Charting the Pathways of Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trajectories
Abstract
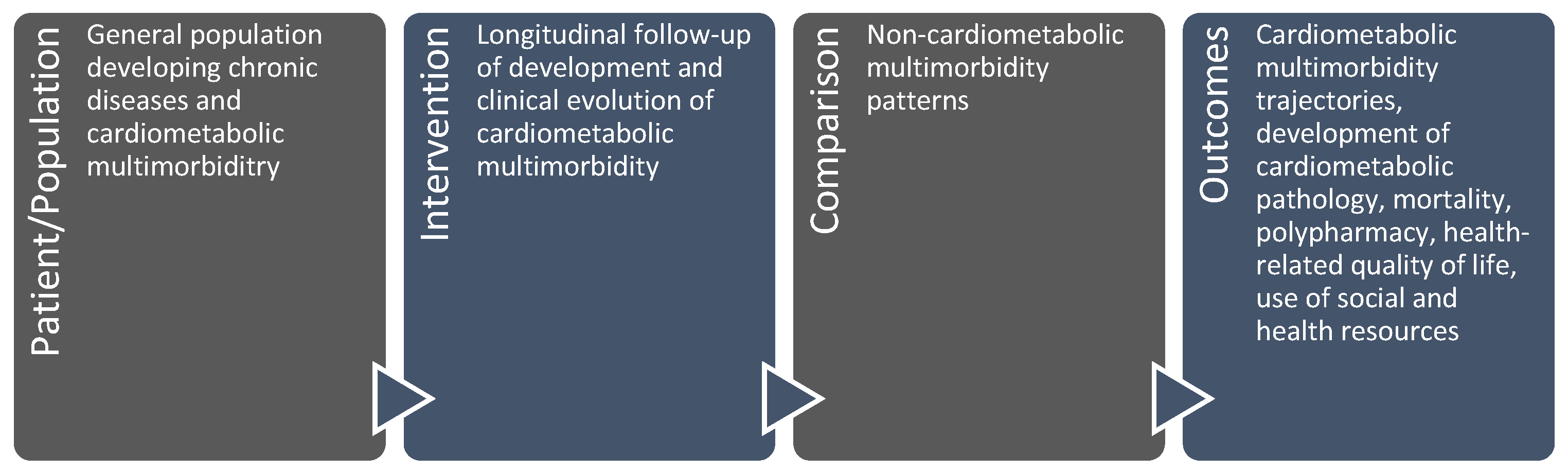
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search Results
3.2. Characteristics of the Studies Included
3.3. Key Information About the Included Studies Using Cluster Analysis
3.4. Key Information About the Included Studies Using Markov Models
3.5. Key Information About the Included Studies Using Other Techniques
4. Discussion
4.1. Incidence and Progression of Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity
4.2. Additional Factors: Sex, Polypharmacy, and Socio-Economic
4.3. Limitations Ans Strengths
4.4. Clinical Implications and Future Research Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Search Algorithm in EMBASE |
| ‘factor analysis, statistical’/de OR ‘cluster analysis’/de OR ‘patter *’:ab,ti OR ‘cluste *’:ab,ti OR ‘networ *’:ab,ti OR ‘profil *’:ab,ti OR ‘factor analysis’:ab,ti OR ‘cluster analysis’:ab,ti OR ‘network analysis’:ab,ti OR ‘Markov’:ab,ti AND ‘evolution’:ab,ti OR ‘longitudinal’:ab,ti OR ‘progress *’:ab,ti OR ‘development’:ab,ti OR ‘trajector *’:ab,ti OR ‘transitio *’:ab,ti AND ‘multiple chronic conditions’/de OR ‘multimorbidity’/de OR ‘multiple chronic conditions’:ab,ti OR ‘multimorbi*’:ab,ti |
| Search algorithm in MEDLINE |
| (“factor analysis, statistical”[MeSH Terms] OR “cluster analysis”[MeSH Terms] OR “patter *”[Title/Abstract] OR “cluste *”[Title/Abstract] OR “networ*”[Title/Abstract] OR “profil *”[Title/Abstract] OR “factor analysis”[Title/Abstract] OR “cluster analysis”[Title/Abstract] OR “network analysis”[Title/Abstract] OR “Markov”[Title/Abstract]) AND (((evolution[Title/Abstract]) OR (longitudinal[Title/Abstract]) OR (progress*[Title/Abstract]) OR (development[Title/Abstract]) OR (trajectory *[Title/Abstract]) OR (transitio*[Title/Abstract])) AND (“multiple chronic conditions”[MeSH Terms] OR “multimorbidity”[MeSH Terms] OR “multiple chronic conditions”[Title/Abstract] OR “multimorbid *”[Title/Abstract])) |
| * Literature search performed on 1 December 2024. |
References
- Brandlmeier, P. Multimorbidität unter den älteren Patienten in einer städtischen Allgemeinpraxis [Multimorbidity among elderly patients in an urban general practice]. ZFA (Stuttgart) 1976, 52, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. The World Health Report 2008: Primary Health Care Now More than Ever; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/43949 (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Prados-Torres, A.; Del Cura-González, I.; Prados-Torres, J.D.; Leiva-Fernández, F.; López-Rodríguez, J.A.; Calderón-Larrañaga, A.; Muth, C. Multimorbilidad en medicina de familia y los principios Ariadne. Un enfoque centrado en la persona [Multimorbidity in general practice and the Ariadne principles. A person-centred approach]. Aten. Primaria 2017, 49, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Academy of Medical Sciences. Multimorbidity: A Priority for Global Health Research; The Academy of Medical Sciences: London, UK, 2018; Available online: https://acmedsci.ac.uk/file-download/82222577 (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Gual, N.; Yuste Font, A.; Enfedaque Montes, B.; Blay Pueyo, C.; Martín Álvarez, R.; Inzitari, M. Perfil y evolución de pacientes crónicos complejos en una unidad de subagudos [Profile and evolution of chronic complex patients in a subacute unit]. Aten. Primaria 2017, 49, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambo-Lizalde, E.; Febrel Bordejé, M.; Urpí-Fernández, A.M.; Abad-Díez, J.M. La atención sanitaria a pacientes con multimorbilidad. La percepción de los profesionales [Health care for patients with multimorbidity. The perception of professionals]. Aten. Primaria 2021, 53, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palladino, R.; Pennino, F.; Finbarr, M.; Millett, C.; Triassi, M. Multimorbidity and Health Outcomes in Older Adults in Ten European Health Systems, 2006-15. Health Aff. (Proj. Hope) 2019, 38, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynn, L.G.; Valderas, J.M.; Healy, P.; Burke, E.; Newell, J.; Gillespie, P.; Murphy, A.W. The prevalence of multimorbidity in primary care and its effect on health care utilization and cost. Fam. Pract. 