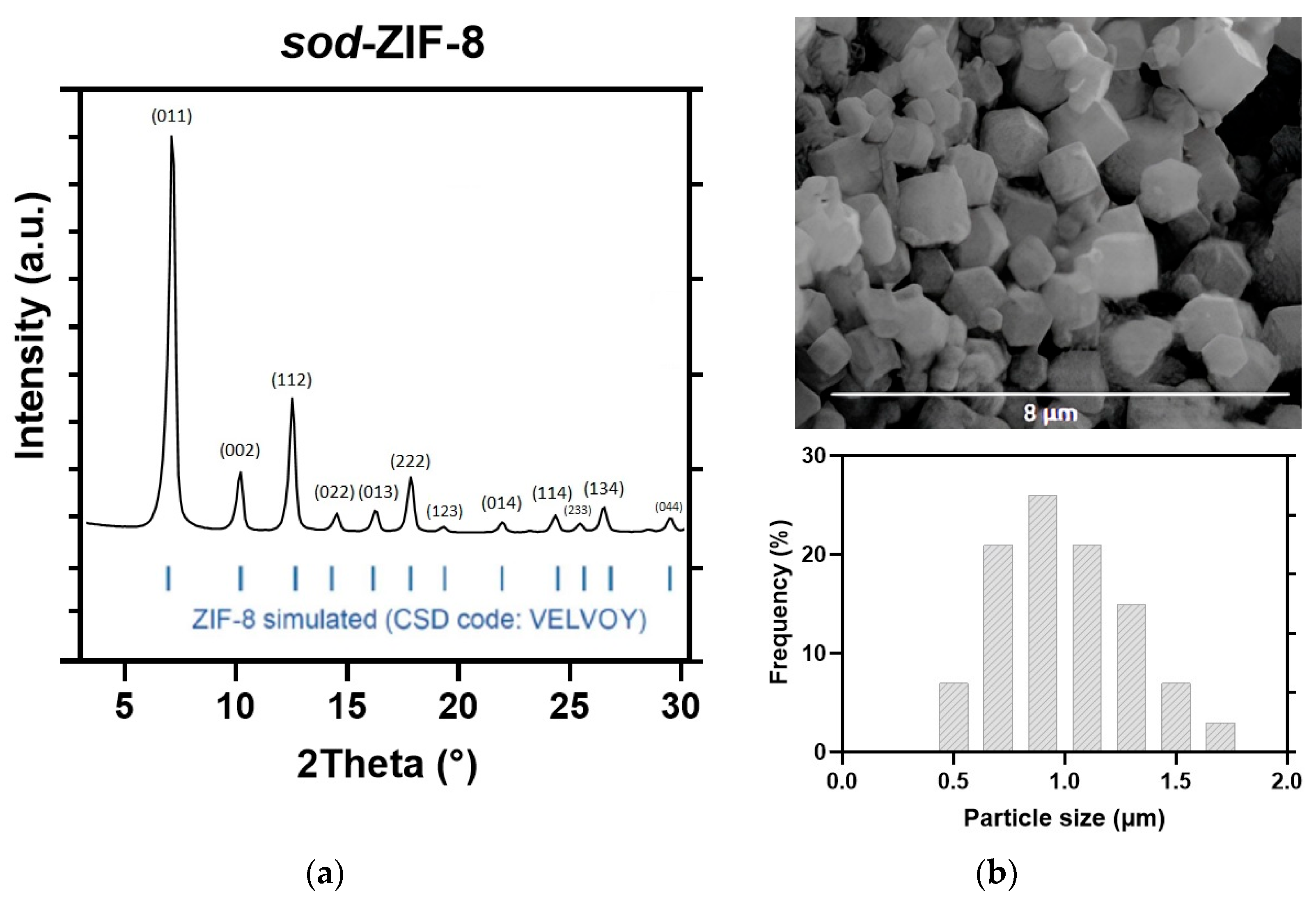
3.1. Characterization of As-Synthetized ZIF-8 Crystals
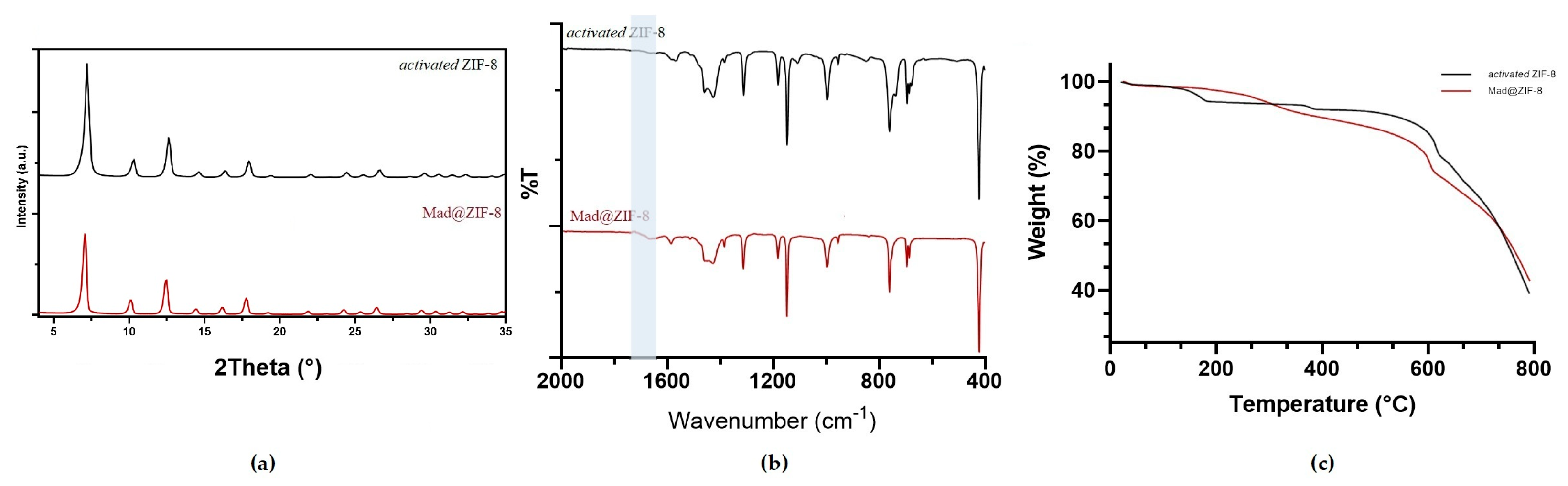
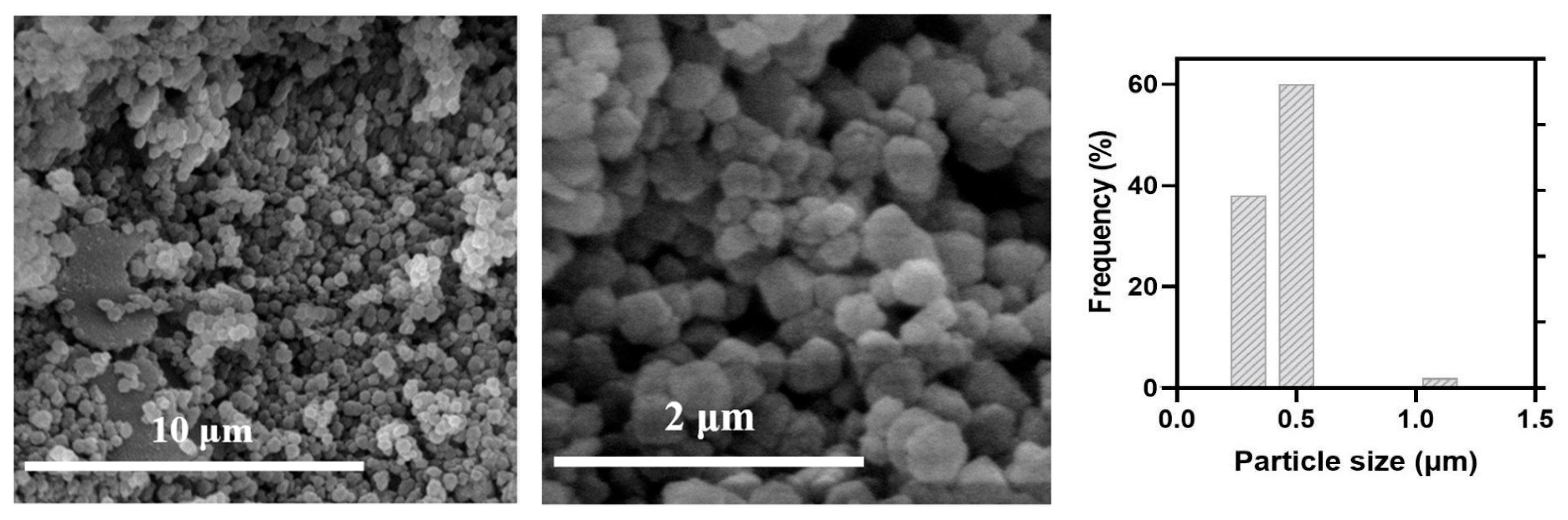
3.2. Synthesis of MAD@ZIF-8 Biocomposite
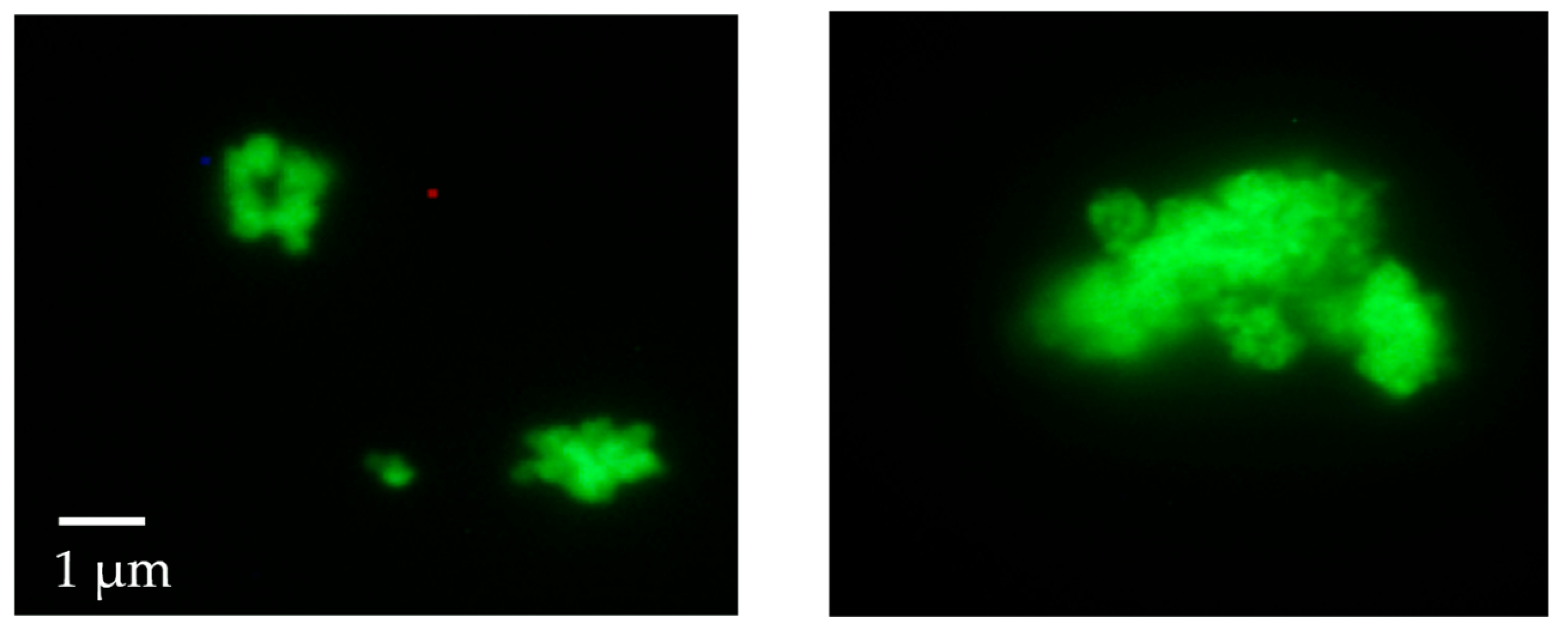
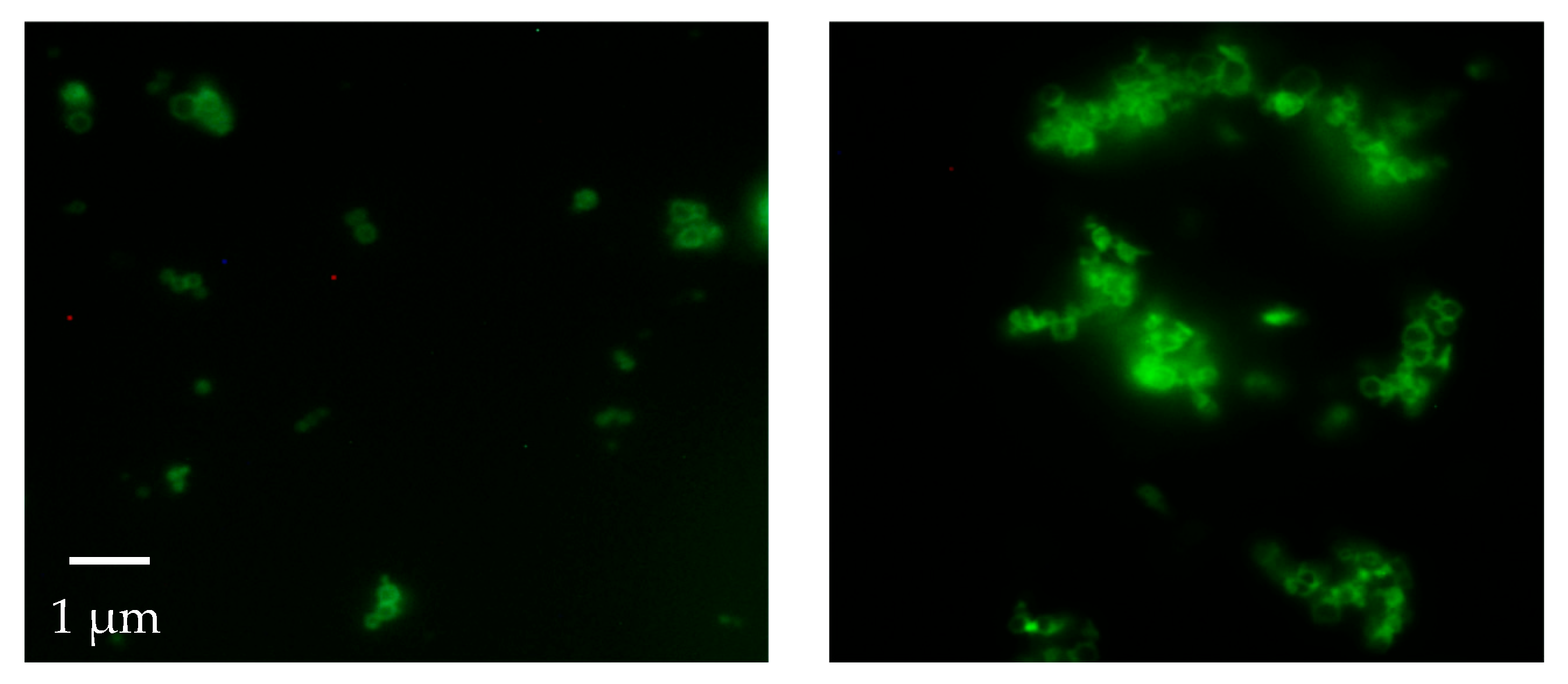
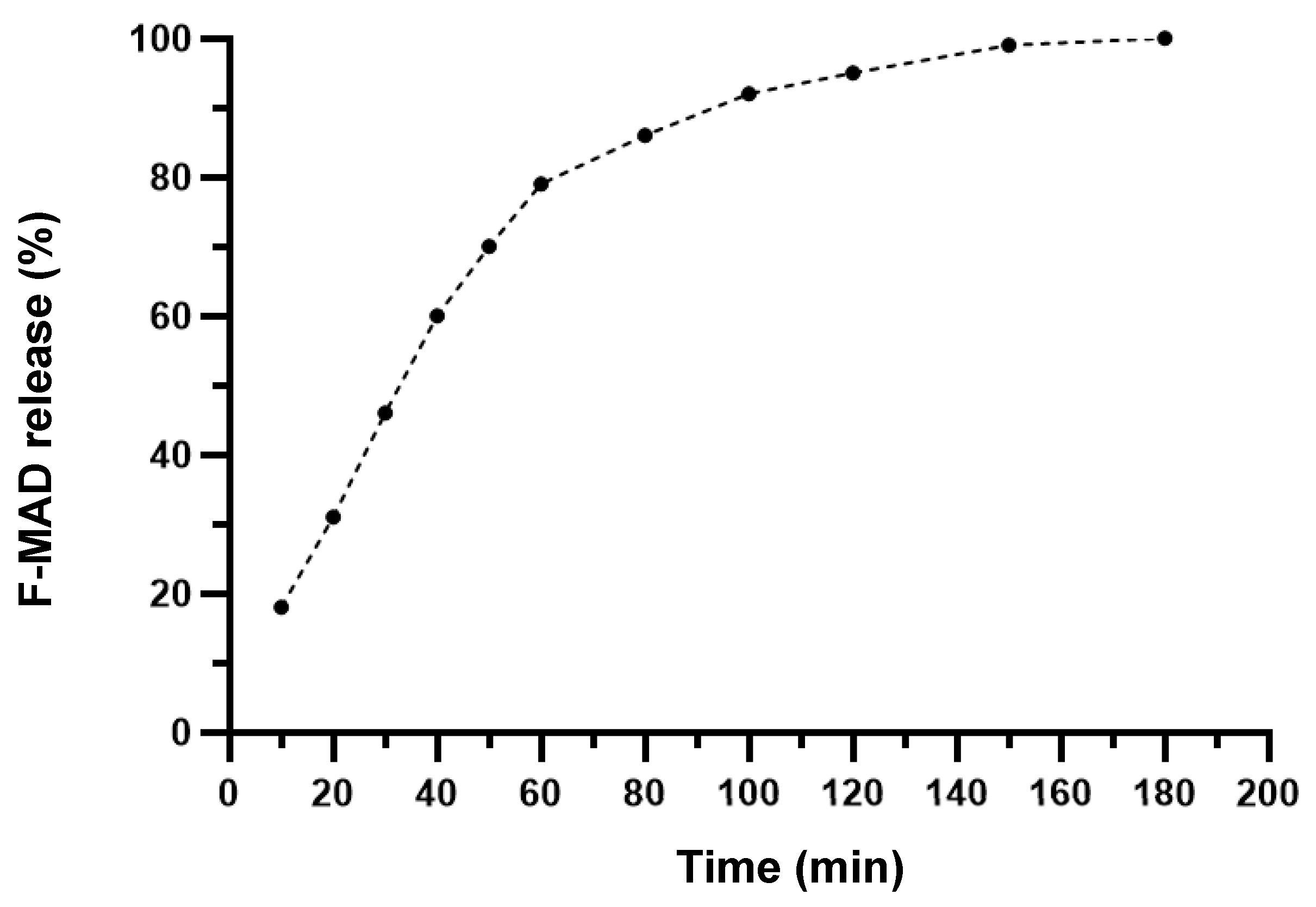
3.3. Synthesis of Fluorophore-Labeled MAD@ZIF-8 Biocomposites
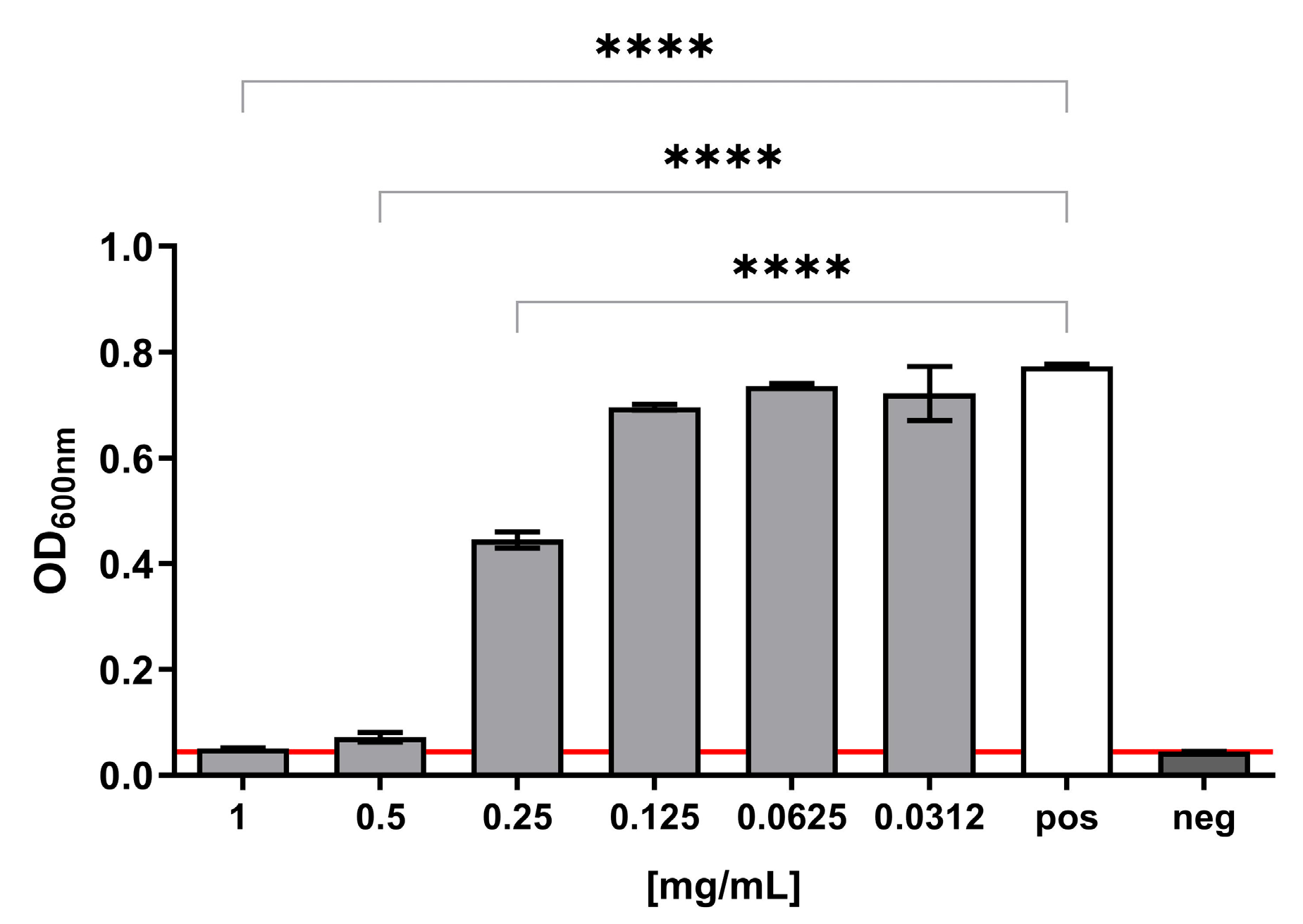
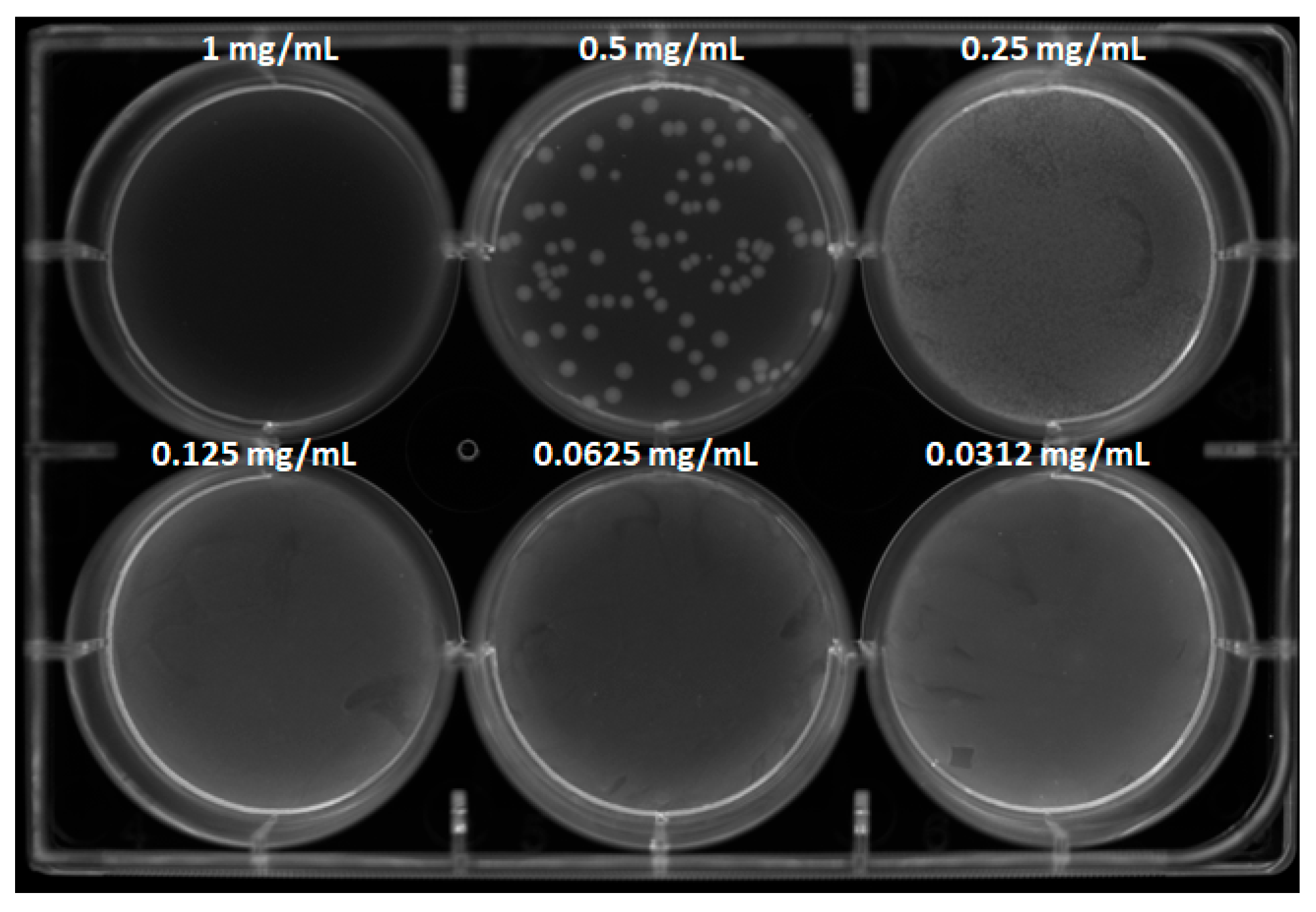
3.4. Antibacterial Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MOF | Metal–Organic Framework |
| ZIF-8 | Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 |
| MAD | “Madonita” snail slime |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| F-MAD | Fluorescein-tagged Madonita snail slime |
| 2-HmIM | 2-methylimidazole |
| Zn(mIM)2 | Referred to Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 |
| PXRD | Powder X-Ray Diffraction |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| ATR-FTIR | Attenuated Total Reflection–Fourier Transform Infrared |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
| MP-AES | Microwave Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller method |
References
- Park, K.S.; Ni, Z.; Côté, A.P.; Choi, J.Y.; Huang, R.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Chae, H.K.