Characteristics of the Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanisms of Soil Organic Matter in the Songnen Plain in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
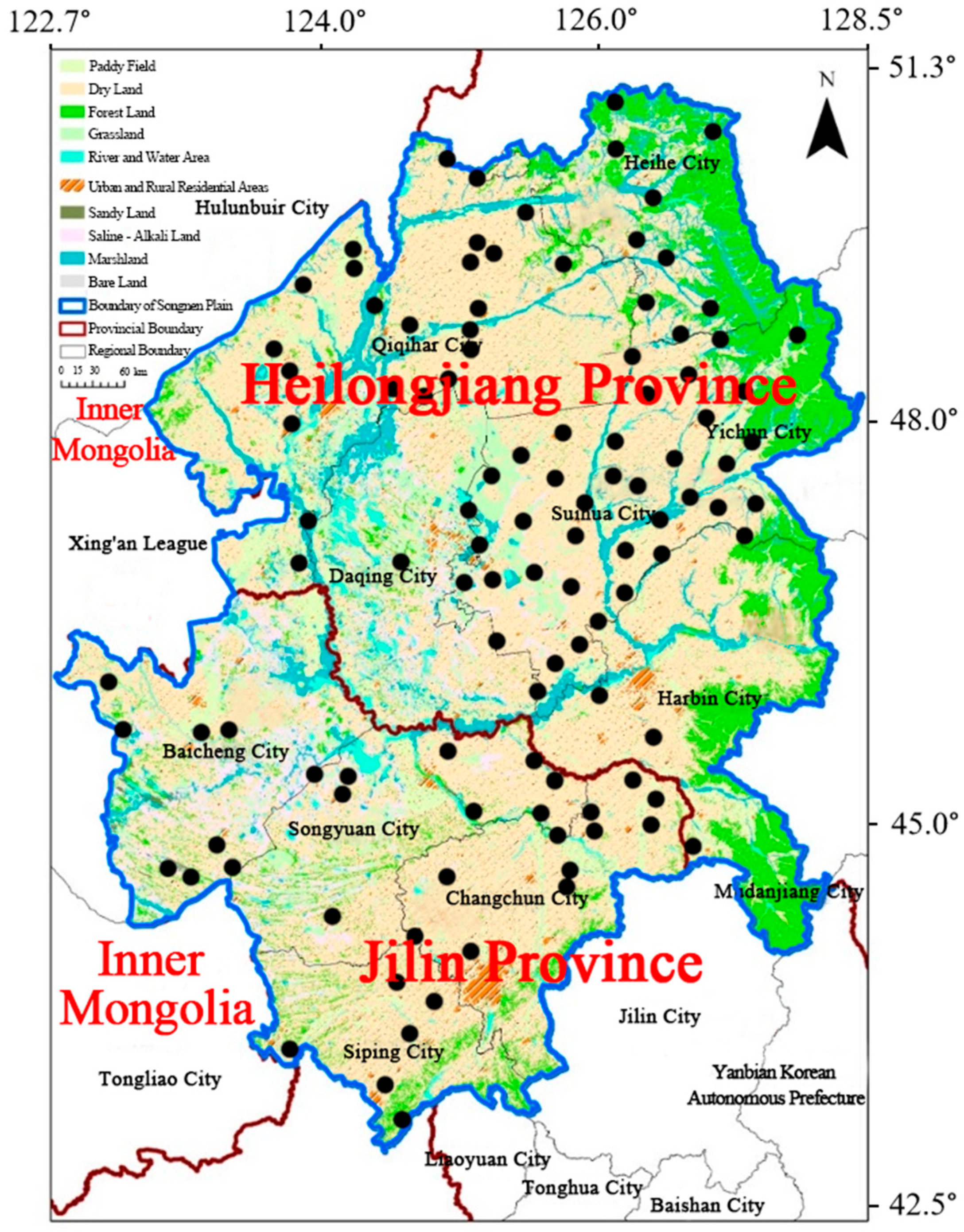
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Samples
2.3. Soil Property Measurement
2.4. Data Source
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
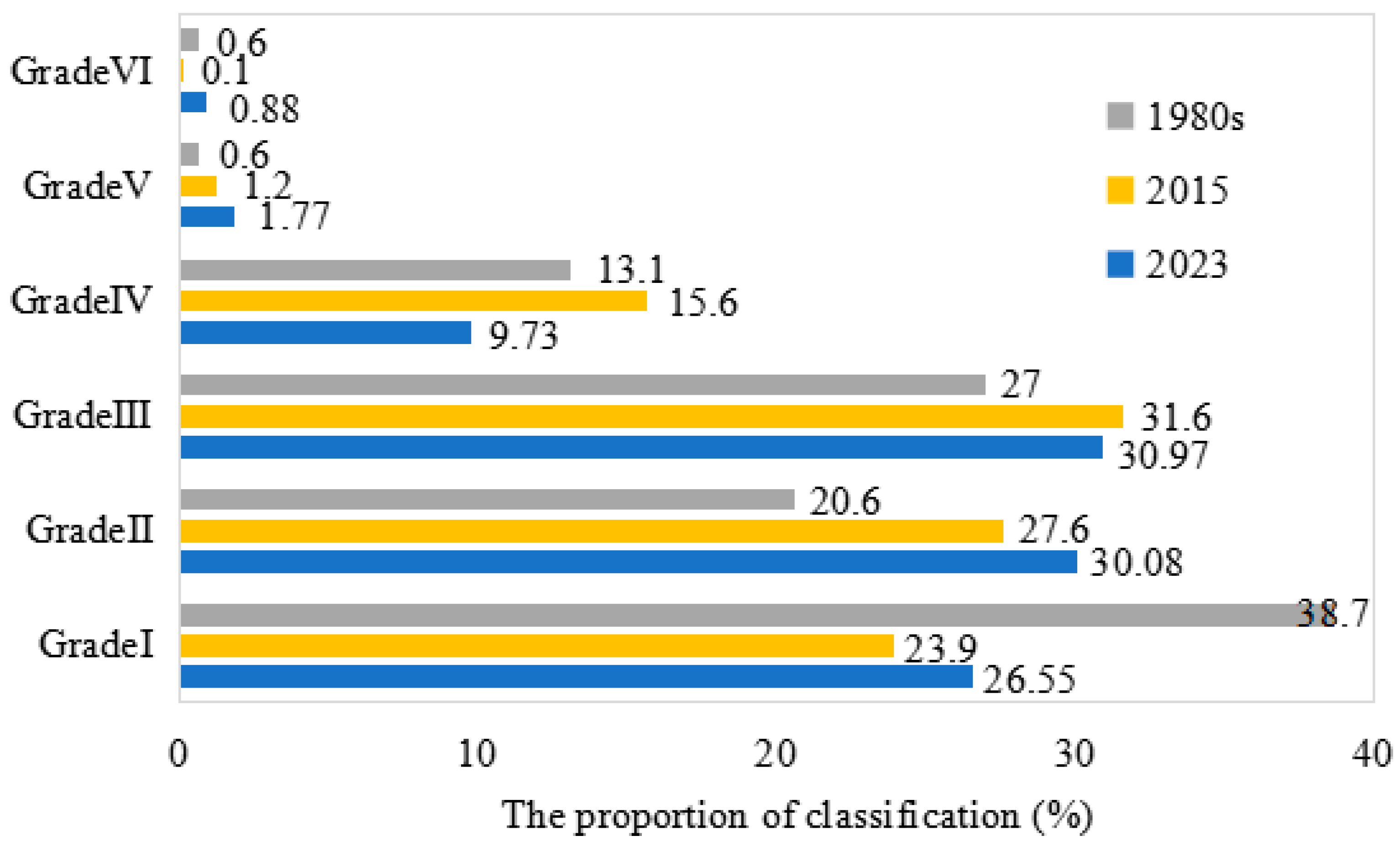
3.1. Temporal Variation Characteristics of SOM Content in the Arable Layer of the Songnen Plain Soil
3.2. Characteristics of Changes in SOM Content in the Songnen Plain
3.2.1. Horizontal Spatial Distribution Pattern
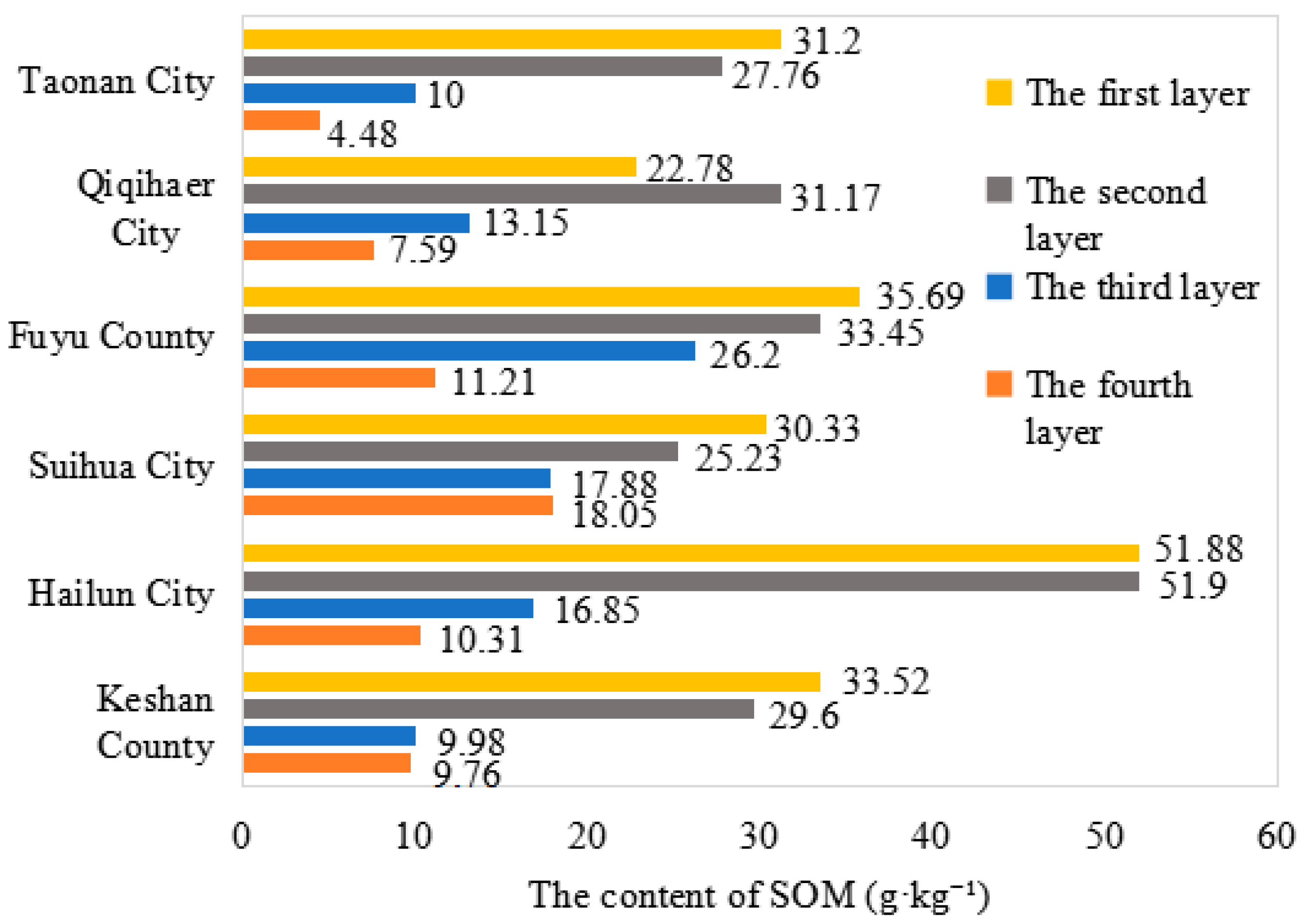
3.2.2. Vertical Spatial Distribution Pattern
3.3. Structural Equation Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Color Response Mechanism
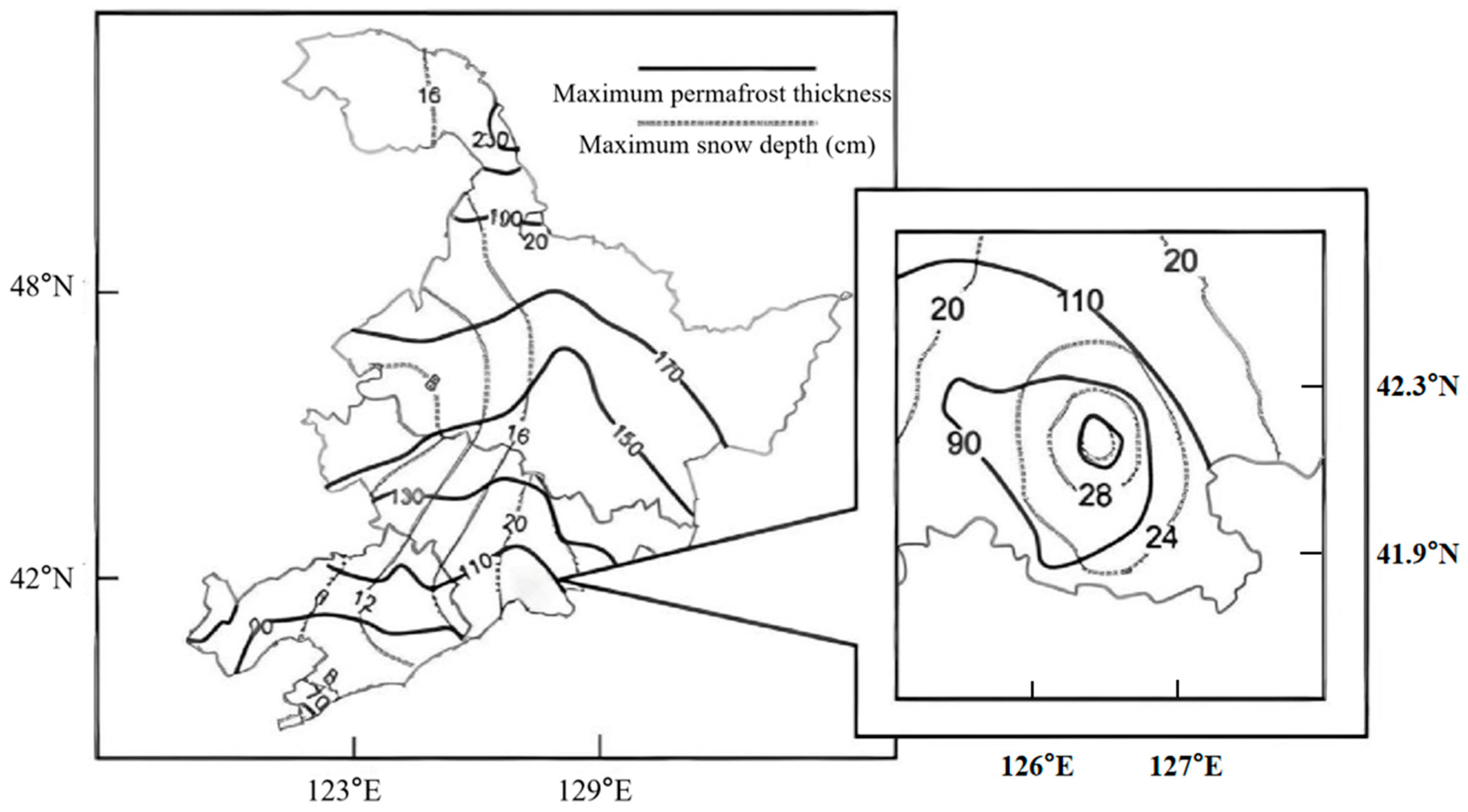
4.2. Analysis of Soil Freeze–Thaw Mechanisms
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Kooch, Y. Remote Estimation of Soil Organic Carbon Under Different Land Use Types in Agroecosystems of Eastern China. J. Catena 2023, 231, 107369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.J.; Song, C.W. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Nutrients in Typical Black Soil Area of the Songnen Plain. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 16, 174–177. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.P.; Zhao, X.; Sun, J.J. Spatiotemporal Changes of Soil Organic Matter in the Songnen and Sanjiang Plains of Heilongjiang Province Over 40 Years. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 48, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Chantigny, M.H.; Harrison-Kirk, T.; Curtin, D.; Beare, M. Temperature and Duration of Extraction Affect the Biochemical Composition of Soil Water-Extractable Organic Matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.W.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhou, Y.N.; Zhang, M.N.; Liu, H.J.; Yang, H.X.; Zeng, L.T.; Sun, X.L. Predicting Spatial–Temporal Soil Organic Matter Dynamics in a Mollisols Region of the Northern Songnen Plain, China, During 2009–2018 Using a Spectral-Temporal Feature Set. Geoderma 2025, 461, 117461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.A.; Bryant, R.B.; De Gloria, S.D.; Post, C.J.; Vassenev, I.I. Modeling Soil Organic Matter Dynamics after Conversion of Native Grassland to Long-Term Continuous Fallow Using the CENTURY Model. Ecol. Modell. 