Green Food Development in China: Experiences and Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classification, Standardization, and Development of Green Food in China
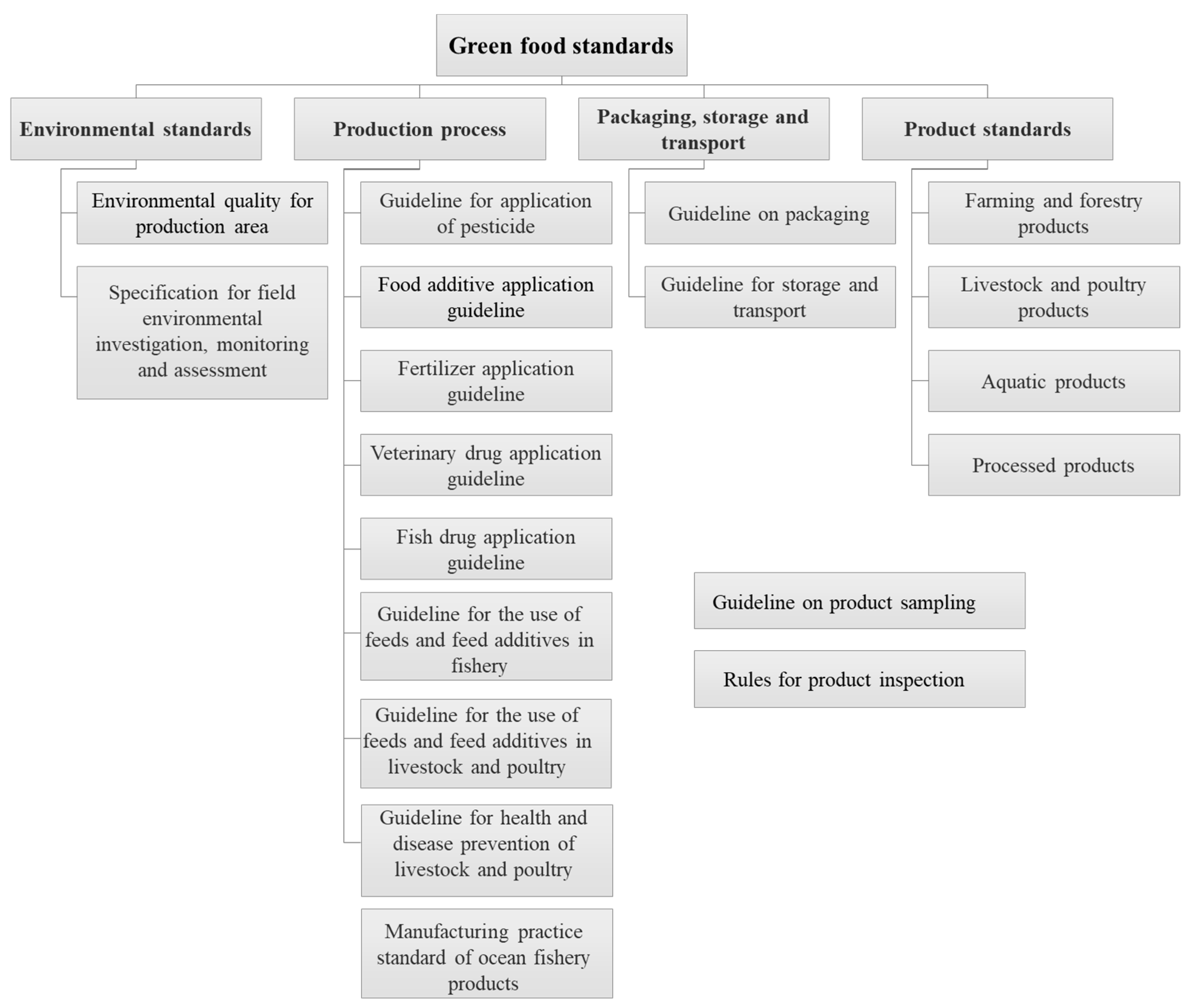
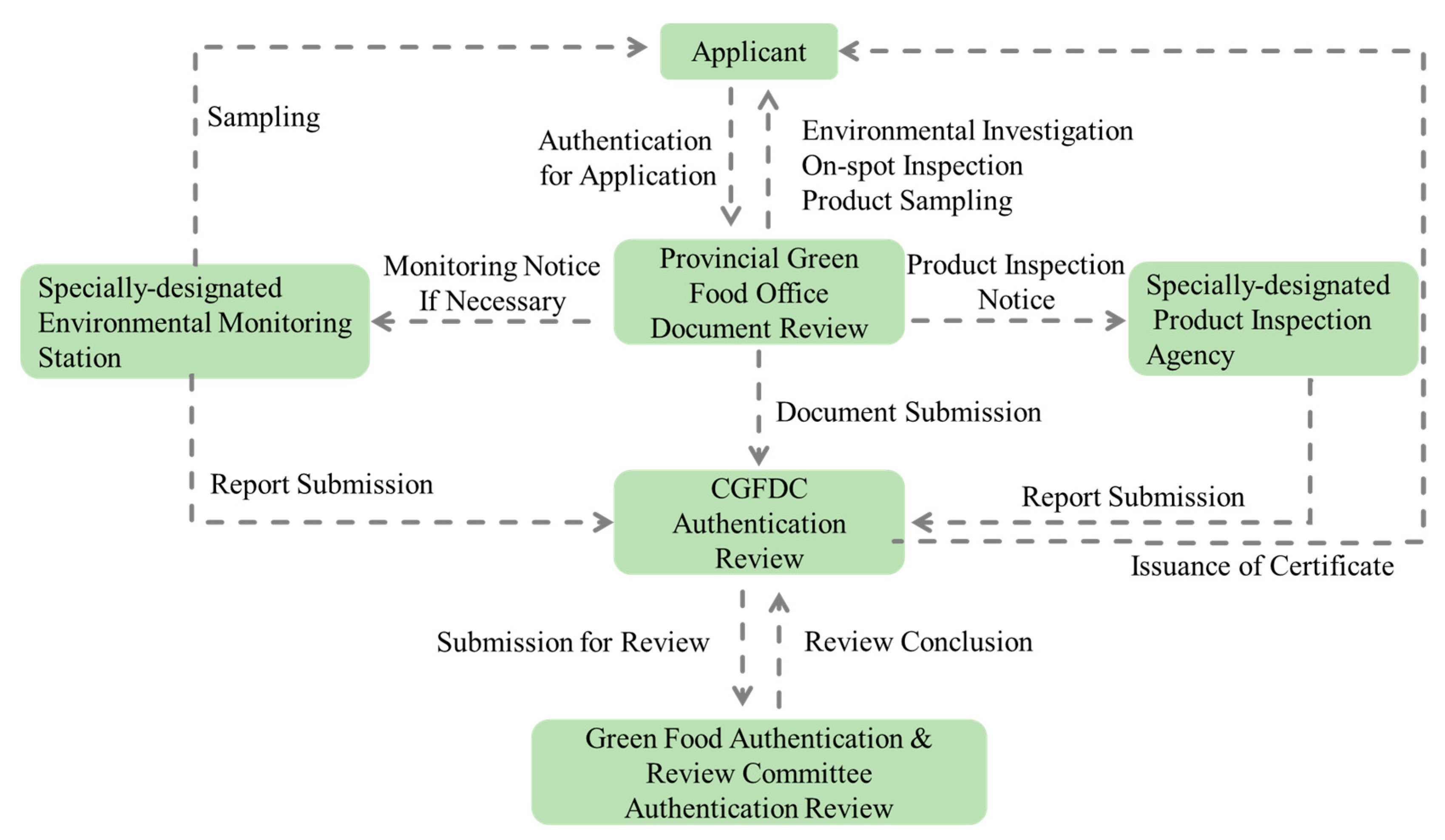
2.1. Administration, Standards, and Authorization of Green Food
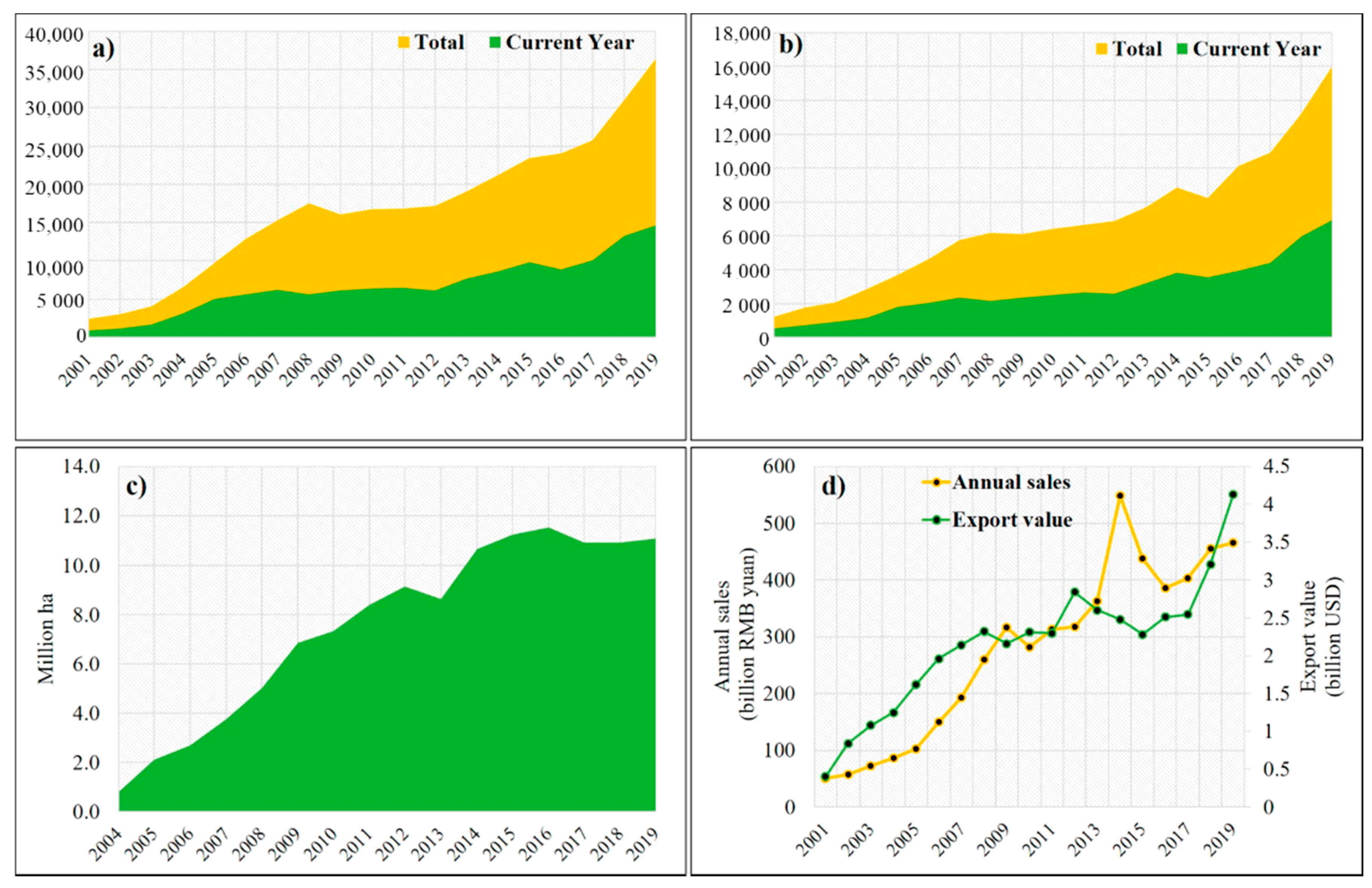
2.2. Rapid and Steady Growth of the Green Food Industry
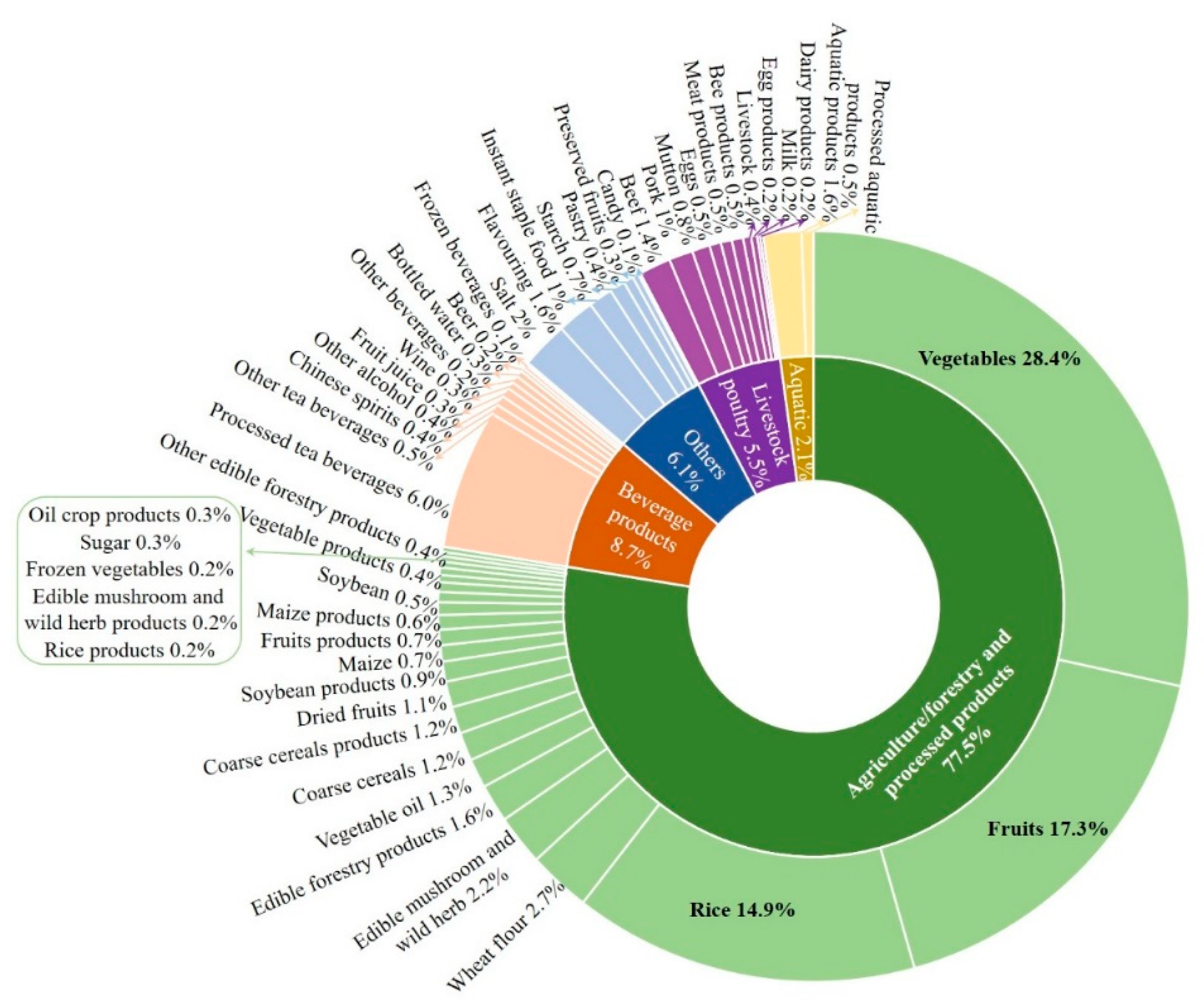
2.3. Categories and Proportions of Green Food Products
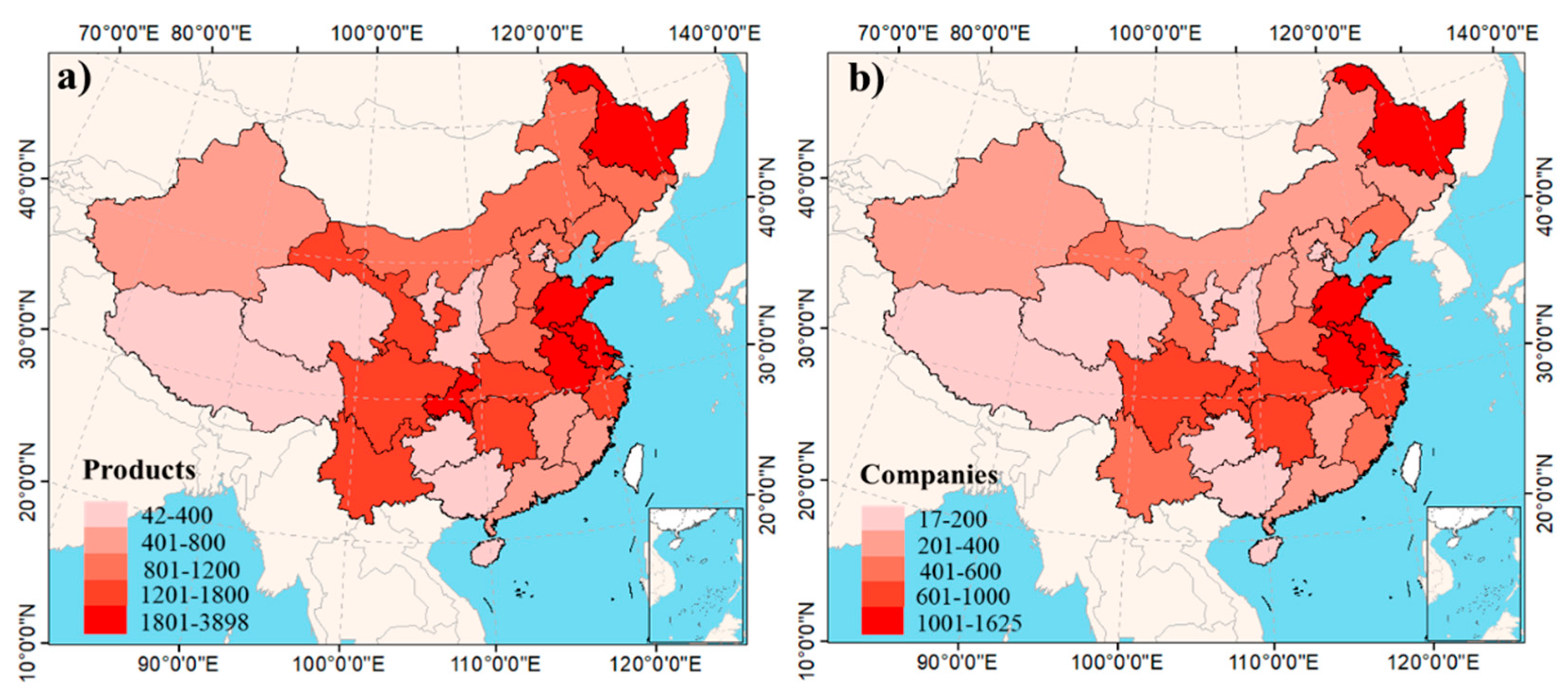
2.4. Distribution Patterns of Green Food Production
3. Agricultural and Environmental Advantages of Green Food
3.1. Crop Yield and Quality
3.2. Environmental Consequences
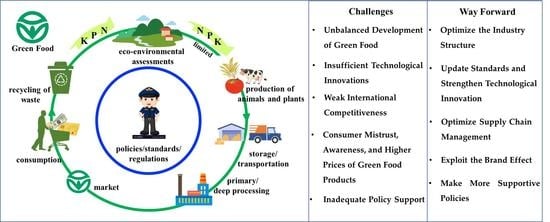
4. Major Challenges of the Green Food Industry
4.1. Unbalanced Development of Green Food
4.2. Insufficient Technological Innovations
4.3. Weak International Competitiveness
4.4. Consumer Mistrust, Awareness, and Higher Prices of Green Food Products
4.5. Inadequate Policy Support
5. Way Forward
5.1. Optimize the Industry Structure
5.2. Update Standards and Strengthen Technological Innovation
5.3. Optimize Supply Chain Management
5.4. Exploit the Brand Effect
5.5. Make More Supportive Policies
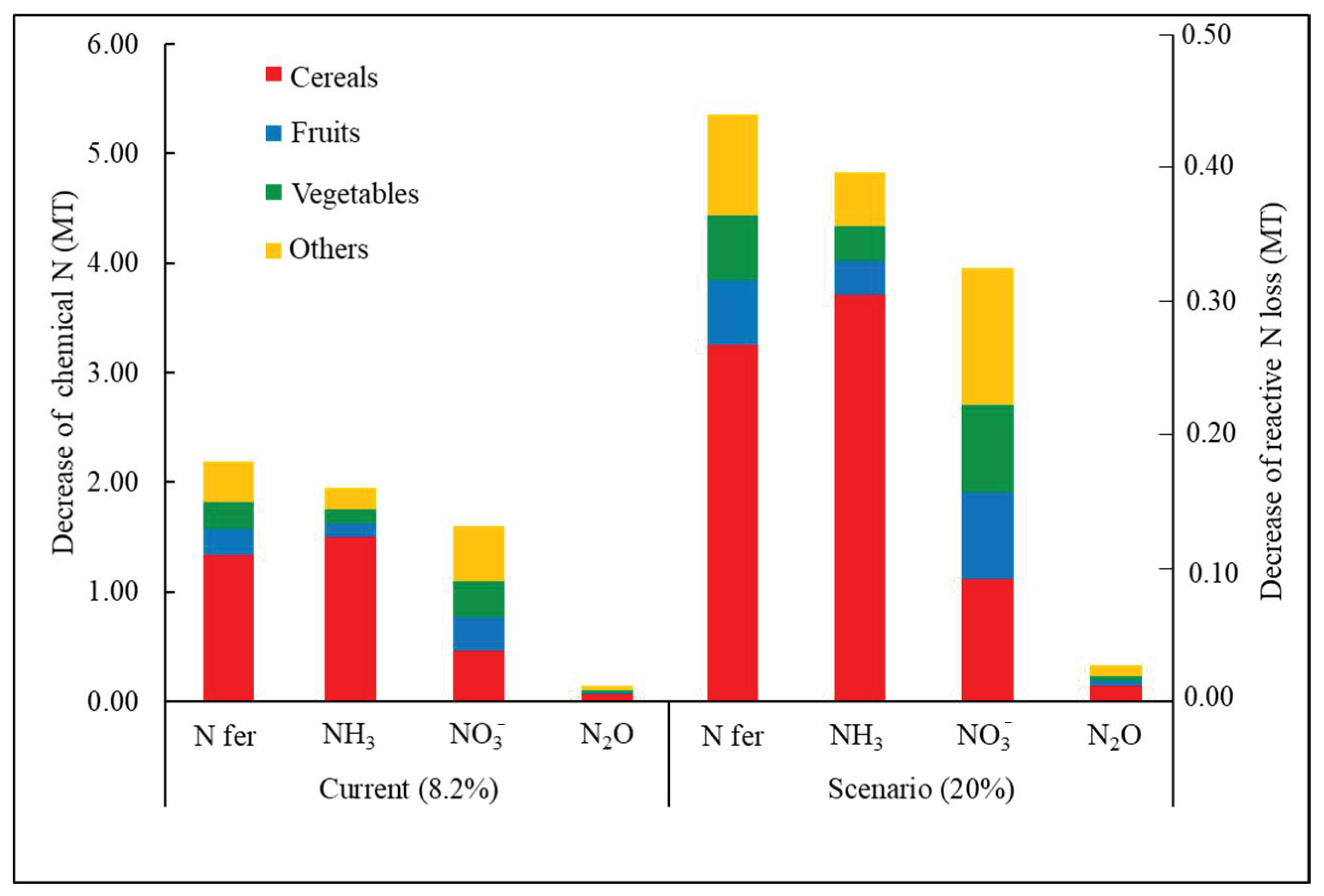
6. Potential and Large-Scale Impact of Green Food Farming Scenario
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, M.S.; Shen, J.B.; Yuan, L.X.; Jiang, R.F.; Zhang, F.S. Improving crop productivity and resource use efficiency to ensure food security and environmental quality in China. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 63, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Sun, J.X.; Sun, S.K.; Yang, F.; Lu, Y.J.; Wang, Y.B.; Wu, F.J.; Liu, P. A comprehensive analysis of regional grain production characteristics in China from the scale and efficiency perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Statistics Division of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Agriculture Database. FAOSTAT. 2018. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC/ (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Ying, H.; Yin, Y.L.; Zheng, H.F.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.S.; Xue, Y.F.; Stefanovski, D.; Cui, Z.L.; Dou, Z.X. Newer and select maize, wheat, and rice varieties can help mitigate N footprint while producing more grain. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 4273–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, C.C.; Ma, W.Q.; Huang, C.D.; Zhang, W.F.; Mi, G.H.; Miao, Y.X.; Li, X.L.; et al. Pursuing sustainable productivity with millions of smallholder farmers. Nature 2018, 555, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.J.; Duan, L.; Mo, J.M.; Du, E.Z.; Shen, J.B.; Lu, X.K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.B.; He, C.N.; Zhang, F.S. Nitrogen deposition and its ecological impact in China: An overview. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2251–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.C.; Liu, X.J.; Hao, T.X.; Zeng, N.F.; Zhang, F.S.; Wim, D.V. Modeling soil acidification in typical Chinese cropping systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, E.P.; Xu, E.Q.; Zhang, H.Q.; Huang, C.H. Temporal-spatial trends in potentially toxic trace element pollution in farmland soil in the major grain-producing regions of China. Sci. Rep. UK 2019, 9, 19463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Zhao, J.; Chang, S.X.; Collins, C.; Xu, J.M.; Liu, X.M. Status assessment and probabilistic health risk modeling of metals accumulation in agriculture soils across China: A synthesis. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.U.; Wen, X.; Xu, J.L.; Zhong, J.H.; Li, X.X. Development and challenges of green food in China. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.J.; Wu, L.H.; Du, L.; Chen, M. Consumers’ purchase intention of organic food in China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Q.; Liu, C.X.; Wang, J.S. Deliberating on renewable and sustainable energy policies in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 17, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.D.; Pieniak, Z.; Verbeke, W. Consumers’ attitudes and behaviour towards safe food in China: A review. Food Control. 