Managing Status Epilepticus in the Older Adult
Abstract
:1. Introduction
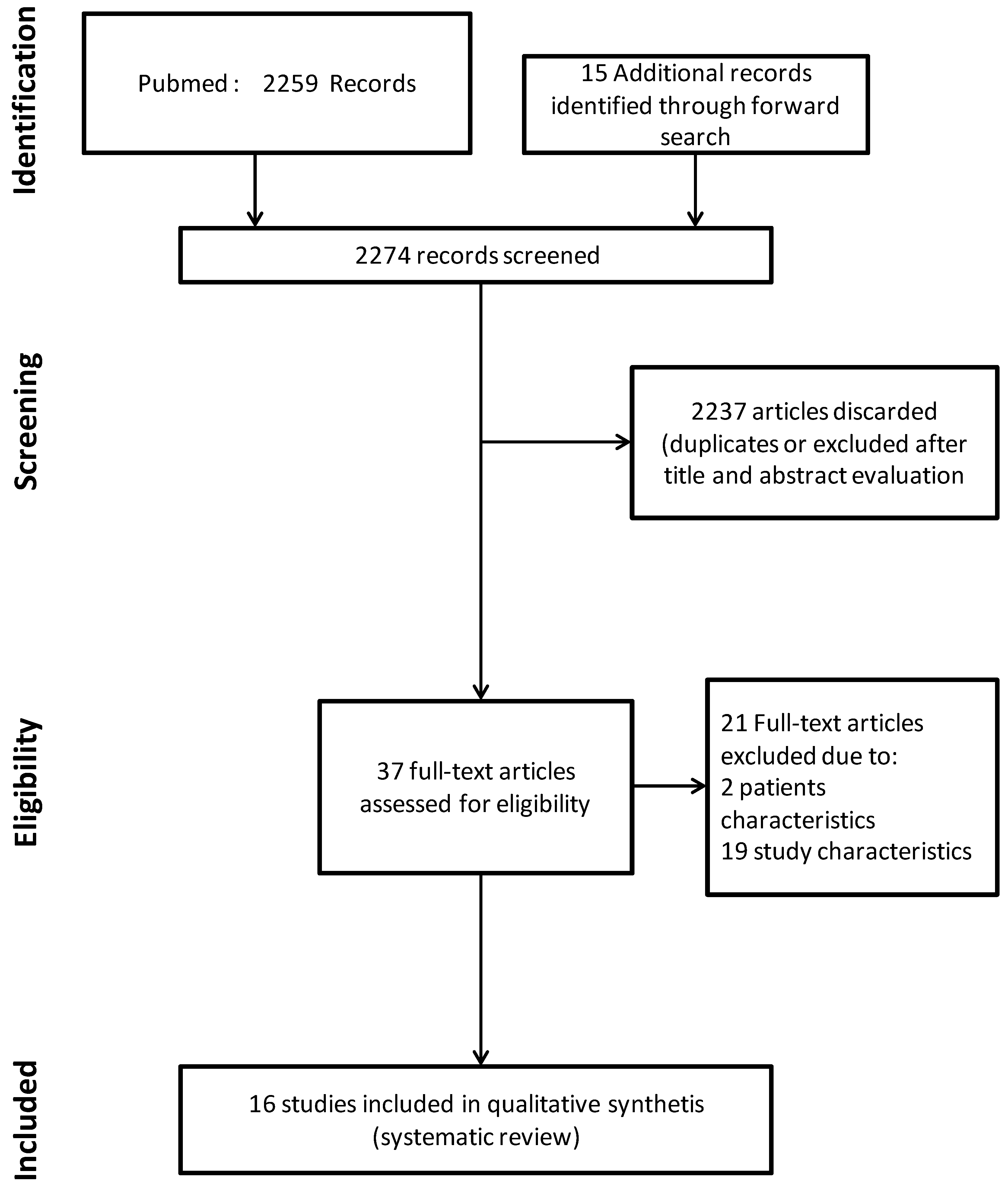
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Definitions
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Study Selection and Data Extraction
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. What Is the Epidemiology of Status Epilepticus in the Older Adults?
