MicroRNAs in the Evaluation and Potential Treatment of Liver Diseases
Abstract
:1. Liver Disease and MicroRNAs
1.1. The Liver in Precision Medicine
1.2. One Diseased Organ, Many Manifestations; Appreciating the Liver’s Uniqueness
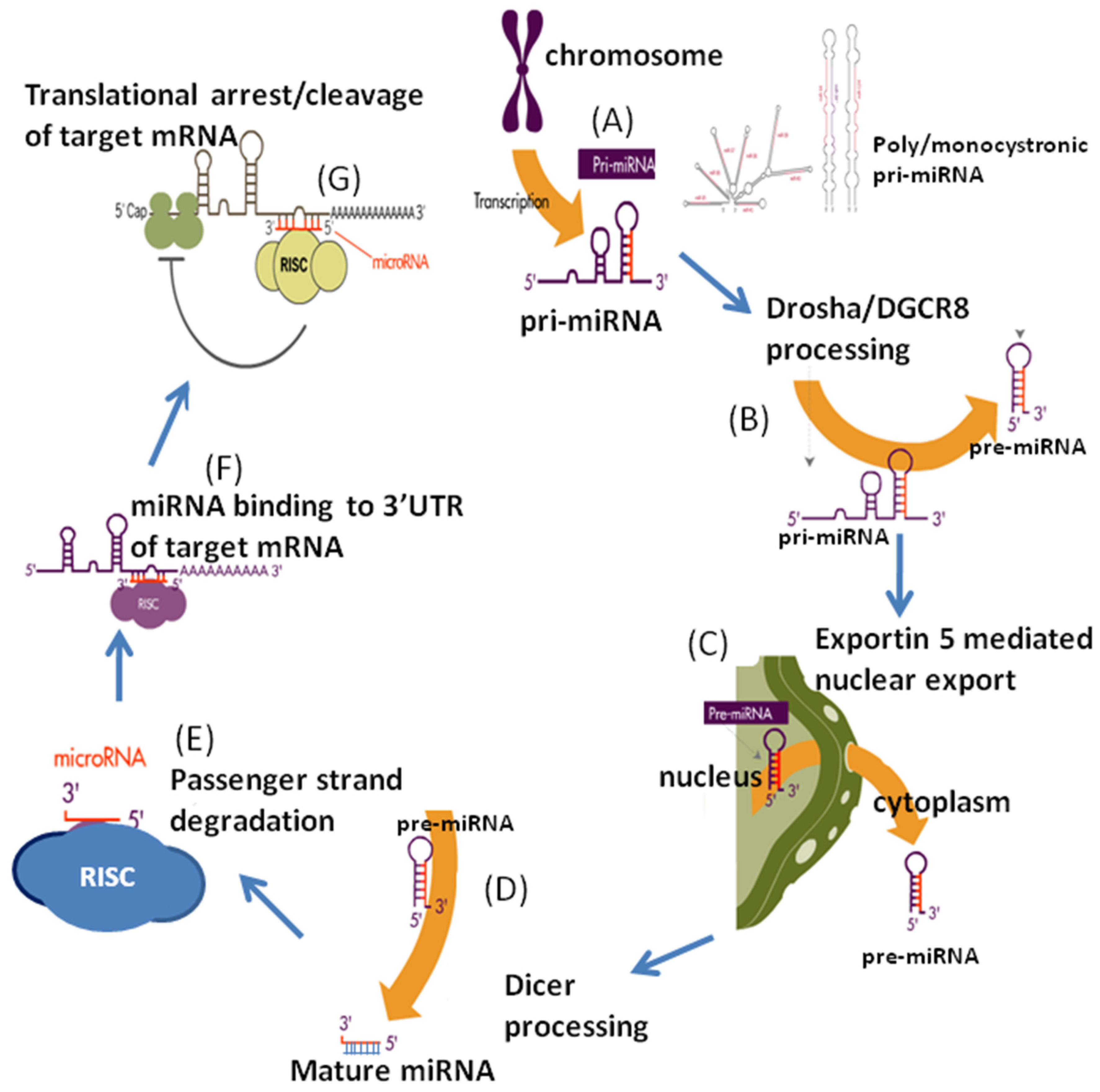
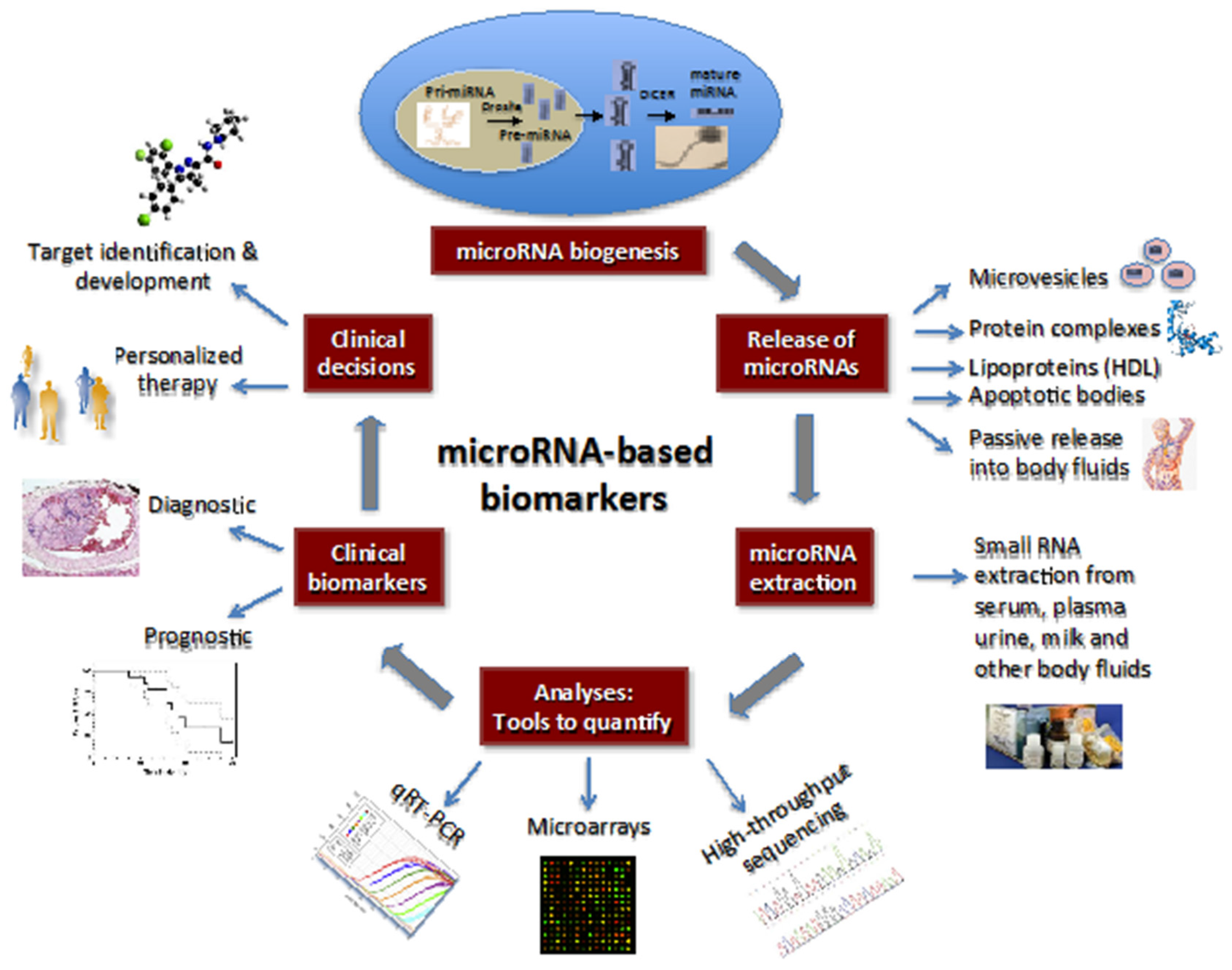
2. MicroRNAs: Biogenesis and Regulation
3. MicroRNAs in Normal Liver Development and Maturation
4. MicroRNAs and Liver Proliferation
4.1. Hepatic Mass Maintenance
4.2. Role of microRNAs and Liver Proliferation
5. MicroRNAs and Liver Pathology
5.1. Hepatocellular Carcinoma
5.2. NAFLD/NASH
5.3. Chronic Viral Hepatitis
5.4. Acute Liver Failure
5.5. Autoimmune Hepatitis
5.6. In-born Errors of Metabolism and MicroRNAs
6. Concluding Remarks
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| α1-AT | alpha-1-antitrypsin |
| ABCA1 | ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 1 |
| AGO | Argonaute protein |
| AIH | autoimmune hepatitis |
| ALF | acute liver failure |
| Arnt | aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator |
| ATP7B | ATPase copper transporting beta |
| Bcl 6 | B-cell lymphoma 6 protein |
| BCR-ABL | breakpoint cluster region Abelson |
| BRCA 1 and 2 | breast cancer genes 1 and 2 |
| BRAF | B-Raf proto-oncogene |
| CN-1 | Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| FGF-1 | fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 |
| FXR | Farnesoid X receptor |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| let-7 | lethal-7 gene |
| LR | liver regeneration |
| miQPCR | open source miRNA specific qPCR platform |
| miRNA | micro-RNA |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NAD | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NASH | non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| NIH | National Institutes of Health |
| nt | nucleotide |
| Odc1 | ornithine decarboxylase 1 |
| P53 | tumor protein 53 |
| PH | partial hepatectomy |
| PPAR | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| PTEN | phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| qPCR | quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| RISC | RNA-induced silencing complex |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| tRNA | transfer RNA |
| rRNA | ribosomal RNA |
| siRNA | small interfering RNA |
| snoRNA | small nuclear RNA |