2013, 33, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Shoemaker, S.P. Public perception of genetically-modified (GM) food: A Nationwide Chinese Consumer Study. NPJ Sci. Food. 2018, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, C.S. GM crops in the media. GM Crop. Food. 2015, 6, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Drummond, C. Environmental management systems in practice: The experiences of LEAF (Linking Environment and Farming) in meeting the needs of farmers, consumers and environmentalists. Asp. Appl. Biol. 2000, 62, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, C.; Harris, C. Linking Environment and Farming: Integrated Systems for Sustainable Farmland Management. In Sustainable Farmland Management: Transdisciplinary Approaches; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2008; p. 169. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.S.; Chen, X.P.; Vitousek, P. An experiment for the world. Nature 2013, 497, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.L. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese Agricultural Systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.L.; Lam, S.K.; Yan, X.Y.; Chen, D.L. How does recycling of livestock manure in agroecosystems affect crop productivity, reactive nitrogen losses, and soil carbon balance? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7450–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Shao, X.H.; Guan, W.H.; Ren, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.L.; Wu, Q.J. Nitrogen-decreasing and yield-increasing effects of combined applications of organic and inorganic fertilizers under controlled irrigation in a paddy field. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.P.; Yan, S.; Liu, F.; Ji, P.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Tong, Y.A. Effects of chemical fertilizer combined with organic manure on Fuji apple quality, yield and soil fertility in apple orchard on the Loess Plateau of China. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2014, 7, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, Y.X.; Ouyang, X.H.; Hao, J.Q.; Yang, X.S. Comparative environmental impact assessments of green food certified cucumber and conventional cucumber cultivation in China. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2018, 33, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedada, W.; Karltun, E.; Lemenih, M.; Tolera, M. Long-term addition of compost and NP fertilizer increases crop yield and improves soil quality in experiments on smallholder farms. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 195, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, B.; Kalita, B.; Deori, B.; Paul, S. Soil properties under rainfed rice (Oryza sativa L.) crop as affected by integrated supply of nutrients. Int. J. Agric. Innov. Res. 2015, 3, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Tao, R.; Ling, N.; Chu, G.X. Chemical, organic and bio-fertilizer management practices effect on soil physicochemical property and antagonistic bacteria abundance of a cotton field: Implications for soil biological quality. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 167, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.T.; Geng, Y.B.; Liang, T. Optimization of reduced chemical fertilizer use in tea gardens based on the assessment of related environmental and economic benefits. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banger, K.; Kukal, S.S.; Toor, G.; Sudhir, K.; Hanumanthraju, T.H. Impact of long-term additions of chemical fertilizers and farm yard manure on carbon and nitrogen sequestration under rice-cowpea cropping system in semi-arid tropics. Plant Soil 2009, 318, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.H. An estimate of greenhouse gas (N2O and CO2) mitigation potential under various scenarios of nitrogen use efficiency in Chinese croplands. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 2958–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C.Y.; Guan, D.H.; Li, S.M.; Xie, F.L.; Chen, J.F.; Hang, X.N.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, A.X.; et al. Significant residual effects of wheat fertilization on greenhouse gas emissions in succeeding soybean growing season. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 169, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, S.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.X.; Li, X.M.; Ning, P.; Liu, M.Z. Environmentally friendly fertilizers: A review of materials used and their effects on the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Wang, H.Y.; Lei, Q.L.; Luo, J.F.; Lindsey, S.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhai, L.M.; Wu, S.X.; Zhang, J.S.; Liu, X.X.; et al. Optimizing the nitrogen application rate for maize and wheat based on yield and environment on the Northern China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xiong, Z.Q.; Wang, J.Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, Q.W.; Shen, Q.R. Mitigating net global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensities by substituting chemical nitrogen fertilizers with organic fertilization strategies in rice-wheat annual rotation systems in China: A 3-year field experiment. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.J.; Ding, W.X.; Luo, J.F. Nitrous oxide emissions from Chinese maize-wheat rotation systems: A 3-year field measurement. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 65, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaluk, O.; Yatsenko, O.; Zakharchuk, O.; Ovcharenko, A.; Khrystenko, O.; Nitsenko, V. Dynamic Development of the global organic food market and opportunities for Ukraine. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christina, H.; Jing, S.; Alice, G.; Michael, S. The psychology of eating insects: A cross-cultural comparison between Germany and China. Food Qual. Prefer. 