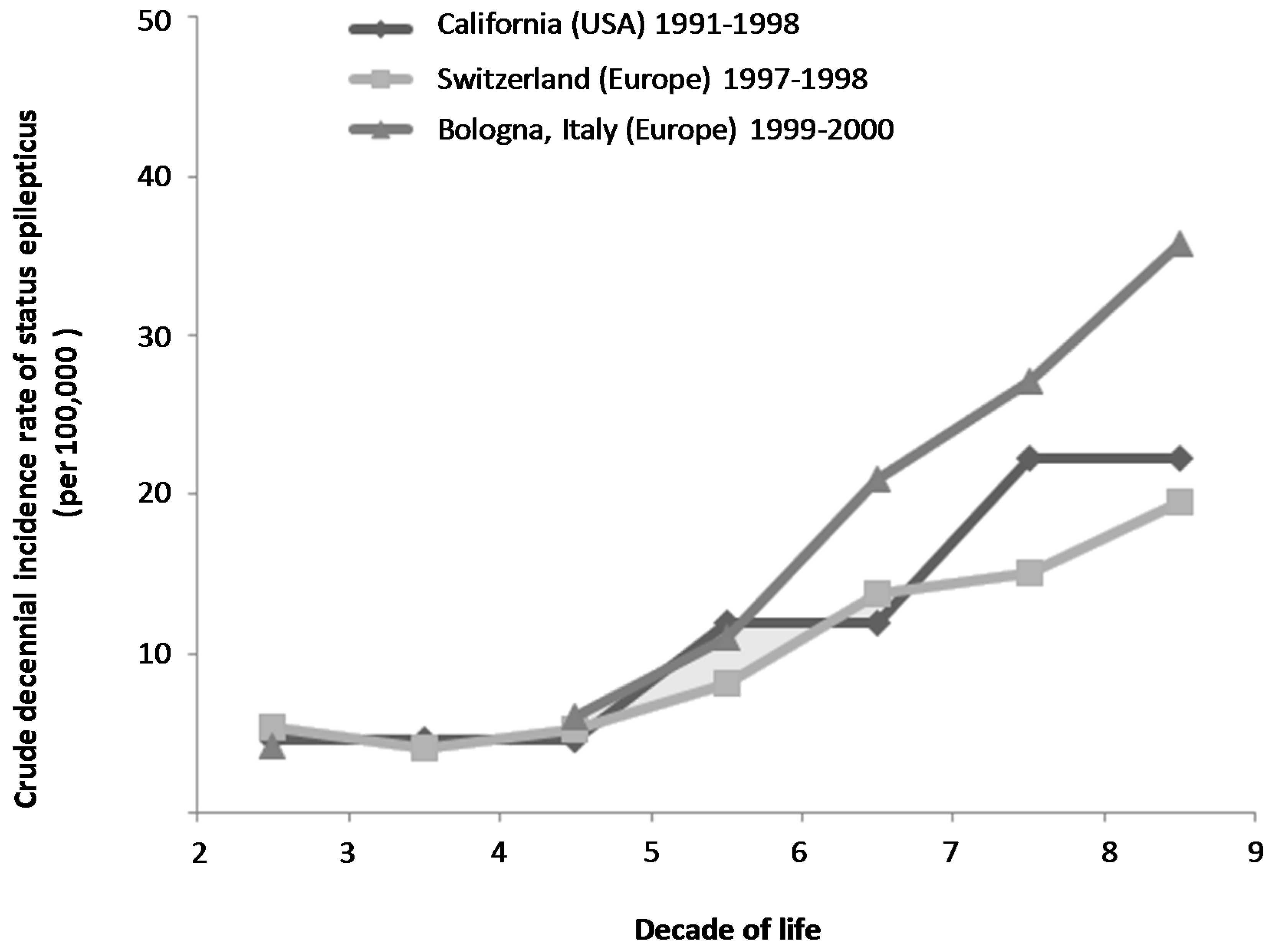
3.1.1. Incidence
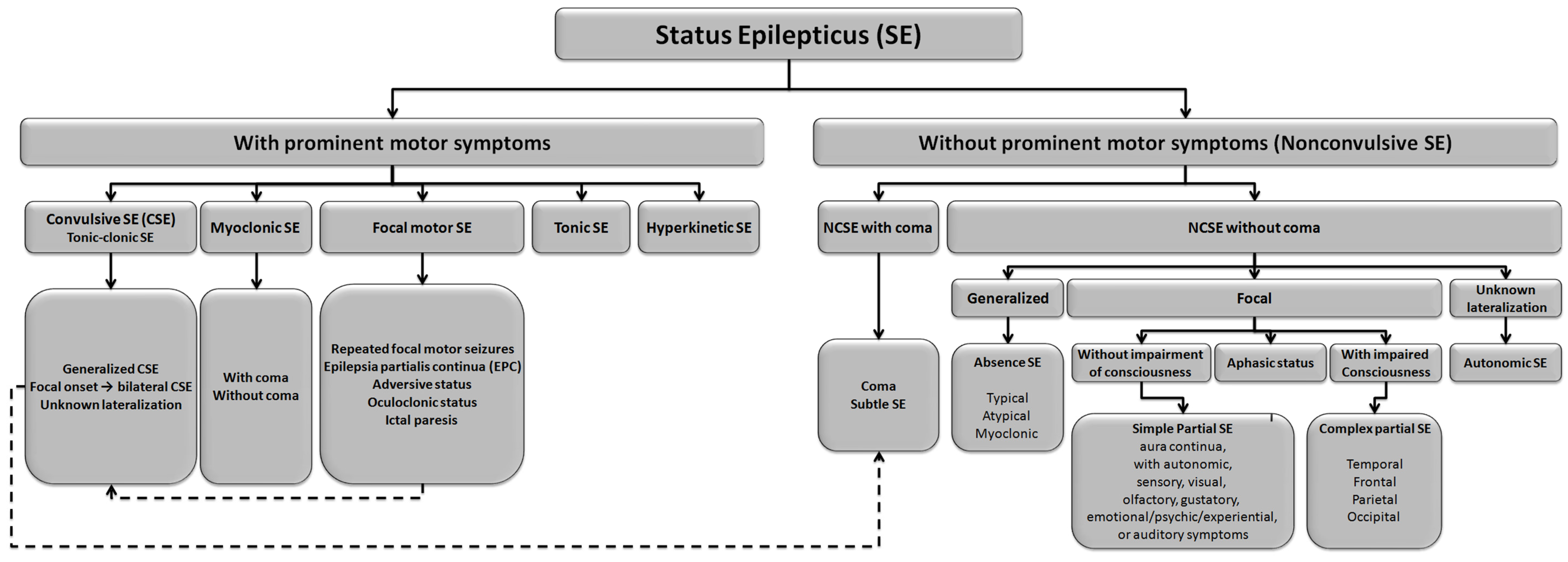
3.1.2. Classification
3.1.3. Mortality, Morbidity, and Determinants of Outcome after SE in the Older Adult
3.2. How Should Status Epilepticus Be Managed in the Older Adult Patient?
3.2.1. Diagnosis of Status Epilepticus
3.2.2. Differential Diagnosis of Status Epilepticus in the Older Adult
3.2.3. Predictors of SE Occurrence in the Older Adult
3.2.4. Therapeutic Management of SE in the Older Adult
3.2.5. Therapeutic Considerations in the Older Adults
3.2.6. Treatment Strategies in Status Epilepticus