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10186–10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venna, S.R.; Jasinski, J.B.; Carreon, M.A. Structural Evolution of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18030–18033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Matteo, V.; Di Filippo, M.F.; Ballarin, B.; Gentilomi, G.A.; Bonvicini, F.; Panzavolta, S.; Cassani, M.C. Cellulose/Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework (ZIF-8) Composites with Antibacterial Properties for the Management of Wound Infections. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Matteo, V.; Di Filippo, M.F.; Ballarin, B.; Bonvicini, F.; Iaquinta, M.R.; Panzavolta, S.; Mazzoni, E.; Cassani, M.C. Porous titanium scaffolds modified with Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework (ZIF-8) with enhanced osteogenic activity for the prevention of implant-associated infections. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1452670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Yao, Q. Synthesis and modification of ZIF-8 and its application in drug delivery and tumor therapy. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 37600–37620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, H.N. Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks (ZIF-8) for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 7023–7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinari, C.; Pettinari, R.; Di Nicola, C.; Tombesi, A.; Scuri, S.; Marchetti, F. Antimicrobial MOFs. Chem. Rev. 2021, 446, 214121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Chen, C.; Pavelic, K.; Ozer, F. ZIF-8 as a pH-Responsive Nanoplatform for 5-Fluorouracil Delivery in the Chemotherapy of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; Xu, L.; Bai, R.; He, F.; Wang, M.; Han, L.; Bao, Z.; Wu, Y.; et al. Nanoscale Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework (ZIF)–8 in Cancer Theranostics: Current Challenges and Prospects. Cancers 2022, 14, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zan, J. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8: A versatile nanoplatform for tissue regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1386534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhang, X.; Shi, D.; Wang, Z. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) for drug delivery: A critical review. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2020, 15, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Kabir, M.; Islam, T.; Wang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Liu, H.; Chen, S.; Wu, S. Curcumin-Loaded ZIF-8 Nanomaterials: Exploring Drug Loading Efficiency and Biomedical Performance. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 3067–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astria, E.; Thonhofer, M.; Ricco, R.; Liang, W.; Chemelli, A.; Tarzia, A.; Alt, K.; Hagemeyer, C.E.; Rattenberger, J.; Schroettner, H.; et al. Carbohydrates@MOFs. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoop, M.; Walde, C.F.; Riccò, R.; Mushtaq, F.; Terzopoulou, A.; Chen, X.