The Role of Synthetic Meshes in Revision Surgery After Breast Augmentation: A Personal Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
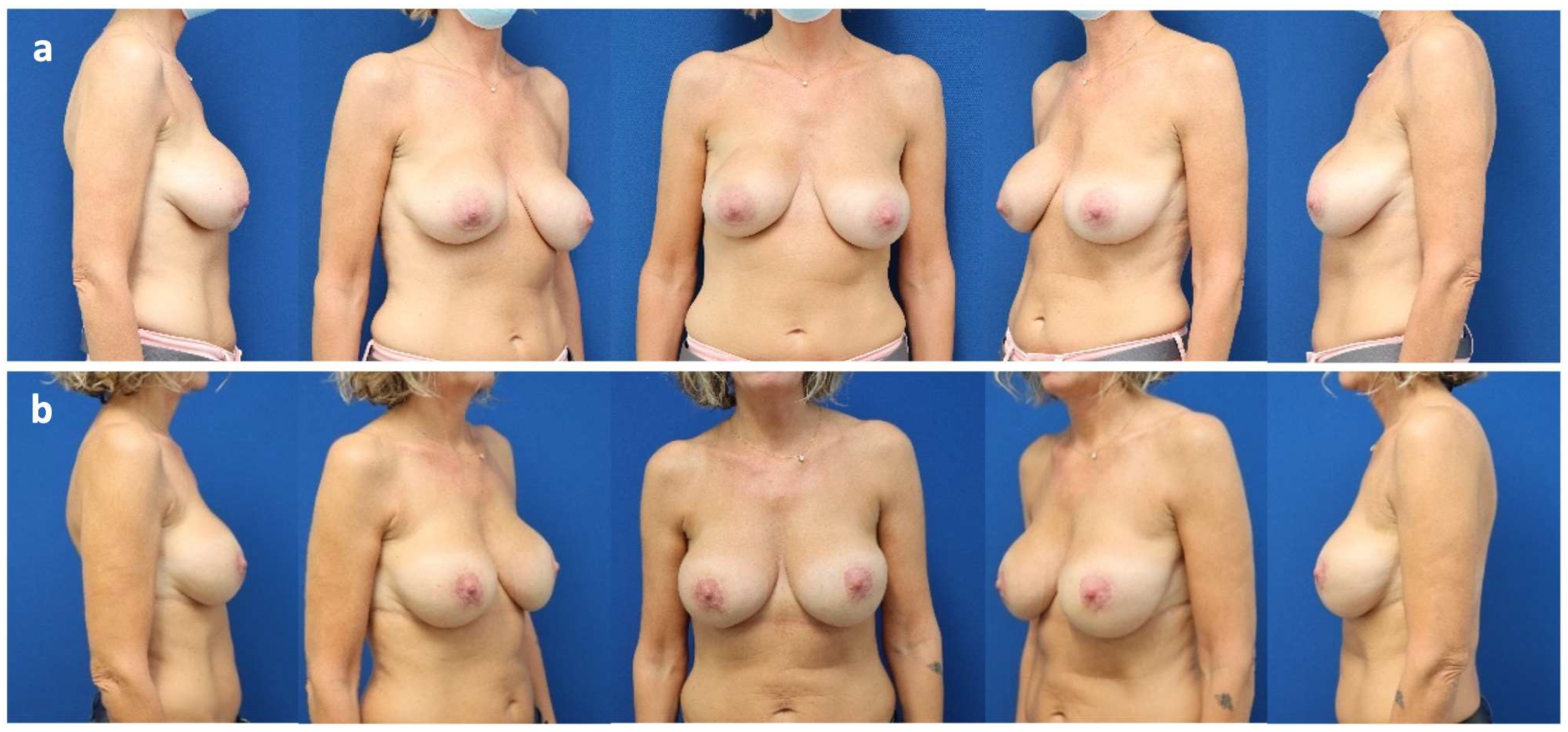
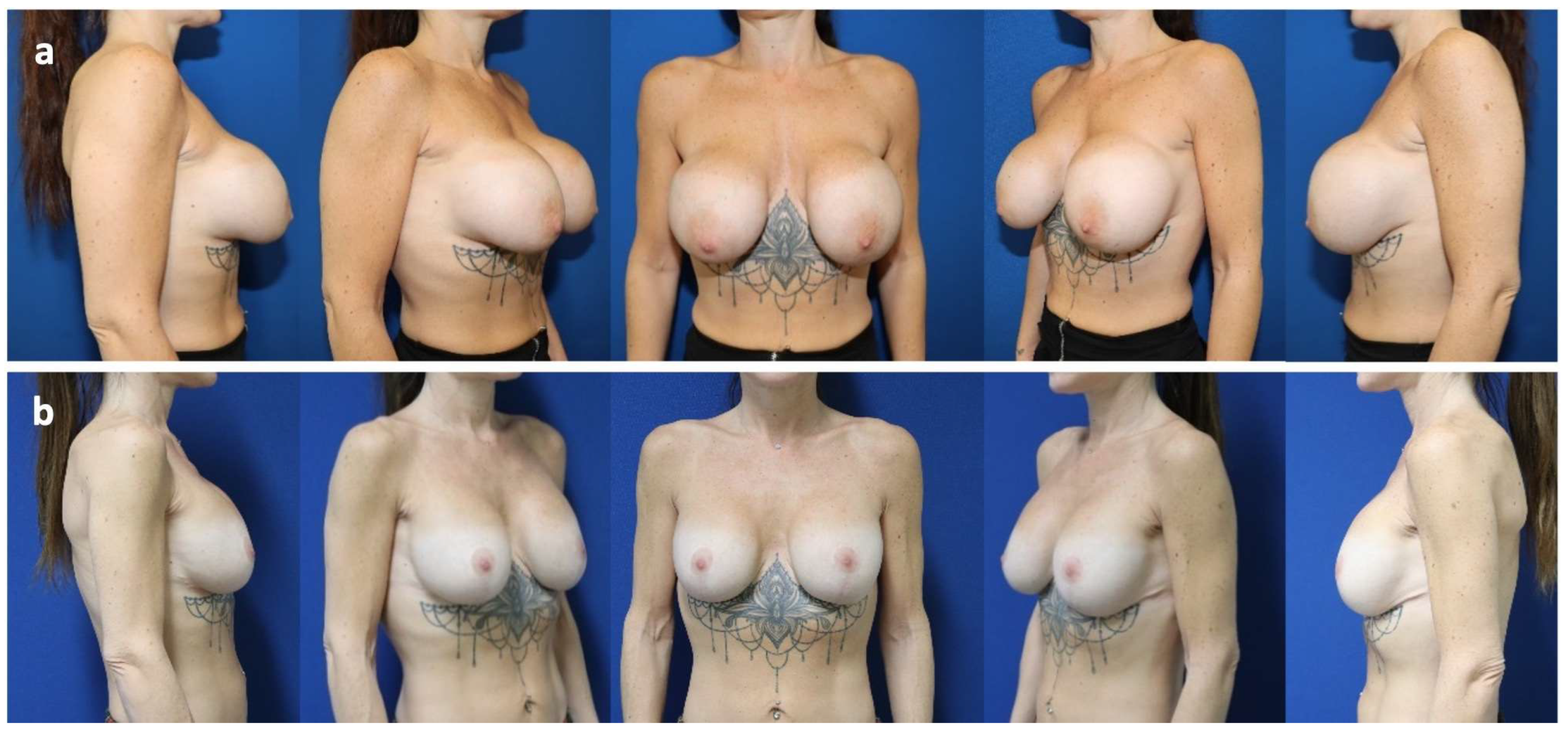
3. Results
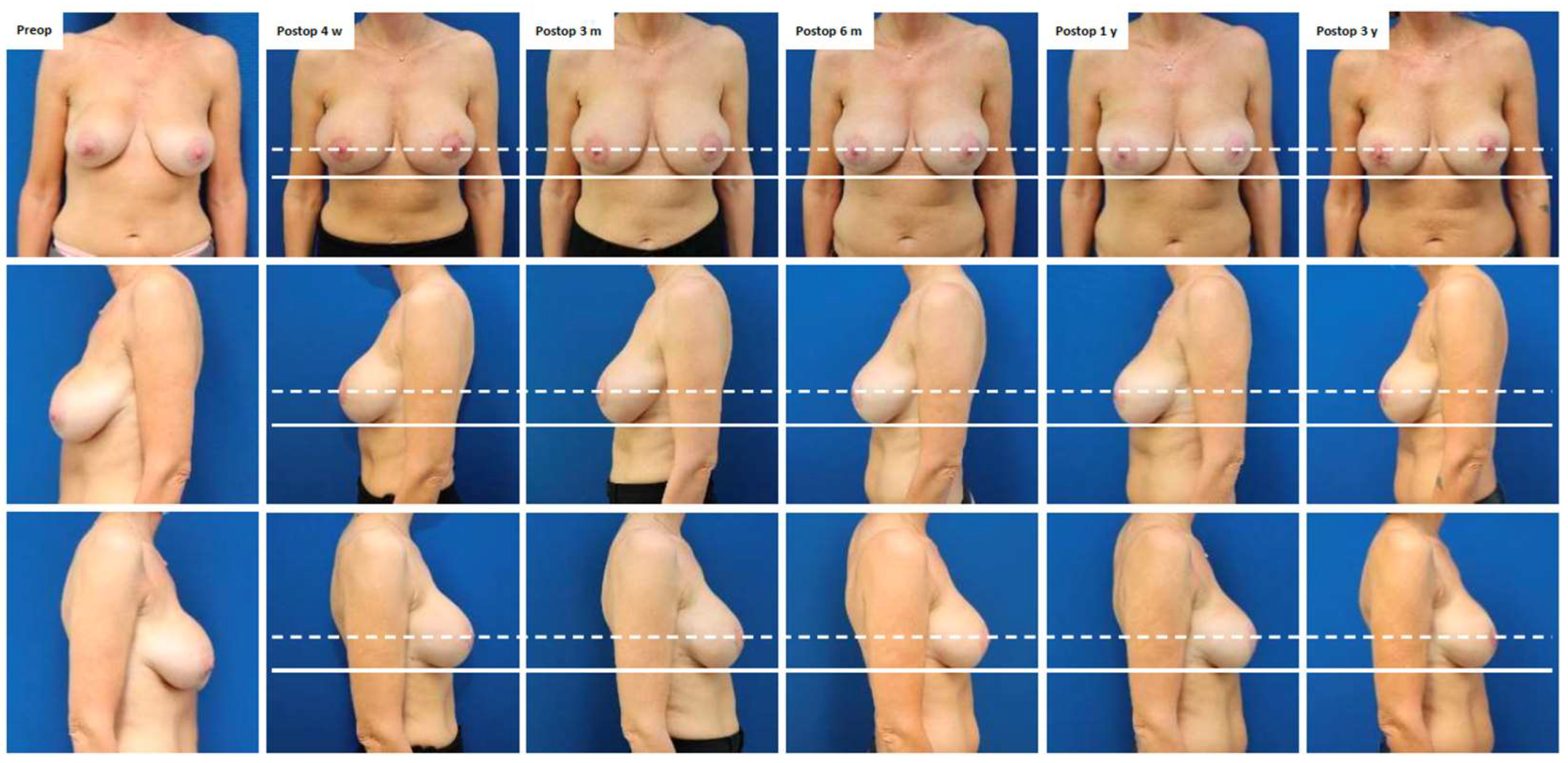
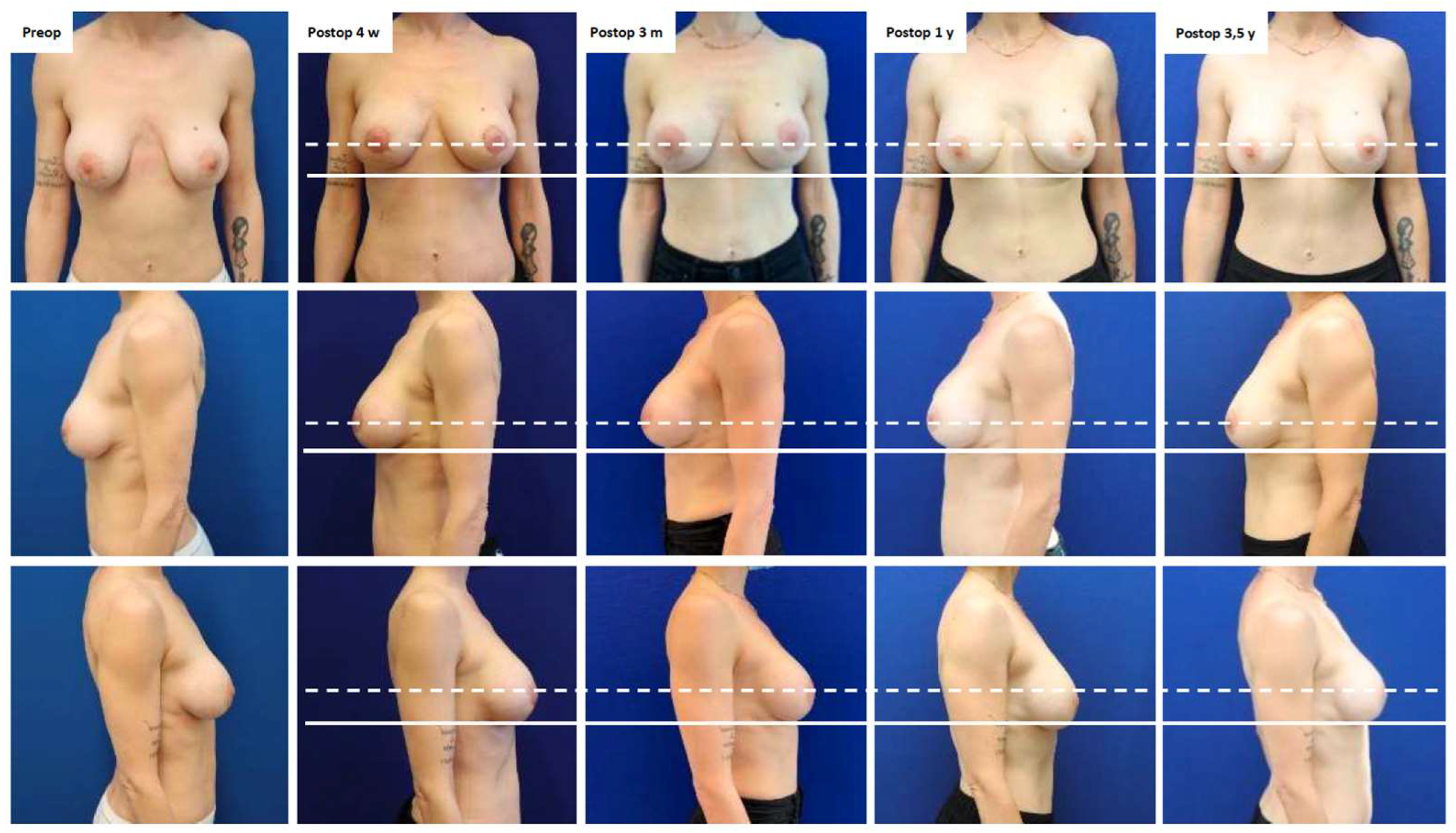
Case Presentation
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Gutowski, K.S.; Chwa, E.S.; Weissman, J.P.; Garg, S.P.; Simmons, C.J.; Brandt, K.E.; Gosain, A.K. Practice Profile of Practicing Plastic Surgeons: A 20-year Review of Plastic Surgery Statistics. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2023, 11, e5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccheri, E.M.; Villanucci, A.; Mallucci, P.; Bistoni, G.; De Vita, R. Synthetic Reabsorbable Mesh (GalaFLEX) as Soft Tissue Adjunct in Breast Augmentation Revision Surgery. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2023, 43, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaps International Survey on Aesthetic/Cosmetic Procedures Performed in 2023. Available online: https://www.isaps.org/media/rxnfqibn/isaps-global-survey_2023.pdf (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Doloff, J.C.; Veiseh, O.; De Mezerville, R.; Sforza, M.; Perry, T.A.; Haupt, J.; Jamiel, M.; Chambers, C.; Nash, A.; Aghlara-Fotovat, S.; et al. The surface topography of silicone breast implants mediates the foreign body response in mice, rabbits and humans. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 1115–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, P.; Bernini, M.; Orzalesi, L.; Sordi, S.; Meattini, I.; Lessi, F.; Kothari, A.; Calabrese, C. Titanium-coated polypropylene mesh as innovative bioactive material in conservatives mastectomies and pre-pectoral breast reconstruction. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4640–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan Ellis, H.; Asaolu, O.; Nebo, V.; Kasem, A. Biological and synthetic mesh use in breast reconstructive surgery: A literature review. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, J.F.; Kumar, A.S. Biologic versus Synthetic Mesh Reinforcement: What are the Pros and Cons? Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2014, 27, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- b4300en_poduct_brochure_titanised_meshes_breast_surgery. Available online: https://www.pfmmedical.com/fileadmin/pim/pfmmedical-com/products/downloads/pb4300en_poduct_brochure_titanised_meshes_breast_surgery.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- Makarewicz, N.; Perrault, D.; Sharma, A.; Shaheen, M.; Kim, J.; Calderon, C.; Sweeney, B.M.; Nazerali, R.M. Comparing the Outcomes and Complication Rates of Biologic vs Synthetic Meshes in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: A Systematic Review. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2023, 90, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusic, A.L.; Klassen, A.F.; Scott, A.M.; Klok, J.A.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Cano, S.J. Development of a new patient-reported outcome measure for breast surgery: The BREAST-Q. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Health C for D and R. Risks and Complications of Breast Implants. 8 September 2024. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/breast-implants/risks-and-complications-breast-implants (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- Headon, H.; Kasem, A.; Mokbel, K. Capsular Contracture after Breast Augmentation: An Update for Clinical Practice. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2015, 42, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzi, M.; Patanè, L.; Redi, U.; Turriziani, G.; Vietti, V.; Zoccali, G.; De Vita, R. Managing the animation deformity in breast reconstruction transposing the implant to a partial prepectoral pocket: Early experience and preliminary results with a new technique. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2023, 86, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santanelli di Pompeo, F.; Clemens, M.W.; Paolini, G.; Firmani, G.; Panagiotakos, D.; Sorotos, M. Epidemiology of Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma in the United States: A Systematic Review. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2023, 44, NP32–NP40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Sträuli, B.D.; Vorburger, D.; Frauchiger-Heuer, H.; Bringolf, L.; Maggi, N.; Talimi-Schnabel, J.; Dedes, K.J. Prepectoral implant-based breast reconstruction with TiLOOP® Bra Pocket—A single-centre retrospective study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2022, 75, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgarello, M.; Barone Adesi, L.; Macrì, G.; Visconti, G. When to Consider Prepectoral Implant Conversion After Subpectoral Implant Breast Reconstruction and How to Plan It. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2023, 43, NP1071–NP1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handel, N.; Cordray, T.; Gutierrez, J.; Jensen, J.A. A long-term study of outcomes, complications, and patient satisfaction with breast implants. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellarini, A.; Bascialla, E.; Paganini, F.; Fasoli, V.; Buttarelli, F.; Marra, E.P.; Tamborini, F.; Corno, M.; Di Giovanna, D.; Baraziol, R.; et al. Breast reconstruction with TiLOOP® Bra: Another arrow in plastic surgeons’ quiver? J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2024, 97, 89–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quah, G.S.; French, J.R.; Cocco, A.; Hsu, J.; Meybodi, F.; Elder, E. Veritas in Immediate Implant-based Breast Reconstruction Is Associated with Higher Complications Compared with TiLOOP. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, e2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casella, D.; Di Taranto, G.; Marcasciano, M.; Sordi, S.; Kothari, A.; Kovacs, T.; Torto, F.L.; Cigna, E.; Calabrese, C.; Ribuffo, D. Evaluation of Prepectoral Implant Placement and Complete Coverage with TiLoop Bra Mesh for Breast Reconstruction: A Prospective Study on Long-Term and Patient-Reported BREAST-Q Outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 143, 1e–9e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieterich, M.; Angres, J.; Stachs, A.; Glass, A.; Reimer, T.; Gerber, B.; Stubert, J. Patient-Report Satisfaction and Health-Related Quality of Life in TiLOOP® Bra-Assisted or Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction Alone. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2015, 39, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, M.; Kapila, A.K.; Peters, E.; Ramaut, L.; Waked, K.; Giunta, G.; De Baerdemaeker, R.; Zeltzer, A. Polyurethane Implants in Revisional Breast Augmentation: A Prospective 5-Year Study. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2024, 44, NP379–NP390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpa, C.; Borso, G.F.; Vindigni, V.; Bassetto, F. Polyurethane foam-covered breast implants: A justified choice? Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar]
