Dietary Fucoxanthin Induces Anoikis in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma by Suppressing Integrin Signaling in a Murine Colorectal Cancer Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Cell Culture
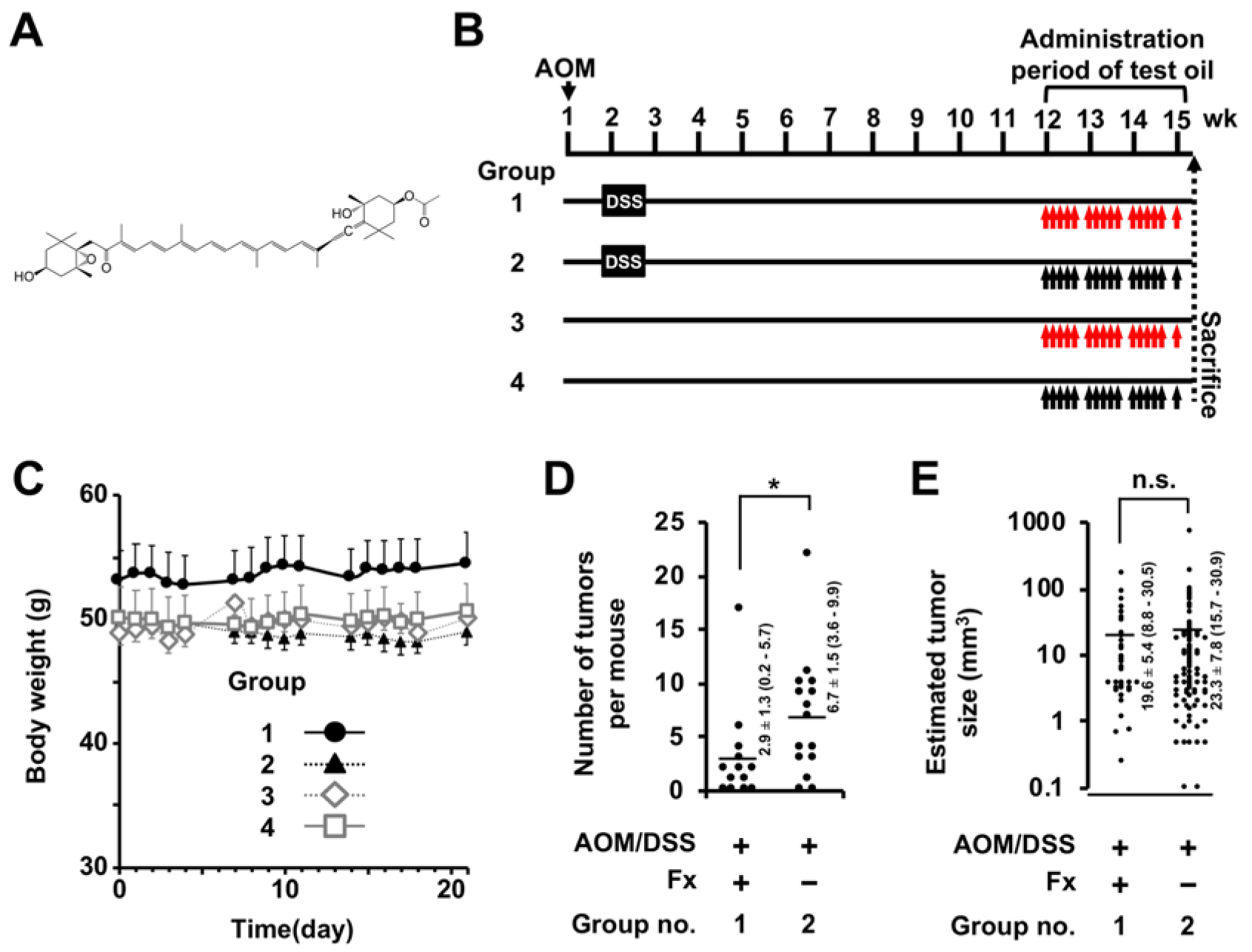
2.2. Animal Experiments
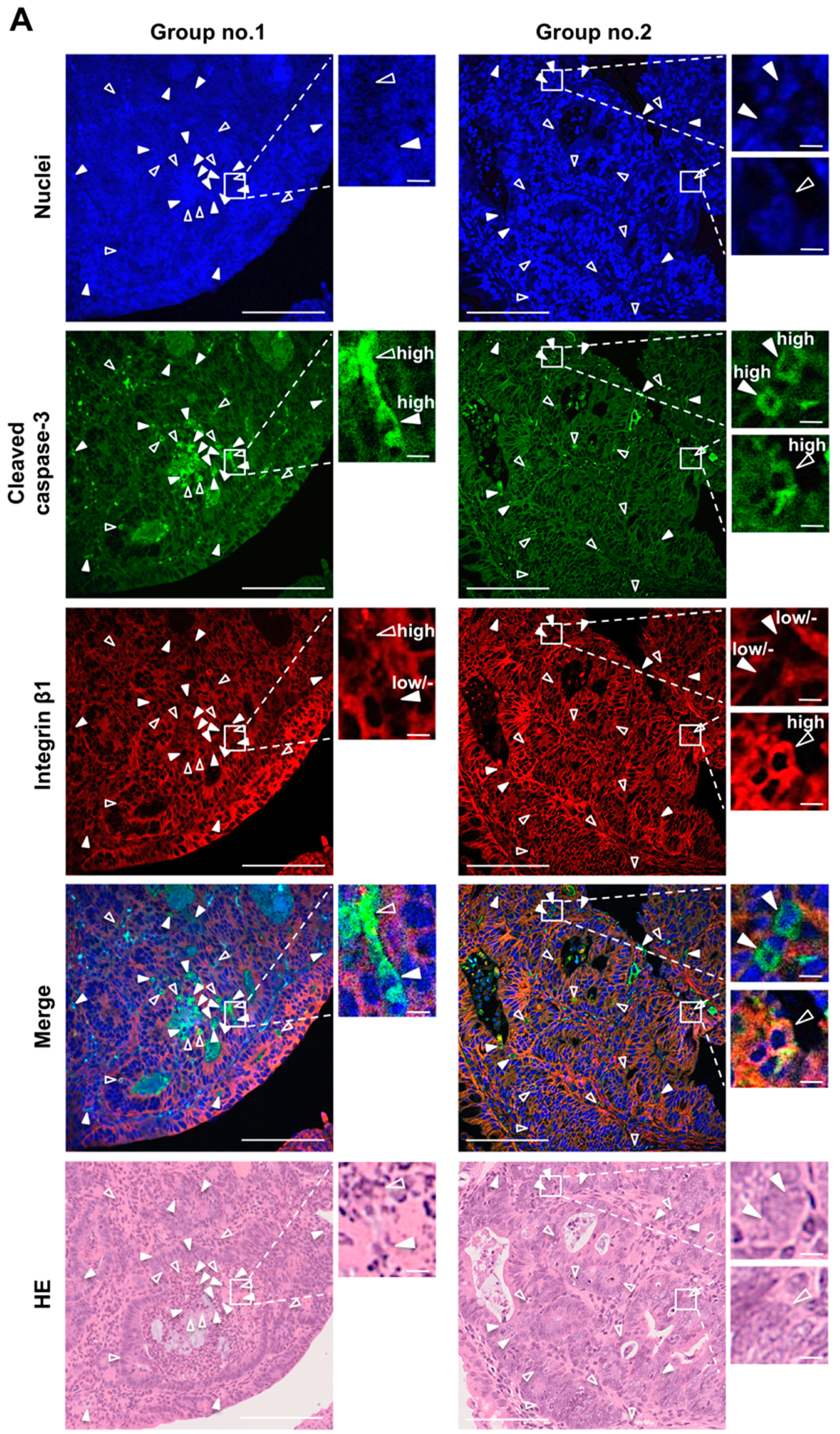
2.3. Fluorescence Immunohistochemistry on Anoikis-Inducing Cells
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Cell Viability
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
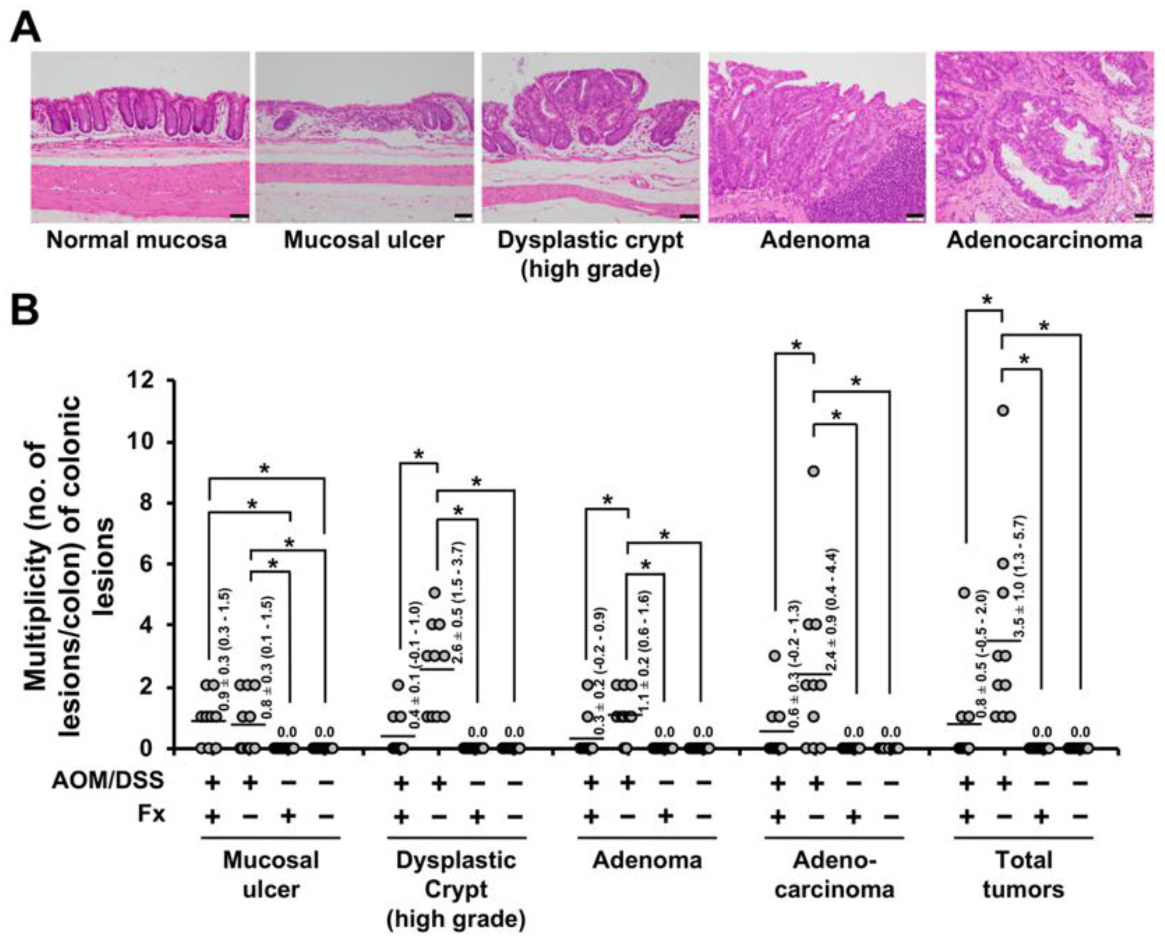
3.1. Histopathological Findings
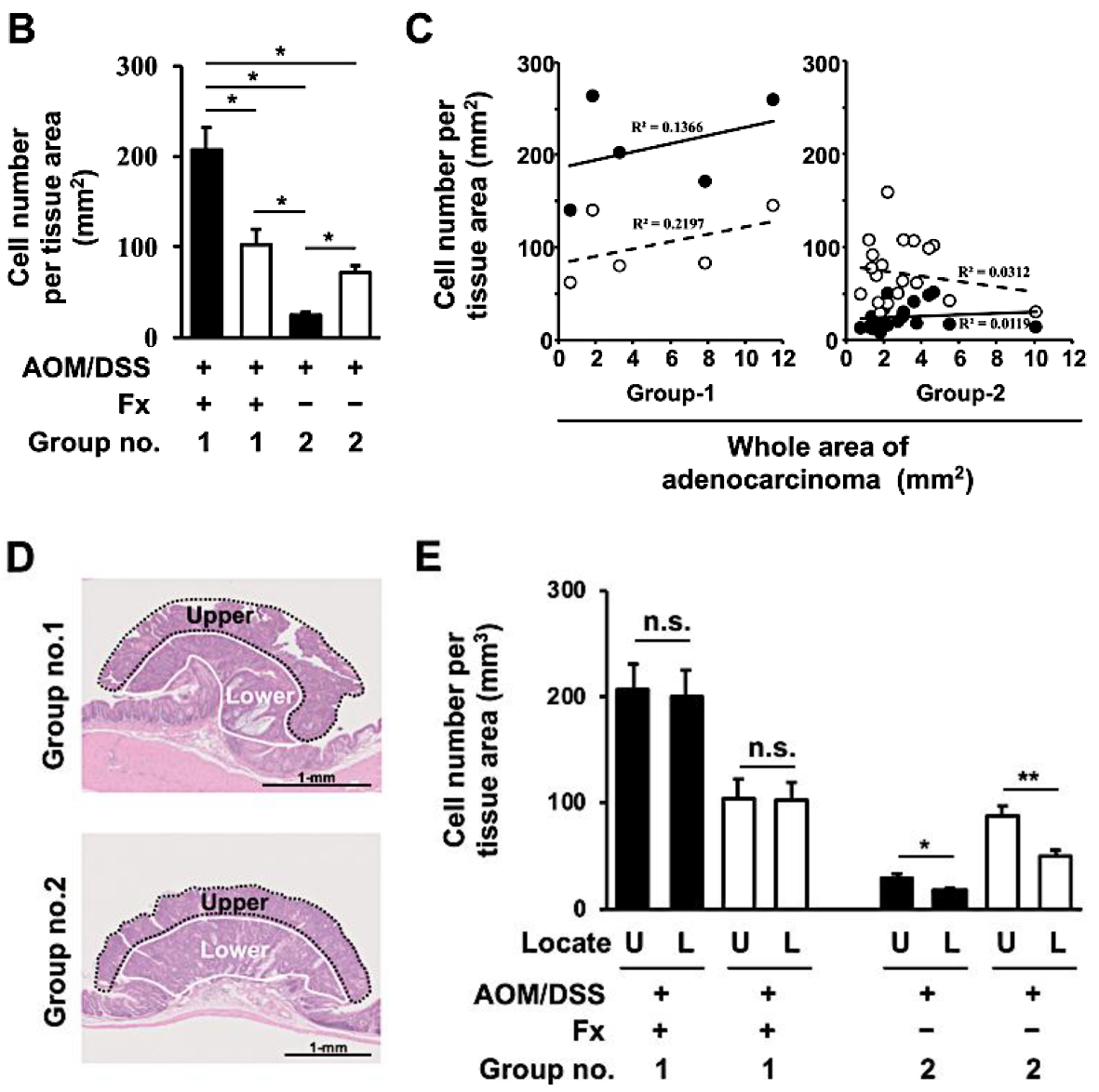
3.2. Enhancement of Anoikis Induction in Colonic Adenocarcinoma and Mucosal Crypts by Fx
3.3. Protein Expression and Activation Related to Integrin Signaling in Colonic Normal Mucosa and Tumor by Fx
3.4. Effect of Fucoxanthinol in DLD-1 Cells Using the Culture Supernatant of Fibroblast MRC-5 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buchheit, C.L.; Weigel, K.J.; Schafer, Z.T. Cancer cell survival during detachment from the ECM: Multiple barriers to tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horbinski, C.; Mojesky, C.; Kyprianou, N. Live free or die: Tales of homeless (cell) in cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoli, P.; Giannoni, E.; Chiarugi, P. Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2013, 1833, 3481–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whilding, L.M.; Vallath, S.; Maher, J. The integrin αvβ6: A novel target for CAR T-cell immunotherapy? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Franceschi, N.; Hamidi, H.; Alanko, J.; Sahgal, P.; Ivaska, J. Integrin traffic-the update. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desgrosellier, J.S.; Cheresh, D.A. Integrins in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Guan, J.L. Signal transduction by focal adhesion kinase in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009, 28, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alday-Parejo, B.; Stupp, R.; Rüegg, C. Are integrins still practicable targets for anti-cancer therapy? Cancers 2019, 11, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weekes, C.D.; Rosen, L.S.; Capasso, A.; Wong, K.M.; Ye, W.; Anderson, M.; McCall, B.; Fredrickson, J.; Wakshull, E.; Eppler, S.; et al. Phase I study of the anti-α5β1 monoclonal antibody MINT1526A with or without bevacizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 82, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, T.; Yang, J.C.; Shitara, K.; Naito, Y.; Cheng, A.L.; Sarashina, A.; Pronk, L.C.; Takeuchi, Y.; Lin, C.C. Phase I study of the focal adhesion kinase inhibitor BI 853520 in Japanese and Taiwanese patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors. Target Oncol. 2019, 14, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.C.; Gan, H.K.; Blagden, S.P.; Plummer, R.; Arkenau, H.T.; Ranson, M.; Evans, T.R.; Zalcman, G.; Bahleda, R.; Hollebecque, A.; et al. A phase I, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of GSK2256098, a focal adhesion kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 2268–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzmaier, F.J.; Jean, C.; Schlaepfer, D.D. FAK in cancer: Mechanistic findings