An Automatic System for Remote Monitoring of Bactrocera dorsalis Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
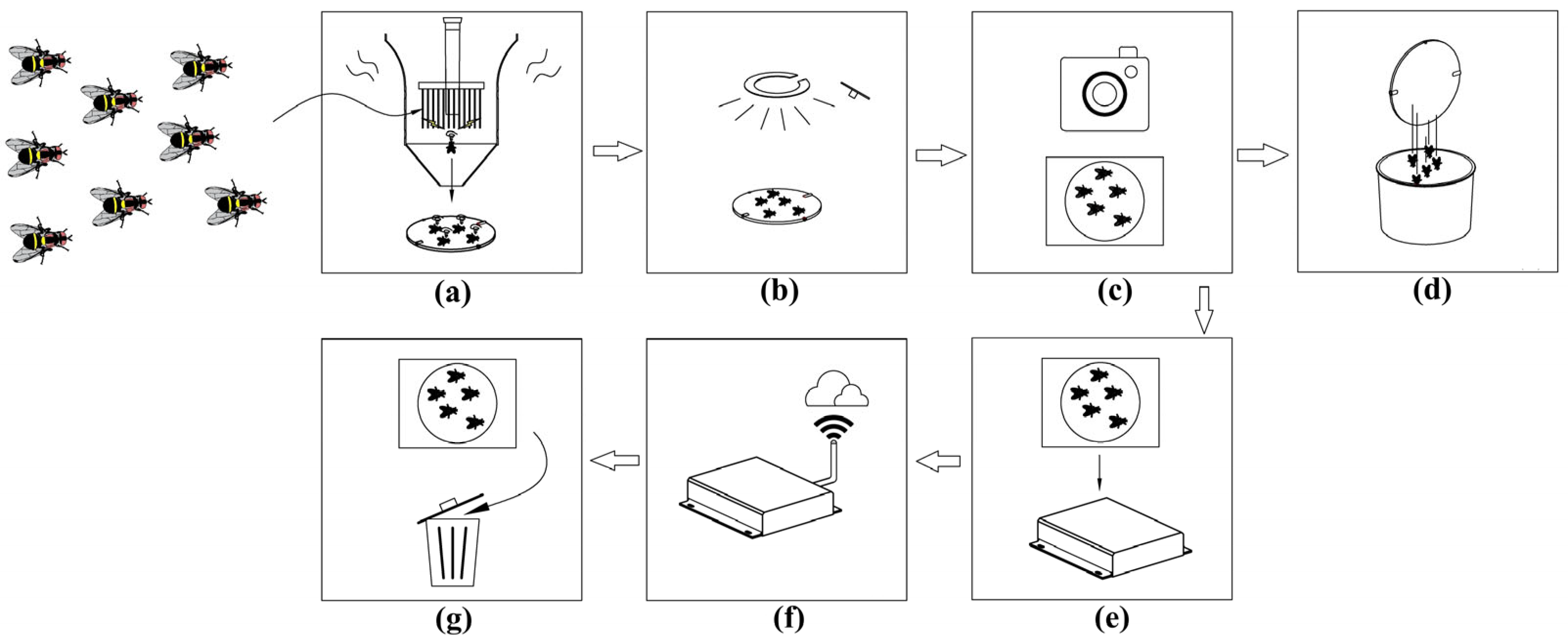
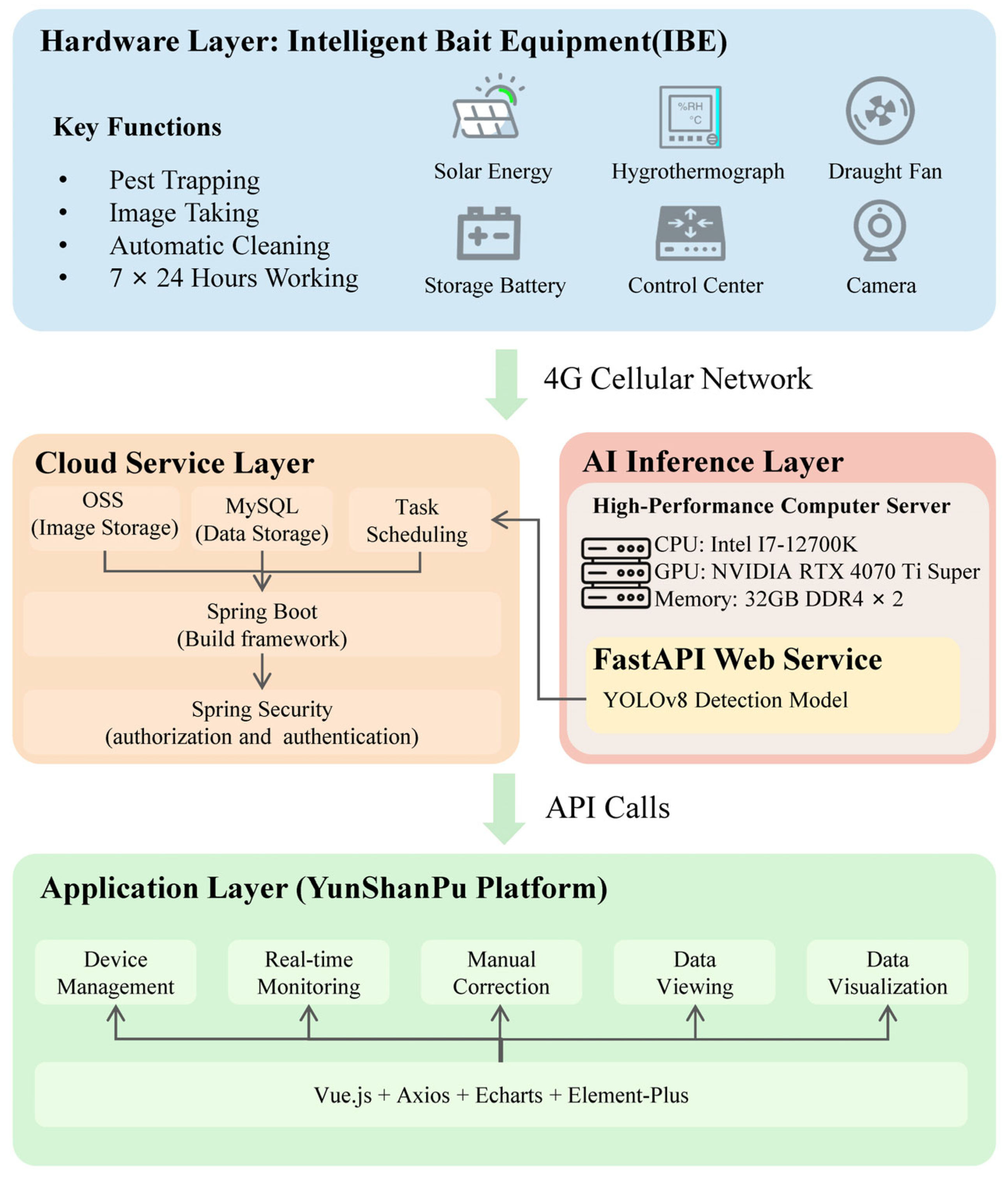
2.1. The Design of Intelligent Bait Equipment
2.2. Short-Term Field Test of Intelligent Bait Equipment
2.3. Automatic Pest Counting
2.3.1. Image Dataset Construction and Annotation
2.3.2. Automatic Pest Counting Models Based on YOLOv8
2.3.3. Model Evaluation
2.4. Long-Term Field Deployment of Integrated Pest Monitoring System
3. Results
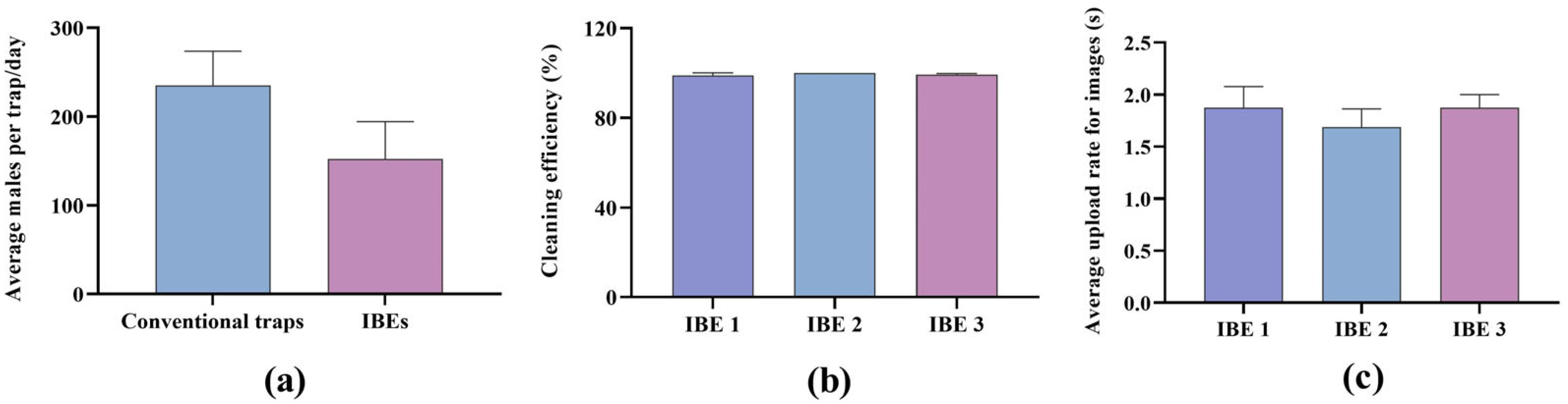
3.1. Intelligent Bait Equipment Function and Attractiveness of B. dorsalis
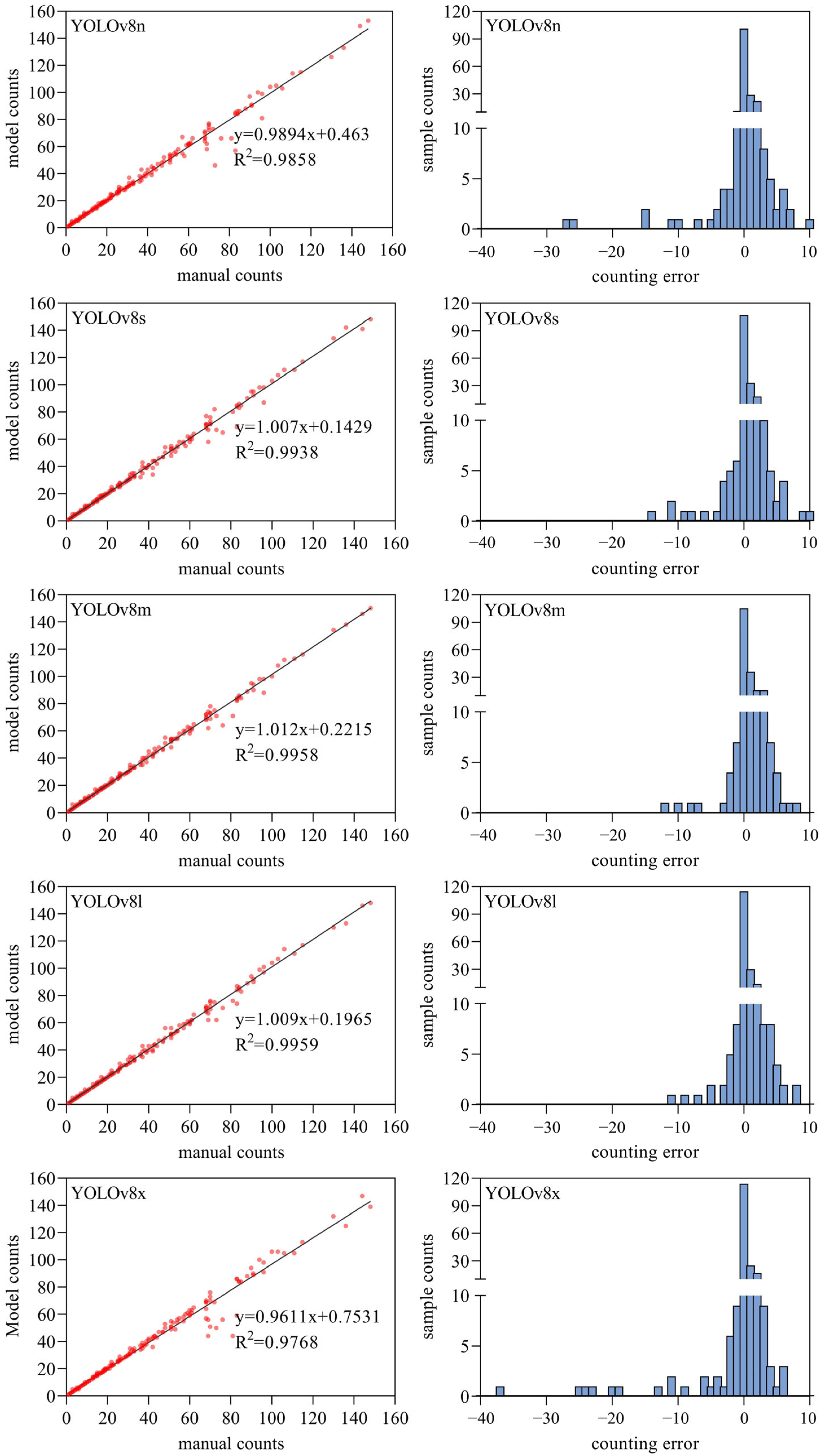
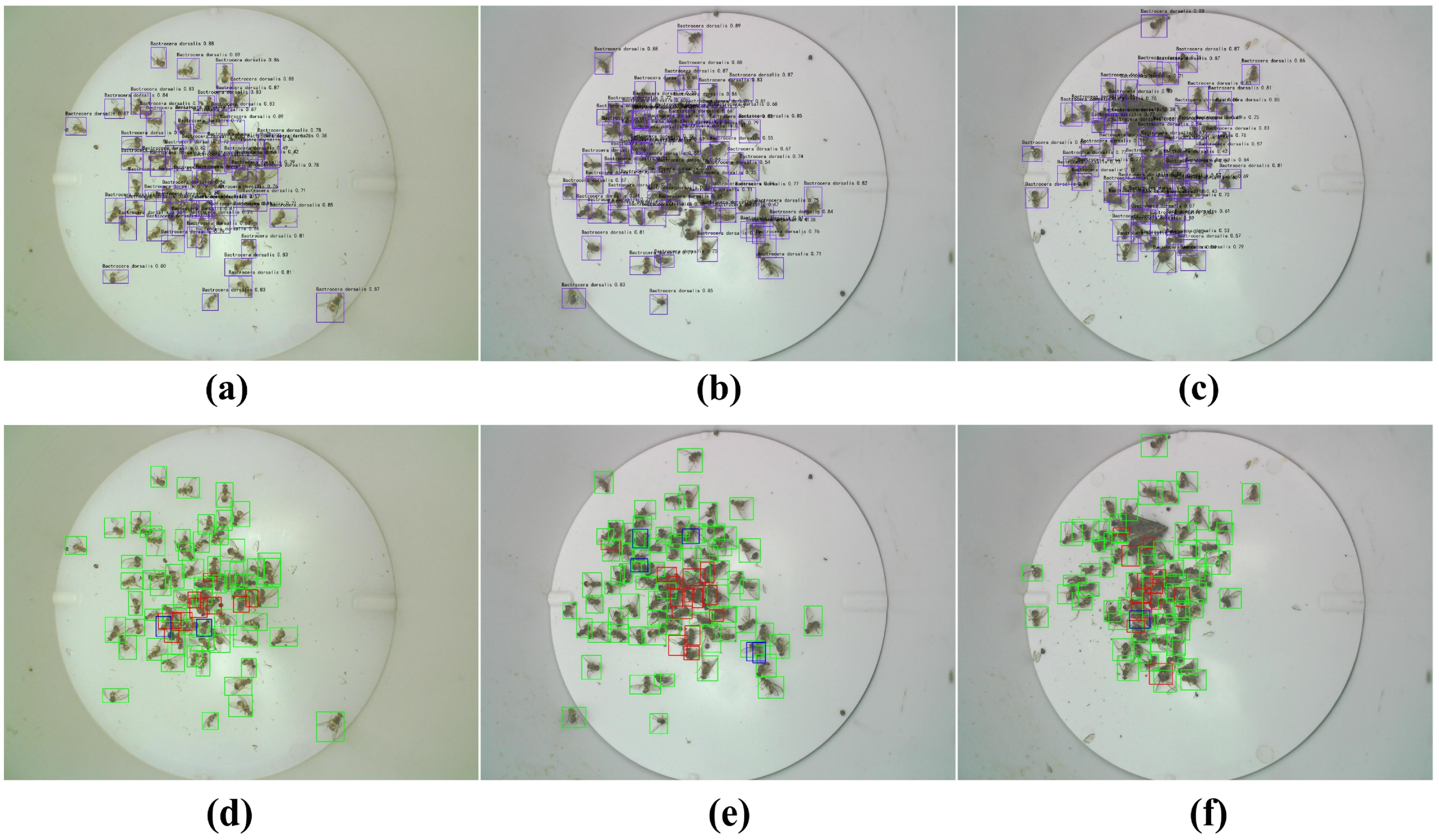
3.2. The Pest Detection Results Based on YOLOv8 Models
3.3. Effect of B. dorsalis Densities on YOLOv8l Model Detection Performance
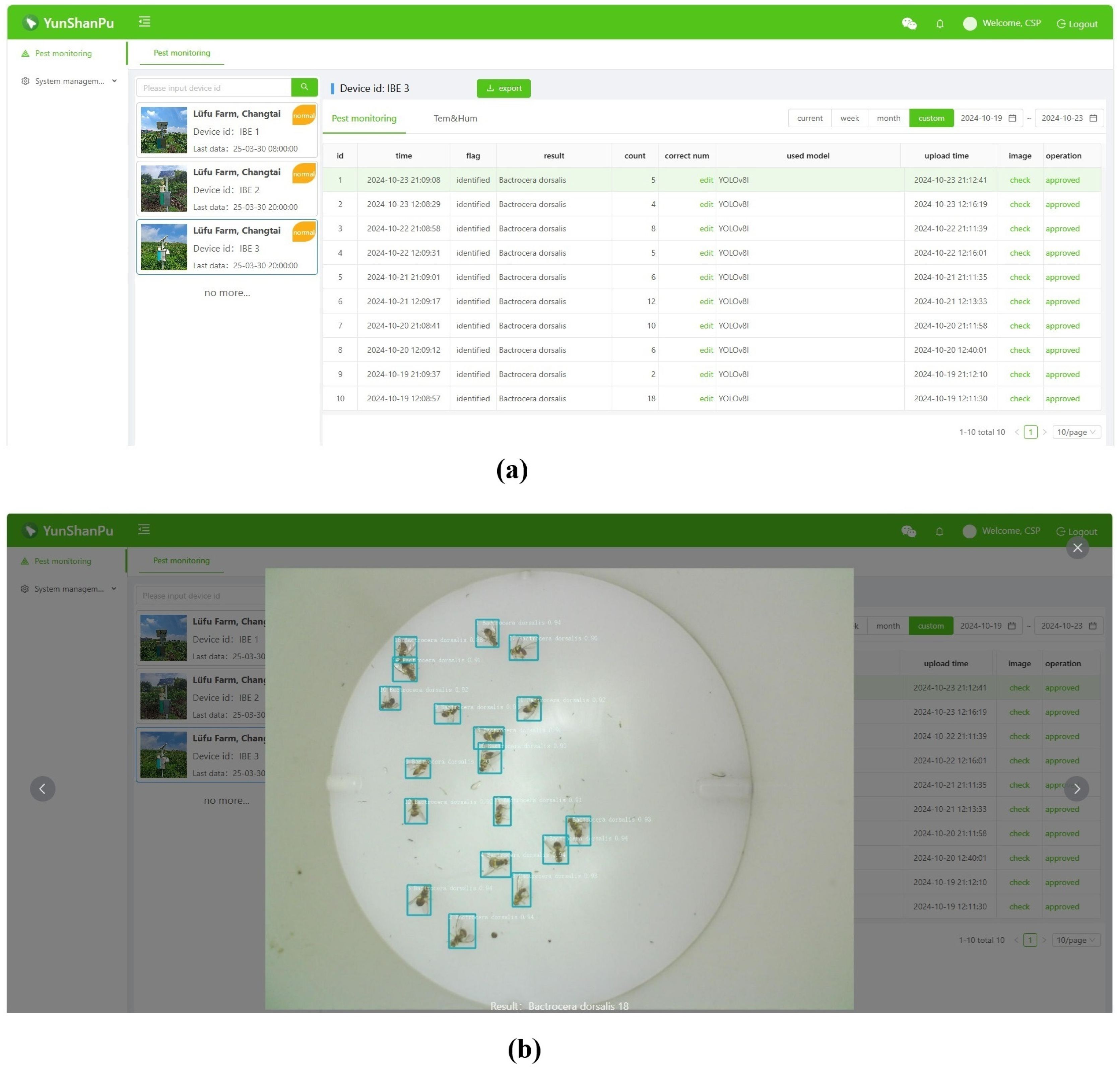
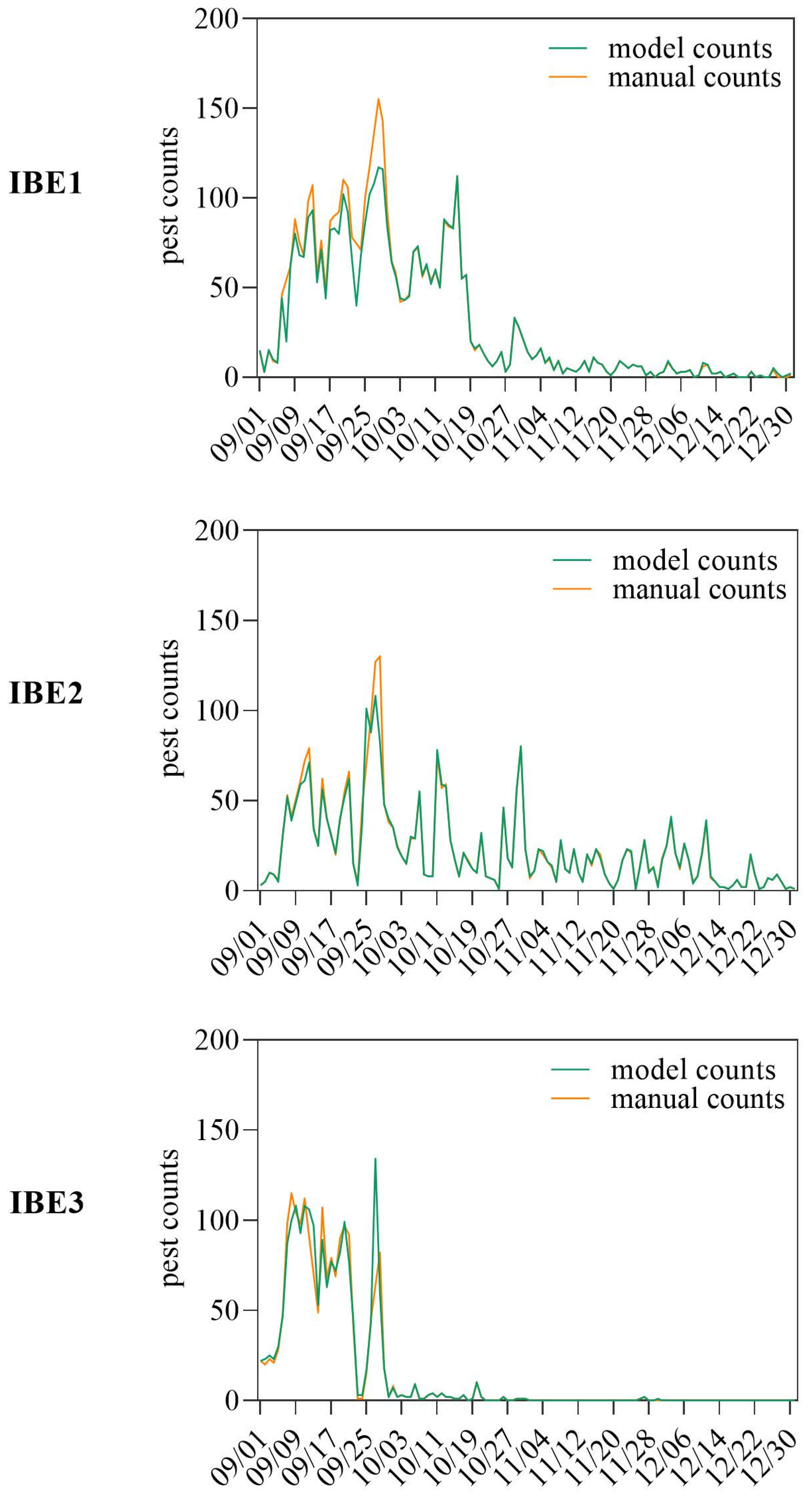
3.4. Pest Online Remote Monitoring
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaleel, W.; Tao, X.; Wang, D.; Lu, L.; He, Y. Using two-sex life table traits to assess the fruit preference and fitness of Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 2936–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lello, F.; Dida, M.; Mkiramweni, M.; Matiko, J.; Akol, R.; Nsabagwa, M.; Katumba, A. Fruit fly automatic detection and monitoring techniques: A review. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 5, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffar, S.; Rizvi, S.A.H.; Lu, Y. Understanding the invasion, ecological adaptations, and management strategies of Bactrocera dorsalis in China: A review. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Wee, S.L.; De Faveri, S.; Gagic, V.; Hossain, S.; Cheng, D.F.; Chouangthavy, B.; Han, P.; Jiang, H.B.; Krutmuang, P.; et al. Advancements in integrated pest management strategies for Bactrocera dorsalis in Asia: Current status, insights, and future prospects. Entomol. Gen. 2024, 44, 1091–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Reddy, G.V.P.; Li, Z.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Jiang, F.; Gao, F.; Zhao, Z.H. Global distribution and invasion pattern of oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Appl. Entomol. 2019, 143, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Li, D.D.; Cai, X.Y.; Cheng, D.F.; Lu, Y. Reproductive behavior of fruit flies: Courtship, mating, and oviposition. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.W.; Yuan, G.R.; Lu, X.P.; Jing, T.X.; Zheng, L.S.; Yong, H.X.; Wang, J.J. Two delta class glutathione S-transferases involved in the detoxification of malathion in Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chailleux, A.; Thiao, D.S.; Diop, S.; Bouvery, F.; Ahmad, S.; Caceres-Barrios, C.; Faye, E.; Brévault, T.; Diatta, P. Understanding Bactrocera dorsalis trapping to calibrate area-wide management. J. Appl. Entomol. 2021, 145, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, D.D.; Wan, L.; Hu, Z.Y.; He, T.T.; Wang, J.B.; Deng, S.Z.; Wang, X.S. Assessment of attractancy and safeness of (E)-coniferyl alcohol for management of female adults of oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tian, S.H.