2011, 28, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 29, 372. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.A.; Forrest, J.L. Enhancing your practice through evidence-based decision making: PICO, learning how to ask good questions. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2001, 1, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granholm, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Møller, M.H. Use of the GRADE approach in systematic reviews and guidelines. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.; Hill, S. How to GRADE the Quality of the Evidence. Cochrane Consumers and Communication Group. CCCG. Version 3.0 December 2016. Available online: http://cccrg.cochrane.org/author-resources (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Vetrano, D.L.; Roso-Llorach, A.; Fernández, S.; Guisado-Clavero, M.; Violán, C.; Onder, G.; Fratiglioni, L.; Calderón-Larrañaga, A.; Marengoni, A. Twelve-year clinical trajectories of multimorbidity in a population of older adults. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violán, C.; Fernández-Bertolín, S.; Guisado-Clavero, M.; Foguet-Boreu, Q.; Valderas, J.M.; Vidal Manzano, J.; Roso-Llorach, A.; Cabrera-Bean, M. Five-year trajectories of multimorbidity patterns in an elderly Mediterranean population using Hidden Markov Models. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, N.; Sorger, J.; Gisinger, T.; Gyimesi, M.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Thurner, S.; Klimek, P. Decompression of Multimorbidity Along the Disease Trajectories of Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Front. Physiol. 2021, 11, 612604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cezard, G.; Sullivan, F.; Keenan, K. Understanding multimorbidity trajectories in Scotland using sequence analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velek, P.; Luik, A.I.; Brusselle, G.G.O.; Stricker, B.C.; Bindels, P.J.E.; Kavousi, M.; Kieboom, B.C.T.; Voortman, T.; Ruiter, R.; Ikram, M.A.; et al. Sex-specific patterns and lifetime risk of multimorbidity in the general population: A 23-year prospective cohort study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Ribelles, L.A.; Cabrera-Bean, M.; Danés-Castells, M.; Zabaleta-Del-Olmo, E.; Roso-Llorach, A.; Violán, C. Contribution of Frailty to Multimorbidity Patterns and Trajectories: Longitudinal Dynamic Cohort Study of Aging People. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2023, 9, e45848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiñones, A.R.; Hwang, J.; Heintzman, J.; Huguet, N.; Lucas, J.A.; Schmidt, T.D.; Marino, M. Trajectories of Chronic Disease and Multimorbidity Among Middle-aged and Older Patients at Community Health Centers. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e237497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roso-Llorach, A.; Vetrano, D.L.; Trevisan, C.; Fernández, S.; Guisado-Clavero, M.; Carrasco-Ribelles, L.A.; Fratiglioni, L.; Violán, C.; Calderón-Larrañaga, A. 12-year evolution of multimorbidity patterns among older adults based on Hidden Markov Models. Aging 2022, 14, 9805–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioakeim-Skoufa, I.; González-Rubio, F.; Aza-Pascual-Salcedo, M.; Laguna-Berna, C.; Poblador-Plou, B.; Vicente-Romero, J.; Coelho, H.; Santos-Mejías, A.; Prados-Torres, A.; Moreno-Juste, A.; et al. Multimorbidity patterns and trajectories in young and middle-aged adults: A large-scale population-based cohort study. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1349723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lleal, M.; Baré, M.; Herranz, S.; Orús, J.; Comet, R.; Jordana, R.; Baré, M. Trajectories of chronic multimorbidity patterns in older patients: MTOP study. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Larrañaga, A.; Vetrano, D.L.; Onder, G.; Gimeno-Feliu, L.A.; Coscollar-Santaliestra, C.; Carfí, A.; Pisciotta, M.S.; Angleman, S.; Melis, R.J.F.; Santoni, G.; et al. Assessing and Measuring Chronic Multimorbidity in the Older Population: A Proposal for Its Operationalization. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017, 72, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.K.; Tawiah, R.; Sawyer, M.; Scuffham, P. Patterns of multimorbid health conditions: A systematic review of analytical methods and comparison analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 47, 1687–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violán, C.; Foguet-Boreu, Q.; Roso-Llorach, A.; Rodriguez-Blanco, T.; Pons-Vigués, M.; Pujol-Ribera, E.; Valderas, J.M. Patrones de multimorbilidad en adultos jóvenes en Cataluña: Un análisis de clústeres [Multimorbidity patterns in young adults in Catalonia: An analysis of clusters]. Aten. Primaria 2016, 48, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzinsky-Fay, C.; Kohler, U. New Developments in Sequence Analysis. Sociol. Methods Res. 2010, 38, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studer, M.; Ritschard, G. What Matters in Differences Between Life Trajectories: A Comparative Review of Sequence Dissimilarity Measures. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 2016, 179, 481–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, P.; Lagan, J.; Fortune, C.; Bhatt, D.L.; Vestbo, J.; Niven, R.; Chaudhuri, N.; Schelbert, E.B.; Potluri, R.; Miller, C.A. Association of Cardiovascular Disease with Respiratory Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2166–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioakeim-Skoufa, I.; Poblador-Plou, B.; Carmona-Pírez, J.; Díez-Manglano, J.; Navickas, R.; Gimeno-Feliu, L.A.; González-Rubio, F.; Jureviciene, E.; Dambrauskas, L.; Prados-Torres, A.; et al. Multimorbidity Patterns in the General Population: Results from the EpiChron Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioakeim-Skoufa, I.; Clerencia-Sierra, M.; Moreno-Juste, A.; Elías de Molins Peña, C.; Poblador-Plou, B.; Aza-Pascual-Salcedo, M.; González-Rubio, F.; Prados-Torres, A.; Gimeno-Miguel, A. Multimorbidity Clusters in the Oldest Old: Results from the EpiChron Cohort. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Pírez, J.; Poblador-Plou, B.; Díez-Manglano, J.; Morillo-Jiménez, M.J.; Marín Trigo, J.M.; Ioakeim-Skoufa, I.; Gimeno-Miguel, A.; Prados-Torres, A. Multimorbidity networks of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and heart failure in men and women: Evidence from the EpiChron Cohort. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 193, 111392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Nikolic, G.; Van Pottelbergh, G.; van den Akker, M.; Vos, R.; De Moor, B. Development of Multimorbidity Over Time: An Analysis of Belgium Primary Care Data Using Markov Chains and Weighted Association Rule Mining. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappenschaar, M.; Hommersom, A.; Lucas, P.J.; Lagro, J.; Visscher, S.; Korevaar, J.C.; Schellevis, F.G. Multilevel temporal Bayesian networks can model longitudinal change in multimorbidity. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 66, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Xu, Y.; Sun, J.; Han, Y.; An, L.; Liu, J. Chronic diseases and multimorbidity patterns, their recent onset, and risk of new-onset Parkinson’s disease and related functional degeneration in older adults: A prospective cohort study. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 65, 102265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Villén, N.; Guisado-Clavero, M.; Fernández-Bertolín, S.; Troncoso-Mariño, A.; Foguet-Boreu, Q.; Amado, E.; Pons-Vigués, M.; Roso-Llorach, A.; Violán, C. Multimorbidity patterns, polypharmacy and their association with liver and kidney abnormalities in people over 65 years of age: A longitudinal study. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 206. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yu, C.; Sun, D.; Pang, Y.; Pei, P.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Du, H.; Liu, J.; et al. Duration-dependent impact of cardiometabolic diseases and multimorbidity on all-cause and cause-specific mortality: A prospective cohort study of 0.5 million participants. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kivimäki, M.; Strandberg, T.; Pentti, J.; Nyberg, S.T.; Frank, P.; Jokela, M.; Ervasti, J.; Suominen, S.B.; Vahtera, J.; Sipilä, P.N.; et al. Body-mass index and risk of obesity-related complex multimorbidity: An observational multicohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ho, H.E.; Yeh, C.J.; Wei, J.C.; Chu, W.M.; Lee, M.C. Trends of Multimorbidity Patterns over 16 Years in Older Taiwanese People and Their Relationship to Mortality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonaglioni, A.; Lonati, C.; Tescaro, L.; Nicolosi, G.L.; Proietti, M.; Lombardo, M.; Harari, S. Prevalence and clinical outcome of main echocardiographic and hemodynamic heart failure phenotypes in a population of hospitalized patients 70 years old and older. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 34, 1081–1094. [Google Scholar]
- Strauss, V.Y.; Jones, P.W.; Kadam, U.T.; Jordan, K.P. Distinct trajectories of multimorbidity in primary care were identified using latent class growth analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 67, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Evert, J.; Lawler, E.; Bogan, H.; Perls, T. Morbidity profiles of centenarians: Survivors, delayers, and escapers. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2003, 58, 232–237. [Google Scholar]
- Hitt, R.; Young-Xu, Y.; Silver, M.; Perls, T. Centenarians: The older you get, the healthier you have been. Lancet 1999, 354, 652. [Google Scholar]
- Singh-Manoux, A.; Fayosse, A.; Sabia, S.; Tabak, A.; Shipley, M.; Dugravot, A.; Kivimäki, M. Clinical, socioeconomic, and behavioural factors at age 50 years and risk of cardiometabolic multimorbidity and mortality: A cohort study. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002571. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas-Huerta, A.; Giraldo-Rodríguez, L.; Agudelo-Botero, M.; Mino-León, D. Differences by Sex in the Presentation of Multimorbidity: Longitudinal Study in Mexican Adults Living in the Community, 2001–2018. J. Women’s Health 2022, 31, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioakeim-Skoufa, I.; Atkins, K.; Hernández-Rodríguez, M.Á. Optimizing real-world evidence studies for regulatory decision-making and impact assessment in pharmacovigilance. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2025, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Author (Year) | Country | Clinical Setting | Age at Baseline | Methodological Approach | Diseases Assessed, n (Cardiometabolic/Total) | Additional Information Assessed | Quality of Evidence (GRADE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vetrano DL et al. (2020) [13] | Sweden | Community or in institutions (SNAC-K database) | ≥60 years | Cluster analysis (fuzzy c-means) | 16/60 | Education, level of disability, walking speed, cognitive status, drug information | Low ⨁⨁◯◯ |