| Setd8 | SET domain-containing protein 8 |
| SIRT1 | silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog-1 |
| SOCS3 | suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 |
| SREBP1c | sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c |
| STAT3 | signal transduce and activator of transcription factor 3 |
| TGF-beta | transforming growth factor-beta |
| TIMP3 | tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 3 |
| UGT1A1 | uridine 5′-diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| WD | Wilson’s disease |
| Wnt | wingless-related integration site |
References
- Saxema, R.; Zucker, S.D.; Crawford, J.M. Hepatology: A Textbook of Liver Disease; Zakim, D.Z., Boyer, T.D., Eds.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003; Chapter 1; pp. 3–30. [Google Scholar]
- Si-Tayeb, K.; Lemaigre, F.P.; Duncan, S.A. Organogenesis and development of the liver. Dev. Cell 2010, 18, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, G.M.; Anderson, R.M. Experimental pathology of the liver. I. Restoration of the liver of the white rat following partial surgical removal. Arch. Pathol. 1931, 12, 186–202. [Google Scholar]
- Steer, C.J. Liver regeneration. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Finch, M.L.; Marquardt, J.U.; Yeoh, G.C.; Callus, B.A. Regulation of microRNAs and their role in liver development, regeneration and disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 54, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence and outcomes. Hepatology 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergoulis, T.; Kanellos, I.; Kostoulas, N.; Georgakilas, G.; Sellis, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.; Dalamagas, T. mirPub: A database for searching microRNA publications. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1502–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahams, E.; Silver, M. The history of personalized medicine. In Integrative Neuroscience and Personalized Medicine; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- FDA Publication: Paving the Way for Personalized Medicine: FDA’s Role in a New Era of Medical Product Development. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/ScienceResearch/SpecialTopics/PersonalizedMedicine/UCM372421.pdf (accessed on 24 December 2015).