- Paepke, S.; Klein, E.; Paepke, D.; Kiechle, M.; Dieterich, M. Titanized polypropylene mesh Tiloop® Bra in reconstructive breast surgery—Indication and complication rate. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 40, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lin, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G. Application of TiLOOP bra in implant-based breast reconstruction is associated with decreased complication risk compared with other meshes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Surg. 2024, 48, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlinger, R.; Nawroth, F.; Kohlmann, T.; Alwafai, Z.; Schueler, K.; Zygmunt, M.; Paepke, S. Retrospective Study of Radiotherapy Impact on the Outcome of Material-assisted Implant-based Subpectoral Breast Reconstruction. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiyeh, B.; Ghieh, F.; Chahine, F.; Oneisi, A. Ptosis and Bottoming out Following Mastopexy and Reduction Mammoplasty. Is Synthetic Mesh Internal Breast Support the Solution? A Systematic Review of the Literature. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2022, 46, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.; Shauly, O.; Menon, A.; Jolkoysky, E.; Gould, D.J.; Losken, A. Efficacy of Mesh Use in Breast Surgery: A Comprehensive Review of Complications and Aesthetic Outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2025, 13, e6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Case No. | Age (Years) | Previous Breast Surgery, Year | Symptoms Leading to Surgical Revision | Revision Surgery, Year | Follow-Up (Months) | Implant-Related Complications After Revision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
