Deciphering the Genetics of Primary Angioedema with Normal Levels of C1 Inhibitor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Patients
2.2. Genotyping
2.3. Variant Pathogenicity Curation
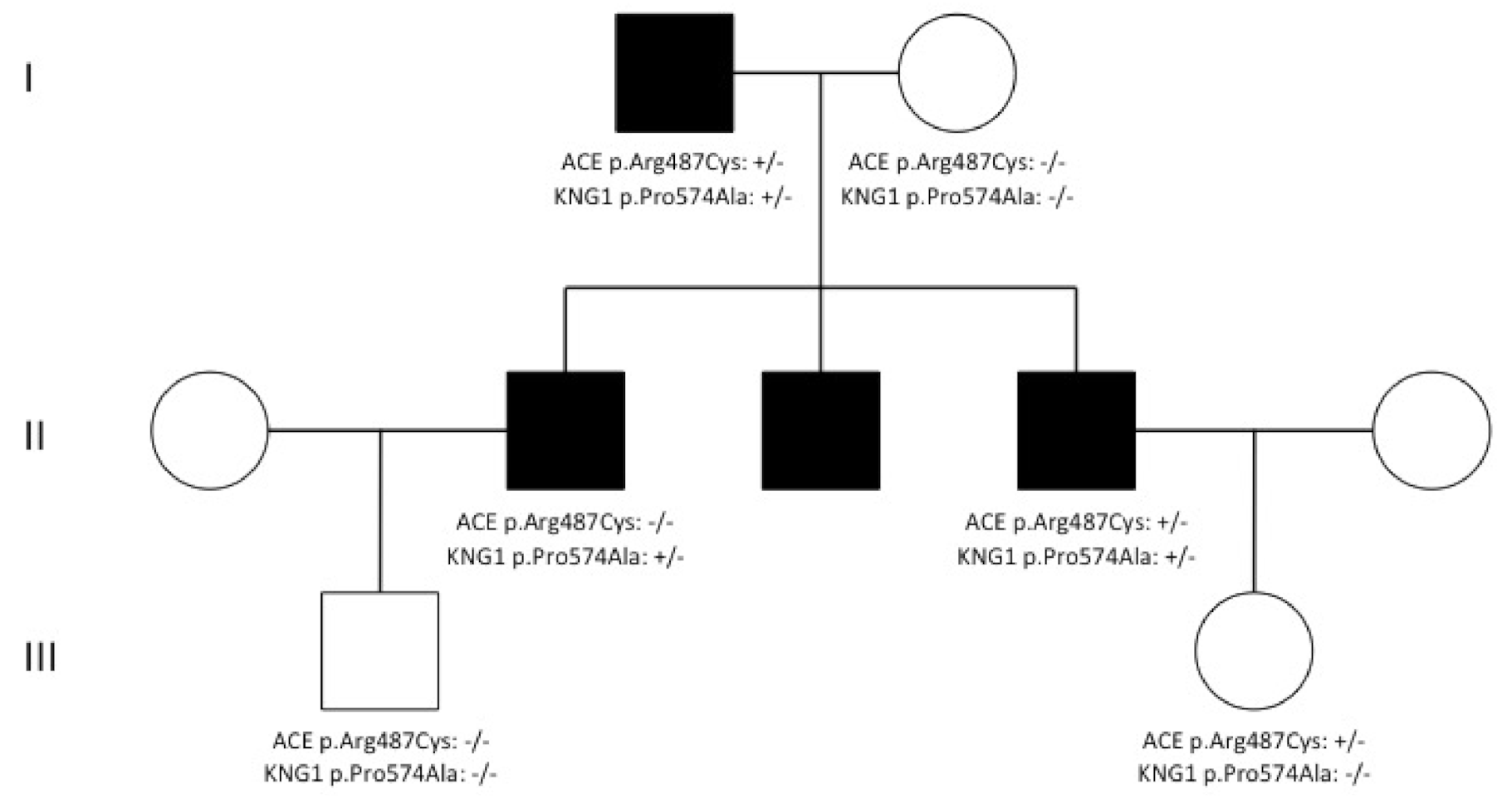
3. Results and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cicardi, M.; Aberer, W.; Banerji, A.; Bas, M.; Bernstein, J.A.; Bork, K.; Caballero, T.; Farkas, H.; Grumach, A.; Kaplan, A.P.; et al. Classification, diagnosis, and approach to treatment for angioedema: Consensus report from the Hereditary Angioedema International Working Group. Allergy 2014, 69, 602–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bork, K.; Davis-Lorton, M. Overview of hereditary angioedema caused by C1-inhibitor deficiency: Assessment and clinical management. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 45, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bork, K. Hereditary angioedema with normal C1 inhibitor. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2013, 33, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bork, K.; Wulff, K.; Witzke, G.; Hardt, J. Hereditary angioedema with normal C1-INH with versus without specific F12 gene mutations. Allergy 2015, 70, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magerl, M.; Germenis, A.E.; Maas, C.; Maurer, M. Hereditary angioedema with normal C1 inhibitor: Update on evaluation and treatment. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2017, 37, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bafunno, V.; Firinu, D.; D’Apolito, M.; Cordisco, G.; Loffredo, S.; Leccese, A.; Bova, M.; Barca, M.P.; Santacroce, R.; Cicardi, M.; et al. Mutation of the angiopoietin-1 gene (ANGPT1) associates with a new type of hereditary angioedema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bork, K.; Wulff, K.; Steinmüller-Magin, L.; Braenne, I.; Staubach-Renz, P.; Witzke, G.; Hardt, J. Hereditary angioedema with a mutation in the plasminogen gene. Allergy 2018, 73, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewald, G. A missense mutation in the plasminogen gene, within the plasminogen kringle 3 domain, in hereditary angioedema with normal C1 inhibitor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 498, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bork, K.; Wulff, K.; Rossmann, H.; Steinmüller-Magin, L.; Braenne, I.; Witzke, G.; Hardt, J. Hereditary angioedema cosegregating with a novel kininogen 1 gene mutation changing the N-terminal cleavage site of bradykinin. Allergy 2019, 74, 2479–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuraw, B.L. Hereditary angioedema with normal C1 inhibitor: Four types and counting. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 884–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Apolito, M.; Santacroce, R.; Colia, A.L.; Cordisco, G.; Maffione, A.B.; Margaglione, M. Angiopoietin-1 haploinsufficiency affects the endothelial barrier and causes hereditary angioedema. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firinu, D.; Loffredo, S.; Bova, M.; Cicardi, M.; Margaglione, M.; Del Giacco, S. The role of genetics in the current diagnostic workup of idiopathic non-histaminergic angioedema. Allergy 2019, 74, 810–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dbSNP. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/SNP/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- ExAC. Available online: http://exac.broadinstitute.org (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- The 1000 Genomes Project Consortium. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinVar. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- HGVS. Available online: http://www.hgvs.org/mutnomen/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- SIFT. Available online: http://sift.jcvi.org/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- PolyPhen-2. Available online: http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Germenis, A.E.; Loules, G.; Zamanakou, M.; Psarros, F.; González-Quevedo, T.; Speletas, M.; Bork, K.; Wulff, K.; Steinmüller-Magin, L.; Braenne, I.; et al. On the pathogenicity of the plasminogen K330E mutation for hereditary angioedema. Allergy 2018, 73, 1751–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recke, A.; Massalme, E.G.; Jappe, U.; Steinmüller-Magin, L.; Schmidt, J.; Hellenbroich, Y.; Hüning, I.; Gillessen-Kaesbach, G.; Zillikens, D.; Hartmann, K. Identification of the recently described plasminogen gene mutation p.Lys330Glu in a family from Northern Germany with hereditary angioedema. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2019, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hedge, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponting, C.P.; Marshall, J.M.; Cederholm-Williams, S.A. Plasminogen: A structural review. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 1992, 3, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regner, K.R.; Riegert-Johnson, D.L.; Volcheck, G.W. Serial measurement of serum tryptase in angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-associated angioedema. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2003, 78, 655–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fok, J.S.; Hissaria, P.; Giri, P.; Heddle, R.; Smith, W. Acquired angioedema with raised serum tryptase. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013, 110, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariano, A.; D’Apolito, M.; Bova, M.; Bellanti, F.; Loffredo, S.; D’Andrea, G.; Intrieri, M.; Petraroli, A.; Maffione, A.B.; Spadaro, G.; et al. A myoferlin gain-of-function variant associates with a new type of hereditary angioedema. Allergy 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Genes | Coding | Amino Acid Change | dbSNP | SIFT | PolyPhen | EMAF | ExAC ENFAF | nl-C1-INH-HAE AF | C1-INH-HAE AF | P1 | P2 | P3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDKRB1 | c.721G>A | p.Gly241Arg | rs45528332 | tolerated | probably damaging | 0.0037 | 0.0052 | 0.0113 | 0.0148 | 0.1500 | 0.0350 | 0.7000 |
| MME | c.674G>C | p.Gly225Ala | rs147564881 | tolerated | probably damaging | 0.0023 | 0.0033 | 0.0113 | 0.0030 | 0.0310 | 0.7400 | 0.2100 |
| PLAUR | c.802A>G | p.Met268Val | rs138492321 | tolerated | possibly damaging | 0.0062 | 0.0045 | 0.0188 | 0.0000 | 0.0440 | 0.1500 | 0.0110 |
| C1S | c.943G>A | p.Asp315Asn | rs117907409 | deleterious | probably damaging | 0.0053 | 0.0052 | 0.0113 | 0.0059 | 0.2400 | 0.8300 | 0.4700 |
| F13B | c.1025T>C | p.Ile342Thr | rs17514281 | deleterious | possibly damaging | 0.0097 | 0.0098 | 0.0263 | 0.0059 | 0.0380 | 0.4900 | 0.0390 |
| F2 | c.*97G>A | rs1799963 | 0.0080 | 0.0263 | 0.0148 | 0.0130 | 0.2600 | 0.3100 | ||||
| TLR4 | c.842G>A | p.Cys281Tyr | rs137853920 | deleterious | probably damaging | 0.0044 | 0.0027 | 0.0150 | 0.0030 | 0.0420 | 0.7900 | 0.1000 |
| KRT1 | c.1669A>G | p.Ser557Gly | rs77846840 | tolerated | benign | 0.0019 | 0.0263 | 0.0296 | 0.8000 | |||
| SERPINE1 | c.*180C>T | rs41334349 | 0.0110 | 0.0226 | 0.0266 | 0.1400 | 0.0400 | 0.7500 | ||||
| AR | c.-207C>A | rs189146053 | 0.0000 | 0.0188 | 0.0030 | <0.0001 | 0.0844 | 0.0500 | ||||
| AR | c.1174C>T | p.Pro392Ser | rs201934623 | tolerated | benign | 0.0000 | 0.0041 | 0.0113 | 0.0000 | 0.0007 | 0.0500 | |
| TPSAB1 | c.407A>G | p.His136Arg | rs201820654 | tolerated | benign | 0.0034 | 0.0113 | 0.0089 | 0.7600 | |||
| TPSG1 | c.508G>A | p.Gly170Arg | rs117769620 | tolerated | benign | 0.0065 | 0.0073 | 0.0188 | 0.0118 | 0.0757 | 0.3893 | 0.4832 |
| ELANE | c.770C>T | p.Pro257Leu | rs17216663 | tolerated | benign | 0.0108 | 0.0080 | 0.0188 | 0.0030 | 0.3062 | 0.1775 | 0.0530 |
| F12 | c.418C>G | p.Leu140Val | rs35515200 | tolerated | possibly damaging | 0.0042 | 0.0033 | 0.0075 | 0.0030 | 0.4533 | 0.7904 | 0.4287 |
| F12 | c.530C>T | p.Ala177Val | rs144821595 | tolerated | benign | 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.0075 | 0.0000 | <0.0001 | 0.7948 | 0.1103 |
| ACE | c.1453C>G | p.Pro485Ala | rs202178737 | deleterious | benign | 0.0000 | 0.0001 | 0.0075 | 0.0000 | 0.0059 | 0.1103 | |
| BDKRB1 | c.844C>T | p.Arg282Ter | rs145322761 | 0.0035 | 0.0038 | 0.0075 | 0.0030 | 0.4533 | 0.7904 | 0.4287 | ||
