Viscoelastic Compression Behavior and Model Characterization of Alfalfa Blocks Under Different Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Equipment
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Stress Relaxation Test
2.4. Creep Test
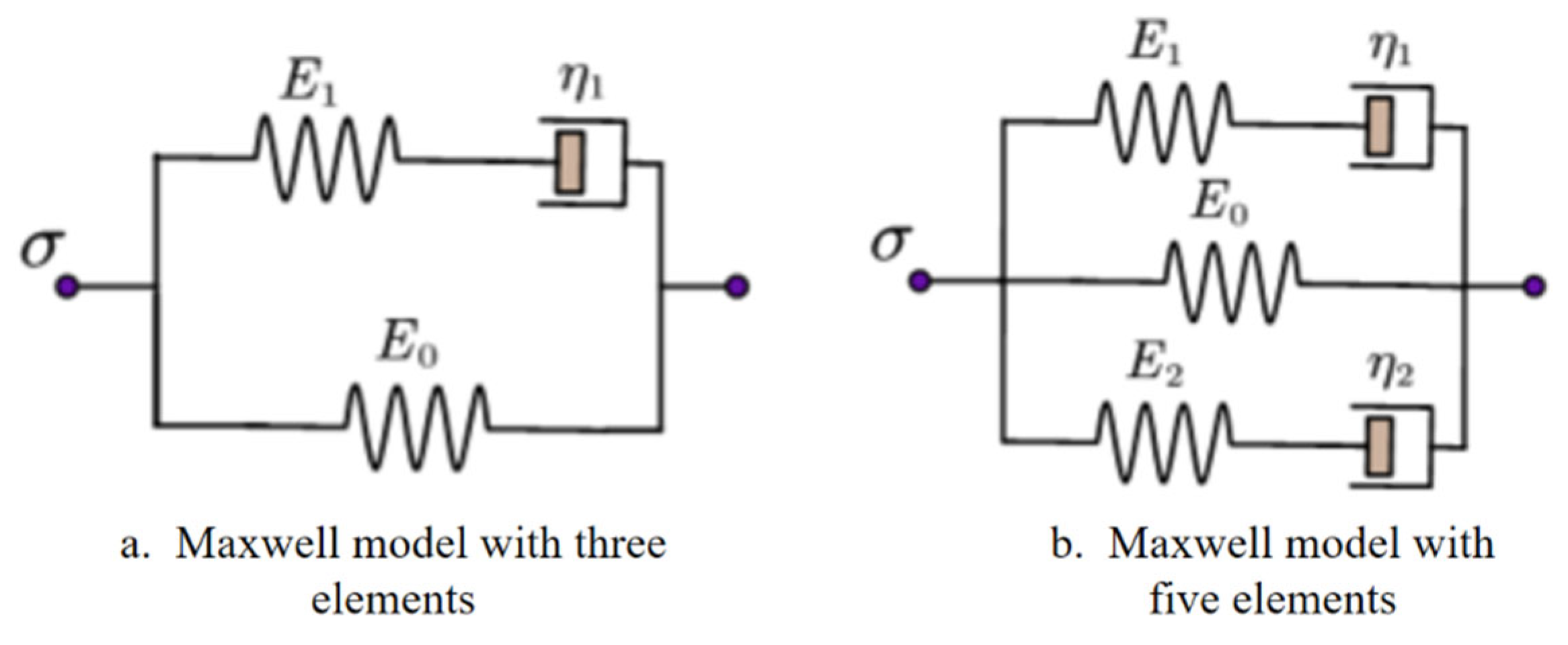
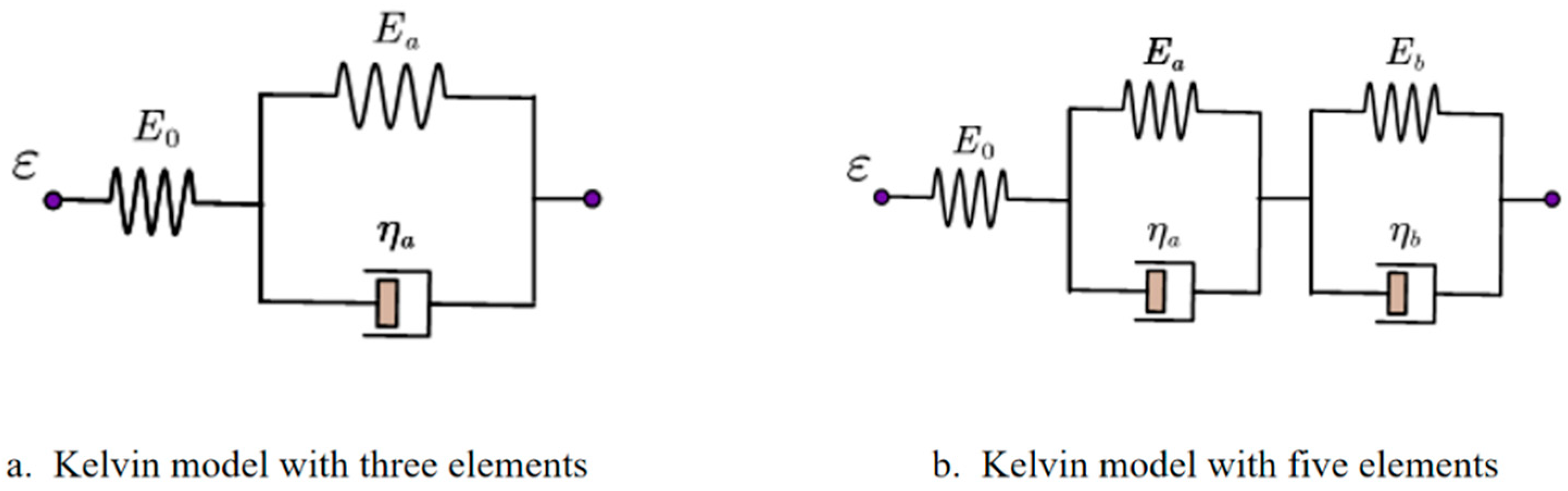
2.5. Viscoelastic Modeling
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Compression Process Analysis
3.2. Stress Relaxation Behavior Analysis and Model Representation
3.2.1. Analysis of Stress Relaxation Tests
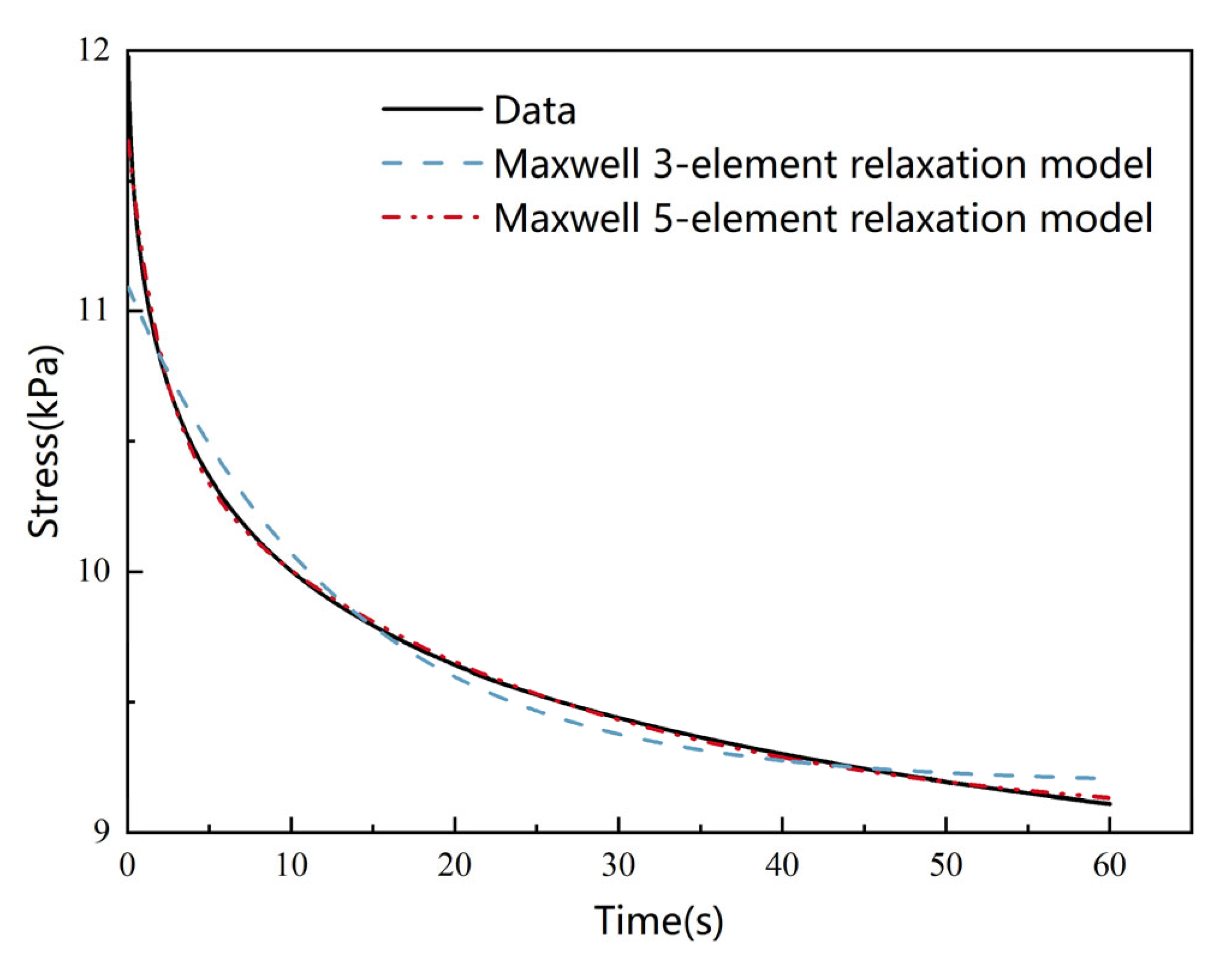
3.2.2. Relaxation Model Fitting and Parameter Comparison
3.3. Creep Behavior Analysis and Model Representation
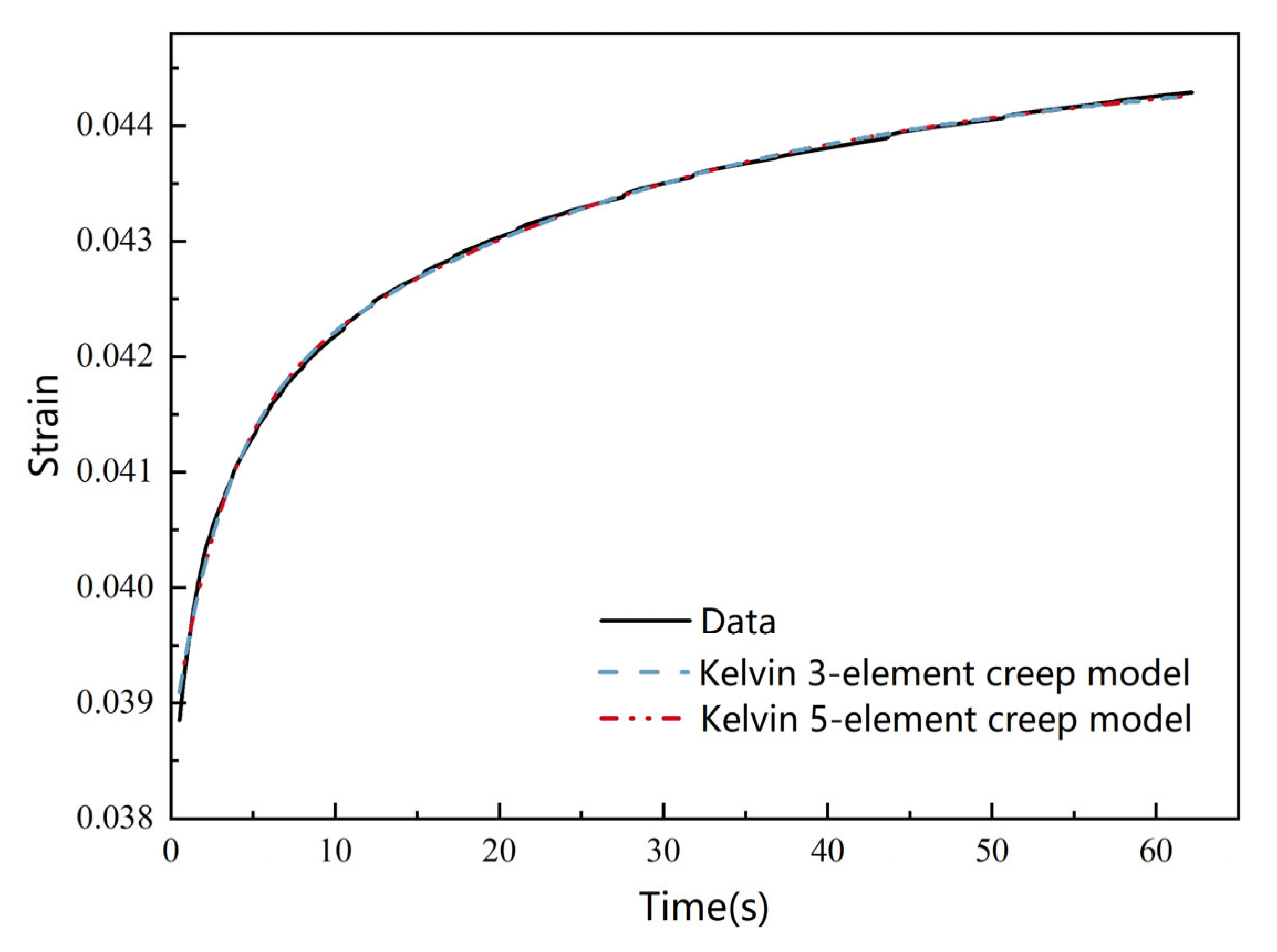
3.3.1. Analysis of Creep Tests
3.3.2. Creep Model Fitting and Parameter Comparison
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borreani, G.; Bisaglia, C.; Tabacco, E. Effects of a new-concept wrapping system on alfalfa round-bale silage. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; He, C.; Wu, H.; You, Y.; Wang, G. Review of Alfalfa Full-mechanized Production Technology. Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2017, 48, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coblentz, W.K.; Akins, M.S. Silage review: Recent advances and future technologies for baled silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4075–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Mou, X.; Sun, Y.; Geng, D.; Wang, C.; Zhao, N. Experimental study on influencing factors of bale stability. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2021, 42, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Guo, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Jin, M.; Liu, X.; Li, J. Experimental study on stress relaxation characteristics and parameter optimization of forage sweet sorghum stalks. J. China Agric. Univ. 2019, 24, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Jia, H.; Li, M.; Zhao, J.; Deng, J.; Fu, J.; Yuan, H. Mechanism of restraining maize stalk block springback under pressure maintenance/strain maintenance. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, S.; Tabil, L.; Opoku, A.; Shaw, M. Compression and relaxation properties of timothy hay. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2011, 4, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Chen, T.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Yuan, H. Effects of Pressure Maintenance and Strain Maintenance during Compression on Subsequent Dimensional Stability and Density after Relaxation of Blocks of Chopped Corn Straw. Bioresources 2020, 15, 3717–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, A.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Gao, J.; Li, H. Stress relaxation behavior and modeling of alfalfa during rotary compression. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo-Zuniga, J.; Casanova, F.; Jaime Garcia, J. Visco-elastic-plastic model to represent the compression behaviour of sugarcane agricultural residue. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 212, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASAE S358.2; Moisture Measurement—Forages. American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2008.
- Lei, M.; Lei, J.; Luo, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; You, B. Compression Creep Characteristics of Crushed Sugarcane End-Leaves. Bioresources 2024, 19, 4486–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wei, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ma, F.; Liu, D. Optimization of process parameters for multi-frequency rapid compression molding of corn stalk silk used for forage. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C. Study on Compression Properties and Rheological Characteristics of Straw Blocks. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- NY/T 4338-2023; Technical Specification for Alfalfa Hay-Making. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs: Beijing, China, 2023.