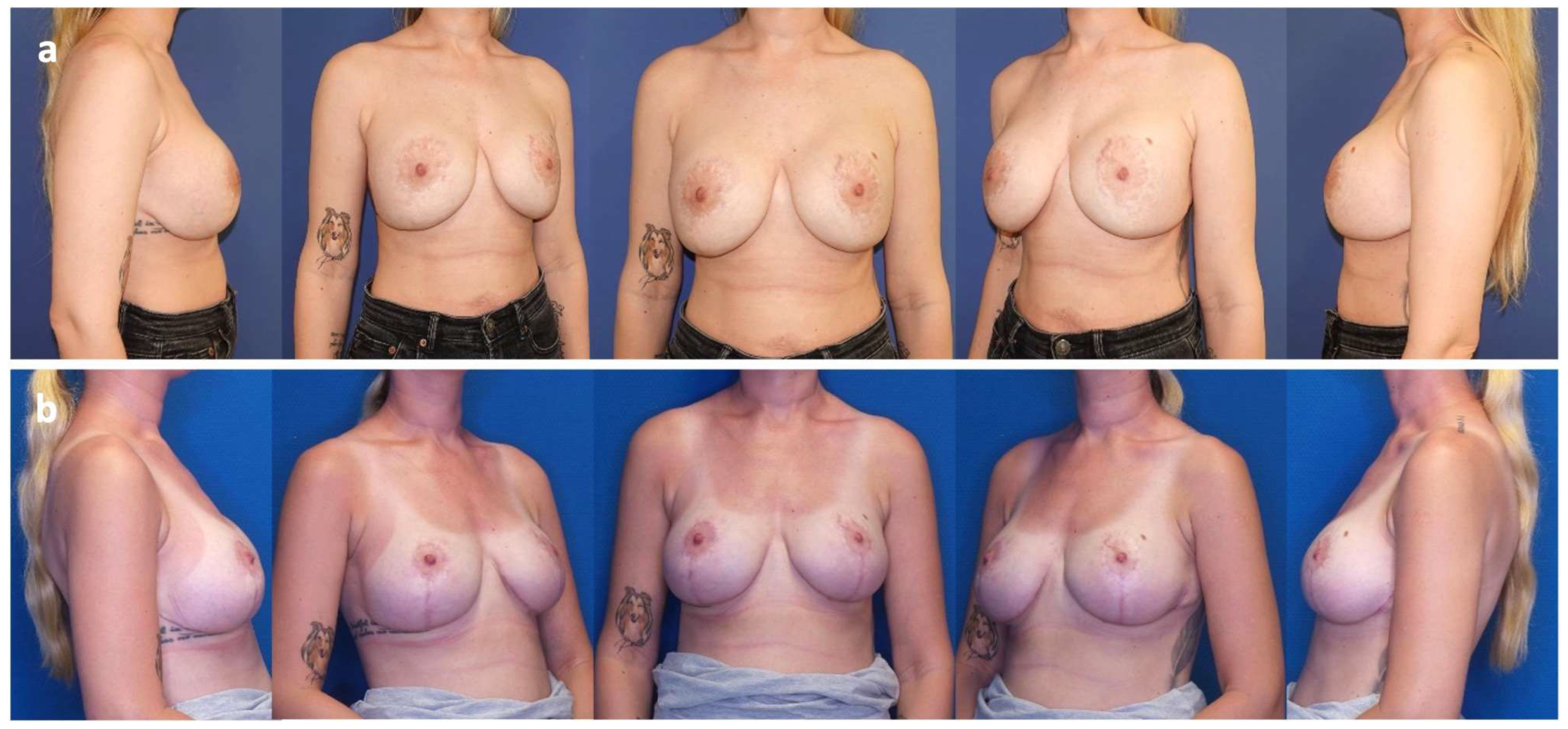
| 1 | 45 | Pre-pectoral breast augmentation (2015) | Symptomatic capsular contracture (Baker grade III) and bilateral breast ptosis (Regnault grade I) | Bilateral implant exchange, mesh insertion and peri-areolar mastopexy (2021) (Figure 1, Figure A1) | 36 | Mild capsular contracture (Baker grade II) |
| 2 | 40 | Peri-areolar mastopexy and sub-pectoral breast augmentation (dual plane II: 2021) | Severe breast pain | Bilateral implant exchange, change of plane from partially sub-pectoral to pre-pectoral, mesh insertion and peri-areolar mastopexy (2022) (Figure A2) | 42 | No, pain resolved |
| 3 | 24 | Pre-pectoral breast augmentation (2010) | Symptomatic capsular contracture (Baker grade IV) and waterfall deformity | Bilateral implant exchange associated with inverted T-mastopexy and mesh insertion (2023) | 18 | Mild capsular contracture (Baker grade II) |
| 4 | 43 | Sub-pectoral breast augmentation (dual-plane II: 1999), capsulectomy and breast implant exchange (2010) | Inferior implant displacement (bottoming out) and lateralization of left implant | Bilateral implant exchange, change of plane from partially sub-pectoral to pre-pectoral and mesh insertion (2023) | 18 | No |
| 5 | 37 | Sub-pectoral breast augmentation (dual-plane II: 2022) | Inferior implant displacement (bottoming out) | Bilateral implant exchange, change of plane from partially sub-pectoral to pre-pectoral, reconstruction of inframammary fold and mesh insertion (2024) | 6 | No |
| 6 | 30 | Pre-pectoral breast augmentation and autologous fat grafting (2022) for breast asymmetry after pectus excavatum correction | Synmastia (medial implant displacement) | Reconstruction of intermammary fold, bilateral exchange of breast implants and mesh insertion (2024) | 11 | No |
