Differential Soil Organic Carbon Accumulation Patterns Following Cropland-to-Grassland Conversion in Non-Saline and Saline–Alkali Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Sampling
2.2. Soil Properties
2.3. Soil Lignin Phenols and Amino Sugars Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
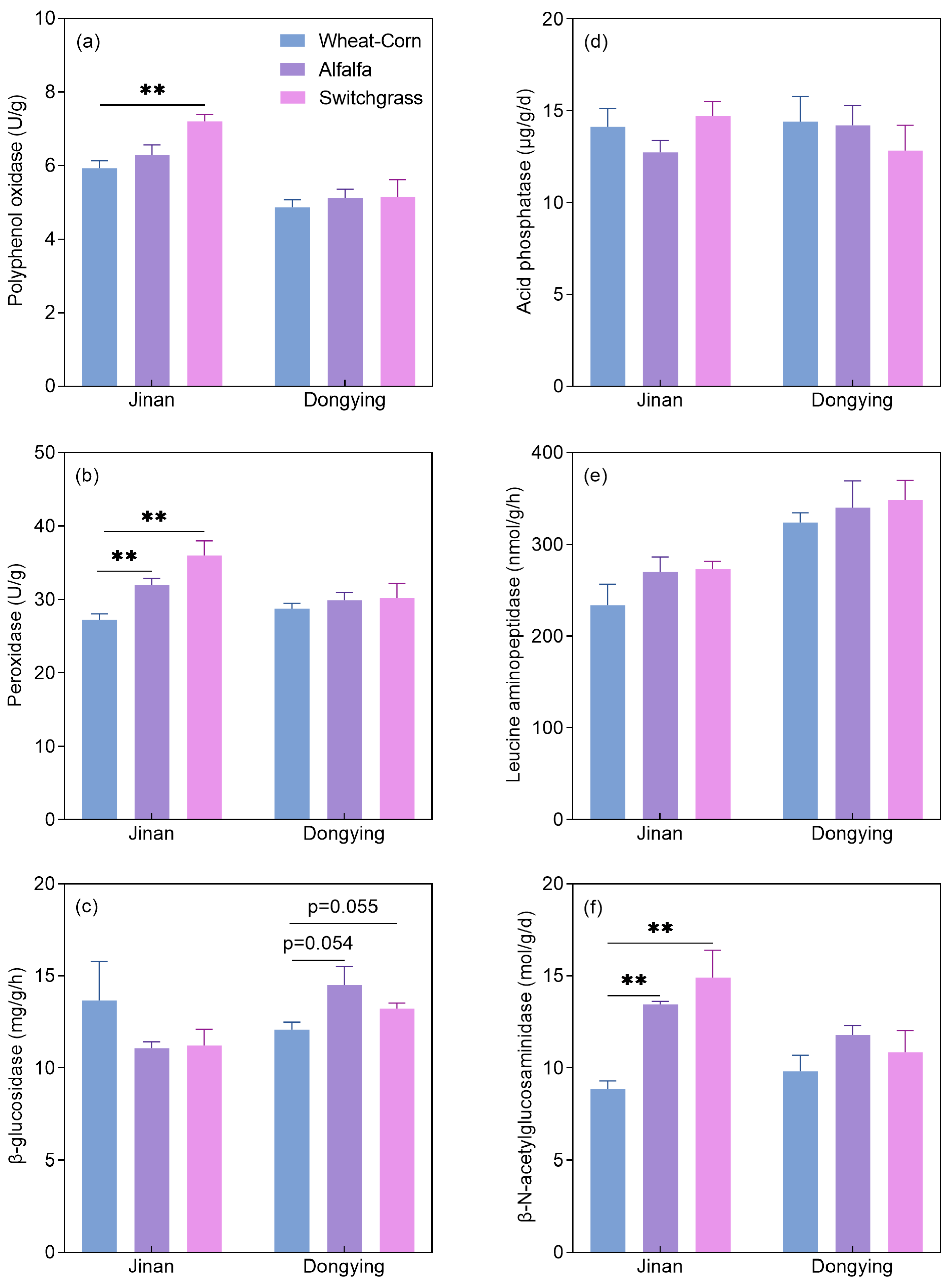
3.1. Soil Properties and Enzyme Activities
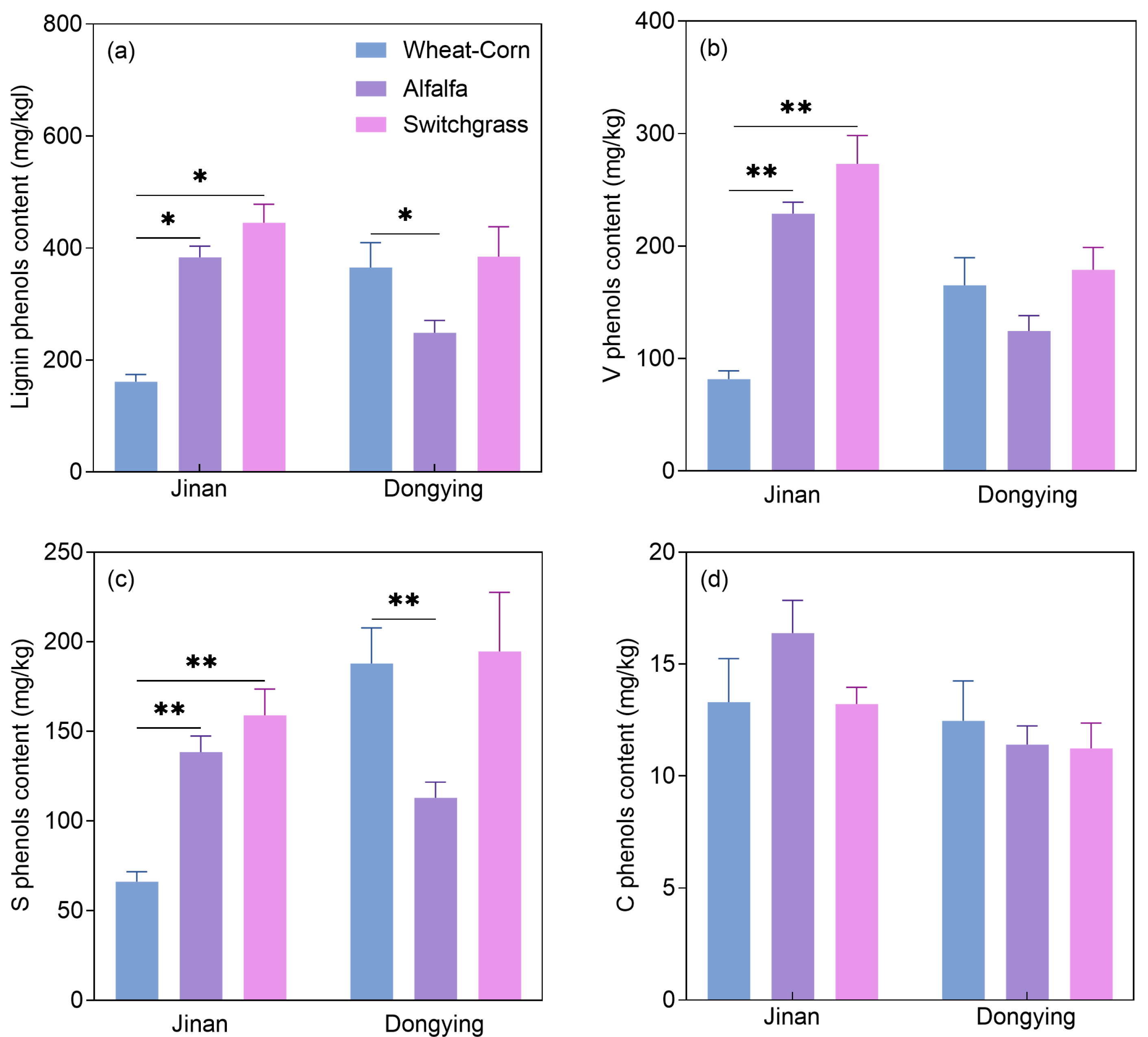
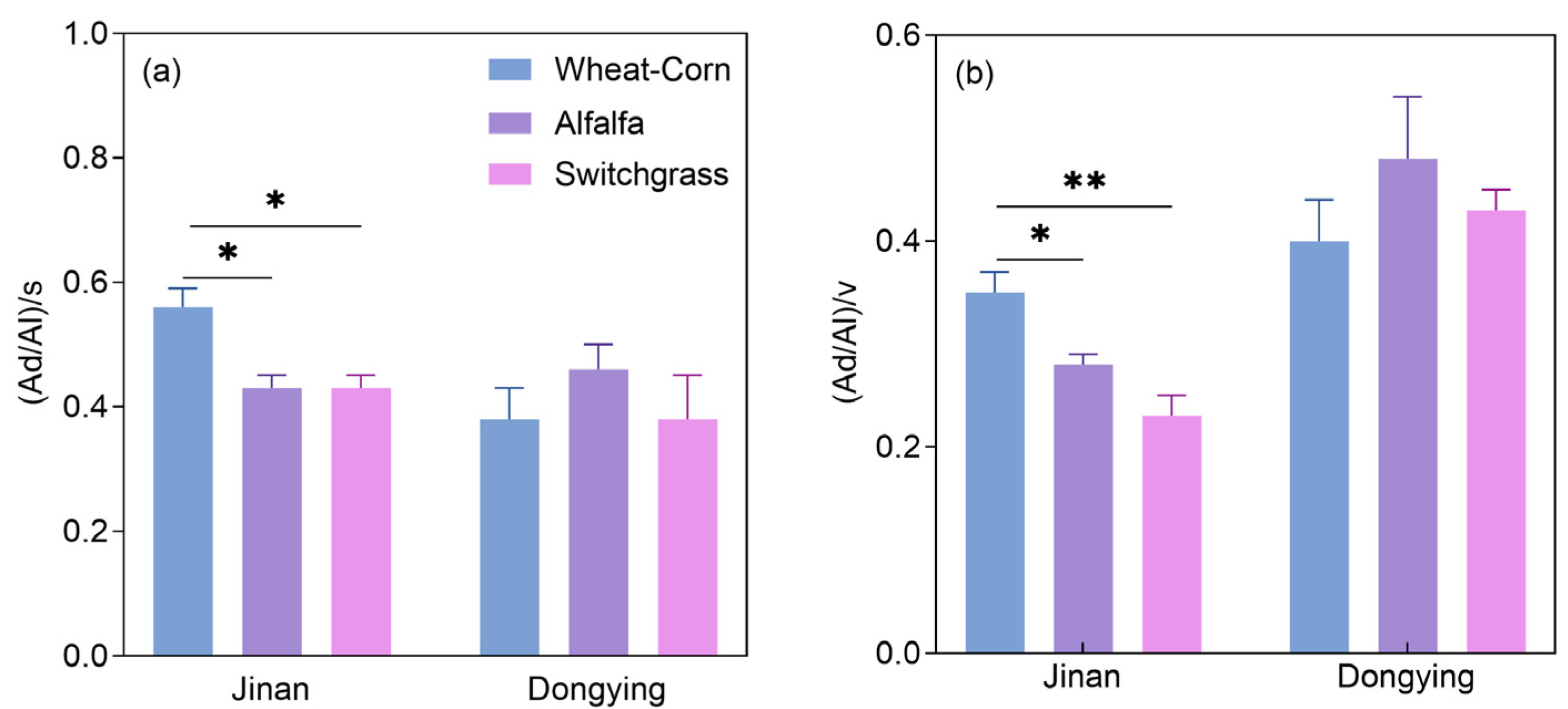
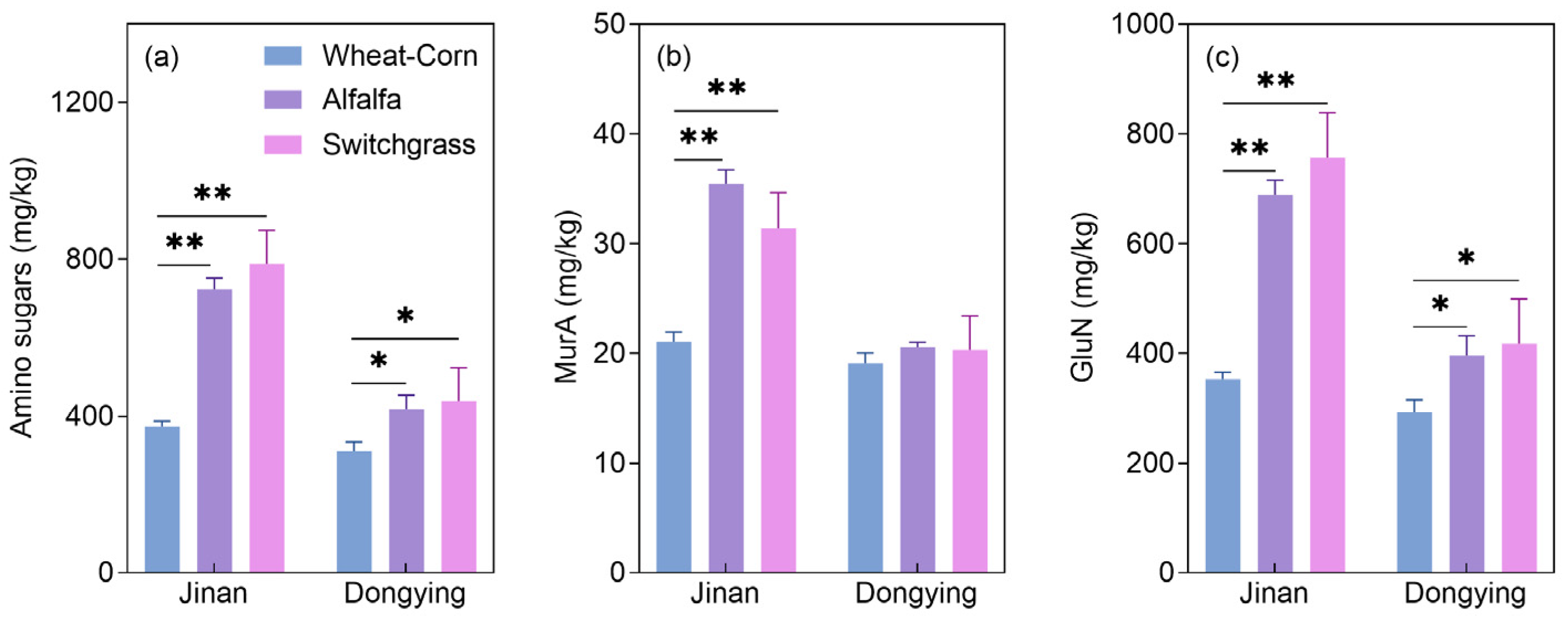
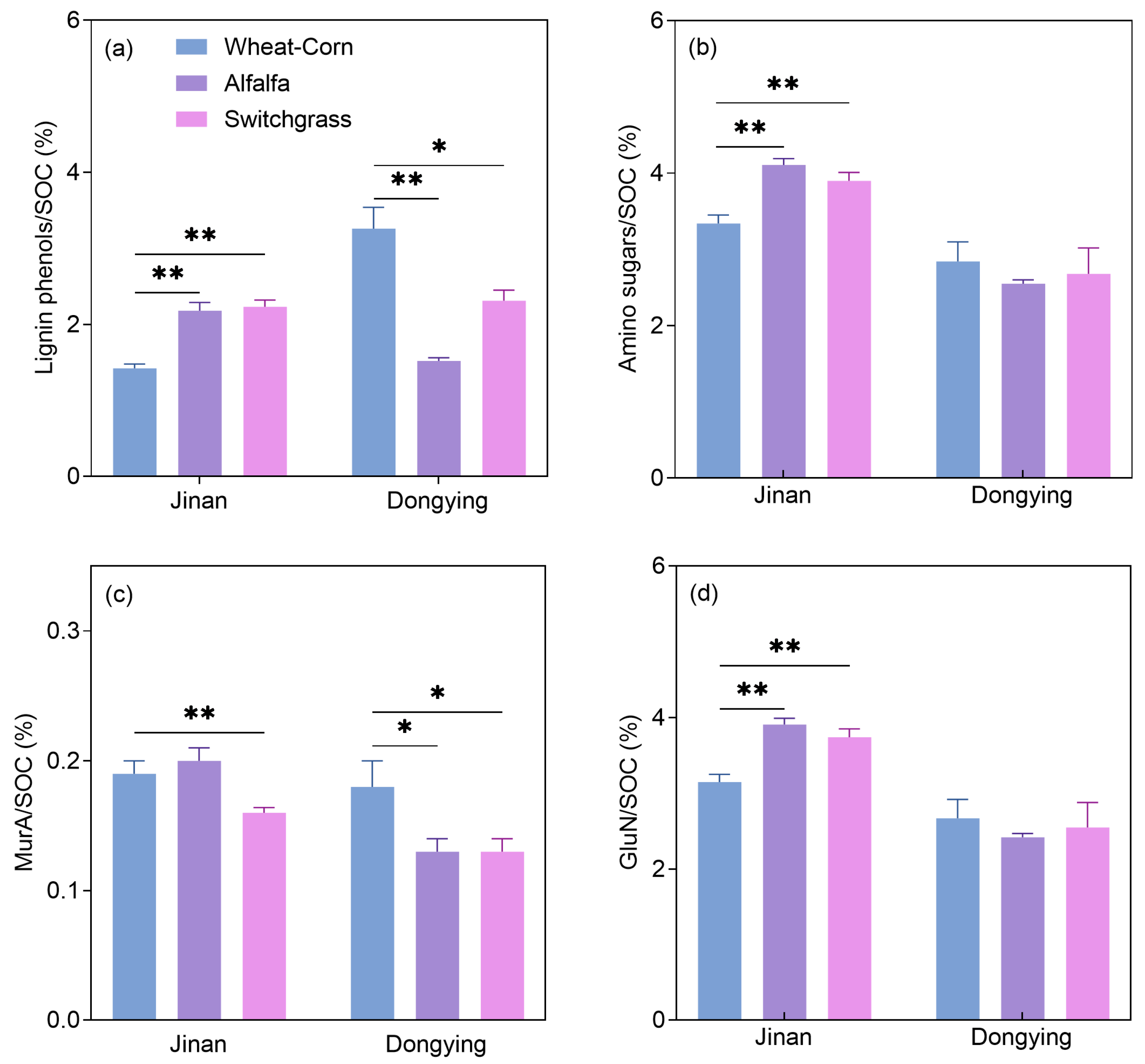
3.2. Lignin Phenols and Amino Sugars: Contents and Contributions to SOC
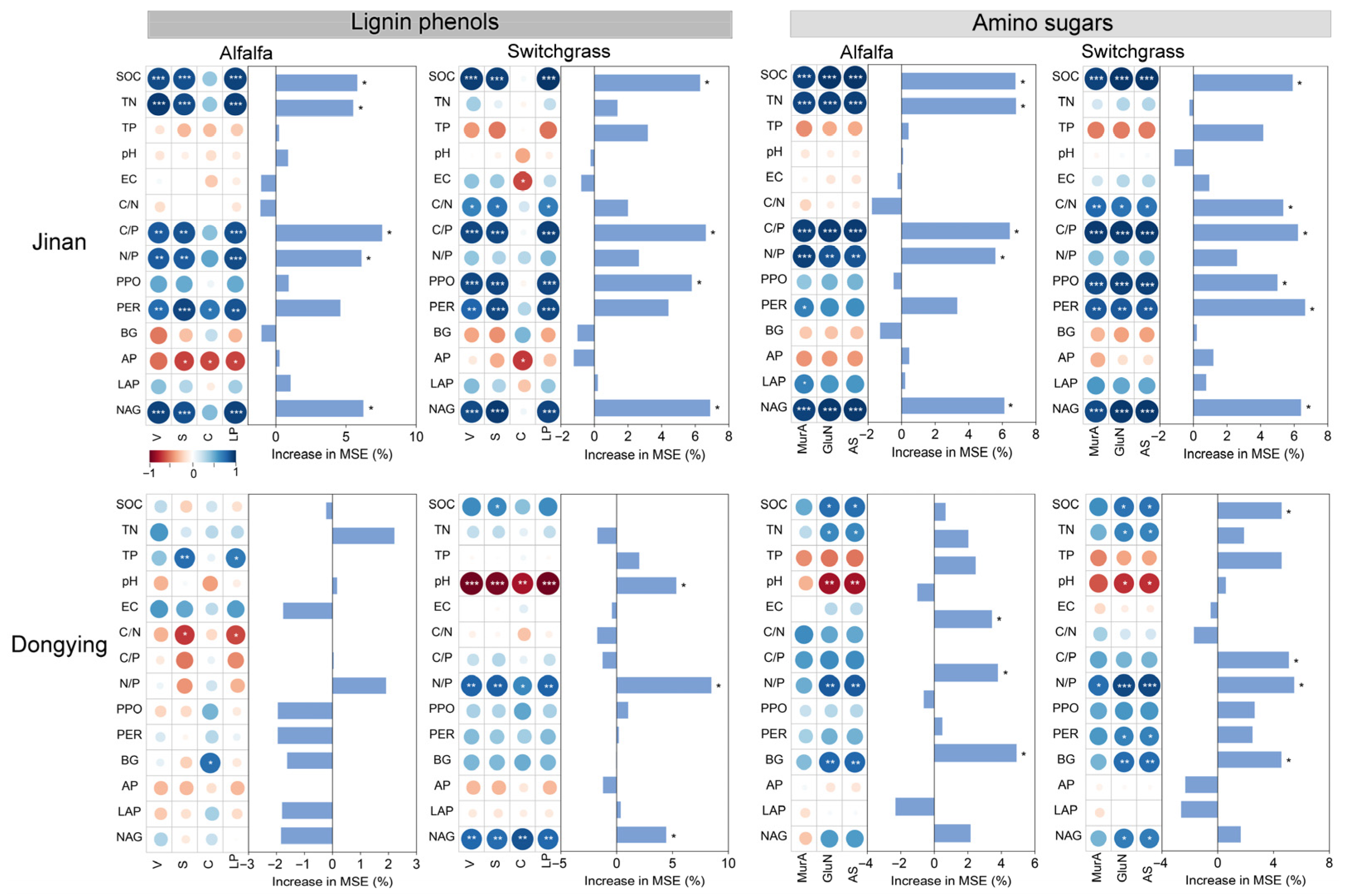
3.3. Relationships Between Soil Properties and Organic C Components
4. Discussion
4.1. The Influence of Cropland-to-Grassland Conversion on Plant-Derived C
4.2. The Influence of Cropland-to-Grassland Conversion on Microbial-Derived C
4.3. The Contributions of Plant- and Microbial-Derived C to SOC
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SOC | Soil organic carbon. |
| MurA | Muramic acid. |
| GluN | Glucosamine |
References
- Schmidt, M.W.; Torn, M.S.; Abiven, S.; Dittmar, T.; Guggenberger, G.; Janssens, I.A.; Kleber, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Lehmann, J.; Manning, D.A.C.; et al. Persistence of Soil Organic Matter as an Ecosystem Property. Nature 2011, 478, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.X.; Huang, Y.W.; Ren, W.; Coyne, M.; Jacinthe, P.A.; Tao, B.; Hui, D.F.; Yang, J.; Matocha, C. Responses of Soil Carbon Sequestration to Climate-Smart Agriculture Practices: A Meta-Analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 2591–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domeignoz-Horta, L.A.; Cappelli, S.L.; Shrestha, R.; Gerin, S.; Lohila, A.K.; Heinonsalo, J.; Nelson, D.B.; Kahmen, A.; Duan, P.; Sebag, D.; et al. Plant Diversity Drives Positive Microbial Associations in the Rhizosphere Enhancing Carbon Use Efficiency in Agricultural Soils. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, Y.; Jackson, R.D.; Cotrufo, M.F.; Sanford, G.R.; Spiesman, B.J.; Deiss, L.; Culman, S.W.; Liang, C.; Ruark, M.D. Persistent Soil Carbon Enhanced in Mollisols by Well-Managed Grasslands but Not Annual Grain or Dairy Forage Cropping Systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2118931119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, A.L.; Lin, B.J.; Kan, Z.R.; Qi, J.Y.; Dang, Y.P.; Lal, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.L. Simultaneous Effects of Legume Cultivation on Carbon and Nitrogen Accumulation in Soil. Adv. Agron. 2022, 171, 75–110. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, T.L.; Szutu, D.J.; Verfaillie, J.G.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Silver, W.L. Carbon-Sink Potential of Continuous Alfalfa Agriculture Lowered by Short-Term Nitrous Oxide Emission Events. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cha, X.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Cai, A.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, G.; Han, X.; Ren, C. A Global Meta-Analysis of Land Use Change on Soil Mineral-Associated and Particulate Organic Carbon. Glob. Change Biol. 2025, 31, e70111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Schimel, J.P.; Jastrow, J.D. The Importance of Anabolism in Microbial Control Over Soil Carbon Storage. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Q.; Fang, C.; Ma, T.; Pei, J.Y.; Song, X.; Yao, G.Q.; Sardans, J.; Penuelas, J.; Fang, X.W.; Li, F.M. Distinct Mechanisms of Soil Organic Carbon Formation in Natural and Legume-Based Grasslands on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 211, 109978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, D.; Dai, G.; Feng, B.; Su, X.; Hu, H.; Li, K.; Han, W.; et al. Divergent Accumulation of Microbial Necromass and Plant Lignin Components in Grassland Soils. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Q.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, K.; Jiang, Y.; Li, D.; Xie, Z.; Sun, B.; Wang, X. Divergent Accumulation of Microbe-and Plant-Derived Carbon in Different Soil Organic Matter Fractions in Paddy Soils Under Long-Term Organic Amendments. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 366, 108934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, G.; Mueller, K.E.; Nierop, K.G.; Simpson, M.J. Plant-or Microbial-Derived? A Review on the Molecular Composition of Stabilized Soil Organic Matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 156, 108189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Du, J.; Chong, F.; Li, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhai, G.; Song, Z.; Mao, J. Spatio-Temporal Variation and Prediction of Carbon Storage in Terrestrial Ecosystems in the Yellow River Basin. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Kong, B.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y. Variation of Soil Organic Carbon and Physical Properties in Relation to Land Uses in the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, G.; Feng, B.; Wang, C.; Luo, Y.; Li, F.; Shen, C.; Ma, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J. Saline-Alkali Land Reclamation Boosts Topsoil Carbon Storage by Preferentially Accumulating Plant-Derived Carbon. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 2948–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Z.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Luo, Y.Q.; Jiang, L.F.; Chen, J.; Hou, E.Q. Land Use Change Alters Soil Organic Carbon: Constrained Global Patterns and Predictors. Earths Future 2024, 12, e2023EF004254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Qin, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, G.; Xue, S. Microbial Necromass Carbon Drives Soil Organic Carbon Accumulation During Long-Term Vegetation Succession. J. Appl. Ecol. 2025, 62, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, F.; Ma, D.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Dong, H.; Liang, X.; Yin, G.; Han, P.; Liu, M.; et al. Microbial Necromass Carbon in Estuarine Tidal Wetlands of China: Influencing Factors and Environmental Implication. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Smith, P.; Shokri, N. Negative Correlation Between Soil Salinity and Soil Organic Carbon Variability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2317332121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, R.; Petropoulos, E.; Yu, B.; Zhang, J.; Lin, X.; Gao, M.; Feng, Y. Interactive Effects of Salinity and SOM on the Ecoenzymatic Activities Across Coastal Soils Subjected to a Saline Gradient. Geoderma 2022, 406, 115519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Mao, H.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jia, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.G. Salinity Decreases the Contribution of Microbial Necromass to Soil Organic Carbon Pool in Arid Regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172786. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Boot, C.M.; Denef, K.; Paul, E. The Microbial Efficiency-Matrix Stabilization (MEMS) Framework Integrates Plant Litter Decomposition with Soil Organic Matter Stabilization: Do Labile Plant Inputs Form Stable Soil Organic Matter? Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, X.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y.; Xia, L.; Fan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W. Ecosystem multifunctionality and soil microbial communities in response to ecological restoration in an alpine degraded grassland. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1173962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Simpson, M.J. The Distribution and Degradation of Biomarkers in Alberta Grassland Soil Profiles. Org. Geochem. 2007, 38, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Amelung, W. Gas Chromatographic Determination of Muramic Acid, Glucosamine, Mannosamine, and Galactosamine in Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1996, 28, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Du, N.; Li, Q.; Wei, G. Soil Microbiomes with Distinct Assemblies through Vertical Soil Profiles Drive the Cycling of Multiple Nutrients in Reforested Ecosystems. Microbiome 2018, 6, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, R.; Kelkar, A.; Baraniya, D.; Molaei, A.; Moulick, A.; Meena, R.S.; Formanek, P. Enzymatic Degradation of Lignin in Soil: A Review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Wang, L.; Fang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Du, Z. Conservation Agriculture Boosts Topsoil Organic Matter by Restoring Free Lipids and Lignin Phenols Biomarkers in Distinct Fractions. Soil Till. Res. 2025, 248, 106463. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Vancov, T.; Jin, X.; Gao, Q.; Dong, W.; Du, Z. No-Tillage Farming for Two Decades Increases Plant-and Microbial-Biomolecules in the Topsoil Rather than Soil Profile in Temperate Agroecosystem. Soil Till. Res. 2024, 241, 106108. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Simpson, M.J. Temperature Responses of Individual Soil Organic Matter Components. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, G03036. [Google Scholar]
- Rath, K.M.; Rousk, J. Salt Effects on the Soil Microbial Decomposer Community and Their Role in Organic Carbon Cycling: A Review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 81, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Song, Z.; Li, Q.; Guo, L.; Yu, C.; Singh, B.P.; Fu, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Distribution, Sources, and Decomposition of Soil Organic Matter Along A Salinity Gradient in Estuarine Wetlands Characterized by C:N Ratio, δ13C-δ15N, and Lignin Biomarker. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Gu, R.; Gao, K.; Li, D. High Plant Species Diversity Enhances Lignin Accumulation in a Subtropical Forest of Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Yang, Z.; Shi, B.; Gao, W.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; He, J.S. Phosphorus Supply Suppressed Microbial Necromass but Stimulated Plant Lignin Phenols Accumulation in Soils of Alpine Grassland on the Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma 2023, 431, 116376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Song, Z.; Wang, W.; Fan, Y.; Guo, L.; Van Zwieten, L.; Hartley, L.P.