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.J.; Wei, D.D. Overexpression of ABCB transporter genes confer multiple insecticide tolerances in Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 197, 105690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.L.; Zhang, S.X.; Guo, P.Y.; Qin, Q.S.; Meng, L.W.; Yuan, G.R.; Wang, J.J. Identification and characterization of UDP-glycosyltransferase genes and the potential role in response to insecticides exposure in Bactrocera dorsalis. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, M.; Bai, W.; Zhang, S.; Meng, L.; Dou, W.; Wang, J.; Yuan, G. Identification, expression profiles and involvement in insecticides tolerance and detoxification of carboxylesterase genes in Bactrocera dorsalis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 193, 105443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.S.; Chuang, C.L.; Lin, T.S.; Chen, C.P.; Zheng, X.Y.; Chen, P.T.; Liao, K.C.; Jiang, J.A. Development of an autonomous early warning system for Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) outbreaks in remote fruit orchards. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2012, 88, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Wang, G.L.; Wang, C.L.; Li, W.J.; Lu, T.; Ge, Y.G.; Xu, C.K.; Zhong, X.; Wang, J.G.; Yang, H.Y. Long-term monitoring of Bactrocera and Zeugodacus spp. (Diptera: Tephritidae) in China and evaluation of different control methods for Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Crop Prot. 2024, 182, 106708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, C.; Xiao, D.; Huang, Q. Automatic monitoring of flying vegetable insect pests using an RGB camera and YOLO-SIP detector. Precis. Agric. 