Metabolic Basis of Breast Muscle Flavor in Houdan Chicken Crossbreeds Revealed by GC/LC-MS Metabolomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Reagents and Materials
2.3. Animals and Tissue Sampling
3. Experimental Methods
3.1. pH Measurement
3.2. Meat Color Measurement
3.3. Drip Loss Measurement
3.4. Shear Force Measurement
3.5. Sensory Evaluation of Breast Muscle Samples
3.6. GC-TOF-MS Metabolomics Processing
3.7. UHPLC-QE-MS Metabolomics Processing
3.8. Data Processing and Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Analysis of Breast Muscle Composition
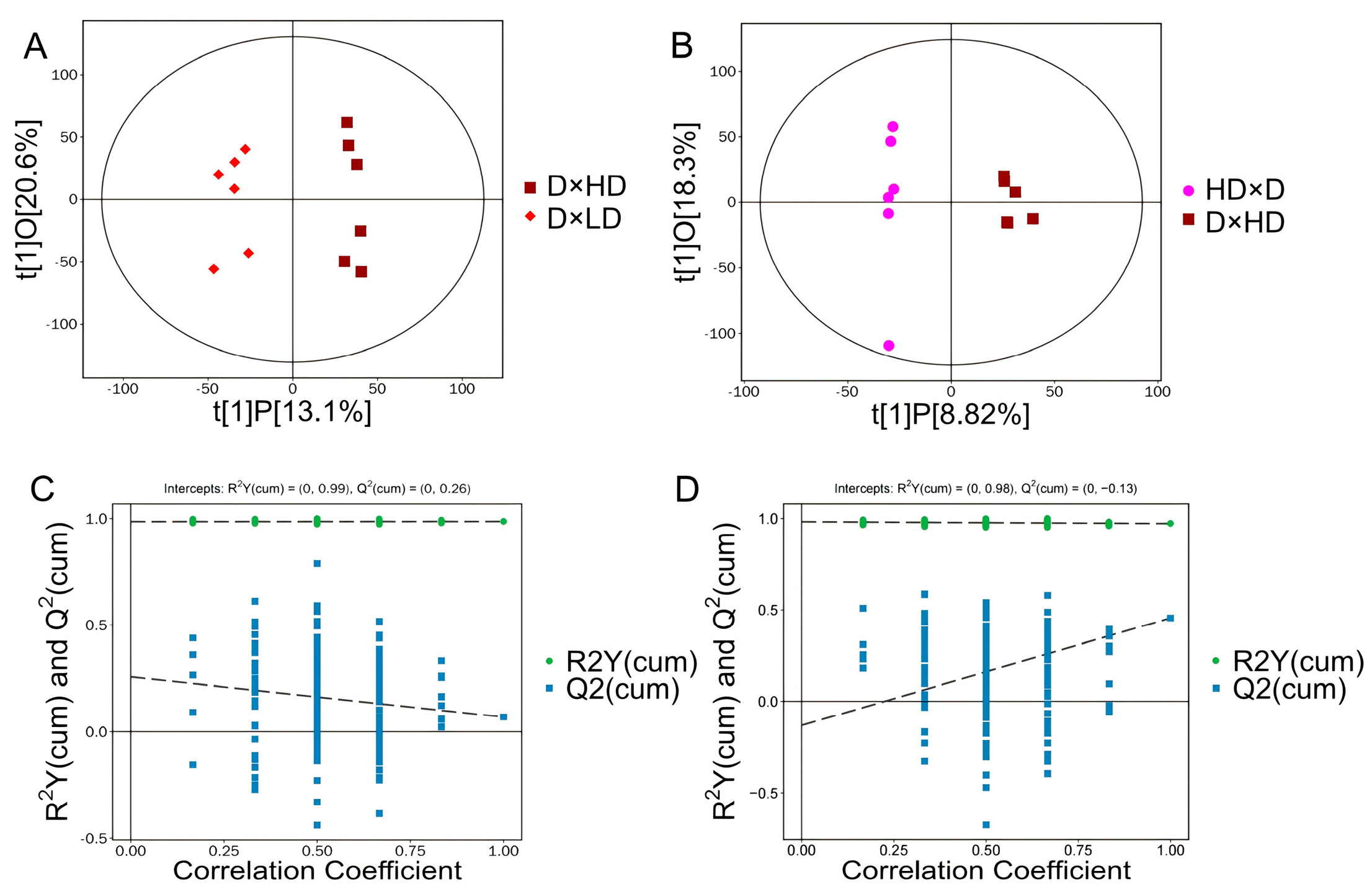
4.2. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
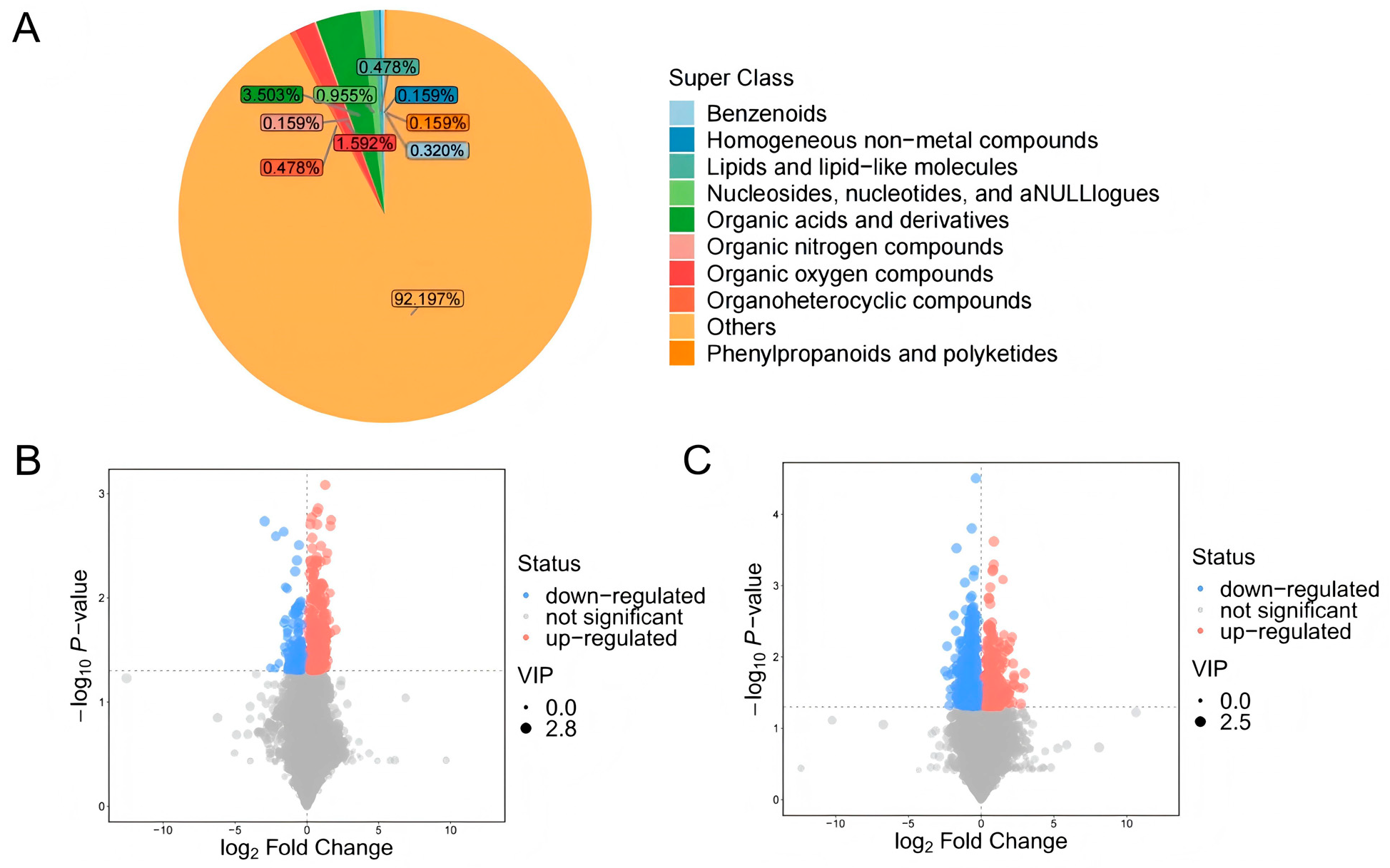
4.3. Screening and Analysis of Differential Metabolites
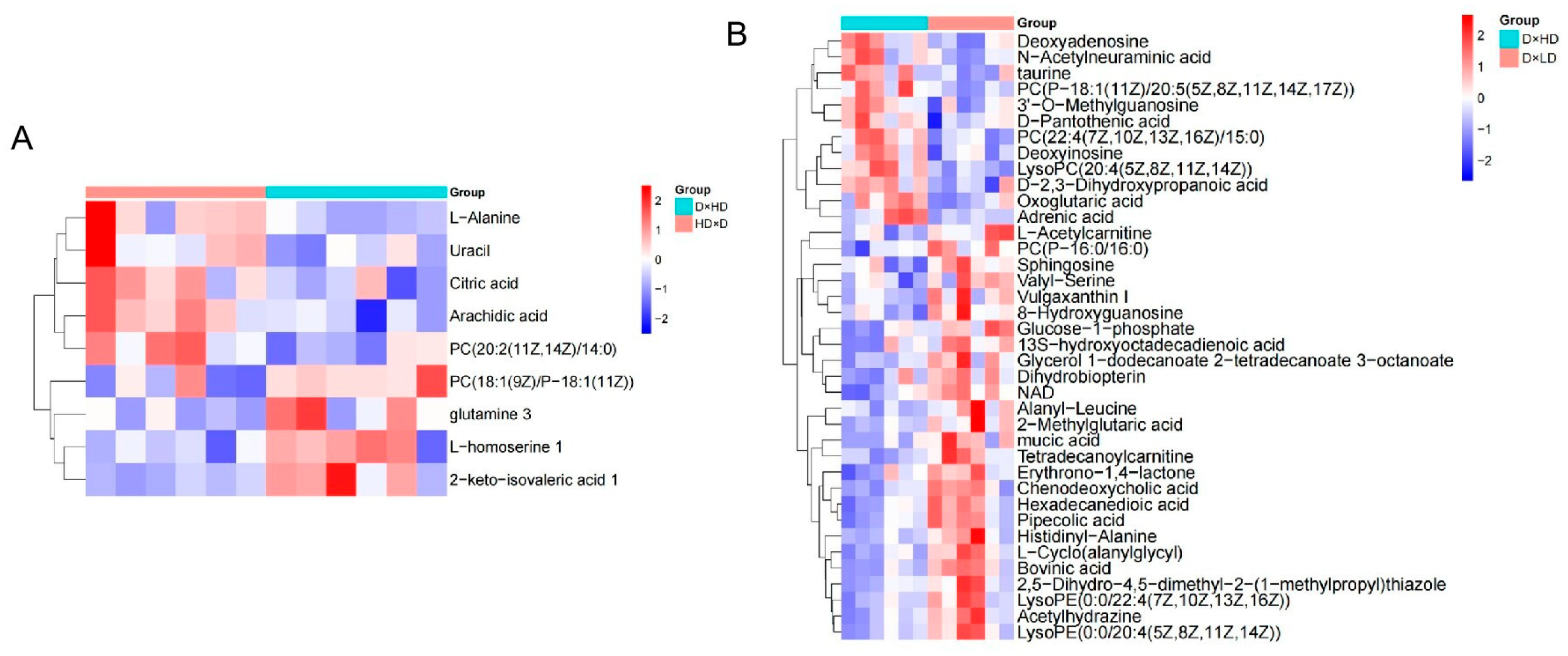
4.4. Hierarchical Clustering Analysis of Differential Metabolites
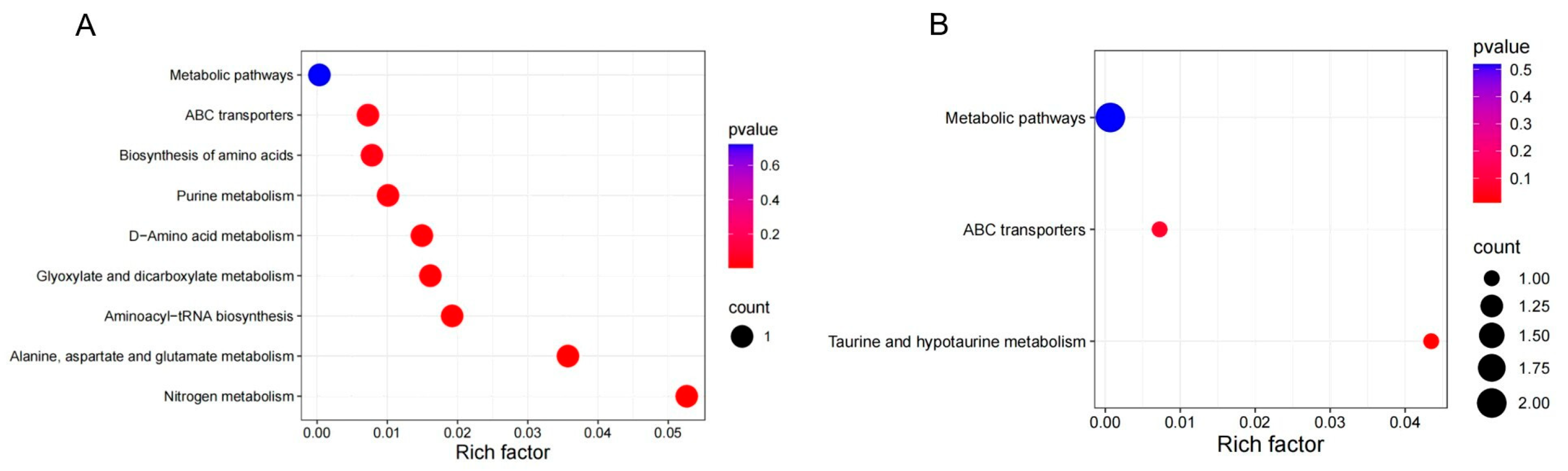
4.5. Differential Metabolite KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
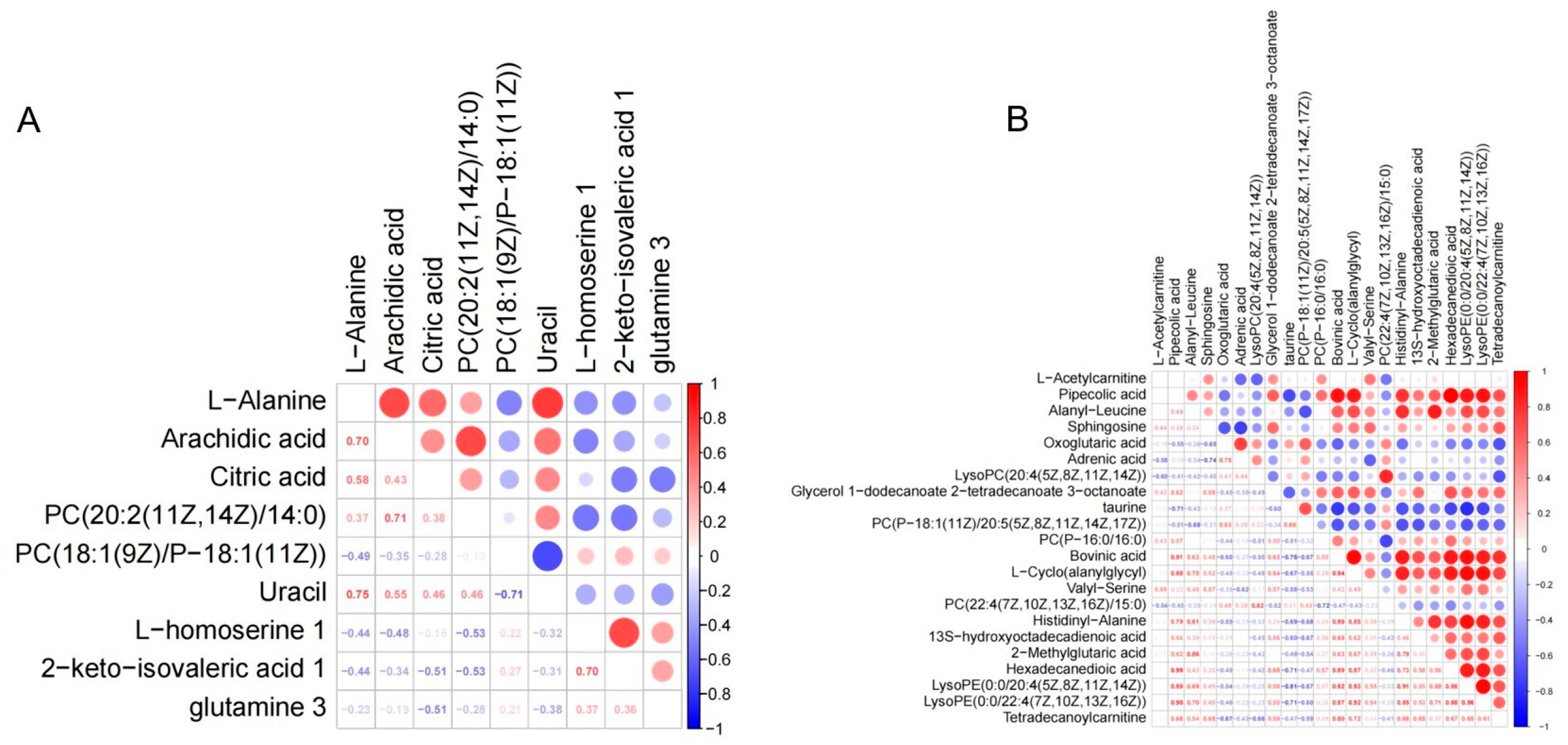
4.6. Analysis of the Correlation of Metabolites with Differences
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations and Nomenclatures
References
- Ueda, S.; Iwamoto, E.; Kato, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Shirai, Y.; Yamanoue, M. Comparative Metabolomics of Japanese Black Cattle Beef and Other Meats Using Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S. Analysis of the Application of Metabolomics in Livestock and Poultry Genetic Breeding. Chin. Livest. Poult. Breed. 2021, 17, 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Marrocco, C.; Zolla, V.; Zolla, L. Meat Quality of the Longissimus Lumborum Muscle of Casertana and Large White Pigs: Metabolomics and Proteomics Intertwined. J. Proteom. 2011, 75, 610–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastrebski, S.F.; Lamont, S.J.; Schmidt, C.J. Chicken Hepatic Response to Chronic Heat Stress Using Integrated Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldansaz, S.A.; Guo, A.C.; Sajed, T.; Steele, M.A.; Plastow, G.S.; Wishart, D.S. Livestock Metabolomics and the Livestock Metabolome: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baira, E.; Dagla, I.; Siapi, E.; Zoumpoulakis, P.; Simitzis, P.; Goliomytis, M.; Deligeorgis, S.G.