2015, 44, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; Van Broekhoven, S.; Van Huis, A.; van Loon, J.J.A. Feed conversion, survival and development, and composition of four insect species on diets composed of food by-products. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, D.; Carrascosa, C.; Oluwole, O.B.; Nieuwland, M.; Saraiva, A.; Millán, R.; Raposo, A. Traditional consumption of and rearing edible insects in Africa, Asia and Europe. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2169–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, A.; Coimbra, A.; Amaral, L.; Gonçalves, A.; Morais, Z. Eating jellyfish: Safety, chemical and sensory properties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 3973–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorsi, G.; Garamella, G.; Cavallo, G.; Lorini, C. A systematic review of risk assessment associated with jellyfish consumption as a potential novel food. Foods 2020, 9, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khong, N.M.; Yusoff, F.M.; Jamilah, B.; Basri, M.; Maznah, I.; Chan, K.W.; Nishikawa, J. Nutritional composition and total collagen content of three commercially important edible jellyfish. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleve, G.; Ramires, A.; Gallo, A. Leone Identification of safety and quality parameters for preparation of jellyfish based novel food products. Foods 2019, 8, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chu, Y.; Xue, Y.; Ying, H.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, W.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Yin, Y.; et al. Outlook of China’s agriculture transforming from smallholder operation to sustainable production. Glob. Food Sec. 2020, 26, 100444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L. Quantitative Analysis of Reactive Nitrogen Losses and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Three Major Grain Crops in China. Ph.D. Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, May 2014. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Wang, G.; Yue, S.; Wu, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X. Closing the N-use efficiency gap to achieve food and environmental security. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5780–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z. Environmental Impacts, Mitigation Potentials and Management Approaches in Chinese Vegetable Production System—Pepper as a Case. Ph.D. Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, May 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.; Zhou, F. Zero Growth of Chemical Fertilizer and Pesticide Use: China’s Objectives, Progress and Challenges. BioOne Complet. 2018, 9, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.Y.; Wu, G.L.; Li, Y.; Li, C.H.; Liu, W.J.; Meng, J.; Liu, H.T.; Yu, X.F.; Jiang, G.M. Effects of cattle manure compost combined with chemical fertilizer on topsoil organic matter, bulk density and earthworm activity in a wheat–maize rotation system in Eastern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 156, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.K.; Khaliq, A.; Shafiq, M.M.; Kazmi, M.; Ali, I. Comparative effectiveness of urea n, poultry manure and their combination in changing soil properties and maize productivity under rainfed conditions in Northeast. Pakistan. Exp. Agric. 2010, 46, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, A.; Schulz, S.; Oyewole, B.; Diels, J.; Tobe, O. The role of cattle manure in enhancing on-farm productivity, macro-and micro-nutrient uptake, and profitability of maize in the Guinea savanna. Exp. Agric. 2008, 44, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Zou, L.; Li, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Peng, M. Rhizosphere soil properties and banana Fusarium wilt suppression influenced by combined chemical and organic fertilizations. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 254, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Jiang, Y.; He, X.; Liu, H.; Yu, K. Increasing organic fertilizer and decreasing drip chemical Fertilizer for two consecutive years improved the fruit quality of ‘Summer Black’ grapes in arid areas. HortScience 2020, 55, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Green Food 1 | Safety Food 2 | CAC 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | ≤0.2 | ≤0.2 | ≤0.2 |