- DB15/T 2664-2022; Technical Regulations for Alfalfa Baling Production. Market Supervision and Administration Bureau of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region: Hohhot, China, 2022.
- Zhang, H.; Liu, T.; Lian, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Analysis of the Development Prospects of Wrapped Silage Feed Made from Alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Cereal Feed Ind. 2023, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J. Experimental Study and Numerical Simulation on Cold Compression Molding of Straw Pellet Fuel. Ph.D. Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Wang, D.; Tabil, L.G.; Wang, G. Compression and relaxation properties of selected biomass for briquetting. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 148, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielewicz, I.; Fitz, C.; Hofbauer, W.; Klatecki, M.; Krick, B.; Krueger, N.; Krus, M.; Minke, G.; Otto, F.; Scharmer, D. Grundlagen zur Bauaufsichtlichen Anerkennung der Strohballenbauweise-Weiterentwicklung der Lasttragenden Konstruktionsart und Optimierung der Bauphysikalischen Performance; Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt: Osnabrück, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nona, K.D.; Lenaerts, B.; Kayacan, E.; Saeys, W. Bulk compression characteristics of straw and hay. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 118, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, K.; Bilanski, W. Stress relaxation of alfalfa under constant displacement. Trans. ASAE 1991, 34, 2491–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, N.; Chen, L.; Huang, G.; He, C.; Han, L. Grey relation analysis of lignocellulose content and compression stress relaxation of corn stalk. Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2011, 42, 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Study on Open Compression Creep Test of Crushed Corn Stalks. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Pan, J. Introduction to Agricultural Rheology; Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 1990; pp. 49–63, ISBN/ISSN 7109012107. [Google Scholar]