and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raab-Westphal, S.; Marshall, J.F.; Goodman, S.L. Integrins as therapeutic targets: Successes and cancers. Cancers 2017, 9, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, R.G.; Lund, E.K.; Latham, P.; Pinder, A.C.; Johnson, I.T. Effect of eicosapentaenoic acid on the proliferation and incidence of apoptosis in the colorectal cell line HT29. Lipids 1999, 34, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchsaka, P.; Chaotham, C.; Chanvorachote, P. α-Lipoic acid sensitizes lung cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents and anoikis via integrin β1/β3 downregulation. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnat, M.A.; Pervin, M.; Lim, J.H.; Lim, B.O. Apigenin attenuates melanoma cell migration by inducing anoikis through integrin and focal adhesion kinase inhibition. Molecules 2015, 20, 21157–21166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Araki, S.; Kim, D.J.; Park, C.B.; Takasuka, N.; Baba-Toriyama, H.; Ota, T.; Nir, Z.; Khachik, F.; Shimidzu, N.; et al. Chemopreventive effects of carotenoids and curcumins on mouse colon carcinogenesis after 1,2-dimethylhydrazine initiation. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, H.; Murakoshi, M.; Tokuda, H.; Satomi, Y. Cancer prevention by carotenoids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 483, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori, K.; Ohgami, K.; Ilieva, I.; Jin, X.H.; Koyama, Y.; Miyashita, K.; Yoshida, K.; Kase, S.; Ohno, S. Effects of fucoxanthin on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Eye Res. 2005, 81, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitoe, S.; Shimoda, H. Seaweed fucoxanthin supplementation improves obesity parameters in mild obese Japanese subjects. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2017, 7, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, N.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K.; Sohma, H.; Ito, Y.M.; Kokai, Y. Reduction of HbA1c levels by fucoxanthin-enriched akamoku oil possibly involves the thrifty allele of uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1): A randomised controlled trial in normal-weight and obese Japanese adults. J. Nutr. Sci. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beppu, F.; Niwano, Y.; Tsukui, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Single and repeated oral dose toxicity study of fucoxanthin (FX), a marine carotenoid, in mice. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 34, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iio, K.; Okada, Y.; Ishikura, M. Single and 13-week oral toxicity study of fucoxanthin oil from microalgae in rats. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi J. Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 52, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Qiu, S.; Shao, N.; Zheng, J. Fucoxanthin and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) synergistically promotes apoptosis of human cervical cancer cells by targeting PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2018, 24, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.X.; Yu, R.T.; Liu, Z. Inhibition of two gastric cancer cell lines induced by fucoxanthin involves downregulation of Mcl-1 and STAT3. Hum. Cell 2018, 31, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, C.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, L.; Ming, J.; Zeng, F.; Xu, R. Antitumor effects of Laminaria extract fucoxanthin of lung cancer. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Bai, M.; Dai, Y. Fucoxanthin activates apoptosis via inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and suppresses invasion and migration by restriction of p38-MMP-2/9 pathway in human glioblastoma cells. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 2728–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotake-Nara, E.; Terasaki, M.; Nagao, A. Characterization of apoptosis induced by fucoxanthin in human promyelocytic leukemia cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, M.; Kudo, M.; Maeda, H.; Kohno, H.; Tanaka, T.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin induces apoptosis and enhances the anti-proliferative effect of the PPARγ ligand, troglitazone, on colon cancer cell. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2004, 1675, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, M.; Maeda, H.; Miyashita, K.; Mutoh, M. Induction of anoikis in human colorectal cancer cells by fucoxanthinol. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, M.; Iida, T.; Kikuchi, F.; Tamura, K.; Endo, T.; Kuramitsu, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Maeda, H.; Miyashita, K.; Mutoh, M. Fucoxanthin potentiates anoikis in colon mucosa and prevents carcinogenesis in AOM/DSS model mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 64, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; de Azevedo, M.B.; Durán, N.; Alderete, J.B.; Epifano, F.; Genovese, S.; Tanaka, M.; Curini, M. Colorectal cancer chemoprevention by 2 beta-cyclodextrin inclusion compounds of auraptene and 4’-geranyloxyferulic acid. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, H.; Suzuki, R.; Curini, M.; Epifano, F.; Maltese, F.; Gonzales, S.P.; Tanaka, T. Dietary administration with prenyloxycoumarins, auraptene and collinin, inhibits colitis-related colon carcinogenesis in mice. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 2936–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deakin, N.O.; Pignatelli, J.; Turner, C.E. Diverse roles for the paxillin family of proteins in cancer. Genes Cancer 2012, 3, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terasaki, M.; Masaka, S.; Fukada, C.; Houzaki, M.; Endo, T.; Tanaka, T.; Maeda, H.; Miyashita, K.; Mutoh, M. Salivary glycine is a significant predictor for the attenuation of polyp and tumor microenvironment formation by fucoxanthin in AOM/DSS mice. In Vivo 2019, 33, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegboyega, P.A.; Mifflin, R.C.; DiMari, J.F.; Saada, J.I.; Powell, D.W. Immunohistochemical study of myofibroblasts in normal colonic mucosa, hyperplastic polyps, and adenomatous colorectal polyps. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2002, 126, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, D.; Miyake, T.; Shimizu, T.; Sonoda, H.; Mukaisho, K.I.; Tokuda, A.; Ueki, T.; Sugihara, H.; Tani, M. Fibrosis in metastatic lymph nodes is clinically correlated to poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 29574–29586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Zeisberg, M. Fibroblasts