Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Glycemic Status and Growth Delay in Korean Children Aged 18–36 Months: A Population-Based Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
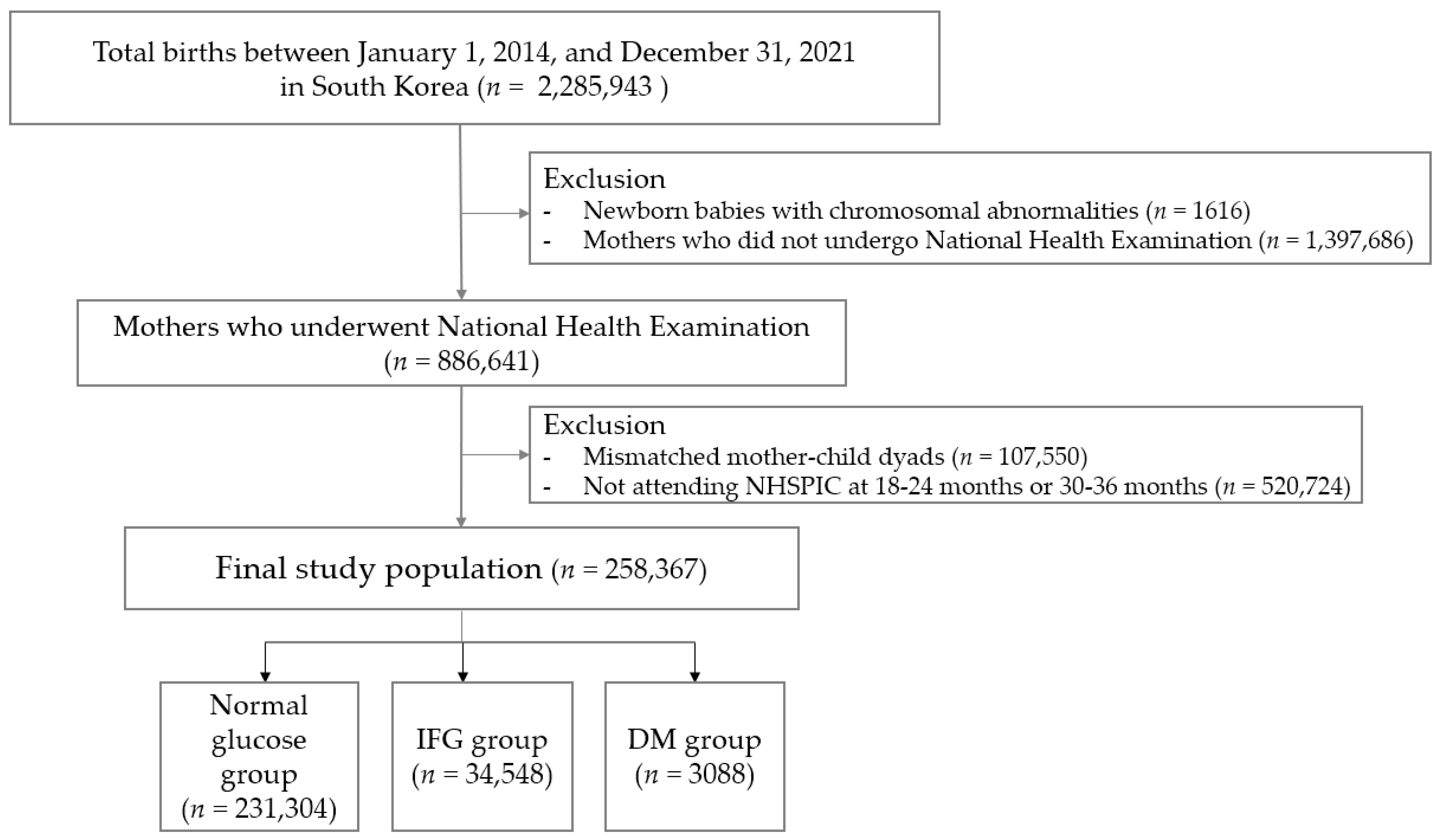
2.1. Study Data Sources and Participants
2.2. Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Glycemic Status
2.3. Growth Delay
2.4. Assessment of Visual and Auditory Development
2.5. Other Variables
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics by Maternal Glucose Status
3.2. Growth Delay, Visual, and Auditory Problems of Offspring
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | body mass index |
| CIs | confidence intervals |
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| GDM | gestational diabetes mellitus |
| ICD-10 | International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision |
| IFG | impaired fasting glucose |
| IRs | incidence rates |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| IPTW | inverse probability of treatment weighting |
| LGA | large for gestational age |
| NHIS | National Health Insurance Service |
| NHSPIC | National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children |
| NICU | neonatal intensive care unit |
| PS | propensity scores |
| RRs | relative risks |
| SGA | small for gestational age |
References
- Benhalima, K.; Geerts, I.; Calewaert, P.; Van Rijsselberghe, M.; Lee, D.; Bochanen, N.; Verstraete, S.; Buyse, L.; Lewi, L.; Caron, R.; et al. The 2024 Flemish consensus on screening for gestational diabetes mellitus early and later in pregnancy. Acta Clin. Belg. 2024, 79, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, B.E.; Lowe, L.P.; Dyer, A.R.; Trimble, E.R.; Chaovarindr, U.; Coustan, D.R.; Hadden, D.R.; McCance, D.R.; Hod, M.; McIntyre, H.D.; et al. Hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Nilsson, I.A.K.; Gissler, M.; Lavebratt, C. Associations of Maternal Diabetes and Body Mass Index With Offspring Birth Weight and Prematurity. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.E. Long-term outcomes in mothers diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus and their offspring. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 50, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabiat, D.; Jabery, M.A.; Kemp, V.; Jenkins, M.; Whitehead, L.C.; Adams, G. Motor Developmental Outcomes in Children Exposed to Maternal Diabetes during Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.H.; Jung, S.H.; Choi, D.; Kim, B.Y.; Kim, C.H.; Mok, J.O. Gestational diabetes in Korea: Temporal trends in prevalence, treatment, and short-term consequences from a national health insurance claims database between 2012 and 2016. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 171, 108586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Lee, K.W. High pre-pregnancy BMI with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes in Korean women. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Cui, M.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, G.; Zuo, H.; Xiu, Q.; Shah, P.S. Pre-pregnancy body mass index, gestational diabetes mellitus, and gestational weight gain: Individual and combined effects on fetal growth. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1354355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.H.; Jang, H.C. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-D.; Luo, Y.-R.; Lee, M.-C.; Yeh, C.-J. Factors affecting the growth of children till the age of three years with overweight whose mothers have diabetes mellitus: A population-based cohort study. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabiat, D.; Al Jabery, M.; Whitehead, L. Does Intrauterine Exposure to Diabetes Impact Mental and Motor Skills? A Meta-Analysis of the Bayley Scales of Infant Development. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saros, L.; Vahlberg, T.; Koivuniemi, E.; Houttu, N.; Tertti, K.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Niinikoski, H.; Laitinen, K. Maternal diet and gestational diabetes mellitus modestly influence children’s growth during their first 24 months. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2025, 81, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, J.; Zhu, L.; Hao, X.; Yan, S.; Tong, J.; Tao, S.; Xu, S.; Tao, F.; et al. Association Between Maternal Fasting Glucose Levels Throughout Pregnancy and Preschoolers’ Refractive Errors. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 2815–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, K.; Ravi, R. Effect of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus on Newborn Hearing: A Systematic Review. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2025, 134, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.S. Review of National Health Screening Program for Infant and Children in Korea. J. Korean Med. Assoc. 2010, 53, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-S.; Choi, Y.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, M.-H.; Lee, N. Association between the COVID-19 pandemic and childhood development aged 30 to 36 months in South Korea, based on the National health screening program for infants and children database. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.J.; Kim, T.E.; Park, S.H.; Park, H.W.; Kweon, H.J.; Choi, J.; Shin, J. Association Between Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index and Growth Delay in Korean Children Aged 18–36 Months: A Population-Based Study. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Physician Counseling Manual for the Infant and Child Health Screening Program. Available online: https://www.kdca.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a20507020000&bid=0019&list_no=726955&act=view (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Hammoud, N.M.; Visser, G.H.A.; van Rossem, L.; Biesma, D.H.; Wit, J.M.; de Valk, H.W. Long-term BMI and growth profiles in offspring of women with gestational diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womack, S.R.; Beam, C.R.; Giangrande, E.J.; Scharf, R.J.; Tong, X.; Ponnapalli, M.; Davis, D.W.; Turkheimer, E. Nonlinear Catch-Up Growth in Height, Weight, and Head Circumference from Birth to Adolescence: A Longitudinal Twin Study. Behav. Genet. 2023, 53, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Chen, S.; Gao, X. A retrospective study to investigate the risk factors for gestational diabetes mellitus and its impact on maternal and neonatal outcomes. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2025, 39, 109035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, M.H.; Sacks, D.A.; Xiang, A.H.; Lawrence, J.M. The relative contribution of prepregnancy overweight and obesity, gestational weight gain, and IADPSG-defined gestational diabetes mellitus to fetal overgrowth. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodolaki, K.; Pergialiotis, V.; Iakovidou, N.; Boutsikou, T.; Iliodromiti, Z.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C. The impact of maternal diabetes on the future health and neurodevelopment of the offspring: A review of the evidence. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1125628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titialii-Torres, K.F.; Morris, A.C. Embryonic hyperglycemia perturbs the development of specific retinal cell types, including photoreceptors. J. Cell Sci. 2022, 135, jcs259187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, E.; Dezateux, C.; Cortina-Borja, M.; Knowles, R.L. Prevalence of permanent childhood hearing loss detected at the universal newborn hearing screen: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, E.H.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, N.; Jung, J.E.; Han, S.H.; Cho, H.Y. Effect of Endogenic and Exogenic Oxidative Stress Triggers on Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes: Preeclampsia, Fetal Growth Restriction, Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Preterm Birth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Chen, S.; Hu, J. Diabetes mellitus and hearing loss. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, K.; Mathmann, P.; Chadha, S.; Euler, H.A.; White, K.R. Newborn Hearing Screening Benefits Children, but Global Disparities Persist. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.Y.; Park, S.K.; Choi, S.; Chang, J. Analysis of Newborn Hearing Screening Results in South Korea after National Health Insurance Coverage: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillick, D.; O’Reilly, D.; Murphy, L.; Breathnach, F.; McCallion, N. Increased risk of admission to neonatal intensive care unit in neonates born to mothers with pregestational diabetes. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2025, 184, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakotey, D.A.; Clarke, A.M.; Cormack, B.E.; Bloomfield, F.H.; Harding, J.E.; Bloomfield, F.H.; Jiang, Y.; Crowther, C.A.; Cormack, B.E.; Bloomfield, F.; et al. Postnatal growth and neurodevelopment at 2 years’ corrected age in extremely low birthweight infants. Pediatr. Res. 2024, 96, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Normal Glucose | IFG | DM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother–child dyads, N (%) | 231,304 (89.5) | 23,975 (9.3) | 3088 (1.2) | |
| Maternal Characteristics | ||||
| Maternal age, years | 32.24 ± 3.9 | 32.96 ± 4.1 | 34.17 ± 4.3 | <0.001 |
| Maternal age, ≥35 years | 60,544 (26.2) | 8028 (33.5) | 1398 (45.3) | <0.001 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 21.61 ± 3.2 | 22.82 ± 3.9 | 25.68 ± 5.2 | <0.001 |
| Pre-gestational hypertension | 4506 (2.0) | 723 (3.0) | 345 (11.2) | <0.001 |
| Pregnancy-induced hypertension | 24,764 (10.7) | 3129 (13.1) | 604 (19.6) | <0.001 |
| Gestational DM | 33,457 (14.5) | 5495 (22.9) | 1666 (54.0) | <0.001 |
| Depression | 4028 (1.7) | 461 (1.9) | 89 (2.9) | <0.001 |
| Preterm birth | 9728 (4.2) | 1172 (4.9) | 277 (9.0) | <0.001 |
| Vaginal delivery | 129,697 (56.1) | 12,124 (50.6) | 1059 (34.3) | <0.001 |
| Offspring Characteristics | ||||
| Sex, male | 118,058 (51.0) | 12,202 (50.9) | 1583 (51.3) | 0.882 |
| Gestational age at birth, weeks | 35.43 ± 2.4 | 35.17 ± 2.5 | 34.85 ± 2.4 | <0.001 |
| Birthweight, mean, kg | 3.18 ± 0.4 | 3.22 ± 0.5 | 3.26 ± 0.6 | <0.001 |
| Birthweight group | <0.001 | |||
| <2 kg | 2354 (1.0) | 277 (1.2) | 60 (1.9) | |
| 2–3 kg | 60,480 (26.2) | 5736 (23.9) | 771 (25.0) | |
| 3–4 kg | 161,695 (69.9) | 16,807 (70.1) | 1897 (61.7) | |
| ≥4 kg | 6775 (2.9) | 1155 (4.8) | 360 (11.7) | |
| Multiple birth | 8220 (3.6) | 938 (3.9) | 183 (5.9) | <0.001 |