| Cd | ≤0.2 | ≤0.2 | ≤0.4 |
| Aflatoxin B1 | ≤0.005 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.005 |
| Fenitrothion | ≤0.01 | ≤1.0 | ≤0.01 |
| Triazoophos | ≤0.01 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.02 |
| Dimethoate | ≤0.01 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.01 |
| Bisultap | ≤0.01 | ≤0.2 | - |
| Butachlor | ≤0.01 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 |
| Buprofezin | ≤0.3 | ≤0.3 | - |
| Item | Number |
|---|---|
| Product | 36,345 |
| Company | 15,984 |
| Farm | 721 |
| Farmer (million) | 21.7 |
| Cultivation area (million ha) | 11.1 |
| Domestic sales (billion CNY) | 465.7 |
| Export value (billion USD) | 4.1 |
| Technical standards | 15 |
| Product standards | 125 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ishfaq, M.; Zhong, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, X. Green Food Development in China: Experiences and Challenges. Agriculture 2020, 10, 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10120614
Xu J, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Ishfaq M, Zhong J, Li W, Zhang F, Li X. Green Food Development in China: Experiences and Challenges. Agriculture. 2020; 10(12):614. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10120614
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jiuliang, Zhihua Zhang, Xian Zhang, Muhammad Ishfaq, Jiahui Zhong, Wei Li, Fusuo Zhang, and Xuexian Li. 2020. "Green Food Development in China: Experiences and Challenges" Agriculture 10, no. 12: 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10120614
APA StyleXu, J., Zhang, Z., Zhang, X., Ishfaq, M., Zhong, J., Li, W., Zhang, F., & Li, X. (2020). Green Food Development in China: Experiences and Challenges. Agriculture, 10(12), 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10120614