-Z.; Demello, A.J.; Doonan, C.J.; Falcaro, P.; Nelson, B.J.; et al. Biocompatibility characteristics of the metal organic framework ZIF-8 for therapeutical applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 11, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wied, P.; Carraro, F.; Sumby, C.J.; Nidetzky, B.; Tsung, C.-K.; Falcaro, P.; Doonan, C.J. Metal–Organic Framework-Based Enzyme Biocomposites. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1077–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.; Ricco, R.; Doherty, C.M.; Styles, M.J.; Bell, S.; Kirby, N.; Mudie, S.; Haylock, D.; Hill, A.J.; Doonan, C.J.; et al. Biomimetic mineralization of metal-organic frameworks as protective coatings for biomacromolecules. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doonan, C.; Riccò, R.; Liang, K.; Bradshaw, D.; Falcaro, P. Metal–Organic Frameworks at the Biointerface: Synthetic Strategies and Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, F.; Velásquez-Hernández, M.d.J.; Astria, E.; Liang, W.; Twight, L.; Parise, C.; Ge, M.; Huang, Z.; Ricco, R.; Zou, X.; et al. Phase dependent encapsulation and release profile of ZIF-based biocomposites. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 3397–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, A.F.; Rakowski, A.M.; Carpenter, B.P.; Fishman, D.A.; Merham, J.G.; Hurst, P.J.; Patterson, J.P. Direct Observation of Amorphous Precursor Phases in the Nucleation of