Haptic Visual and Superimposed Digital Imaging Analysis Improves the Interrater Reliability of J-Sign Assessment in Patients with Patellofemoral Instability: A Prospective Diagnostic Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Exclusion Citeria
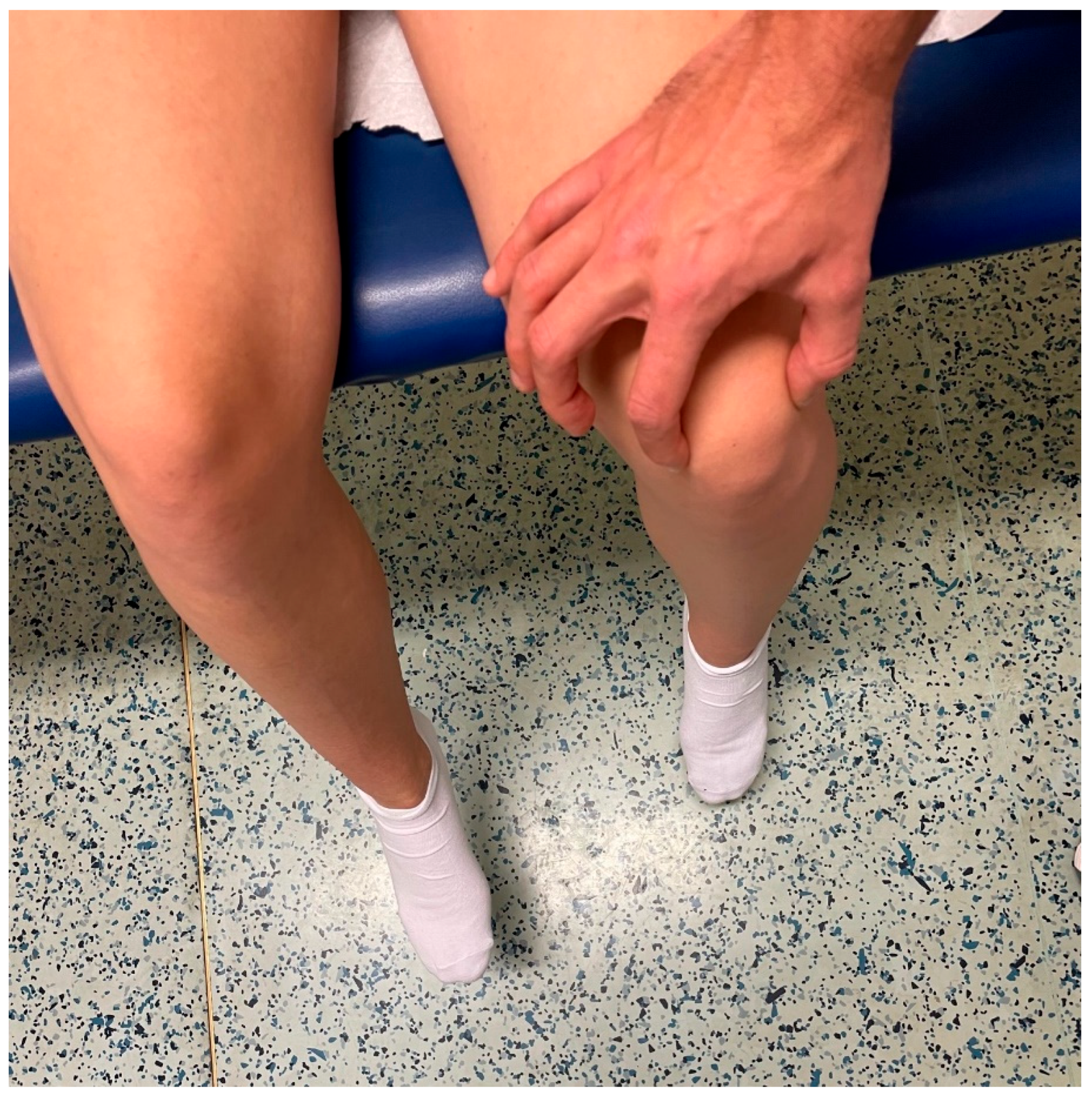
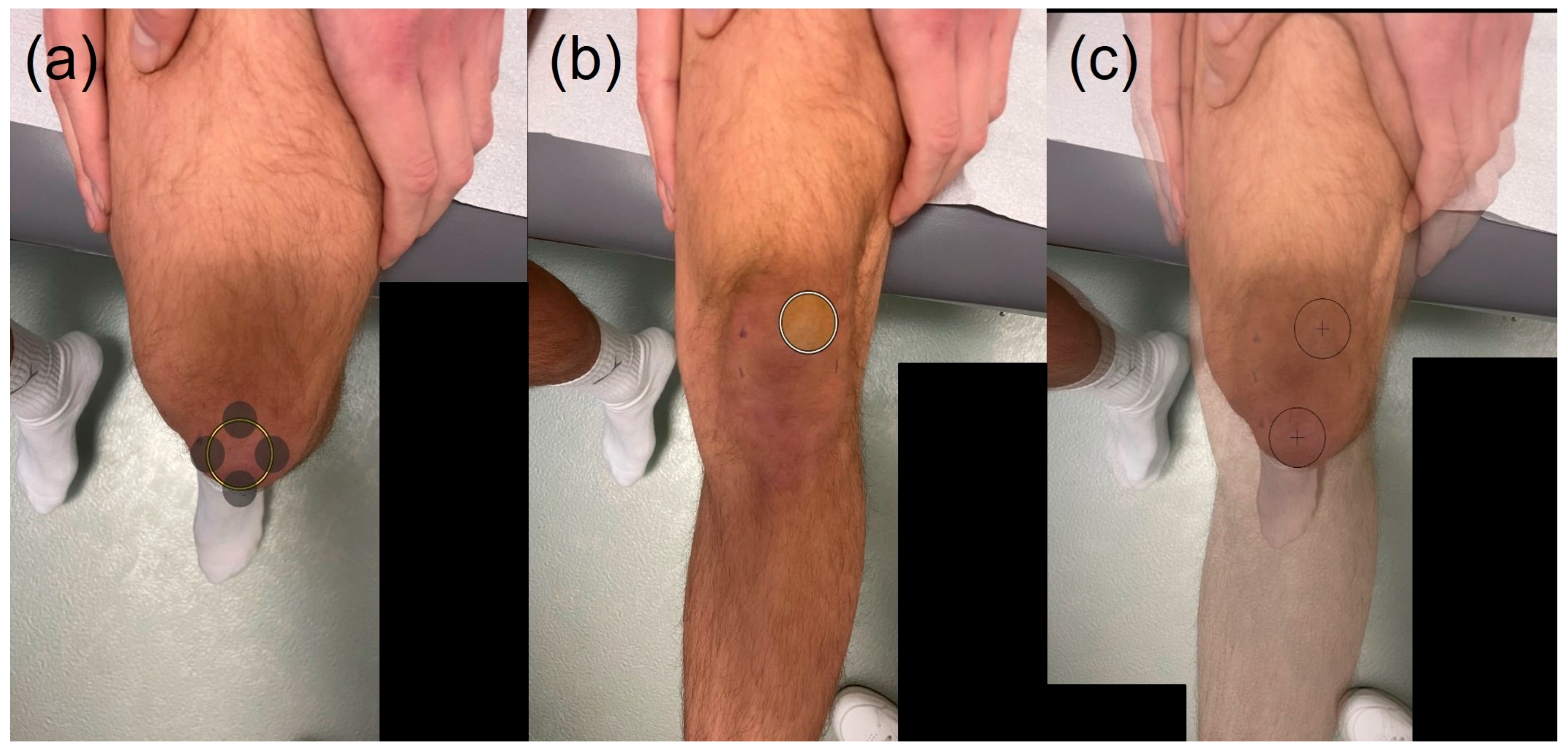
2.3. J-Sign Evaluation Methods
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fithian, D.C.; Paxton, E.W.; Stone, M.L.; Silva, P.; Davis, D.K.; Elias, D.A.; White, L.M. Epidemiology and natural history of acute patellar dislocation. Am. J. Sports Med. 2004, 32, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, T.L.; Pareek, A.; Hewett, T.E.; Stuart, M.J.; Dahm, D.L.; Krych, A.J. Incidence of First-Time Lateral Patellar Dislocation: A 21-Year Population-Based Study. Sports Health 2018, 10, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, F.; Pilone, M.; Eschweiler, J.; Marsilio, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Maffulli, N. High Rates of Damage to the Medial Patellofemoral Ligament, Lateral Trochlea, and Patellar Crest After Acute Patellar Dislocation: Magnetic Resonance Imaging Analysis. Arthroscopy 2022, 38, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Toritsuka, Y.; Amano, H.; Uchida, R.; Takao, R.; Horibe, S. Factors Affecting the Outcomes of Double-Bundle Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction for Recurrent Patellar Dislocations Evaluated by Multivariate Analysis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 2988–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, S.N.; Nathan, S.T.; Wall, E.J.; Eismann, E.A. Complications of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction in young patients. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, D.K.; Grawe, B.; Magnussen, R.A.; Ceasar, A.; Parikh, S.N.; Wall, E.J.; Colosimo, A.J.; Kaeding, C.C.; Myer, G.D. Outcomes After Isolated Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction for the Treatment of Recurrent Lateral Patellar Dislocations: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2016, 44, 2993–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, N.D.; Smith, N.A.; Parsons, N.; Spalding, T.; Thompson, P.; Sprowson, A.P. Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction for Patellar Dislocation: A Systematic Review. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2014, 2, 2325967114544021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, F.; Marsilio, E.; Oliva, F.; Eschweiler, J.; Hildebrand, F.; Maffulli, N. Chondral injuries in patients with recurrent patellar dislocation: A systematic review. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2022, 17, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cregar, W.M.; Huddleston, H.P.; Wong, S.E.; Farr, J.; Yanke, A.B. Inconsistencies in Reporting Risk Factors for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Failure: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Sports Med. 2022, 50, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthieu, L.; Pedro Augusto, G.T.; Gabriela, H.; Romain, G.; Nicolas, D.; Alain, B.; Andrea, F. Four-dimensional CT analysis of patellofemoral instability: A prospective cohorte study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2025, 194, 112450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, F.; Gligor, A.; Bataga, T. Structured Integration and Alignment Algorithm: A Tool for Personalized Surgical Treatment of Tibial Plateau Fractures. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frings, J.; Dust, T.; Krause, M.; Ohlmeier, M.; Frosch, K.-H.; Adam, G.; Warncke, M.; Maas, K.-J.; Henes, F.O. Objective assessment of patellar maltracking with 3 T dynamic magnetic resonance imaging: Feasibility of a robust and reliable measuring technique. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, F.; Milinkovic, D.D.; Zimmerer, A.; Balcarek, P. When Should Bony Correction Be Considered in Addition to Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction? Results of a Clinically Derived 2-Group Classification of Lateral Patellar Instability Based on 122 Patients at 2- to 5-Year Follow-up. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2023, 11, 23259671221147572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinkovic, D.D.; Jovandic, I.; Zimmermann, F.; Balcarek, P. The J-sign and the body mass index determine the disease-specific quality of life in patients with lateral patellar instability. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2022, 30, 1672–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemstra, L.A.; Kerslake, S.A.; Lafave, M.R. Influence of Risky Pathoanatomy and Demographic Factors on Clinical Outcomes After Isolated Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction: A Regression Analysis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 2904–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Song, G.; Zheng, T.; Feng, H. A pre-operative grade 3 J-sign adversely affects short-term clinical outcome and is more likely to yield MPFL residual graft laxity in recurrent patellar dislocation. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2020, 28, 2147–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Song, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, T.; Ni, Q.; Feng, H. A High-Grade J Sign Is More Likely to Yield Higher Postoperative Patellar Laxity and Residual Maltracking in Patients with Recurrent Patellar Dislocation Treated with Derotational Distal Femoral Osteotomy. Am. J. Sports Med. 2020, 48, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-J.; Dimeng, L.-Q.; Cao, Y.-W.; Zheng, T.; Song, G.-Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Predictors of Graft Failure After Primary Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2022, 10, 23259671221138854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Bai, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z. Clinical Outcomes and Prognostic Factors in Patients with Recurrent Patellar Lateral Dislocation Treated with Isolated Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction: A Retrospective Single-Center Analysis. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2021, 9, 2325967121995803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, M.J.; Tanaka, M.J.; Demehri, S.; Cosgarea, A.J. Accuracy and Reliability of the Visual Assessment of Patellar Tracking. Am. J. Sports Med. 2020, 48, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemstra, L.A.; Sheehan, B.; Sasyniuk, T.M.; Kerslake, S. Inter-rater Reliability of the Classification of the J-Sign Is Inadequate Among Experts. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2022, 32, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimenko, O.; Sousa, T.C.; Baker, R.; Carl, J.; Mader, S.; Holden, K.; McMulkin, M.L. How Reliable is a J-sign Severity Scale When Assessing Lateral Patellar Instability? J. Pediatr. Orthop. Soc. N. Am. 2023, 5, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.O.; Clark, A.; Neda, S.; Arendt, E.A.; Post, W.R.; Grelsamer, R.P.; Dejour, D.; Almqvist, K.F.; Donell, S.T. The intra- and inter-observer reliability of the physical examination methods used to assess patients with patellofemoral joint instability. Knee 2012, 19, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemstra, L.A.; O’Brien, C.L.; Lafave, M.R.; Kerslake, S. Common Physical Examination Tests for Patellofemoral Instability Demonstrate Weak Inter-Rater Reliability. Arthrosc. Sports Med. Rehabil. 2021, 3, e673–e677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujang, M.A.; Baharum, N. Guidelines of the minimum sample size requirements for Kappa agreement test. Epidemiol. Biostat. Public Health 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walla, N.; Moore, T.; Harangody, S.; Fitzpatrick, S.; Flanigan, D.C.; Duerr, R.A.; Siston, R.; Magnussen, R.A. Qualitative visual assessment of the J-sign demonstrates high inter-rater reliability. J. ISAKOS 2023, 8, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigrist, R.; Rauter, G.; Riener, R.; Wolf, P. Augmented visual, auditory, haptic, and multimodal feedback in motor learning: A review. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2013, 20, 21–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, M.C.; Snowden, R.J. Identification of visual stimuli is improved by accompanying auditory stimuli: The role of eye movements and sound location. Perception 2001, 30, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feygin, D.; Keehner, M.; Tendick, R. Haptic guidance: Experimental evaluation of a haptic training method for a perceptual motor skill. In Proceedings of the 10th Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems. HAPTICS 