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.M.; et al. Patterns and Determinants of Plant-Derived Lignin Phenols in Coastal Wetlands: Implications for Organic C Accumulation. Funct. Ecol. 2023, 37, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, F.; Zegada-Lizarazu, W.; Lambertini, C.; Monti, A. Salinity Effects on Germination, Seedlings and Full-Grown Plants of Upland and Lowland Switchgrass Cultivars. Biomass Bioenerg. 2019, 120, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Duan, X.; Wu, Y.; Huang, H.; Fu, T.; Chu, H.; Xue, S. Carbon Sequestration Potential and Its Main Drivers in Soils under Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, N.W.; Sanderman, J.; Bradford, M.A. Pathways of Mineral-Associated Soil Organic Matter Formation: Integrating the Role of Plant Carbon Source, Chemistry, and Point of Entry. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, Z.; You, Y.; Guo, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, S.; Sun, O.J. Differential Effects of Forest-Floor Litter and Roots on Soil Organic Carbon Formation in a Temperate Oak Forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 180, 109017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.X.; Wei, Y.X.; Li, R.C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.D.; Virk, A.L.; Lal, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.L. Improving Soil Aggregates Stability and Soil Organic Carbon Sequestration by No-Till and Legume-Based Crop Rotations in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuest, S.B.; Schillinger, W.F.; Machado, S. Variation in Soil Organic Carbon Over Time in No-Till Versus Minimum Tillage Dryland Wheat-Fallow. Soil Till. Res. 2023, 229, 105677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Chenu, C.; Kappler, A.; Rillig, M.C.; Fierer, N. The interplay between microbial communities and soil properties. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Hu, G.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhuge, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, X. Distinct Accumulation of Bacterial and Fungal Residues Along a Salinity Gradient in Coastal Salt-Affected Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 158, 108266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B. Salinity-Driven