Spatiotemporal Coupling and Simulation Prediction of Socioecological Systems in the Qilian Mountain Life Community
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
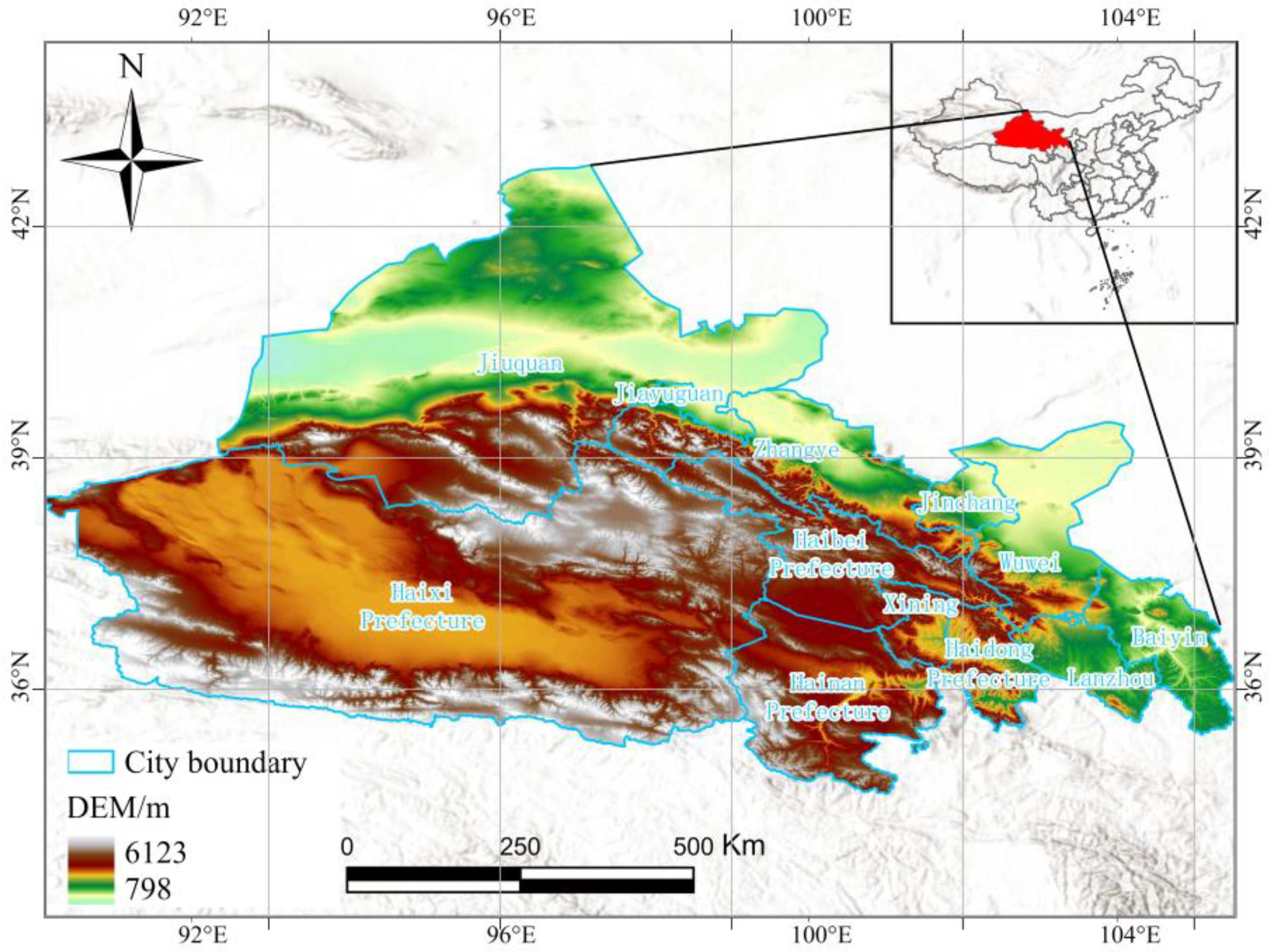
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods and Data Sources
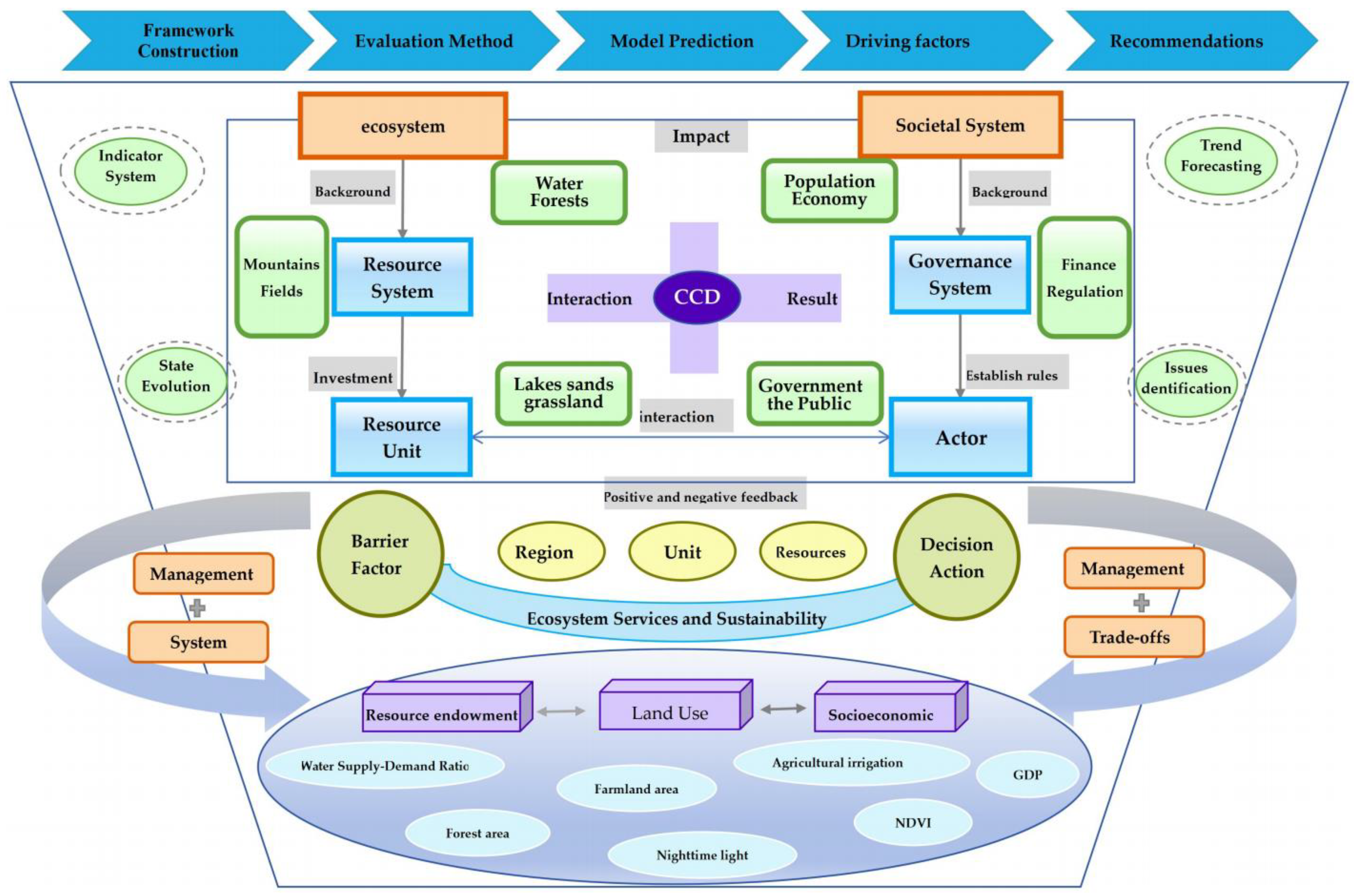
2.2.1. Conceptual Framework and Research Workflow
2.2.2. Socio-Ecosystem Assessment Indicator System
2.2.3. Calculation of Integrated Assessment Index for Socio-Ecosystem and Subsystems
- (1)
- Standardization: Raw data matrix for years (24) and indicators (26) was normalized to eliminate dimensional differences.where is the standardized value, xij is the original value, and a and b denote the lower (fixed at 0) and upper (fixed at 1) bounds of the normalization spectrum, respectively. Furthermore, min () and max () are the minimum and maximum values of factor quantification, respectively. For negative indicators, the normalized value should be deducted from the set normalized upper limit during computation.
- (2)
- Entropy Calculation: The information entropy for each indicator was calculated.
- (3)
- Weight Determination: The weight for each indicator was derived from its entropy.
- (4)
- Comprehensive Index Calculation: The comprehensive assessment index for each year was calculated.
2.2.4. Multi-System Coupling Coordination Model
2.2.5. Obstruction Degree Model
- (1)
- Factor contribution:
- (2)
- Index deviation:
- (3)
- Barrier degree:
2.2.6. GM(1,1) Grey Prediction Model
- (1)
- Establish the original system sequence:where n is the number of data points (11 years, 2013–2023).X(0) = [x(0)(1), x(0)(2), …, x(0)n],
- (2)
- Accumulated Generating Operation (AGO):where x(1)(k) = ;X(1) = [x(1)(1), x(1)(2), …, x(1)n],
- (3)
- Mean Sequence: The mean sequence Z(1) of X(1) is generated:where Z(1)(k) = ;Z(1) = [z(1)(2), z(1)(3), …, z(1)n],
- (4)
- Grey Differential Equation: The basic form of the GM(1,1) model is x0(k) + az1(k) = a, +
- (5)
- Parameter Estimation: The parameters aa and bb are estimated using the least squares method: â = [a,b]T = (BT × B)−1 × BTY, where
- (6)
- Establish the first-order cumulative time–response sequence prediction, as follows:
- (7)
- Calculate the predicted value, as follows:
- (8)
2.2.7. Data Sources and Processing
3. Results and Analysis
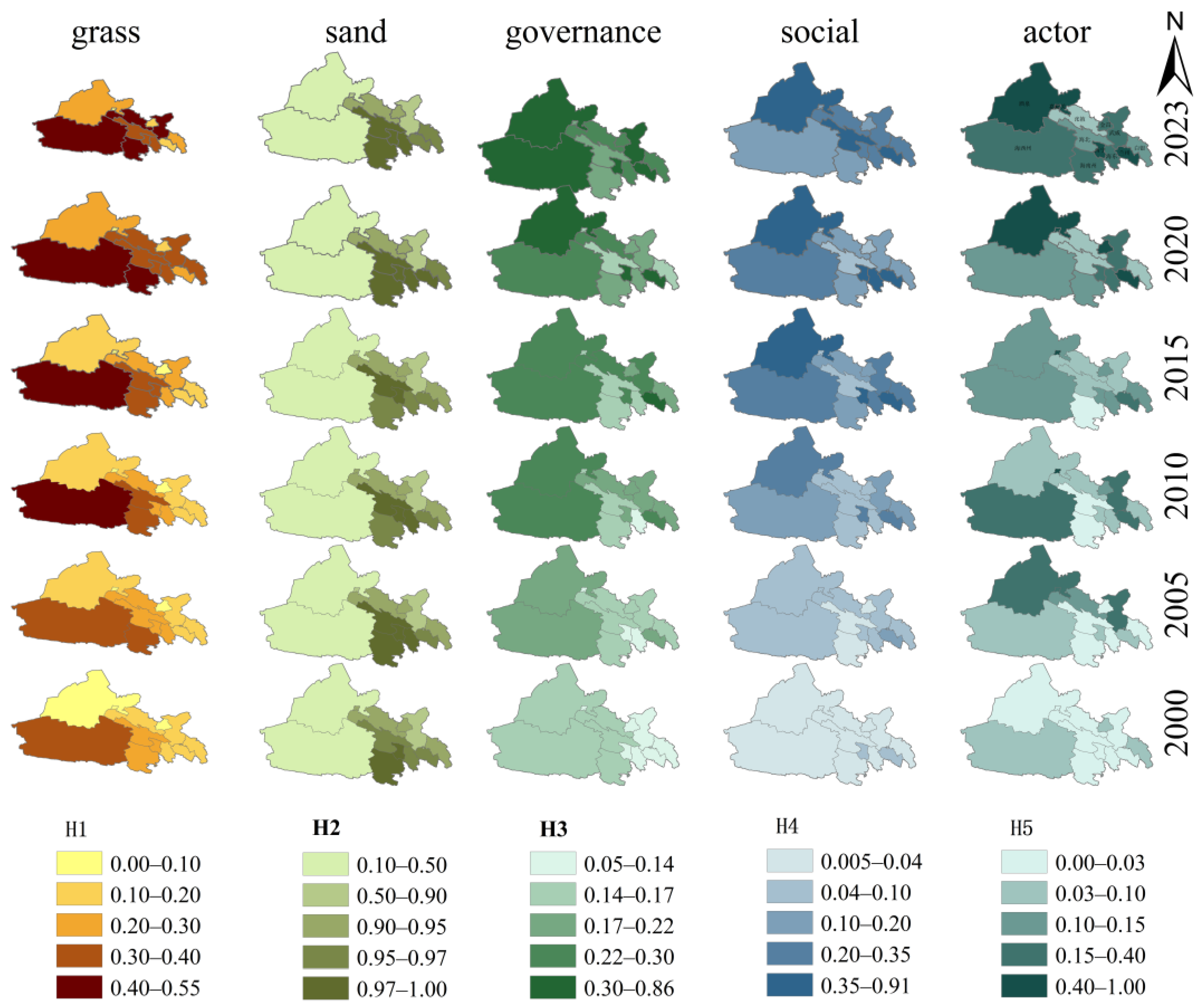
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variations in Life Community and Subsystem Assessment Indices
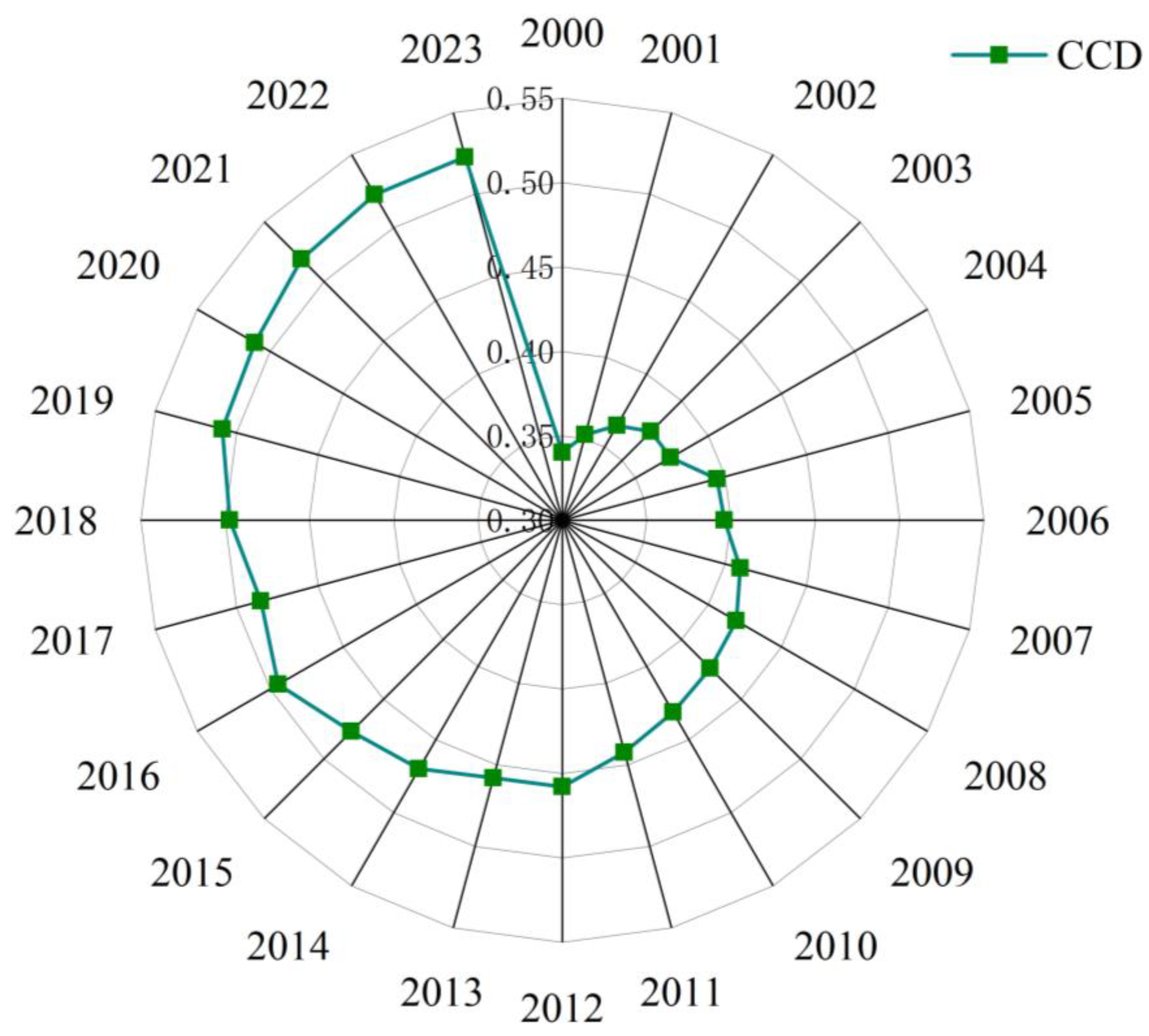
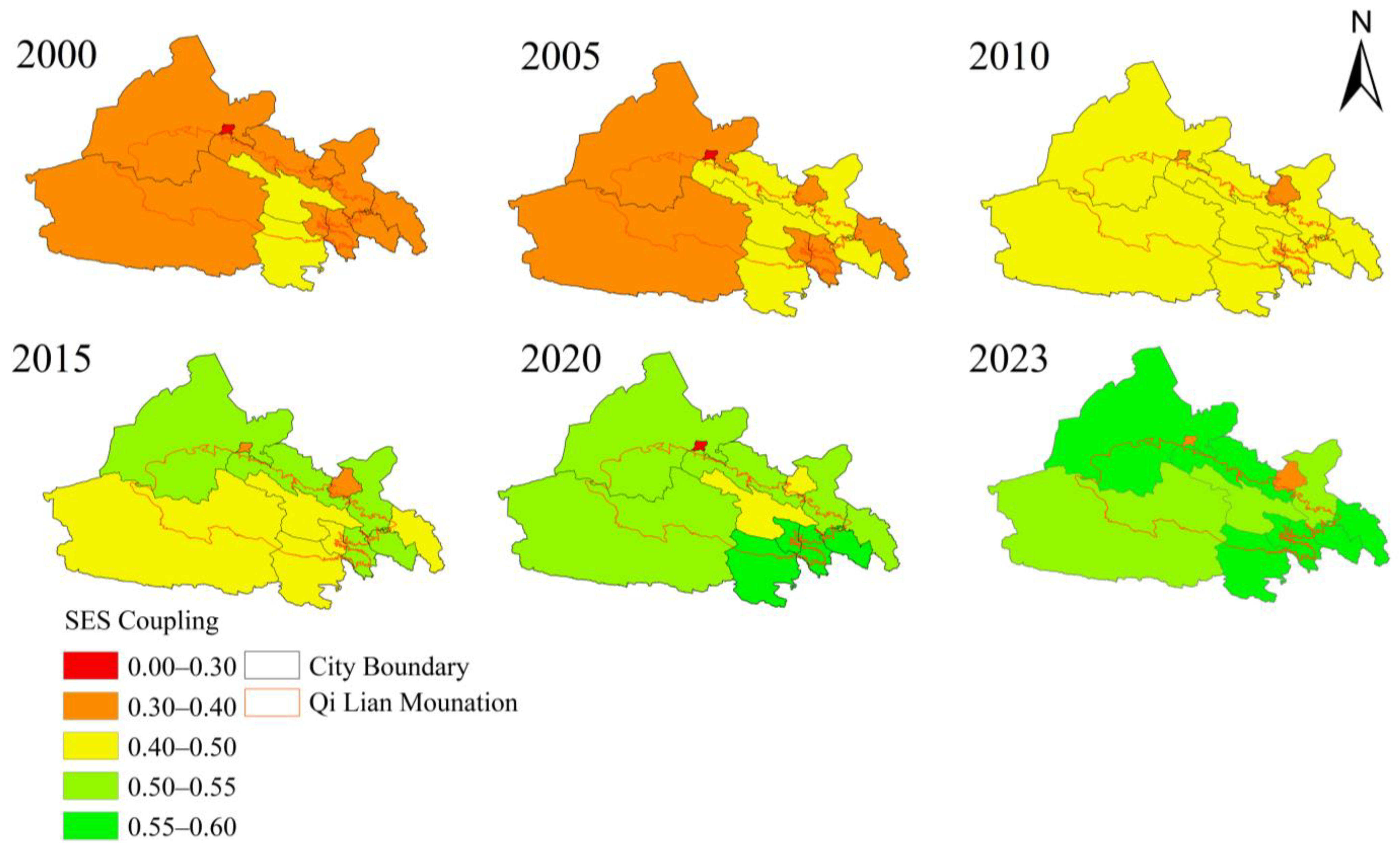
3.2. Analysis of Coupling Coordination Between Society and Ecosystem
3.3. Barrier Factor Analysis
3.4. GM Model Prediction
4. Discussion
4.1. Systems Spatiotemporal Patterns
4.2. SES Coordination Trends