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Gikas, E. Uhplc–Hrms-Based Tissue Untargeted Metabolomics Study of Naringin and Hesperidin after Dietary Supplementation in Chickens. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, G.J.; Yanes, O.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: The Apogee of the Omics Trilogy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Jia, X.; Tang, X.; Fan, Y.; Lu, J. Comparative Study on the Chicken Quality among Different Local Chicken Breeds. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2023, 51, 80–88. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D. Meat Quality Evaluation of Different Varieties of Quality Broilers. China Poult. 2019, 41, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Harlina, P.W.; Maritha, V.; Musfiroh, I.; Huda, S.; Sukri, N.; Muchtaridi, M. Possibilities of Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (Lc-Ms)-Based Metabolomics and Lipidomics in the Authentication of Meat Products: A Mini Review. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2022, 42, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Ding, H.; Wu, P.; Zhang, G.; Xie, K.; Dai, G.; Wang, J. Uhplc–Ms/Ms-Based Nontargeted Metabolomics Analysis Reveals Biomarkers Related to the Freshness of Chilled Chicken. Foods 2020, 9, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Qian, K.; Shao, H.; Yao, Y.; Nair, V.; Ye, J.; Qin, A. Metabolomics Analysis of Cef Cells Infected with Avian Leukosis Virus Subgroup J Based on Uhplc-Qe-Ms. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and Quantifying Mammalian Transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with Deseq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylesjö, M.; Eriksson, D.; Kusano, M.; Moritz, T.; Trygg, J. Data Integration in Plant Biology: The O2pls Method for Combined Modeling of Transcript and Metabolite Data. Plant J. 2007, 52, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, G.M.; Johansson, E.; Kleemann, R.; Verheij, E.R.; Wheelock, Å.M.; Goto, S.; Trygg, J.; Wheelock, C.E. Building Multivariate Systems Biology Models. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 7064–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albergamo, A.; Vadalà, R.; Metro, D.; Giuffrida, D.; Monaco, F.; Pergolizzi, S.; Leonardi, M.; Bartolomeo, G.; Petracci, M.; Cicero, N. Effect of Dietary Enrichment with Flaxseed, Vitamin E and Selenium, and of Market Class on the Broiler Breast Meat—Part 2: Technological and Sensorial Traits. Foods 2022, 11, 2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, C.Y.; Feng, Y.C.; Sheng, Y.N.; Fu, T.X.; Zhang, Y.W.; Jiang, Y.J.; Yu, M.; Zhang, L.Y. Analysis of Metabolites in Rice Produced in Different Regions by Gc-Ms-Based Metabonomics. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 206–213. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, R.A.; Souza, E.; Avendano, S. Characterising the Influence of Genetics on Breast Muscle Myopathies in Broiler Chickens. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Mitchell, A.; McMurtry, J.; Ashwell, C.; Lamont, S.J. Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Gene Polymorphism Associations with Growth, Body Composition, Skeleton Integrity, and Metabolic Traits in Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2005, 84, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, K.; Allymehr, M.; Talebi, A.; Tukmechi, A. A Comparative Study on the Expression of Myogenic Genes, and Their Effects on Performance and Meat Quality in Broiler Chicken Strains. Vet. Res. Forum 2024, 15, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nattrass, G.S.; Quigley, S.P.; Gardner, G.E.; Bawden, C.S.; McLaughlan, C.J.; Hegarty, R.S.; Greenwood, P.L. Genotypic and Nutritional Regulation of Gene Expression in Two Sheep Hindlimb Muscles with Distinct Myofibre and Metabolic Characteristics. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2006, 57, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, H.; Tian, Y.; Li, J.; Scheben, A.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, L.; Fan, X. The Chicken Pan-Genome Reveals Gene Content Variation and a Promoter Region Deletion in Igf2bp1 Affecting Body Size. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5066–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, A.H.; Ding, J.; Ali, M.; Leng, D.; Mukhtar, N.; Ali, A.; Feng, C. Decoding Chicken Growth Regulation through Multi-Omics Insights and Emerging Genetic Tools for Growth Optimization. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 105542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehfeldt, C.; Te Pas, M.F.W.; Wimmers, K.; Brameld, J.M.; Nissen, P.M.; Berri, C.; Valente, L.M.P.; Power, D.M.; Picard, B.; Stickland, N.C. Advances in Research on the Prenatal Development of Skeletal Muscle in Animals in Relation to the Quality of Muscle-Based Food. Ii–Genetic Factors Related to Animal Performance and Advances in Methodology. Animal 2011, 5, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tian, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.X. The Changes of Metabolites During the Withering Process of White Tea Based on Hilic Lc-Qqq Ms Method. J. Tea Sci. 2020, 40, 238–249. [Google Scholar]
- Kawarasaki, S.; Matsuo, K.; Kuwata, H.; Zhou, L.; Kwon, J.; Ni, Z.; Takahashi, H.; Nomura, W.; Kenmotsu, H.; Inoue, K. Screening of Flavor Compounds Using Ucp1-Luciferase Reporter Beige Adipocytes Identified 5-Methylquinoxaline as a Novel Ucp1-Inducing Compound. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2022, 86, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoen, J.R.; Vollebregt, H.M.; Van Der Sman, R.G. Prediction of the Time Evolution of Ph in Meat. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2363–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.Y.; Al-Beitawi, N.A.; Rjoup, M.M.S.; Qudsieh, R.I.; Ishmais, M.A.A. Growth Performance, Carcass and Meat Quality Characteristics of Different Commercial Crosses of Broiler Strains of Chicken. J. Poult. Sci. 2010, 47, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Xiao, Z.; Ge, C.; Wu, Y. Application and Research Progress of Proteomics in Chicken Meat Quality and Identification: A Review. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z. Study on Changes of Flavor Compounds of Chinese Local Chicken with Different Age and Breed Based on Metabolomic; Nanjing Agricultural University: Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mottram, D.S. Flavour Formation in Meat and Meat Products: A Review. Food Chem. 1998, 62, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.D.; Enser, M.; Fisher, A.V.; Nute, G.R.; Sheard, P.R.; Richardson, R.I.; Hughes, S.I.; Whittington, F.M. Fat Deposition, Fatty Acid Composition and Meat Quality: A Review. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, I.; Aasen, I.M.; Rustad, T.; Eikevik, T.M. Manufacture of Dry-Cured Ham: A Review. Part 1. Biochemical Changes During the Technological Process. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 241, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Xiao, Q.