Differentiation of Bacterial and Fungal communities in Coastal Wetlands: Contrasting Assembly Processes and Spatial Dynamics. Environ. Res. 2025, 279, 121895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollister, E.B.; Engledow, A.S.; Hammett, A.J.M.; Provin, T.L.; Wilkinson, H.H.; Gentry, T.J. Shifts in Microbial Community Structure Along an Ecological Gradient of Hypersaline Soils and Sediments. ISME J. 2010, 4, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Luo, M.; Liu, Y.; Tan, J.; Zhang, C.; Tan, F.; Huang, J. Linking Carbon-Degrading Enzyme Activity to Microbial Carbon-Use Trophic Strategy Under Salinization in a Subtropical Tidal Wetland. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 174, 104421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenbach, C.M.; Grandy, A.S.; Frey, S.D.; Diefendorf, A.F. Microbial Physiology and Necromass Regulate Agricultural Soil Carbon Accumulation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 91, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Amelung, W.; Lehmann, J.; Kästner, M. Quantitative Assessment of Microbial Necromass Contribution to Soil Organic Matter. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 3578–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, R.; Vanlauwe, B.; Six, J. Litter Quality Impacts Short-but Not Long-Term Soil Carbon Dynamics in Soil Aggregate Fractions. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzgall, K.; Vidal, A.; Schubert, D.I.; Höschen, C.; Schweizer, S.A.; Buegger, F.; Pouteau, V.; Chenu, C.; Mueller, C.W. Particulate Organic Matter as a Functional Soil Component for Persistent Soil Organic Carbon. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, E.D.; Grandy, A.S.; Sokol, N.W.; Keiluweit, M.; Ernakovich, J.; Smith, R.G.; Frey, S.D. Clarifying the Evidence for Microbial- and Plant- Derived Soil Organic Matter, and the Path Toward a More Quantitative Understanding. Glob. Change Biol 2022, 28, 7167–7185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study Sites | Crops | SOC (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | TP (g/kg) | pH | EC (µs/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jinan | Wheat–corn | 11.30 ± 0.76 b | 1.17 ± 0.03 b | 1.27 ± 0.03 a | 8.38 ± 0.06 | 117.32 ± 5.94 |