| Violán C et al. (2020) [14] | Spain | Primary care (SIDIAP database) | ≥65 | Hidden Markov models | 16/60 | Socio-economic status, number of invoiced drugs and polypharmacy, visits to primary care | Low ⨁⨁◯◯ |
| Haug N et al. (2021) [15] | Austria | Specialised care | Not defined as an exclusion criteria | Hierarchical cluster analysis | ≥9/131 | Low ⨁⨁◯◯ | |
| Cezard G et al. (2022) [16] | UK | Specialised care (Scottish Longitudinal Study) | 40–74 years | Sequence analysis, optimal matching, hierarchical cluster analysis | 2/3 | Marital status, household size, education, household tenure | Low ⨁⨁◯◯ |
| Velek P et al. (2022) [17] | Netherlands | Community-dwelling (Rotterdam Study) | ≥45 | Chronological sequence (first three diagnoses), combinations (pairs) | 4/10 | Marital status, education, smoking status, blood pressure, ancestry | Low ⨁⨁◯◯ |
| Carrasco-Ribelles LA et al. (2023) [18] | Spain | Primary care (SIDIAP database) | 65–100 years | Cluster analysis (fuzzy c-means) | 16/60 | Socio-economic status, visits to primary care, clinical parameters, lab tests, lifestyle (smoking status, alcohol intake), emergency admission episodes, drug information, inclusion in social assistance programs | Low ⨁⨁◯◯ |
| Quiñones AR et al. (2023) [19] | USA | Primary care (ADVANCE database) | ≥45 | Clinically relevant groups | 8/22 | Socio-economic status | Low ⨁⨁◯◯ |
| Roso-Llorach A et al. (2023) [20] | Sweden | Community or in institutions (SNAC-K database) | ≥60 years | Hidden Markov models | 16/60 | Education, walking speed, cognitive status, clinical parameters, lab tests, drug information | Low ⨁⨁◯◯ |
| Ioakeim-Skoufa I et al. (2024) [21] | Spain | Primary and specialised care (EpiChron database) | 18–65 years | Cluster analysis (k-means) | ≥11/153 | Drug information, acute diseases | Low ⨁⨁◯◯ |
| Lleal M. et al. (2024) [22] | Spain | Primary care (MRisk-COVID study) | 65–95 years (women); 65–90 years (men) | Cluster analysis (fuzzy c-means) | ≥20/73 | Low ⨁⨁◯◯ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ioakeim-Skoufa, I.; Ledesma-Calvo, R.; Moreno-Juste, A.; Roque, F.; Atkins, K.; Hernández-Rodríguez, M.Á.; Aza-Pascual-Salcedo, M.; González-Rubio, F.; Lasala-Aza, C.; Esteban-Jiménez, Ó.; et al. Charting the Pathways of Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trajectories. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082615
Ioakeim-Skoufa I, Ledesma-Calvo R, Moreno-Juste A, Roque F, Atkins K, Hernández-Rodríguez MÁ, Aza-Pascual-Salcedo M, González-Rubio F, Lasala-Aza C, Esteban-Jiménez Ó, et al. Charting the Pathways of Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trajectories. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082615
Chicago/Turabian StyleIoakeim-Skoufa, Ignatios, Rubén Ledesma-Calvo, Aida Moreno-Juste, Fátima Roque, Kerry Atkins, Miguel Ángel Hernández-Rodríguez, Mercedes Aza-Pascual-Salcedo, Francisca González-Rubio, Carmen Lasala-Aza, Óscar Esteban-Jiménez, and et al. 2025. "Charting the Pathways of Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trajectories" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082615
APA StyleIoakeim-Skoufa, I., Ledesma-Calvo, R., Moreno-Juste, A., Roque, F., Atkins, K., Hernández-Rodríguez, M. Á., Aza-Pascual-Salcedo, M., González-Rubio, F., Lasala-Aza, C., Esteban-Jiménez, Ó., Avedillo-Salas, A., Cebollada-Herrera, C., Gimeno-Miguel, A., & Vicente-Romero, J. (2025). Charting the Pathways of Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trajectories. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082615