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Sun, B.; Du, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T. Aroma Compounds in Chicken Broths of Beijing Youji and Commercial Broilers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10242–10251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrizo, D.; Chevallier, O.P.; Woodside, J.V.; Brennan, S.F.; Cantwell, M.M.; Cuskelly, G.; Elliott, C.T. Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis of Human Serum Samples Associated with Exposure Levels of Persistent Organic Pollutants Indicate Important Perturbations in Sphingolipids and Glycerophospholipids Levels. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrivan, M.; Skrivanova, V.; Marounek, M.; Tumova, E.; Wolf, J. Influence of Dietary Fat Source and Copper Supplementation on Broiler Performance, Fatty Acid Profile of Meat and Depot Fat, and on Cholesterol Content in Meat. Br. Poult. Sci. 2000, 41, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Ma, N.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Zhao, X. Untargeted and Targeted Metabolomics Profiling Reveals the Underlying Pathogenesis and Abnormal Arachidonic Acid Metabolism in Laying Hens with Fatty Liver Hemorrhagic Syndrome. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayabuchi, H.; Morita, R.; Ohta, M.; Nanri, A.; Matsumoto, H.; Fujitani, S.; Yoshida, S.; Ito, S.; Sakima, A.; Takase, H. Validation of Preferred Salt Concentration in Soup Based on a Randomized Blinded Experiment in Multiple Regions in Japan—Influence of Umami (L-Glutamate) on Saltiness and Palatability of Low-Salt Solutions. Hypertens. Res. 2020, 43, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Bai, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Xiao, F.; Guo, H.; Gao, H.; Leng, L.; Li, H. Identification of Biomarkers Associated with the Feed Efficiency by Metabolomics Profiling: Results from the Broiler Lines Divergent for High or Low Abdominal Fat Content. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Han, L.; Li, Z.L. Amino Acids and Volatile Flavor Components in Meat of San Huang Chicken in Stocking Mode. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2012, 33, 172–176. [Google Scholar]