- Theerarattananoon, K.; Xu, F.; Wilson, J.; Ballard, R.; Mckinney, L.; Staggenborg, S.; Vadlani, P.; Pei, Z.; Wang, D. Physical properties of pellets made from sorghum stalk, corn stover, wheat straw, and big bluestem. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 33, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q. Study on Mechanical Properties of Alfalfa and King Grass and Development of a Flexible Cutting Test Bench. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Taian, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H. Multiscale Mechanical Analysis and Parameter Optimization of Alfalfa Compression Molding. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Wear Analysis and Experimental Study of Alfalfa Compression Molding Die Based on EDEM. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Maraldi, M.; Molari, L.; Regazzi, N.; Molari, G. Analysis of the parameters affecting the mechanical behaviour of straw bales under compression. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 160, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Lei, D.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z. Stress Relaxation Characteristics of Crushed Cane Tail Straw. BioResources 2023, 18, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cai, D.; Xie, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Chen, L. Parameters Calibration of Discrete Element Model for Corn Stalk Powder Compression Simulation. Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-J.; Lei, T.-Z.; Xu, G.-Y.; Shen, S.-Q.; Liu, J.-W. Experimental study of stress relaxation in the process of cold molding with straw. BioResources 2009, 4, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Peng, W.; Han, L.; Xiao, W.; Liu, X. Effects of different pretreatments on compression molding of wheat straw and mechanism analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 251, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Ma, P.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Hui, Y.; You, Y.; Wang, D. A review of research progress in the compaction of major crop waste by mechanical equipment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 213, 115484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, L.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Qi, W.; Lei, T. Effects of Different Biomass Types on Pellet Qualities and Processing Energy Consumption. Agriculture 2025, 15, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.; Tabil, L.G.; Sokhansanj, S. Effects of compressive force, particle size and moisture content on mechanical properties of biomass pellets from grasses. Biomass Bioenergy 2006, 30, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herak, D.; Kabutey, A.; Choteborsky, R.; Petru, M.; Sigalingging, R. Mathematical models describing the relaxation behaviour of Jatropha curcas L. bulk seeds under axial compression. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 131, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liao, N.; Xing, L.; Han, L. Description of Wheat Straw Relaxation Behavior Based on a Fractional-Order Constitutive Model. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wang, C.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Jin, M.; Liu, X.; Li, J. Stress Relaxation Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Sweet Sorghum: Experimental Study. Bioresources 2018, 13, 8761–8774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig-Arnavat, M.; Shang, L.; Sárossy, Z.; Ahrenfeldt, J.; Henriksen, U.B. From a single pellet press to a bench scale pellet mill—Pelletizing six different biomass feedstocks. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 142, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, N.; García-Maraver, A.; Zamorano, M. Influence of densification parameters on quality properties of rice straw pellets. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 138, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Fang, X.; Li, L. Effect of different moisture contents on flow ability parameters of chopped rice straw. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 2013, 44, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- McAfee, J.R.; Shinners, K.J.; Friede, J.F.; Walters, C.P. Creating high-density large square bales by recompression. Trans. ASABE 2019, 62, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasick, G.T.; Liu, J. Lab scale studies of miscanthus mechanical conditioning and bale compression. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 200, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lei, T.; Shen, S.; Zhang, Q. Specific Energy Consumption Regression and Process Parameters Optimization in Wet-Briquetting of Rice Straw at Normal Temperature. Bioresources 2013, 8, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, W.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y. Effects of Wet Soybean Dregs on Forming Relaxation Ratio, Maximum Compressive Force and Specific Energy Consumption of Corn Stover Pellets. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, G.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y. Experimental study on creep properties prediction of reed bales based on SVR and MLP. Plant Methods 2021, 17, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Yu, Z. Creep Characteristics of Corn Straw Particles Simulated Based on Burgers Model. Bioresources 2024, 19, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Liang, S.; Zhang, L. Construction Method of Viscoelastic Constitutive Relation and Application Examples. Mech. Eng. Pract. 2022, 44, 1411–1415. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, M.; Wang, M.; Cen, H.; Li, L.; Li, T.; Jing, W.; Li, J.; Wen, B. Experimental Study on Compression and Rheological Properties of Different Licorice Stem Varieties. J. Shihezi Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 41, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M. Rheology of Agricultural Materials; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 16–55. [Google Scholar]

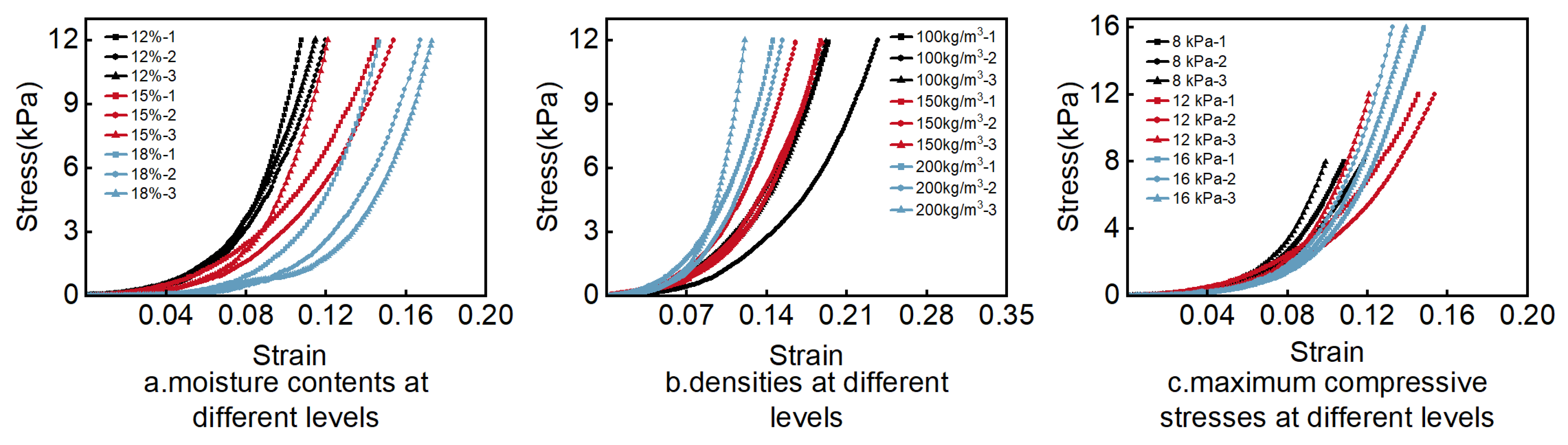
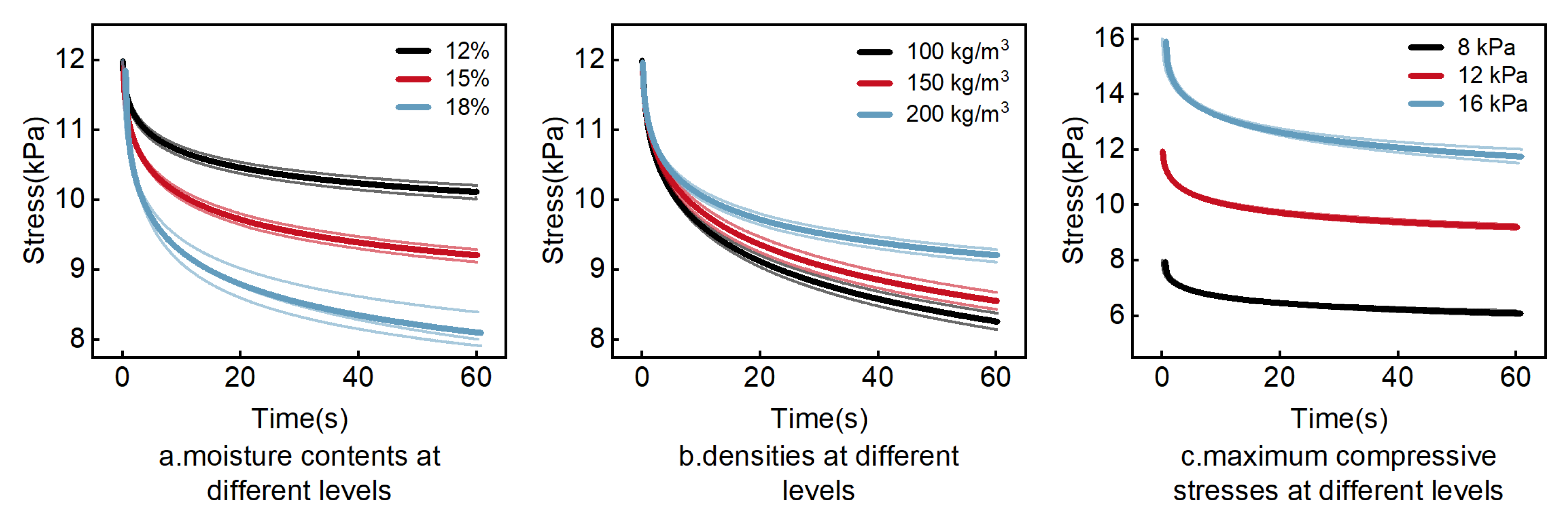
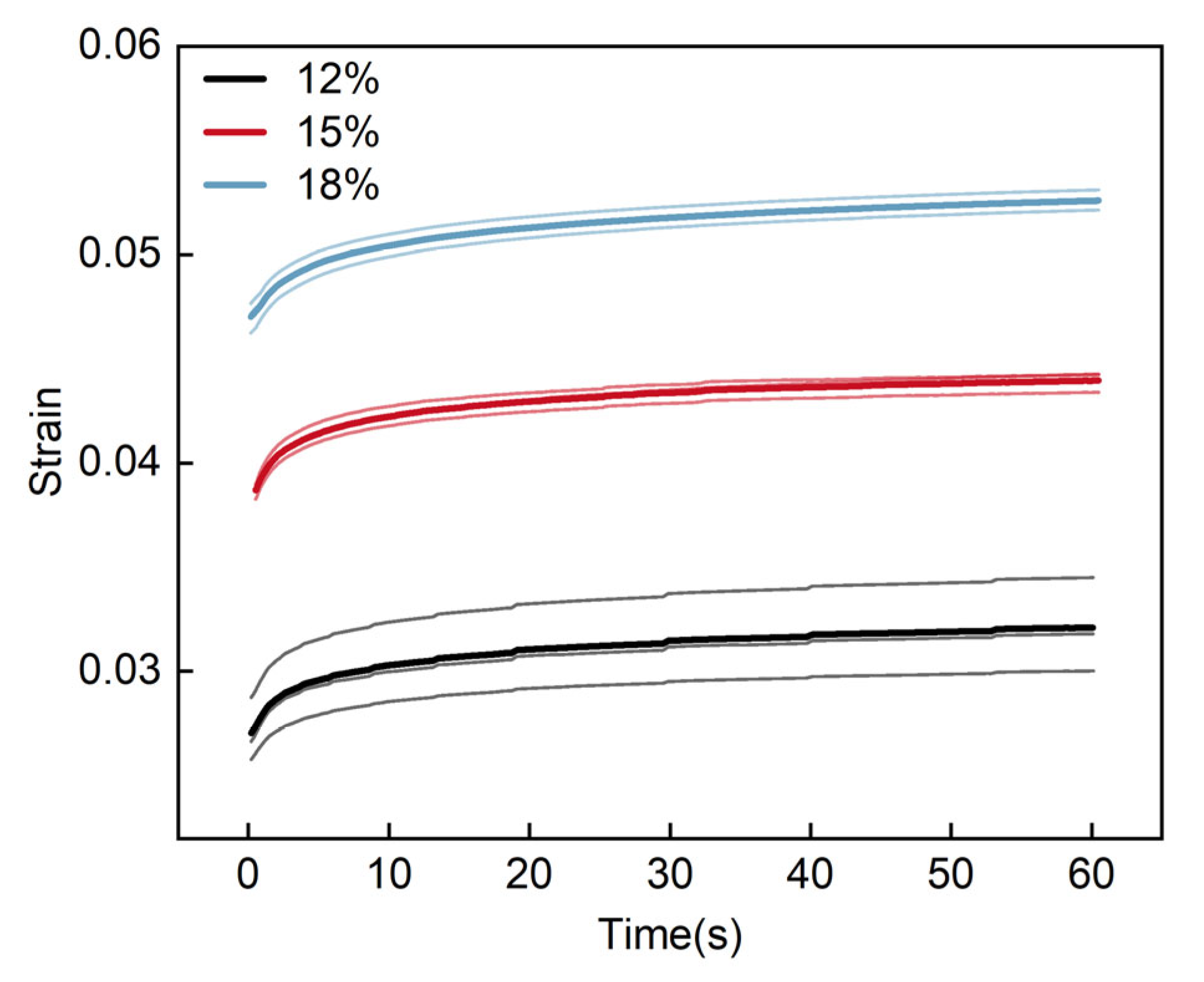
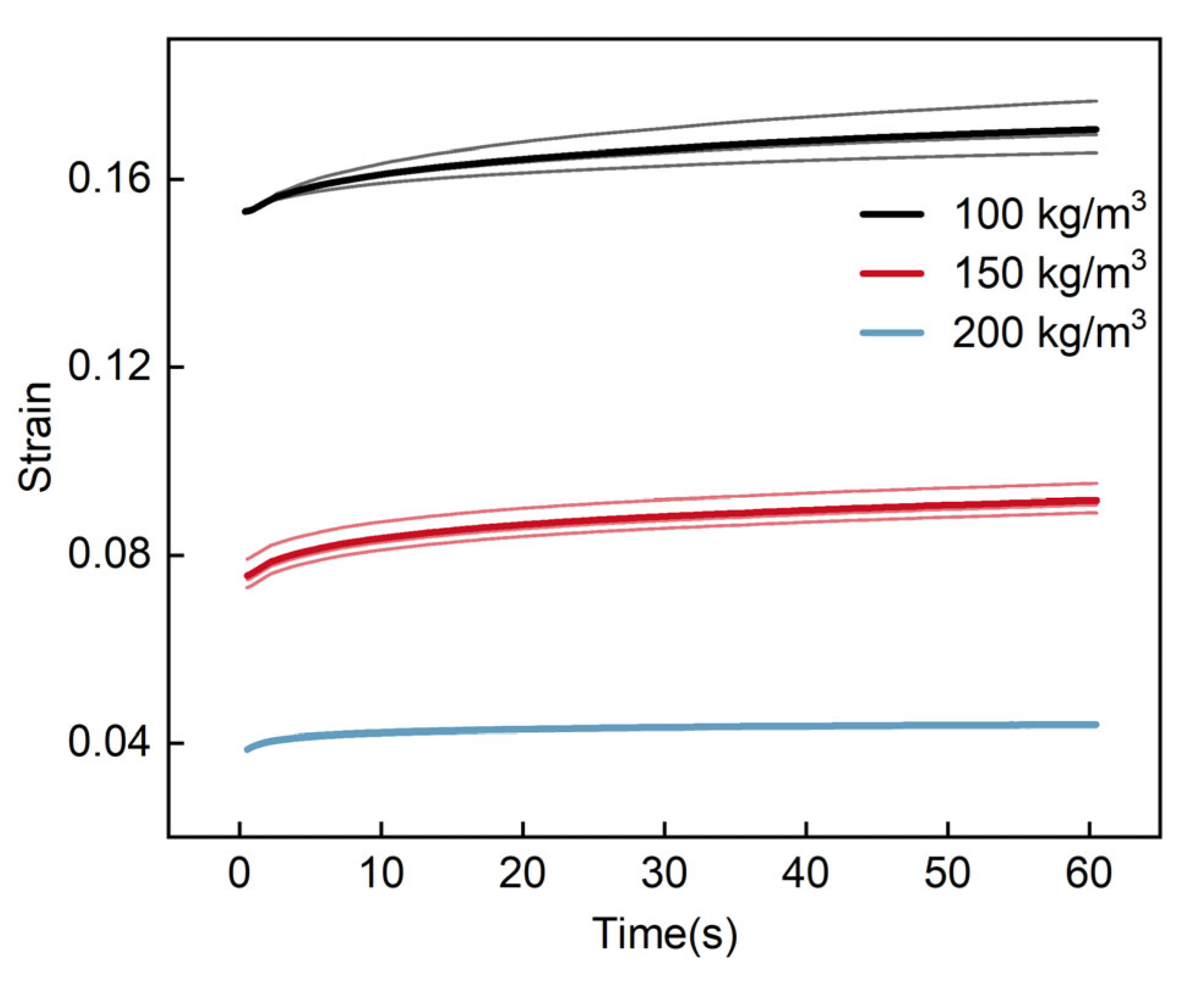
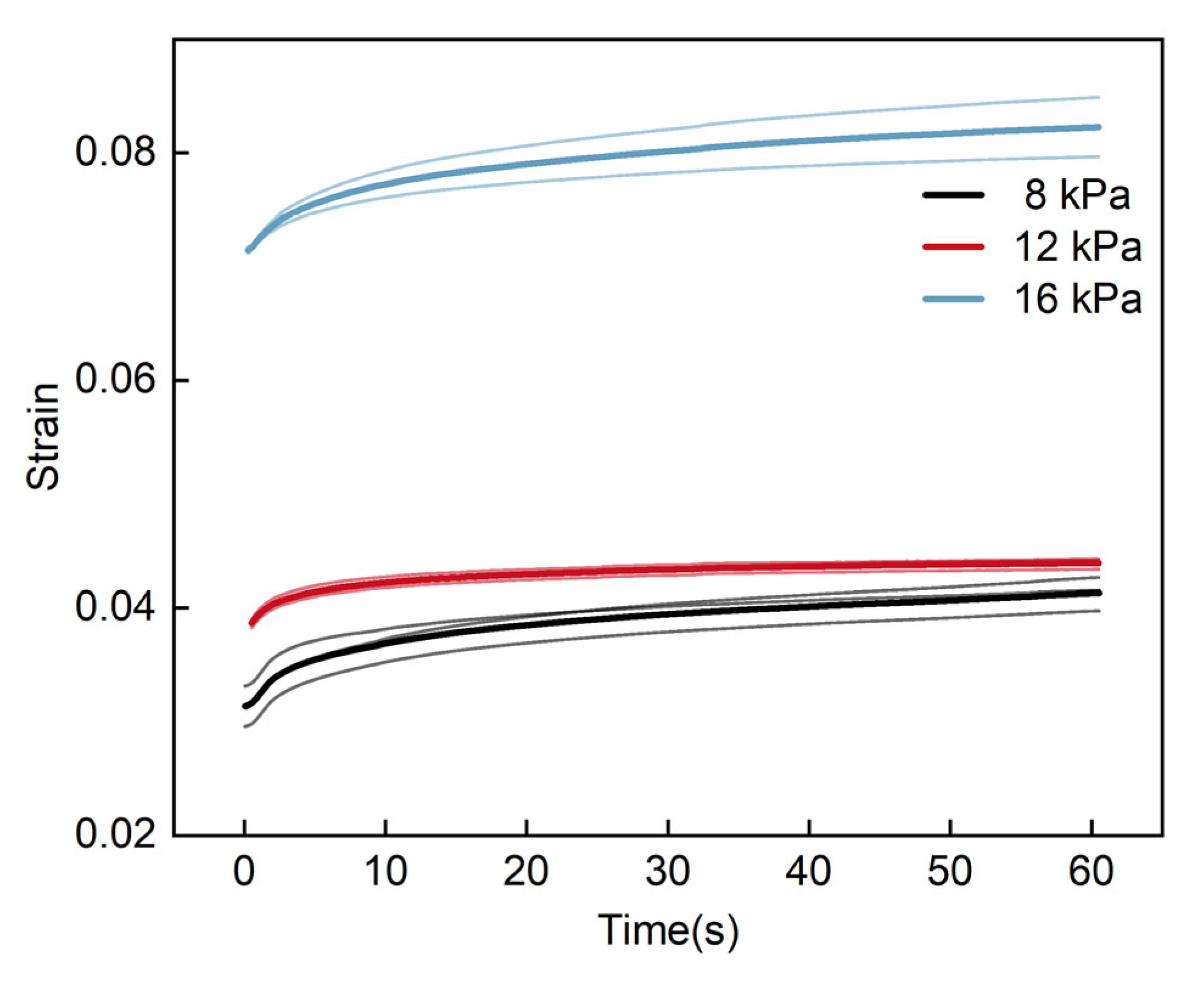
| Moisture Content | (kPa) | (kPa) | (kPa) | (s) | (s) | (kPa∙s) | (kPa∙s) | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12% | 0.029 | 25.86 | 33.45 | 347.24 | 2.04 | 23.51 | 52.75 | 786.41 | 0.9986 |
| 15% | 0.039 | 29.74 | 38.72 | 231.28 | 2.08 | 23.27 | 61.86 | 901.01 | 0.9987 |
| 18% | 0.047 | 34.04 | 39.36 | 177.45 | 1.29 | 20.36 | 43.91 | 801.37 | 0.9970 |
| Density (kg/m3) | (kPa) | (kPa) | (kPa) | (s) | (s) | (kPa∙s) | (kPa∙s) | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.153 | 9.28 | 14.90 | 52.48 | 2.19 | 27.73 | 20.32 | 413.17 | 0.9990 |
| 150 | 0.074 | 16.35 | 28.51 | 112.43 | 2.41 | 28.97 | 39.40 | 825.93 | 0.9992 |
| 200 | 0.039 | 29.74 | 38.72 | 231.28 | 2.08 | 23.27 | 61.86 | 907.01 | 0.9987 |
| Maximum Compressive Stress (kPa) | (kPa) | (kPa) | (kPa) | (s) | (s) | (kPa∙s) | (kPa∙s) | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 0.030 | 26 | 36.33 | 198 | 1.43 | 23.69 | 37.18 | 860.66 | 0.9971 |
| 12 | 0.039 | 29.74 | 38.72 | 231.28 | 2.08 | 23.27 | 61.86 | 901.01 | 0.9987 |