in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuchel, S.; Anderle, P.; Werfelli, P.; Diamantis, E.; Rüegg, C. Fibroblast surface-associated FGF-2 promotes contact-dependent colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion through FGFR-SRC signaling and integrin αvβ5-mediated adhesion. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 14300–14317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, C.; Lock, R.; Gao, S.; Salas, E.; Debnath, J. Induction of autophagy during extracellular matrix detachment promotes cell survival. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E. Entosis: It’s a cell-eat-cell world. Cell 2007, 131, 840–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Frederick, A.M.; Jin, Y.; Guo, C.; Xiao, H.; Wood, R.J.; Liu, Z. The prevention of a high dose of vitamin D or its combination with sulforaphane on intestinal inflammation and tumorigenesis in Apc1638N mice fed a high-fat diet. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, 1800824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, F.; Wang, G.; Yang, T.; Wei, D.; Guo, L.; Xiao, H. Induction of entosis in prostate cancer cells by nintedanib and its therapeutic implications. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 3151–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
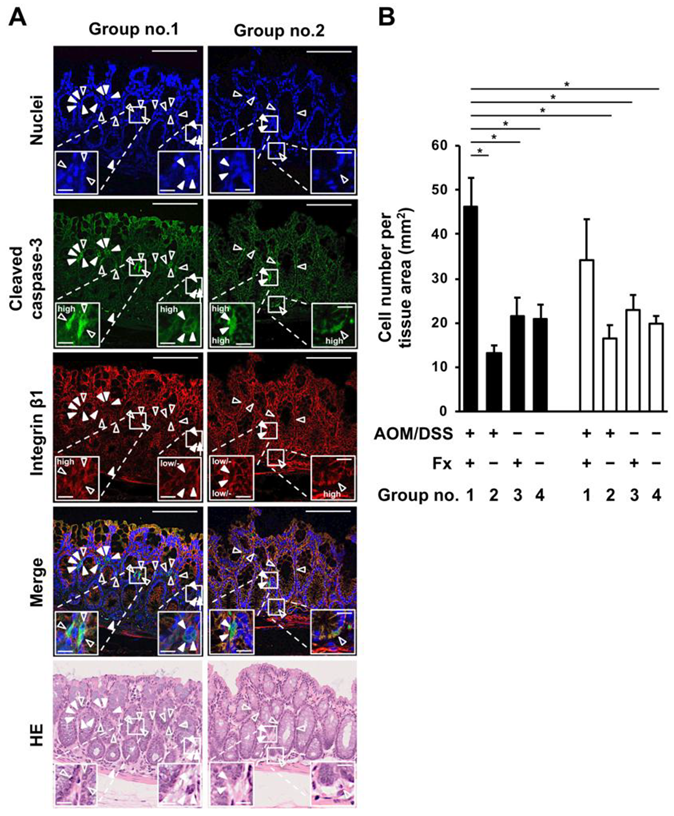
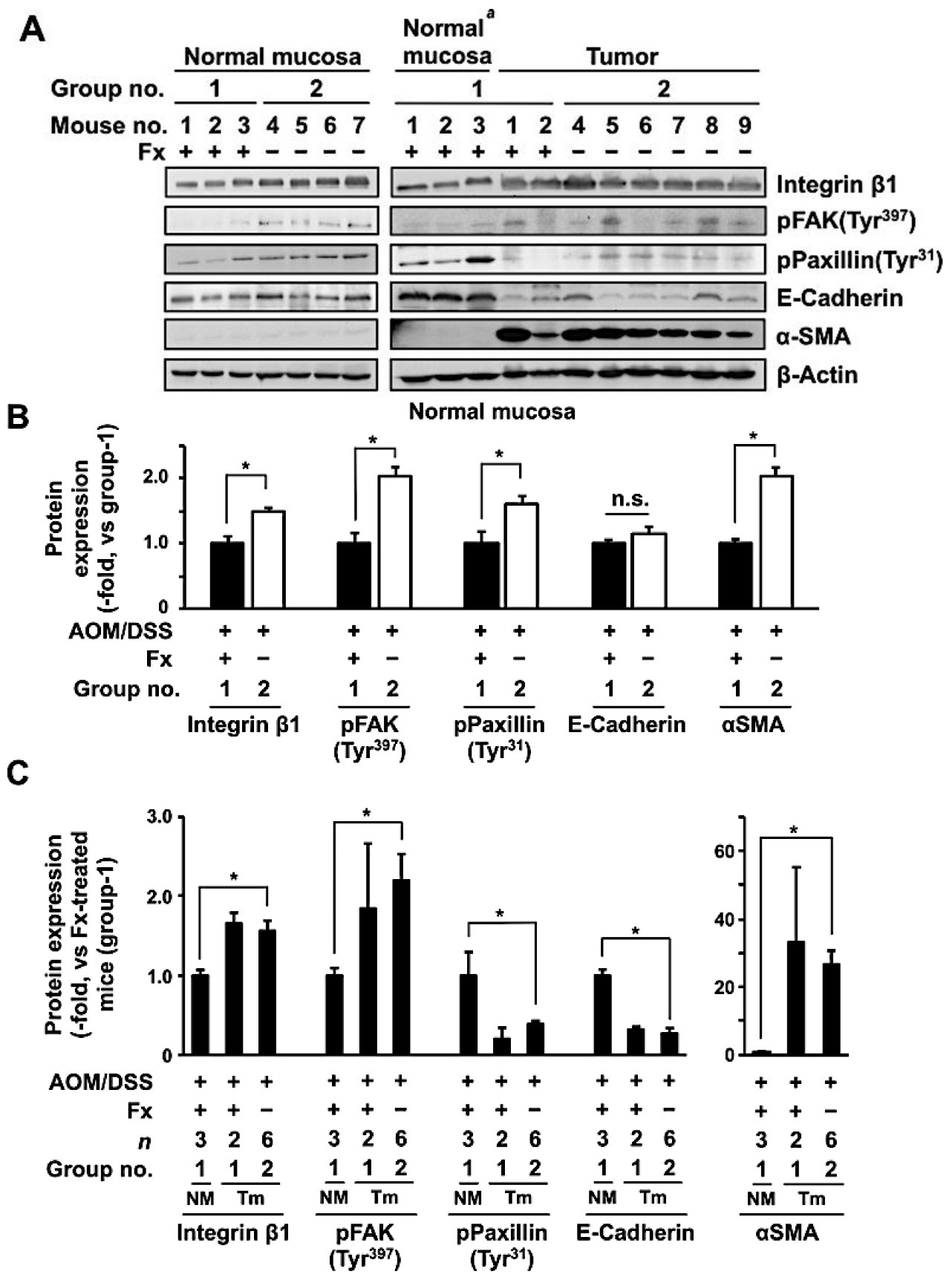

| Group No. | Treatment | Mucosal Ulcer 2 | Dysplastic Crypts | Adenoma | Adenocarcinoma | Total Tumors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AOM-DSS, Fx 30 mg/kg bw | 67% | 33% ** | 22% * | 33% | 33% ** |
| 2 | AOM-DSS | 50% | 100% | 80% | 70% | 100% |