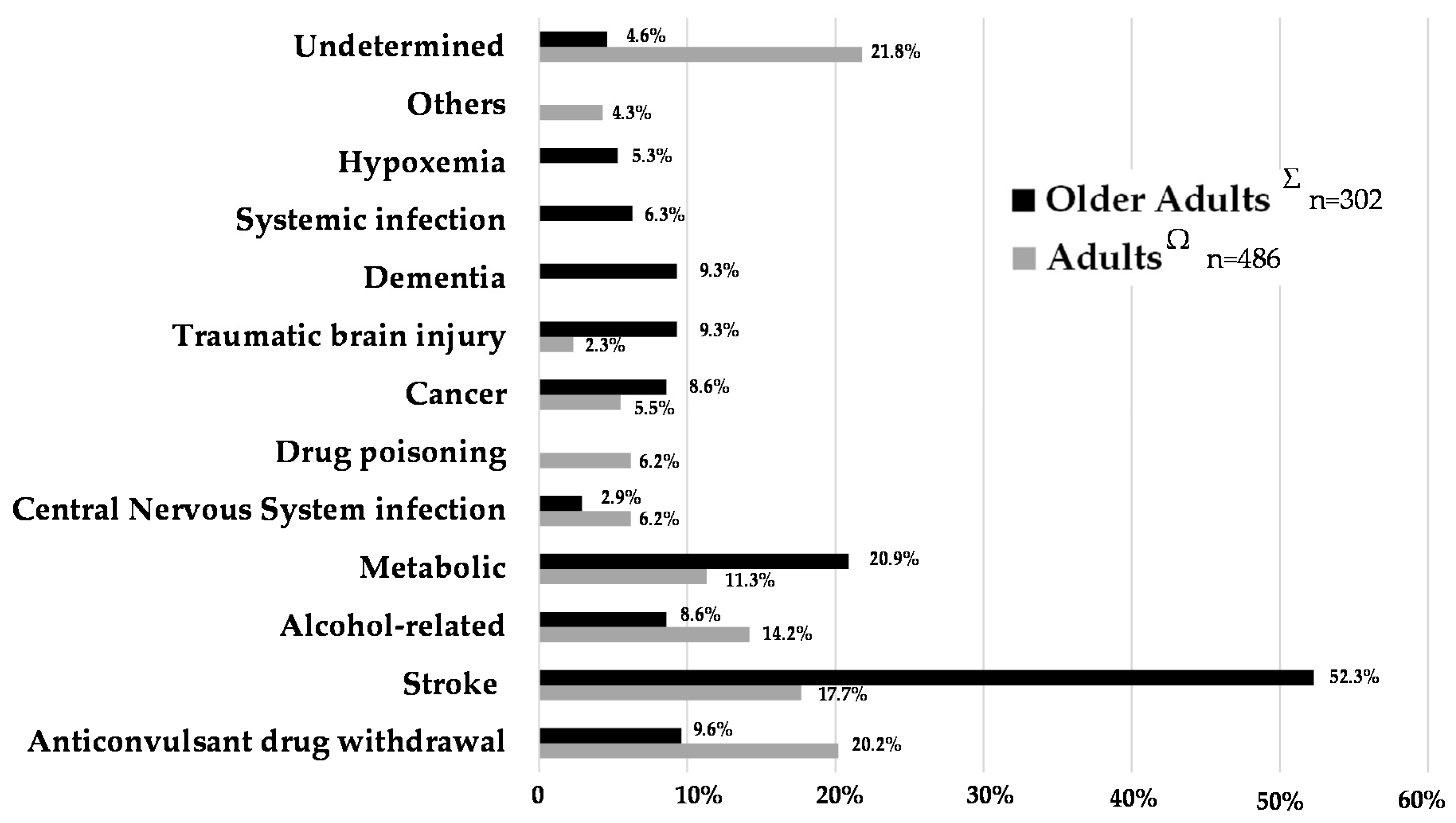
3.2.7. Etiological Investigations of Status Epilepticus in the Older Adult
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Status Epilepticus (SE) |
| Glasgow Outcomes Scale (GOS) |
| Electroencephalogram (EEG) |
| Modified Rankin Scale (mRS) |
| Convulsive Status Epilepticus (CSE) |
| NonConvulsive Status Epilepticus (NCSE) |
| Positive Predictive Value (PPV) |
References
- Betjemann, J.P.; Lowenstein, D.H. Status epilepticus in adults. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, R.F.; Neville, B.G.; Scott, R.C. A systematic review of the epidemiology of status epilepticus. Eur. J. Neurol. 2004, 11, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brophy, G.M.; Bell, R.; Claassen, J.; Alldredge, B.; Bleck, T.P.; Glauser, T.; Laroche, S.M.; Riviello, J.J., Jr.; Shutter, L.; Sperling, M.R.; et al. Guidelines for the evaluation and management of status epilepticus. Neurocritical Care 2012, 17, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Indicators for the minimum data set project on ageing: A critical review in sub-saharan africa. Dar es salaam, Tanzania. 21–22 June. In Epidemiology and Burden of Disease; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001.
