Insecticide Resistance and Plant Virus Status of Bemisia tabaci on Soybean in Suzhou
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Populations
2.2. Insecticides
2.3. Adult Bioassays with the Fourteen Pesticides
2.4. Identification of the Biotypes and Viruses of B. tabaci
2.4.1. Total DNA Extraction from B. tabaci
2.4.2. Identification of B. tabaci Biotypes
2.4.3. Detection of B. tabaci Viruses
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
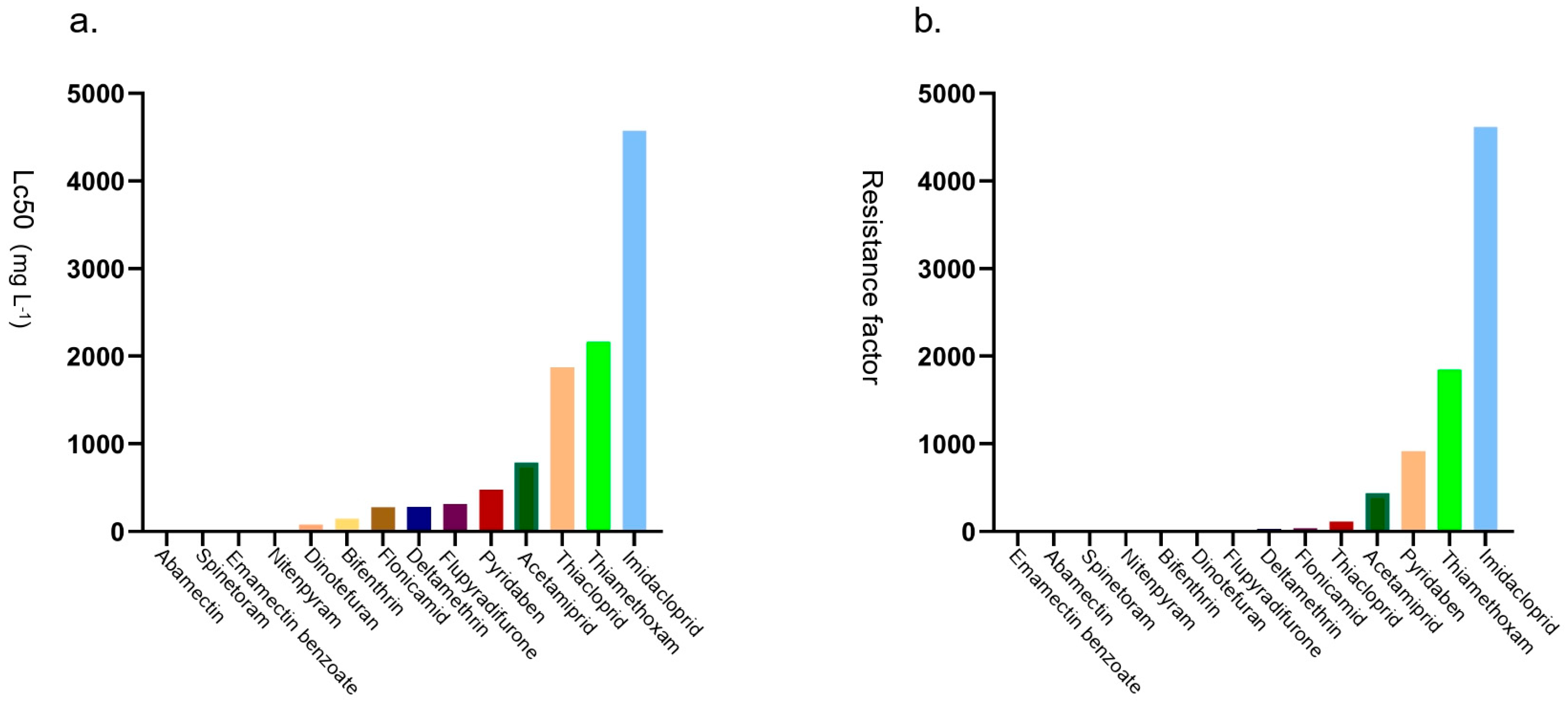
3.1. Resistance of Adult B. tabaci to Fourteen Pesticides
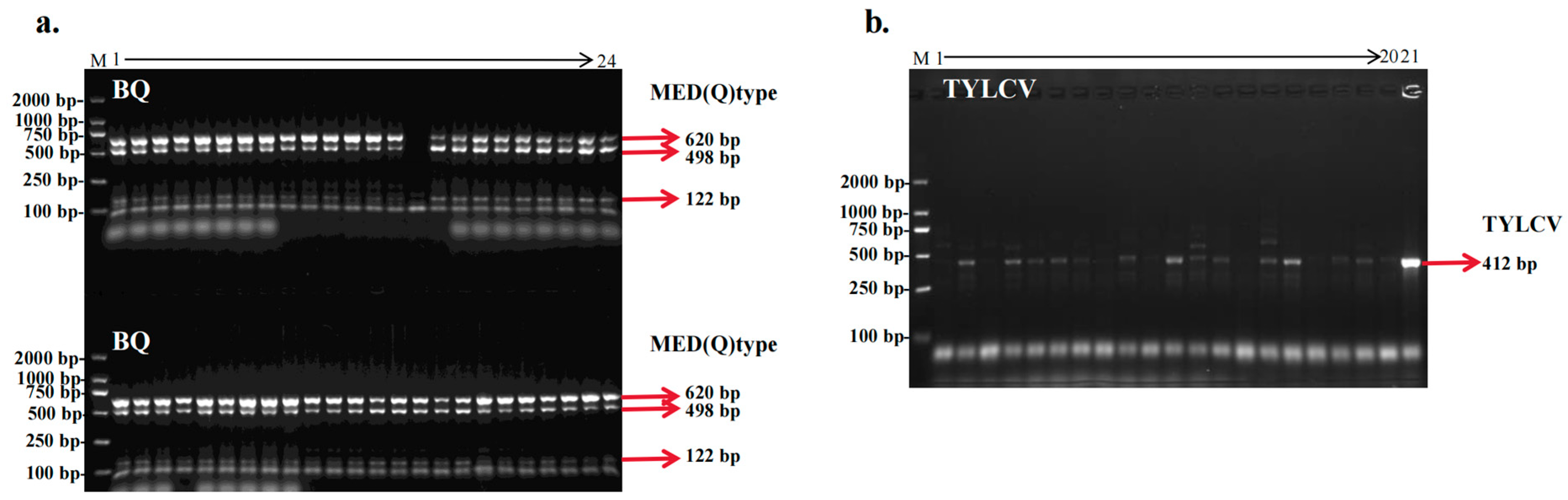
3.2. Results of the Determination of B. tabaci Biotypes and Viruses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Navas-Castillo, J.; Fiallo-Olivé, E.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Emerging virus diseases transmitted by whiteflies. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 219–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.R. Plant viruses transmitted by whiteflies. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2003, 109, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.R.V.; Henneberry, T.J.; Anderson, P. History, current status, and collaborative research projects for Bemisia tabaci. Crop Prot. 2001, 20, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Guo, Z.; Yang, Z.; Han, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, F.; Wu, Q.; Xie, W.; et al. Whitefly hijacks a plant detoxification gene that neutralizes plant toxins. Cell 2021, 184, 1693–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, F.J.; Devonshire, A.L. Biochemical evidence of haplodiploidy in the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Biochem. Genet. 1996, 34, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Barro, P.J.; Liu, S.S.; Boykin, L.M.; Dinsdale, A.B. Bemisia tabaci: A statement of species status. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Zhang, Y.J.; Brown, J.K.; Cong, B.; Xu, B.Y.; Wu, Q.J.; Zhu, G.R. The introduction of the exotic Q biotype of Bemisia tabaci from the mediterranean region into China on ornamental crops. Fla. Entomol. 2006, 89, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dângelo, R.A.C.; Michereff-Filho, M.; Inoue-Nagata, A.K.; da Silva, P.S.; Chediak, M.; Guedes, R.N.C. Area-wide insecticide resistance and endosymbiont incidence in the whitefly Bemisia tabaci MEAM1 (B biotype): A Neotropical context. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 1056–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Chu, D.; Ge, D.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; Xie, W.; Jiao, X.; Liu, B.; Yang, X.; Yang, N.; et al. Further spread of and domination by Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) biotype Q on field crops in China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Q.; Luo, C.; Zhang, H.; Guo, X.; Devine, G.J. Distribution and dynamics of Bemisia tabaci invasive biotypes in central China. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2011, 101, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, A.R.; Ishaaya, I. Dynamics of biotypes B and Q of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci and its impact on insecticide resistance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1568–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowder, D.W.; Horowitz, A.R.; De Barro, P.J.; Liu, S.S.; Showalter, A.M.; Kontsedalov, S.; Khasdan, V.; Shargal, A.; Liu, J.; Carrière, Y. Mating behaviour, life history and adaptation to insecticides determine species exclusion between whiteflies. J. Anim. Ecol. 2010, 79, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, A.R.; Kontsedalov, S.; Khasdan, V.; Ishaaya, I. Biotypes B and Q of Bemisia tabaci and their relevance to neonicotinoid and pyriproxyfen resistance. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2005, 58, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielza, P.; Moreno, I.; Belando, A.; Grávalos, C.; Izquierdo, J.; Nauen, R. Spiromesifen and spirotetramat resistance in field populations of Bemisia tabaci Gennadius in Spain. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grávalos, C.; Fernández, E.; Belando, A.; Moreno, I.; Ros, C.; Bielza, P. Cross-resistance and baseline susceptibility of Mediterranean strains of Bemisia tabaci to cyantraniliprole. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkinson, J.; Balzer, J.; Fang, C.; Walsh, T. Insecticide resistance management of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) in Australian cotton-pyriproxyfen, spirotetramat and buprofezin. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 1829–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, A.R.; Kontsedalov, S.; Denholm, I.; Ishaaya, I. Dynamics of insecticide resistance in Bemisia tabaci: A case study with the insect growth regulator pyriproxyfen. Pest Manag. Sci. 2002, 58, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, N.C.; Chaubey, R.; Kumar, D.; Rebijith, K.B.; Rajagopal, R.; Subrahmanyam, B.; Subramanian, S. Insecticide resistance status in the whitefly, Bemisia tabaci genetic groups Asia-I, Asia-II-1 and Asia-II-7 on the Indian subcontinent. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, C.; Tan, X.; He, C.; Fu, B.; Du, T.; Liang, J.; Wei, X.; Gong, P.; et al. Dynamic monitoring of the insecticide resistance status of Bemisia tabaci across China from 2019–2021. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Jones, C.M.; Devine, G.; Zhang, F.; Denholm, I.; Gorman, K. Insecticide resistance in Bemisia tabaci biotype Q (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) from China. Crop Prot. 2010, 29, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriones, E.; Navas-Castillo, J. Tomato yellow leaf curl virus, an emerging virus complex causing epidemics worldwide. Virus Res. 2000, 71, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Chu, D.; Liu, B.; Shi, X.; Guo, L.; Xie, W.; Carrière, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Differential effects of an exotic plant virus on its two closely related vectors. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.Y.; Liao, J.Y.; Fajar, A.; Chen, J.B.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L.M.; Tan, X.Q.; Zhou, X.G.; et al. Co-infection of TYLCV and ToCV increases cathepsin B and promotes ToCV transmission by Bemisia tabaci MED. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1107038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, X.; Song, D.; Yan, F. Impacts of cucurbit chlorotic yellows virus (CCYV) on biological characteristics of its vector Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) MED species. J. Insect Sci. 2021, 21, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Preisser, E.L.; Jiao, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y. Lethal and Sublethal Effects of Flupyradifurone on Bemisia tabaci MED (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) Feeding Behavior and TYLCV Transmission in Tomato. J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wu, D.; Wyckhuys, K.A.; Wu, K. Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) under laboratory conditions. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimase, M.; Rossitto De Marchi, B.; Barreto da Silva, F.; Lahiri, S.; Beuzelin, J.; Hutton, S.; Smith, H.A. Monitoring the susceptibility of Bemisia tabaci Middle East-Asia Minor 1 (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) to afidopyropen, cyantraniliprole, dinotefuran, and flupyradifurone in south Florida vegetable fields. J. Econ. Entomol. 2024, 117, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, S.E.; Akey, D.H. Conservation of natural enemies in cotton: Comparative selectivity of acetamiprid in the management of Bemisia tabaci. Pest Manag. Sci. 2005, 61, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Tian, Y.A.; Biondi, A.; Desneux, N.; Gao, X.W. Short-term and transgenerational effects of the neonicotinoid nitenpyram on susceptibility to insecticides in two whitefly species. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.A.; Nagle, C.A.; MacVean, C.A.; McKenzie, C.L. Susceptibility of Bemisia tabaci MEAM1 (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) to Imidacloprid, Thiamethoxam, Dinotefuran and Flupyradifurone in South Florida. Insects 2016, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Xie, W.; Wu, Q. Resistance monitoring for eight insecticides on the sweetpotato whitefly (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) in China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacci, L.; Crespo, A.L.; Galvan, T.L.; Pereira, E.J.; Picanço, M.C.; Silva, G.A.; Chediak, M. Toxicity of insecticides to the sweetpotato whitefly (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) and its natural enemies. Pest Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.I.; Chae, S.H.; Youn, H.S.; Yeon, S.H.; Ahn, Y.J. Contact and fumigant toxicity of plant essential oils and efficacy of spray formulations containing the oils against B- and Q-biotypes of Bemisia tabaci. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roditakis, E.; Fytrou, N.; Staurakaki, M.; Vontas, J.; Tsagkarakou, A. Activity of flonicamid on the sweet potato whitely Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) and its natural enemies. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Akhtar, K.P. Susceptibility of cotton whitefly Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) to diverse pesticides in Pakistan. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Xie, W.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Dynamic monitoring (B versus Q) and further resistance status of Q-type Bemisia tabaci in China. Crop Prot. 2017, 94, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Wan, F.H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Brown, J.K. Change in the biotype composition of Bemisia tabaci in Shandong province of China from 2005 to 2008. Environ. Entomol. 2010, 39, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wan, F.H. Cryptic invasion of the exotic Bemisia tabaci biotype Q occurred widespread in Shandong province of China. Fla. Entomol. 2010, 93, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Huang, M.; Wang, S.; Li, T.; Huang, Y. Tomato yellow leaf curl virus: Characteristics, influence, and regulation mechanism. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 213, 108812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Che, W.; Feng, H.; Luo, C. Characterization of flupyradifurone resistance in the whitefly Bemisia tabaci mediterranean (Q biotype). Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 4286–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, J.; Geng, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chu, D.; Guo, L. Resistance to dinotefuran in Bemisia tabaci in China: Status and characteristics. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, M.A.M.; Ahmed, F.S.; Alfuhaid, N.A.; El-Said, N.A.; Ibrahim, E.S.; Awad, M. The synergistic effect of lemongrass essential oil and flometoquin, flonicamid, and sulfoxaflor on Bemisia tabaci (Genn.) (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae): Insights into toxicity, biochemical impact, and molecular docking. Insects 2024, 15, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y. Biotype and insecticide resistance status of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci from China. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; He, C.; Xie, W.; Liu, Y.; Xia, J.; Yang, Z.; Guo, L.; Wen, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; et al. Glutathione S-transferases are involved in thiamethoxam resistance in the field whitefly Bemisia tabaci Q (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 134, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.B.; Liu, Y.Q.; Qin, L.; Xu, J.; Li, F.F.; Liu, S.S. Competitive displacement between two invasive whiteflies: Insecticide application and host plant effects. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2013, 103, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Hopkinson, J.E.; Balzer, J.; Frese, M.; Tay, W.T.; Walsh, T. Screening for insecticide resistance in Australian field populations of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) using bioassays and DNA sequencing. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 3248–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, I.; Ismail, S.I.; Abdullah, S.; Jalinas, J.; Jamian, S.; Saad, N. A Review of the Biology and Control of Whitefly, Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae), with Special Reference to Biological Control Using Entomopathogenic Fungi. Insects 2020, 11, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Hussain, D.; Hasan, M.U.; Sagheer, M.; Ghouse, G.; Zubair, M.; Brown, J.K.; Cheema, S.A. Differential insecticide resistance in Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) field populations in the Punjab Province of Pakistan. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, C.; Denholm, I.; Williamson, M.S.; Nauen, R. The global status of insect resistance to neonicotinoid insecticides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 121, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Insecticide | Formulation | Class of Insecticide | Active Ingredient | Manufacturer | Recommended Field Concentration (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abamectin | Emulsifiable Concentrate (EC) | Biological | 1.8% | Chemical Industry Co. Ltd. | 10.8–14.4 |
| Spinetoram | Suspension Concentrate (SC) | Biological | 6% | Corteva Agriscience | 10–20 |
| Thiamethoxam | Water-Dispersible Granule (WG) | Neonicotinoid | 25% | Syngenta | 35–75 |
| Flupyradifurone | Soluble Concentrate (SL) | Neonicotinoid | 17% | Bayer (China) Limited | 333–666 |
| Imidacloprid | Water-Dispersible Granule (WG) | Neonicotinoid | 70% | Bayer (China) Limited | 133.3–200 |
| Dinotefuran | Suspension Concentrate (SC) | Neonicotinoid | 20% | Xinbaihu Biotechnology Co. Ltd. | 666.6–1333.2 |
| Acetamiprid | Emulsifiable Concentrate (EC) | Neonicotinoid | 10% | Qingdao Taiyuan Technology Development Co., Ltd. | 50–100 |
| Thiacloprid | Suspension Concentrate (SC) | Neonicotinoid | 40% | Limin Group Co. Ltd. | 0.33–0.66 |
| Nitenpyram | Water-Dispersible Granule (WG) | Neonicotinoid | 20% | Beijing Huarong Kaiwei Plant Protection Biological Technology Co., Ltd. | 0.5–1 |
| Bifenthrin | Water-Dispersible Granule (WG) | pyrethroid | 4.5% | Qingdao Audis Bio-Tech Co. Ltd. | 0.66–1.66 |
| Deltamethrin | Emulsion in Water (EW) | pyrethroid | 2.5% | Bayer (China) Limited | 20–30 |
| Pyridaben | Emulsifiable Concentrate (EC) | Pyridazine ketone | 15% | Yifan Biotechnology Group Co. Ltd. | 50–70 |
| Flonicamid | Water dispersible Granule (WG) | Pyridine amide | 50% | Shandong Yijia Agrochemical Co., Ltd. | 140–233.3 |
| Emamectin benzoate | Suspension Concentrate (SC) | Organophosphorus | 11.6% | Keagio | 17–20 |
| Insecticide | N a | Slope (±SE) | LC50 (mg L−1) | 95% FL b | Df c | χ2 | RF | Resistance Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abamectin | 300 | 1.529 ± 0.222 | 0.020 | 0.004–0.035 | 3 | 5.2478 | 0.33 | Susceptible |
| Spinetoram | 300 | 1.142 ± 0.185 | 0.578 | 0.364–0.800 | 3 | 1.939 | 0.41 | Susceptible |
| Thiamethoxam | 357 | 0.786 ± 0.141 | 2169.316 | 1346.905–4890.116 | 4 | 0.148 | 1845.64 | Very high |
| Flupyradifurone | 356 | 0.949 ± 0.143 | 313.435 | 221.359–504.028 | 4 | 0.330 | 16.82 | Moderate |
| Imidacloprid | 418 | 0.780 ± 0.123 | 4572.568 | 2769.194–10398.846 | 5 | 0.907 | 4618.75 | Very high |
| Dinotefuran | 354 | 1.027 ± 0.145 | 78.641 | 37.725–193.042 | 4 | 8.724 | 13.08 | Moderate |
| Acetamiprid | 371 | 0.922 ± 0.142 | 786.568 | 543.991–1331.099 | 4 | 0.394 | 436.98 | Very high |