2023, 24, 436–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čirjak, D.; Miklečić, I.; Lemić, D.; Kos, T.; Pajač Živković, I. Automatic pest monitoring systems in apple production under changing climatic conditions. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Qin, Y.; Yin, X.; Dong, X.; Desneux, N.; Zhou, H. Monitoring the methyl eugenol response and non-responsiveness mechanisms in oriental fruit fly Bactrocera dorsalis in China. Insects 2022, 13, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Taylor, G. Automatic moth detection from trap images for pest management. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 123, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukatsu, T.; Watanabe, T.; Hu, H.; Yoichi, H.; Hirafuji, M. Field monitoring support system for the occurrence of Leptocorisa chinensis Dallas (Hemiptera: Alydidae) using synthetic attractants, field servers, and image analysis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2012, 80, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.A.; Tseng, C.L.; Lu, F.M.; Yang, E.C.; Wu, Z.S.; Chen, C.P.; Lin, S.H.; Lin, K.C.; Liao, C.S. A GSM-based remote wireless automatic monitoring system for field information: A case study for ecological monitoring of the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 62, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, S.; Hakim, A.; Siddiqi, A.A.; Owais, M. An image dataset of fruit fly species (Bactrocera zonata and Bactrocera dorsalis) and automated species classification through object detection. Data Brief 2022, 43, 108366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diller, Y.; Shamsian, A.; Shaked, B.; Altman, Y.; Danziger, B.C.; Manrakhan, A.; Serfontein, L.; Bali, E.; Wernicke, M.; Egartner, A.; et al. A real-time remote surveillance system for fruit flies of economic importance: Sensitivity and image analysis. J. Pest Sci. 2023, 96, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilaris, A.