- Sadee, W.; Dai, Z. Pharmacogenetics/genomics and personalized medicine. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, R207–R214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council: Committee on a Framework for Developing a New Taxonomy of Disease. Toward Precision Medicine: Building a Knowledge Network for Biomedical Research and a New Taxonomy of Disease; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Grullich, C.; Von Kalle, C. Recent developments and future perspectives of personalized oncology. Onkologie 2012, 35, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalejska, E.; Maczwynska, E. Prognostic and predictive biomarkers: Tools in personalized oncology. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2014, 18, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato, J.M.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Lu, S.C. Systems biology for hepatologists. Hepatology 2014, 60, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jablonka, E.; Lamb, M.J. The changing concept of epigenetics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 981, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y. Genetic and epigenetic variants influencing the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 6546–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.W.; Friso, S. Epigenetics: A new bridge between nutrition and health. Adv. Nutr. 2010, 1, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallego-Durán, R.; Romero-Gómez, M. Epigenetic mechanisms in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An emerging field. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2497–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, A.M.; Mott, J.L. Overview of microRNA biology. Semin. Liver Dis. 2015, 35, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoshechkin, I.; Bell, I.; Bernstein, B.E.; Birney, E.; Dunham, I.; Green, E.D.; Gunter, C.; Shahab, A.; Snyder, M.; Tenenbaum, S.A.; et al. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012, 489, 57–74. [Google Scholar]
- Mattick, J.S.; Makunin, I.V. Non-coding RNA. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, R17–R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponting, C.P.; Oliver, P.L.; Reik, W. Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, F.F. Non-coding RNAs: Meet thy masters. Bioessays 2010, 32, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axtell, M.J.; Westholm, J.O.; Lai, E.C. Vive la difference: Biogenesis and evolution of microRNAs in plants and animals. Genome Biol. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, H.R.; Schoenfield, L.W.; Ruby, J.G.; Auyeung, V.C.; Spies, N.; Baek, D.; Johnston, W.K.; Russ, C.; Luo, S.; Babiarz, J.E.; et al. Mammalian microRNAs: Experimental evaluation of novel and previously annotated genes. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 992–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D68–D73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Jeon, K.; Lee, J.T.; Kim, S.; Kim, V.N. MicroRNA maturation: Stepwise processing and subcellular localization. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 4663–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roush, S.; Slack, F.J. The let-7 family of microRNAs. Trends Cell Biol. 2008, 18, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.S.; Lai, E.C. Alternative miRNA biogenesis pathways and the interpretation of core miRNA pathway mutants. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Lu, Z.H. The fate of miRNA* strand through evolutionary analysis: Implication for degradation as merely carrier strand or potential regulatory molecule? PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, M.; Kim, V.N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheloufi, S.; Dos Santos, C.O.; Chong, M.M.; Hannon, G.J. A Dicer-independent miRNA biogenesis pathway that requires Ago catalysis. Nature 2010, 465, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Wang, L. Transcriptional mechanism for the paired miR-433 and miR-127 genes by nuclear receptors SHP and ERRγ. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 5727–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Wang, L. miR-433 and miR-127 arise from independent overlapping primary transcripts encoded by the miR-433–127 locus. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. microRNA-206 targets notch3, activates apoptosis, and inhibits tumor cell migration and focus formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 31921–31927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Wang, L. Nuclear receptor SHP activates miR-206 expression via a cascade dual inhibitory mechanism. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kuruba, R.; Gao, X.; Gandhi, C.R.; Xie, W.; Li, S. Roles of microRNA-29a in the antifibrotic effect of farnesoid X receptor in hepatic stellate cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 80, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.A.; Baxter, D.H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.Y.; Huang, K.H.; Lee, M.J.; Galas, D.J.; Wang, K. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phua, L.; Chue, X.; Koh, P.; Cheah, P.; Chan, E.; Ho, H. Global fecal microRNA profiling in the identification of biomarkers for colorectal cancer screening among Asians. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Nishida, N.; Calin, G.A.; Pantel, K. Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrese, M.; Eguchi, A.; Feldstein, A.E. Circulating microRNAs: Emerging biomarkers of liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2015, 35, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benes, V.; Collier, P.; Kordes, C.; Stolte, J.; Rausch, T.; Muckentaler, M.U.; Häussinger, D.; Castoldi, M. Identification of cytokine-induced modulation of microRNA expression and secretion as measured by a novel microRNA specific qPCR assay. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.W.; Heegaard, N.H.; Orum, H. MicroRNAs in liver disease. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolewski, C.; Calo, N.; Portius, D.; Foti, M. MicroRNAs in fatty liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2015, 35, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, T.; Miyajima, A. Liver regeneration by stem/progenitor cells. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Kim, H.; Jung, I.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.; Han, Y.M. Expression profiles of miRNAs in human embryonic stem cells during hepatocyte differentiation. Hepatol. Res. 2011, 41, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.G.; Qiu, R.L.; Wu, Y.H.; Li, Z.X.; Xie, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.J.; Zeng, L.X.; Tang, J.; Maharjan, A.; et al. Overexpression of miR-122 promotes the hepatic differentiation and maturation of mouse ESCs through a miR-122/FoxA1/HNF4a-positive feedback loop. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Nicolas, E.; Marks, D.; Sander, C.; Lerro, A.; Buendia, M.A.; Xu, C.; Mason, W.S.; Moloshok, T.; Bort, R.; et al. miR-122, a mammalian liver-specific microRNA, is processed from HCR mRNA and may downregulate the high affinity cationic amino acid transporter CAT-1. RNA Biol. 2004, 1, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; He, J.H.; Xiao, Z.D.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Chen, Y.Q.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H. Liver-enriched transcription factors regulate microRNA-122 that targets CUTL1 during liver development. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1431–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hand, N.J.; Master, Z.R.; Lay, J.L.; Friedman, J.R. Hepatic function is preserved in the absence of mature microRNAs. Hepatology 2009, 49, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Chu, J.; Zheng, L.; Wu, Q.; Han, Z.; et al. Dynamic microRNA profiles of hepatic differentiated human umbilical cord lining-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rompolas, P.; Mesa, K.R.; Greco, V. Spatial organization within a niche as a determinant of stem-cell fate. Nature 2013, 502, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Mowry, L.E.; Nejak-Bowen, K.N.; Okabe, H.; Diegel, C.R.; Lang, R.A.; Williams, B.O.; Monga, S.P. β-catenin signaling in murine liver zonation and regeneration: A Wnt-Wnt situation! Hepatology 2014, 60, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magami, Y.; Azuma, T.; Inokuchi, H.; Kokuno, S.; Moriyasu, F.; Kawai, K.; Hattori, T. Cell proliferation and renewal of normal hepatocytes and bile duct cells in adult mouse liver. Liver 2002, 5, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, R.; Kofman, A.V.; Landis, C.S.; Swenson, E.S.; Barendswaard, E.; Theise, N.D. The hepatic stem cell niche: Identification by label-retaining cell assay. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1994–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalopoulos, G.K.; DeFrances, M.C. Liver regeneration. Science 1997, 276, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taub, R.; Greenbaum, L.E.; Peng, Y. Transcriptional regulatory signals define cytokine-dependent and -independent pathways in liver regeneration. Semin. Liver Dis. 1999, 19, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fausto, N.; Webber, E.M. The Liver: Biology and Pathobiology; Arias, I.M., Boyer, J.L., Fausto, N., Jacoby, W.B., Schachter, D., Shafritz, D.A., Eds.; Raven Press Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Michalopoulos, G.K. Liver regeneration. J. Cell Physiol. 2007, 213, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilgenkrantz, H.; deI’Hortet, A.C. New insights into liver regeneration. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2011, 35, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C. Advances in the regulation of liver regeneration. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 5, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Court, F.G.; Wemyss-Holden, S.A.; Dennison, A.R.; Maddern, G.J. The mystery of liver regeneration. Br. J. Surg. 2002, 89, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menthena, A.; Koehler, C.I.; Sandhu, J.S.; Yovchev, M.I.; Hurston, E.; Shafritz, D.A.; Oertel, M. Activin A, p15INK4b signaling, and cell competition promote stem/progenitor cell repopulation of livers in aging rats. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oe, S.; Lemmer, E.R.; Conner, E.A.; Factor, V.M.; Leveen, P.; Larsson, J.; Karlsson, S.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Intact signaling by transforming growth factor beta is not required for termination of liver regeneration in mice. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, A.L.; Kumar, T.R.; Nishimori, K.; Bonadio, J.; Matzuk, M.M. Activin βC and βE genes are not essential for mouse liver growth, differentiation, and regeneration. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 6127–6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygard, I.E.; Mortensen, K.E.; Hedegaard, J.; Conley, L.N.; Kalstad, T.; Bendixen, C.; Revhaug, A. The genetic regulation of the terminating phase of liver regeneration. Comp. Hepatol. 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liska, V.; Treska, V.; Mirka, H.; Kobr, J.; Sykora, R.; Skalicky, T.; Sutnar, A.; Vycital, O.; Bruha, J.; Pitule, P.; et al. Inhibition of transforming growth factor beta-1 augments liver regeneration after partial portal vein ligation in porcine experimental model. Hepatogastroenterology 2012, 59, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shu, J.; Kren, B.T.; Xia, Z.; Wong, P.Y.; Li, L.; Hanse, E.A.; Min, M.X.; Li, B.; Albrecht, J.H.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Genome-wide microRNA down-regulation as negative feedback mechanism in the early phases of liver regeneration. Hepatology 2011, 54, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Sharma, A.D.; Roll, G.R.; Ng, R.; Lee, AY.; Blelloch, R.H.; Frandsen, N.M.; Willenbring, H. MicroRNAs control hepatocytes proliferation during liver regulation. Hepatology. 2010, 51, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Fu, H.; Wan, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Tie, Y.; Xing, R.; Zhu, J.; et al. X. Hepato-specific microRNA-122 facilitates accumulation of newly synthesized miRNA through regulating PRKRA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, R.; Song, G.; Roll, G.R.; Frandsen, N.M.; Willenbring, H.A. MicroRNA-21 surge facilitates rapid cyclin D1 translation and cell cycle progression in mouse liver regeneration. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan-nan, B.; Zhao-yan, Y.; Li-xi, L.; Jiang, Y.; Qing-Jie, X.; Yong, Z. MicroRNA-21 accelerates hepatocytes proliferation in vitro via PI3K/Akt signaling by targeting PTEN. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, R.E.; Ferreira, D.M.; Zhang, X.; Borralho, P.M.; Sarver, A.L.; Zheng, Y.; Steer, C.J.; Kren, B.T.; Rodrigues, C.M. Identification of microRNAs during rat liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy and modulation by ursodeoxycholic acid. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F.; Bei, Y.; Xiao, J.; Yang, C. MicroRNAs in liver regeneration. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015, 37, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Gusev, Y.; Aderca, I.; Mettler, T.A.; Nagorney, D.M.; Brackett, D.J.; Roberts, L.R.; Schmittgen, T.D. Association of microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Loya, K.; Rani, B.; Mobus, S.; Balakrishnan, A.; Lamle, J.; Cathomen, T.; Vogel, A.; Manns, M.P.; Ott, M.; et al. MicroRNA-221 overexpression accelerates hepatocytes proliferation during liver regeneration. Hepatology 2013, 57, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Dong, R.; Shi, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Miao, M.; Jiao, B. Down-regulation of miR-23b may contribute to activation of the TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway during the termination stage of liver regeneration. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, W.; Gu, M.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, G. Helicobacter pylori infection causes hepatic insulin resistance by the c-Jun/miR-203/SOCS3 signaling pathway. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, F.; Barkinge, J.; Hawkins, S.; Gudi, R.; Salgia, R.; Kanteti, P.V. Expression of Siva-1 protein or its putative amphipathic helical region enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells: Effect of elevated levels of BCL-2. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 5301–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Ju, W.; Wang, D.; Wu, L.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, Z.; He, X. Down-regulation of microRNA-26a promotes mouse hepatocyte proliferation during liver regeneration. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayner, K.J.; Suarez, Y.; Davalos, A.; Parathath, S.; Fitzgerald, M.L.; Tamehiro, N.; Fisher, E.A.; Moore, K.J.; Fernandez-Hernando, C. MiR-33 contributes to the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Science 2010, 328, 1570–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Bao, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Z.F.; Zhou, J.Y. MicroRNA-34a overcomes HGF-mediated gefitinib resistance in EGFR mutant lung cancer cells partly by targeting MET. Cancer Lett. 2014, 351, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apte, U.; Gkretski, V.; Bowen, W.C.; Mars, W.M.; Luo, J.H.; Donthamsetty, S.; Orr, A.; Monga, S.P.; Wu, C.; Michalopoulos, G.K. Enhanced liver regeneration following changes induced by hepatocytes-specific genetic ablation of integrin-linked kinase. Hepatology 2009, 50, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Liang, G.; Egger, G.; Friedman, J.M.; Chuang, J.C.; Coetzee, G.A.; Jones, P.A. Specific activation of microRNA-127 with down-regulation of the proto-oncogene BCL6 by chromatin-modifying drugs in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wou, W.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J. Plasma miR-127 and miR-218 might serve as potential biomarkers for cervical cancer. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 22, 1037–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, S.; Fu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Miao, M.; Jiao, B. Down-regulation of mir-127 facilitates hepatocyte proliferation during rat liver regeneration. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Sun, L.; Li, Q.; Han, X.; Lei, L.; Zhang, H.; Shang, Y. Set8 promotes epitherlial-mesenchymal transition and confers twist dual transcriptional activities. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.Y.; Bai, Y.N.; Luo, L.X.; Wu, H.; Zeng, Y. Expression of microRNA-150 targeting vascular endothelial growth factor-α is down-regulated under hypoxia during liver regeneration. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 8, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salehi, S.; Brereton, H.C.; Arno, M.J.; Darling, D.; Quaglia, A.; O’grady, J.; Heaton, N.; Aluvihare, V.R. Human liver regeneration is characterized by the coordinated expression of distinct microRNA governing cell cycle fate. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, A.; Helou, K.; Walentinsson, A.; Hedrich, H.J.; Szpirer, C.; Levan, G. Amplification of Mycn, Ddx1, Rrm2, and Odc1 in rat uterine endometrial carcinomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2001, 31, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Rudolph, L. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2557–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2006, 6, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Burroughs, A.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2003, 362, 1907–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Lin, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Ding, G.; Dong, Q.; Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Identification of miRNomes in human liver and hepatocellular carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p as therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramantieri, L.; Fornari, F.; Callegari, E.; Sabbioni, S.; Lanza, G.; Croce, C.M.; Bolondi, L.; Negrini, M. MicroRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 2189–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Cob, G.P.; Anderson, T.A. MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev. Biol. 2007, 302, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineau, P.; Volinia, S.; McJunkin, K.; Marchio, A.; Battiston, C.; Terris, B.; Mazzaferro, V.; Lowe, S.W.; Croce, C.M.; Dejean, A.; et al. miR-221 overexpression contributes to liver tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, M.; Di Leva, G.; Romano, G.; Nuovo, G.; Suh, S.S.; Ngankeu, A.; Taccioli, C.; Pichiorri, F.; Alder, H.; Secchiero, P.; et al. miR-221 & 222 regulate TRAIL resistance and enhance tumorigenicity through PTEN and TIMP3 downregulation. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Henson, R.; Wehbe-Janek, H.; Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S.T.; Patel, T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, C.M.; Varley, R.B.; Lawless, M.W. MicroRNAs and liver cancer associated with iron overload: Therapeutic targets unraveled. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 5212–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.B.; Hong, L.; Teng, M.J.; Fan, J.W.; Tang, H.M.; Wu, J.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, Z.W.; Qiu, G.Q.; Peng, Z.H.; et al. Identification of recurrence-related microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma following liver transplantation. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liese, J.; Peveling-oberhag, J.; Doering, C.; Schnitzbauer, A.A.; Hermann, E.; Zangos, S.; Hansmann, M.L.; Moench, C.; Welker, M.W.; Zeuzem, S.; et al. A possible role of miRNAs as predictive markers for the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2016, 29, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanova, M.; Younossi, Z.M. Independent association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular disease in the US population. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 6, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, O.; Puri, P.; Eicken, C.; Contos, M.J.; Mirshahi, F.; Maher, J.W.; Kellum, J.M.; Min, H.; Luketic, V.A.; Sanyal, A.J. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with altered hepatic microRNA expression. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, R.E.; Ferreira, D.M.; Afonso, M.B.; Borralho, P.M.; Machado, M.V.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Rodrigues, C.M. Mir-34a/SIRT1/p53 is suppressed by ursodeoxycholic acid in the rat liver and activated by disease severity in human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.C.; Guarente, L. Sirt1 and other sirtuins in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Li, M.; Wan, X.; Jin, X.; Chen, S.; Yu, C.; Li, Y. Effect of mir-34a in regulating steatosis by targeting PPARα expression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derdak, Z.; Villegas, K.A.; Harb, R.; Wu, A.M.; Sousa, A.; Wands, J.R. Inhibition of p53 attenuates steatosis and liver injury in a mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmen, J.; Lindow, M.; Silahtaroglu, A.; Bak, M.; Christensen, M.; Lind-Thomsen, A.; Hedtjarn, M.; Hansen, J.B.; Hansen, H.F.; Straarup, E.M.; et al. Antagonism of microRNA-122 in mice by systemically administered LNA-antimiR leads to up-regulation of a large set of predicted target mRNAs in the liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dávalos, A.; Goedeke, L.; Smibert, P.; Ramírez, C.M.; Warrier, N.P.; Andreo, U.; Cirera-Salinas, D.; Rayner, K.; Suresh, U.; Pastor-Pareja, J.C.; et al. miR-33a/b contribute to the regulation of fatty acid metabolism and insulin signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9232–9237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirola, C.J.; Gianotti, T.F.; Castano, G.O.; Mallardi, P.; San Martino, J.; Ledesma, M.M.G.L.; Flichman, D.; Mirshahi, F.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sookoian, S. Circulating microRNA signature in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: From serum non-coding RNAs to liver histology and disease pathogenesis. Gut 2015, 64, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J. Additional stories of microRNAs. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, D.M.; Simao, A.L.; Rodrigues, C.M.; Castro, R.E. Revisiting the metabolic syndrome and paving the way for microRNAs in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 2503–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, D.; Rane, S.; Lypowy, J.; He, M.; Chen, I.Y.; Vashistha, H.; Yan, L.; Malhotra, A.; Vatner, D.; Abdellatif, M. MicroRNA-21 targets Sprouty2 and promotes cellular outgrowths. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 3272–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ura, S.; Honda, M.; Yamashita, T.; Ueda, T.; Takatori, H.; Nishino, R.; Sunakozaka, H.; Sakai, Y.; Horimoto, K.; Kaneko, S.; et al. Differential microRNA expression between hepatitis B and hepatitis C leading disease progression to hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1098–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jopling, C.L.; Yi, M.; Lancaster, A.M.; Lemon, S.M.; Sarnow, P. Modulation of hepatitis C virus RNA abundance by a liver-specific microRNA. Science 2005, 309, 1577–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meer, A.J.; Farid, W.R.; Sonneveld, M.J.; de Ruiter, P.E.; Boonstra, A.; Van Vuuren, A.J.; Verheij, J.; Hansen, B.E.; de Knegt, R.J.; van der Laan, L.J.; et al. Sensitive detection of hepatocellular injury in chronic hepatitis C patients with circulating hepatocyte-derived microRNA-122. J. Viral Hepat. 2013, 20, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, L.; Yan, X.; Jin, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, E.; Ye, X.; Gao, G.F.; Wang, F.; et al. Loss of microRNA 122 expression in patients with hepatitis B enhances hepatitis B virus replication through cyclin G1-modulated P53 activity. Hepatology 2012, 55, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirasaki, T.; Honda, M.; Shimakami, T.; Horii, R.; Yamashita, T.; Sakai, Y.; Sakai, A.; Okada, H.; Watanabe, R.; Murakami, S.; et al. MicroRNA-27a regulates lipid metabolism and inhibits hepatitis C virus replication in human hepatoma cells. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5270–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, K.; Hadem, J.; Krech, T.; Wahl, K.; Manns, M.P.; Dooley, S.; Batkai, S.; Thum, T.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Bantel, H. MicroRNAs play a role for spontaneous recovery from acute liver failure. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1346–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migita, K.; Komori, A.; Kozuru, H.; Jiuchi, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Yasunami, M.; Furukawa, H.; Abiru, S.; Yamasaki, K.; Nagaoka, S.; et al. Circulating microRNA profiles in patients with type-1 autoimmune hepatitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, T.; Carroll, T.P.; Buckley, P.G.; Cummings, R.; O’Neill, S.J.; McElvaney, N.G.; Greene, C.M. miR-199a-5p silencing regulates the unfolded protein response in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and α1-antitrypsin deficiency. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siaj, R.; Sauer, V.; Stoppeler, S.; Gerb, J.; Spiegel, H.U.; Kohler, G.; Zibert, A.; Schmidt, H.H. Longitudinal analysis of serum miR-122 in a rat model of Wilson’s Disease. Hepatol. Int. 2012, 6, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, F.; Remy, S.; Dariel, A.; Flageul, M.; Pichard, V.; Boni, S.; Usal, C.; Myara, A.; Laplanche, S.; Anegon, I.; et al. Lentiviral vectors that express UGT1A1 in liver and contain miR-142 target sequences normalize hyperbilirubinemia in Gunn rats. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| miR a | Δ | Process/Disease Etiology | Model/Tissue/Cell Type | Method | Target/s | Target Validation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| let-7 | ↑ | Regeneration | Rat liver 3–72 h post PH | MA, qPCR | Dicer1 | Inhibitor in Huh-7 cells with qPCR | Shu et al. (2011) |
| Tarbp2 | |||||||
| let-7a | ↓ | Viral hepatitis (HBV) | Human HepG2 cells ± transduction HBV protein X, HCCT and NT liver | MA, qPCR | STAT3 | Mimic/inhibitor with qPCR, W, β-Gal RA. Phenotype of target KD | Wang et al. (2010) |
| let-7c | ↑ | Development (embryo-adult) | Human embryonic (7–10 weeks) and adult liver | MA, qPCR | TGF βR1 | Mimic/inhibitor in Huh-7 cells with mRNA/protein quantification, LA | Tzur et al. (2009) |