Protein–Metal–Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Ricco, R.; Maddigan, N.K.; Dickinson, R.P.; Xu, H.; Li, Q.; Sumby, C.J.; Bell, S.G.; Falcaro, P.; Doonan, C.J. Control of Structure Topology and Spatial Distribution of Biomacromolecules in Protein@ZIF-8 Biocomposites. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez-Hernández, M.d.J.; Linares-Moreau, M.; Astria, E.; Carraro, F.; Alyami, M.Z.; Khashab, N.M.; Sumby, C.J.; Doonan, C.J.; Falcaro, P. Towards applications of bioentities@MOFs in biomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2021, 429, 213651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Filippo, M.F.; Di Matteo, V.; Dolci, L.S.; Albertini, B.; Ballarin, B.; Cassani, M.C.; Passerini, N.; Gentilomi, G.A.; Bonvicini, F.; Panzavolta, S. Effectiveness of Snail Slime in the Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Filippo, M.F.; Dolci, L.S.; Bonvicini, F.; Sparla, F.; Gentilomi, G.A.; Panzavolta, S.; Passerini, N.; Albertini, B. Influence of the extraction method on functional properties of commercial snail secretion filtrates. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubitosa, J.; Rizzi, V.; Fini, P.; Laurenzana, A.; Fibbi, G.; Veiga-Villauriz, C.; Fanelli, F.; Fracassi, F.; Onzo, A.; Bianco, G.; et al. Biomolecules from snail mucus (Helix aspersa) conjugated gold nanoparticles, exhibiting potential wound healing and anti-inflammatory activity. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 10876–10888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Filippo, M.F.; Albertini, B.; Dolci, L.S.; Bonvicini, F.; Bigi, A.; Gentilomi, G.A.; Passerini, N.; Panzavolta, S. Novel drug-loaded film forming patch based on gelatin and snail slime. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 598, 120408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Filippo, M.F.; Panzavolta, S.; Albertini, B.; Bonvicini, F.; Gentilomi, G.A.; Orlacchio, R.; Passerini, N.; Bigi, A.; Dolci, L.S. Functional properties of chitosan films modified by snail mucus extract. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, K.; Okita, M.; Fujita, K.; Tanaka, S.; Miyake, Y. Formation of high crystalline ZIF-8 in an aqueous solution. CrystEngComm 2012, 15, 1794–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gualdrón, D.A.; Moghadam, P.Z.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K.; Snurr, R.Q. Application of Consistency Criteria To Calculate BET Areas of Micro- And Mesoporous Metal–Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 138, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapdiqov, S.Z.; Taghiyev, D.B. Application of kinetic results of doxorubicin release from polyacrylic acid-based hydrogel to Higuchi, Korsmeyer-Peppas, Hixon-Crowell equations. Socar Proc. 2025, 1, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Yao, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, K.; Chen, F.; Wang, H. Facile synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 