| 7 | 24 | Mastopexy (2021) and sub-pectoral breast augmentation (dual-plane II: 2022) | Implant malposition (latero-caudal displacement/bottoming out), breast animation deformity, and asymmetry | Bilateral implant exchange, change of plane from partially sub-pectoral to pre-pectoral, mesh insertion and inverted T mastopexy | 12 | No |
| 8 | 37 | Peri-areolar mastopexy and sub-pectoral breast augmentation (2008) | Symptomatic capsular contracture (Baker grade IV), waterfall deformity and bilateral implant rupture | Bilateral implant exchange with change of plane from partially sub-pectoral to pre-pectoral, mesh insertion and peri-areolar mastopexy (2024) | 8 | Mild capsular contracture (Baker grade II) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zucal, I.; Cresta, E.; De Pellegrin, L.; Weinzierl, A.; Harder, Y. The Role of Synthetic Meshes in Revision Surgery After Breast Augmentation: A Personal Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175978
Zucal I, Cresta E, De Pellegrin L, Weinzierl A, Harder Y. The Role of Synthetic Meshes in Revision Surgery After Breast Augmentation: A Personal Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175978
Chicago/Turabian StyleZucal, Isabel, Ester Cresta, Laura De Pellegrin, Andrea Weinzierl, and Yves Harder. 2025. "The Role of Synthetic Meshes in Revision Surgery After Breast Augmentation: A Personal Experience" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175978
APA StyleZucal, I., Cresta, E., De Pellegrin, L., Weinzierl, A., & Harder, Y. (2025). The Role of Synthetic Meshes in Revision Surgery After Breast Augmentation: A Personal Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175978