| 3 | Fx 30 mg/kg bw | 0% * | 0% ***** | 0% *** | 0% ** | 0% ***** |
| 4 | None | 0% * | 0% ***** | 0% *** | 0% ** | 0% ***** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Terasaki, M.; Ikuta, M.; Kojima, H.; Tanaka, T.; Maeda, H.; Miyashita, K.; Mutoh, M. Dietary Fucoxanthin Induces Anoikis in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma by Suppressing Integrin Signaling in a Murine Colorectal Cancer Model. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010090
Terasaki M, Ikuta M, Kojima H, Tanaka T, Maeda H, Miyashita K, Mutoh M. Dietary Fucoxanthin Induces Anoikis in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma by Suppressing Integrin Signaling in a Murine Colorectal Cancer Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(1):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010090
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerasaki, Masaru, Mimori Ikuta, Hiroyuki Kojima, Takuji Tanaka, Hayato Maeda, Kazuo Miyashita, and Michihiro Mutoh. 2020. "Dietary Fucoxanthin Induces Anoikis in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma by Suppressing Integrin Signaling in a Murine Colorectal Cancer Model" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 1: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010090
APA StyleTerasaki, M., Ikuta, M., Kojima, H., Tanaka, T., Maeda, H., Miyashita, K., & Mutoh, M. (2020). Dietary Fucoxanthin Induces Anoikis in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma by Suppressing Integrin Signaling in a Murine Colorectal Cancer Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(1), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010090