from a concentrated aqueous solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 184, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, M.; Liu, B.; Liu, R.; Qu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Water-based synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 with high morphology level at room temperature. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48433–48441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.F.; Sherman, E.; Vajo, J.J. Aqueous room temperature synthesis of cobalt and zinc sodalite zeolitic imidizolate frameworks. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 5458–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velásquez-Hernández, M.d.J.; Ricco, R.; Carraro, F.; Limpoco, F.T.; Linares-Moreau, M.; Leitner, E.; Wiltsche, H.; Rattenberger, J.; Schröttner, H.; Frühwirt, P.; et al. Degradation of ZIF-8 in phosphate buffered saline media. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 4538–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.B.; Lin, Y.S. Kinetics of ZIF-8 Thermal Decomposition in Inert, Oxidizing, and Reducing Environments. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 14015–14026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez-Hernández, M.d.J.; Astria, E.; Winkler, S.; Liang, W.; Wiltsche, H.; Poddar, A.; Shukla, R.; Prestwich, G.; Paderi, J.; Salcedo-Abraira, P.; et al. Modulation of metal-azolate frameworks for the tunable release of encapsulated glycosaminoglycans. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 10835–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, P.; Strudwick, X.L.; Song, Y.; Cowin, A.J.; Garg, S. Influence of Acidic pH on Wound Healing In Vivo: A Novel Perspective for Wound Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cassani, M.C.; Bonvicini, F.; Di Filippo, M.F.; Ballarin, B.; Panzavolta, S.; Di Matteo, V. Encapsulation of Snail Slime in Metal–Organic Framework ZIF-8. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16120443
Cassani MC, Bonvicini F, Di Filippo MF, Ballarin B, Panzavolta S, Di Matteo V. Encapsulation of Snail Slime in Metal–Organic Framework ZIF-8. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2025; 16(12):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16120443
Chicago/Turabian StyleCassani, Maria Cristina, Francesca Bonvicini, Maria Francesca Di Filippo, Barbara Ballarin, Silvia Panzavolta, and Valentina Di Matteo. 2025. "Encapsulation of Snail Slime in Metal–Organic Framework ZIF-8" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 16, no. 12: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16120443
APA StyleCassani, M. C., Bonvicini, F., Di Filippo, M. F., Ballarin, B., Panzavolta, S., & Di Matteo, V. (2025). Encapsulation of Snail Slime in Metal–Organic Framework ZIF-8. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 16(12), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16120443