| 1 | ↑ | Viral hepatitis (HBV) | Transfected miR mimic into ± constitutively expressing HBV human HepG2, and Huh-7 cell line | qPCR for HBV | HDAC4 FXRA E2F5 | Mimic in HepG2, Huh-7 cells ± constitutively expressing HBV human with qPCR, W, LA. Phenotype of target KD | Zhang et al. (2011) |
| 10b | ↑ | NAFLD/NASH | Steatotic human L02 heps with high free fatty acid | MA, qPCR | PPARα | Mimic/inhibitor in L02 heps with qPCR, W, LA | Zhang et al. (2010) |
| 15a | ↓ | Viral hepatitis (HBV) | Human HepG2 cells with overexpression or knockdown of miR-15a | Mimic/inhibitor | HBx | Mimic/inhibitor in HepG2 cells with LA, qPCR, W | Wang et al. (2013) |
| 15b | ↓ | Cancer (HCC) | Human HCC tissue ± recurrence post resection | MA | BCL-W | Mimic/inhibitor in SNU-475 cells with W | Chung et al. (2010) |
| 20a | ↓ | Development (embryo-adult) | Mouse foregut endoderm, hepatoblasts and adult liver | NGS | Tgfbr2 | Inhibitor in HEK293T cells with LA and W | Wei et al. (2013a) |
| ↑ | Viral hepatitis | Human HepAD38 cells ± HBV replication | qPCR, N | HBV DNA fragment | Inhibitor in HepAD38 cells with LA | Jung et al. (2013) | |
| 21 | ↑ | Regeneration | Liver of rats ± Lieber-DeCarli diet for 5 weeks, assessed 1–36 h post PH | MA, qPCR | Crebl2 | Precursor in HEK293 cells with LA | Dippold et al. (2012) |
| ↑ | Regeneration (proliferation) | Mouse liver 1 h–7 days post PH | N | Peli1 | Mimic in HEK293 cells with LA | Marquez et al. (2010) | |
| ↑ | Regeneration (proliferation) | Mouse liver 0–36 h post PH | qPCR | RhoB | Mimic/inhibitor in Hepa 1–6 cells with qPCR, W, LA | Ng et al. (2012) | |
| ↑ | Regeneration (proliferation) | Mouse liver 0–18 h post PH | MA, qPCR | Btg2 | Mimic/inhibitor in Hepa 1–6 cells with qPCR, LA | Song et al. (2010) | |
| ↑ | Regeneration | Rat liver 3–72 h post PH | MA, qPCR | Dicer1 | Inhibitor in Huh-7 cells with qPCR, W, LA | Shu et al. (2011) | |
| ↑ | Cancer (HCC) | Human T (HCC) and NT liver tissues and HCC cell lines | MA, qPCR, N | PTEN | Inhibitor in SK-HEP-1, SNU-182, HepG2, and PLC/PRF-5 cells with LA. Correlated target expression in tissue and cells | Meng et al. (2007) | |
| 22 | ↓ | Cancer (HCC) | T (HCC) and NT human liver | qPCR | HDAC4 | Mimic in Hep3B, SMMC-7721 cells with W, LA. Phenotype of target KD. Correlated target expression in tissue | Zhang et al. (2010b) |
| 23b | ↓ | Regeneration (termination) | Rat liver 24–168 h post PH | qPCR | Smad3 | Mimic in BRL-3A cells with qPCR, W, LA | Yuan et al. (2011) |
| 25 | ↑ | Cancer (CC) | Human CC and benign cell lines. T (CC) and NT human liver | qPCR | TRAIL-DR4 | Mimic/ inhibitor in KMCH, H69, Mz-Cha-1 cells with W, LA, IF. Correlated target expression in tissue | Razumilava et al. (2012) |
| 26a | ↓ | Regeneration (proliferation) | Mouse liver 24–168 h post PH | qPCR | Ccnd2 Ccne2 | Mimic/inhibitor in mouse liver and Nctc-1469 cells with qPCR, W | Zhou et al. (2012) |
| ↓ | Regeneration (proliferation) | Rat liver 24–72 h post PH | MA, qPCR | Ccne2 | Mimic in HepG2 cells with qPCR, W | Chen et al. (2011b) | |
| ↓ | Cancer (HCC) | Mouse liver ± specific overexpression of liver-tumour initiating MYC, panel of human HCC | N, qPCR | Ccnd2 Ccne2 | Mimic in HepG2 cells with W, LA | Kota et al. (2009) | |
| ↓ | Cancer (HCC) | Human T (HCC) and NT liver tissues, and ± metastasis | qPCR | IL-6 | Mimic/inhibitor in HCC-3, MHCC97-H, HepG2 and PLC cells with LA, qPCR, Elisa | Yang et al. (2013) | |
| 27a | ↑ | Viral hepatitis (HCV) | Human HCV-compared to HBV-infected liver | qPCR | RXRα ABCA1 | Mimic/inhibitor in Huh-7.5 cells with LA, W | Shirasaki et al. (2013) |
| 27b | ↑ | Viral hepatitis (HCV) | Human cells (Huh-7.5) and mouse liver tissues infected with HCV | qPCR | PPARα | Mimic in Huh-7 cells with qPCR | Singaravelu et al. (2014) |
| 29/29a | ↑ | Regeneration | Rat liver 3–72 h post PH | MA, qPCR | Dicer1 | Inhibitor in Huh-7 cells with qPCR, W, LA | Shu et al. (2011) |
| ↑ | Viral hepatitis (HBV) | Transgenic mouse liver, human HepG2 cells expression HBV protein X | qPCR | PTEN | Mimic/inhibitor in HepG2, MHCC-97L cells with qPCR, W, LA. Phenotype of target KD. Correlated target expression in HCC | Kong et al. (2011) | |
| 30a | ↑ | Development (biliary) | Mouse and human embryonic (E12.5–18.5) and adult liver. Knockdown in zebrafish | MA, N, qPCR, ISH | Ak1 Tnrc6a | Inhibitor in BMEL cells with MA, LA | Hand et al. (2009a) |
| 34a | ↑ | Regeneration (termination) | Rat liver 1–9 days post PH | MA, qPCR | Inhbb c-Met | Mimic in BRL-3A cells with qPCR, W, LA. Phenotype of target KD. | Chen et al. (2011a) |
| ↑ | ALD | Liver of mice fed 22.7–35 g/kg/day EtOH for 4 weeks, human heps, cholangiocytes and HepG2 cells ± EtOH, human ALD and paired normal liver | MA, qPCR | CASP2 SIRT1 MMP-2 MMP-9 | Mimic in human heps with HPLC-Chip/MS analysis, qPCR, W, LA. Correlated target protein expression in heps ± EtOH. | Meng et al. (2012) | |
| ↑ | NAFLD/NASH | Human liver biopsy from NASH, NAFLD, weight matched normal, and lean normal subjects | qPCR | SIRT1 | Mimic/inhibitor in Huh-7 cells with qPCR, W | Min et al. (2012) | |
| ↑ | NAFLD/NASH | Human liver samples from NAFLD patients with steatosis and NASH | qPCR | SIRT1 | Precursor in primary rat heps with W, LA | Castro et al. (2013) | |
| ↓ | Cancer (HCC) | Human HCC tissue ± metastasis | qPCR | c-MET | Mimic in HepG2 cells with qPCR, W. Correlated target protein expression in liver. Phenotype of target KD | Li et al. (2009) | |
| 92a-1 | ↑ | Viral hepatitis | Human HepAD38 cells ± HBV replication | qPCR, N | HBV DNA fragment | Inhibitor in HepAD38 cells with LA | Jung et al. (2013) |
| 99a | ↓ | Cancer (HCC) | T (HCC) and NT human liver | Deep seq., qPCR | IGF-1R mTOR | Mimic/inhibitor in HepG2, SMMC-7721, Huh-7, HL-7702 cells, SMMC-LTNM tumor mass, with, LA, W. Correlated target expression in liver | Li et al. (2011) |
| 101 | ↓ | Cancer (HCC) | T (HCC) and NT human liver. Mouse and human liver/non-liver cells | MA, N | MCL1 | Mimic in HEK293T cells with LA. Mimic/inhibitor in HepG2 cells with qPCR, W | Su et al. (2009) |
| 122/122a | ↑ | Development (embryo-adult) | Mouse embryonic (E12.5–18.5) and adult liver | N, qPCR | Cutl1 | Mimic/inhibitor in human HCC cell lines with W. Correlated target protein expression during development | Xu et al. (2010) |
| ↓ | Viral hepatitis (HBV) | Liver of chronically infected HBV human patients | AP-ISH, qPCR | CCNG1 | Mimic/inhibitor in HepG2, Huh-7 cells with LA, W. Correlated target expression to HBV load in human liver | Wang et al. (2012) | |
| ↓ | Cancer (HCC) | Human HCC arisen on cirrhotic livers and HCC derived cell lines | MA, N, qPCR | CCNG1 | Precursor in SNU-449 and Hep 3B cells with LA, W. Correlated target expression in HCC | Gramantieri et al. (2007) | |
| ↓ | Cancer (HCC) | Mice with germline deletion of miR-122a, develop spontaneous HCC | Deletin | KLF6 | Mimic in HEK293T cells with LA. Correlation of protein in knockout liver | Tsai et al. (2012) | |