2000, 132, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lü, J.S.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ren, C. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Soil Organic Matter and its Influencing Factors in the Black Soil Region of the Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Catena 2025, 244, 108–119. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Zang, S.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L.; Yan, B. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Organic Carbon and Evaluation of Carbon Sequestration Potential in the Agricultural Topsoil of the Songnen Plain. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 7068–7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.H.; Sun, J.G.; Chang, K.; Xu, Y.D.; Wang, J.K. Spatial-Temporal Variation of Soil Organic Matter Content and Its Influencing Factors in the Black Soil Area of the Songnen Plain. J. Agric. Res. Environ. 2025, 42, 120–128. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Soil Organic Carbon and Its Influencing Factors in Western Songnen Plain. Ph.D. Dissertation, Harbin Normal University, Harbin, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Bao, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Ji, X. Improving Spatial Prediction of Soil Organic Matter in Typical Black Soil Area of Northeast China Using Structural Equation Modeling Integration Framework. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 236, 110404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, M. Construction and Optimization of Ecological Security Patterns in the Songnen Plain. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1302896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yang, S.; Dong, H.; Li, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y. Effects of Marsh Wetland Degradation on the Soil Nematode Community Composition and Functions in the Songnen Plain, Northeastern China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 56, e03277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F. Optimal Sowing Date and Yield Effect Evaluation of Spring Maize Adaptation to Climate Change in Songnen Plain. Ph.D. Dissertation, Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, Daqing, China, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.H.; Zhang, Z.B.; Chen, B.