- Walaszek, Z.; Szemraj, J.; Hanausek, M.; Adams, A.K.; Sherman, U. D-Glucaric Acid Content of Various Fruits and Vegetables and Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Dietary D-Glucarate in the Rat. Nutr. Res. 1996, 16, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.H.; He, R.H.; Huang, L.R.; Ma, H.L. Effects of Taurine on the Nutrition and Physiological Function of Animals. Anim. Breed. Feed 2023, 22, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.K.; Singh, A.K.; Wang, J.; Applegate, T. Functional Role of Branched Chain Amino Acids in Poultry: A Review. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, S.; Wang, K.; Zi, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, G.; Kang, J.; Li, Z.; Dou, T.; Ge, C. Physicochemical, Nutritional Properties and Metabolomics Analysis Fat Deposition Mechanism of Chahua Chicken No. 2 and Yao Chicken. Genes 2022, 13, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, M.; Okiyama, A.; Ueda, Y. Taste Enhancements between Various Amino Acids and Imp. Chem. Senses 2002, 27, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchiba-Manabe, M.; Matoba, T.; Hasegawa, K. Sensory Changes in Umami Taste of Inosine 5′-Monophosphate Solution after Heating. J. Food Sci. 1991, 56, 1429–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Barbagallo, M.; Muñoz-Garcia, M.; Godos, J.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A. Dietary Patterns and Cognitive Decline: Key Features for Prevention. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2428–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, M.; Rutkowski, B.; Dębska-Ślizień, A. Vitamins and Microelement Bioavailability in Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Effects of Citric Acid on Growth, Immune, Digestive Tract and Blood Indexes in Broilers; Inner Mongolia Agricultural University: Hohhot, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Glucose-1-Phosphate Production from Starch by Recombinant Glucan Phosphorylase; Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dashdorj, D.; Amna, T.; Hwang, I. Influence of Specific Taste-Active Components on Meat Flavor as Affected by Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors: An Overview. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 241, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Diet Composition | Nutrient Contents | 520 Content (%) | 511 Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | Water | ≤14.0 | ≤14.0 |