| Thiacloprid | 350 | 0.786 ± 0.144 | 1875.588 | 1156.237–4337.336 | 4 | 0.345 | 116.43 | Very high |
| Nitenpyram | 294 | 1.654 ± 0.211 | 7.720 | 4.239–12.557 | 3 | 4.820 | 2.88 | Low |
| Bifenthrin | 369 | 0.916 ± 0.138 | 144.085 | 99.432–201.976 | 4 | 3.687 | 6.99 | Low |
| Deltamethrin | 352 | 0.832 ± 0.138 | 281.181 | 192.966–452.265 | 4 | 2.637 | 27.11 | Moderate |
| Pyridaben | 358 | 0.787 ± 0.139 | 476.117 | 319.227–802.671 | 4 | 0.237 | 915.60 | Very high |
| Flonicamid | 357 | 0.725 ± 0.139 | 279.454 | 177.446–571.761 | 4 | 0.208 | 37.16 | high |
| Emamectin benzoate | 362 | 1.414 ± 0.153 | 0.667 | 0.519–0.844 | 4 | 0.313 | 0.22 | Susceptible |
| Insecticide | N a | Slope (±SE) | LC50 (mg L−1) | 95% FL b | Df c | χ2 | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abamectin | 498 | 1.95 ± 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.03–0.14 | 3 | 2.33 | Yang et al. [44] |
| Spinetoram | 516 | 1.96 ± 0.16 | 1.38 | 1.03–1.86 | 3 | 1.85 | Wang et al. [31] |
| Thiamethoxam | - | 1.54 ± 0.15 | 1.19 | 0.95–1.46 | - | - | Wang et al. [43] |
| Flupyradifurone | 356 | 1.35 ± 0.11 | 18.63 | 15.98–21.50 | 3 | 2.35 | Wang et al. [40] |
| Imidacloprid | - | 2.34 ± 0.21 | 0.99 | 0.83–1.17 | - | - | Wang et al. [43] |
| Dinotefuran | 285 | 1.67 ± 0.28 | 6.01 | 4.13–8.43 | 3 | 1.92 | Li et al. [41] |
| Acetamiprid | 328 | 1.57± 0.25 | 1.80 | 0.80–3.80 | 4 | 2.46 | Yang et al. [44] |
| Thiacloprid | 294 | 1.38 ± 0.454 | 16.10 | 10.139–20.631 | 4 | 1.441 | Strain THS |
| Nitenpyram | 663 | 2.78 ± 0.20 | 2.68 | 2.21–3.26 | 3 | 4.820 | Wang et al. [40] |
| Bifenthrin | 279 | 1.11 ± 0.193 | 20.61 | 10.473–76.813 | 4 | 4.559 | Strain THS |
| Deltamethrin | 285 | 1.11 ± 0.191 | 10.37 | 4.865–35.825 | 4 | 5.074 | Strain THS |
| Pyridaben | 700 | 1.52 ± 0.12 | 0.52 | 0.32–0.77 | 4 | 0.237 | Ahmad and Akhtar [35] |
| flonicamid | - | 2.44 ± 0.18 | 7.52 | 6.64–8.54 | - | - | Moustafa et al. [42] |
| Emamectin benzoate | 600 | 1.46 ± 0.12 | 2.92 | 2.30–3.65 | 4 | - | Ahmad and Akhtar [35] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Ji, Y.; Du, H.; Ma, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, D.; Belyakova, N.A.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X. Insecticide Resistance and Plant Virus Status of Bemisia tabaci on Soybean in Suzhou. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101071
Li Q, Ji Y, Du H, Ma S, Zhu J, Zhu D, Belyakova NA, Zhang Y, Yang X. Insecticide Resistance and Plant Virus Status of Bemisia tabaci on Soybean in Suzhou. Agriculture. 2025; 15(10):1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101071
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qi, Yao Ji, He Du, Shufang Ma, Jifei Zhu, Dehui Zhu, Natalia A. Belyakova, Youjun Zhang, and Xin Yang. 2025. "Insecticide Resistance and Plant Virus Status of Bemisia tabaci on Soybean in Suzhou" Agriculture 15, no. 10: 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101071
APA StyleLi, Q., Ji, Y., Du, H., Ma, S., Zhu, J., Zhu, D., Belyakova, N. A., Zhang, Y., & Yang, X. (2025). Insecticide Resistance and Plant Virus Status of Bemisia tabaci on Soybean in Suzhou. Agriculture, 15(10), 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101071