| ↓ | Cancer (HCC) | Human HCC tumour and non-tumour pairs | N, qPCR | SLC7A1 AKT3 ADAM17 | Mimic in HEK293T cells with LA | Tsai et al. (2009) | |
| 127 | ↓ | Regeneration (proliferation) | Rat liver 0–168 h post PH | MA, qPCR | Bcl6 Setd8 | Mimic/inhibitor in BRL-3A, Huh-7 cells with LA, qPCR, W. Phenotype of target KD | Pan et al. (2012) |
| 129-5p | ↓ | Cancer (HCC) | Human T (HCC) and NT liver tissues | qPCR | VCP | Mimic/inhibitor in HepG2, MHCC-LM3, SK-HEP1, cells with, LA. Correlated target expression in liver | Liu et al. (2012) |
| 141 | ↑ | Viral hepatitis (HCV) | Primary human heps infected with HCV | RPA-KA | DLC1 | Mimic/inhibitor in primary heps with qPCR, W, LA | Banaudha et al. (2011) |
| 146 | ↑ | Cancer | Human PLC/PRF/5 hepatoma cells ± IFN-α resistance | MA, qPCR | SMAD4 | Mimic in PLC/PRF/5 cells with W. Phenotype of target KD | Tomokuni et al. (2011) |
| 148a | ↓ | Cancer (HCC) | Human T (HCC) and NT liver ± HBV | qPCR | HPIP | Mimic/inhibitor in HepG2, BEL-7402, SMMC-7721, MHCC97-H and LO2 cells with WB, LA | Xu et al. (2013) |
| 150 | ↓ | Regeneration (proliferation) | Rodent liver 12–48 h post PH | qPCR | Vegfa | Inhibitor in primary heps with qPCR, W | Yu et al. (2013) |
| 155 | ↑ | ALD | RAW 264.7 mouse macrophages ± 50mM EtOH. Isolated Kupffer cells from mice fed Lieber-DeCarli diet (5% EtOH (v/v)) for 4 weeks | qPCR | TNFα | Mimic/inhibitor in RAW 264.7 cells, and inhibitor in isolated Kuppfer cells with TNFα production by ELISA | Bala et al. (2011) |
| ↑ | NAFLD/NASH | Liver of mice fed choline-deficient, low methionine, amino acid-defined diet for 6–65 weeks | MA. qPCR | Cebpβ | Inhibitor in HepG2, Hep3B cells with qPCR, W. Correlated expression in liver | Wang et al. (2009) | |
| ↑ | NAFLD/NASH | Liver of mice fed lipogenic, methyl-deficient diet for 12 weeks | MA. qPCR | Cebpβ Socs1 | Correlated protein expression with lipogenic diet by W. mimic in primary heps with W | Pogribny et al. (2010) | |
| 193a–3p | ↑ | Cancer (HCC) | Human hepatoma cell lines sensitive (QGY-7703) or resistant (SMMC-7721) to 5-fluorouracil | Deep seq. qPCR | SRSF2 | Correlated target mRNA/protein expression with sensitive/resistant cell lines. Mimic/inhibitor in hepatoma cell lines with qPCR, W. Phenotype of target KD | Ma et al. (2012) |
| 199a/b–3p | Cancer (HCC) | NT, viral infected and T (HCC) human liver | MPSS, qPCR | PAK4 | Mimic/inhibitor in Hep3B with LA, W. | Hou et al. (2011) | |
| 199a–5p | ↓ | Cancer (HCC) | Blood from human patients with cisplatin treated un resectable/metastatic HCC. Hepatoma cell lines ± cisplatin | qPCR | ATG7 | Mimic in HEK293T cells with LA. Mimic in Huh-7 cells with W | Xu et al. (2012) |
| 200b | ↑ | NAFLD/NASH | Liver of mice fed lipogenic, methyl-deficient diet for 12 weeks | MA, qPCR | Zeb1 | Correlated target protein expression with lipogenic diet. Mimic in primary mouse heps with W | Pogribny et al. (2010) |
| 200c | ↑ | Viral hepatitis (HCV) | Chronic HCV infected human liver | MA | FAP-1 | Mimic/inhibitor in normal human liver fibroblasts with qPCR, W | Ramachandran et al. (2013) |
| 214 | ↓ | Cancer (CC) | Human CC tissue ± metastasis | qPCR | TWIST1 | Mimic in HEK293T cells with LA. Mimic in ICC-9810 cells with W | Li et al. (2012) |
| 217 | ↑ | ALD | Mouse AML-12 heps ± 25–100 mM EtOH for 24 h. Liver of mice fed low fat Lieber-DeCarli diet for 4 weeks | qPCR | Sirt1 | Mimic/inhibitor in AML-12 cells with LA, qPCR, W and FTAA | Yin et al. (2012) |
| 221/222 | ↑ | Regeneration | Primary heps and mice with overexpression of miR-221 | Overexpression | Arnt | Mimic/inhibitor in primary heps with qPCR, W, LA. Correlated target protein in post PH tissue | Yuan et al. (2013) |
| ↑ | Cancer (HCC) | Human T (HCC), cirrhotic and NT liver tissues and cell lines | MA, qPCR, N | CDKN1B (p27) | Mimic in HeLa and HEK293T cells with W, LA. Correlated target protein in tissue samples | Pineau et al. (2010) | |
| ↑ | Cancer (HCC) | Human T (HCC) and NT liver tissues and cell lines | N, qPCR | PTEN TIMP3 | Mimic/inhibitor in MEG01, H460, and Calu-1-lung cells with LA, W, qPCR. | Garofolo et al. (2009) | |
| 296–5p | ↓ | NAFLD/NASH | Human livers-obese normal, simple steatosis and NASH | qPCR | PUMA | Mimic/inhibitor in Huh-7, KMCH cells with qPCR, WB, LA. Correlated target mRNA and protein in human livers-normal, simple steatosis and NASH | Cazanave et al. (2011) |
| 302b | ↓ | Development (embryo-adult) | Mouse foregut endoderm, hepatoblasts and adult liver | NGS | Tgfbr2 | Mimic in HEK293T cells with LA and W | Wei et al. (2013a) |
| 372 | ↑ | Viral hepatitis (HBV) | HBV infected human liver, HepG2 cells ± constitutive HBV production | MA, qPCR | NFIB | Cluster mimic in HepG2 cells with MA. Mimic in HeLa, HepG2 cells with W, LA | Guo et al. (2011) |
| 373 | ↑ | Viral hepatitis (HBV) | HBV infected human liver, HepG2 cells ± constitutive HBV production | MA, qPCR | NFIB | Cluster mimic in HepG2 cells with MA. Mimic in HeLa, HepG2 cells with W, LA | Guo et al. (2011) |
| 378 | ↓ | Regeneration (proliferation) | Mouse liver 0–18 h post PH | MA, qPCR | Odc1 | Mimic/inhibitor in Hepa 1–6 cells with qPCR, LA | Song et al. (2010) |
| 467b | ↓ | NAFLD/NASH | Liver of mice fed high fat diet for 8 weeks. Mouse Hepa 1–6 cells ± 50 µM SFA for 24 h | qPCR | Lpl | Mimic/inhibitor in Hepa 1–6 cells with qPCR, W, LA. Correlated target mRNA with high fat diet and SFA treatment of heps | Ahn et al. (2011) |
| 501 | ↑ | Viral hepatitis (HBV) | Human HepG2 ± constitutive HBC production, human HBV related HCC tissue with high/low HBV replication | MA, qPCR | HBXIP | Inhibitor in HepG2.2.15 cells with qPCR and W | Jin et al. (2013) |
| 612 | ↓ | Cancer (HCC) | HCC tissues and paired lung metastases | MA, qPCR | AKT2 | Mimic/inhibitor in HCCLM3 and HepG2 cells by W, LA | Tao et al. (2013) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahgoub, A.; Steer, C.J. MicroRNAs in the Evaluation and Potential Treatment of Liver Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5050052
Mahgoub A, Steer CJ. MicroRNAs in the Evaluation and Potential Treatment of Liver Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2016; 5(5):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5050052
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahgoub, Amar, and Clifford J. Steer. 2016. "MicroRNAs in the Evaluation and Potential Treatment of Liver Diseases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 5, no. 5: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5050052
APA StyleMahgoub, A., & Steer, C. J. (2016). MicroRNAs in the Evaluation and Potential Treatment of Liver Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 5(5), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm5050052