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, N.; Qi, H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Gong, X.W.; Xue, X.W.; Islam, M.U. A Six-site Field Study on Assessing the Suitability of Conservation and Conventional Tillage in the Black Soil Region, Northeast China. J. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 248, 106379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Soil Census Office. Soil in Inner Mongolia; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1994; pp. 40–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, D.P.; Luo, C.; Liu, H.J. Enhancing Soil Organic Matter Mapping in Saline-Alkali and Black Soil Areas with Prior Knowledge and Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing. J. Integr. Agric. 2025, 24, 1829–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singbah, P.T.; Huang, J.; Ahmed, I.; Abdelaziz, M.; Tadesse, K.A.; Daba, N.A.; Li, J.; Yan, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, L.; et al. Soil Humus and Aluminum-iron Interactions Enhance Carbon Sequestration and Yield Sustainability after Long-Term Fertilization in Three Different Soils. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 21, 101995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Dai, Y. Analysis of Conservation Practices for Black Soil Based on Organic Matter and Nitrogen Contents in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wang, L. Systematic Identification of Factors Influencing the Spatial Ddistribution of Soil Organic Matter in Croplands Within the Black Soil Region of Northeastern China Across Multiple Scales. J. Catena 2025, 249, 108633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Sha, J.; Liu, C.; Qi, H.; Liu, Z.; Dai, Y. New Discovery of a Promising Cellulose Degrading Bacterium and its Degradation Mechanism. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, E.S.; Alameddine, I.; Qian, S.S. Using Structural Equation Modeling to Better Understand Microcystis Biovolume Dynamics in a Mediterranean Hypereutrophic Reservoir. Ecol. Model. 2020, 435, 109282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.Y.; Sun, H.J.; Xue, J.W.; Liu, M.Y. Soil Quality Assessment and Constraining Factor Analysis in Plantation Forests of North China Plain. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 1, 18–27. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Ji, X.; Wang, F. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Soil Organic Matter and Its Response to Dynamic Factors in the Southern Part of Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 248, 106475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Gong, X.; Yao, C.; Cao, W.; Lian, J. Application of Predictor Variables to Support Regression Kriging for the Spatial Distribution of Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Native Temperate Grasslands. J. Soils Sediment 2023, 23, 700–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidhuner, A.; Hanauer, A.; Krausz, R.; Crittenden, S.J.; Gage, K.; Sadeghpour, A. Tillage Impacts on Soil Aggregation and Aggregate-Associated Carbon and Nitrogen After 49 Years. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 208, 104852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappel, A.; Webb, N.P.; Leys, J.F.; Waters, C.M.; Orgill, S.; Eyres, M.J. Minimising Soil Organic Carbon Erosion by Wind is Critical for Land Degradation Neutrality. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 93, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinsch, T.; Loges, R.; Kluß, C.; Taube, F. Effect of Grassland Ploughing and Reseeding on CO2 Emissions and Soil Carbon Stocks. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 264, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhao, M.; Ma, M.; Dong, T. Research Progress on the Interaction Mechanism and Ecological Function of Soil Microorganisms and Physical-Chemical Properties in Orchards. J. Fruit Sci. 2025, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, B.; Hou, H.; Sui, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cao, M.; Zhan, Z. Climate Change at Orbital Scale in Songnen Plain During the Middle and Late Pleistocene. J. Geol. Bull. China 2025, 44, 392–403. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, E.A.; Janssens, I.A. Temperature Sensitivity of Soil Carbon Decomposition and Feedbacks to Climate Change. J. Nat. 2006, 440, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Hao, M.; Wu, Y. Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Carbon Dynamics in a Rain-Fed Agro-Ecosystem on the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalhais, N.; Forkel, M.; Khomik, M.; Bellarby, J.; Jung, M.; Migliavacca, M.; Reichstein, M. Global Covariation of Carbon Turnover Times With Climate in Terrestrial Ecosystems. Nature 2014, 514, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Feng, Q.; Qin, Y.Y.; Cao, J.J.; Zhua, M.X.; Liu, W.; Deo, R.C.; Zhang, C.Q.; Liu, R.L.; Liao, B.F. The Role of Topography in Shaping the Spatial Patterns of Soil Organic Carbon. Geoderma 2019, 348, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-García, B.; Parras-Alcántara, L.; Brevik, E.C. Impact of Topographic Aspect and Vegetation (Native and Reforested Areas) on Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Budgets in Mediterranean Natural Areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Yan, J.; Chen, X.; Zou, W. Anthropogenic Soil Management Performs an Important Role in Increasing Soil Organic Carbon Content in Northeastern China: A Meta-Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 350, 108481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofiti, N.O.; Zosso, C.U.; Soong, J.L.; Solly, E.F.; Torn, M.S.; Wiesenberg, G.L.; Schmidt, M.W. Warming Promotes Loss of Subsoil Carbon Through Accelerated Degradation of Plant-Derived Organic Matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 156, 108185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.Y.; Zhang, L.; Meng, H.; Zhao, J.X.; Wang, H.; Shang, L.X.; Guo, Q.Y.; Xing, Y.P.; Song, X.L.; Sun, X.Z.; et al. The Different Pathways of Microbial Regulation of Organic Carbon Turnover in the Topsoil and Subsoil of Coastal Saline Soil after Long-Term Stubble Return and Subsoiling. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 197, 105324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.; Kline, R.B.; Kline, R. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2006, 101, 406. [Google Scholar]
- Abu, H.; Nidal, H. Thermal Properties of Soils as Affected By Density and Water Content. Biosyst. Eng. 2003, 86, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Wan, S.; Niu, S. Increased Temperature and Precipitation Interact to Affect Root Production, Mortality, and Turnover in A Temperate Steppe: Implications for Ecosystem C Cycling. J. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 16, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiluweit, M.; Wanzek, T.; Kleber, M. Anaerobic Microsites Have an Unaccounted Role in Soil Carbon Stabilization. J. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melillo, J.M.; Frey, S.D.; DeAngelis, K.M. Long-Term Pattern and Magnitude of Soil Carbon Feedback to the Climate System in A Warming World. J. Sci. 2017, 358, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Zhang, T.; Guo, J. Warming and Nitrogen Deposition Accelerate Soil Phosphorus Cycling in a Temperate Meadow Ecosystem. Soil Res. 2019, 58, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.E.; Giguere, A.T.; Zoebelein, C.M.; Myrold, D.D.; Bottomley, P.J. Modeling of Soil Nitrification Responses to Temperature Reveals Thermodynamic Differences Between Ammonia-Oxidizing Activity of Archaea and Bacteria. ISME J. 2017, 11, 896–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yin, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, P.; Suo, Z. Preparation of Biochar from Straw in Northeast China to Assist in Carbon Neutrality: Data Visualization and Comprehensive Evaluation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Dou, Y.; Liang, C.; Liu, C.; Ao, D.; Yao, H.; Yang, E.; An, S.; Wen, Z. Microbial Necromass in Soil Profiles Increases Less Efficiently Than Root Biomass in Long-Term Fenced Grassland: Effects of Microbial Nitrogen Limitation and Soil Depth. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 956, 177058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.J.; Tariq, A.; Zeng, F.J.; Sardans, J.; Al-Bakre, D.A.; Peñuelas, J. Drying and Rewetting Affect the Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability of Soil Phosphorus in a Hyper-Arid Desert Ecosystem. Pedosphere 2024, 34, 101354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Li, W.; Shao, Z.; Liu, X.; Dai, Y. Enhanced Removal of Tetracycline by Vitamin C-modified Cow Manure Biochar in Water. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.; Vishwakarma, K.; Hossen, M.S.; Kumar, V.; Shackira, A.M.; Puthur, J.T.; Abdi, G.