Multi-Year Pseudo-Persistence, Mobility, and Degradation of Glyphosate and Its Degradation Product (AMPA) in a Gleysol in Quebec (Canada)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Agricultural Managements
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Carbon Analyzes
2.4. Analysis of Glyphosate and AMPA Contents in Soils
2.5. Data Processing
- ith
- [Gly], [AMPA] = weight of glyphosate and AMPA per unit weight of dry soil;
- MGly, MAMPA = molar mass of glyphosate and AMPA;
- Vh = volume of soil from the “h” horizon sampled over 1 ha;
- ρh = apparent soil density of the sampled horizon. ρh is calculated from the total organic carbon measured in the sample according to the formula used by Kämpf et al. [51]:
2.6. Statistical Analyzes
3. Results
3.1. AMPA and Glyphosate Levels in Soils
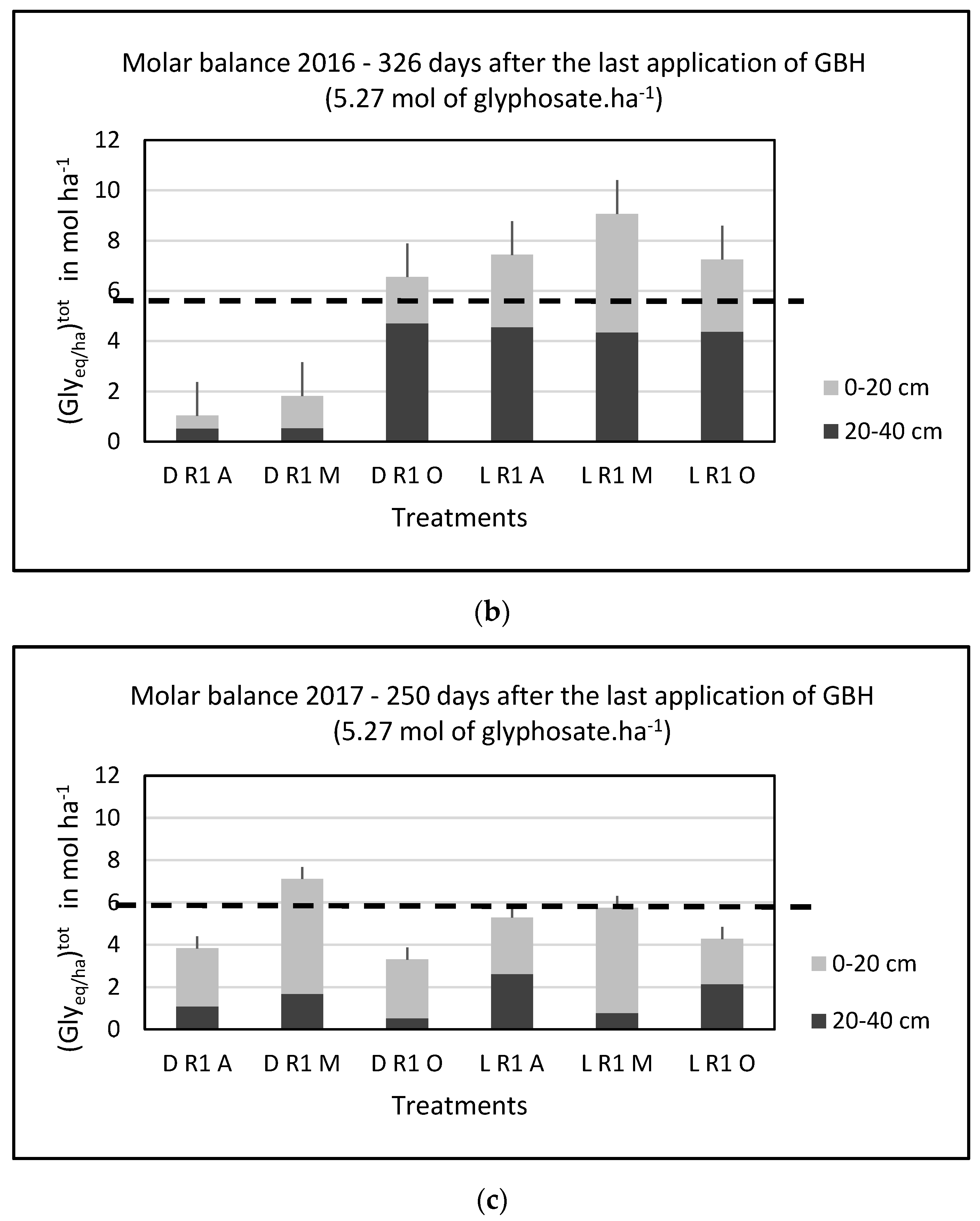
3.2. Annual Molar Balance and the Effect of Agricultural Practices
4. Discussion
4.1. AMPA Persistence in Soil from One Growing Season to the Next
4.2. Pseudo-Persistence of AMPA in Agricultural Soils
4.3. Pseudo-Persistence of AMPA Favored by Tillage Practices
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Myers, J.P.; Antoniou, M.N.; Blumberg, B.; Carroll, L.; Colborn, T.; Everett, L.G.; Hansen, M.; Landrigan, P.J.; Lanphear, B.P.; Mesnage, R.; et al. Concerns over use of glyphosate-based herbicides and risks associated with exposures: A consensus statement. Environ. Health 2016, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, S.O.; Lyon, D.J.; Koskinen, W.C.; Moorman, T.B.; Chaney, R.L.; Hammerschmidt, R. Glyphosate effetcs on plant Mineral nutrition, Crop rhizosphere, microbiota, and plant disease in glyphosate-resistant Crops. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10375–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O.; Powles, S.B. Glyphosate: A once-in-a-century herbicide. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Réchauffement planétaire de 1.5 °C, Rapport spécial du GIEC sur les conséquences d’un réchauffement planétaire de 1.5 °C par rapport aux niveaux préindustriels et les trajectoires associées d’émissions mondiales de gaz à effet de serre, dans le contexte du renforcement de la parade mondiale au changement climatique, du développement durable et de la lutte contre la pauvreté. Résumé À L’intention Des Décideurs 2018, 32. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/sites/2/2019/09/SR15_Summary_Volume_french.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Cuhra, M.; Bøhn, T.; Cuhra, P. Glyphosate: Too Much of a Good Thing? Front. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorse, I.; Rivard, L. Bilan des Ventes de Pesticides au Québec pour L’année 2008. Québec Ministère Du Développement Durable De L’environnement Et Des Parcs, 31 p. 2011. Available online: https://www.bibliotheque.assnat.qc.ca/DepotNumerique_v2/AffichageFichier.aspx?idf=26957 (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- MELCCFP. Ministère de l’Environnement, de la Lutte Contre Les Changements Climatiques, de la Faune et des Parcs, Bilan des Ventes de Pesticides au Québec, Année 2022. 2024. Available online: https://www.environnement.gouv.qc.ca/ (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Benbrook, C.M. Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, V.C.; De Gerónimo, E.; Marino, D.; Primost, J.; Carriquiriborde, P.; Costa, J.L. Environmental fate of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in surface waters and soil of agricultural basins. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hébert, M.-P.; Fugère, V.; Gonzalez, A. The overlooked impact of rising glyphosate use on phosphorus loading in agricultural watersheds. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2019, 17, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Evaluation of Five Organophosphate Insecticides and Herbicides; IARC: Lyon, France, 2015; Volume 112.