- Hauser, W.A. Seizure disorders: The changes with age. Epilepsia 1992, 33 (Suppl. S4), S6–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, H.; Shorvon, S.; Tallis, R. Age-specific incidence and prevalence rates of treated epilepsy in an unselected population of 2,052,922 and age-specific fertility rates of women with epilepsy. Lancet 1998, 352, 1970–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dham, B.S.; Hunter, K.; Rincon, F. The epidemiology of status epilepticus in the united states. Neurocritical Care 2014, 20, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coeytaux, A.; Jallon, P.; Galobardes, B.; Morabia, A. Incidence of status epilepticus in french-speaking switzerland: (Epistar). Neurology 2000, 55, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesdorffer, D.C.; Logroscino, G.; Cascino, G.; Annegers, J.F.; Hauser, W.A. Incidence of status epilepticus in rochester, Minnesota, 1965–1984. Neurology 1998, 50, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignatelli, L.; Tonon, C.; D’Alessandro, R.; Bologna Group for the Study of Status Epilepticus. Incidence and short-term prognosis of status epilepticus in adults in Bologna, Italy. Epilepsia 2003, 44, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M. Status epilepticus: An evidence based guide. BMJ 2005, 331, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinka, E.; Cock, H.; Hesdorffer, D.; Rossetti, A.O.; Scheffer, I.E.; Shinnar, S.; Shorvon, S.; Lowenstein, D.H. A definition and classification of status epilepticus—Report of the ilae task force on classification of status epilepticus. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canoui-Poitrine, F.; Bastuji-Garin, S.; Alonso, E.; Darcel, G.; Verstichel, P.; Caillet, P.; Paillaud, E. Risk and prognostic factors of status epilepticus in the elderly: A case-control study. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litt, B.; Wityk, R.J.; Hertz, S.H.; Mullen, P.D.; Weiss, H.; Ryan, D.D.; Henry, T.R. Nonconvulsive status epilepticus in the critically ill elderly. Epilepsia 1998, 39, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towne, A.R. Epidemiology and outcomes of status epilepticus in the elderly. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2007, 81, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.T.; Sheu, S.M.; Tsai, C.F.; Wong, Y.S.; Chen, S.C. Age-dependent sex difference of the incidence and mortality of status epilepticus: A twelve year nationwide population-based cohort study in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLorenzo, R.J.; Towne, A.R.; Pellock, J.M.; Ko, D. Status epilepticus in children, adults, and the elderly. Epilepsia 1992, 33 (Suppl. S4), S15–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayalakshmi, S.; Vooturi, S.; Chepuru, R.; Sahu, S.; Surath, M. Aetiology and outcome of generalized convulsive status epilepticus in elderly. Seizure 2015, 29, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantanen, A.M.; Reinikainen, M.; Parviainen, I.; Ruokonen, E.; Ala-Peijari, M.; Backlund, T.; Koskenkari, J.; Laitio, R.; Kalviainen, R. Incidence and mortality of super-refractory status epilepticus in adults. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 49, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claassen, J.; Lokin, J.K.; Fitzsimmons, B.F.; Mendelsohn, F.A.; Mayer, S.A. Predictors of functional disability and mortality after status epilepticus. Neurology 2002, 58, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drislane, F.W.; Blum, A.S.; Lopez, M.R.; Gautam, S.; Schomer, D.L. Duration of refractory status epilepticus and outcome: Loss of prognostic utility after several hours. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legriel, S.; Mourvillier, B.; Bele, N.; Amaro, J.; Fouet, P.; Manet, P.; Hilpert, F. Outcomes in 140 critically ill patients with status epilepticus. Intensive Care Med. 2008, 34, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legriel, S.; Azoulay, E.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Lemiale, V.; Mourvillier, B.; Kouatchet, A.; Troche, G.; Wolf, M.; Galliot, R.; Dessertaine, G.; et al. Functional outcome after convulsive status epilepticus. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 2295–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetti, A.O.; Hurwitz, S.; Logroscino, G.; Bromfield, E.B. Prognosis of status epilepticus: Role of aetiology, age, and consciousness impairment at presentation. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 77, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagduyu, A.; Tarlaci, S.; Sirin, H. Generalized tonic-clonic status epilepticus: Causes, treatment, complications and predictors of case fatality. J. Neurol. 1998, 245, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logroscino, G.; Hesdorffer, D.C.; Cascino, G.D.; Annegers, J.F.; Bagiella, E.; Hauser, W.A. Long-term mortality after a first episode of status epilepticus. Neurology 2002, 58, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shavit, L.; Grenader, T.; Galperin, I. Nonconvulsive status epilepticus in elderly a possible diagnostic pitfall. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 23, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Torre, J.L.; Diaz-Castroverde, A.G. Non-convulsive status epilepticus in elderly individuals: Report of four representative cases. Age Ageing 2004, 33, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.C. Treatment of nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2007, 81, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beniczky, S.; Hirsch, L.J.; Kaplan, P.W.; Pressler, R.; Bauer, G.; Aurlien, H.; Brogger, J.C.; Trinka, E. Unified eeg terminology and criteria for nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Epilepsia 2013, 54 (Suppl. S6), 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeije, G.; Depondt, C.; Meeus, C.; Korpak, K.; Pepersack, T.; Legros, B. Eeg patterns compatible with nonconvulsive status epilepticus are common in elderly patients with delirium: A prospective study with continuous eeg monitoring. Epilepsy Behav. 2014, 36, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlazzo, E. Confusional status epilepticus in elderly. BMC Geriatr. 2010, 10, L35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, R.E.; Macias, F.M.; Rowan, A.J. Diagnosing epilepsy in the elderly. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2007, 81, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Veran, O.; Kahane, P.; Thomas, P.; Hamelin, S.; Sabourdy, C.; Vercueil, L. De novo epileptic confusion in the elderly: A 1-year prospective study. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellinghaus, C.; Loddenkemper, T.; Dinner, D.S.; Lachhwani, D.; Luders, H.O. Non-epileptic seizures of the elderly. J. Neurol. 2004, 251, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.S.; Gerber, P.; Kirlin, K.A. Ictal eye closure is a reliable indicator for psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Neurology 2006, 66, 1730–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, R.; Oto, M.; Martin, E.; Pelosi, A. Late onset psychogenic nonepileptic attacks. Neurology 2006, 66, 1644–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, L.J.; LaRoche, S.M.; Gaspard, N.; Gerard, E.; Svoronos, A.; Herman, S.T.; Mani, R.; Arif, H.; Jette, N.; Minazad, Y.; et al. American clinical neurophysiology society’s standardized critical care eeg terminology: 2012 version. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 30, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, C.Y.; Chu, N.S. Status epilepticus in the elderly: Etiology, seizure type and outcome. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1989, 80, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminoff, M.J.; Simon, R.P. Status epilepticus. Causes, clinical features and consequences in 98 patients. Am. J. Med. 1980, 69, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLorenzo, R.J.; Pellock, J.M.; Towne, A.R.; Boggs, J.G. Epidemiology of status epilepticus. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1995, 12, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treiman, D.M.; Walker, M.C. Treatment of seizure emergencies: Convulsive and non-convulsive status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res. 2006, 68 (Suppl. S1), S77–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treiman, D.M. Treatment of convulsive status epilepticus. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2007, 81, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Legriel, S.; Bedos, J.; Azoulay, E. Managing critically ill patients with status epilepticus. In Intensive Care Medicine; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 822–836. [Google Scholar]