| Alfalfa | 17.62 ± 0.64 a | 1.92 ± 0.11 a | 1.16 ± 0.04 b | 8.27 ± 0.05 | 118.02 ± 2.50 | |
| Switchgrass | 20.08 ± 1.65 a | 1.39 ± 0.18 b | 1.01 ± 0.06 b | 8.42 ± 0.01 | 127.90 ± 5.66 | |
| Dongying | Wheat–corn | 11.17 ± 0.96 b | 1.38 ± 0.13 | 1.26 ±0.07 a | 8.48 ± 0.02 | 154.10 ± 12.59 |
| Alfalfa | 16.36 ± 1.30 a | 1.62 ± 0.10 | 0.99 ± 0.04 b | 8.42 ± 0.05 | 138.14 ± 7.53 | |
| Switchgrass | 15.82 ± 1.54 a | 1.35 ± 0.10 | 1.08 ± 0.03 b | 8.56 ± 0.08 | 129.0 ± 64.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Bai, S.; Jia, C.; Kang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, C.; Zhang, J.; Basigalup, D.H.; Wu, B.; Wang, G. Differential Soil Organic Carbon Accumulation Patterns Following Cropland-to-Grassland Conversion in Non-Saline and Saline–Alkali Soils. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222393
Zhang J, Bai S, Jia C, Kang L, Zhang Y, Guan C, Zhang J, Basigalup DH, Wu B, Wang G. Differential Soil Organic Carbon Accumulation Patterns Following Cropland-to-Grassland Conversion in Non-Saline and Saline–Alkali Soils. Agriculture. 2025; 15(22):2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222393
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jinglei, Shanshan Bai, Chunlin Jia, Lele Kang, Yuxue Zhang, Cong Guan, Jinhong Zhang, Daniel Horacio Basigalup, Bo Wu, and Guoliang Wang. 2025. "Differential Soil Organic Carbon Accumulation Patterns Following Cropland-to-Grassland Conversion in Non-Saline and Saline–Alkali Soils" Agriculture 15, no. 22: 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222393
APA StyleZhang, J., Bai, S., Jia, C., Kang, L., Zhang, Y., Guan, C., Zhang, J., Basigalup, D. H., Wu, B., & Wang, G. (2025). Differential Soil Organic Carbon Accumulation Patterns Following Cropland-to-Grassland Conversion in Non-Saline and Saline–Alkali Soils. Agriculture, 15(22), 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222393