- Portier, C.J.; Armstrong, B.K.; Baguley, B.C.; Baur, X.; Belyaev, I.; Bellé, R.; Belpoggi, F.; Biggeri, A.; Bosland, M.C.; Bruzzi, P.; et al. Differences in the carcinogenic evaluation of glyphosate between the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2016, 70, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarone, R.E. On the International Agency for Research on Cancer classification of glyphosate as a probable human carcinogen. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 27, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hénault-Ethier, L.; Lucotte, M.; Moingt, M.; Paquet, S.; Maccario, S.; Smedbol, É.; Gomes, M.P.; Lepage, L.; Juneau, P.; Labrecque, M. Herbaceous or Salix miyabeana ‘SX64’ narrow buffer strips as a means to minimize glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid leaching from row crop fields. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smedbol, É.; Gomes, M.P.; Paquet, S.; Labrecque, M.; Lepage, L.; Lucotte, M.; Juneau, P. Effects of low concentrations of glyphosate-based herbicide factor 540® on an agricultural stream freshwater phytoplankton community. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bruggen, A.H.C.; He, M.M.; Shin, K.; Mai, V.; Jeong, K.C.; Finckh, M.R.; Morris, J.G. Environmental and health effects of the herbicide glyphosate. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giroux, I.; Pelletier, L. Présence de Pesticides Dans L’eau au Québec: Bilan Dans Quatre Cours D’eau De Zones en Culture de Maïs et de Soya en 2008, 2009 et 2010. 2012. Available online: https://www.environnement.gouv.qc.ca/eau/flrivlac/mais_soya/index.htm (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Giroux, I. Pesticides Dans Les Sédiments de Cours D’eau au Québec—Échantillonnages Exploratoires Réalisés de 2018 à 2021, Québec, Ministère de L’environnement, de la Lutte Contre les Changements Climatiques, de la Faune et des Parcs, Direction du Suivi de L’état de L’environnement, 38p. + 4 Annexes. 2023. Available online: https://www.environnement.gouv.qc.ca/eau/flrivlac/pesticides-sediments-echantillonnages-2018-2021.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Giroux, I. Présence de Pesticides Dans L’eau au Québec: Portrait et Tendances Dans Les Zones de Maïs et de Soya—2011 à 2014. Québec, Ministère du Développement Durable, De L’environnement et de la Lutte Contre les Changements Climatiques, Direction du Suivi de L’état de L’environnement, 47p. + 5 Annexes. 2015. Available online: https://www.environnement.gouv.qc.ca/eau/flrivlac/mais_soya/portrait2011-2014/rapport2011-2014.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Giroux, I. Présence de Pesticides Dans L’eau Au Québec: Portrait et Tendances Dans les Zones de Maïs et de Soya—2015 à 2017. Québec, Ministère de l’Environnement et de la Lutte Contre les Changements Climatiques, Direction Générale du Suivi de L’état de L’environnement, 64p. + 6 ann. 2019. Available online: https://www.environnement.gouv.qc.ca/EAU/flrivlac/mais_soya/portrait2015-2017/index.htm (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Montiel-León, J.M.; Munoz, G.; Vo Duy, S.; Do, D.T.; Vaudreuil, M.-A.; Goeury, K.; Guillemette, F.; Amyot, M.; Sauvé, S. Widespread occurrence and spatial distribution of glyphosate, atrazine, and neonicotinoids pesticides in the St. Lawrence and tributary rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struger, J.; Van Stempvoort, D.R.; Brown, S.J. Sources of aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) in urban and rural catchments in Ontario, Canada: Glyphosate or phosphonates in wastewater? Environ. Pollut. 2015, 204, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglin, W.A.; Meyer, M.T.; Kuivila, K.M.; Dietze, J.E. Glyphosate and Its Degradation Product AMPA Occur Frequently and Widely in U.S. Soils, Surface Water, Groundwater, and Precipitation. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, F.; Lavison, G.; Couturier, G.; Alliot, F.; Moreau-Guigon, E.; Fauchon, N.; Guery, B.; Chevreuil, M.; Blanchoud, H. Transfer of glyphosate and its degradate AMPA to surface waters through urban sewerage systems. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borggaard, O.K.; Gimsing, A.L. Fate of glyphosate in soil and the possibility of leaching to ground and surface waters: A review. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borggaard, O.K.; Raben-Lange, B.; Gimsing, A.L.; Strobel, B.W. Influence of humic substances on phosphate adsorption by aluminium and iron oxides. Geoderma 2005, 127, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, P.; Rämö, S.; Nikunen, U.; Jauhiainen, L.; Siimes, K.; Turtola, E. Glyphosate and phosphorus leaching and residues in boreal sandy soil. Plant Soil 2009, 323, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, L.; Caballero, J.; Ronen, D. Glyphosate transport through weathered granite soils under irrigated and non-irrigated conditions—Barcelona, Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2509–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Garnier, P.; Rumpel, C.; Parent, S.E.; Benoit, P. Adsorption and desorption behavior of selected pesticides as influenced by decomposition of maize mulch. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erban, T.; Stehlik, M.; Sopko, B.; Markovic, M.; Seifrtova, M.; Halesova, T.; Kovaricek, P. The different behaviors of glyphosate and AMPA in compost-amended soil. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helander, M.; Saloniemi, I.; Saikkonen, K. Glyphosate in northern ecosystems. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, P.; Siimes, K. Glyphosate translocation from plants to soil—Does this constitute a significant proportion of residues in soil? Plant Soil. 2007, 300, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleto, L.; Coquet, Y.; Benoit, P.; Heddadj, D.; Barriuso, E. Tillage management effects on pesticide fate in soils. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 367–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, E.; Costa, J.L.; Bedmar, F. Adsorption and mobility of glyphosate in different soils under no-till and conventional tillage. Geoderma 2016, 263, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, O.; Dion, S.; St-Laurent, L.; April, M.-H. Indicateur de Risque des Pesticides du Québec—IRPeQ—Santé et Environnement, Québec; Ministère de l’Agriculture, des Pêcheries et de l’Alimentation; Ministère du Développement Durable, de l’Environnement et des Parcs; Institut National de Santé Publique du Québec: Québec, QC, Canada, 2012; 48p.