4.3. Analysis of Barriers to Socio-Ecosystem Development
4.4. Policy Implications and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.C.; Liu, Y.Y.; Guo, R.Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.J.; Hua, S.J. Cooperation and resource sustainability in coupling social-ecological systems with dynamic growth rates. Chaos Solit. Fractals 2024, 182, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.D.; Bai, J.Z. Regional social-ecological system coupling process from a water flow perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.D.; Zhang, Y.B.; Huang, F.X.; Gao, J.B. Assessing regional sustainability from the perspective of reconciling social-ecological resilience and human well-being: Empirical evidence from China. Appl. Geogr. 2025, 182, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, Y.Q.; He, G.H.; Wang, Q.M.; Liu, R.; Ren, H.; Yao, J.Q.; Li, W. Evaluating Sustainability of Water-Energy-Food-Ecosystems Nexus in Water-Scarce Regions via Coupled Simulation Model. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, F.; Andres, G.; Casiraghi, G.; Gote, C.; Roller, R.; Scholtes, I.; Vaccario, G.; Zingg, C. Modeling Social Resilience: Questions, Answers, Open Problems. Adv. Complex Syst. 2022, 25, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, N.; Zhao, J.Y.; Kou, X.Y.; Zheng, S.N.; Lu, Z.H.; Fu, X.; He, X.J.; Wu, G.; Sang, W.G. Coupling mountains-waters-forests-farmlands-lakes-grasslandssandlands life community: Framework, models and prospect. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 4333–4343. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.M.; Lin, Y.B.; Liu, S.C.; Luo, M. Social-ecological system (SES) analysis framework for application inecological restoration engineering of mountains-rivers-forests-farmlands-lakes-grasslands: Utilizing the source area of Qiantang Riverin Zhejiang Province as an example. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 8846–8856. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhang, Y. The institutional construction of territorial spatial governance for’integrated mountains, rivers, forests, fields, lakes, grasses and desertsin China. J. Nat. Resour. 2025, 40, 1174–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Zhao, W.Z.; Wang, X.P.; Luo, W.C.; Zhou, T. System Cognition and Key Challenges for the Future of Qilian Mountains Community of Life: A Case Study of Gansu Province. Adv. Earth Sci. 2024, 39, 957–967. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, L.H. An analysis on the land use change characteristics and driving forces in Gansu part of the Qilian Mountain. J. Desert Res. 2023, 43, 188–198. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.S.; Feng, Q.; Adamowski, J.F.; Deo, R.C.; Yin, Z.L.; Wen, X.H.; Tang, X.; Wu, M. Causality of climate, food production and conflict over the last two millennia in the Hexi Corridor, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.J.; Zhao, Y.R.; Huang, P.; Zhao, X.; Feng, W.; Li, Q.Q.; Xue, D.X.; Dou, J.; Shi, W.; Wei, W.; et al. Impacts of ecological restoration projects on the ecosystem carbon storage of inland river basin in arid area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.R.; Huang, Y.H.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, J.; Bai, Z.K.; Guan, Y.J.; Zheng, L.F.; Zhan, P.Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Exploration and practice of ecological protection and restoration about mountains-rivers-forests-farmlands-lakes-grasslands in the Qilian Mountains. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 8990–8997. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.H.; You, Z. Scientific connotation and practical paths about the principle of ‘taking mountains, rivers, forests, farmlands, lakes, and grasslands as a life community’. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2019, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, S.J.; Chen, N.; Li, Z.G. Enhancing ecosystem services and socio-ecological system coupling coordination through LULC optimization. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 179, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.T.; Zhang, A.L. Identification of land use conflicts and dynamic response analysis of Natural-Social factors in rapidly urbanizing areas- a case study of urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of Yangtze River. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 161, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.L.; Guan, D.J.; Xie, T.T.; Zhou, L.L.; He, X.J. Identification of health diagnosis types and restoration pathway optimization for the mountains-rivers-forests-fields-lakes-grasslandssands life community in China. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 32, 418–429. [Google Scholar]
- Croese, S.; Green, C.; Morgan, G. Localizing the Sustainable Development Goals Through the Lens of Urban Resilience: Lessons and Learnings from 100 Resilient Cities and Cape Town. Sustainability 2020, 12, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yu, Y.; He, J.; Li, C.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Malik, I.; Wistuba, M. Vulnerability assessment of Social-Ecological systems in arid Regions: A Cross-Efficiency modified DEA model with entropy weight aggregation. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 179, 114149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Feng, H.; Arashpour, M.; Zhang, F. Enhancing urban flood resilience: A coupling coordinated evaluation and geographical factor analysis under SES-PSR framework. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2024, 101, 104243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.G.; Zhao, J.H.; Chen, J. Coevolutionary dynamics in the grass-livestock social-ecological system of China’s alpine pastoral areas: A case study of the Qilian Mountains region in China. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Chen, R.S.; Li, K.L. Glacial Change and Its Hydrological Response in Three Inland River Basins in the Qilian Mountains, Western China. Water 2021, 13, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Gou, X.H.; Xue, B.; Ma, W.J.; Kuang, W.N.; Tu, Z.Y.; Gao, L.L.; Yin, D.C.; Zhang, J.Z. Research on the change of alpine ecosystem service value and its sustainable development path. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.T.; Li, Z.X.; Feng, Q.; Lu, Z.X.; Zhang, B.J.; Cheng, W.J. Evolution of ecosystem service values in Qilian Mountains based on land-use change from 1990 to 2020. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 4187–4202. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.J.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, H.; Du, D.S.; Zhu, X.L.; Che, X.C. Vegetation coverage variation in the Qilian Mountains before and after ecological restoration. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Qu, H.J.; Guo, L. Spatio-temporal coupling and prediction of social-ecological systems under the “concept of life community of mountains, water, forests, fields, lakes, grasses, and sands”. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 2745–2760. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Shi, X.Q. Dynamic evaluation of China’s ecological civilization construction based on target correlation degree and coupling coordination degree. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 93, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, M. The effect of urban planning on urban formations determining bioclimatic comfort area’s effect using satellitia imagines on air quality: A case study of Bursa city. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, D.; Satriani, S.; Zudi, S.L.; Ekka, A. To What Extent Does Indigenous Local Knowledge Support the Social-Ecological System? A Case Study of the Ammatoa Community, Indonesia. Resources 2022, 11, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Wang, R.H.; Peng, Q.; Liu, C.W.; Zhou, L.M. Analysis of Hydrothermal Characteristics based on Different Drought Indices in Qilian Mountain National Park. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2023, 38, 200–213. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Y.F.; Li, C.H. Spatiotemporal Pattern of Vegetation Net Primary Productivity (NPP) and Its Response to Climate Change in Qilian Mountains during the past 16 Years. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2022, 30, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Wu, X.T.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, F.Y.; Lu, N.; Kou, L.B. Land use optimization for future ecosystem service demands: A case study in the Yanhe watershed. J. Clean Prod. 2025, 520, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.T.; Yuan, J.; Li, X.Y.; Tang, J.T. Research on land use change and spatiotemporal distribution of carbon storage on the southern slope of Qilian Mountains based on the InVEST model. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 32, 332–342. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Shi, F.F. New urbanization and high-quality urban and rural development: Based on the interactive coupling analysis of industrial green transformation. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Q.; Tang, Y.Y.; Sun, X.S. Rural Industrial Integration and New Urbanization in China: Coupling Coordination, Spatial-Temporal Differentiation, and Driving Factors. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.F.; Zhang, X.E. The Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Driving Forces of the Coupled and Coordinated Development between New Urbanization and Rural Revitalization. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, T.F.; Li, X.H.; Cai, W.G.; Zuo, J.; Jia, F.Y.; Wei, H.F. Exploring the impact of urbanization on urban building carbon emissions in China: Evidence from a provincial panel data model. Sust. Cities Soc. 2020, 56, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Sun, W.X.; Zhu, L. The impact of new urbanization and industrial structural changes on regional water stress based on water footprints. Sust. Cities Soc. 2022, 79, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, V. Water Quality, Air Pollution, and Climate Change: Investigating the Environmental Impacts of Industrialization and Urbanization. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.R.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, C.W.; Zhou, J.T.; Feng, X.M. Analysis of the spatio-temporal change of social-ecological system coupling: A case study in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 33, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.R.; Jin, Y.Z.; Li, D.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Liu, W.Y. Spatiotemporal variation and evolutionary analysis of the coupling coordination between urban social-economic development and ecological environments in the Yangtze River Delta cities. Sust. Cities Soc. 2024, 111, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhao, L.; Guo, J.M.; Du, M.H.; Hao, C.X.; Hu, R. Analysis of coordinated development of ?society-ecology-policy? and spatio-temporal variation of people?s livelihoods and well-being in the Yellow River basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, P.; Deng, H.D.; Qi, F.; Li, Q.; Chang, X.W.; Cheng, P. Scientific cognition, path and governance system guarantee of the Life Community of Mountains, Rivers, Forests, Fields, Lakes and Grasses. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 3005–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bai, W.C.; Du, B. Coupling Coordination and Spatial Correlation Network Structure of Economic Resilience and Ecological Resilience. Environ. Sci. 2025, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, D.X.; Li, Z.H.; Xu, M.; Wang, D.; Hou, X.S. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Interactions of Vegetation and Water Balance Elements. Strateg. Study CAE 2024, 26, 140–156. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.F.; Yang, H.; Jia, J.; Shen, Y.; Liu, J.Q. Index system of sustainable rural development based on the concept of ecological livability. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 86, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Xue, D.Q.; Song, Y.Y. Spatio-temporal Characteristics and Trend Warnings of Water Resources Carrying Capacity in China. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2021, 30, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Q.; Liu, H.B.; Wang, J.T.; Liu, H.; Shang, Y. Multiscale analysis on spatiotemporal dynamics of energy consumption CO2 emissions in China: Utilizing the integrated of DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS nighttime light datasets. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.F.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.L.; Xu, T.B.; Chen, Z.Q.; Liu, R.; Li, L.Y.; Wu, J.P. Modeling spatiotemporal CO2 (carbon dioxide) emission dynamics in China from DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data using panel data analysis. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.B.; Wen, S.M.; Han, G.; Wang, X.; Feng, Q.C. Wastewater Treatment in Mineral Processing of Non-Ferrous Metal Resources: A Review. Water 2022, 14, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Hou, J.Z.; Jiang, Y.N. Multi-objective optimization of water and land resources in typical oasis irrigation areas of the Hexi Corridor: A case study of the Fengle River Irrigation Area. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng. 2025, 43, 414–426. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.W.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yan, D.T.; Xia, K.Y.; He, S.Y.; He, Y.Q. Coupling Agricultural Green Development and Park City Development: An Empirical Analysis from Chengdu, China. Agriculture 2025, 15, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Guo, S.S.; Guo, P.; Shan, B.Y.; Zhang, Y. Agricultural water and land resources allocation considering carbon sink/source and water scarcity/degradation footprint. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Lu, X.; Liu, B.Y.; Wu, D.T.; Fu, G.; Zhao, Y.T.; Sun, P.L. Spatial relationships between ecosystem services and socioecological drivers across a large-scale region: A case study in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Han, M.Y.; Peng, K.; Zhou, S.L.; Shao, L.; Wu, X.F.; Wei, W.D.; Liu, S.Y.; Li, Z.; Li, J.S.; et al. Global land-water nexus: Agricultural land and freshwater use embodied in worldwide supply chains. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, L.X.; Zhang, M.Y.; Li, X.J.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Y.S. Response of plant community structure and soil water conservation function to forbidden grazing and enclosure in alpine steppe of thed Qinghai Lake. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2024, 44, 1488–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.M.; Jing, X.; Xiao, B.W.; Ma, X.L.; He, J.S. Climate and land-use change jointly determine the spatial-temporal changes of ecosystem services in Hainan and Haibei Tibetan Autonomous Prefectures, Qinghai Province. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2022, 31, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.H.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, Y.J.; Su, C.; Lei, Q.L.; Li, W.P.; Li, C.Y. Climate change threatens water resources over the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lian, W.H.; Wei, J.F.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y.S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.G. Status and problems of water resources on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Adv. Water Sci. 2023, 34, 812–826. [Google Scholar]

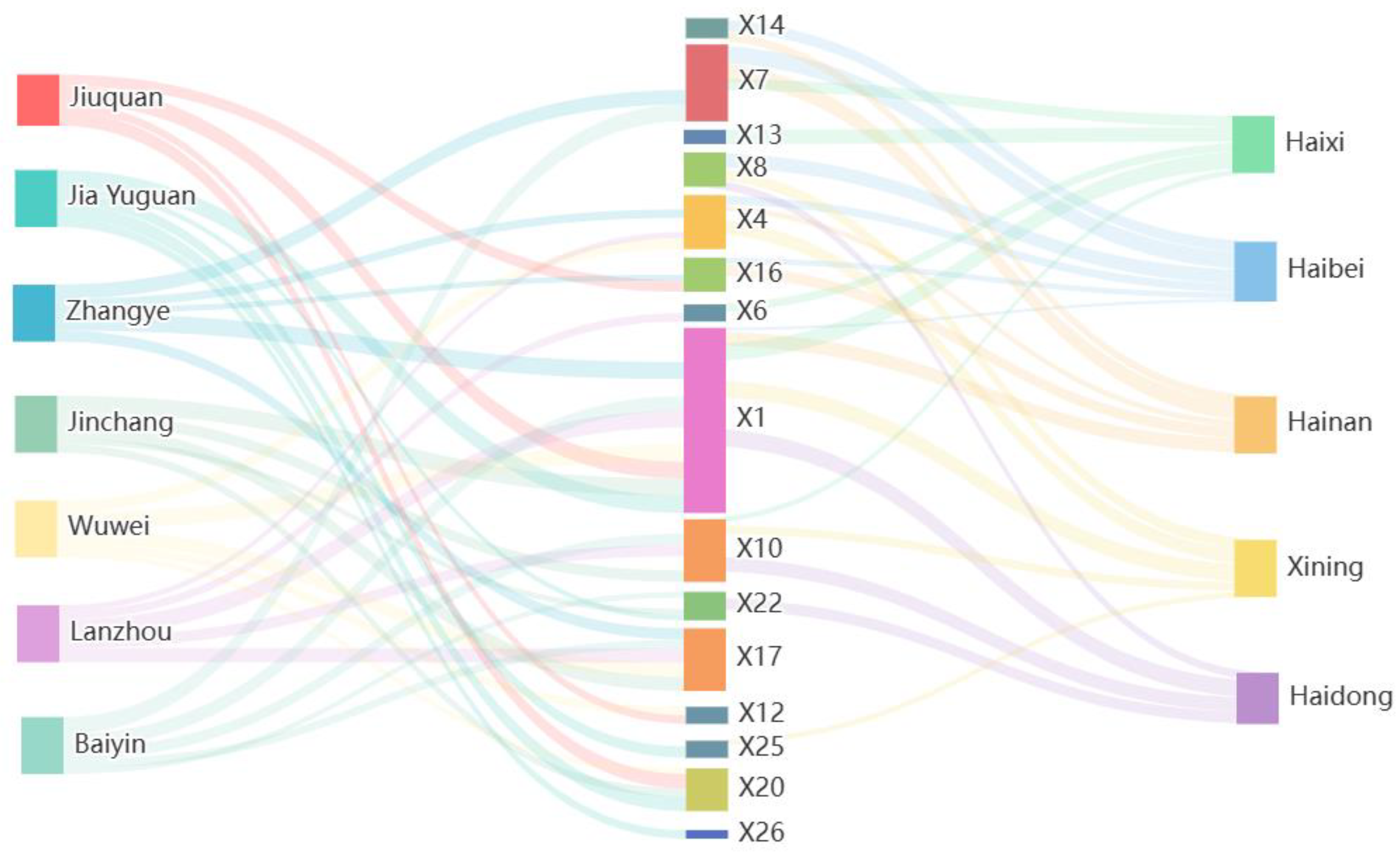

| Target Layer | System Layer | Subsystem Layer | Index | Index Layer | Indicator Attributes | Entropy Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-factor Evaluation Index System Based on SES | Ecosystem | Water | X1 | Water Supply–demand Ratio | (+) | 0.002 |
| X2 | Water consumption per ten thousand CNY | (−) | 0.002 | |||
| X3 | Wastewater discharge volume | (−) | 0.004 | |||
| Forests | X4 | Forest area | (+) | 0.053 | ||
| X5 | Forestry output value | (+) | 0.049 | |||
| X6 | Water consumption in fores | (−) | 0.004 | |||
| Resource System | Mountains | X7 | Average terrain relief | (−) | 0.020 | |
| X8 | Water production coefficient | (+) | 0.049 | |||
| X9 | Tertiary industry output value | (+) | 0.082 | |||
| Fields | X10 | Farmland area | (+) | 0.027 | ||
| X11 | Agricultural irrigation water consumption | (−) | 0.008 | |||
| X12 | Agricultural output value | (+) | 0.052 | |||