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Potassium in Plants: Growth Regulation, Signaling, and Environmental Stress Tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 172, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, V.S.; Bahadur, I.; Maurya, B.R.; Kumar, A.; Meena, R.K.; Meena, S.K.; Verma, J.P. Potassium-Solubilizing Microorganism in Evergreen Agriculture: An Overview. In Potassium Solubilizing Microorganisms for Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Strawn, D.G. Sorption Mechanisms of Chemicals in Soils. Soil Syst. 2021, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zihms, S.G.; Switzer, C.; Irvine, J.; Karstunen, M. Effects of High Temperature Processes on Physical Properties of Silica Sand. Eng. Geol. 2013, 164, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.F.; Du, Y.; Guan, C.L.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, G.L. Color Variations of the Quaternary Red Clay in Southern China and Its Paleoclimatic Implications. Sediment. Geol. 2014, 303, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, T.; Han, W.; Xu, X.; Yan, X.; Yan, J. The Color Formation of “Lumu Stone” in the Weathering Processes: The Role of Secondary Hematite and Goethite. Minerals 2023, 13, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawire, A.W.; Csorba, Á.; Kovács, E.; Mairura, F.S.; Tóth, J.A.; Michéli, E. Comparing Farmers’ Soil Fertility Knowledge Systems and Scientific Assessment in Upper Eastern Kenya. Geoderma 2021, 396, 115090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Cheng, X.Y.; Hu, X. Soil Organic Matter Content Prediction in Tobacco Fields Based on Hyperspectral Remote Sensing and Generative Adversarial Network Data Augmentation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 229, 108339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, R.; Zhou, X.; Yang, S.; Luo, X.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, Z. Effects of Biochar on Soil Quality in a Maize Soybean Rotation on Mollisols. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, P.D.; Ben-Dor, E. Effect of Organic Matter Content on the Spectral Signature of Iron Oxides Across the VIS–NIR Spectral Region in Artificial Mixtures: An Example From a Red Soil From Israel. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, T.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, A.; Li, H. Combined Effect of Freeze–Thaw Cycles and Biochar Addition on Soil Nitrogen Leaching Characteristics in Seasonally Frozen Farmland in Northeast China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parewa, H.P.; Meena, V.S.; Meena, S.K.; Choudhary, A.; Kumar, M. Carbon Management Strategies for Sustainable Food Production Systems. In Agricultural Soil Sustainability and Carbon Management; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 69–98. [Google Scholar]