- Health Canada. Proposed Re-Evaluation Decision PRVD2015-01, Glyphosate. Pest Management Regulatory Agency. Government of Canada, Canada. 2015. Available online: https://publications.gc.ca/collections/collection_2015/sc-hc/H113-27-2015-1-eng.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Bento, C.P.M.; van der Hoeven, S.; Yang, X.; Riksen, M.M.J.P.M.; Mol, H.G.J.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Dynamics of glyphosate and AMPA in the soil surface layer of glyphosate-resistant crop cultivations in the loess Pampas of Argentina. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bento, C.P.M.; Yang, X.; Gort, G.; Xue, S.; van Dam, R.; Zomer, P.; Mol, H.G.J.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Persistence of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in loess soil under different combinations of temperature, soil moisture and light/darkness. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergström, L.; Börjesson, E.; Stenström, J. Laboratory and Lysimeter Studies of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid in a Sand and a Clay Soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, R.K.; Ray, D.P. Reviewing Mathematical Models for Pesticide Leaching Studies. Int. J. Bioresour. Sci. 2016, 3, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gaupp-Berghausen, M.; Hofer, M.; Rewald, B.; Zaller, J.G. Glyphosate-based herbicides reduce the activity and reproduction of earthworms and lead to increased soil nutrient concentrations. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiosi, R.; Lucio Ferrarese, M.d.L.; Bonini, E.A.; Fernandes, N.G.; Ferro, A.P.; Ferrarese-Filho, O. Glyphosate-induced metabolic changes in susceptible and glyphosate-resistant soybean (Glycine max L.) roots. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2009, 93, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, M.-A.; Lefebvre, R.; Rivard, C.; Parent, M.; Ballard, J.-M.; Benoit, N.; Vigneault, H.; Beaudry, C.; Malet, X.; Laurencelle, M.; et al. Portrait des Ressources en Eau Souterraine en Montérégie Est, Québec, Canada. Projet Réalisé Conjointement par l’INRS, la CGC, l’OBV Yamaska et l’IRDA dans le Cadre du Programme D’acquisition de Connaissances sur les Eaux Souterraines, Rapport Final INRS R-1433, Soumis en Juin 2013. Available online: https://www.environnement.gouv.qc.ca/_PACES/rapports-projets/MonteregieEst/MON-scientif-INRS-201306.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Martin, A.; Nolin, M.C. Etude Pédologique du Comté de Chambly; Volume 2 Description et Classification des Séries de Sols; Direction Générale de la Recherche Agriculture Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1991; 151p. [Google Scholar]
- Bérubé, M.-E.; Vanasse, A.; Rioux, S.; Bourget, N.; Dion, Y.; Tremblay, G. Effect of Glyphosate on Fusarium Head Blight in Wheat and Barley Under Different Soil Tillages. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moingt, M.; Lucotte, M.; Paquet, S. Lignin biomarkers signatures of common plants and soils of Eastern Canada. Biogeochemistry 2016, 129, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alferness, P.L.; Iwata, Y. Determination of Glyphosate and (Aminomethy1)phosphonic Acid in Soil, Plant and Animal Matrices, and Water by Capillary Gas Chromatography with Mass-Selective Detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 2751–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedbol, É.; Lucotte, M.; Maccario, S.; Gomes, M.P.; Paquet, S.; Moingt, M.; Mercier, L.L.C.; Sobarzo, M.R.P.; Blouin, M.-A. Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid Content in Glyphosate-Resistant Soybean Leaves, Stems, and Roots and Associated Phytotoxicity Following a Single Glyphosate-Based Herbicide Application. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6133–6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccario, S.; Lucotte, M.; Moingt, M.; Samson-Brais, E.; Smedbol, É.; Labrecque, M. Impact of Soil Characteristics and Weed Management Practices on Glyphosate and AMPA Persistence in Field Crops Soils from the St. Lawrence Lowlands (Quebec, Canada). Agronomy 2022, 12, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kämpf, I.; Hölzel, N.; Störrle, M.; Broll, G.; Kiehl, K. Potential of temperate agricultural soils for carbon sequestration: A meta-analysis of land-use effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 428–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Montanarella, L.; Jones, A.; Fernández-Ugalde, O.; Mol, H.G.J.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Distribution of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) in agricultural topsoils of the European Union. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bento, C.P.M.; Goossens, D.; Rezaei, M.; Riksen, M.; Mol, H.G.J.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Glyphosate and AMPA distribution in wind-eroded sediment derived from loess soil. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandcoin, A.; Piel, S.; Baurès, E. AminoMethylPhosphonic acid (AMPA) in natural waters: Its sources, behavior and environmental fate. Water Res. 2017, 117, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, M.; Höss, S.; Neumann, G.; Afzal, J.; Reichenbecher, W. Glyphosate, a chelating agent—Relevant for ecological risk assessment? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 5298–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.P.; Smedol, E.; Chalifour, A.; Hénault-Ethier, L.; Labrecque, M.; Lepage, L.; Lucotte, M.; Juneau, P. Alteration of plant physiology by glyphosate and its by-product aminomethylphosphonic acid: An overview. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 4691–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, E.; Costa, J.L.; Bedmar, F. Glyphosate Dissipation in Different Soils under No-Till and Conventional Tillage. Pedosphere 2019, 29, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidoli, P.; Baran, N.; Angulo-Jaramillo, R. Glyphosate and AMPA adsorption in soils: Laboratory experiments and pedotransfer rules. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 5733–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernier Brillon, J.; Lucotte, M.; Bernier, A.; Fontaine, M.; Moingt, M. Using Cover Crops as Means of Controlling Weeds and Reducing the Applied Quantity of Glyphosate-Based Herbicide in No-Till Glyphosate Tolerant Soybean and Corn. Agriculture 2024, 14, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampazzo, N.; Rampazzo Todorovic, G.; Mentler, A.; Blum, W.E.H. Adsorption of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in soils. Int. Agrophys 2013, 27, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampazzo Todorovic, G.; Rampazzo, N.; Mentler, A.; Blum, W.E.H.; Eder, A.; Strauss, P. Influence of soil tillage and erosion on the dispersion of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in agricultural soils. Int. Agrophys. 2014, 28, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soracco, C.G.; Villarreal, R.; Lozano, L.A.; Vittori, S.; Melani, E.M.; Marino, D.J.G. Glyphosate dynamics in a soil under conventional and no-till systems during a soybean growing season. Geoderma 2018, 323, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, R.; Soracco, C.G.; Salazar, M.P.; Bellora, G.L.; Valdés-Abellán, J.; Lozano, L.A. Glyphosate dynamics prediction in a soil under conventional and no-tillage systems during the crop cycle. Rev. Bras. de Ciência do Solo 2020, 44, e0190130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sviridov, A.V.; Shushkova, T.V.; Ermakova, I.T.; Ivanova, E.V.; Epiktetov, D.O.; Leontievsky, A.A. Microbial degradation of glyphosate Herbicides (review). Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2015, 51, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.K.; Dörfler, U.; Welzl, G.; Munch, J.C.; Schroll, R.; Suhadolc, M. Large variation in glyphosate mineralization in 21 different agricultural soils explained by soil properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- la Cecilia, D.; Maggi, F. Analysis of glyphosate degradation in a soil microcosm. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogusu, E.O.; Wolbert, B.; Kujawinski, D.M.; Jochmann, M.A.; Elsner, M. Dual element (15N/14N, 13C/12C) isotope analysis of glyphosate and AMPA by derivatization-gas chromatography isotope ratio mass spectrometry (GC/IRMS) combined with LC/IRMS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 5249–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, K.A.; McBride, M.B. Oxidative Degradation of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonate by Manganese Oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9223–9228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebo, B.M.; Johnson, H.A.; McCarthy, J.K.; Templeton, A.S. Geomicrobiology of manganese(II) oxidation. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.; Saez, J.M.; Davila Costa, J.S.; Colin, V.L.; Fuentes, M.S.; Cuozzo, S.A.; Benimeli, C.S.; Polti, M.A.; Amoroso, M.J. Actinobacteria: Current research and perspectives for bioremediation of pesticides and heavy metals. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Schwinghamer, T.; Smith, D.L. Isolation and diversity of culturable rhizobacteria associated with economically important crops and uncultivated plants in Québec, Canada. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 41, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, F.; Bouziri, L.; Nicolardot, B.; Ranjard, L. Impact of wheat straw decomposition on successional patterns of soil microbial community structure. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, W.; Lucotte, M.; D’Astous-Pagé, J.; Jeanne, T.; Pin, C.; Moingt, M.; Hogue, R. Impacts of Cropping Systems on Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid Contents and Microbial Community in Field Crop Soils in Quebec (Canada). Agronomy 2024, 14, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronick, C.J.; Lal, R. Soil structure and management: A review. Geoderma 2005, 124, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhne, J.M.; Köhne, S.; Šimůnek, J. A review of model applications for structured soils: B) Pesticide transport. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2009, 104, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barré, P.; Fernandez-Ugalde, O.; Virto, I.; Velde, B.; Chenu, C. Impact of phyllosilicate mineralogy on organic carbon stabilization in soils: Incomplete knowledge and exciting prospects. Geoderma 2014, 235–236, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiluweit, M.; Bougoure, J.J.; Nico, P.S.; Pett-Ridge, J.; Weber, P.K.; Kleber, M. Mineral protection of soil carbon counteracted by root exudates. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Crop | Sampling AAAA/MM/JJ | GBH Application AAAA/MM/JJ | Total Precipitation (mm)/Average Temperature (°C) 15 Days After GBH Application | Total Precipitation (mm)/Average Temperature (°C) 15 Days Before GBH Application | Number of Days Between the Last GBH Application and Sampling/Total Rainfall (mm) During This Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | Corn | not applicable | 12 May 2014 a | 70/16.4 | 27/10.9 | |
| 2015 | Soy | 18 June 2015 | 19 June 2015 b | 55.4/18 | 89/17.8 | 398 days/1166 mm |
| 2016 | Wheat | 10 May 2016 | 27 August 2016 b | 43/18.4 | 155 */19.3 | 326 days/973 mm |
| 2017 | Corn | 4 May 2017 | 17 May 2017 a | 48/17.5 | 72/18.4 | 250 days/865 mm |
| Treatments | [AMPA] μg.g−1 | Bloc | Sampling Year | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 398 Days a.a | 2016 326 Days a.a | 2017 250 Days a.a | |||
| D R1 A | [AMPA] 0–20 | 1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| 2 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.25 | ||
| 3 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | ||
| [AMPA] 20–40 | 1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 2 | 0.13 | <LOQ | <LOQ | ||
| 3 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | ||
| D R1 M | [AMPA] 0–20 | 1 | 0.14 | <LOQ | 0.18 |
| 2 | 0.46 | 0.11 | 0.25 | ||
| 3 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.21 | ||