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X. Deep learning in agriculture: A survey. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 147, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buslaev, A.; Iglovikov, V.I.; Khvedchenya, E.; Parinov, A.; Druzhinin, M.; Kalinin, A.A. Albumentations: Fast and flexible image augmentations. Information 2020, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.Z.; Chen, S.P.; Chi, M.X.; Wang, R.B.; Huang, T.; Fan, G.C.; Zhao, J.; Weng, Q.Y. An automatic identification system for citrus greening disease (huanglongbing) using a YOLO convolutional neural network. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1002606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea-Wheller, T.A.; Corbett, A.; Osborne, J.L.; Recker, M.; Kennedy, P.J. VespAI: A deep learning-based system for the detection of invasive hornets. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, B.; Li, D.; Zhang, Q.; Desneux, N.; Luo, C.; Hu, Z. Image detection model construction of Apolygus lucorum and Empoasca spp. based on improved YOLOv5. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 2577–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Fu, S.; Rao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ding, M. Insect-YOLO: A new method of crop insect detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 232, 110085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wu, X. AgriPest-YOLO: A rapid light-trap agricultural pest detection method based on deep learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1079384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Chen, H.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, T.; Yang, C.; Su, H.; Chen, H. Pest-YOLO: A model for large-scale multi-class dense and tiny pest detection and counting. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 973985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohan, M.; Sai Ram, T.; Rami Reddy, C.V. A review on YOLOv8 and its advancements. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Intelligence and Cognitive Informatics, Tirunelveli, India, 18–20 November 2024; pp. 529–545. [Google Scholar]
- Hossin, M.; Sulaiman, M.N. A review on evaluation metrics for data classification evaluations. Int. J. Data Min. Knowl. Manag. Process 2015, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Preti, M.; Verheggen, F.; Angeli, S. Insect pest monitoring with camera-equipped traps: Strengths and limitations. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, K.; Zhong, H.; Xie, J.; Xue, X.; Yan, M.; Wu, W.; Li, J. Efficient tobacco pest detection in complex environments using an enhanced YOLOv8 model. Agriculture 2024, 14, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Huang, P.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, B. A lightweight rice pest detection algorithm using improved attention mechanism and YOLOv8. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Yuan, M.; Ren, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Automatic in-trap pest detection using deep learning for pheromone-based Dendroctonus valens monitoring. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 176, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosjen, P.P.J.; Kellenberger, B.; Kooistra, L.; Green, D.R.; Fahrentrapp, J. Deep learning for automated detection of Drosophila suzukii: Potential for UAV-based monitoring. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2994–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Wang, F.; Yang, D.; Lin, S.; Chen, X.; Lan, Y.; Deng, X. Detection method of citrus psyllids with field high-definition camera based on improved cascade region-based convolution neural networks. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 816272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J. A lightweight YOLOv8 based on attention mechanism for mango pest and disease detection. J. Real-Time Image Process 2024, 21, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, T.; Jiang, Y.; Shao, S.; Sun, J.; Shen, C. Repulsion loss: Detecting pedestrians in a crowd. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7774–7783. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, G.; Cui, Y.; Srinivas, A.; Qian, R.; Lin, T.Y.; Cubuk, E.D.; Le, Q.V.; Zoph, B. Simple copy-paste is a strong data augmentation method for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 2918–2928. [Google Scholar]




| Datasets | Number of Images | Number of Labels |
|---|---|---|
| Training set | 682 | 12,472 |
| Validation set | 170 | 3415 |
| Test set | 203 | 7148 |
| Density | Number of Images | Number of Labels | Number of Labels Per Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | 69 | 438 | n < 15 |
| Medium | 66 | 1732 | 15 ≤ n ≤ 40 |