| PLG | c.266G>A | p.Arg89Lys | rs143079629 | tolerated | benign | 0.0100 | 0.0108 | 0.0075 | 0.0030 | 0.7164 | 0.2177 | 0.4287 |
| KLK3 | c.629C>G | p.Ser210Trp | rs61729813 | deleterious | probably damaging | 0.0110 | 0.0109 | 0.0075 | 0.0178 | 0.6223 | 0.3319 | 0.2748 |
| DPP4 | c.796G>A | p.Val266Ile | rs56179129 | tolerated | benign | 0.0060 | 0.0045 | 0.0075 | 0.0000 | 0.7755 | 0.1547 | 0.1103 |
| PLAU | c.1048T>C | p.Tyr350His | rs72816325 | deleterious | probably damaging | 0.0058 | 0.0059 | 0.0075 | 0.0000 | 0.7755 | 0.1547 | 0.1103 |
| PLAUR | c.-87C>T | rs147665588 | 0.0060 | 0.0075 | 0.0089 | 0.7755 | 0.5702 | 0.8550 | ||||
| F13A1 | c.1730C>T | p.Thr577Met | rs143711562 | tolerated | benign | 0.0029 | 0.0020 | 0.0075 | 0.0000 | 0.2930 | 0.3149 | 0.1103 |
| TNF | c.251C>T | p.Pro84Leu | rs4645843 | tolerated | benign | 0.0030 | 0.0028 | 0.0075 | 0.0030 | 0.2930 | 0.9945 | 0.4287 |
| GPER1 | c.14C>T | p.Ser5Phe | rs117290655 | tolerated | benign | 0.0048 | 0.0045 | 0.0075 | 0.0089 | 0.6173 | 0.4193 | 0.8550 |
| MPO | c.2031-2A>C | rs35897051 | 0.0072 | 0.0071 | 0.0075 | 0.0059 | 0.9227 | 0.8391 | 0.8096 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loules, G.; Parsopoulou, F.; Zamanakou, M.; Csuka, D.; Bova, M.; González-Quevedo, T.; Psarros, F.; Porebski, G.; Speletas, M.; Firinu, D.; et al. Deciphering the Genetics of Primary Angioedema with Normal Levels of C1 Inhibitor. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113402
Loules G, Parsopoulou F, Zamanakou M, Csuka D, Bova M, González-Quevedo T, Psarros F, Porebski G, Speletas M, Firinu D, et al. Deciphering the Genetics of Primary Angioedema with Normal Levels of C1 Inhibitor. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(11):3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113402
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoules, Gedeon, Faidra Parsopoulou, Maria Zamanakou, Dorottya Csuka, Maria Bova, Teresa González-Quevedo, Fotis Psarros, Gregor Porebski, Matthaios Speletas, Davide Firinu, and et al. 2020. "Deciphering the Genetics of Primary Angioedema with Normal Levels of C1 Inhibitor" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 11: 3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113402
APA StyleLoules, G., Parsopoulou, F., Zamanakou, M., Csuka, D., Bova, M., González-Quevedo, T., Psarros, F., Porebski, G., Speletas, M., Firinu, D., del Giacco, S., Suffritti, C., Makris, M., Vatsiou, S., Zanichelli, A., Farkas, H., & Germenis, A. E. (2020). Deciphering the Genetics of Primary Angioedema with Normal Levels of C1 Inhibitor. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(11), 3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113402