| [AMPA] 20–40 | 1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 2 | 0.09 | <LOQ | <LOQ | ||
| 3 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.15 | ||
| D R1 O | [AMPA] 0–20 | 1 | 0.35 | 0.15 | <LOQ |
| 2 | 0.22 | <LOQ | 0.30 | ||
| 3 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | ||
| [AMPA] 20–40 | 1 | 0.15 | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 2 | 0.32 | 0.31 | <LOQ | ||
| 3 | <LOQ | 0.21 | <LOQ | ||
| L R1 A | [AMPA] 0–20 | 1 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.16 |
| 2 | 0.29 | 0.09 | <LOQ | ||
| 3 | 0.29 | 0.12 | 0.10 | ||
| [AMPA] 20–40 | 1 | 0.13 | 0.14 | <LOQ | |
| 2 | 0.12 | 0.34 | <LOQ | ||
| 3 | 0.12 | <LOQ | 0.26 | ||
| L R1 M | [AMPA] 0–20 | 1 | 0.09 | 0.33 | 0.22 |
| 2 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.10 | ||
| 3 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.28 | ||
| [AMPA] 20–40 | 1 | 0.28 | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 2 | 0.19 | 0.23 | <LOQ | ||
| 3 | <LOQ | 0.24 | <LOQ | ||
| L R1 O | [AMPA] 0–20 | 1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.10 |
| 2 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | ||
| 3 | 0.17 | 0.31 | 0.13 | ||
| [AMPA] 20–40 | 1 | 0.13 | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 2 | <LOQ | 0.20 | <LOQ | ||
| 3 | <LOQ | 0.29 | 0.18 | ||
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | 0–40 cm | 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | 0–40 cm | 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | 0–40 cm | |
| D R1 A | b | a | b | a | a | c | a | a | a |
| D R1 M | ab | a | ab | a | a | bc | a | a | a |
| D R1 O | ab | a | ab | a | a | a | a | a | a |
| L R1 A | a | a | a | a | a | a | a | a | a |
| L R1 M | ab | a | ab | a | a | a | a | a | a |
| L R1 O | ab | a | ab | a | a | ab | a | a | a |
| F (α = 0.05) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | ||||||||
| Origin of Variation | dof | 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | 0–40 cm | 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | 0–40 cm | 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | 0–40 cm |
| F | 2 | 0.3237 | 0.0349 | 0.1131 | 0.1145 | 1.0220 | 0.7733 | 2.6494 | 0.1301 | 0.3865 |
| T | 1 | 0.7942 | 1.2577 | 0.2039 | 3.5078 | 3.4753 | 7.4350 | 0.1436 | 0.4147 | 0.8228 |
| T × F | 2 | 4.2890 | 2.5817 | 3.6904 | 1.1511 | 0.9719 | 1.3747 | 0.1354 | 0.8719 | 0.7308 |
| Total | 17 | |||||||||
| IP 2015 | IP 2016 | IP 2017 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| D R1 A | 63.3 ± 21.6 (a) | 51.5 ± 1.1 (a) | 39.9 ± 18.9 (a) |
| D R1 M | 27.3 ± 20.23 (a) | 39.7 ± 20.7 (a) | 20.4 ± 19.2 (a) |
| D R1 O | 48.4 ± 15.4 (a) | 63.6 ± 44.3 (a) | 36.2 ± 25.8 (a) |
| L R1 A | 36.9 ± 10.1 (a) | 49.4 ± 32.8 (a) | 37.9 ± 31.5 (a) |
| L R1 M | 59.1 ± 32.3 (a) | 51.2 ± 43.4 (a) | 14.1 ± 5.7 (a) |
| L R1 O | 49.9 ± 38.7 (a) | 63.8 ± 23.9 (a) | 47.5 ± 13.2 (a) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petit, S.; Lucotte, M.; Tremblay, G. Multi-Year Pseudo-Persistence, Mobility, and Degradation of Glyphosate and Its Degradation Product (AMPA) in a Gleysol in Quebec (Canada). Agriculture 2025, 15, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15010110
Petit S, Lucotte M, Tremblay G. Multi-Year Pseudo-Persistence, Mobility, and Degradation of Glyphosate and Its Degradation Product (AMPA) in a Gleysol in Quebec (Canada). Agriculture. 2025; 15(1):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15010110
Chicago/Turabian StylePetit, Stéphane, Marc Lucotte, and Gilles Tremblay. 2025. "Multi-Year Pseudo-Persistence, Mobility, and Degradation of Glyphosate and Its Degradation Product (AMPA) in a Gleysol in Quebec (Canada)" Agriculture 15, no. 1: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15010110
APA StylePetit, S., Lucotte, M., & Tremblay, G. (2025). Multi-Year Pseudo-Persistence, Mobility, and Degradation of Glyphosate and Its Degradation Product (AMPA) in a Gleysol in Quebec (Canada). Agriculture, 15(1), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15010110