| Soybean meal | Crude protein | ≥21.0 | ≥19.0 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | Calcium | 0.60–1.20 | 0.60–1.20 |
| Limestone | Total phosphorus | ≥0.50 | ≥0.40 |
| NaCl | NaCl | 0.20–0.80 | 0.20–0.80 |
| Minerals and their chelating agents | Coarse fiber | ≤6.0 | ≤6.0 |
| Vitamin | Crude ash | ≤8.0 | ≤8.0 |
| Vitamer | Methionine + Cystine | ≥0.82 | ≥0.71 |
| Assembly | D×LD | D×HD | HD×D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | ♂ | ♀ | ♂ | ♀ | ♂ | ♀ |
| Drip loss (%) | 0.96 ± 0.23 | 1.42 ± 1.09 | 0.82 ± 0.33 | 1.44 ± 0.18 | 0.86 ± 0.12 | 1.15 ± 1.04 |
| Shearing force (N) | 26.32 ± 12.55 | 13.34 ± 5.60 | 20.71 ± 7.49 | 16.66 ± 13.45 | 29.99 ± 8.80 | 22.93 ± 10.89 |
| pH45 | 6.18 ± 0.23 | 6.13 ± 0.44 | 6.14 ± 0.34 | 6.16 ± 0.26 | 6.06 ± 0.19 | 6.03 ± 0.19 |
| pH24 | 5.87 ± 0.09 | 5.67 ± 0.06 | 5.83 ± 0.20 | 5.86 ± 0.07 | 5.85 ± 0.11 | 5.69 ± 0.09 |
| L* | 47.95 ± 3.61 | 51.76 ± 6.17 | 48.61 ± 4.30 | 56.01 ± 4.94 | 51.12 ± 3.82 | 47.45 ± 7.26 |
| a* | 3.45 ± 0.78 ab | 4.70 ± 1.38 ab | 2.95 ± 0.80 b | 3.30 ± 1.06 ab | 7.01 ± 4.45 a | 3.18 ± 0.60 ab |
| b* | 3.88 ± 0.94 | 6.32 ± 4.18 | 3.15 ± 1.73 | 6.48 ± 1.96 | 6.55 ± 2.97 | 4.19 ± 0.95 |
| color | 8.05 ± 1.07 | 8.24 ± 1.09 | 7.95 ± 1.02 | 8.36 ± 1.04 | 8.14 ± 1.01 | 8.19 ± 1.21 |
| aroma | 7.64 ± 1.13 | 8.02 ± 1.08 | 8.12 ± 0.89 | 8.29 ± 0.78 | 7.88 ± 1.22 | 8.05 ± 0.97 |
| flavor | 7.33 ± 1.23 | 7.86 ± 1.29 | 7.71 ± 0.85 | 7.76 ± 0.94 | 7.79 ± 1.33 | 7.61 ± 1.31 |
| Taste evaluated value | 7.67 ± 1.16 b | 7.93 ± 0.92 ab | 7.94 ± 1.19 ab | 8.04 ± 1.15 ab | 7.95 ± 1.18 ab | 8.13 ± 0.95 a |
| Metabolite | VIP | p-Value | MZ | RT | Fold Change | Analysis Mode | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/14:0) | 2.10 | 0.02 | 759.63 | 204.02 | 1.18 | POS | up |
| L-Alanine | 2.18 | 0.05 | 90.06 | 52.74 | 1.25 | POS | up |
| Arachidic acid | 2.38 | 0.01 | 170.12 | 617.23 | 1.34 | ENG | up |
| Citric acid | 2.29 | 0.02 | 772.58 | 169.31 | 1.36 | NEG | up |
| Uracil | 1.93 | 0.04 | 104.07 | 398.00 | 1.43 | NEG | up |
| Glutamine 3 | 1.43 | 0.04 | 71.00 | 832.99 | 0.26 | POS | down |
| 2-keto-isovaleric acid 1 | 2.54 | 0.02 | 89.00 | 491.52 | 0.40 | POS | down |
| L-homoserine 1 | 1.72 | 0.04 | 218.00 | 764.77 | 0.66 | POS | down |
| PC(18:1(9Z)/P-18:1(11Z)) | 2.01 | 0.04 | 258.59 | 333.11 | 0.77 | POS | down |