- Murtaza, G.; Ahmed, Z.; Usman, M.; Rizwan, M.; Iqbal, R.; Ali, B.; Ali, I. Modeling Climate Change Impact Over Soil Productivity and Agriculture. Chall. Solut. Clim. Impact Agric. 2025, 10, 259–281. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.Z.; Zou, W.X. Research Perspectives and Footprint of Utilization and Protection of Black Soil in Northeast China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2021, 58, 1341–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.N.; Song, X.J.; Wu, X.P.; Zheng, F.J.; Li, S.P.; Zhuang, Y.; Man, X.L.; Degré, A. Microbial Regulation of Aggregate Stability and Carbon Sequestration Under Long-Term Conservation Tillage and Nitrogen Application. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 44, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Sui, Y.; Dai, Y. Characteristics of the Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanisms of Soil Organic Matter in the Songnen Plain in China. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202156
Wang Y, Chen Y, Wang X, Zhang B, Sun Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Sui Y, Dai Y. Characteristics of the Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanisms of Soil Organic Matter in the Songnen Plain in China. Agriculture. 2025; 15(20):2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202156
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yao, Yimin Chen, Xinyuan Wang, Baiting Zhang, Yining Sun, Yuhan Zhang, Yuxuan Li, Yueyu Sui, and Yingjie Dai. 2025. "Characteristics of the Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanisms of Soil Organic Matter in the Songnen Plain in China" Agriculture 15, no. 20: 2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202156
APA StyleWang, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, B., Sun, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Sui, Y., & Dai, Y. (2025). Characteristics of the Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanisms of Soil Organic Matter in the Songnen Plain in China. Agriculture, 15(20), 2156. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202156