| Major anomaly | 14,611 (6.3) | 1616 (6.7) | 357 (11.6) | <0.001 |
| Small for gestational age | 1953 (0.8) | 162 (0.7) | 37 (1.2) | <0.001 |
| NICU admission | 13,769 (6.0) | 1695 (7.1) | 497 (16.1) | <0.001 |
| 18–24 Months | 30–36 Months | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycemic Status | N | Event | IR | RR (95% CI) | p-Value | Event | IR | RR (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Height < 10 Percentile | |||||||||
| Normal | 231,304 | 8104 | 3.50 | 1 (ref.) | 9434 | 4.08 | 1 (ref.) | ||
| IFG | 23,975 | 862 | 3.60 | 1.064 (1.033–1.097) | <0.001 | 979 | 4.08 | 1.036 (1.008–1.065) | <0.001 |
| DM | 3088 | 180 | 5.83 | 1.150 (1.117–1.185) | <0.001 | 168 | 5.44 | 1.039 (1.010–1.069) | <0.001 |
| Weight < 10 Percentile | |||||||||
| Normal | 231,304 | 8897 | 3.85 | 1 (ref.) | 8975 | 3.88 | 1 (ref.) | ||
| IFG | 23,975 | 874 | 3.65 | 1.078 (1.047–1.109) | <0.001 | 882 | 3.68 | 1.077 (1.047–1.108) | <0.001 |
| DM | 3088 | 148 | 4.79 | 1.646 (1.603–1.690) | <0.001 | 134 | 4.34 | 1.354 (1.318–1.391) | <0.001 |
| Head Circumference < 10 Percentile | |||||||||
| Normal | 231,304 | 9793 | 4.23 | 1 (ref.) | 10,934 | 4.73 | 1 (ref.) | ||
| IFG | 23,975 | 1090 | 4.55 | 1.143 (1.113–1.174) | <0.001 | 1188 | 4.96 | 1.128 (1.100–1.157) | <0.001 |
| DM | 3088 | 192 | 6.22 | 1.234 (1.202–1.267) | 0.073 | 195 | 6.31 | 1.406 (1.373–1.441) | <0.001 |
| Visual Developmental Problem | |||||||||
| Normal | 231,304 | 2689 | 1.16 | 1 (ref.) | 3748 | 1.62 | 1 ( ref.) | ||
| IFG | 23,975 | 303 | 1.26 | 1.019 (0.966–1.074) | 0.496 | 437 | 1.82 | 1.103 (1.056–1.152) | <0.001 |
| DM | 3088 | 57 | 1.85 | 1.236 (1.174–1.301) | <0.001 | 69 | 2.23 | 1.313 (1.259–1.370) | <0.001 |
| Auditory Developmental Problem | |||||||||
| Normal | 231,304 | 18,598 | 8.04 | 1 (ref.) | 5505 | 2.38 | 1 (ref.) | ||
| IFG | 23,975 | 2168 | 9.04 | 1.101 (1.08–1.122) | <0.001 | 681 | 2.84 | 1.154 (1.113–1.196) | <0.001 |
| DM | 3088 | 307 | 9.94 | 0.952 (0.933–0.971) | <0.001 | 118 | 3.82 | 0.823 (0.791–0.855) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, E.-J.; Han, Y.; Kim, T.-E.; Park, S.-H.; Park, H.W.; Kweon, H.J.; Choi, J.; Shin, J. Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Glycemic Status and Growth Delay in Korean Children Aged 18–36 Months: A Population-Based Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7230. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207230
Oh E-J, Han Y, Kim T-E, Park S-H, Park HW, Kweon HJ, Choi J, Shin J. Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Glycemic Status and Growth Delay in Korean Children Aged 18–36 Months: A Population-Based Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7230. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207230
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Eun-Jung, Yeeun Han, Tae-Eun Kim, Sang-Hyun Park, Hye Won Park, Hyuk Jung Kweon, Jaekyung Choi, and Jinyoung Shin. 2025. "Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Glycemic Status and Growth Delay in Korean Children Aged 18–36 Months: A Population-Based Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7230. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207230
APA StyleOh, E.-J., Han, Y., Kim, T.-E., Park, S.-H., Park, H. W., Kweon, H. J., Choi, J., & Shin, J. (2025). Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Glycemic Status and Growth Delay in Korean Children Aged 18–36 Months: A Population-Based Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7230. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207230