| Metabolite | VIP | p-Value | MZ | RT | Fold Change | Analysis Mode | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC(P-18:1(11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z) | 1.77 | 0.02 | 222.10 | 145.73 | 1.59 | POS | up |
| Deoxyinosine | 1.77 | 0.02 | 880.59 | 210.00 | 1.75 | NEG | up |
| N-Acetylneuraminic acid | 1.48 | 0.04 | 310.09 | 465.94 | 1.76 | NEG | up |
| PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/15:0) | 2.06 | <0.01 | 863.56 | 210.02 | 1.76 | POS | up |
| Adrenic acid | 1.89 | 0.04 | 621.30 | 252.15 | 2.27 | NEG | up |
| Mucic acid | 1.38 | 0.02 | 335.00 | 1160.01 | 0.23 | NEG | down |
| Glucose-1-phosphate | 1.38 | 0.03 | 217.00 | 988.15 | 0.31 | NEG | down |
| 2,5-Dihydro-4,5-dimethyl-2-(1-methylpropyl)thiazole | 1.73 | 0.04 | 210.60 | 530.29 | 0.34 | POS | down |
| 13S-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid | 1.41 | 0.04 | 276.05 | 467.10 | 0.36 | NEG | down |
| Sphingosine | 1.52 | 0.03 | 560.08 | 415.00 | 0.47 | POS | down |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, Y.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, C.; Xie, W.; Shi, J.; Jia, X.; Wang, S.; Ma, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, D.; et al. Metabolic Basis of Breast Muscle Flavor in Houdan Chicken Crossbreeds Revealed by GC/LC-MS Metabolomics. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2360. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222360
Lei Y, Xiao C, Zhang C, Xie W, Shi J, Jia X, Wang S, Ma Y, Cai Z, Li D, et al. Metabolic Basis of Breast Muscle Flavor in Houdan Chicken Crossbreeds Revealed by GC/LC-MS Metabolomics. Agriculture. 2025; 15(22):2360. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222360
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Yanru, Chengpeng Xiao, Chenxi Zhang, Wanying Xie, Junlai Shi, Xintao Jia, Shu Wang, Yulong Ma, Zhao Cai, Donghua Li, and et al. 2025. "Metabolic Basis of Breast Muscle Flavor in Houdan Chicken Crossbreeds Revealed by GC/LC-MS Metabolomics" Agriculture 15, no. 22: 2360. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222360
APA StyleLei, Y., Xiao, C., Zhang, C., Xie, W., Shi, J., Jia, X., Wang, S., Ma, Y., Cai, Z., Li, D., Jiang, R., Sun, G., Kang, X., & Li, W. (2025). Metabolic Basis of Breast Muscle Flavor in Houdan Chicken Crossbreeds Revealed by GC/LC-MS Metabolomics. Agriculture, 15(22), 2360. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222360