| Resource Unit | Lakes | X13 | River runoff | (+) | 0.077 | |
| X14 | Water area and wetland coverage | (+) | 0.104 | |||
| X15 | Fisheries output value | (+) | 0.131 | |||
| Grasslands | X16 | Grassland area | (+) | 0.043 | ||
| X17 | NDVI | (+) | 0.023 | |||
| X18 | Livestock output value | (+) | 0.049 | |||
| sands | X19 | Bare land area | (−) | 0.012 | ||
| X20 | Aridity index | (−) | 0.004 | |||
| Social Systems | X21 | GDP | (+) | 0.057 | ||
| X22 | Population density | (−) | 0.010 | |||
| Governance Systems | X23 | Annual fiscal expenditure | (−) | 0.002 | ||
| X24 | Total fixed-asset investment | (+) | 0.059 | |||
| Actors | X25 | Nighttime light index | (−) | 0.002 | ||
| X26 | Proportion of ecological water consumption | (+) | 0.075 | |||
| Barrier Factor (System Layer) | Water | Fields | Grasslands | Mountains | Forests | Others | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obstacle Level | 16.51% | 14.16% | 14.03% | 12.10% | 11.16% | <10% | ||
| Barrier Factors (Indicator Layer) | X1 | X17 | X10 | X7 | X21 | X8 | X11 | Others |
| Obstacle Level | 9.68% | 6.34% | 5.81% | 5.61% | 4.83% | 4.63% | 4.60% | <4.5% |
| System | C | P | MRE | System | C | P | MRE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCD | 0.04 | 1.00 | 0.69% | Grasslands | 0.05 | 1.00 | 2.36% |
| Mountains | 0.11 | 1.00 | 3.81% | Sands | 0.16 | 0.91 | 1.01% |
| Water | 0.19 | 0.73 | 1.49% | Social | 0.11 | 1.00 | 3.81% |
| Forests | 0.08 | 1.00 | 2.43% | Governance | 0.16 | 0.82 | 4.75% |
| Fields | 0.06 | 1.00 | 3.25% | Actors | 0.03 | 1.00 | 7.35% |
| Lakes | 0.07 | 1.00 | 3.25% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Zhou, T.; Ren, H.; Jiang, S.; Xu, E.; Yuan, F. Spatiotemporal Coupling and Simulation Prediction of Socioecological Systems in the Qilian Mountain Life Community. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15242528
Xu H, Zhou T, Ren H, Jiang S, Xu E, Yuan F. Spatiotemporal Coupling and Simulation Prediction of Socioecological Systems in the Qilian Mountain Life Community. Agriculture. 2025; 15(24):2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15242528
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hua, Tao Zhou, Heng Ren, Shengji Jiang, Erwen Xu, and Feng Yuan. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Coupling and Simulation Prediction of Socioecological Systems in the Qilian Mountain Life Community" Agriculture 15, no. 24: 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15242528
APA StyleXu, H., Zhou, T., Ren, H., Jiang, S., Xu, E., & Yuan, F. (2025). Spatiotemporal Coupling and Simulation Prediction of Socioecological Systems in the Qilian Mountain Life Community. Agriculture, 15(24), 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15242528