2002, Orlando, FL, USA, 24–25 March 2002; IEEE: New York City, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Patrizio, H.A.; Phyu, R.; Kim, B.; Brolis, N.V. Improved cardiac auscultation competency interweaving visual, auditory, and tactile stimuli: A preliminary study. Int. J. Med. Educ. 2024, 15, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Grade 0 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual (Rater 1) | 20 (39%) | 19 (37%) | 11 (22%) | 1 (2%) |
| Visual (Rater 2) | 32 (63%) | 16 (31%) | 2 (4%) | 1 (2%) |
| Haptic visual (Rater 1) | 17 (33%) | 18 (35%) | 15 (29%) | 1 (2%) |
| Haptic visual (Rater 2) | 18 (35%) | 20 (39%) | 11 (22%) | 2 (4%) |
| Photo application (Rater 1) | 21 (41%) | 13 (25%) | 15 (29%) | 2 (4%) |
| Photo application (Rater 2) | 21 (41%) | 17 (33%) | 13 (25%) | - |
| Weighted Cohen’s Kappa (κ) | Standard Deviation | Lower 95% Confidence Interval | Upper 95% Confidence Interval | Level of Agreement | Percent of Agreement | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual | 0.39 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.6 | Fair | 54.9% |
| Haptic visual | 0.89 | 0.05 | 0.8 | 0.98 | Almost perfect | 90.2% |
| Photo Application | 0.85 | 0.05 | 0.74 | 0.95 | Almost perfect | 84.3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zimmermann, F.; Mandelka, E.; Gierse, J.; Grützner, P.A.; Vetter, S.Y.; Balcarek, P. Haptic Visual and Superimposed Digital Imaging Analysis Improves the Interrater Reliability of J-Sign Assessment in Patients with Patellofemoral Instability: A Prospective Diagnostic Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8559. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238559
Zimmermann F, Mandelka E, Gierse J, Grützner PA, Vetter SY, Balcarek P. Haptic Visual and Superimposed Digital Imaging Analysis Improves the Interrater Reliability of J-Sign Assessment in Patients with Patellofemoral Instability: A Prospective Diagnostic Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(23):8559. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238559
Chicago/Turabian StyleZimmermann, Felix, Eric Mandelka, Jula Gierse, Paul Alfred Grützner, Sven Y. Vetter, and Peter Balcarek. 2025. "Haptic Visual and Superimposed Digital Imaging Analysis Improves the Interrater Reliability of J-Sign Assessment in Patients with Patellofemoral Instability: A Prospective Diagnostic Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 23: 8559. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238559
APA StyleZimmermann, F., Mandelka, E., Gierse, J., Grützner, P. A., Vetter, S. Y., & Balcarek, P. (2025). Haptic Visual and Superimposed Digital Imaging Analysis Improves the Interrater Reliability of J-Sign Assessment in Patients with Patellofemoral Instability: A Prospective Diagnostic Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(23), 8559. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238559