| 16 | 0.071 | 24.37 | 33.66 | 163.80 | 1.43 | 22.72 | 34.85 | 764.76 | 0.9977 |
| Moisture Content | (kPa) | (kPa) | (kPa) | (s) | (s) | (kPa∙s) | (kPa∙s) | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12% | 12 | 413.79 | 3324.10 | 4477.61 | 25.55 | 2.07 | 84,930.76 | 9268.65 | 0.9984 |
| 15% | 12 | 310.88 | 3636.36 | 4477.61 | 27.01 | 2.97 | 98,218.08 | 13,298.50 | 0.9993 |
| 18% | 12 | 255.32 | 2977.67 | 3809.52 | 27.69 | 3.13 | 82,451.68 | 11,923.80 | 0.9996 |
| Density (kg/m3) | (kPa) | (kPa) | (kPa) | (s) | (s) | (kPa∙s) | (kPa∙s) | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 12 | 78.95 | 801.07 | 2185.79 | 40.77 | 3.82 | 32,659.62 | 8349.71 | 0.9999 |
| 150 | 12 | 162.16 | 913.94 | 1826.48 | 39.92 | 3.95 | 36,484.48 | 7214.60 | 0.9997 |
| 200 | 12 | 310.88 | 3636.36 | 4477.61 | 27.01 | 2.97 | 98,218.08 | 13,298.50 | 0.9993 |
| Maximum Compressive Stress (kPa) | (kPa) | (kPa) | (kPa) | (s) | (s) | (kPa∙s) | (kPa∙s) | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 8 | 275.86 | 1123.59 | 1785.71 | 34.35 | 3.30 | 38,595.31 | 5892.84 | 0.9990 |
| 12 | 12 | 310.88 | 3636.36 | 4477.61 | 27.01 | 2.97 | 98,218.08 | 13,298.50 | 0.9993 |
| 16 | 16 | 225.35 | 1909.31 | 3678.16 | 35.44 | 3.23 | 67,665.95 | 11,880.46 | 0.9999 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Fu, Q.; Xing, H.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Fu, J. Viscoelastic Compression Behavior and Model Characterization of Alfalfa Blocks Under Different Conditions. Agriculture 2026, 16, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010119
Hu J, Fu Q, Xing H, Yang X, Li Y, Fu J. Viscoelastic Compression Behavior and Model Characterization of Alfalfa Blocks Under Different Conditions. Agriculture. 2026; 16(1):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010119
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jiawen, Qiankun Fu, Hongxu Xing, Xiucheng Yang, Yang Li, and Jun Fu. 2026. "Viscoelastic Compression Behavior and Model Characterization of Alfalfa Blocks Under Different Conditions" Agriculture 16, no. 1: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010119
APA StyleHu, J., Fu, Q., Xing, H., Yang, X., Li, Y., & Fu, J. (2026). Viscoelastic Compression Behavior and Model Characterization of Alfalfa Blocks Under Different Conditions. Agriculture, 16(1), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010119