- Elger, C.E.; Schmidt, D. Modern management of epilepsy: A practical approach. Epilepsy Behav. 2008, 12, 501–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodie, M.J.; Mintzer, S.; Pack, A.M.; Gidal, B.E.; Vecht, C.J.; Schmidt, D. Enzyme induction with antiepileptic drugs: Cause for concern? Epilepsia 2013, 54, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnbaum, A.K. Pharmacokinetics of antiepileptic drugs in elderly nursing home residents. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2007, 81, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, D. Drug treatment of epilepsy: Options and limitations. Epilepsy Behav. 2009, 15, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verellen, R.M.; Cavazos, J.E. Pathophysiological considerations of seizures, epilepsy, and status epilepticus in the elderly. Aging Dis. 2011, 2, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, D.; Schachter, S.C. Drug treatment of epilepsy in adults. BMJ 2014, 348, g254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, R.H.; Collins, C. Risk and predictability of drug interactions in the elderly. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2007, 81, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gidal, B.E. Antiepileptic drug formulation and treatment in the elderly: Biopharmaceutical considerations. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2007, 81, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Velez, L.; Selwa, L.M. Seizure disorders in the elderly. Am. Family Phys. 2003, 67, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Lawn, N.; Kelly, A.; Dunne, J.; Lee, J.; Wesseldine, A. First seizure in the older patient: Clinical features and prognosis. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 107, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silbergleit, R.; Durkalski, V.; Lowenstein, D.; Conwit, R.; Pancioli, A.; Palesch, Y.; Barsan, W.; Investigators, N. Intramuscular versus intravenous therapy for prehospital status epilepticus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigo, F.; Nardone, R.; Tezzon, F.; Trinka, E. Nonintravenous midazolam versus intravenous or rectal diazepam for the treatment of early status epilepticus: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 49, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, V.; Dagron, C.; Elie, C.; Lamhaut, L.; Demeret, S.; Urien, S.; An, K.; Bolgert, F.; Treluyer, J.M.; Baulac, M.; et al. Prehospital treatment with levetiracetam plus clonazepam or placebo plus clonazepam in status epilepticus (samukeppra): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, V.; Lee, J.W.; Drislane, F.W.; Westover, M.B.; Novy, J.; Dworetzky, B.A.; Rossetti, A.O. Practice variability and efficacy of clonazepam, lorazepam, and midazolam in status epilepticus: A multicenter comparison. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treiman, D.M.; Meyers, P.D.; Walton, N.Y.; Collins, J.F.; Colling, C.; Rowan, A.J.; Handforth, A.; Faught, E.; Calabrese, V.P.; Uthman, B.M.; et al. A comparison of four treatments for generalized convulsive status epilepticus. Veterans affairs status epilepticus cooperative study group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, J. Use of levetiracetam in special populations. Epilepsia 2001, 42 (Suppl. S4), 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawello, W.; Fuhr, U.; Hering, U.; Maatouk, H.; Halabi, A. Impact of impaired renal function on the pharmacokinetics of the antiepileptic drug lacosamide. Clin. Pharm. 2013, 52, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lexicomp online (lexi-drugs online): Lexi-comp, inc., hudson, ohio. Available online: Http://online.Lexi.Com/ (login and subscription required) (accessed on 26 April 2016).
- Taniguchi, G.; Miyajima, M.; Watanabe, M.; Murata, Y.; Sone, D.; Watanabe, Y.; Okazaki, M.; Kobayashi-Kimura, M.; Kato, M.; Onuma, T. Nonconvulsive status epilepticus in the elderly associated with newer antidepressants used at therapeutic doses: A report of three cases. Epilepsy Behav. Case Rep. 2015, 3, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Legriel, S.; Brophy, G.M. Managing Status Epilepticus in the Older Adult. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5050053
Legriel S, Brophy GM. Managing Status Epilepticus in the Older Adult. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2016; 5(5):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5050053
Chicago/Turabian StyleLegriel, Stephane, and Gretchen M. Brophy. 2016. "Managing Status Epilepticus in the Older Adult" Journal of Clinical Medicine 5, no. 5: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5050053
APA StyleLegriel, S., & Brophy, G. M. (2016). Managing Status Epilepticus in the Older Adult. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 5(5), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5050053