| High | 68 | 4978 | n > 40 |
| Models | P | R | F1 | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 94.68% | 92.21% | 93.43% | 224 |
| YOLOv8s | 95.03% | 93.10% | 94.06% | 215 |
| YOLOv8m | 95.04% | 93.85% | 94.44% | 151 |
| YOLOv8l | 95.17% | 94.15% | 94.66% | 90 |
| YOLOv8x | 94.69% | 92.87% | 93.77% | 61 |
| Density | P | R | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n < 15) | 97.94% | 99.06% | 98.50% |
| Medium (15 ≤ n ≤ 40) | 96.86% | 98.10% | 97.48% |
| High (n > 40) | 94.21% | 92.52% | 93.36% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.-P.; Zhu, S.-L.; Qiu, R.-Z.; Chi, M.-X.; Shi, Y.; Chen, J.-X.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, J. An Automatic System for Remote Monitoring of Bactrocera dorsalis Population. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222391
Chen S-P, Zhu S-L, Qiu R-Z, Chi M-X, Shi Y, Chen J-X, Liang Y, Zhao J. An Automatic System for Remote Monitoring of Bactrocera dorsalis Population. Agriculture. 2025; 15(22):2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222391
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shao-Ping, Shi-Lei Zhu, Rong-Zhou Qiu, Mei-Xiang Chi, Yan Shi, Jia-Xiong Chen, Yong Liang, and Jian Zhao. 2025. "An Automatic System for Remote Monitoring of Bactrocera dorsalis Population" Agriculture 15, no. 22: 2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222391
APA StyleChen, S.-P., Zhu, S.-L., Qiu, R.-Z., Chi, M.-X., Shi, Y., Chen, J.-X., Liang, Y., & Zhao, J. (2025). An Automatic System for Remote Monitoring of Bactrocera dorsalis Population. Agriculture, 15(22), 2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222391






